9c125647ad03cf5caacf2d59f0771161.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 QUIT World War II, 1939– 1945 CHAPTER 32 Chapter Overview Time Line 1 Hitler’s Lightning War 2 Japan Strikes in the Pacific SECTION 3 The Holocaust SECTION GRAPH SECTION MAP 4 The Allies Are Victorious SECTION 5 The Devastation of Europe and Japan Visual Summary
QUIT World War II, 1939– 1945 CHAPTER 32 Chapter Overview Time Line 1 Hitler’s Lightning War 2 Japan Strikes in the Pacific SECTION 3 The Holocaust SECTION GRAPH SECTION MAP 4 The Allies Are Victorious SECTION 5 The Devastation of Europe and Japan Visual Summary
 HOME CHAPTER 32 World War II, 1939– 1945 Chapter Overview The expansionist designs of Germany and Japan lead to worldwide conflict. After initial defeats in Europe and the Pacific, the Allies are victorious but at the cost of millions of lives and the economic and political devastation of Europe and Japan.
HOME CHAPTER 32 World War II, 1939– 1945 Chapter Overview The expansionist designs of Germany and Japan lead to worldwide conflict. After initial defeats in Europe and the Pacific, the Allies are victorious but at the cost of millions of lives and the economic and political devastation of Europe and Japan.
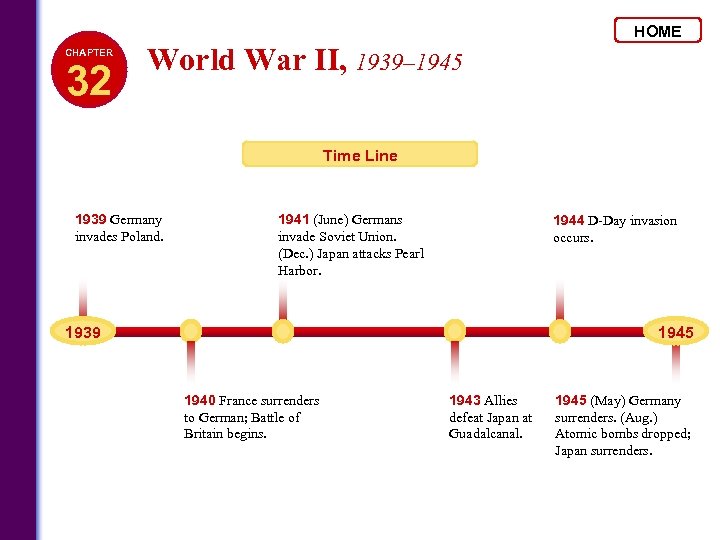 HOME CHAPTER 32 World War II, 1939– 1945 Time Line 1939 Germany invades Poland. 1941 (June) Germans invade Soviet Union. (Dec. ) Japan attacks Pearl Harbor. 1944 D-Day invasion occurs. 1939 1945 1940 France surrenders to German; Battle of Britain begins. 1943 Allies defeat Japan at Guadalcanal. 1945 (May) Germany surrenders. (Aug. ) Atomic bombs dropped; Japan surrenders.
HOME CHAPTER 32 World War II, 1939– 1945 Time Line 1939 Germany invades Poland. 1941 (June) Germans invade Soviet Union. (Dec. ) Japan attacks Pearl Harbor. 1944 D-Day invasion occurs. 1939 1945 1940 France surrenders to German; Battle of Britain begins. 1943 Allies defeat Japan at Guadalcanal. 1945 (May) Germany surrenders. (Aug. ) Atomic bombs dropped; Japan surrenders.
