a8d5758e9ac00f70350e106a1c0d2e31.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 62
 Quanta, ciphers and computers Artur Ekert
Quanta, ciphers and computers Artur Ekert
 The Gambling Scholar Girolamo Cardano described himself as "Hot-tempered, single-minded, and given to women, “… "cunning, crafty, sarcastic, diligent, impertinent, sad, treacherous, magician and sorcerer, miserable, hateful, lascivious, obscene, lying, obsequious, " and "fond of the prattle of old men. " 1501 -1576
The Gambling Scholar Girolamo Cardano described himself as "Hot-tempered, single-minded, and given to women, “… "cunning, crafty, sarcastic, diligent, impertinent, sad, treacherous, magician and sorcerer, miserable, hateful, lascivious, obscene, lying, obsequious, " and "fond of the prattle of old men. " 1501 -1576
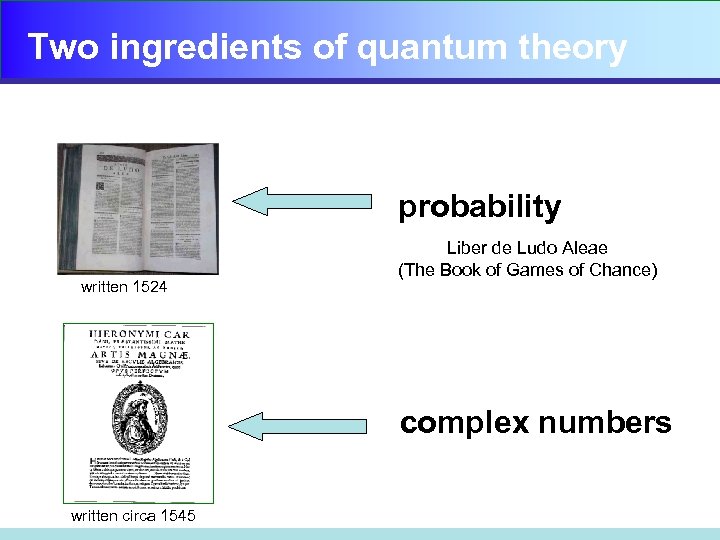 Two ingredients of quantum theory probability written 1524 Liber de Ludo Aleae (The Book of Games of Chance) complex numbers written circa 1545
Two ingredients of quantum theory probability written 1524 Liber de Ludo Aleae (The Book of Games of Chance) complex numbers written circa 1545
 Complex numbers Niccolo Fontana Tartaglia The oath sworn by Cardan (according to Tartaglia) I swear to you, by God's holy Gospels, and as a true man of honour, not only never to publish your discoveries, if you teach me them, but I also promise you, and I pledge my faith as a true Christian, to note them down in code, so that after my death no one will be able to understand them.
Complex numbers Niccolo Fontana Tartaglia The oath sworn by Cardan (according to Tartaglia) I swear to you, by God's holy Gospels, and as a true man of honour, not only never to publish your discoveries, if you teach me them, but I also promise you, and I pledge my faith as a true Christian, to note them down in code, so that after my death no one will be able to understand them.
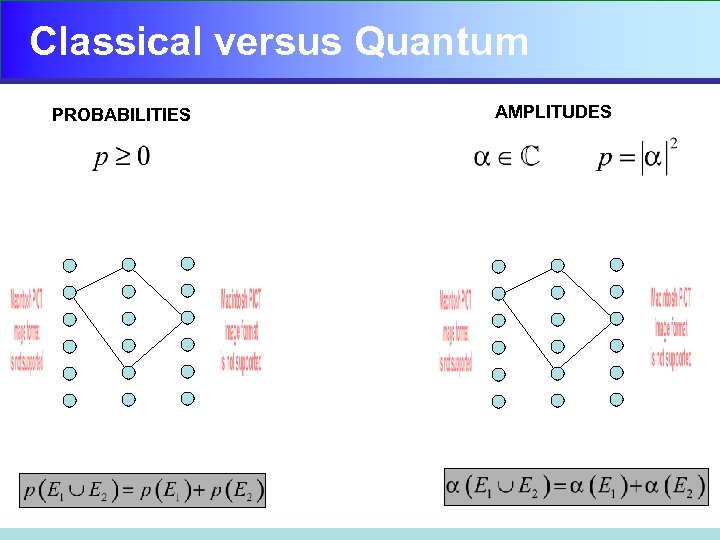 Classical versus Quantum PROBABILITIES AMPLITUDES
Classical versus Quantum PROBABILITIES AMPLITUDES
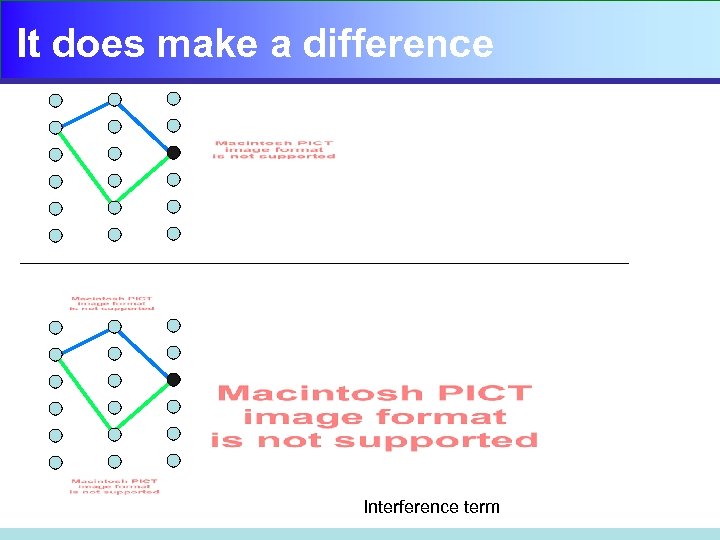 It does make a difference Interference term
It does make a difference Interference term
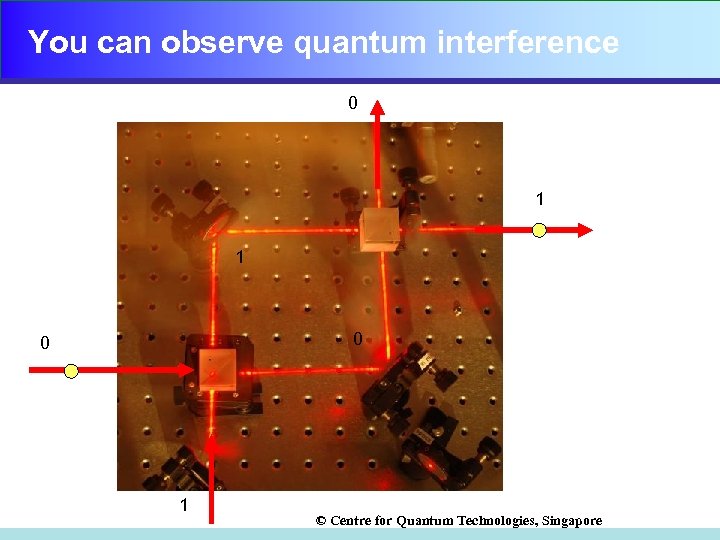 You can observe quantum interference 0 1 1 0 0 1 © Centre for Quantum Technologies, Singapore
You can observe quantum interference 0 1 1 0 0 1 © Centre for Quantum Technologies, Singapore
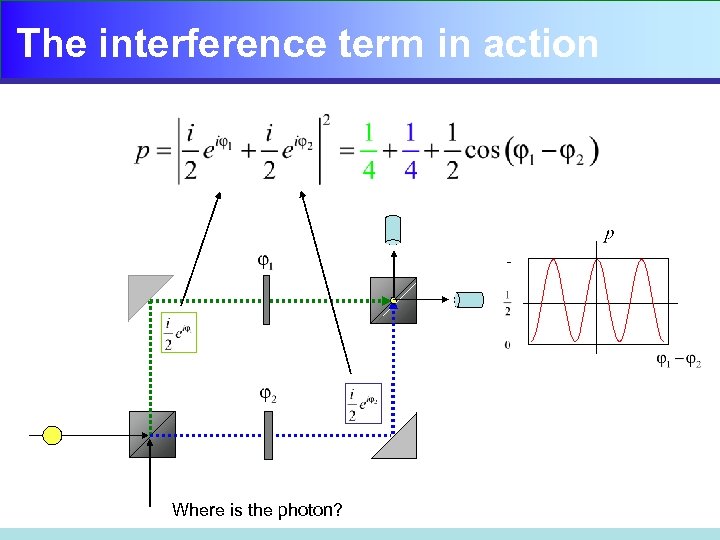 The interference term in action Where is the photon?
The interference term in action Where is the photon?
