2f1a5ae49f34e422522fd4135332b148.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22

Quantum Opacity and Refractivity in HBT Puzzle Jin-Hee Yoon Dept. of Physics, Inha University, Korea John G. Cramer, Gerald A. Miller, M. S. Wu Dept. of Physics, University of Washington, US 2005. 11. 5 Inha Nuclear Physics Group
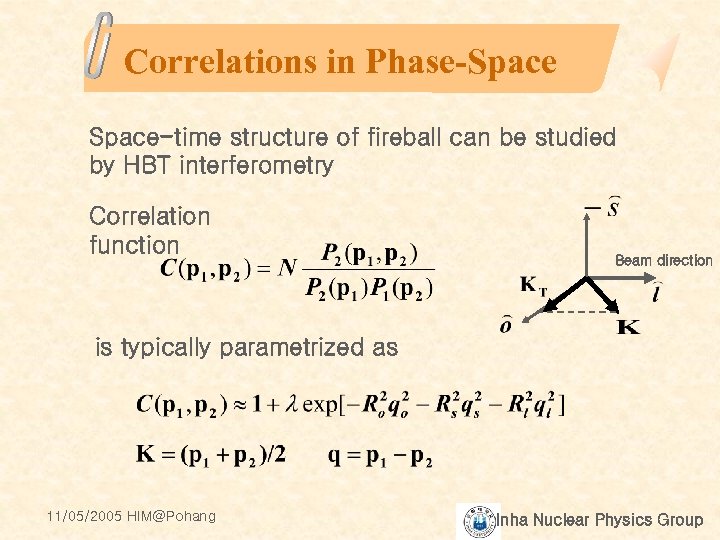
Correlations in Phase-Space-time structure of fireball can be studied by HBT interferometry Correlation function Beam direction is typically parametrized as 11/05/2005 HIM@Pohang Inha Nuclear Physics Group
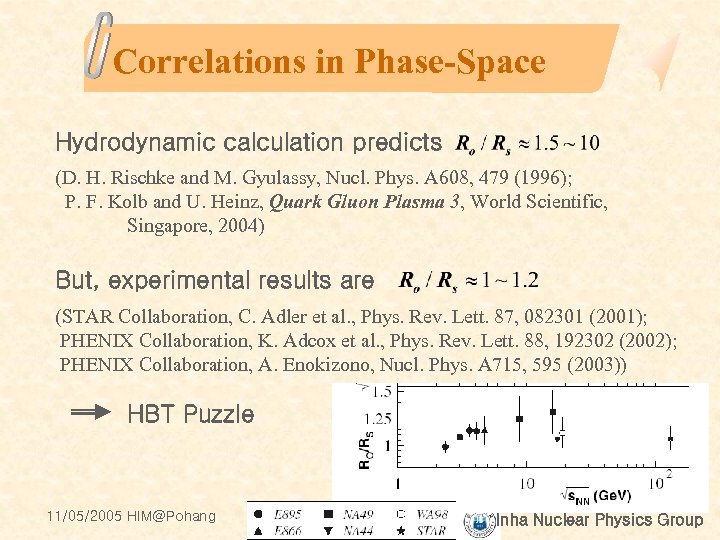