 1 HOME Hitler’s Lightning War MAP Key Idea Hitler launches a surprise attack on Poland, overruns much of Europe, and invades Russia. Britain survives to fight on alone, aided by arms from the United States. Overview Assessment
1 HOME Hitler’s Lightning War MAP Key Idea Hitler launches a surprise attack on Poland, overruns much of Europe, and invades Russia. Britain survives to fight on alone, aided by arms from the United States. Overview Assessment
 1 HOME Hitler’s Lightning War MAP TERMS & NAMES Overview • nonaggression pact • blitzkrieg MAIN IDEA WHY IT MATTERS NOW • Charles de Gaulle Using the sudden, mass attack called the blitzkrieg, Germany overran much of Europe and North Africa. Hitler’s actions set off World War II. The results of the war still affect the politics and economics of today’s world. • Winston Churchill Assessment • Battle of Britain • Atlantic Charter
1 HOME Hitler’s Lightning War MAP TERMS & NAMES Overview • nonaggression pact • blitzkrieg MAIN IDEA WHY IT MATTERS NOW • Charles de Gaulle Using the sudden, mass attack called the blitzkrieg, Germany overran much of Europe and North Africa. Hitler’s actions set off World War II. The results of the war still affect the politics and economics of today’s world. • Winston Churchill Assessment • Battle of Britain • Atlantic Charter
 1 HOME Hitler’s Lightning War MAP Section 1 Assessment 1. Look at the graphic to help organize your thoughts. Identify the effects of each of the early events of World War II that are listed below. Cause Effect First blitzkrieg The fall of Poland Allies stranded at Dunkirk 338, 000 soldiers saved British forces leave Western Europe. British radar detects German aircraft British able to hold off German occupation Lend-Lease Act U. S. supplied Allies with war goods. U. S. decision to favor the Allies continued. . .
1 HOME Hitler’s Lightning War MAP Section 1 Assessment 1. Look at the graphic to help organize your thoughts. Identify the effects of each of the early events of World War II that are listed below. Cause Effect First blitzkrieg The fall of Poland Allies stranded at Dunkirk 338, 000 soldiers saved British forces leave Western Europe. British radar detects German aircraft British able to hold off German occupation Lend-Lease Act U. S. supplied Allies with war goods. U. S. decision to favor the Allies continued. . .
 1 Hitler’s Lightning War HOME MAP Section 1 Assessment 2. Great Britain and the Soviet city of Leningrad each fought off a German invasion. Other countries gave in to the Germans without much resistance. What factors do you think a country’s leaders consider when deciding whether to surrender or to fight? THINK ABOUT • the country’s ability to fight • the costs of resisting • the costs of surrendering ANSWER continued. . .
1 Hitler’s Lightning War HOME MAP Section 1 Assessment 2. Great Britain and the Soviet city of Leningrad each fought off a German invasion. Other countries gave in to the Germans without much resistance. What factors do you think a country’s leaders consider when deciding whether to surrender or to fight? THINK ABOUT • the country’s ability to fight • the costs of resisting • the costs of surrendering ANSWER continued. . .
 1 Hitler’s Lightning War HOME MAP Section Possible Responses: 1 Assessment Ability to Fight: army large enough to fight the enemy, sufficient weapons Costs of Resisting: major civilian and military deaths, destruction of property, economic chaos Costs of Surrendering: enemy control of the government, repression of the population End of Section 1
1 Hitler’s Lightning War HOME MAP Section Possible Responses: 1 Assessment Ability to Fight: army large enough to fight the enemy, sufficient weapons Costs of Resisting: major civilian and military deaths, destruction of property, economic chaos Costs of Surrendering: enemy control of the government, repression of the population End of Section 1
 2 HOME Japan Strikes in the Pacific Key Idea Japan’s attack on Pearl Harbor draws the United States into the war. Initial Japanese victories in the Pacific are overturned as U. S. naval forces fight back, gaining the offensive. Overview Assessment
2 HOME Japan Strikes in the Pacific Key Idea Japan’s attack on Pearl Harbor draws the United States into the war. Initial Japanese victories in the Pacific are overturned as U. S. naval forces fight back, gaining the offensive. Overview Assessment
 2 HOME Japan Strikes in the Pacific TERMS & NAMES Overview • Isoroku Yamamoto • Pearl Harbor MAIN IDEA WHY IT MATTERS NOW • Battle of Midway Carving out an empire, Japan attacked Pearl Harbor in Hawaii and brought the United States into World War II established the role of the United States as a leading player in international affairs. • Douglas Mac. Arthur Assessment • Battle of Guadalcanal
2 HOME Japan Strikes in the Pacific TERMS & NAMES Overview • Isoroku Yamamoto • Pearl Harbor MAIN IDEA WHY IT MATTERS NOW • Battle of Midway Carving out an empire, Japan attacked Pearl Harbor in Hawaii and brought the United States into World War II established the role of the United States as a leading player in international affairs. • Douglas Mac. Arthur Assessment • Battle of Guadalcanal
 2 HOME Japan Strikes in the Pacific Section 2 Assessment 1. Look at the graphic to help organize your thoughts. List four major events of the war in the Pacific between 1941 and 1943. Event 1: Japan bombs Pearl Harbor Event 2: United States bombs Tokyo Event 3: Battle of Midway Event 4: Battle of Guadalcanal continued. . .