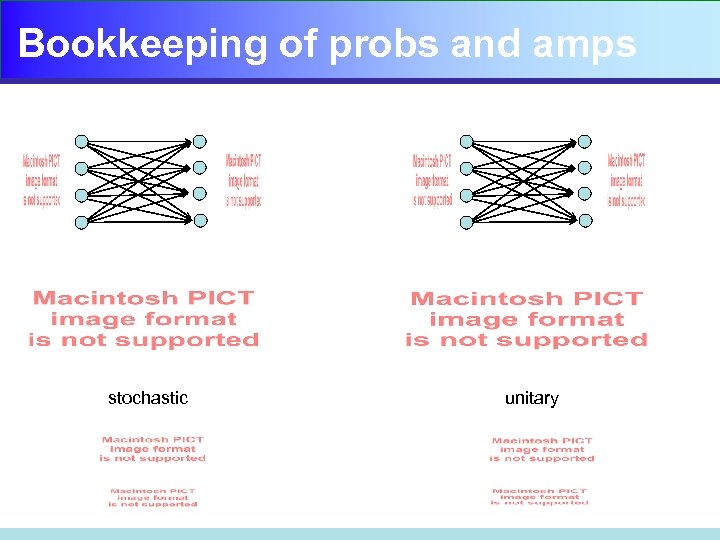 Bookkeeping of probs and amps stochastic unitary
Bookkeeping of probs and amps stochastic unitary
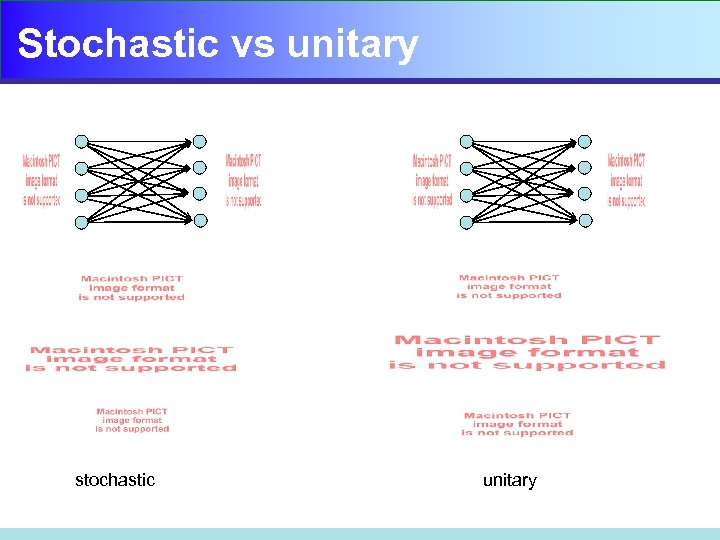 Stochastic vs unitary stochastic unitary
Stochastic vs unitary stochastic unitary
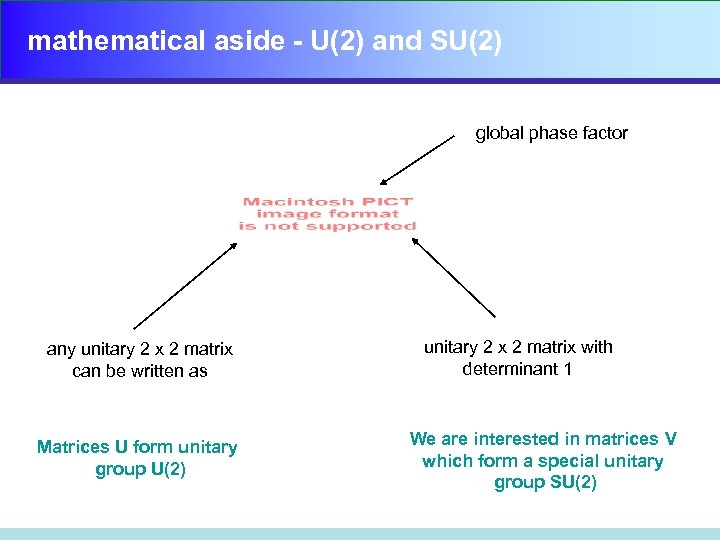 mathematical aside - U(2) and SU(2) global phase factor any unitary 2 x 2 matrix can be written as Matrices U form unitary group U(2) unitary 2 x 2 matrix with determinant 1 We are interested in matrices V which form a special unitary group SU(2)
mathematical aside - U(2) and SU(2) global phase factor any unitary 2 x 2 matrix can be written as Matrices U form unitary group U(2) unitary 2 x 2 matrix with determinant 1 We are interested in matrices V which form a special unitary group SU(2)
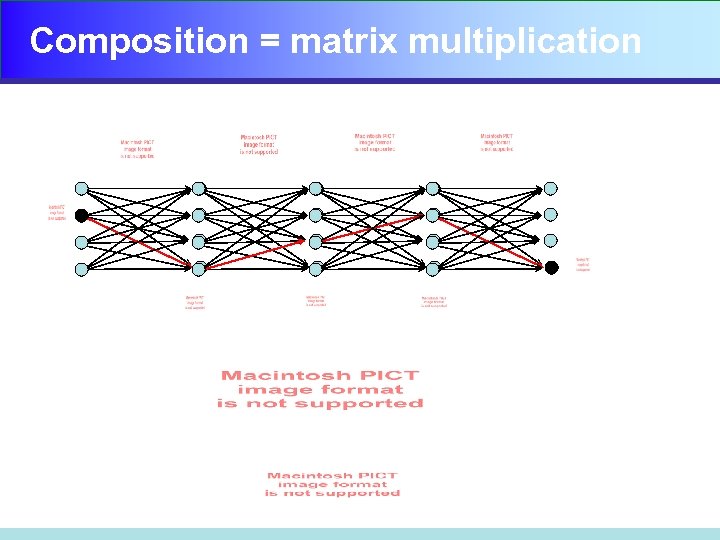 Composition = matrix multiplication
Composition = matrix multiplication
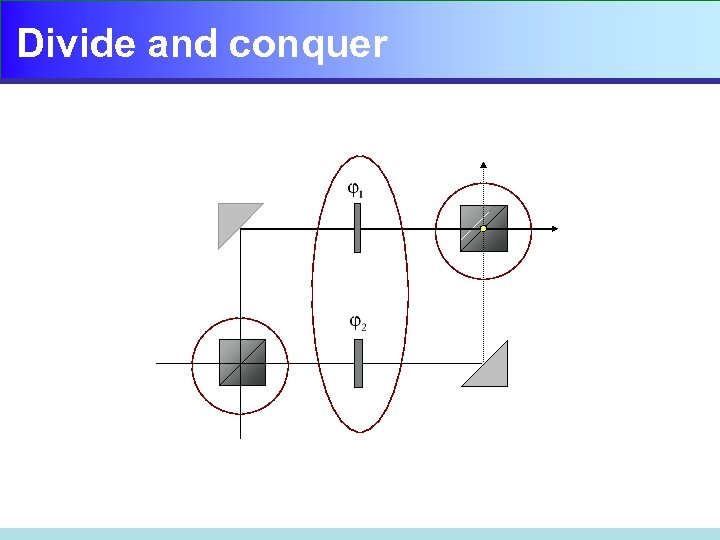 Divide and conquer
Divide and conquer
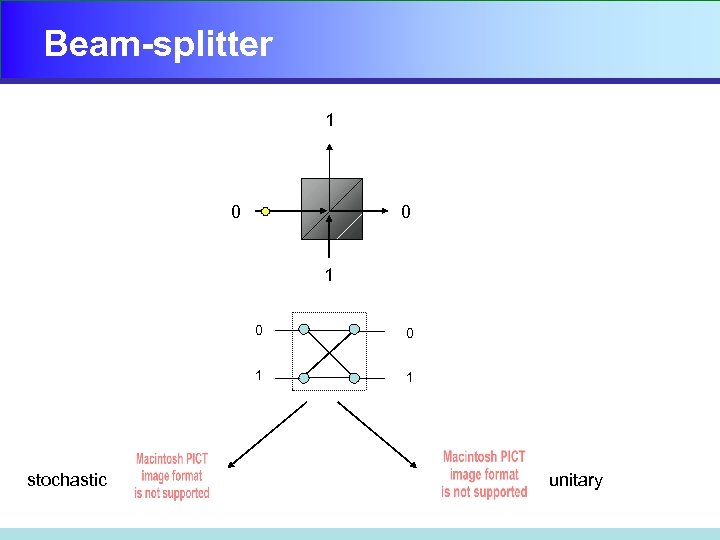 Beam-splitter 1 0 0 1 stochastic 0 1 unitary
Beam-splitter 1 0 0 1 stochastic 0 1 unitary
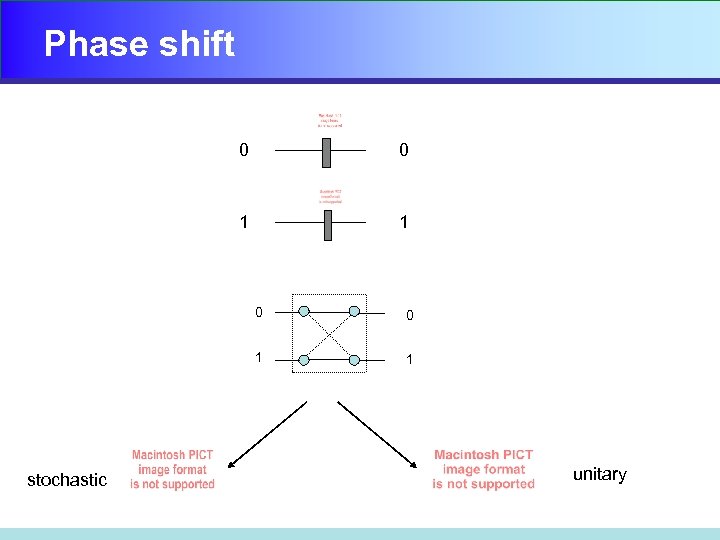 Phase shift 0 0 1 1 0 1 stochastic 0 1 unitary
Phase shift 0 0 1 1 0 1 stochastic 0 1 unitary