Correlations in Phase-Space Hydrodynamic calculation predicts (D. H. Rischke and M. Gyulassy, Nucl. Phys. A 608, 479 (1996); P. F. Kolb and U. Heinz, Quark Gluon Plasma 3, World Scientific, Singapore, 2004) But, experimental results are (STAR Collaboration, C. Adler et al. , Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 082301 (2001); PHENIX Collaboration, K. Adcox et al. , Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 192302 (2002); PHENIX Collaboration, A. Enokizono, Nucl. Phys. A 715, 595 (2003)) HBT Puzzle 11/05/2005 HIM@Pohang Inha Nuclear Physics Group

Correlations in Phase-Space Experimental Data(Au+Au@200 Ge. V) shows Dense Medium OPACITY and Refractive Effects Our Purpose : Quantum mechanical treatment of Opacity & Refractive effects which reproduces 11/05/2005 HIM@Pohang Inha Nuclear Physics Group
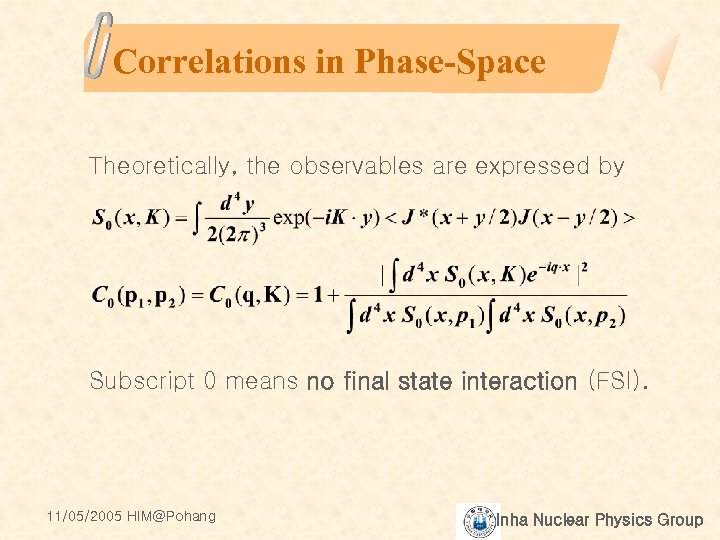
Correlations in Phase-Space Theoretically, the observables are expressed by Subscript 0 means no final state interaction (FSI). 11/05/2005 HIM@Pohang Inha Nuclear Physics Group
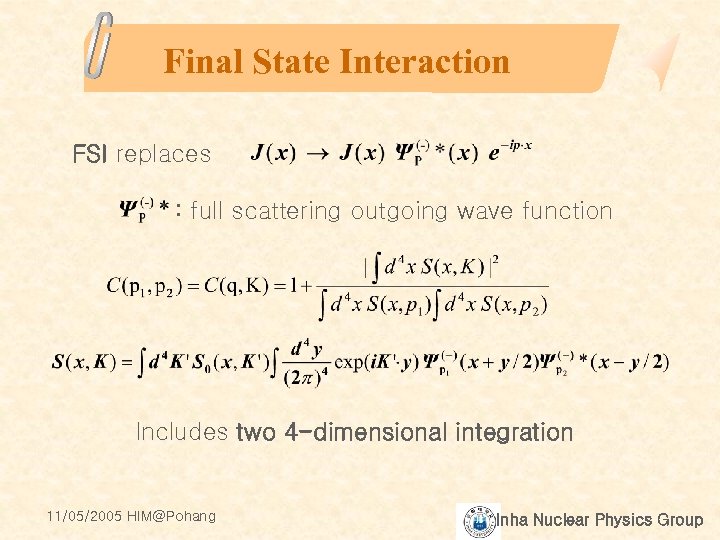
Final State Interaction FSI replaces : full scattering outgoing wave function Includes two 4 -dimensional integration 11/05/2005 HIM@Pohang Inha Nuclear Physics Group
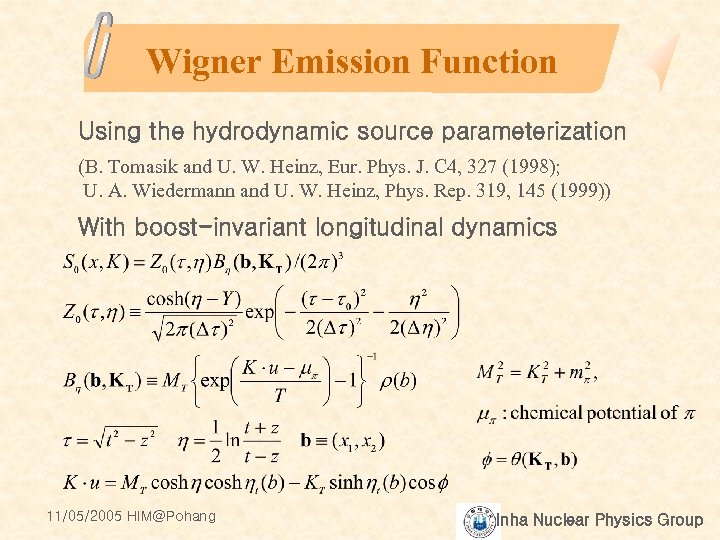
Wigner Emission Function Using the hydrodynamic source parameterization (B. Tomasik and U. W. Heinz, Eur. Phys. J. C 4, 327 (1998); U. A. Wiedermann and U. W. Heinz, Phys. Rep. 