118611daeb229cf9f6c6a1f5366eabb3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14
 Quality of Life
Quality of Life
 Patient’s evaluation of quality of life § Provides understanding of impact of illness from patient’s viewpoint – Different from health status or physical functioning – Quality of life can be good even with physical disability – More than health problems, loss of abilities, or functional deficits § Incorporation of patient’s values sets QOL assessment apart from measures of health status
Patient’s evaluation of quality of life § Provides understanding of impact of illness from patient’s viewpoint – Different from health status or physical functioning – Quality of life can be good even with physical disability – More than health problems, loss of abilities, or functional deficits § Incorporation of patient’s values sets QOL assessment apart from measures of health status
 Patient’s evaluation of quality of life § Important tool for understanding individual differences in response to illness – Individual responses in adapting to cancer and treatment – Re-evaluation of life in context of life-threatening disease § Ultimate purpose for QOL assessment Enhanced well-being – Particularly in palliative care and at end of life (interventions aimed at providing comfort and emotional support) – Maximize QOL
Patient’s evaluation of quality of life § Important tool for understanding individual differences in response to illness – Individual responses in adapting to cancer and treatment – Re-evaluation of life in context of life-threatening disease § Ultimate purpose for QOL assessment Enhanced well-being – Particularly in palliative care and at end of life (interventions aimed at providing comfort and emotional support) – Maximize QOL
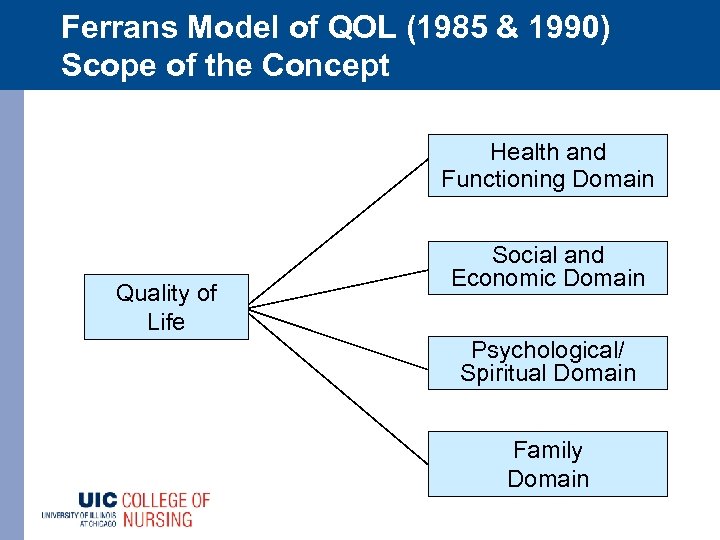 Ferrans Model of QOL (1985 & 1990) Scope of the Concept Health and Functioning Domain Quality of Life Social and Economic Domain Psychological/ Spiritual Domain Family Domain
Ferrans Model of QOL (1985 & 1990) Scope of the Concept Health and Functioning Domain Quality of Life Social and Economic Domain Psychological/ Spiritual Domain Family Domain
