 Quick Neurological Examination Ø Conscious level (Glasgow Coma Score ) Ø Pupillary Response/Limb weakness Ø Scalp lacerations / bruising-CSF leak, herniation of brain matter Ø Evidence of Skull fracture: Vault/Base 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Subconjunctival haemorrhage Bleeding from external auditory meatus CSF rhinorrhoea/otorrhoea Battle’s sign/Bilateral periorbital haematomas (Racoon eyes) Facial nerve palsy
Quick Neurological Examination Ø Conscious level (Glasgow Coma Score ) Ø Pupillary Response/Limb weakness Ø Scalp lacerations / bruising-CSF leak, herniation of brain matter Ø Evidence of Skull fracture: Vault/Base 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Subconjunctival haemorrhage Bleeding from external auditory meatus CSF rhinorrhoea/otorrhoea Battle’s sign/Bilateral periorbital haematomas (Racoon eyes) Facial nerve palsy
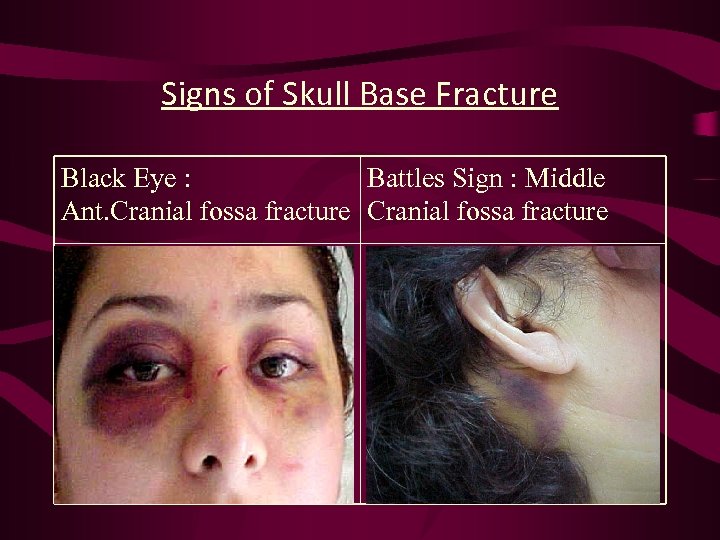 Signs of Skull Base Fracture Black Eye : Battles Sign : Middle Ant. Cranial fossa fracture
Signs of Skull Base Fracture Black Eye : Battles Sign : Middle Ant. Cranial fossa fracture
 Head Injury Assessment Glasgow Coma Score (GCS=3 to 15) Eye Opening (E) Spontaneous To speech To pain None 4 3 2 1
Head Injury Assessment Glasgow Coma Score (GCS=3 to 15) Eye Opening (E) Spontaneous To speech To pain None 4 3 2 1
 Head Injury Assessment Glasgow Coma Score (GCS=3 to 15) Motor Response (M) Obeys commands Localises pain Flexion Abnormal flexion (decorticate) Extension (decerebrate) None 6 5 4 3 2 1
Head Injury Assessment Glasgow Coma Score (GCS=3 to 15) Motor Response (M) Obeys commands Localises pain Flexion Abnormal flexion (decorticate) Extension (decerebrate) None 6 5 4 3 2 1
 Head Injury Assessment Glasgow Coma Score (GCS=3 to 15) Verbal Response (V) Oriented Confused Inappropriate words Incomprehensible sounds None 5 4 3 2 1
Head Injury Assessment Glasgow Coma Score (GCS=3 to 15) Verbal Response (V) Oriented Confused Inappropriate words Incomprehensible sounds None 5 4 3 2 1
 Imaging in head injury Ø Plain X Ray ØCT scan Ø MRI Ø Angiography
Imaging in head injury Ø Plain X Ray ØCT scan Ø MRI Ø Angiography
 X Ray Skull Ø Lateral view • Sphenoid Sinus – look for Fluid /air Level • Pneumocele • Double Densities • Linear Fracture Ø PA View • Frontal Sinus - look for Fluid /air Level • Pineal Shift
X Ray Skull Ø Lateral view • Sphenoid Sinus – look for Fluid /air Level • Pneumocele • Double Densities • Linear Fracture Ø PA View • Frontal Sinus - look for Fluid /air Level • Pineal Shift
 CT Scan ØIt is the most important investigation as it clearly depicts the extent of injury. ØUsually a Plain CT head with bone window is required ØMany times the first CT scan is done quite early a repeat CT scan should be done, preferably within 12 -24 hours after injury.
