QC.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 44
 Quantum computers, quantum computations H. Gomonay National Technical University of Ukraine JGU, Mainz, Germany
Quantum computers, quantum computations H. Gomonay National Technical University of Ukraine JGU, Mainz, Germany
 Take-home message The quest for a quantum computer reminds me of the endless quests for WIMPs, strings, sparticles, magnetic monopoles, etc. Succeed they or not, they bring to development of new knowledges and technologies, push the most talented people into science and keep fun from research. Same as it ever was.
Take-home message The quest for a quantum computer reminds me of the endless quests for WIMPs, strings, sparticles, magnetic monopoles, etc. Succeed they or not, they bring to development of new knowledges and technologies, push the most talented people into science and keep fun from research. Same as it ever was.
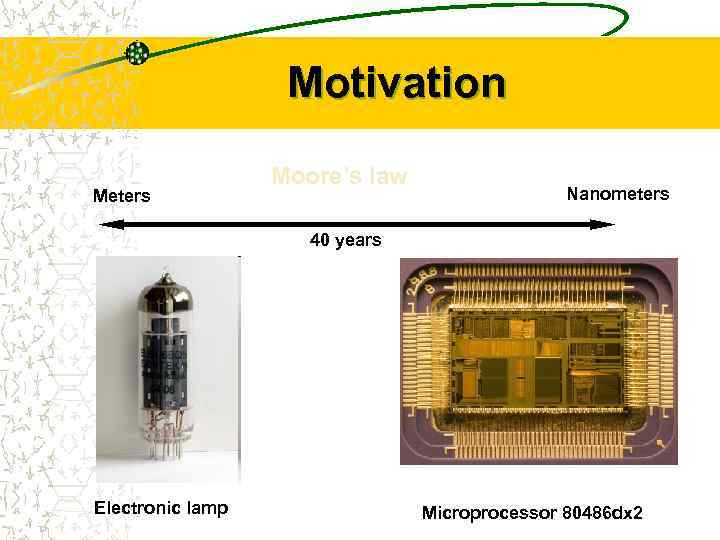 Motivation Meters Moore’s law Nanometers 40 years Electronic lamp Microprocessor 80486 dx 2
Motivation Meters Moore’s law Nanometers 40 years Electronic lamp Microprocessor 80486 dx 2
 Outline History Principles of quantum computation Di Vincenzo criteria Superconducting qubit Some algorithms Architecture Challenges and problems
