24200d7c0df15a0b65ee457eac88543c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34

Quick and Yeast Breads Chapter 30 1
• What are breads made of? • • Flour **main ingredient (gives structure) **source of complex carbohydrates **mostly wheat flour (barley, corn, rye) 2

• All-purpose flour = white flour—grain’s endosperm • Whole wheat flour = milled from whole grain, more fiber • Self-rising flour = includes salt and baking powder • Bread flour = strong structure 3

• Liquid • **milk and water to moisten and bind • batter = thin enough to be poured or dropped • dough = stiff enough to be molded or rolled on a board 4

• Fat • **adds flavor and richness • shortening = solid fat made from vegetable oil 5

Leavening Agents • Leavening agent = makes baked product rise by causing pockets of air expand in the batter or dough as it bakes • **baking soda, baking powder, yeast 6

• Yeast breads = yeast to raise • Quick breads = baking powder or baking soda • Flat breads = little or no leavening agent 7

Other ingredients • **add flavor • **boost fiber and nutrition 8

Focaccia Bread • Round yeast bread brushed with olive oil and flavored with rosemary 9

Making Quick Breads • Muffins and More • **sift together all dry ingredients (combine ingredients evenly) • **blend liquid ingredients together • **add liquid ingredients to dry ingredients • **stir until moist, lumpy 10

• Biscuits • **sift together all dry ingredients • **cut fat into dry ingredients (use pastry blender • **add liquid ingredients and stir just until blended 11

• knead = work and press it with the hands • ** press with heels of hands, fold over, give a quarter turn, press again 12

Faster Bread Making • **use dry bread mix • **buy frozen or refrigerated dough for breads and rolls • **brown-and-serve products • **use bread machine 13

Microwave Tips • **fill containers half full • **put containers on rack or inverted saucer to let air circulate • **rotate containers • **use batters with color or add topping for a more appealing look 14

Storing • **airtight containers for several days • **freeze in aluminum and then plastic bag • **cool dry place • **warmth and humidity increase mold growth 15

Summary • Breads are made of flour, liquid, fat, and often a leavening agent • Breads fall into three basic categories: yeast breads, quick breads, and flat breads 16

• The mixing method for quick bread depends on the kind of quick bread you’re making • When making yeast bread from scratch, allow several hours for the dough to rise 17

• Using convenience products or a microwave oven saves time when making homemade bread • Store homemade breads properly to keep them fresh and appealing 18

Tips for Using My. Pyramid 19

They’re Good for You!! Eating foods rich in fiber, such as whole grains, provides several health benefits: – ► Reduces the risk of heart disease – ► Decreases the incidence of constipation – ► Helps with weight management 20

Eat six “ 1 ounce-equivalents” of grain products daily (for a 2, 000 calorie diet): Make at least half of grains whole grain e uld com ts. sho r grains rain produc f you e rest o d or whole g Th riche rom en f 21

Definition: 1 ounce-equivalent In the grains food group, a “ 1 ounce-equivalent” is the amount of a food counted as equal to a 1 ounce slice of bread. Some equivalents include … 1 slice bread ½ cup cooked pasta, rice or cereal 1 cup ready-to-eat cereal 1 “mini” bagel ½ English muffin 1 small (2 -½” diameter) muffin 3 cups popcorn 1 small (6”) flour or corn tortilla 22

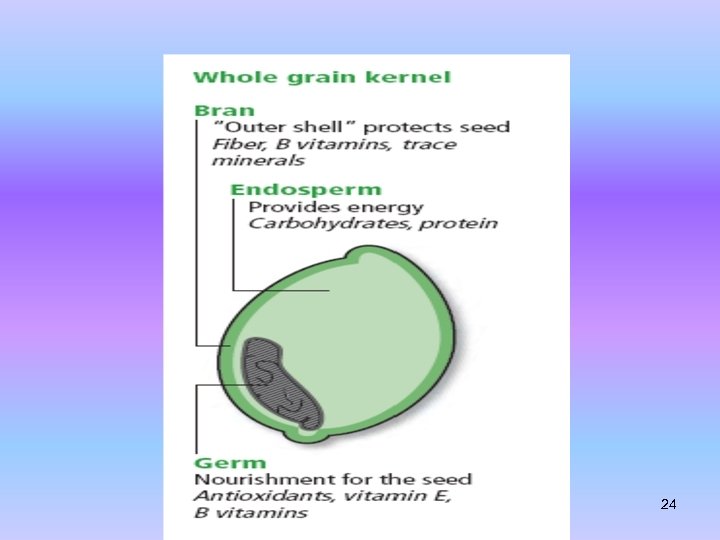
Refined grains have been milled — the bran and germ are removed. This process also removes much of the B vitamins, iron, and dietary fiber Most refined grains are enriched. This means certain B vitamins (thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, folic acid) and iron are added back after processing. Fiber is not added back to most enriched grains. 23
24