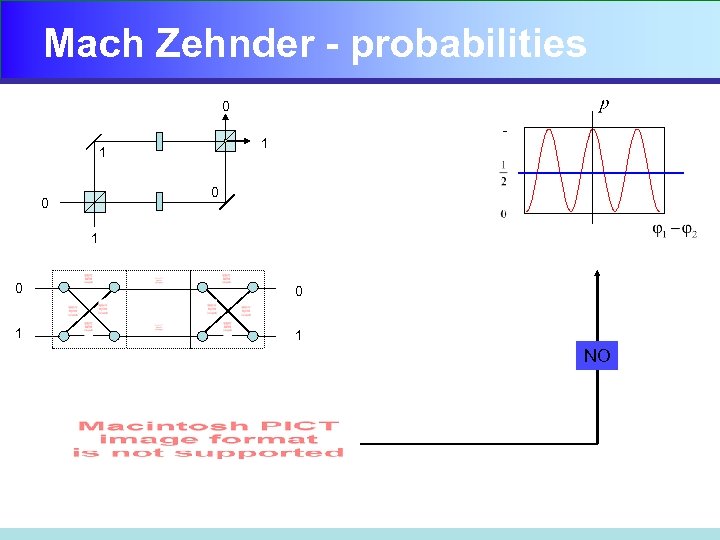 Mach Zehnder - probabilities 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 NO
Mach Zehnder - probabilities 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 NO
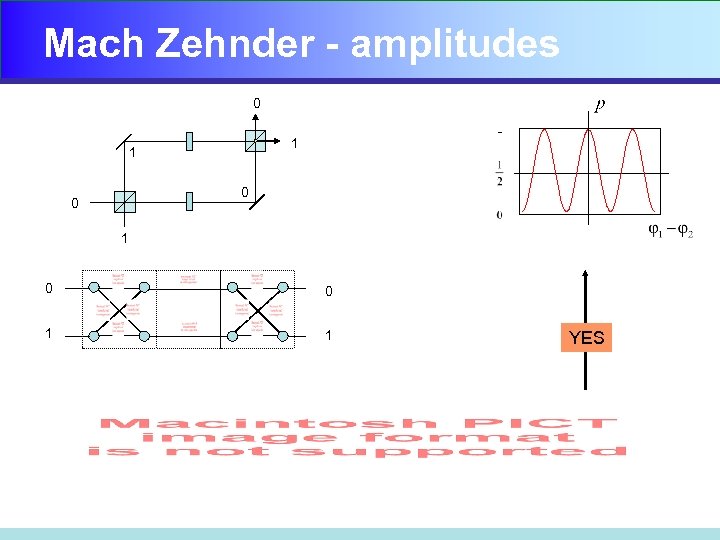 Mach Zehnder - amplitudes 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 YES
Mach Zehnder - amplitudes 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 YES
 Amplitudes & probabilities amplitudes
Amplitudes & probabilities amplitudes
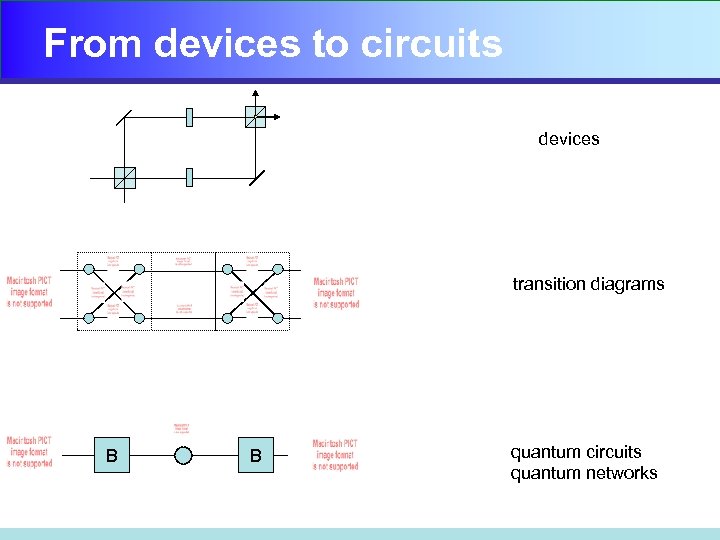 From devices to circuits devices transition diagrams B B quantum circuits quantum networks
From devices to circuits devices transition diagrams B B quantum circuits quantum networks
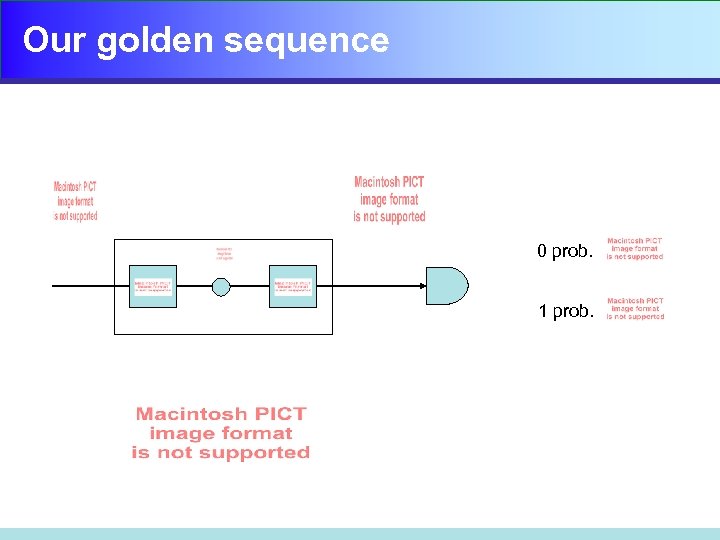 Our golden sequence 0 prob. 1 prob.
Our golden sequence 0 prob. 1 prob.
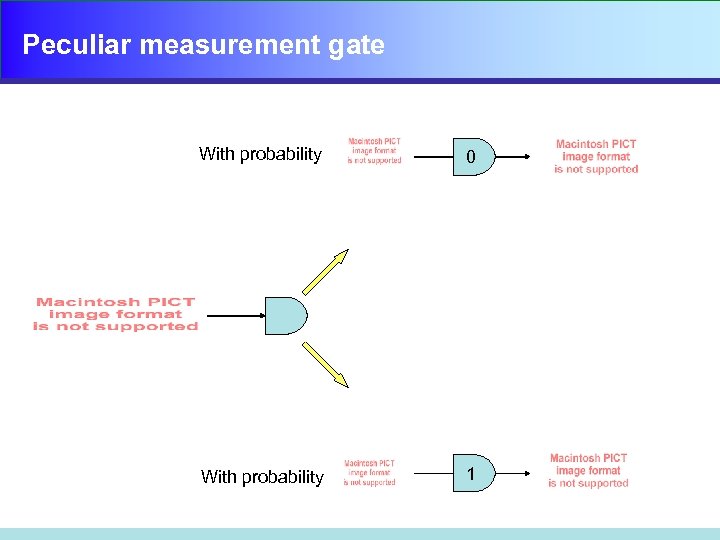 Peculiar measurement gate With probability 0 With probability 1
Peculiar measurement gate With probability 0 With probability 1
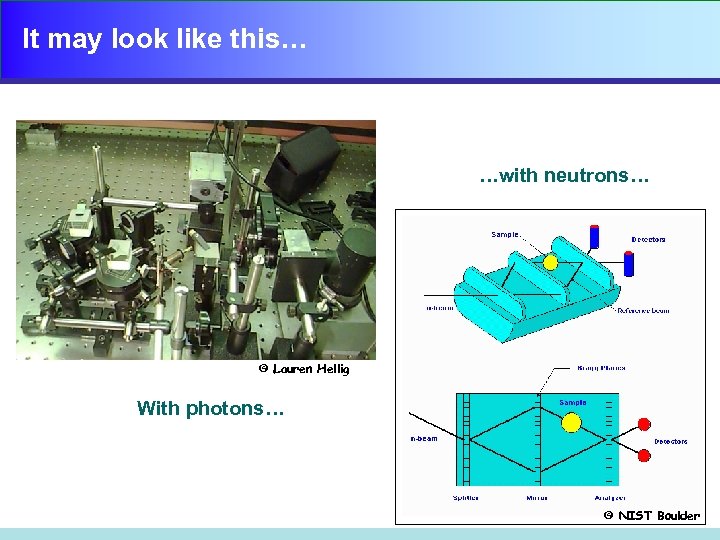 It may look like this… …with neutrons… © Lauren Hellig With photons… © NIST Boulder
It may look like this… …with neutrons… © Lauren Hellig With photons… © NIST Boulder
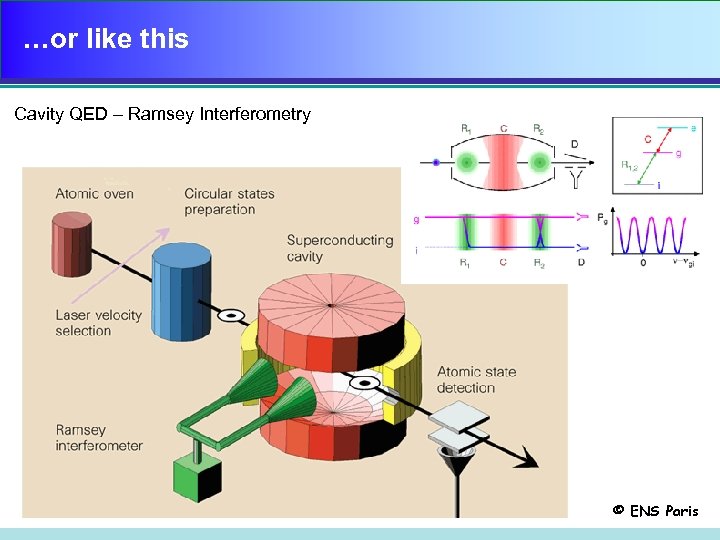 …or like this Cavity QED – Ramsey Interferometry © ENS Paris