CT Scan ØIt is the most important investigation as it clearly depicts the extent of injury. ØUsually a Plain CT head with bone window is required ØMany times the first CT scan is done quite early a repeat CT scan should be done, preferably within 12 -24 hours after injury.
 TOPOGRAM
TOPOGRAM
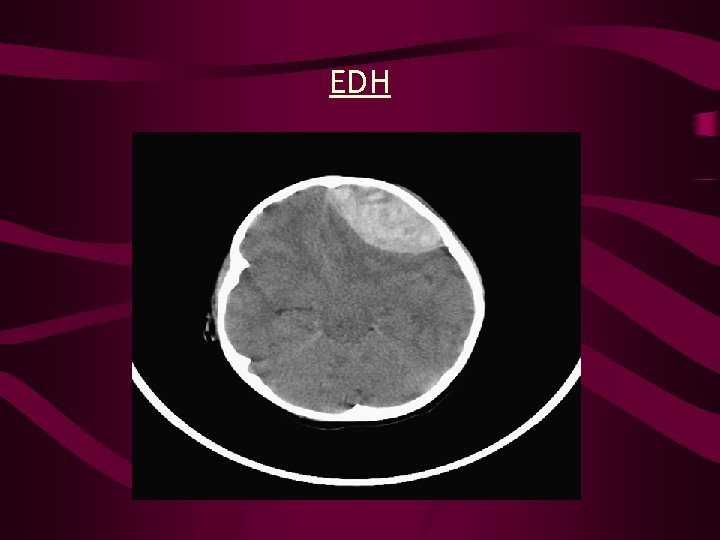
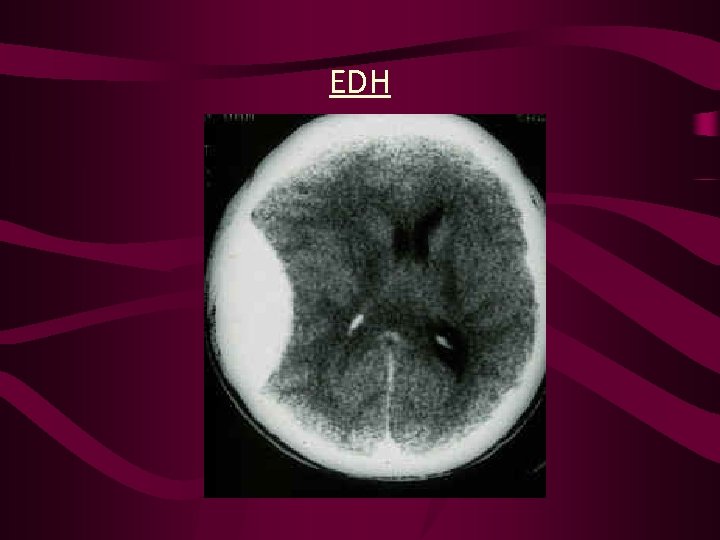 EDH
EDH
 EDH
EDH
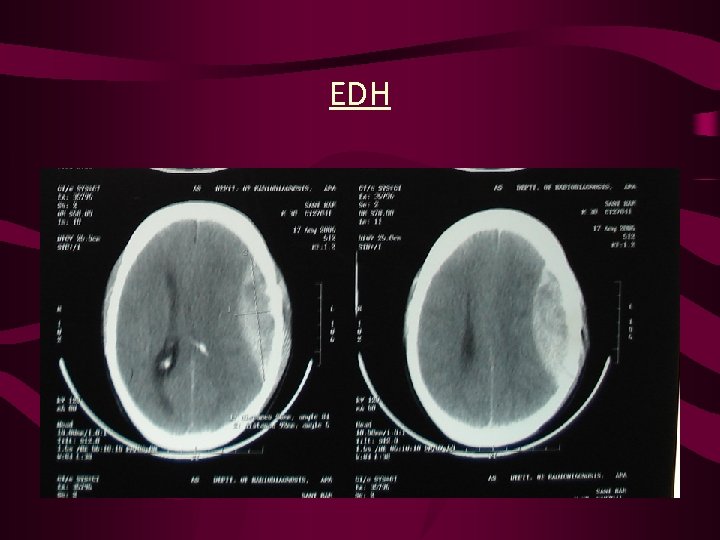 EDH
EDH