Outline History Principles of quantum computation Di Vincenzo criteria Superconducting qubit Some algorithms Architecture Challenges and problems
 History in facts 1935 – A. Einstein doubts in adequacy of 1935 quantum mechanics & introduces entangled states 1982 – R. Feynman predicts possibility 1982 of quantum computations 2007 – D-Wave Systems presents 16 qubit quantum processor Orion
History in facts 1935 – A. Einstein doubts in adequacy of 1935 quantum mechanics & introduces entangled states 1982 – R. Feynman predicts possibility 1982 of quantum computations 2007 – D-Wave Systems presents 16 qubit quantum processor Orion
 2012 – S. Haroche & D. J. Wineland winn 2012 Nobel prize for ground-breaking experimental methods that enable measuring and manipulation of individual quantum systems" 2015 – Google tests the D-Wave 2 X quantum annealer, ~1000 qb
2012 – S. Haroche & D. J. Wineland winn 2012 Nobel prize for ground-breaking experimental methods that enable measuring and manipulation of individual quantum systems" 2015 – Google tests the D-Wave 2 X quantum annealer, ~1000 qb
 History in diagrams Classical vs quantum: speed up
History in diagrams Classical vs quantum: speed up
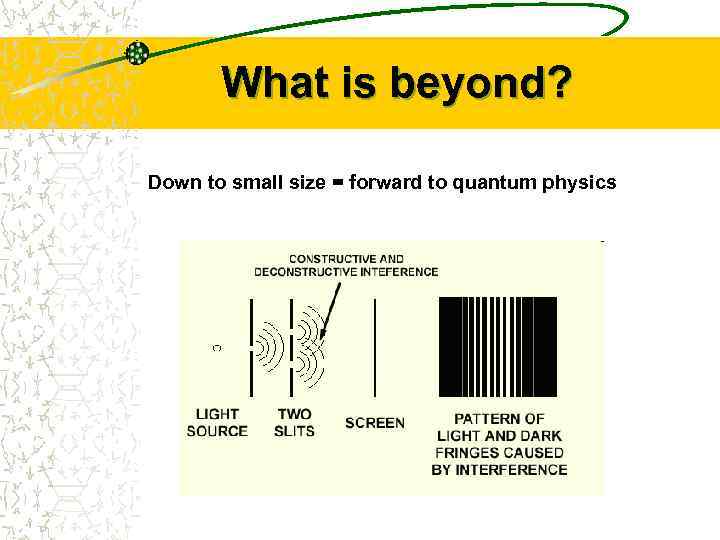 What is beyond? Down to small size = forward to quantum physics
What is beyond? Down to small size = forward to quantum physics
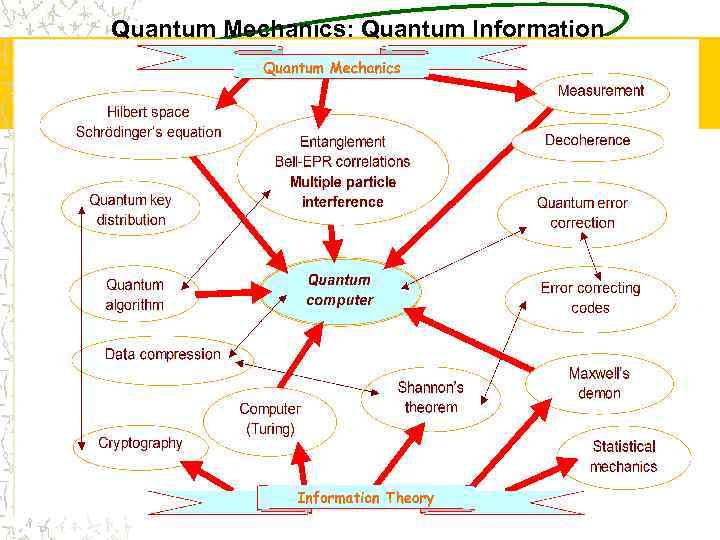 Quantum Mechanics: Quantum Information