Examples of Whole Wheat • • • • Whole wheat Whole oats/oatmeal Whole grain corn Popcorn Brown & wild rice Whole rye Whole grain barley Buckwheat Tritacale Bulgur Millet Quinoa Sorghum 25
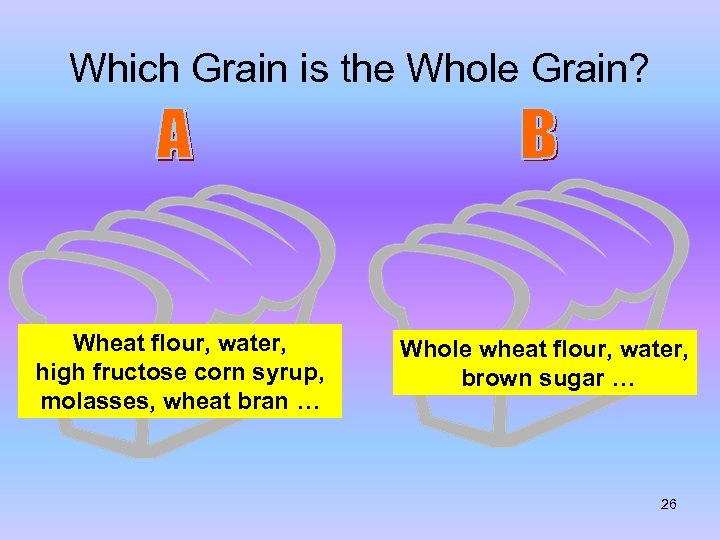
Which Grain is the Whole Grain? Wheat flour, water, high fructose corn syrup, molasses, wheat bran … Whole wheat flour, water, brown sugar … 26
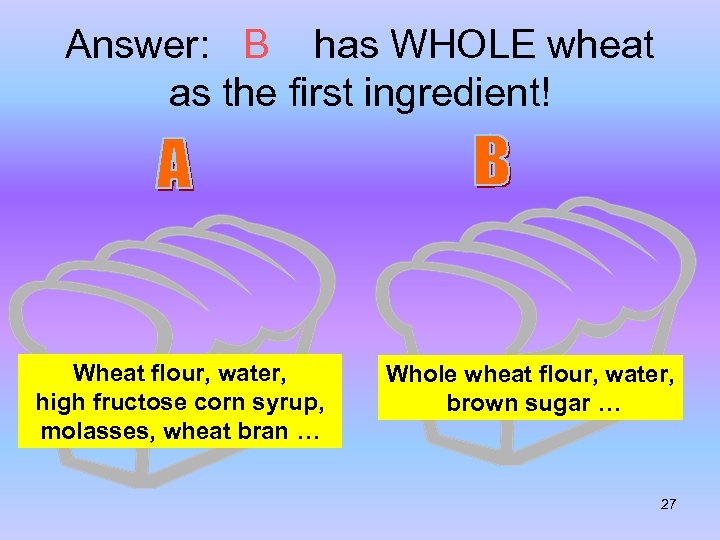
Answer: B has WHOLE wheat as the first ingredient! Wheat flour, water, high fructose corn syrup, molasses, wheat bran … Whole wheat flour, water, brown sugar … 27
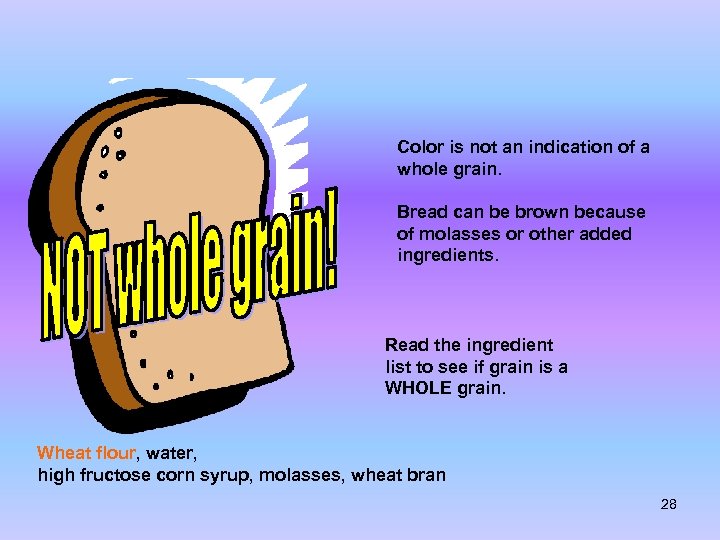
Color is not an indication of a whole grain. Bread can be brown because of molasses or other added ingredients. Read the ingredient list to see if grain is a WHOLE grain. Wheat flour, water, high fructose corn syrup, molasses, wheat bran 28