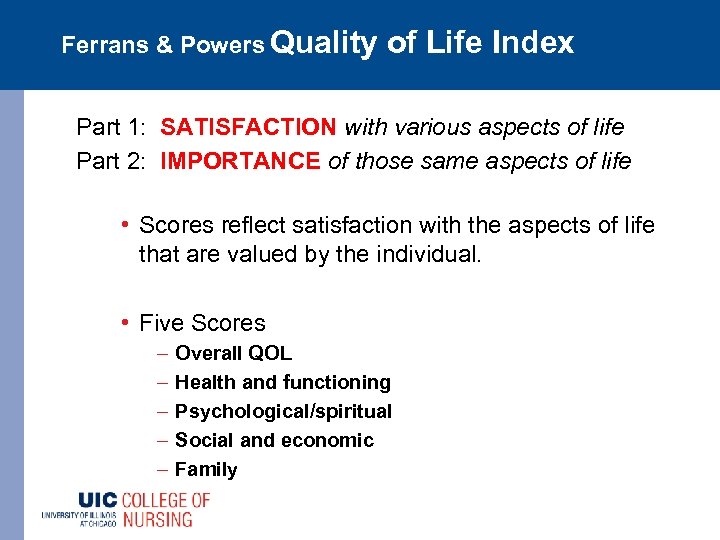 Ferrans & Powers Quality of Life Index Part 1: SATISFACTION with various aspects of life Part 2: IMPORTANCE of those same aspects of life • Scores reflect satisfaction with the aspects of life that are valued by the individual. • Five Scores – – – Overall QOL Health and functioning Psychological/spiritual Social and economic Family
Ferrans & Powers Quality of Life Index Part 1: SATISFACTION with various aspects of life Part 2: IMPORTANCE of those same aspects of life • Scores reflect satisfaction with the aspects of life that are valued by the individual. • Five Scores – – – Overall QOL Health and functioning Psychological/spiritual Social and economic Family
 Ferrans & Powers Quality of Life Index § Published first in 1985 (200+ published studies) § International research (30+ countries) – Americas: USA, Canada, Mexico, Brazil, Chile – Europe: Denmark, France, Great Britain, Hungarian, Italy, Lithuania, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Russia, Spain, Sweden – Middle East: Israel, Jordan, Turkey – Africa: South Africa – Asia: India, China, Korea, Japan, Thailand, Taiwan – Australia and New Zealand § U. S. cross-cultural research – African Americans – Mexican Americans – Korean Americans
Ferrans & Powers Quality of Life Index § Published first in 1985 (200+ published studies) § International research (30+ countries) – Americas: USA, Canada, Mexico, Brazil, Chile – Europe: Denmark, France, Great Britain, Hungarian, Italy, Lithuania, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Russia, Spain, Sweden – Middle East: Israel, Jordan, Turkey – Africa: South Africa – Asia: India, China, Korea, Japan, Thailand, Taiwan – Australia and New Zealand § U. S. cross-cultural research – African Americans – Mexican Americans – Korean Americans
 21 Languages § § § Arabic Chinese Danish English French Hebrew Hungarian Italian Japanese Korean Lithuanian § § § § § Norwegian Polish Portuguese Romanian Russian Spanish Swedish Tamil Thai Turkish
21 Languages § § § Arabic Chinese Danish English French Hebrew Hungarian Italian Japanese Korean Lithuanian § § § § § Norwegian Polish Portuguese Romanian Russian Spanish Swedish Tamil Thai Turkish
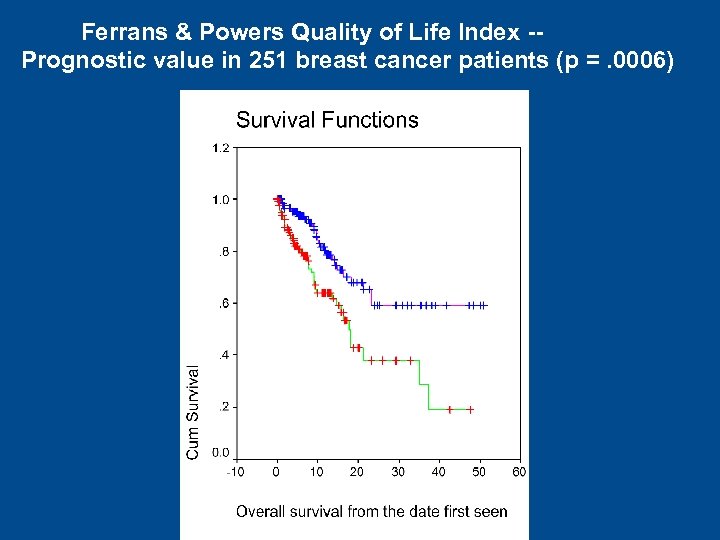 Ferrans & Powers Quality of Life Index -Prognostic value in 251 breast cancer patients (p =. 0006)
Ferrans & Powers Quality of Life Index -Prognostic value in 251 breast cancer patients (p =. 0006)
 Quality of Life of African American Cancer Survivors