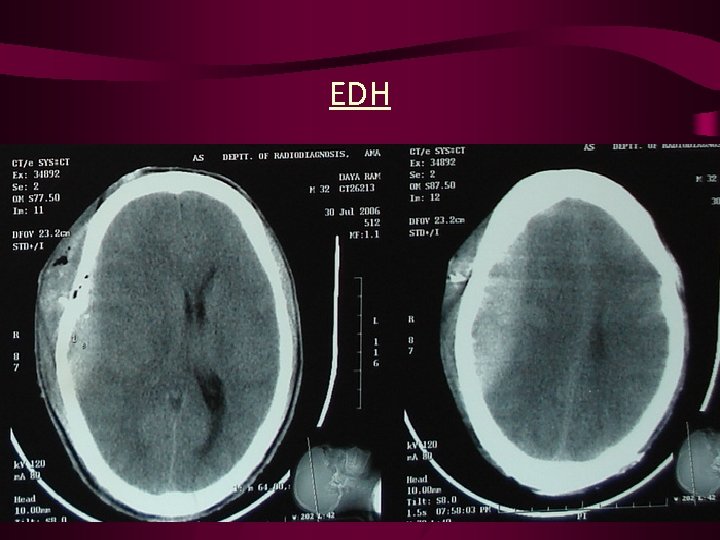 EDH
EDH
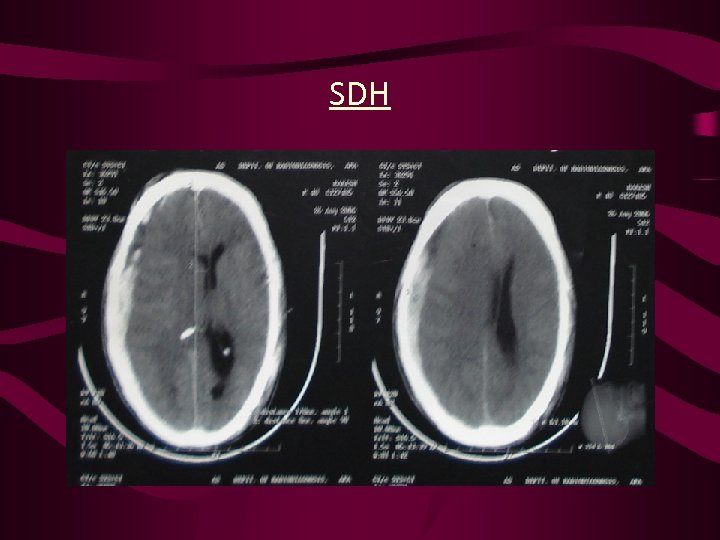 SDH
SDH
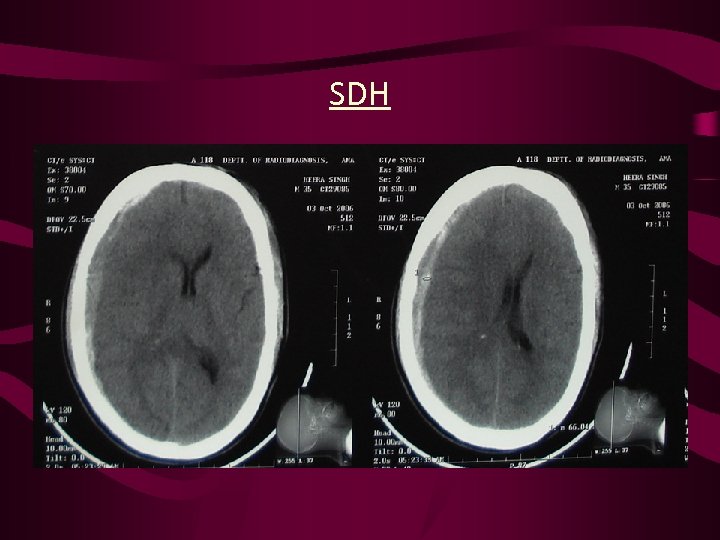 SDH
SDH
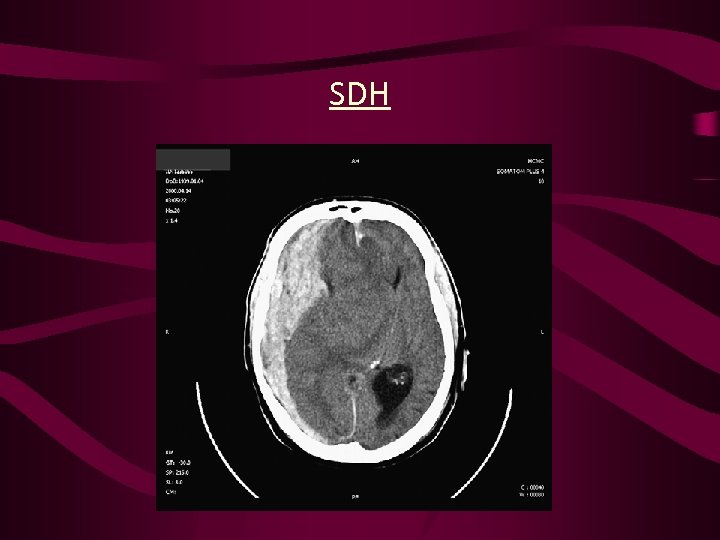 SDH
SDH