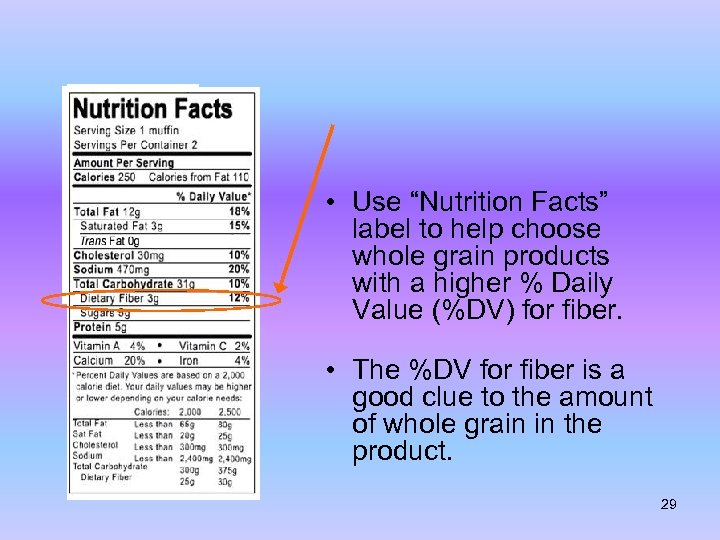
• Use “Nutrition Facts” label to help choose whole grain products with a higher % Daily Value (%DV) for fiber. • The %DV for fiber is a good clue to the amount of whole grain in the product. 29
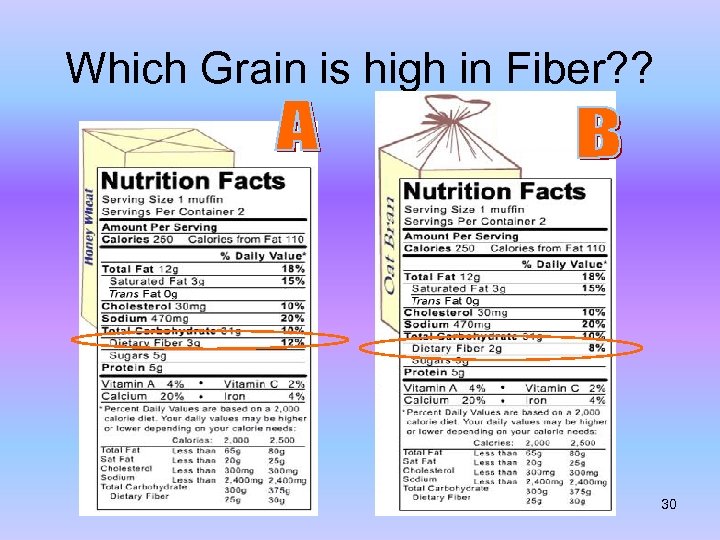
Which Grain is high in Fiber? ? 30

Answer: A with 3 grams of fiber! 31

Watch Wording on Grains Foods are usually not whole grain products if labeled with these words: • • • Multi-grain Stone-ground 100% wheat Cracked wheat Seven-grain Bran 32

• http: //www. schwebels. com/freshly-bakedbreads/whole-grain-and-multi-grainbreads/country-hearth-12 -grain 33
34
24200d7c0df15a0b65ee457eac88543c.ppt