…or like this Cavity QED – Ramsey Interferometry © ENS Paris
 More precisely like this © ENS Paris
More precisely like this © ENS Paris
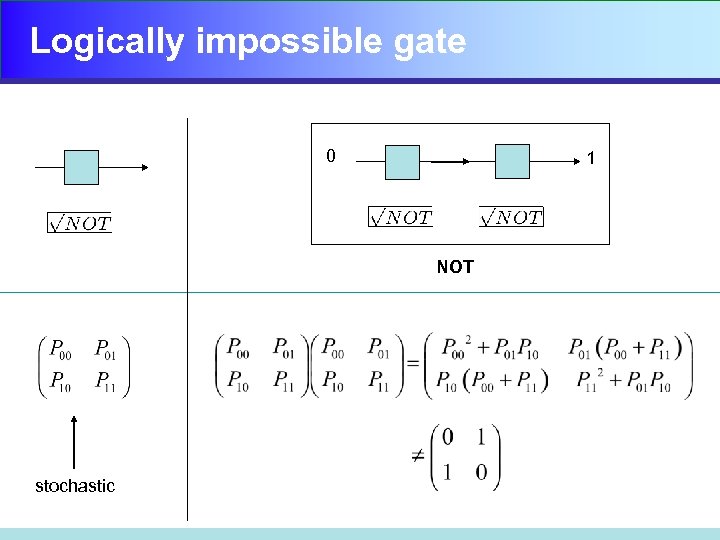 Logically impossible gate 0 1 NOT stochastic
Logically impossible gate 0 1 NOT stochastic
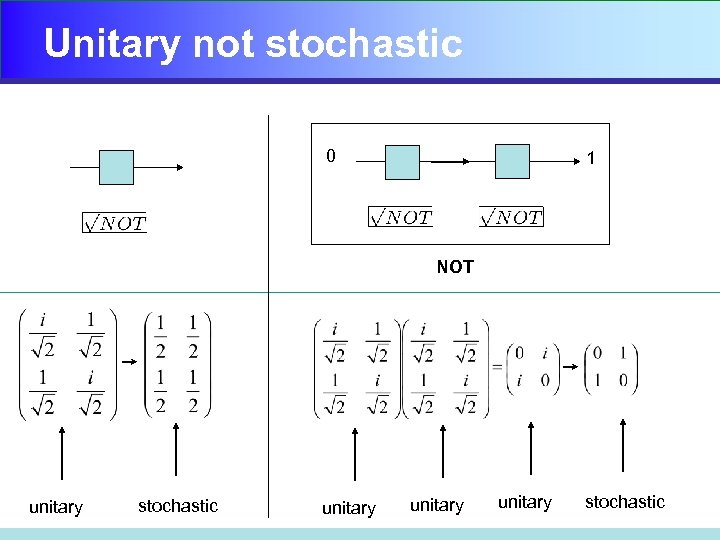 Unitary not stochastic 0 1 NOT unitary stochastic unitary stochastic
Unitary not stochastic 0 1 NOT unitary stochastic unitary stochastic
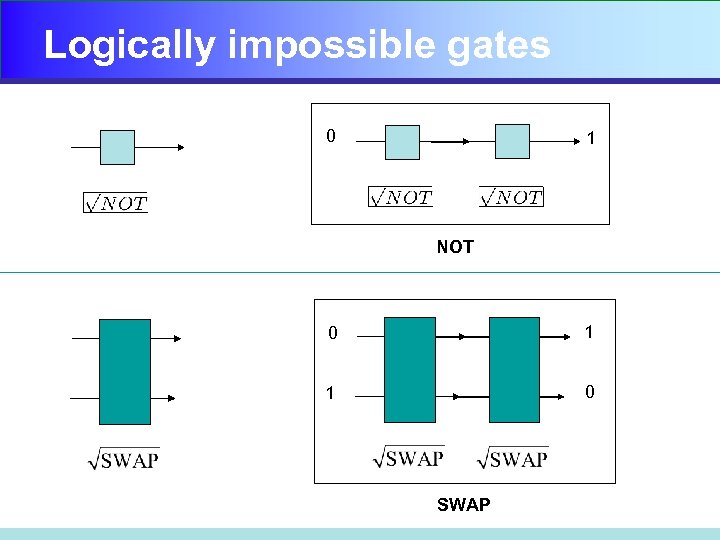 Logically impossible gates 0 1 NOT 0 1 1 0 SWAP
Logically impossible gates 0 1 NOT 0 1 1 0 SWAP
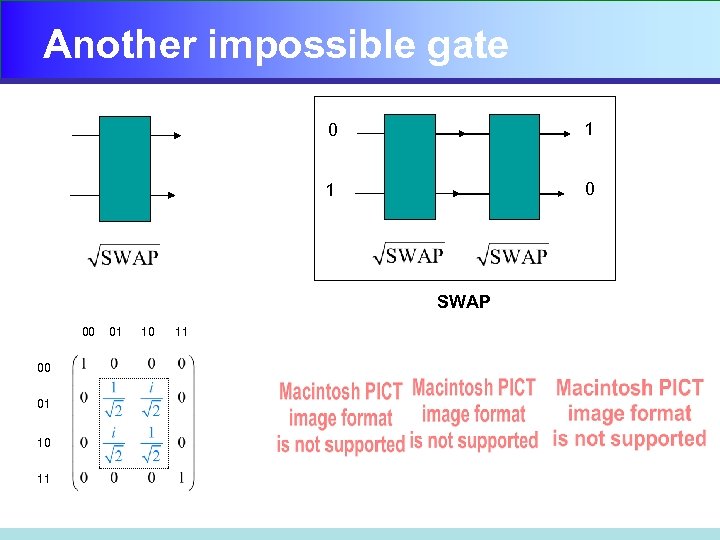 Another impossible gate 0 1 1 0 SWAP 00 00 01 10 11
Another impossible gate 0 1 1 0 SWAP 00 00 01 10 11
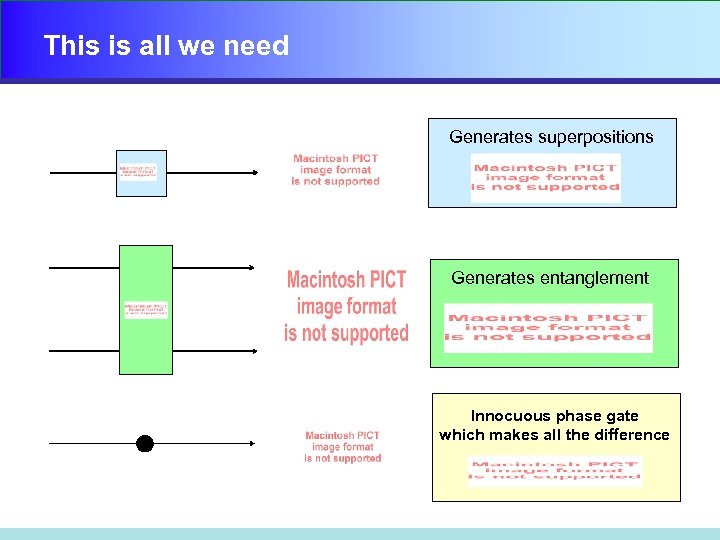 This is all we need Generates superpositions Generates entanglement Innocuous phase gate which makes all the difference
This is all we need Generates superpositions Generates entanglement Innocuous phase gate which makes all the difference
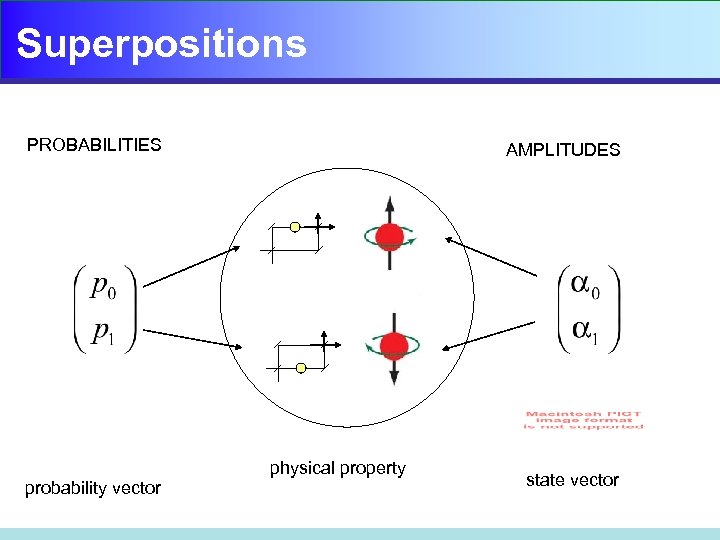 Superpositions PROBABILITIES probability vector AMPLITUDES physical property state vector
Superpositions PROBABILITIES probability vector AMPLITUDES physical property state vector
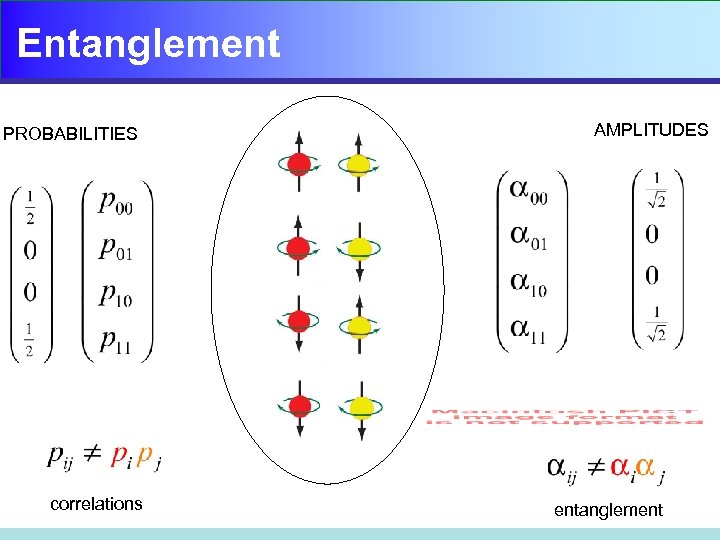 Entanglement PROBABILITIES correlations AMPLITUDES entanglement