319, 145 (1999)) With boost-invariant longitudinal dynamics 11/05/2005 HIM@Pohang Inha Nuclear Physics Group
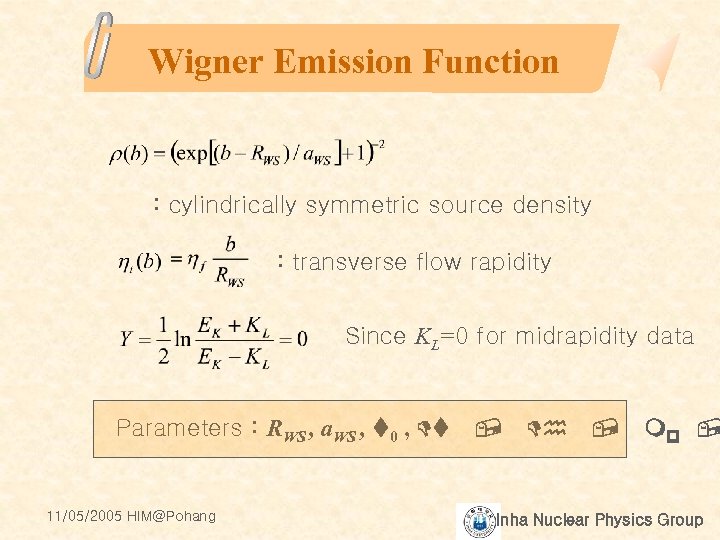
Wigner Emission Function : cylindrically symmetric source density : transverse flow rapidity Since KL=0 for midrapidity data Parameters : RWS , a. WS , t 0 , Dt 11/05/2005 HIM@Pohang , Dh , mp , Inha Nuclear Physics Group
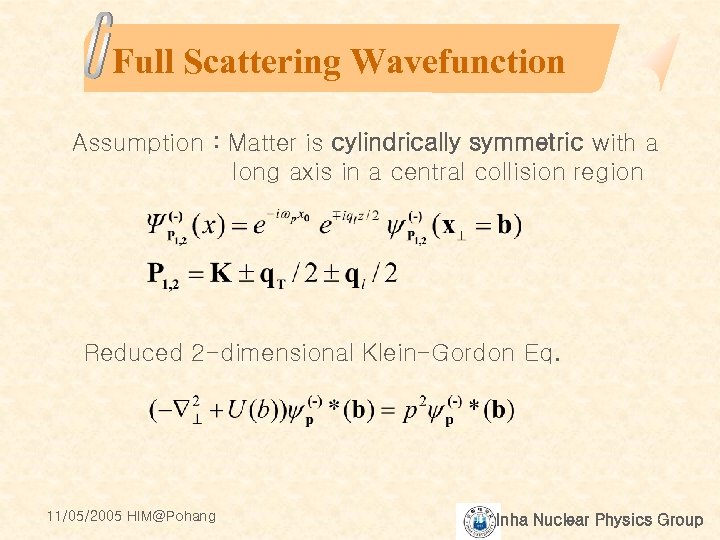
Full Scattering Wavefunction Assumption : Matter is cylindrically symmetric with a long axis in a central collision region Reduced 2 -dimensional Klein-Gordon Eq. 11/05/2005 HIM@Pohang Inha Nuclear Physics Group
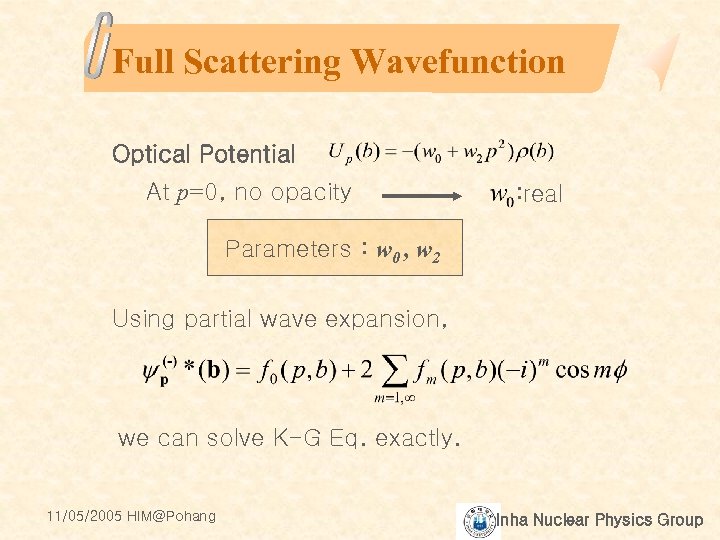