2 HOME Japan Strikes in the Pacific Section 2 Assessment 1. Look at the graphic to help organize your thoughts. List four major events of the war in the Pacific between 1941 and 1943. Event 1: Japan bombs Pearl Harbor Event 2: United States bombs Tokyo Event 3: Battle of Midway Event 4: Battle of Guadalcanal continued. . .
 2 HOME Japan Strikes in the Pacific Section 2 Assessment 2. Judging from the effects of the attack on Pearl Harbor, do you think Yamamoto made a wise decision in bombing Pearl Harbor? Why or why not? THINK ABOUT • Yamamoto’s goals in the bombing • United States involvement in World War II • the effects of the bombing ANSWER Possible Responses: Wise: If the Japanese did not destroy the U. S. Pacific fleet, it would have been used against them. Unwise: If the Japanese did not bomb Pearl Harbor, the United States may never have entered the war. continued. . .
2 HOME Japan Strikes in the Pacific Section 2 Assessment 2. Judging from the effects of the attack on Pearl Harbor, do you think Yamamoto made a wise decision in bombing Pearl Harbor? Why or why not? THINK ABOUT • Yamamoto’s goals in the bombing • United States involvement in World War II • the effects of the bombing ANSWER Possible Responses: Wise: If the Japanese did not destroy the U. S. Pacific fleet, it would have been used against them. Unwise: If the Japanese did not bomb Pearl Harbor, the United States may never have entered the war. continued. . .
 2 HOME Japan Strikes in the Pacific Section 2 Assessment 3. What do you think Yamamoto’s biggest problems were in building the Japanese empire in the Pacific? THINK ABOUT • geographical problems • European/American interests in the Pacific • psychological factors ANSWER Possible Responses: Geography: The Pacific region is so huge that it would be difficult to build an empire. European/American Interests: The United States and certain European countries had military posts in the Pacific. Psychological Factors: After the bombing of Tokyo, Yamamoto had to deal with shaken Japanese confidence. End of Section 2
2 HOME Japan Strikes in the Pacific Section 2 Assessment 3. What do you think Yamamoto’s biggest problems were in building the Japanese empire in the Pacific? THINK ABOUT • geographical problems • European/American interests in the Pacific • psychological factors ANSWER Possible Responses: Geography: The Pacific region is so huge that it would be difficult to build an empire. European/American Interests: The United States and certain European countries had military posts in the Pacific. Psychological Factors: After the bombing of Tokyo, Yamamoto had to deal with shaken Japanese confidence. End of Section 2
 3 HOME The Holocaust Key Idea Nazi persecution of Jews throughout Germany and the conquered nations leads to Hitler’s “Final Solution”: the mass extermination of 6 million of Europe’s Jews. Overview Assessment
3 HOME The Holocaust Key Idea Nazi persecution of Jews throughout Germany and the conquered nations leads to Hitler’s “Final Solution”: the mass extermination of 6 million of Europe’s Jews. Overview Assessment
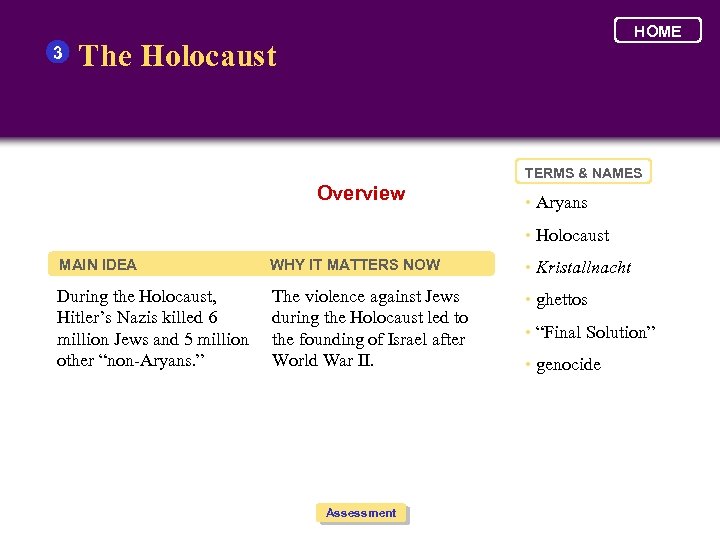 3 HOME The Holocaust TERMS & NAMES Overview • Aryans • Holocaust MAIN IDEA WHY IT MATTERS NOW • Kristallnacht During the Holocaust, Hitler’s Nazis killed 6 million Jews and 5 million other “non-Aryans. ” The violence against Jews during the Holocaust led to the founding of Israel after World War II. • ghettos Assessment • “Final Solution” • genocide
3 HOME The Holocaust TERMS & NAMES Overview • Aryans • Holocaust MAIN IDEA WHY IT MATTERS NOW • Kristallnacht During the Holocaust, Hitler’s Nazis killed 6 million Jews and 5 million other “non-Aryans. ” The violence against Jews during the Holocaust led to the founding of Israel after World War II. • ghettos Assessment • “Final Solution” • genocide
 3 HOME The Holocaust Section 3 Assessment 1. Look at the graphic to help organize your thoughts. Give examples of Nazi persecutions. Burning of Jewish businesses, homes, and synagogues Nuremberg Laws Nazi Persecutions Genocide of Jews Persecution of gypsies, Poles, Russians, homosexuals, the insane, the disabled, the ill Concentration camps continued. . .