Entanglement PROBABILITIES correlations AMPLITUDES entanglement
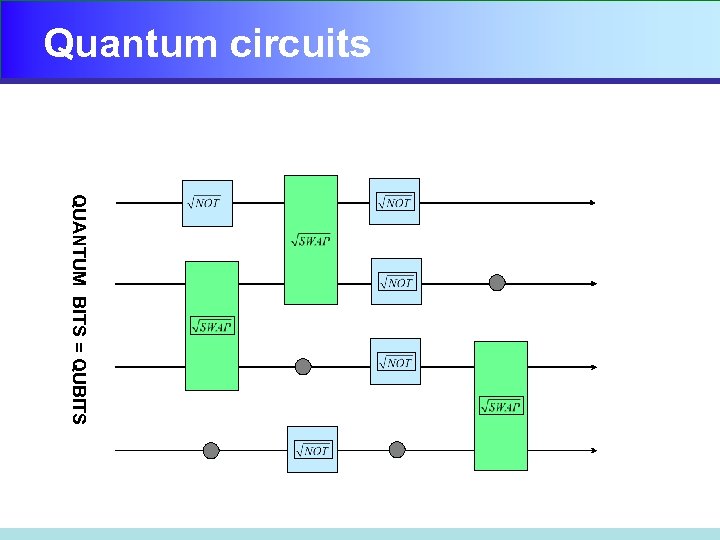 Quantum circuits QUANTUM BITS = QUBITS
Quantum circuits QUANTUM BITS = QUBITS
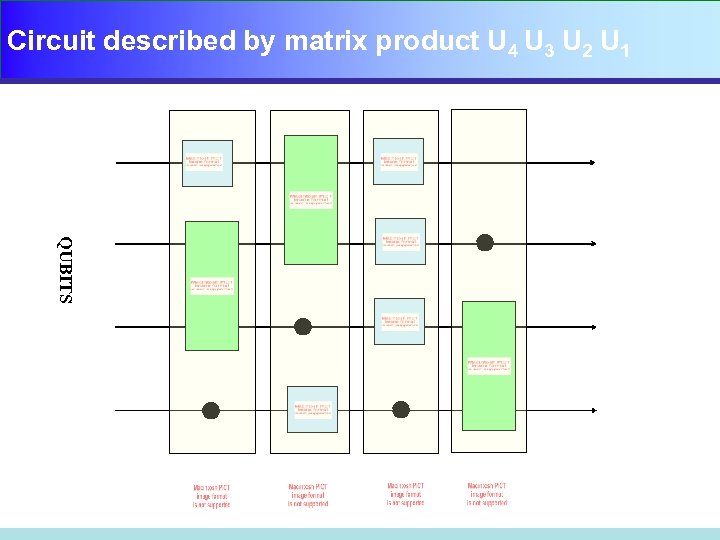 Circuit described by matrix product U 4 U 3 U 2 U 1 QUBITS
Circuit described by matrix product U 4 U 3 U 2 U 1 QUBITS
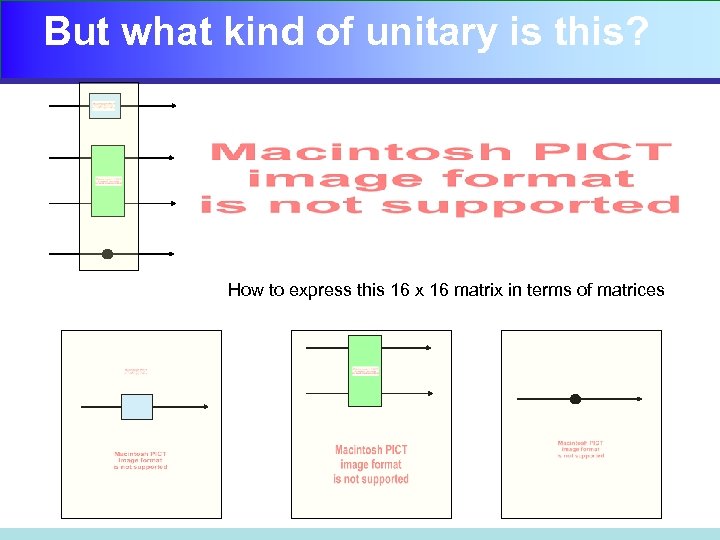 But what kind of unitary is this? How to express this 16 x 16 matrix in terms of matrices
But what kind of unitary is this? How to express this 16 x 16 matrix in terms of matrices
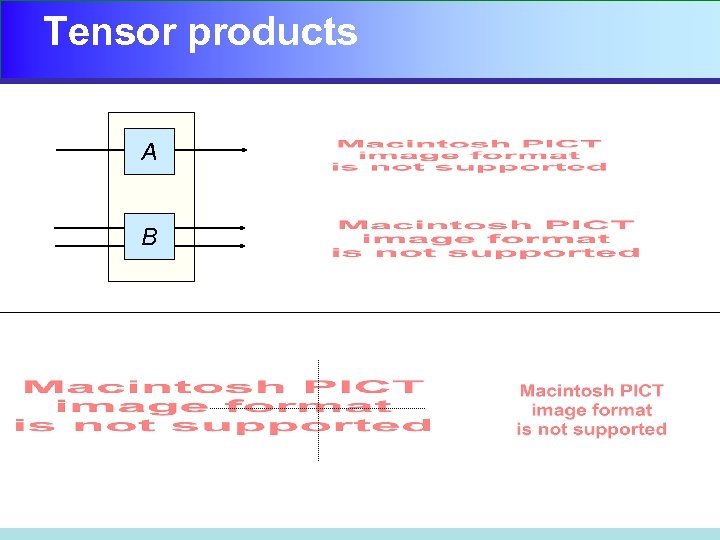 Tensor products A B
Tensor products A B
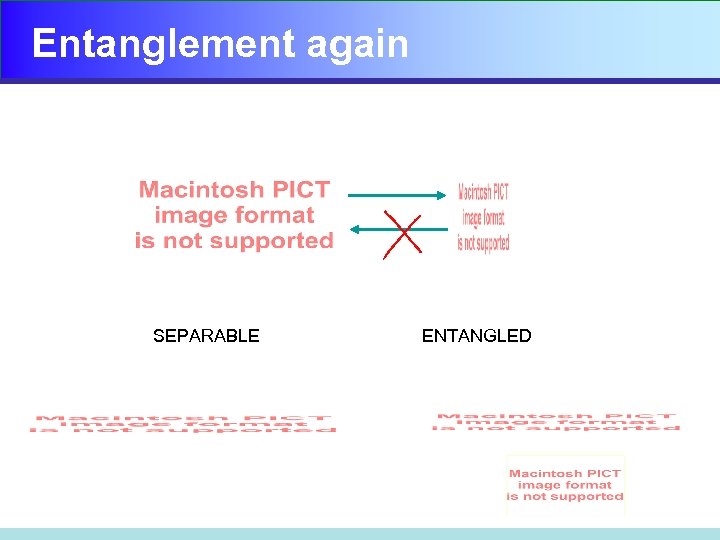 Entanglement again SEPARABLE ENTANGLED
Entanglement again SEPARABLE ENTANGLED
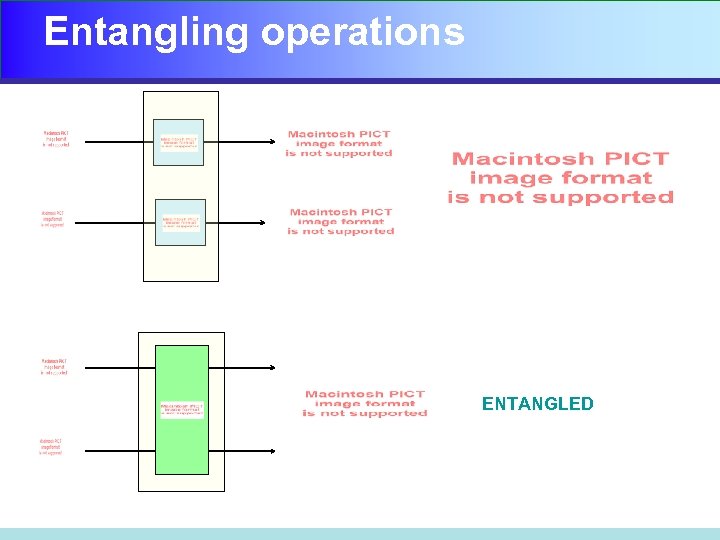 Entangling operations ENTANGLED
Entangling operations ENTANGLED
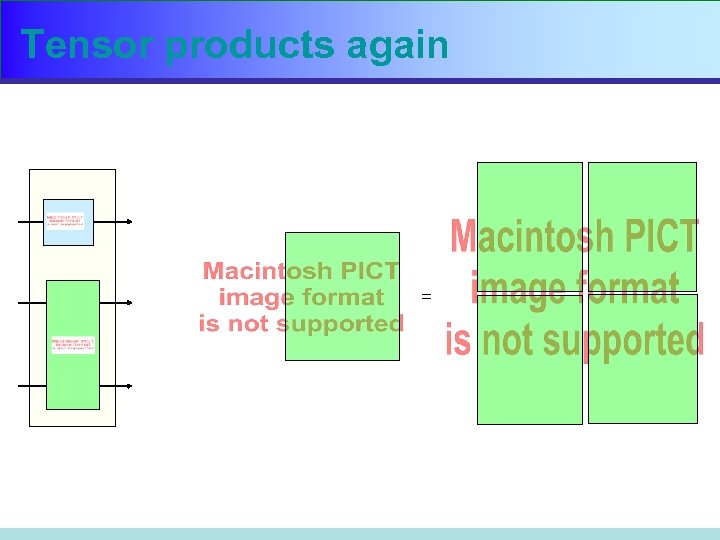 Tensor products again =
Tensor products again =
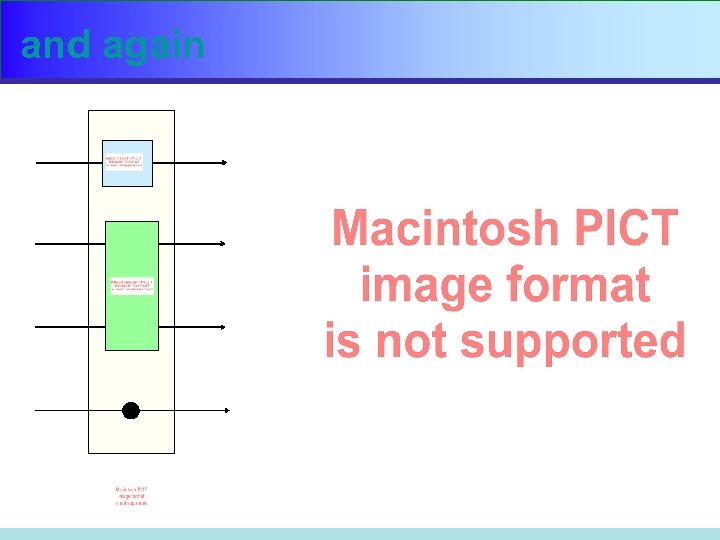 and again
and again
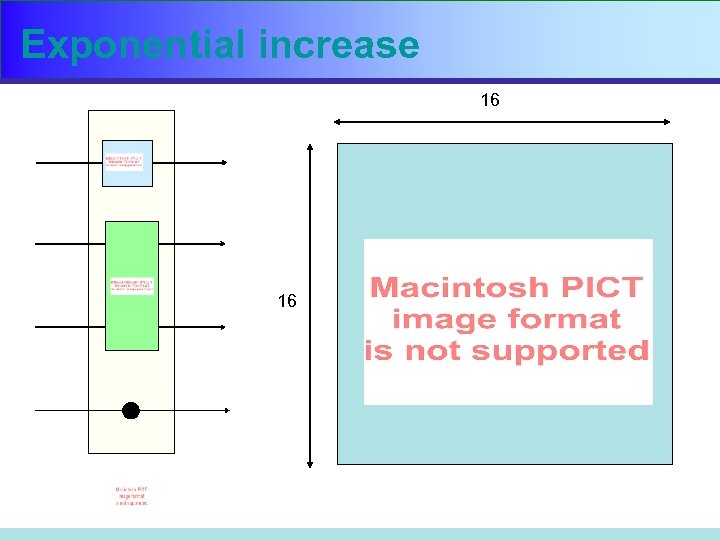 Exponential increase 16 16
Exponential increase 16 16
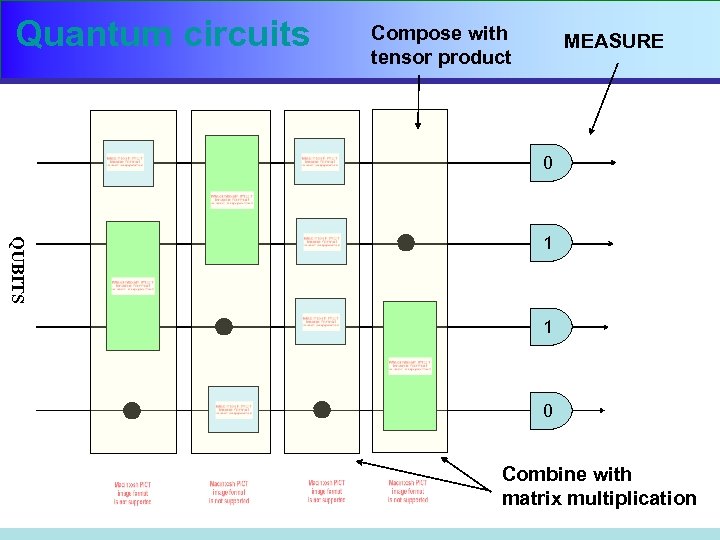 Quantum circuits Compose with tensor product MEASURE 0 QUBITS 1 1 0 Combine with matrix multiplication