Full Scattering Wavefunction Optical Potential At p=0, no opacity : real Parameters : w 0 , w 2 Using partial wave expansion, we can solve K-G Eq. exactly. 11/05/2005 HIM@Pohang Inha Nuclear Physics Group
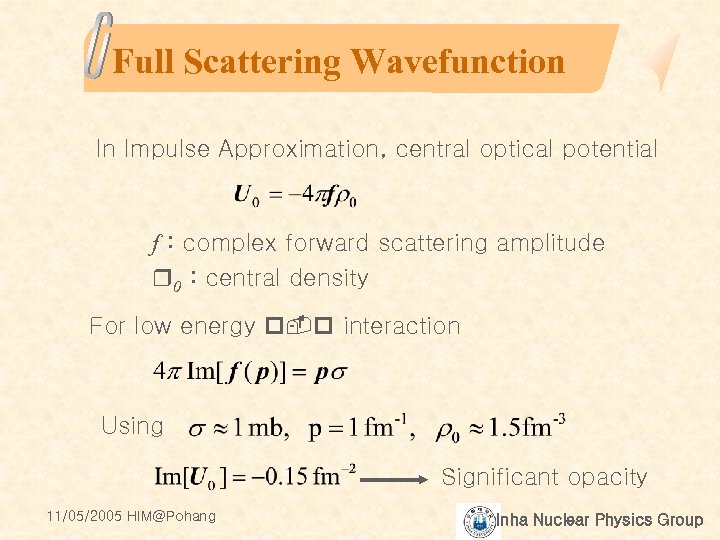
Full Scattering Wavefunction In Impulse Approximation, central optical potential f : complex forward scattering amplitude r 0 : central density For low energy p-p interaction Using Significant opacity 11/05/2005 HIM@Pohang Inha Nuclear Physics Group
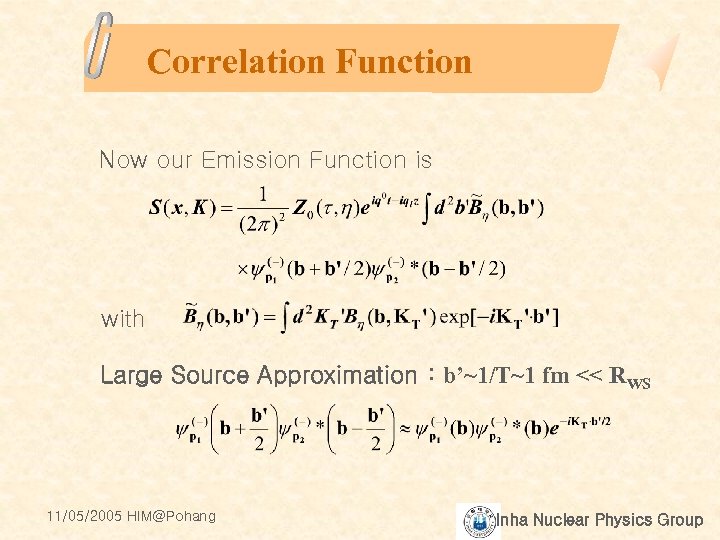
Correlation Function Now our Emission Function is with Large Source Approximation : b’~1/T~1 fm << RWS 11/05/2005 HIM@Pohang Inha Nuclear Physics Group
