a9022e411fa90ae66432a19539fb8291.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Queues, Deques, and Priority Queues Chapter 22
Queues, Deques, and Priority Queues Chapter 22
 Chapter Contents Specifications for the ADT Queue Using a Queue to Simulate a Waiting Line • The Classes Wait. Line and Customer Using a Queue to Compute the capital Gain in a Sale of Stock • The Classes Stock. Ledger and Stock. Purchase Specifications of the ADT Deque Using a Deque to Compute the Capital Gain in a Sale of Stock Specifications of the ADT Priority Queue Using a Priority Queue to Compute the Capital Gain in a Sale of Stock 2
Chapter Contents Specifications for the ADT Queue Using a Queue to Simulate a Waiting Line • The Classes Wait. Line and Customer Using a Queue to Compute the capital Gain in a Sale of Stock • The Classes Stock. Ledger and Stock. Purchase Specifications of the ADT Deque Using a Deque to Compute the Capital Gain in a Sale of Stock Specifications of the ADT Priority Queue Using a Priority Queue to Compute the Capital Gain in a Sale of Stock 2
 Specifications for the ADT Queue organizes entries according to order of entry • Exhibits first-in, first-out behavior • Contrast to stack which is last-in, first-out All additions are at the back of the queue Front of queue has items added first 3
Specifications for the ADT Queue organizes entries according to order of entry • Exhibits first-in, first-out behavior • Contrast to stack which is last-in, first-out All additions are at the back of the queue Front of queue has items added first 3
 Specifications for the ADT Queue Fig. 22 -1 Some everyday queues. 4
Specifications for the ADT Queue Fig. 22 -1 Some everyday queues. 4
 Specifications for the ADT Queue Interface for a queue of objects public interface queue. Interface { /** Task: Adds a new entry to the back of the queue. * @param new. Entry an object to be added */ public void enqueue(Object new. Entry); /** Task: Removes and returns the front of the queue. * @return either the object at the front of the queue or null if the queue was empty */ public Object dequeue(); /** Task: Retrieves the front of the queue. * @return either the object at the front of the queue or null if the queue is empty */ public Object get. Front(); /** Task: Determines whether the queue is empty. * @return true if the queue is empty */ public boolean is. Empty(); /** Task: Removes all entries from the queue. */ public void clear(); } // end queue. Interface 5
Specifications for the ADT Queue Interface for a queue of objects public interface queue. Interface { /** Task: Adds a new entry to the back of the queue. * @param new. Entry an object to be added */ public void enqueue(Object new. Entry); /** Task: Removes and returns the front of the queue. * @return either the object at the front of the queue or null if the queue was empty */ public Object dequeue(); /** Task: Retrieves the front of the queue. * @return either the object at the front of the queue or null if the queue is empty */ public Object get. Front(); /** Task: Determines whether the queue is empty. * @return true if the queue is empty */ public boolean is. Empty(); /** Task: Removes all entries from the queue. */ public void clear(); } // end queue. Interface 5
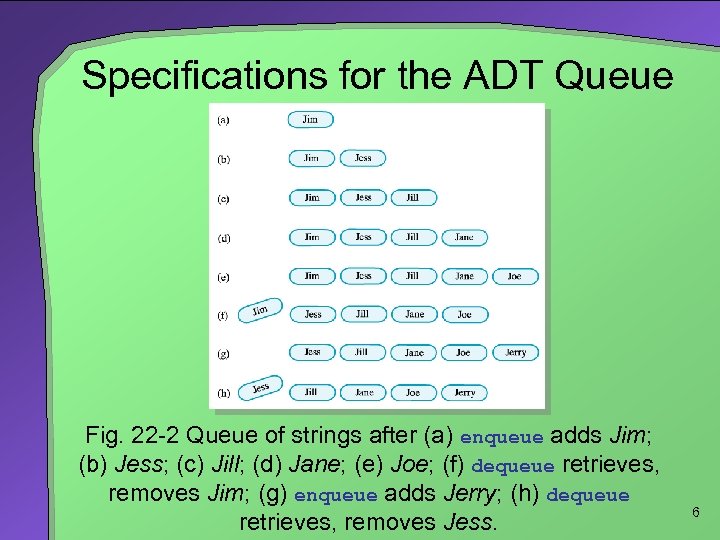 Specifications for the ADT Queue Fig. 22 -2 Queue of strings after (a) enqueue adds Jim; (b) Jess; (c) Jill; (d) Jane; (e) Joe; (f) dequeue retrieves, removes Jim; (g) enqueue adds Jerry; (h) dequeue retrieves, removes Jess. 6
Specifications for the ADT Queue Fig. 22 -2 Queue of strings after (a) enqueue adds Jim; (b) Jess; (c) Jill; (d) Jane; (e) Joe; (f) dequeue retrieves, removes Jim; (g) enqueue adds Jerry; (h) dequeue retrieves, removes Jess. 6
 Using a Queue to Simulate a Waiting Line Fig. 22 -3 A line, or queue of people. 7
Using a Queue to Simulate a Waiting Line Fig. 22 -3 A line, or queue of people. 7
 Classes Wait. Line and Customer Fig. 22 -4 A CRC card for the class Wait. Line. 8
Classes Wait. Line and Customer Fig. 22 -4 A CRC card for the class Wait. Line. 8
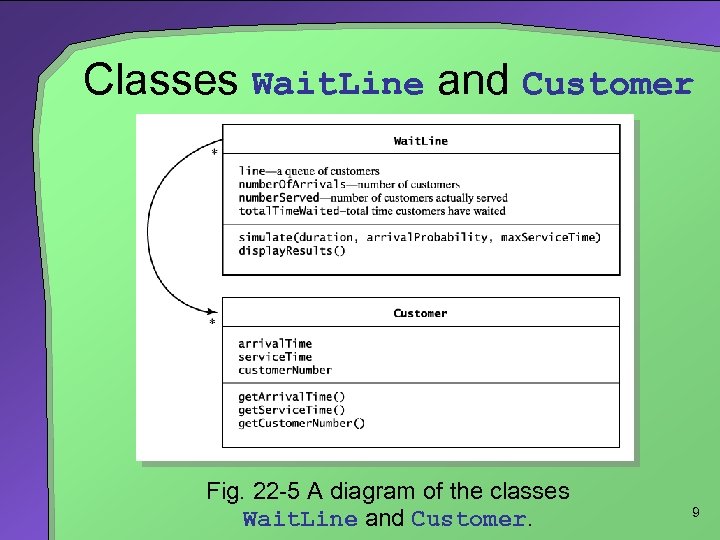 Classes Wait. Line and Customer Fig. 22 -5 A diagram of the classes Wait. Line and Customer. 9