Quantum circuits Compose with tensor product MEASURE 0 QUBITS 1 1 0 Combine with matrix multiplication
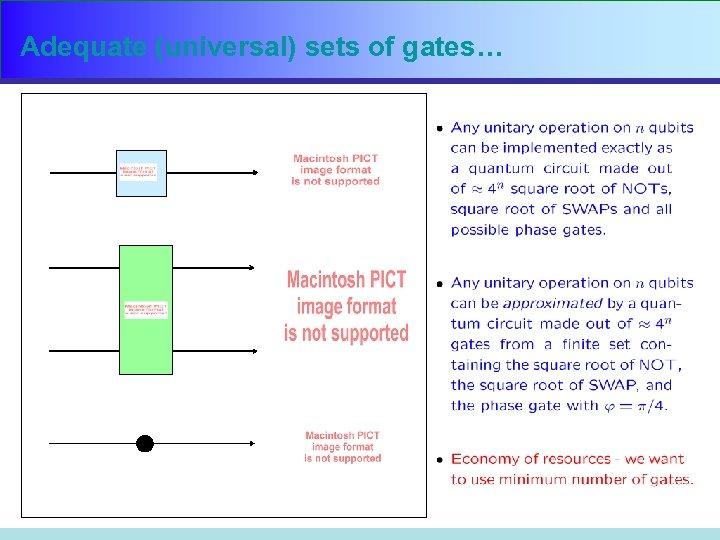 Adequate (universal) sets of gates…
Adequate (universal) sets of gates…
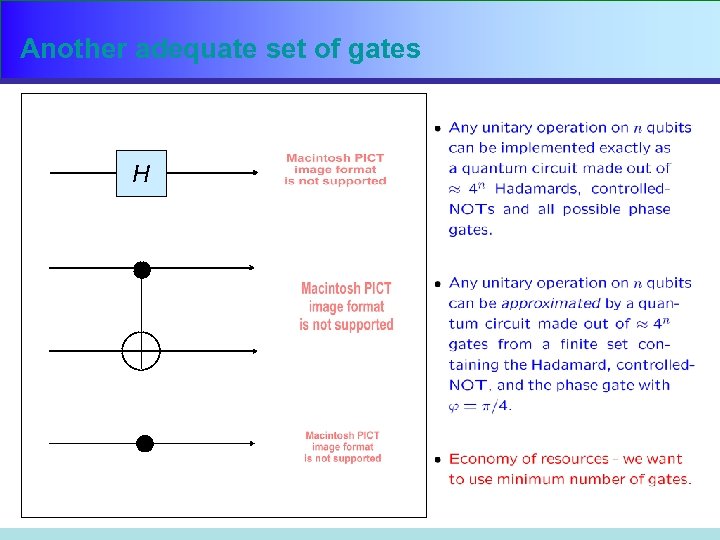 Another adequate set of gates H
Another adequate set of gates H
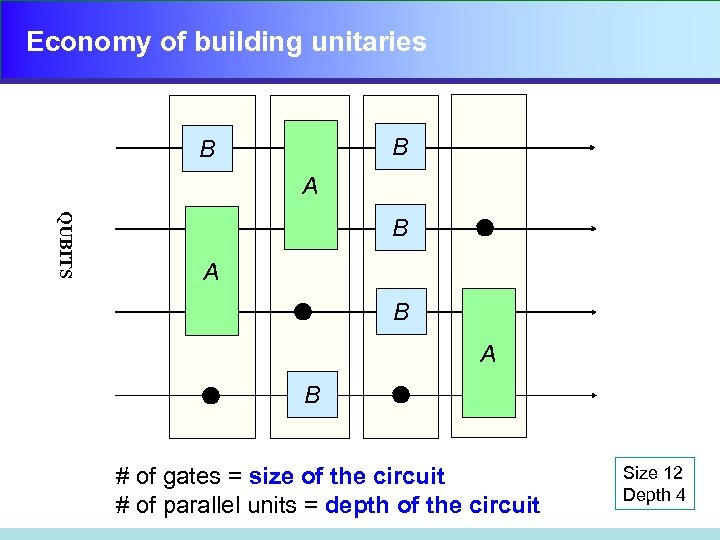 Economy of building unitaries B B A QUBITS B A B # of gates = size of the circuit # of parallel units = depth of the circuit Size 12 Depth 4
Economy of building unitaries B B A QUBITS B A B # of gates = size of the circuit # of parallel units = depth of the circuit Size 12 Depth 4
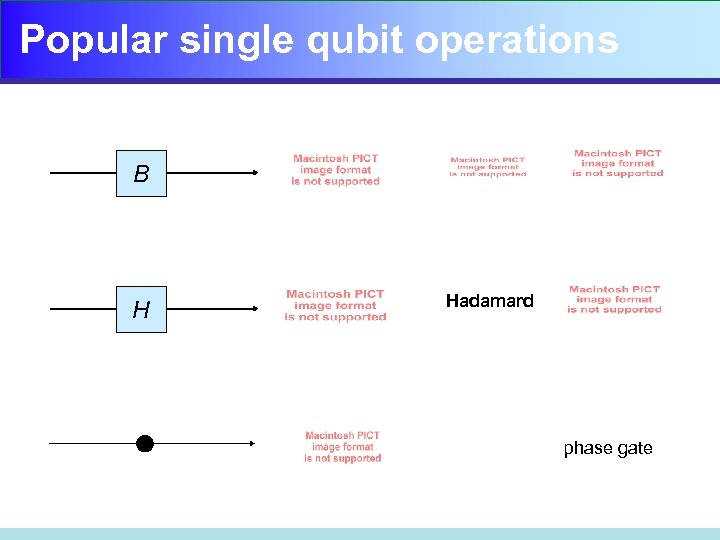 Popular single qubit operations B H Hadamard phase gate
Popular single qubit operations B H Hadamard phase gate
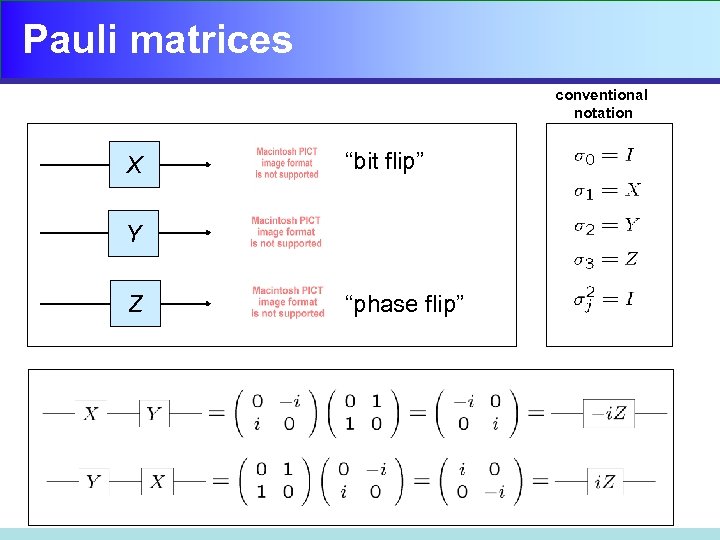 Pauli matrices conventional notation X “bit flip” Y Z “phase flip”
Pauli matrices conventional notation X “bit flip” Y Z “phase flip”
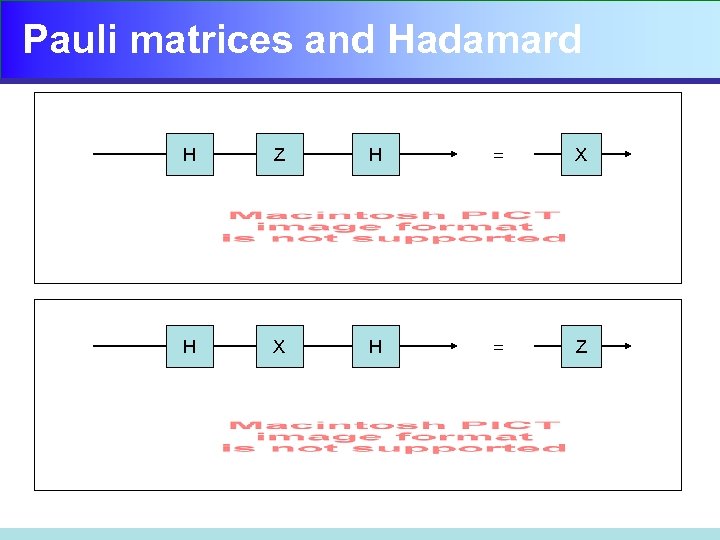 Pauli matrices and Hadamard H Z H = X H = Z
Pauli matrices and Hadamard H Z H = X H = Z
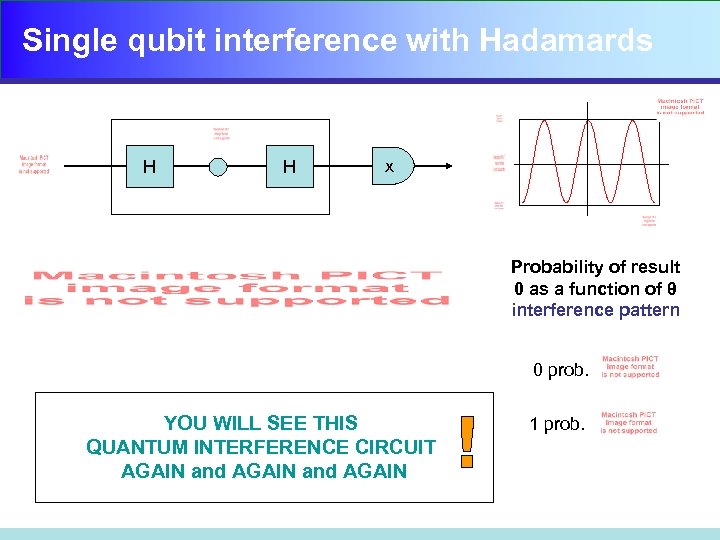 Single qubit interference with Hadamards H H x Probability of result 0 as a function of θ interference pattern 0 prob. YOU WILL SEE THIS QUANTUM INTERFERENCE CIRCUIT AGAIN and AGAIN 1 prob.