3 HOME The Holocaust Section 3 Assessment 1. Look at the graphic to help organize your thoughts. Give examples of Nazi persecutions. Burning of Jewish businesses, homes, and synagogues Nuremberg Laws Nazi Persecutions Genocide of Jews Persecution of gypsies, Poles, Russians, homosexuals, the insane, the disabled, the ill Concentration camps continued. . .
 3 HOME The Holocaust Section 3 Assessment 2. Why do you think German soldiers and the German people went along with the Nazi policy of persecution of the Jews? THINK ABOUT • Nazi treatment of those who disagreed • Nazi propaganda • the political and social conditions in Germany at the time ANSWER Possible Responses: Treatment: The people of Germany were afraid for their lives. Propaganda: It tried to convince Germans that Jewish people were subhuman. Conditions: A repressive dictatorship End of Section 3
3 HOME The Holocaust Section 3 Assessment 2. Why do you think German soldiers and the German people went along with the Nazi policy of persecution of the Jews? THINK ABOUT • Nazi treatment of those who disagreed • Nazi propaganda • the political and social conditions in Germany at the time ANSWER Possible Responses: Treatment: The people of Germany were afraid for their lives. Propaganda: It tried to convince Germans that Jewish people were subhuman. Conditions: A repressive dictatorship End of Section 3
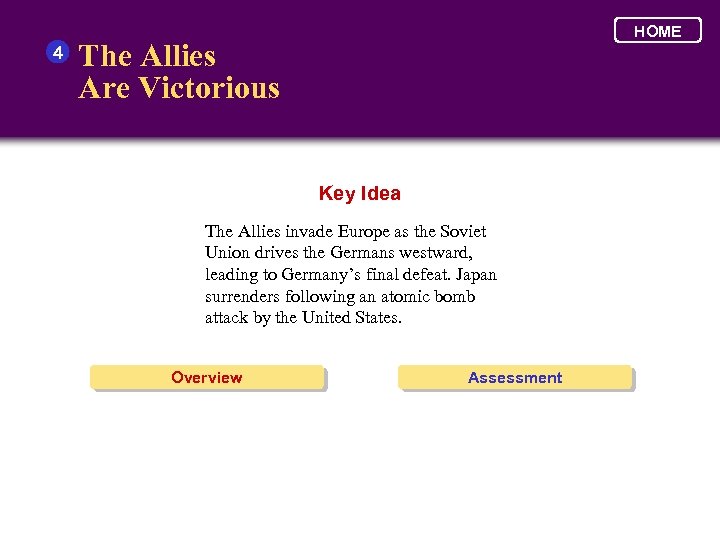 4 HOME The Allies Are Victorious Key Idea The Allies invade Europe as the Soviet Union drives the Germans westward, leading to Germany’s final defeat. Japan surrenders following an atomic bomb attack by the United States. Overview Assessment
4 HOME The Allies Are Victorious Key Idea The Allies invade Europe as the Soviet Union drives the Germans westward, leading to Germany’s final defeat. Japan surrenders following an atomic bomb attack by the United States. Overview Assessment
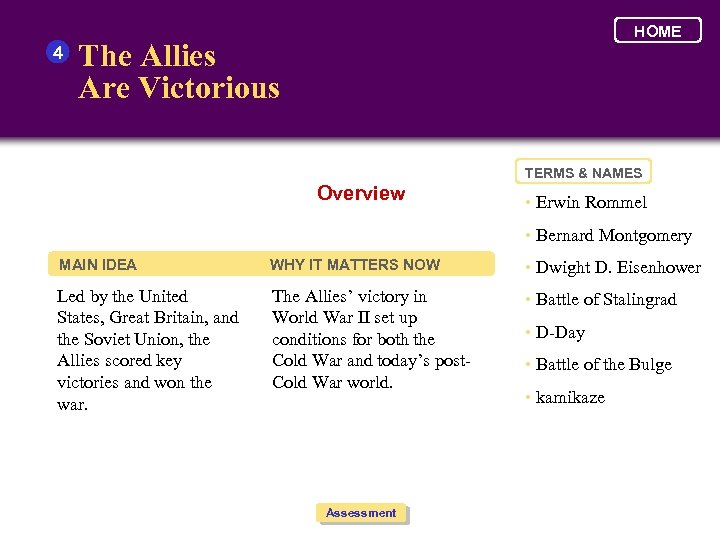 4 HOME The Allies Are Victorious TERMS & NAMES Overview • Erwin Rommel • Bernard Montgomery MAIN IDEA WHY IT MATTERS NOW • Dwight D. Eisenhower Led by the United States, Great Britain, and the Soviet Union, the Allies scored key victories and won the war. The Allies’ victory in World War II set up conditions for both the Cold War and today’s post. Cold War world. • Battle of Stalingrad Assessment • D-Day • Battle of the Bulge • kamikaze