Quantum Mechanics: Quantum Information
 What is all about or new applications of quantum physics “Hacking” crypto Keeping secrets Data search speed up Bioinformatics Outer space opening Fundamental problems Factorization of 256 -digit number: Classic – 2 N 1070 years Classic Quantum – N 2 ~ 10 seconds Quantum
What is all about or new applications of quantum physics “Hacking” crypto Keeping secrets Data search speed up Bioinformatics Outer space opening Fundamental problems Factorization of 256 -digit number: Classic – 2 N 1070 years Classic Quantum – N 2 ~ 10 seconds Quantum
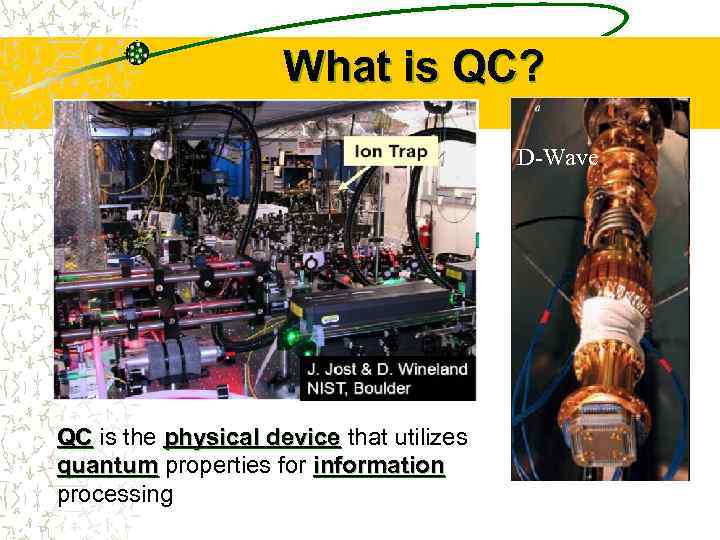 What is QC? D-Wave QC is the physical device that utilizes quantum properties for information processing
What is QC? D-Wave QC is the physical device that utilizes quantum properties for information processing
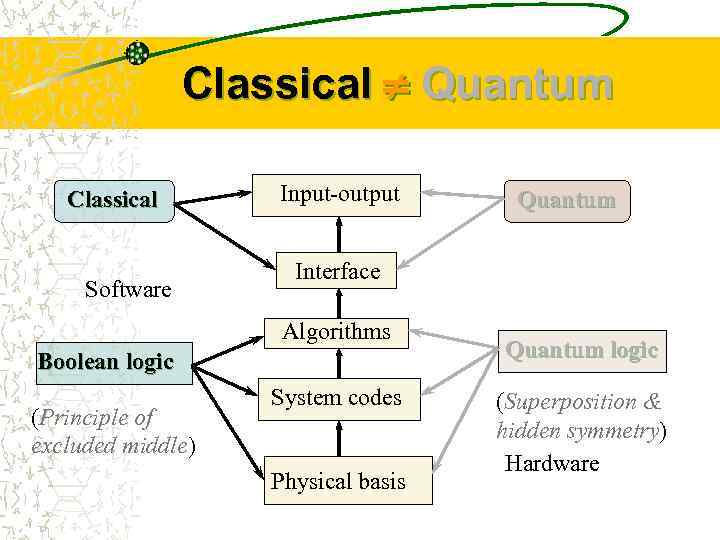 Classical Quantum Classical Software Input-output Interface Algorithms Boolean logic (Principle of excluded middle) Quantum System codes Physical basis Quantum logic (Superposition & hidden symmetry) Hardware
Classical Quantum Classical Software Input-output Interface Algorithms Boolean logic (Principle of excluded middle) Quantum System codes Physical basis Quantum logic (Superposition & hidden symmetry) Hardware
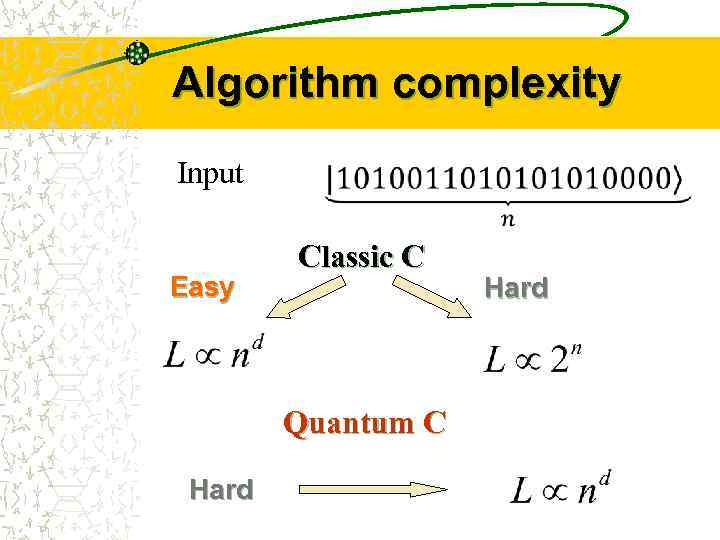 Algorithm complexity Input Easy Classic C Quantum C Hard