Single qubit interference with Hadamards H H x Probability of result 0 as a function of θ interference pattern 0 prob. YOU WILL SEE THIS QUANTUM INTERFERENCE CIRCUIT AGAIN and AGAIN 1 prob.
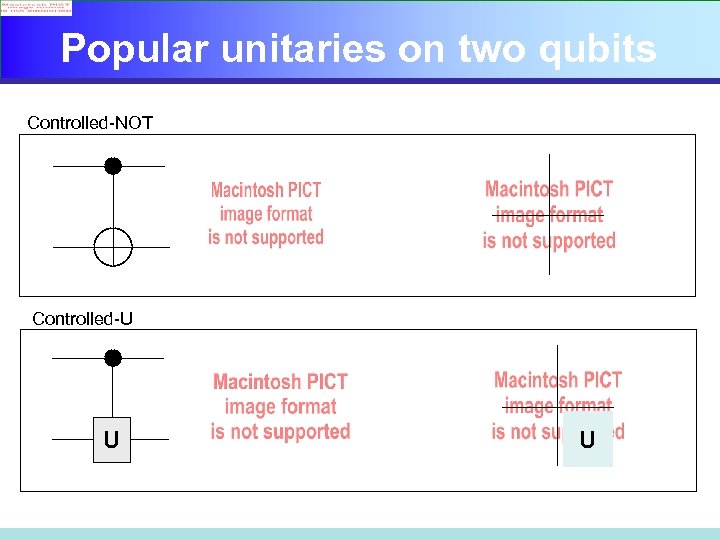 Popular unitaries on two qubits Controlled-NOT Controlled-U U U
Popular unitaries on two qubits Controlled-NOT Controlled-U U U
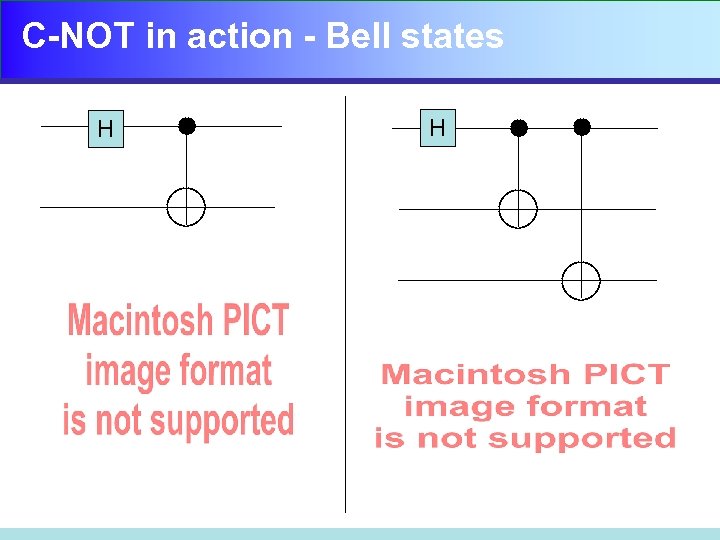 C-NOT in action - Bell states H H
C-NOT in action - Bell states H H
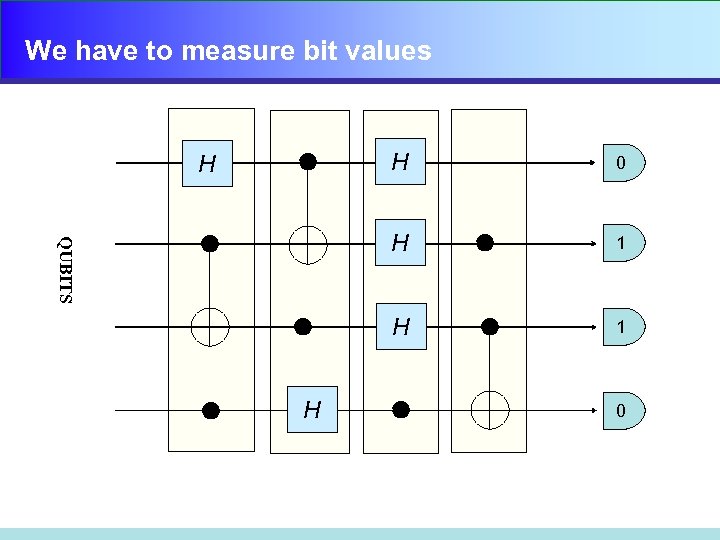 We have to measure bit values H QUBITS 1 H H 0 H H 1 0
We have to measure bit values H QUBITS 1 H H 0 H H 1 0
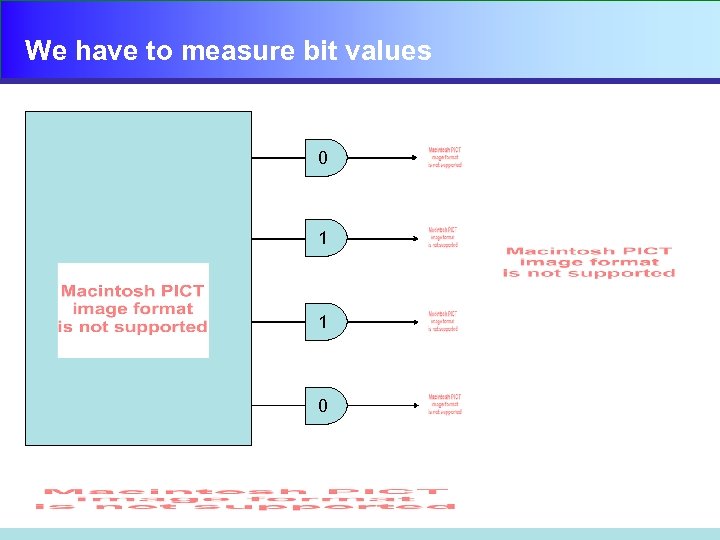 We have to measure bit values 0 1 1 0
We have to measure bit values 0 1 1 0
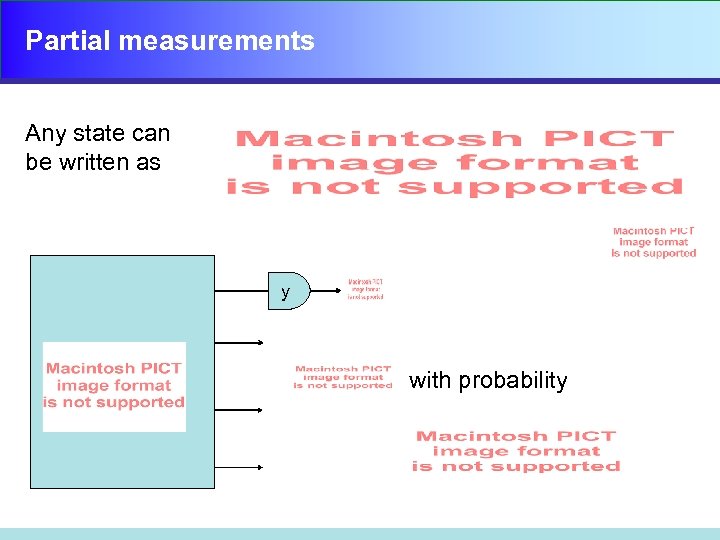 Partial measurements Any state can be written as y with probability
Partial measurements Any state can be written as y with probability
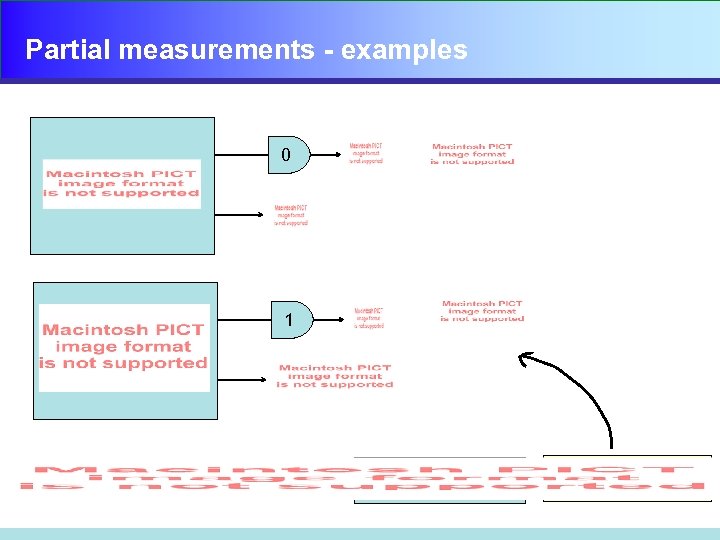 Partial measurements - examples 0 1
Partial measurements - examples 0 1
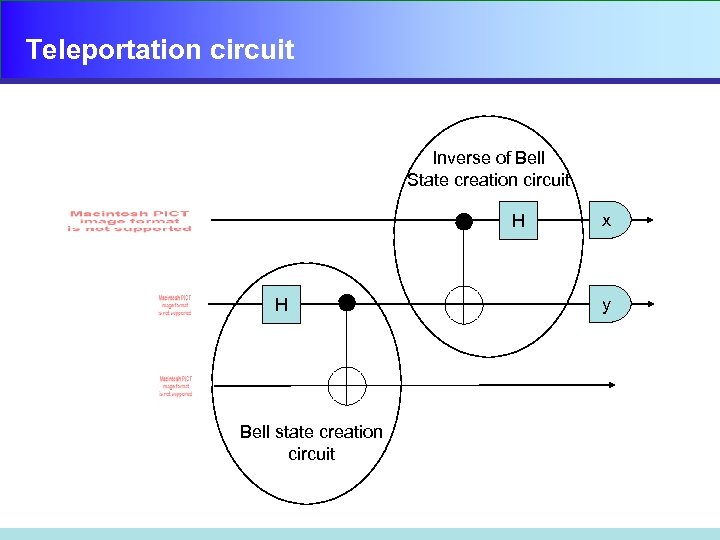 Teleportation circuit Inverse of Bell State creation circuit H H Bell state creation circuit x y
Teleportation circuit Inverse of Bell State creation circuit H H Bell state creation circuit x y
