bef4cbac475e201a7d86b5b87ca50e44.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Question C 1. 01 Description: Eliciting prior conceptions about "work" and introducing the physics definition. Source: A 2 L: UMPERG-ctqpe 50
Question C 1. 01 Description: Eliciting prior conceptions about "work" and introducing the physics definition. Source: A 2 L: UMPERG-ctqpe 50
 In which of the following cases would you do the least amount of work? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. You push a box a distance d across a floor. You pick up the box, walk a distance d, and gently put the box down on the floor. You pick up the box, walk a distance d, and drop the box. Both 1 and 2 are the least. Both 1 and 3 are the least. Both 2 and 3 are the least. The amount of work done is the same in all three cases. The amount of work cannot be determined from information given.
In which of the following cases would you do the least amount of work? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. You push a box a distance d across a floor. You pick up the box, walk a distance d, and gently put the box down on the floor. You pick up the box, walk a distance d, and drop the box. Both 1 and 2 are the least. Both 1 and 3 are the least. Both 2 and 3 are the least. The amount of work done is the same in all three cases. The amount of work cannot be determined from information given.
 Question C 1. 02 a Description: Integrating work and force ideas. Source: Leonard P 151
Question C 1. 02 a Description: Integrating work and force ideas. Source: Leonard P 151
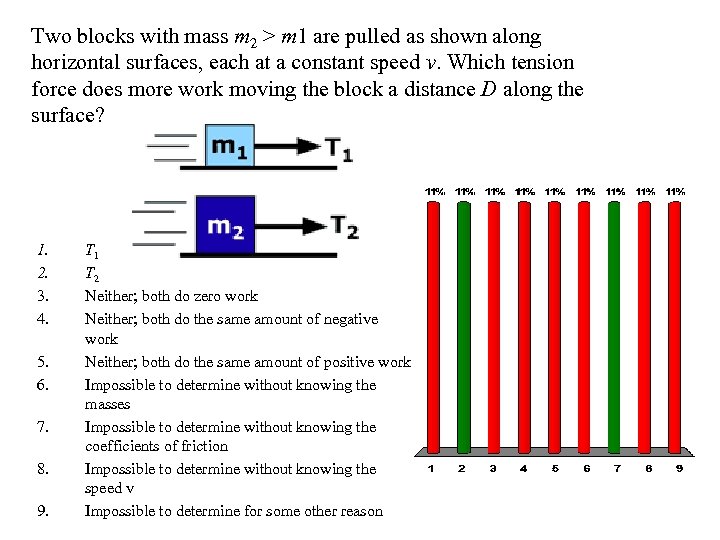 Two blocks with mass m 2 > m 1 are pulled as shown along horizontal surfaces, each at a constant speed v. Which tension force does more work moving the block a distance D along the surface? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. T 1 T 2 Neither; both do zero work Neither; both do the same amount of negative work Neither; both do the same amount of positive work Impossible to determine without knowing the masses Impossible to determine without knowing the coefficients of friction Impossible to determine without knowing the speed v Impossible to determine for some other reason
Two blocks with mass m 2 > m 1 are pulled as shown along horizontal surfaces, each at a constant speed v. Which tension force does more work moving the block a distance D along the surface? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. T 1 T 2 Neither; both do zero work Neither; both do the same amount of negative work Neither; both do the same amount of positive work Impossible to determine without knowing the masses Impossible to determine without knowing the coefficients of friction Impossible to determine without knowing the speed v Impossible to determine for some other reason
 Question C 1. 02 b Description: Integrating work and force ideas, emphasizing what the definition of work depends upon.
Question C 1. 02 b Description: Integrating work and force ideas, emphasizing what the definition of work depends upon.