4 HOME The Allies Are Victorious TERMS & NAMES Overview • Erwin Rommel • Bernard Montgomery MAIN IDEA WHY IT MATTERS NOW • Dwight D. Eisenhower Led by the United States, Great Britain, and the Soviet Union, the Allies scored key victories and won the war. The Allies’ victory in World War II set up conditions for both the Cold War and today’s post. Cold War world. • Battle of Stalingrad Assessment • D-Day • Battle of the Bulge • kamikaze
 4 HOME The Allies Are Victorious Section 4 Assessment 1. Look at the graphic to help organize your thoughts. List the outcomes of the four World War II battles listed below. Battle Outcome Battle of El Alamein Rommel’s army defeated in North Africa Battle of Stalingrad Held by Soviets D-Day Invasion Allies held beachheads Battle of the Bulge Allies eventually pushed Germans back continued. . .
4 HOME The Allies Are Victorious Section 4 Assessment 1. Look at the graphic to help organize your thoughts. List the outcomes of the four World War II battles listed below. Battle Outcome Battle of El Alamein Rommel’s army defeated in North Africa Battle of Stalingrad Held by Soviets D-Day Invasion Allies held beachheads Battle of the Bulge Allies eventually pushed Germans back continued. . .
 4 HOME The Allies Are Victorious Section 4 Assessment 2. Based on what you have read in this section, how do governments gather support for a war effort on the home front? THINK ABOUT • the economy • forms of propaganda • individual participation in the war effort ANSWER Possible Responses: • Rationing of materials (gasoline, metals, rubber, food, etc. ) crucial to the war effort • Collecting war materials donated by individuals • Selling bonds to raise money for the war • Using propaganda to paint themselves as fighters for right against evil enemies continued. . .
4 HOME The Allies Are Victorious Section 4 Assessment 2. Based on what you have read in this section, how do governments gather support for a war effort on the home front? THINK ABOUT • the economy • forms of propaganda • individual participation in the war effort ANSWER Possible Responses: • Rationing of materials (gasoline, metals, rubber, food, etc. ) crucial to the war effort • Collecting war materials donated by individuals • Selling bonds to raise money for the war • Using propaganda to paint themselves as fighters for right against evil enemies continued. . .
