0a0fedc7871cf2ef0e886169ff8f3a66.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25

 Query Expansion Technique In Information Retrieval
Query Expansion Technique In Information Retrieval
 Overview: 1. Query expansion overview 2. QE in Information retrieval 3. Query expansion Techniques
Overview: 1. Query expansion overview 2. QE in Information retrieval 3. Query expansion Techniques
 QUERY EXPANSION :
QUERY EXPANSION :
 What is Query Expansion ? Ú Query Expansion is the term given when a search engine adding search terms to a user’s weighted search. Ú The goal is to improve precision and/or recall. Ú Example: User Query: “car”; Expanded Query: “car cars automobiles auto” etc…
What is Query Expansion ? Ú Query Expansion is the term given when a search engine adding search terms to a user’s weighted search. Ú The goal is to improve precision and/or recall. Ú Example: User Query: “car”; Expanded Query: “car cars automobiles auto” etc…
 What is Query Expansion ? Ú Query expansion (QE) is the process of reformulating a seed query to improve retrieval performance in information retrieval operations Ú Query expansion involves techniques: Ú Finding synonyms of words, and searching for the synonyms as well Ú Finding all the various morphological forms of words by stemming each word in the search query Ú Fixing spelling errors and automatically searching for the corrected form or suggesting it in the results
What is Query Expansion ? Ú Query expansion (QE) is the process of reformulating a seed query to improve retrieval performance in information retrieval operations Ú Query expansion involves techniques: Ú Finding synonyms of words, and searching for the synonyms as well Ú Finding all the various morphological forms of words by stemming each word in the search query Ú Fixing spelling errors and automatically searching for the corrected form or suggesting it in the results
 QE in information retrieval Ú Information retrieval (IR) is the area of study concerned with searching for documents, for information within documents and the World Wide Web Ú The first automated information retrieval systems were introduced in the 1950 s and 1960 s Ú An information retrieval process begins when a user enters a query into the system Ú User queries are matched against the database information.
QE in information retrieval Ú Information retrieval (IR) is the area of study concerned with searching for documents, for information within documents and the World Wide Web Ú The first automated information retrieval systems were introduced in the 1950 s and 1960 s Ú An information retrieval process begins when a user enters a query into the system Ú User queries are matched against the database information.
 Ú Most IR systems compute a numeric score on how well each object in the database match the query, and rank the objects according to this value. The top ranking objects are then shown to the user
Ú Most IR systems compute a numeric score on how well each object in the database match the query, and rank the objects according to this value. The top ranking objects are then shown to the user
 QUERY EXPANSION TECHNIQUES:
QUERY EXPANSION TECHNIQUES:
 Techniques: 1. RELEVANCE FEED BACK 2. LOCAL ANALYSIS 3. GLOBAL ANALYSIS 4. Thesauri Query Expansion
Techniques: 1. RELEVANCE FEED BACK 2. LOCAL ANALYSIS 3. GLOBAL ANALYSIS 4. Thesauri Query Expansion
 1. Relevance feedback: Ú The user issues a (short, simple) query Ú The system returns an initial set of retrieval results Ú The user marks some returned documents as relevant or not relevant Ú The system computes a better representation of the information need based on the user feedback Ú The system displays a revised set of retrieval results Ú This can go through one or more iterations
1. Relevance feedback: Ú The user issues a (short, simple) query Ú The system returns an initial set of retrieval results Ú The user marks some returned documents as relevant or not relevant Ú The system computes a better representation of the information need based on the user feedback Ú The system displays a revised set of retrieval results Ú This can go through one or more iterations
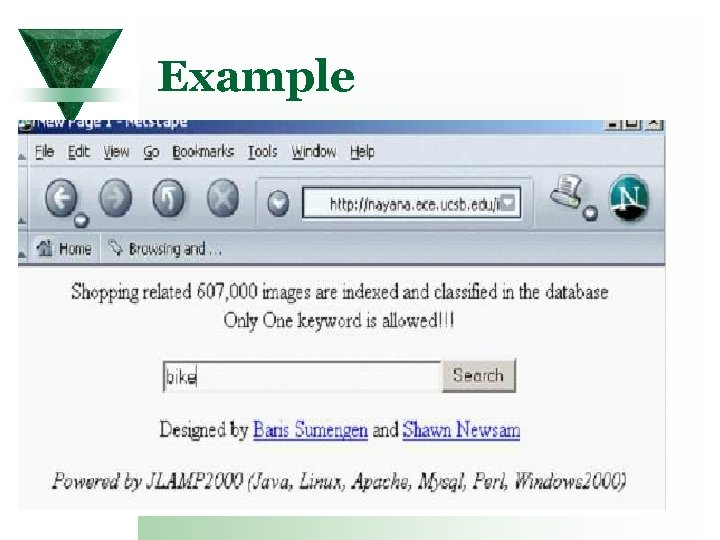 Example
Example
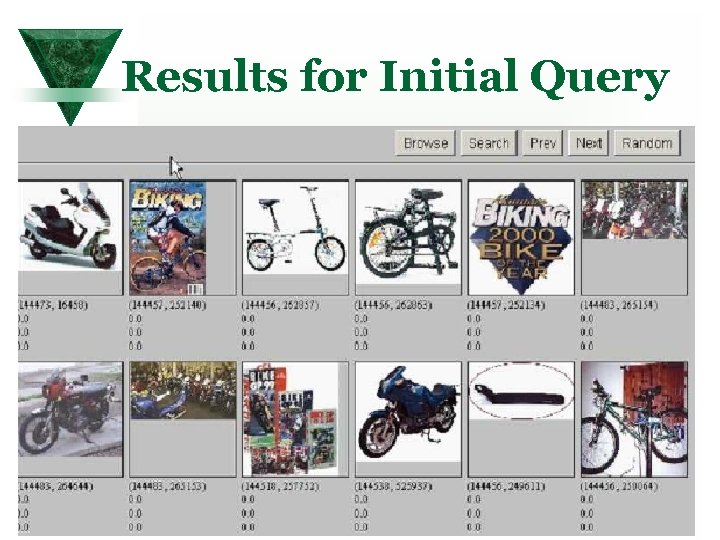 Results for Initial Query
Results for Initial Query
 User Feedback: Select What is Relevant
User Feedback: Select What is Relevant
 Results After Relevance Feedback
Results After Relevance Feedback
 GLOBAL VS. LOCAL ANALYSIS METHODS
GLOBAL VS. LOCAL ANALYSIS METHODS
 Global vs. Local Methods Ú Two general approaches for increasing recall through query reformulation: Ú Local methods are query-dependent Ú Relevance feedback is a local method Ú Global methods are independent of the query Ú Theasuri Query expansion is a global method
Global vs. Local Methods Ú Two general approaches for increasing recall through query reformulation: Ú Local methods are query-dependent Ú Relevance feedback is a local method Ú Global methods are independent of the query Ú Theasuri Query expansion is a global method
 Local Analysis Ú Different from global analysis, local analysis uses only some initially retrieved documents for further query expansion. Ú A well-known local analysis technique is relevance feedback which modifies a query based on user’s relevance judgments of the retrieved documents.