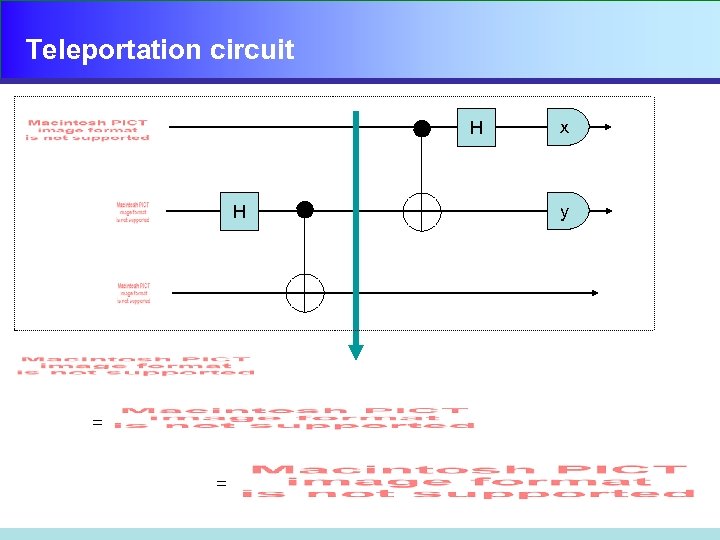 Teleportation circuit H H = = x y
Teleportation circuit H H = = x y
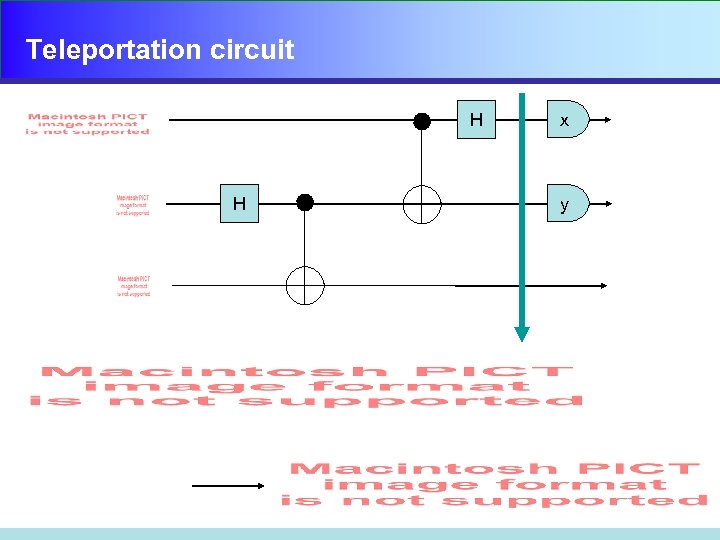 Teleportation circuit H H x y
Teleportation circuit H H x y
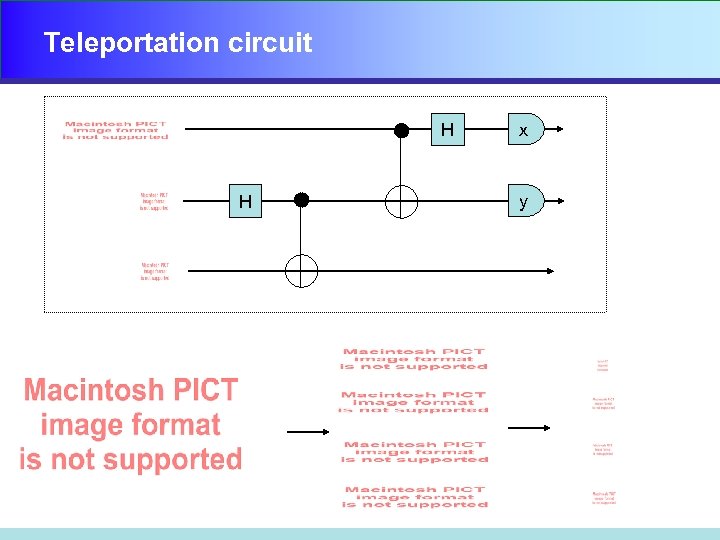 Teleportation circuit H H x y
Teleportation circuit H H x y
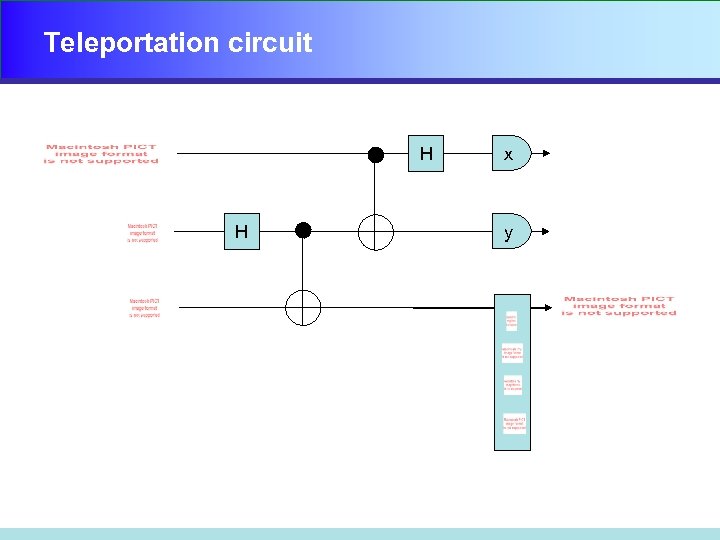 Teleportation circuit H H x y
Teleportation circuit H H x y
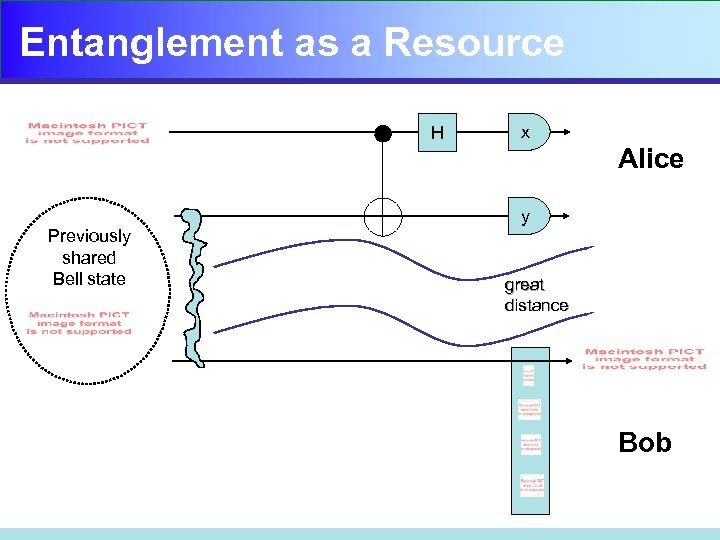 Entanglement as a Resource H x Alice Previously shared Bell state y great distance Bob
Entanglement as a Resource H x Alice Previously shared Bell state y great distance Bob
 Schrödinger’s idea Manuscript by Schrödinger dated back to 1932 or 1933. Discovered by Matthias Christandl and Lawrence Ioannou of Cambridge University in the Schrödinger archive in Vienna.
Schrödinger’s idea Manuscript by Schrödinger dated back to 1932 or 1933. Discovered by Matthias Christandl and Lawrence Ioannou of Cambridge University in the Schrödinger archive in Vienna.
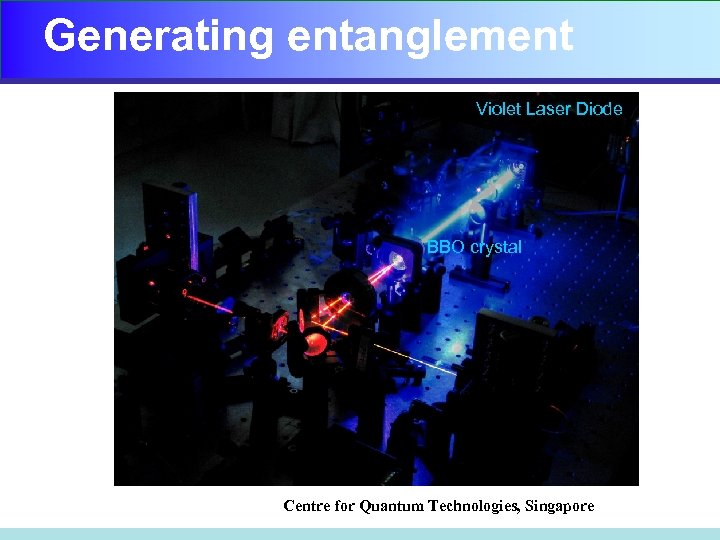 Generating entanglement Violet Laser Diode BBO crystal Centre for Quantum Technologies, Singapore
Generating entanglement Violet Laser Diode BBO crystal Centre for Quantum Technologies, Singapore