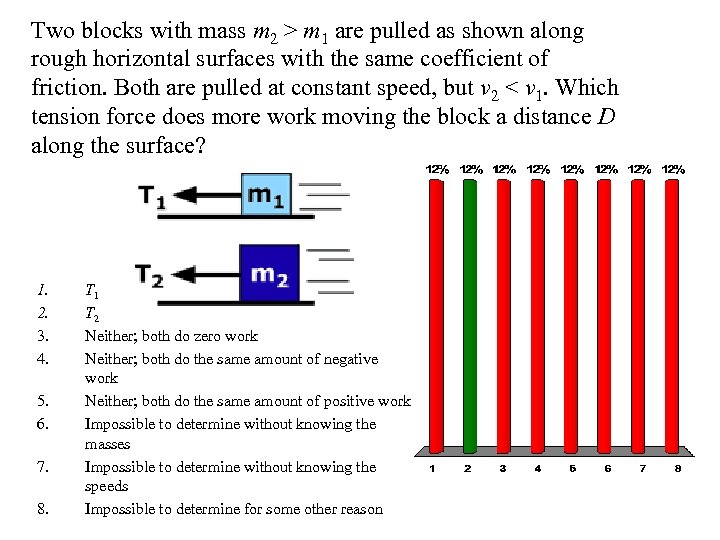 Two blocks with mass m 2 > m 1 are pulled as shown along rough horizontal surfaces with the same coefficient of friction. Both are pulled at constant speed, but v 2 < v 1. Which tension force does more work moving the block a distance D along the surface? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. T 1 T 2 Neither; both do zero work Neither; both do the same amount of negative work Neither; both do the same amount of positive work Impossible to determine without knowing the masses Impossible to determine without knowing the speeds Impossible to determine for some other reason
Two blocks with mass m 2 > m 1 are pulled as shown along rough horizontal surfaces with the same coefficient of friction. Both are pulled at constant speed, but v 2 < v 1. Which tension force does more work moving the block a distance D along the surface? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. T 1 T 2 Neither; both do zero work Neither; both do the same amount of negative work Neither; both do the same amount of positive work Impossible to determine without knowing the masses Impossible to determine without knowing the speeds Impossible to determine for some other reason
 Question C 1. 02 c Description: Integrating work and force ideas, emphasizing the role of a force's components in the work it does.
Question C 1. 02 c Description: Integrating work and force ideas, emphasizing the role of a force's components in the work it does.
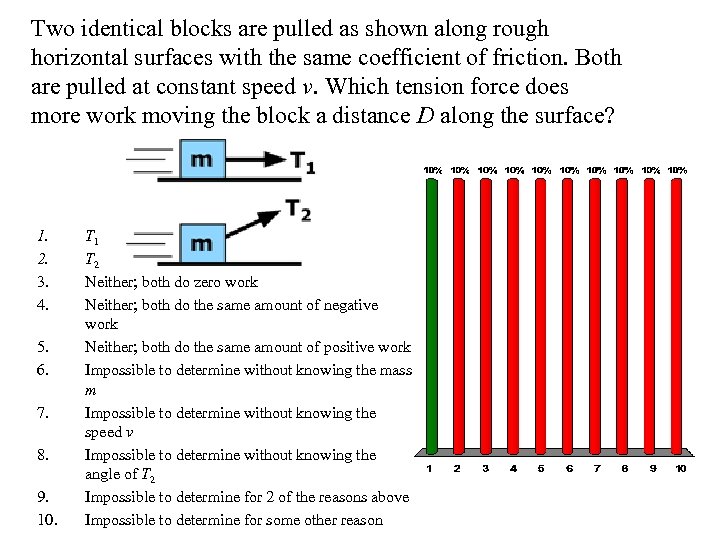 Two identical blocks are pulled as shown along rough horizontal surfaces with the same coefficient of friction. Both are pulled at constant speed v. Which tension force does more work moving the block a distance D along the surface? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. T 1 T 2 Neither; both do zero work Neither; both do the same amount of negative work Neither; both do the same amount of positive work Impossible to determine without knowing the mass m Impossible to determine without knowing the speed v Impossible to determine without knowing the angle of T 2 Impossible to determine for 2 of the reasons above Impossible to determine for some other reason