Local Analysis Ú Different from global analysis, local analysis uses only some initially retrieved documents for further query expansion. Ú A well-known local analysis technique is relevance feedback which modifies a query based on user’s relevance judgments of the retrieved documents.
 Global Analysis Ú Global analysis is one of the first techniques to produce consistent and effective improvements through query expansion. Ú earliest global analysis techniques is term clustering which groups document terms into clusters based on their co-occurrences. Ú To expand a query, terms which are the most similar to the query terms are identified and added.
Global Analysis Ú Global analysis is one of the first techniques to produce consistent and effective improvements through query expansion. Ú earliest global analysis techniques is term clustering which groups document terms into clusters based on their co-occurrences. Ú To expand a query, terms which are the most similar to the query terms are identified and added.
 THESAURI QUERY EXPANSION
THESAURI QUERY EXPANSION
 Thesauri Query Expansion Ú In (global) query expansion, the query is modified based on some global resource, i. e. a resource that is not query-dependent. Ú Main information we use: (near-)synonymy A publication or database that collects (near) synonyms is called a thesaurus. Ú We will look at two types of thesauri: manually created and automatically created.
Thesauri Query Expansion Ú In (global) query expansion, the query is modified based on some global resource, i. e. a resource that is not query-dependent. Ú Main information we use: (near-)synonymy A publication or database that collects (near) synonyms is called a thesaurus. Ú We will look at two types of thesauri: manually created and automatically created.
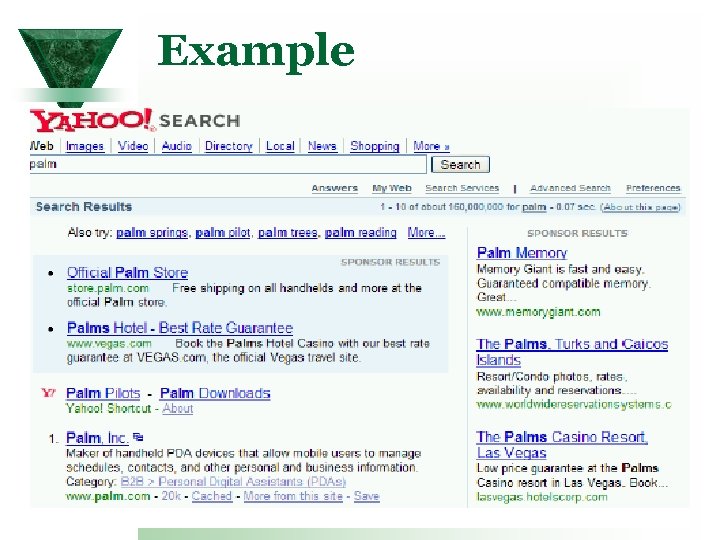 Example
Example
 Thesaurus-based Query Expansion Ú For each term t in the query, expand the query with words thesaurus lists as semantically related with it. Ú Example: hospital → medical
Thesaurus-based Query Expansion Ú For each term t in the query, expand the query with words thesaurus lists as semantically related with it. Ú Example: hospital → medical
 Automatic Thesaurus Generation Ú Attempt to generate a thesaurus automatically by analyzing the distribution of words in documents or by mining query logs Ú Fundamental notion: similarity between two words Ú Definition 1: Two words are similar if they co-occur with similar words. Ú Definition 2: Two words are similar if they occur in a given grammatical relation with the same words. Ú You can harvest, peel, eat, prepare, etc. apples and oranges, so apples and oranges must be similar.
Automatic Thesaurus Generation Ú Attempt to generate a thesaurus automatically by analyzing the distribution of words in documents or by mining query logs Ú Fundamental notion: similarity between two words Ú Definition 1: Two words are similar if they co-occur with similar words. Ú Definition 2: Two words are similar if they occur in a given grammatical relation with the same words. Ú You can harvest, peel, eat, prepare, etc. apples and oranges, so apples and oranges must be similar.
 Examples
Examples