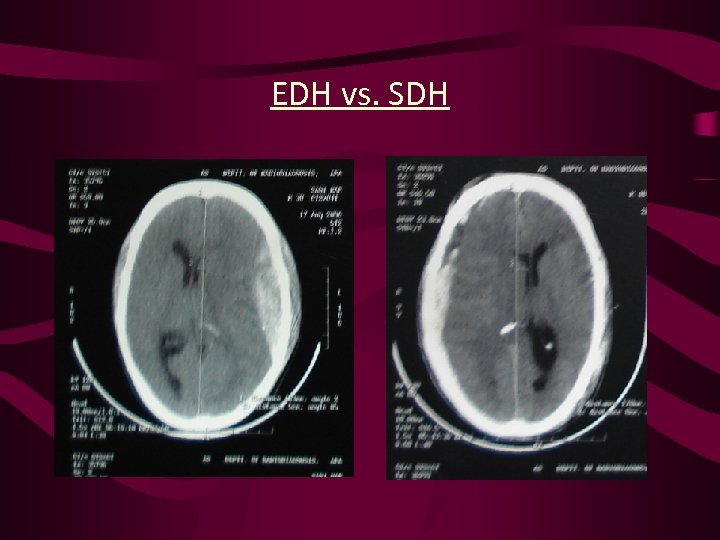 EDH vs. SDH
EDH vs. SDH
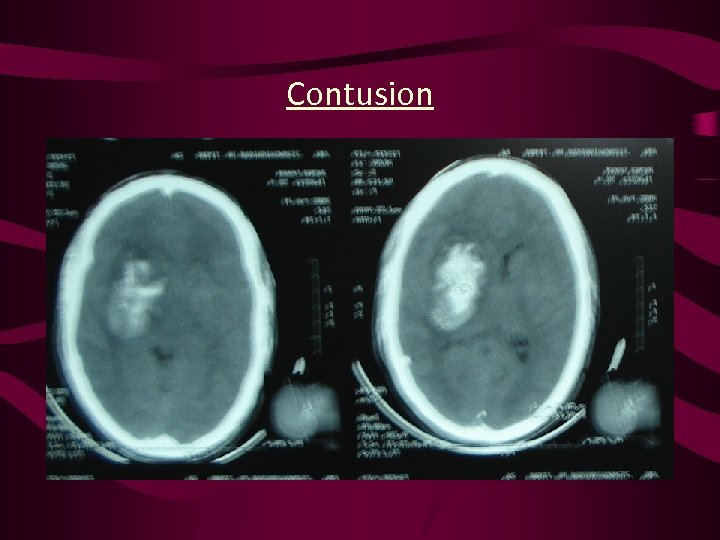 Contusion
Contusion
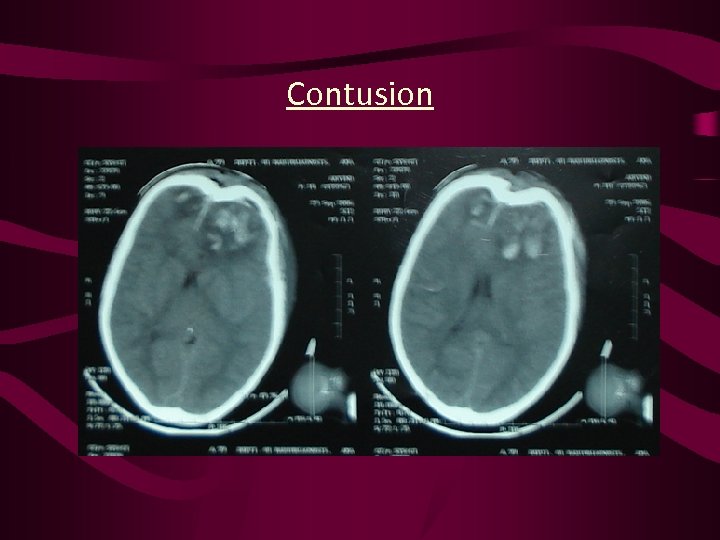 Contusion
Contusion
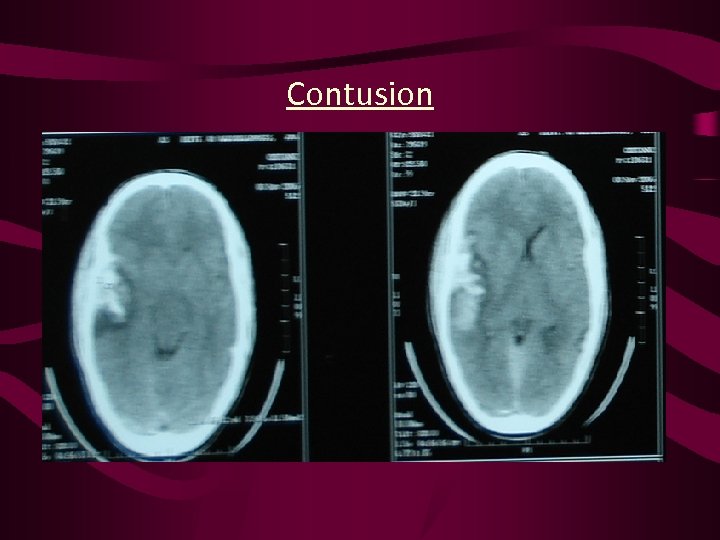 Contusion
Contusion