Algorithm complexity Input Easy Classic C Quantum C Hard
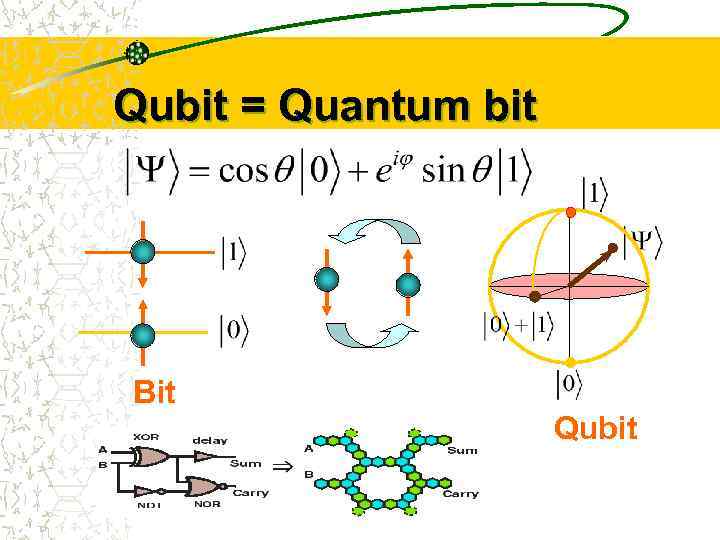 Qubit = Quantum bit Bit Qubit
Qubit = Quantum bit Bit Qubit
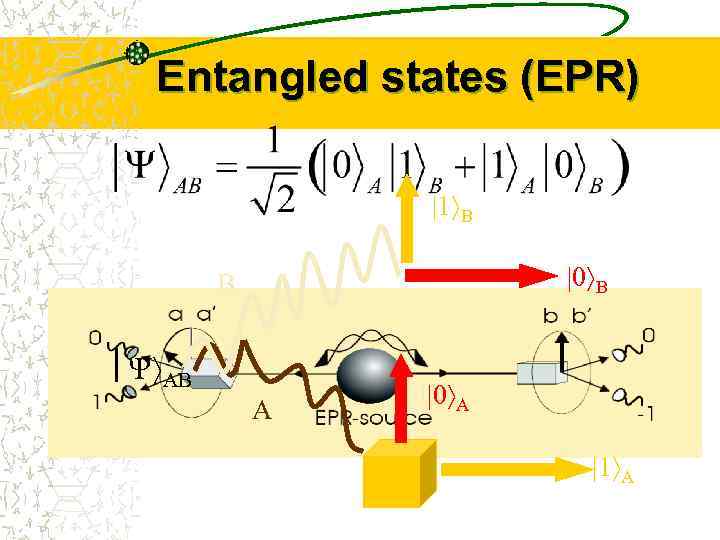 Entangled states (EPR) 1 B 0 B B AB A 0 A 1 A
Entangled states (EPR) 1 B 0 B B AB A 0 A 1 A
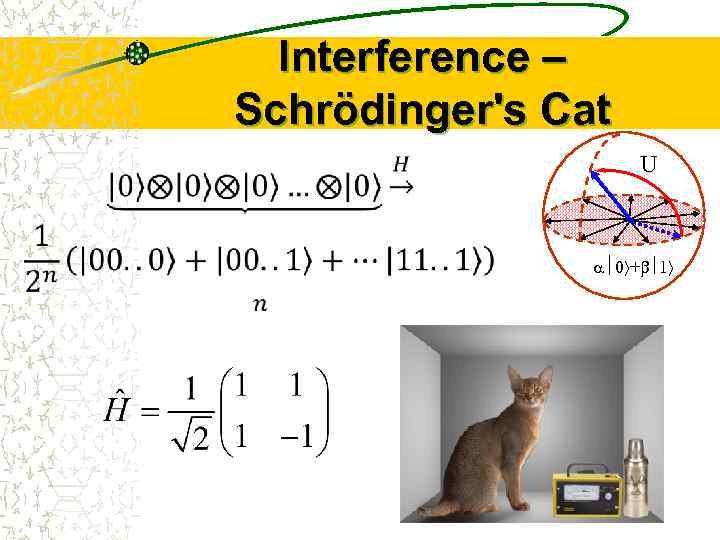 Interference – Schrödinger's Cat U 0 + 1
Interference – Schrödinger's Cat U 0 + 1
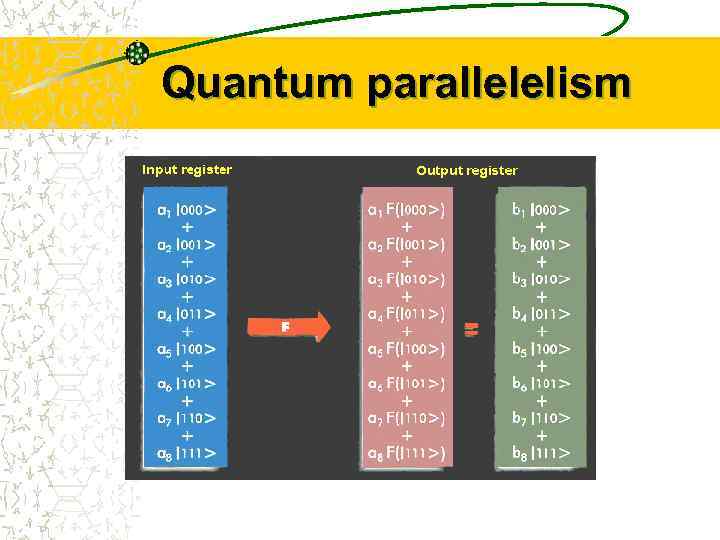 Quantum parallelelism
Quantum parallelelism
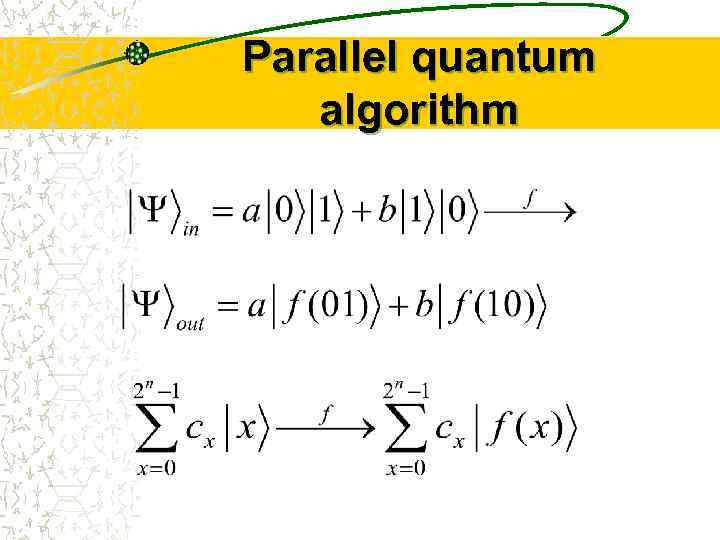 Parallel quantum algorithm
Parallel quantum algorithm
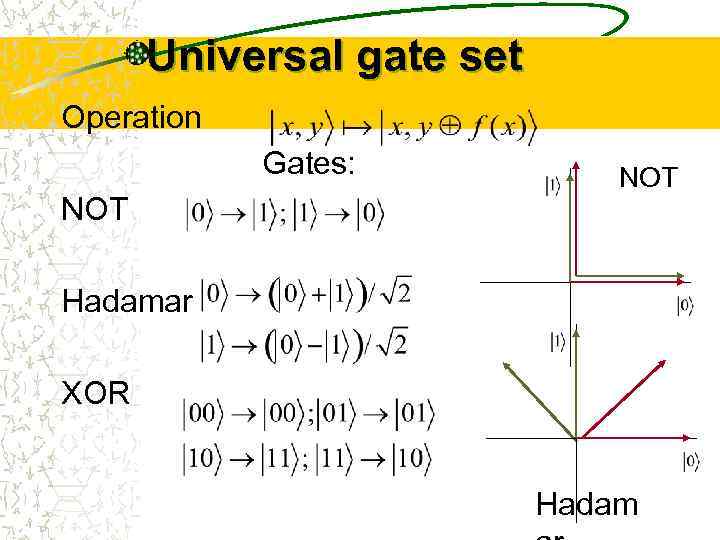 Universal gate set Operation Gates: NOT Hadamar XOR Hadam
Universal gate set Operation Gates: NOT Hadamar XOR Hadam
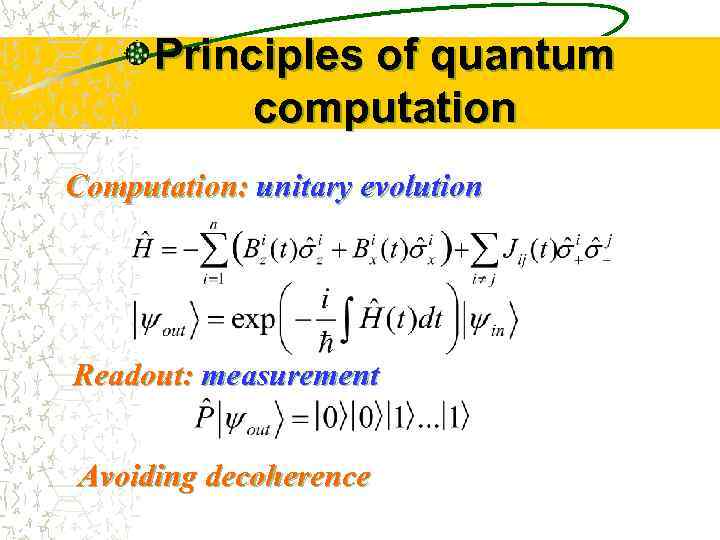 Principles of quantum computation Computation: unitary evolution Readout: measurement Avoiding decoherence
Principles of quantum computation Computation: unitary evolution Readout: measurement Avoiding decoherence
 Di Vincenzo criteria Selectivity (addressing each qubit) High sensitivity = Good control Large decoherence time ( decoh/ gate >104) Readout Measurability Scalability (>100 qubits)
Di Vincenzo criteria Selectivity (addressing each qubit) High sensitivity = Good control Large decoherence time ( decoh/ gate >104) Readout Measurability Scalability (>100 qubits)