Two identical blocks are pulled as shown along rough horizontal surfaces with the same coefficient of friction. Both are pulled at constant speed v. Which tension force does more work moving the block a distance D along the surface? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. T 1 T 2 Neither; both do zero work Neither; both do the same amount of negative work Neither; both do the same amount of positive work Impossible to determine without knowing the mass m Impossible to determine without knowing the speed v Impossible to determine without knowing the angle of T 2 Impossible to determine for 2 of the reasons above Impossible to determine for some other reason
 Question C 1. 03 a Description: Exploring work, preparing for energy conservation. Source: A 2 L: UMPERG-ctqpe 62
Question C 1. 03 a Description: Exploring work, preparing for energy conservation. Source: A 2 L: UMPERG-ctqpe 62
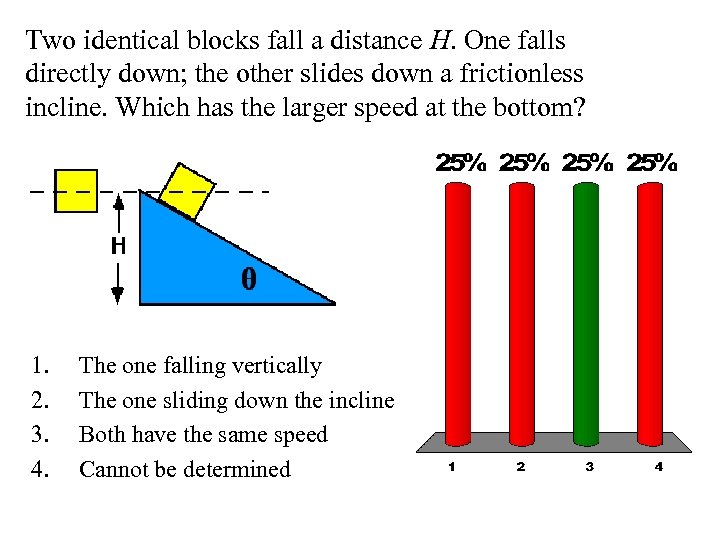 Two identical blocks fall a distance H. One falls directly down; the other slides down a frictionless incline. Which has the larger speed at the bottom? 1. 2. 3. 4. The one falling vertically The one sliding down the incline Both have the same speed Cannot be determined
Two identical blocks fall a distance H. One falls directly down; the other slides down a frictionless incline. Which has the larger speed at the bottom? 1. 2. 3. 4. The one falling vertically The one sliding down the incline Both have the same speed Cannot be determined
 Question C 1. 03 b Description: Exploring work, preparing for energy conservation. Source: A 2 L: UMPERG-ctqpe 64
Question C 1. 03 b Description: Exploring work, preparing for energy conservation. Source: A 2 L: UMPERG-ctqpe 64