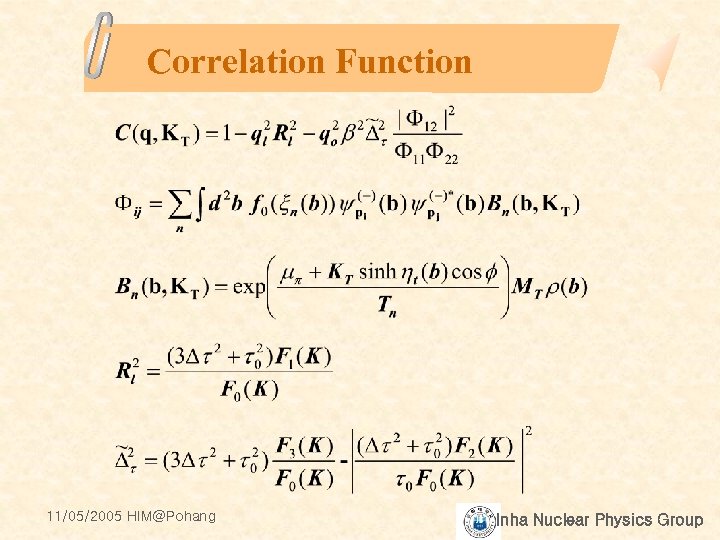
Correlation Function 11/05/2005 HIM@Pohang Inha Nuclear Physics Group
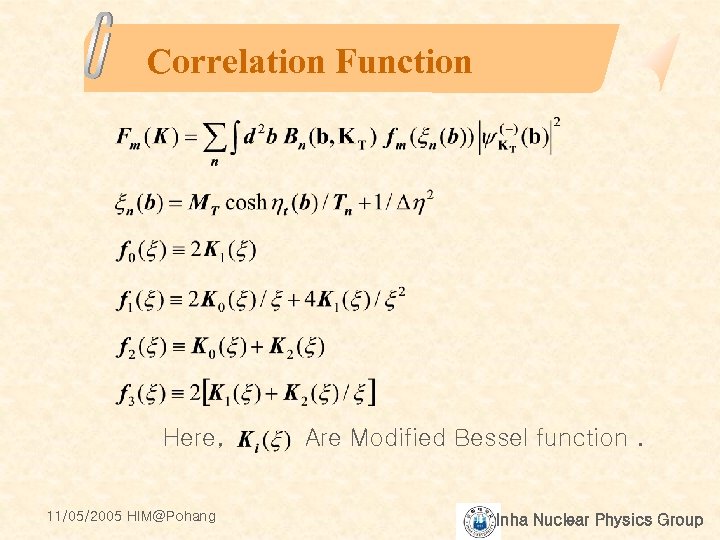
Correlation Function Here, 11/05/2005 HIM@Pohang Are Modified Bessel function. Inha Nuclear Physics Group
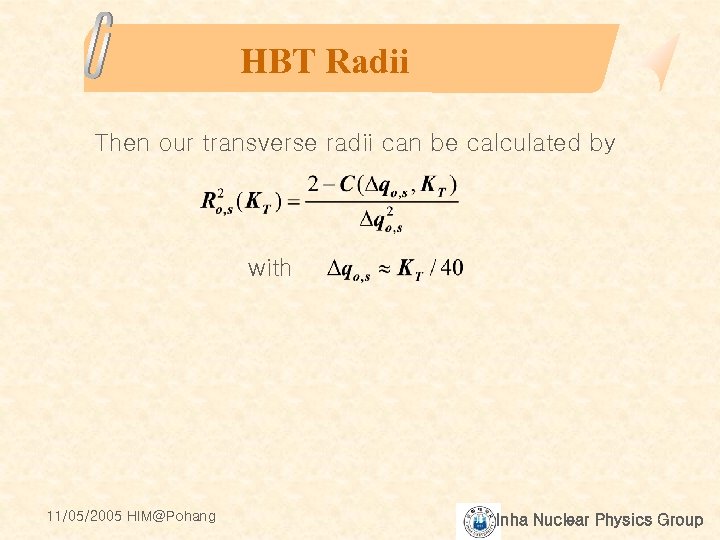
HBT Radii Then our transverse radii can be calculated by with 11/05/2005 HIM@Pohang Inha Nuclear Physics Group
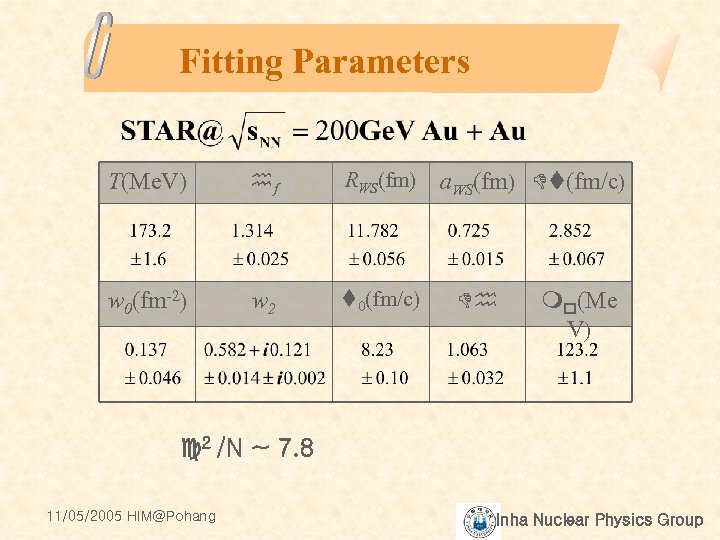
Fitting Parameters T(Me. V) hf RWS(fm) w 0(fm-2) w 2 t 0(fm/c) a. WS(fm) Dt(fm/c) Dh mp(Me V) c 2 /N ~ 7. 8 11/05/2005 HIM@Pohang Inha Nuclear Physics Group
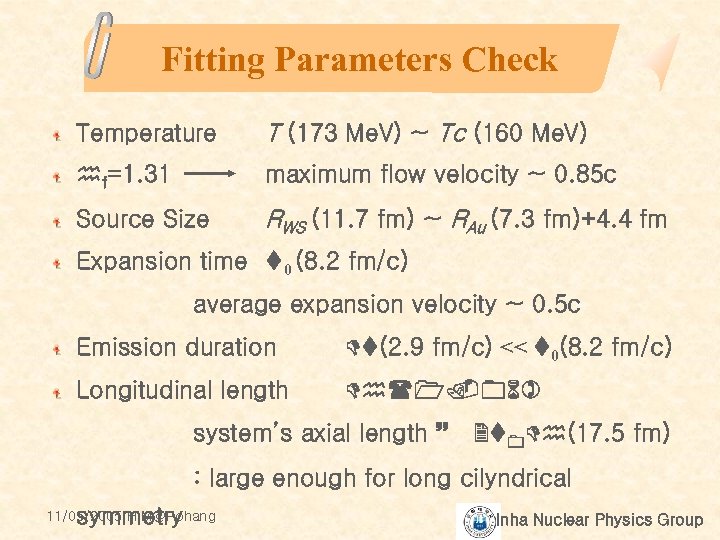