Quality of Life of African American Cancer Survivors
 Quality of Life of African American Cancer Survivors NIH R 01 CA 89418 (CALGB 119901) § Survivors: 500 African American cancer survivors – Breast, prostate, colon – Currently free of cancer § Controls: 500 African American non-cancer controls – Selected via random digit dialing from the areas in which the cancer survivors reside. – Matched (as a group) to the survivor group on age, gender, health insurance status, and education level
Quality of Life of African American Cancer Survivors NIH R 01 CA 89418 (CALGB 119901) § Survivors: 500 African American cancer survivors – Breast, prostate, colon – Currently free of cancer § Controls: 500 African American non-cancer controls – Selected via random digit dialing from the areas in which the cancer survivors reside. – Matched (as a group) to the survivor group on age, gender, health insurance status, and education level
 16 Participating CALGB Institutions § Heme/Onc Associates of Central NY § Northern Indiana § Ohio State University § University of Chicago § University of Illinois at Chicago § Wake Forest § Walter Reed § Washington University – St. Louis § Hartford Hospital § Jersey Shore Medical Center § Navy Medical Center – San Diego § Queens Hospital Medical Center § Roswell Park Cancer Center § Sibley Memorial Hospital § Wayne Memorial Hospital - SCCC § Jesse Brown VA Medical Center
16 Participating CALGB Institutions § Heme/Onc Associates of Central NY § Northern Indiana § Ohio State University § University of Chicago § University of Illinois at Chicago § Wake Forest § Walter Reed § Washington University – St. Louis § Hartford Hospital § Jersey Shore Medical Center § Navy Medical Center – San Diego § Queens Hospital Medical Center § Roswell Park Cancer Center § Sibley Memorial Hospital § Wayne Memorial Hospital - SCCC § Jesse Brown VA Medical Center
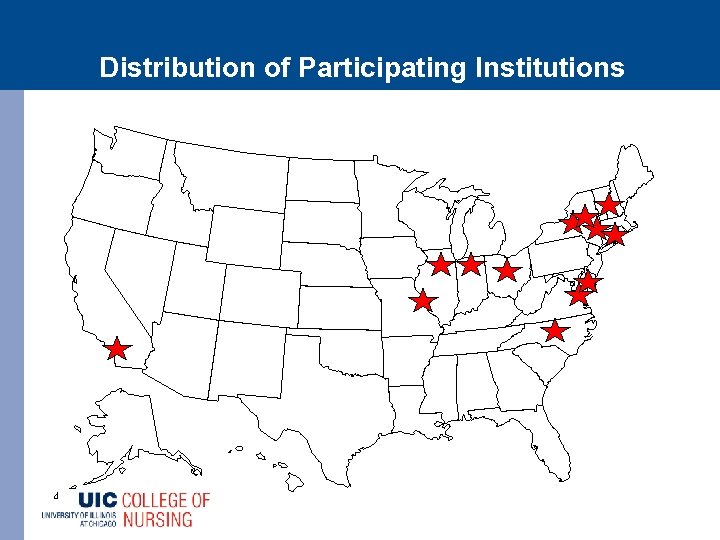 Distribution of Participating Institutions
Distribution of Participating Institutions
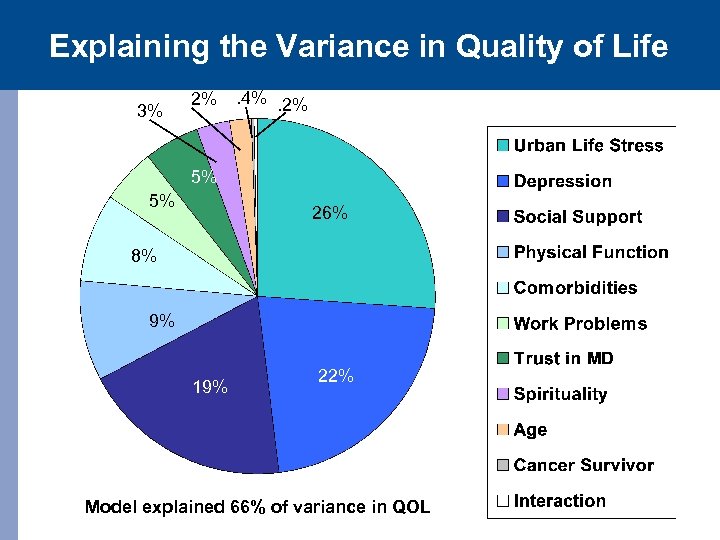 Explaining the Variance in Quality of Life 3% 2% . 4%. 2% 5% 5% 26% 8% 9% 19% 22% Model explained 66% of variance in QOL
Explaining the Variance in Quality of Life 3% 2% . 4%. 2% 5% 5% 26% 8% 9% 19% 22% Model explained 66% of variance in QOL