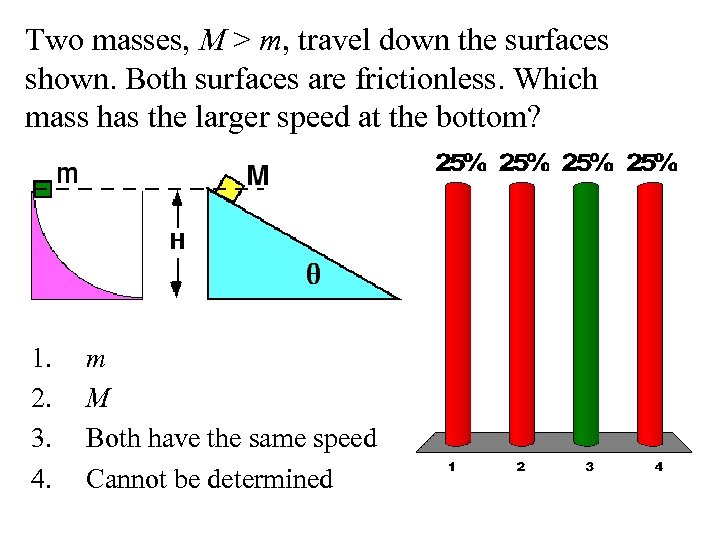 Two masses, M > m, travel down the surfaces shown. Both surfaces are frictionless. Which mass has the larger speed at the bottom? 1. 2. 3. 4. m M Both have the same speed Cannot be determined
Two masses, M > m, travel down the surfaces shown. Both surfaces are frictionless. Which mass has the larger speed at the bottom? 1. 2. 3. 4. m M Both have the same speed Cannot be determined
 Question B 2. 08 Description: Introducing the spring force. Source: Leonard/P 151 S 03
Question B 2. 08 Description: Introducing the spring force. Source: Leonard/P 151 S 03
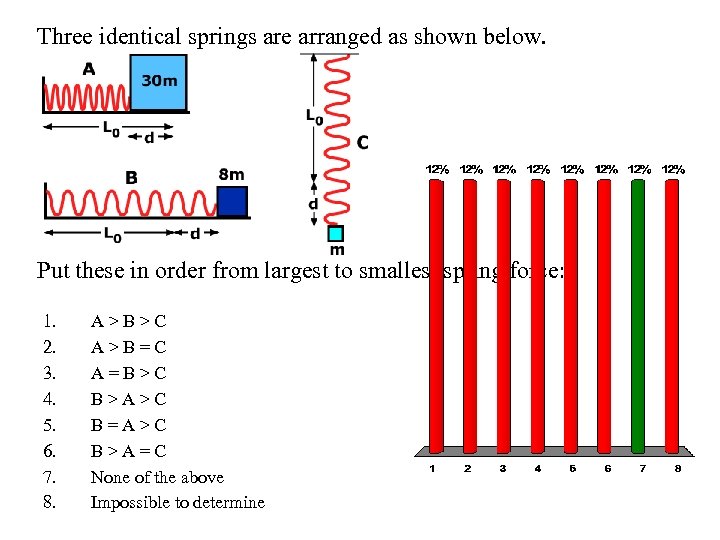 Three identical springs are arranged as shown below. Put these in order from largest to smallest spring force: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. A>B>C A>B=C A=B>C B>A>C B=A>C B>A=C None of the above Impossible to determine
Three identical springs are arranged as shown below. Put these in order from largest to smallest spring force: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. A>B>C A>B=C A=B>C B>A>C B=A>C B>A=C None of the above Impossible to determine
 Question B 2. 09 Description: Reasoning about forces and accelerations with the spring force. Source: A 2 L: UMPERG
Question B 2. 09 Description: Reasoning about forces and accelerations with the spring force. Source: A 2 L: UMPERG
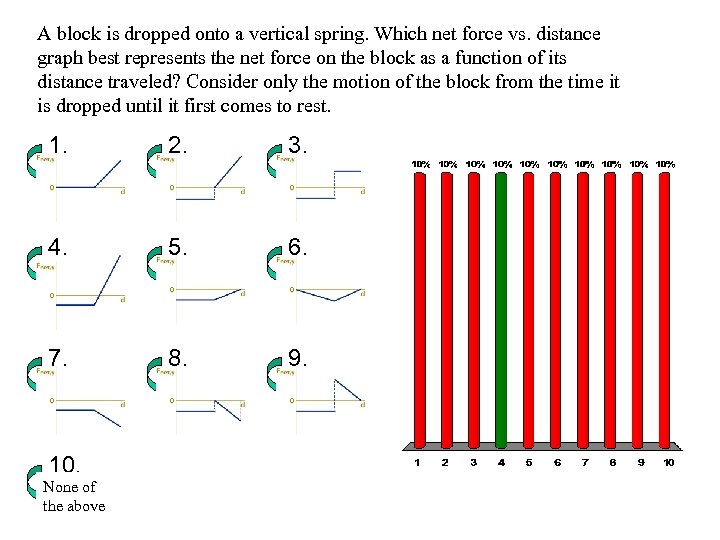 A block is dropped onto a vertical spring. Which net force vs. distance graph best represents the net force on the block as a function of its distance traveled? Consider only the motion of the block from the time it is dropped until it first comes to rest. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. None of the above
A block is dropped onto a vertical spring. Which net force vs. distance graph best represents the net force on the block as a function of its distance traveled? Consider only the motion of the block from the time it is dropped until it first comes to rest. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. None of the above