Classes Wait. Line and Customer Fig. 22 -5 A diagram of the classes Wait. Line and Customer. 9
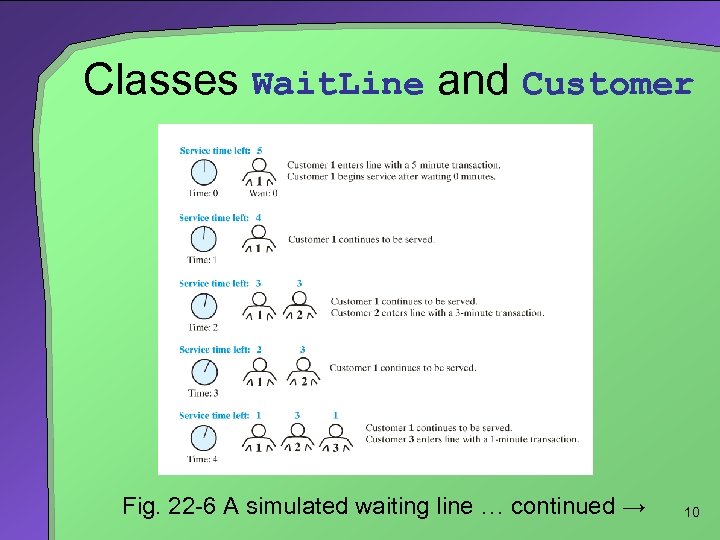 Classes Wait. Line and Customer Fig. 22 -6 A simulated waiting line … continued → 10
Classes Wait. Line and Customer Fig. 22 -6 A simulated waiting line … continued → 10
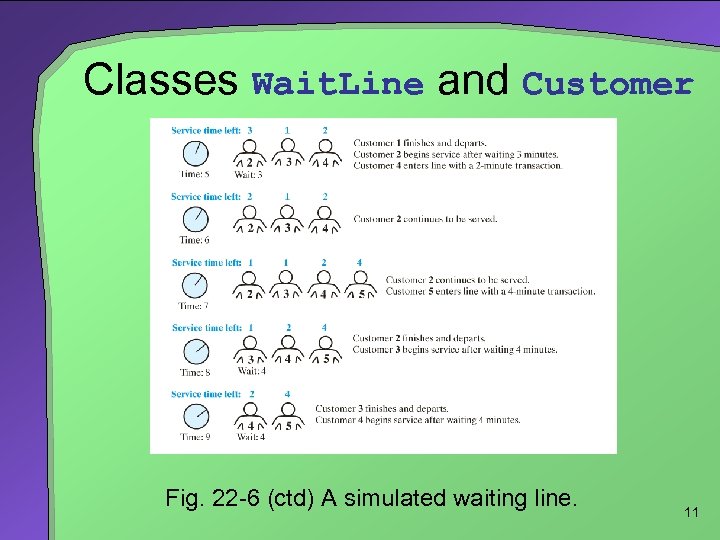 Classes Wait. Line and Customer Fig. 22 -6 (ctd) A simulated waiting line. 11
Classes Wait. Line and Customer Fig. 22 -6 (ctd) A simulated waiting line. 11
 Using a Queue to Compute Capital Gain in a Sale of Stock Must sell stocks in same order they were purchased • Must use the difference in selling price and purchase price to calculate capital gain We use a queue to • Record investment transactions chronologically • Compute capital gain of the stock 12
Using a Queue to Compute Capital Gain in a Sale of Stock Must sell stocks in same order they were purchased • Must use the difference in selling price and purchase price to calculate capital gain We use a queue to • Record investment transactions chronologically • Compute capital gain of the stock 12
 Classes Stock. Ledger and Stock. Purchase Fig. 22 -7 A CRC card for the class Stock. Ledger 13
Classes Stock. Ledger and Stock. Purchase Fig. 22 -7 A CRC card for the class Stock. Ledger 13
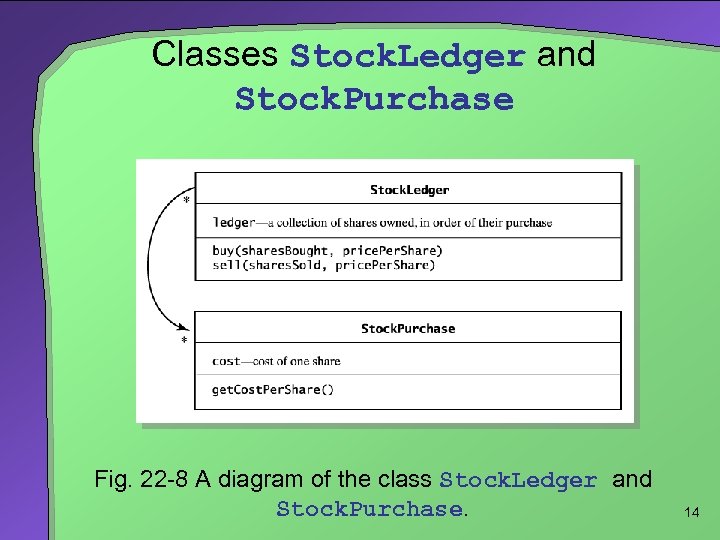 Classes Stock. Ledger and Stock. Purchase Fig. 22 -8 A diagram of the class Stock. Ledger and Stock. Purchase. 14
Classes Stock. Ledger and Stock. Purchase Fig. 22 -8 A diagram of the class Stock. Ledger and Stock. Purchase. 14
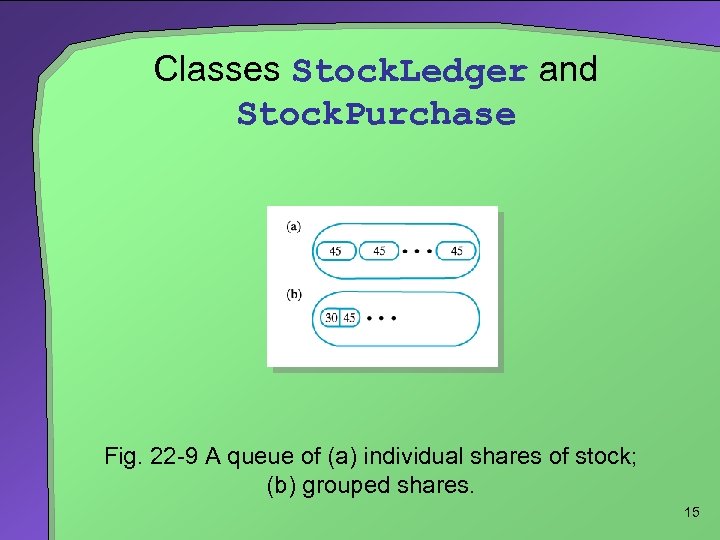 Classes Stock. Ledger and Stock. Purchase Fig. 22 -9 A queue of (a) individual shares of stock; (b) grouped shares. 15
Classes Stock. Ledger and Stock. Purchase Fig. 22 -9 A queue of (a) individual shares of stock; (b) grouped shares. 15
 Specifications of the ADT Deque A Double ended queue Has operations that • Add, remove, or retrieve entries • At both its front and back Combines and expands the operations of queue and stack 16