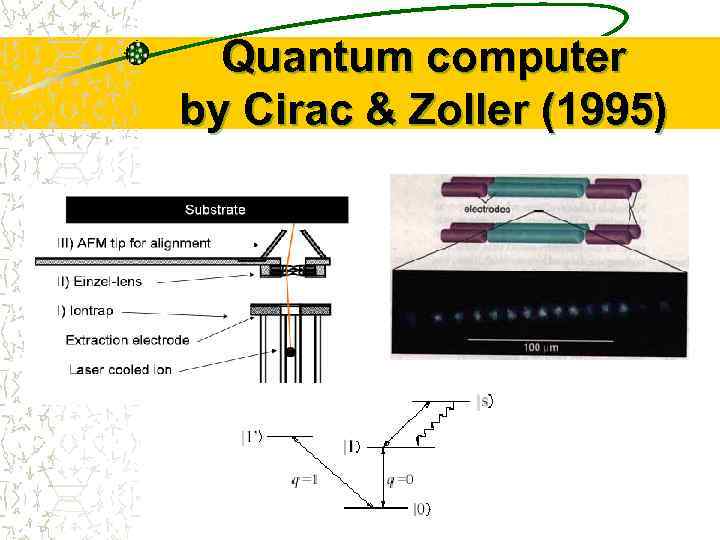 Quantum computer by Cirac & Zoller (1995)
Quantum computer by Cirac & Zoller (1995)
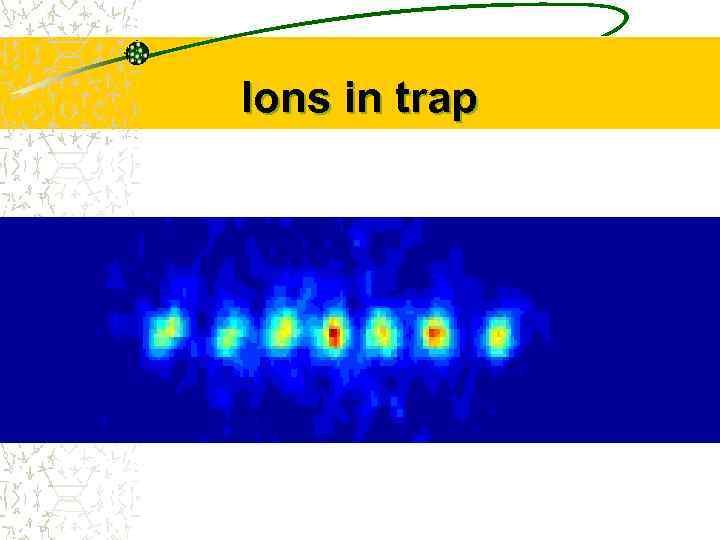 Ions in trap
Ions in trap
 Qubit: micro or macro? Measurement duration: Limitations: Energy splitting: Qubit = 1 electron spin: k~10 -3 – 10 -7 Measured Min splitting ~10 4 T Min field Impossible! We need macrospin! Impossible macrospin
Qubit: micro or macro? Measurement duration: Limitations: Energy splitting: Qubit = 1 electron spin: k~10 -3 – 10 -7 Measured Min splitting ~10 4 T Min field Impossible! We need macrospin! Impossible macrospin
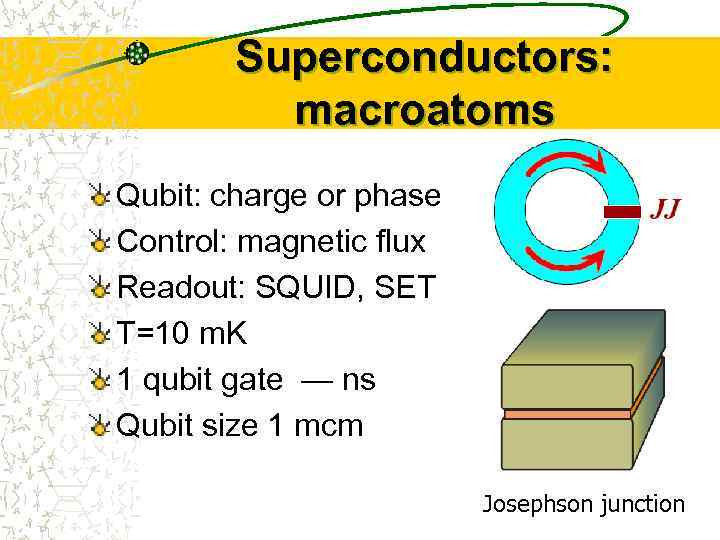 Superconductors: macroatoms Qubit: charge or phase Control: magnetic flux Readout: SQUID, SET T=10 m. K 1 qubit gate — ns Qubit size 1 mcm Josephson junction
Superconductors: macroatoms Qubit: charge or phase Control: magnetic flux Readout: SQUID, SET T=10 m. K 1 qubit gate — ns Qubit size 1 mcm Josephson junction
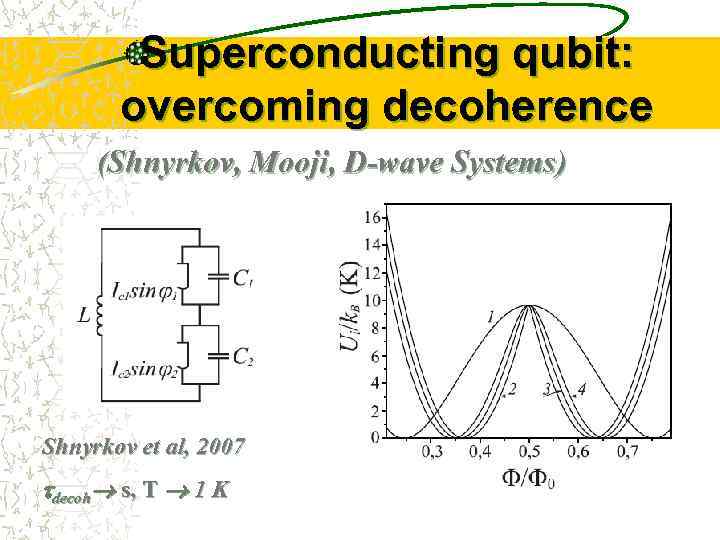 Superconducting qubit: overcoming decoherence (Shnyrkov, Mooji, D-wave Systems) Shnyrkov et al, 2007 decoh s, T 1 K
Superconducting qubit: overcoming decoherence (Shnyrkov, Mooji, D-wave Systems) Shnyrkov et al, 2007 decoh s, T 1 K
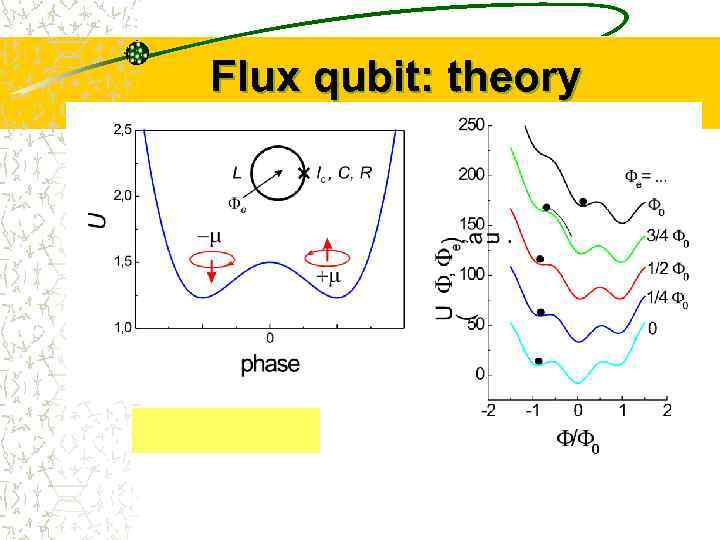 Flux qubit: theory
Flux qubit: theory