 Question C 2. 01 a Description: Developing strategic problemsolving skills. Source: Gerace PRS-ARHS 6/12/01
Question C 2. 01 a Description: Developing strategic problemsolving skills. Source: Gerace PRS-ARHS 6/12/01
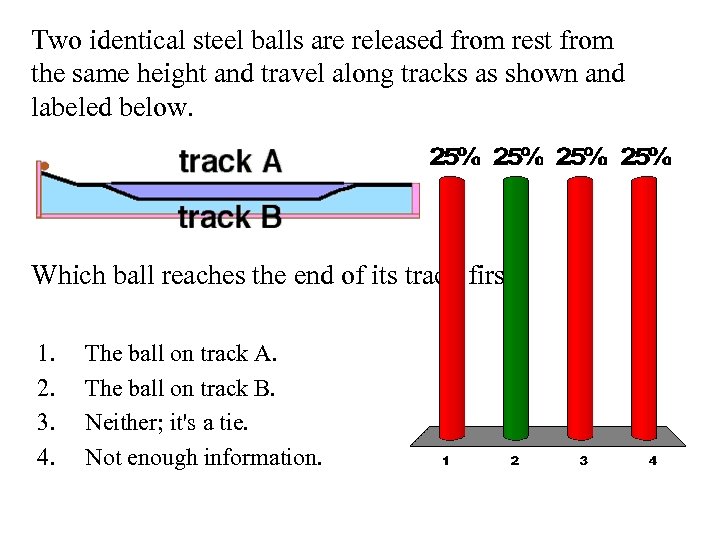 Two identical steel balls are released from rest from the same height and travel along tracks as shown and labeled below. Which ball reaches the end of its track first? 1. 2. 3. 4. The ball on track A. The ball on track B. Neither; it's a tie. Not enough information.
Two identical steel balls are released from rest from the same height and travel along tracks as shown and labeled below. Which ball reaches the end of its track first? 1. 2. 3. 4. The ball on track A. The ball on track B. Neither; it's a tie. Not enough information.
 Question C 2. 01 b Description: Developing strategic problemsolving skills. Source: Gerace PRS-ARHS 6/12/01
Question C 2. 01 b Description: Developing strategic problemsolving skills. Source: Gerace PRS-ARHS 6/12/01
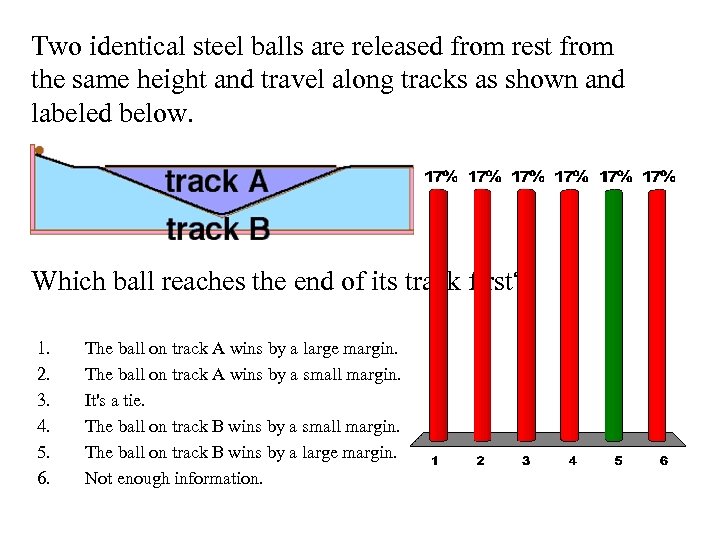 Two identical steel balls are released from rest from the same height and travel along tracks as shown and labeled below. Which ball reaches the end of its track first? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. The ball on track A wins by a large margin. The ball on track A wins by a small margin. It's a tie. The ball on track B wins by a small margin. The ball on track B wins by a large margin. Not enough information.
Two identical steel balls are released from rest from the same height and travel along tracks as shown and labeled below. Which ball reaches the end of its track first? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. The ball on track A wins by a large margin. The ball on track A wins by a small margin. It's a tie. The ball on track B wins by a small margin. The ball on track B wins by a large margin. Not enough information.