Specifications of the ADT Deque A Double ended queue Has operations that • Add, remove, or retrieve entries • At both its front and back Combines and expands the operations of queue and stack 16
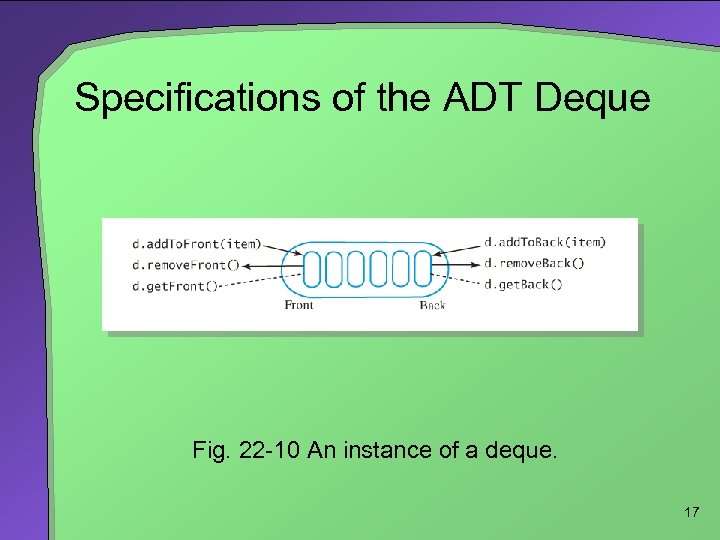 Specifications of the ADT Deque Fig. 22 -10 An instance of a deque. 17
Specifications of the ADT Deque Fig. 22 -10 An instance of a deque. 17
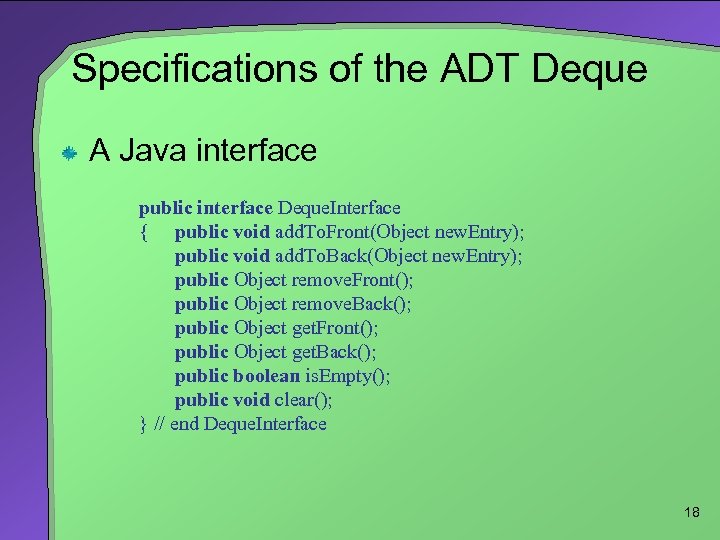 Specifications of the ADT Deque A Java interface public interface Deque. Interface { public void add. To. Front(Object new. Entry); public void add. To. Back(Object new. Entry); public Object remove. Front(); public Object remove. Back(); public Object get. Front(); public Object get. Back(); public boolean is. Empty(); public void clear(); } // end Deque. Interface 18
Specifications of the ADT Deque A Java interface public interface Deque. Interface { public void add. To. Front(Object new. Entry); public void add. To. Back(Object new. Entry); public Object remove. Front(); public Object remove. Back(); public Object get. Front(); public Object get. Back(); public boolean is. Empty(); public void clear(); } // end Deque. Interface 18
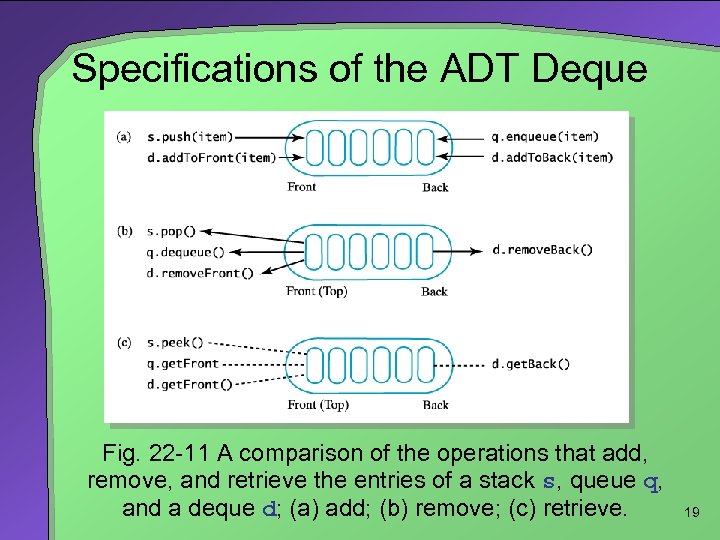 Specifications of the ADT Deque Fig. 22 -11 A comparison of the operations that add, remove, and retrieve the entries of a stack s, queue q, and a deque d; (a) add; (b) remove; (c) retrieve. 19
Specifications of the ADT Deque Fig. 22 -11 A comparison of the operations that add, remove, and retrieve the entries of a stack s, queue q, and a deque d; (a) add; (b) remove; (c) retrieve. 19
 Using a Deque to Compute Capital Gain in Sale of Stock Revise the class Stock. Purchase • Represents purchase of n shares at d dollars per share • Constructor is changed • Accessor methods for new fields added Revise class Stock. Ledger • Method ledger now an instance of a deque • Method buy now creates instance of Stock. Purchase, places it at back of deque • Method sell also altered 20