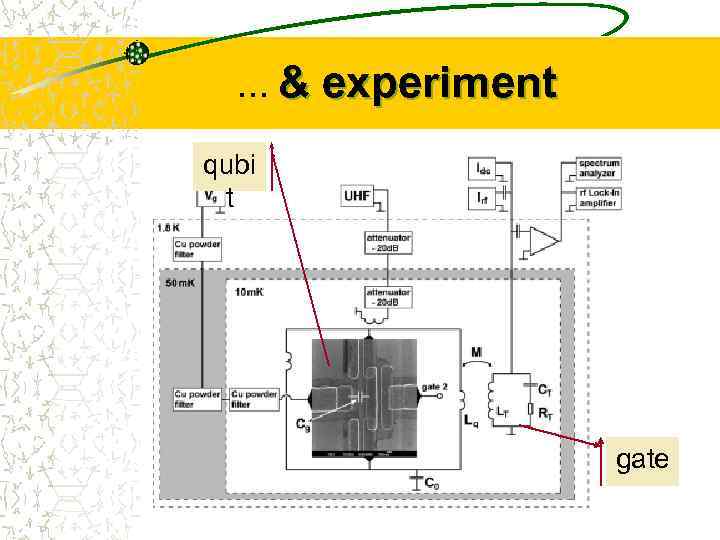 …& experiment qubi t gate
…& experiment qubi t gate
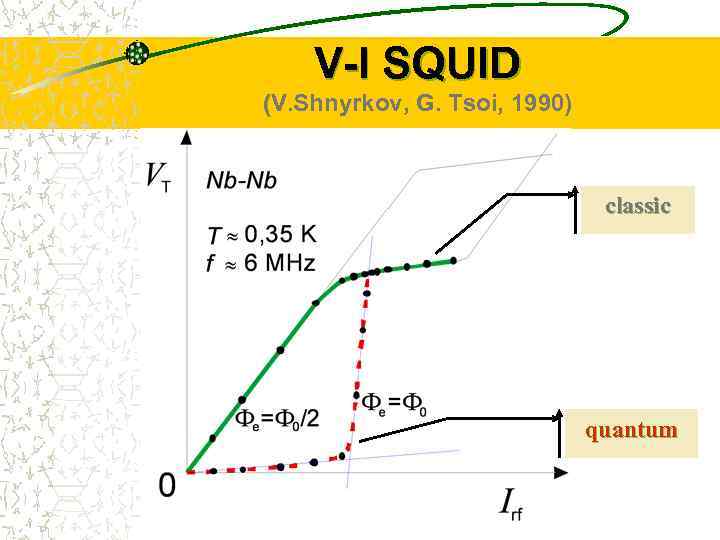 V-I SQUID (V. Shnyrkov, G. Tsoi, 1990) classic quantum
V-I SQUID (V. Shnyrkov, G. Tsoi, 1990) classic quantum
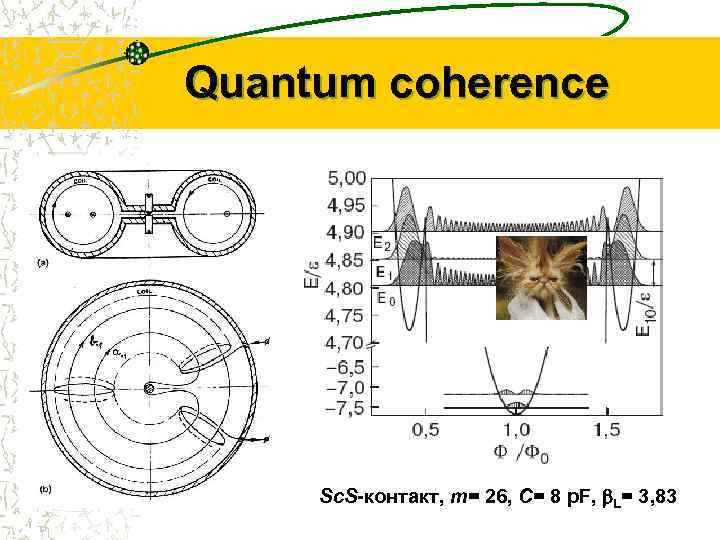 Quantum coherence Sc. S-контакт, m= 26, C= 8 p. F, b. L= 3, 83
Quantum coherence Sc. S-контакт, m= 26, C= 8 p. F, b. L= 3, 83
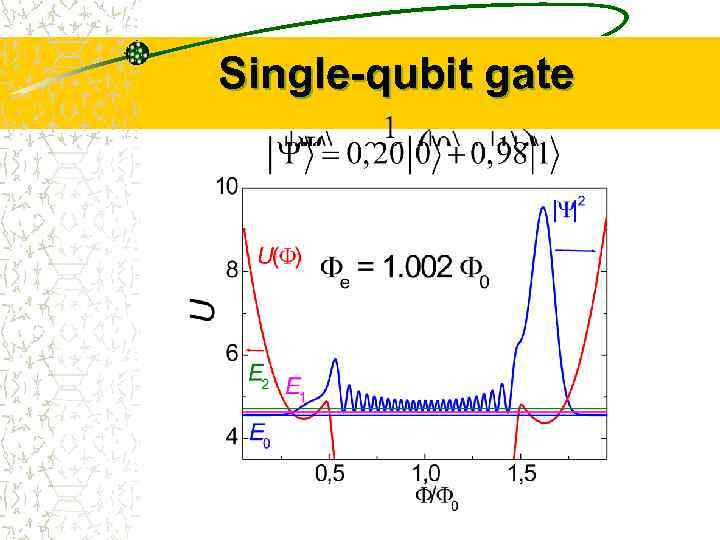 Single-qubit gate
Single-qubit gate
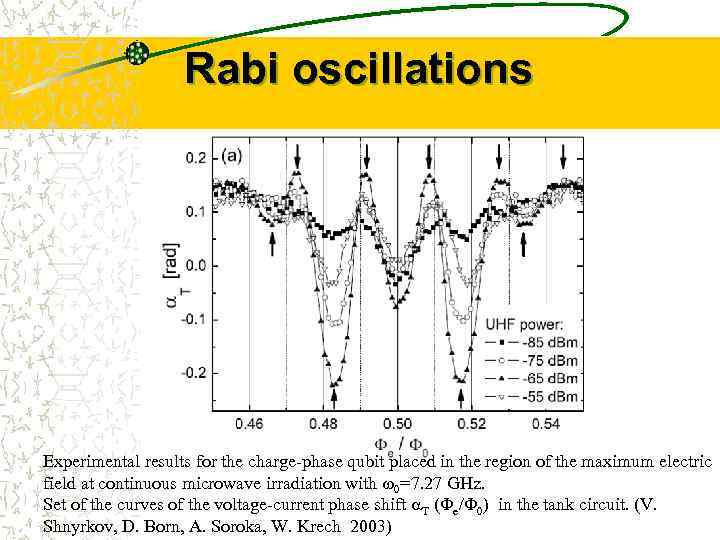 Rabi oscillations Experimental results for the charge-phase qubit placed in the region of the maximum electric field at continuous microwave irradiation with w 0=7. 27 GHz. Set of the curves of the voltage-current phase shift T (Fe/F 0) in the tank circuit. (V. Shnyrkov, D. Born, A. Soroka, W. Krech 2003)
Rabi oscillations Experimental results for the charge-phase qubit placed in the region of the maximum electric field at continuous microwave irradiation with w 0=7. 27 GHz. Set of the curves of the voltage-current phase shift T (Fe/F 0) in the tank circuit. (V. Shnyrkov, D. Born, A. Soroka, W. Krech 2003)
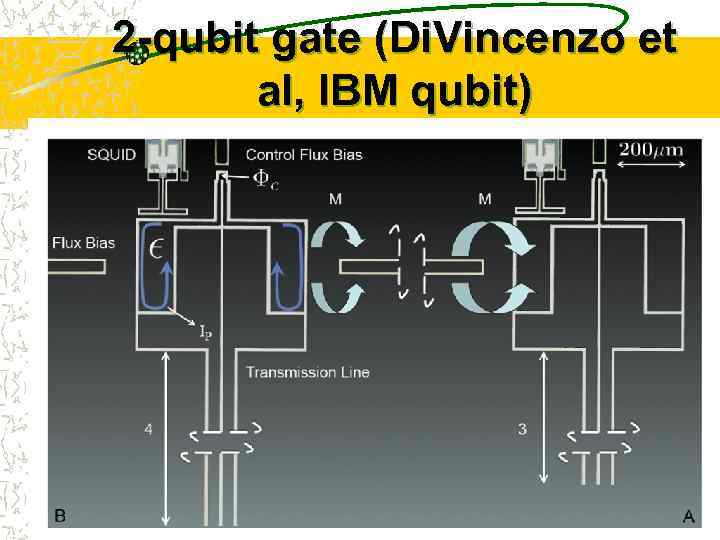 2 -qubit gate (Di. Vincenzo et al, IBM qubit)
2 -qubit gate (Di. Vincenzo et al, IBM qubit)
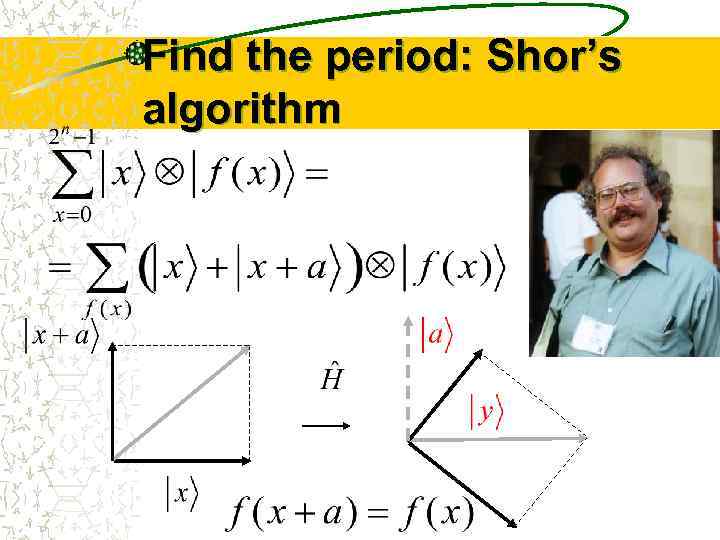 Find the period: Shor’s algorithm