Fitting Parameters Check Temperature T (173 Me. V) ~ Tc (160 Me. V) hf=1. 31 maximum flow velocity ~ 0. 85 c Source Size RWS (11. 7 fm) ~ RAu (7. 3 fm)+4. 4 fm Expansion time t 0 (8. 2 fm/c) average expansion velocity ~ 0. 5 c Emission duration Dt(2. 9 fm/c) << t 0(8. 2 fm/c) Longitudinal length Dh(1. 06) system’s axial length ~ 2 t 0 Dh(17. 5 fm) : large enough for long cilyndrical symmetry 11/05/2005 HIM@Pohang Inha Nuclear Physics Group
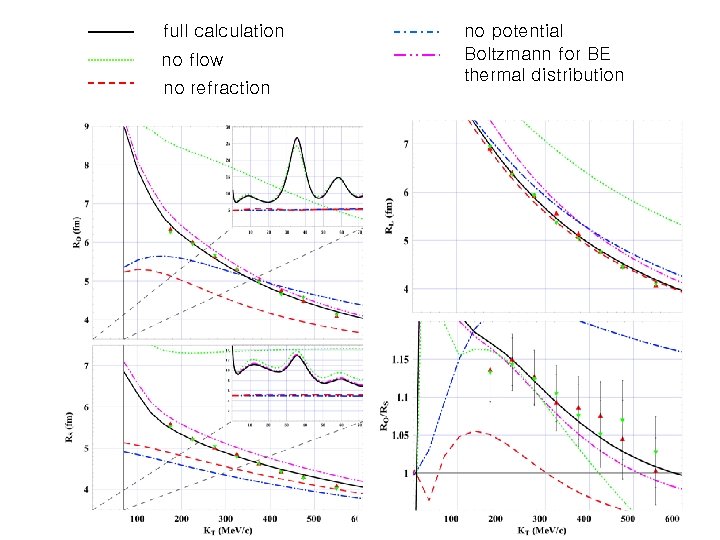
full calculation no flow no refraction no potential Boltzmann for BE thermal distribution
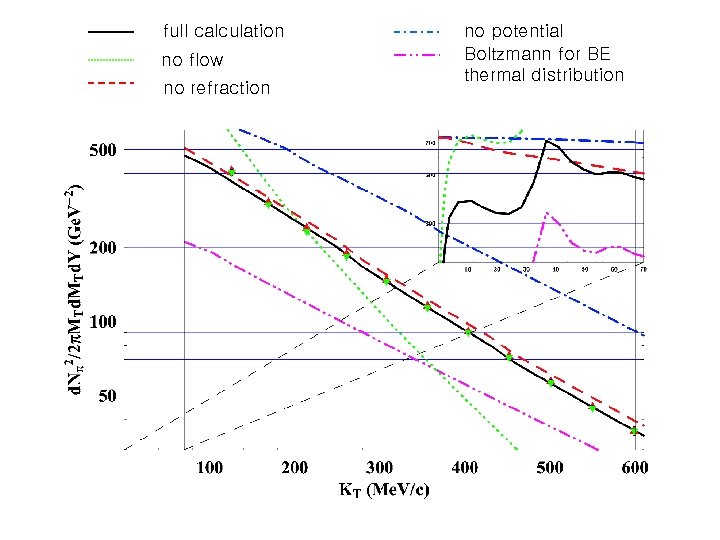
full calculation no flow no refraction no potential Boltzmann for BE thermal distribution



Thank you.
2f1a5ae49f34e422522fd4135332b148.ppt