 4 HOME The Allies Are Victorious Section 4 Assessment 3. Do you think President Truman made the correct decision by ordering the atomic bomb dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki? Why or why not? THINK ABOUT • the likely consequences if the atomic bomb had not been dropped • the destruction caused by the atomic bomb • World War II after the dropping of the atomic bomb ANSWER Possible Responses: Right: Dropping the bomb was an effective way to end the war in the Pacific. Wrong: The atomic bomb caused a huge loss of civilian lives. End of Section 4
4 HOME The Allies Are Victorious Section 4 Assessment 3. Do you think President Truman made the correct decision by ordering the atomic bomb dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki? Why or why not? THINK ABOUT • the likely consequences if the atomic bomb had not been dropped • the destruction caused by the atomic bomb • World War II after the dropping of the atomic bomb ANSWER Possible Responses: Right: Dropping the bomb was an effective way to end the war in the Pacific. Wrong: The atomic bomb caused a huge loss of civilian lives. End of Section 4
 5 HOME The Devastation of Europe and Japan GRAPH Key Idea A ravaged Europe struggles to recover as the United States occupies Japan and begins to bring political change and stability. Overview Assessment
5 HOME The Devastation of Europe and Japan GRAPH Key Idea A ravaged Europe struggles to recover as the United States occupies Japan and begins to bring political change and stability. Overview Assessment
 5 The Devastation of Europe and Japan GRAPH HOME TERMS & NAMES Overview • Nuremberg Trials • demilitarization MAIN IDEA WHY IT MATTERS NOW World War II cost millions of human lives and billions of dollars in damages. It left Europe and Japan in ruins. The United States survived World War II undamaged, allowing it to become a world leader. Assessment
5 The Devastation of Europe and Japan GRAPH HOME TERMS & NAMES Overview • Nuremberg Trials • demilitarization MAIN IDEA WHY IT MATTERS NOW World War II cost millions of human lives and billions of dollars in damages. It left Europe and Japan in ruins. The United States survived World War II undamaged, allowing it to become a world leader. Assessment
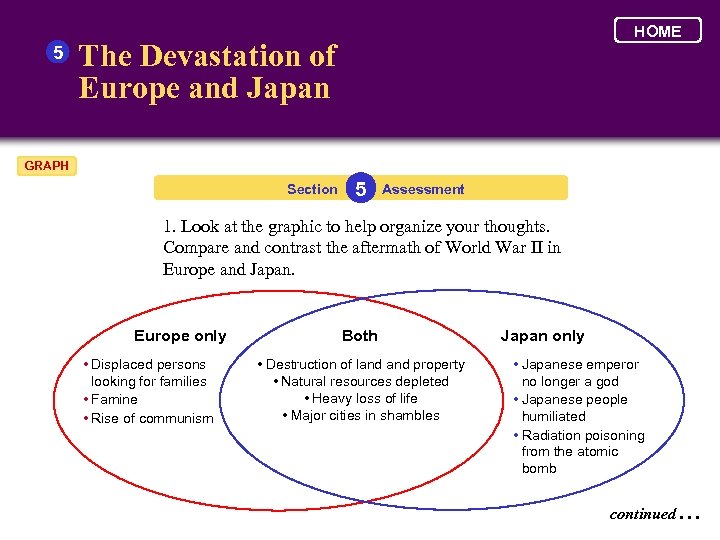 5 HOME The Devastation of Europe and Japan GRAPH Section 5 Assessment 1. Look at the graphic to help organize your thoughts. Compare and contrast the aftermath of World War II in Europe and Japan. Europe only • Displaced persons looking for families • Famine • Rise of communism Both • Destruction of land property • Natural resources depleted • Heavy loss of life • Major cities in shambles Japan only • Japanese emperor no longer a god • Japanese people humiliated • Radiation poisoning from the atomic bomb continued. . .
5 HOME The Devastation of Europe and Japan GRAPH Section 5 Assessment 1. Look at the graphic to help organize your thoughts. Compare and contrast the aftermath of World War II in Europe and Japan. Europe only • Displaced persons looking for families • Famine • Rise of communism Both • Destruction of land property • Natural resources depleted • Heavy loss of life • Major cities in shambles Japan only • Japanese emperor no longer a god • Japanese people humiliated • Radiation poisoning from the atomic bomb continued. . .
 5 HOME The Devastation of Europe and Japan GRAPH Section 5 Assessment 2. Why do you think that many Europeans favored communism directly following World War II? THINK ABOUT • World War II destruction • pre-World War II governments • economic concerns ANSWER Possible Responses: • People lost faith in leaders of the past who had participated in starting or conducting the war. • Communism promised food and prosperity to people who had none. End of Section 5
5 HOME The Devastation of Europe and Japan GRAPH Section 5 Assessment 2. Why do you think that many Europeans favored communism directly following World War II? THINK ABOUT • World War II destruction • pre-World War II governments • economic concerns ANSWER Possible Responses: • People lost faith in leaders of the past who had participated in starting or conducting the war. • Communism promised food and prosperity to people who had none. End of Section 5