Find the period: Shor’s algorithm
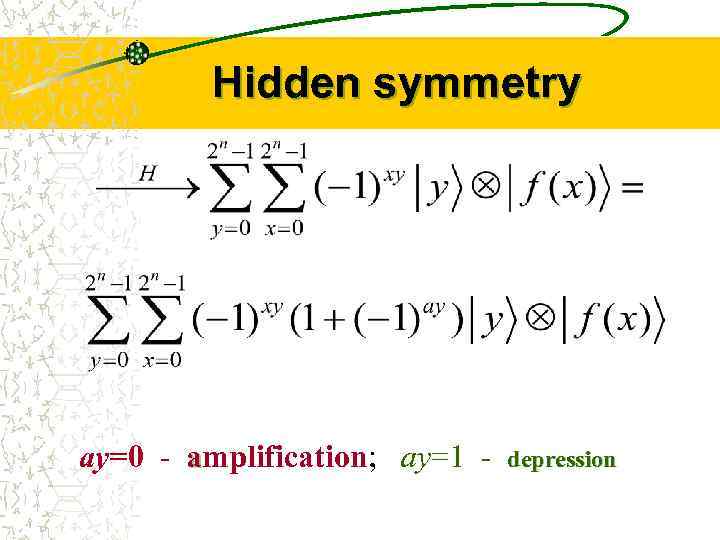 Hidden symmetry ay=0 - amplification; ay=1 - depression
Hidden symmetry ay=0 - amplification; ay=1 - depression
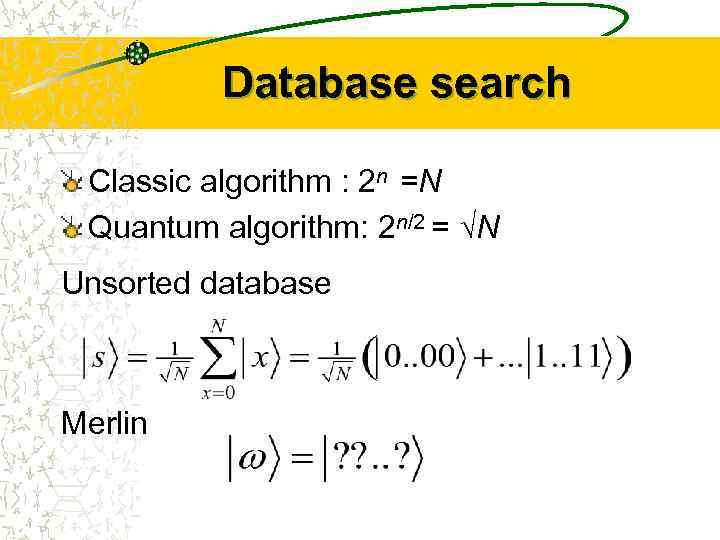 Database search Classic algorithm : 2 n =N Quantum algorithm: 2 n/2 = N Unsorted database Merlin
Database search Classic algorithm : 2 n =N Quantum algorithm: 2 n/2 = N Unsorted database Merlin
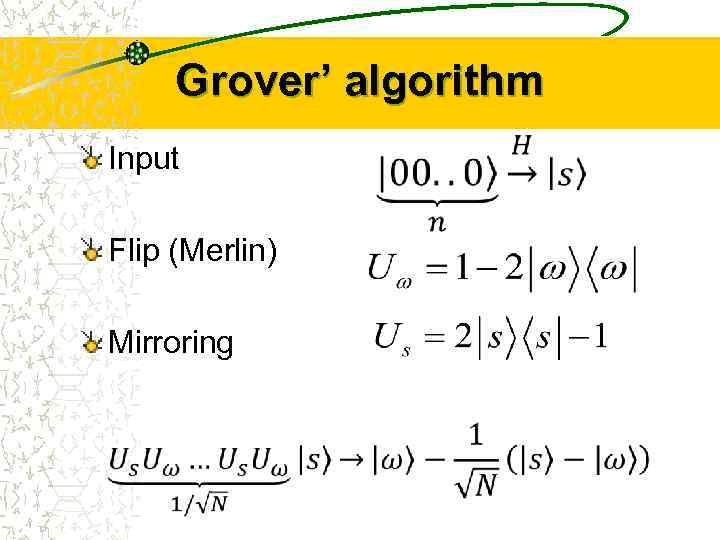 Grover’ algorithm Input Flip (Merlin) Mirroring
Grover’ algorithm Input Flip (Merlin) Mirroring
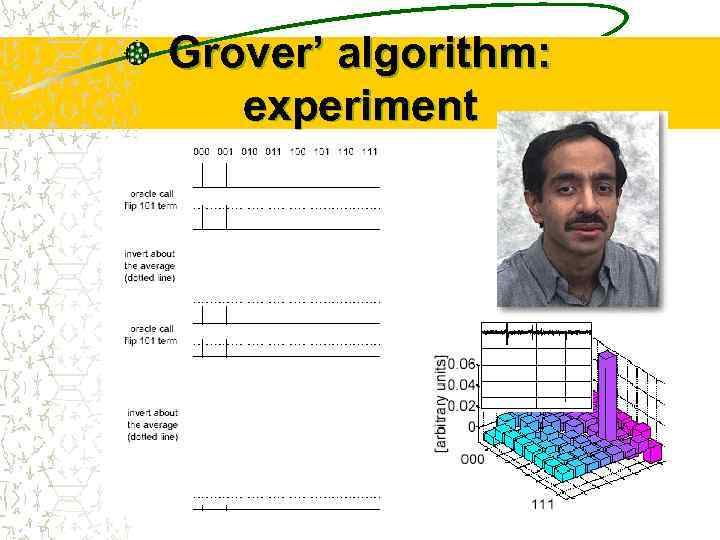 Grover’ algorithm: experiment
Grover’ algorithm: experiment
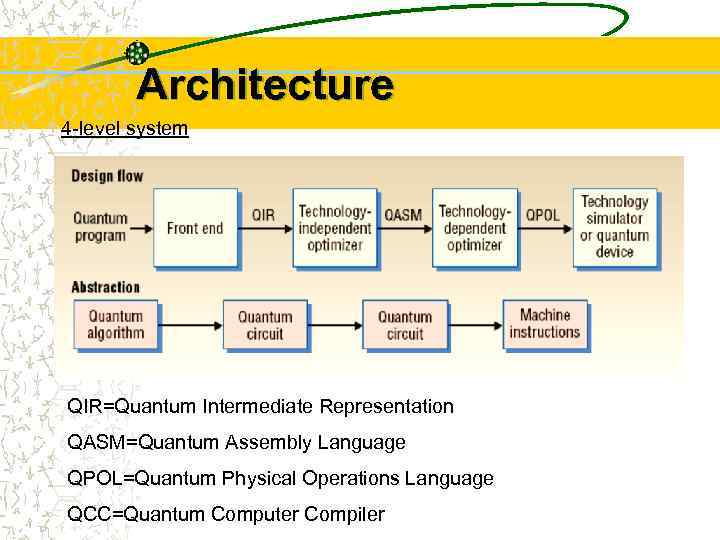 Architecture 4 -level system QIR=Quantum Intermediate Representation QASM=Quantum Assembly Language QPOL=Quantum Physical Operations Language QCC=Quantum Computer Compiler
Architecture 4 -level system QIR=Quantum Intermediate Representation QASM=Quantum Assembly Language QPOL=Quantum Physical Operations Language QCC=Quantum Computer Compiler
 Quantum computer: challenges Decoherence (state instability) Scaling (few number of qubits) Input-output control Extreme conditions (T=10 m. K, …) New math algorithms development Consumer friendly implementation Weak measurement