Using a Deque to Compute Capital Gain in Sale of Stock Revise the class Stock. Purchase • Represents purchase of n shares at d dollars per share • Constructor is changed • Accessor methods for new fields added Revise class Stock. Ledger • Method ledger now an instance of a deque • Method buy now creates instance of Stock. Purchase, places it at back of deque • Method sell also altered 20
 Specifications of the ADT Priority Queue Organizes objects according to priorities • Contrast to regular queue in order of arrival Priority queue example – a hospital ER Priority can be specified by an integer • Must define whether high number is high priority or … • Low number (say 0) is high priority Other objects can specify priority • Object must have a compare. To method 21
Specifications of the ADT Priority Queue Organizes objects according to priorities • Contrast to regular queue in order of arrival Priority queue example – a hospital ER Priority can be specified by an integer • Must define whether high number is high priority or … • Low number (say 0) is high priority Other objects can specify priority • Object must have a compare. To method 21
 Specifications of the ADT Priority Queue public interface Priority. Queue. Interface { public void add(Comparable new. Entry); public Comparable remove(); public Comparable get(); public boolean is. Empty(); public int get. Size(); public void clear(); } // end Priority. Queue. Interface 22
Specifications of the ADT Priority Queue public interface Priority. Queue. Interface { public void add(Comparable new. Entry); public Comparable remove(); public Comparable get(); public boolean is. Empty(); public int get. Size(); public void clear(); } // end Priority. Queue. Interface 22
 Using Priority Queue to Compute Capital Gain in Sale of Stock Revise class Stock. Purchase • Include data field date • Method compare. To is made available • This field is the priority – earliest date is highest priority 23
Using Priority Queue to Compute Capital Gain in Sale of Stock Revise class Stock. Purchase • Include data field date • Method compare. To is made available • This field is the priority – earliest date is highest priority 23