Quantum computer: challenges Decoherence (state instability) Scaling (few number of qubits) Input-output control Extreme conditions (T=10 m. K, …) New math algorithms development Consumer friendly implementation Weak measurement
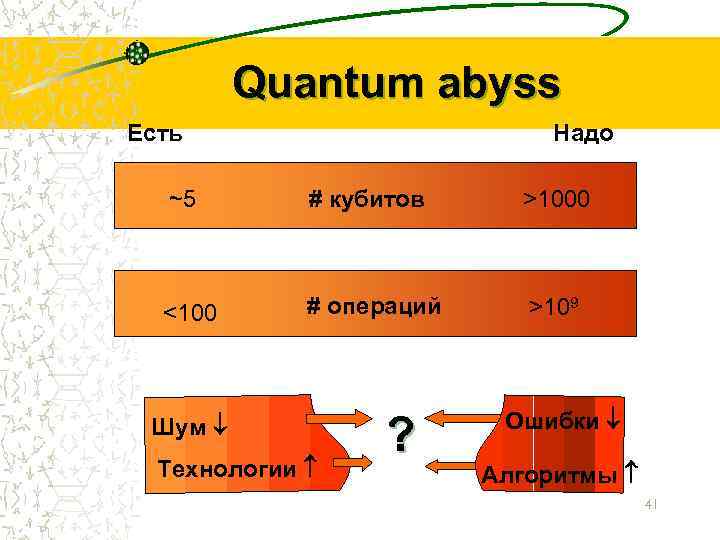 Quantum abyss Есть Надо ~5 # кубитов >1000 <100 # операций >109 Шум Технологии ? Ошибки Алгоритмы 41
Quantum abyss Есть Надо ~5 # кубитов >1000 <100 # операций >109 Шум Технологии ? Ошибки Алгоритмы 41
 When, Where, Who & ho. W? 2 qb — 1999, 7 qb — 2001, 16 qb — 2007, NP — 2012, 1000 qb — 2015, on-table -20 xx? ~ 1000 experimental groups over the world Physics, math, computer science, engineering?
When, Where, Who & ho. W? 2 qb — 1999, 7 qb — 2001, 16 qb — 2007, NP — 2012, 1000 qb — 2015, on-table -20 xx? ~ 1000 experimental groups over the world Physics, math, computer science, engineering?
 Alumni Sergii Strelchuk Vadym Kliuchnikov Junior Research Fellow @ Centre for Quantum Information and Foundations, UC http: //www. qi. damtp. cam. ac. uk/node/72 Post doc researcher @ Microsoft Research http: //research. microsoft. com/enus/people/vadym/
Alumni Sergii Strelchuk Vadym Kliuchnikov Junior Research Fellow @ Centre for Quantum Information and Foundations, UC http: //www. qi. damtp. cam. ac. uk/node/72 Post doc researcher @ Microsoft Research http: //research. microsoft. com/enus/people/vadym/
 QUANTUM COMPUTING JOIN THE TEAM!
QUANTUM COMPUTING JOIN THE TEAM!


