17e7f08867020653b4e1f313641bf9f0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 38
 Quality Management Systems: Elements, implementation of documentation Swamynathan. S. M AP/ECE/SNSCT 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 1
Quality Management Systems: Elements, implementation of documentation Swamynathan. S. M AP/ECE/SNSCT 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 1
 Introduction • ISO- International Organization for Standardization • Founded in 1946, in Geneva, Switzerland • Main function is to promote the development of standardization of goods and services, to better accommodate a world wide market. • ANSI- American National Standards Institute • ANSI represents U. S. in the ISO 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 2
Introduction • ISO- International Organization for Standardization • Founded in 1946, in Geneva, Switzerland • Main function is to promote the development of standardization of goods and services, to better accommodate a world wide market. • ANSI- American National Standards Institute • ANSI represents U. S. in the ISO 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 2
 ISO Registration • Companies can become registered as an ISO company • This involves the registrar giving an assessment of the operations a company, and then making periodic surveillance audits • Primary Reason: To give your customer the comfort of knowing that you have a quality plan in place, and it is being monitored by an objective third party 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 3
ISO Registration • Companies can become registered as an ISO company • This involves the registrar giving an assessment of the operations a company, and then making periodic surveillance audits • Primary Reason: To give your customer the comfort of knowing that you have a quality plan in place, and it is being monitored by an objective third party 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 3
 Internal Reasons for Becoming ISO Registered • 100 Italian manufacturing firms were surveyed to find out what improved after certification. – Internal quality: less scrap, rework, nonconformities – Production reliability: less breakdowns, less time with emergencies, downtime – Time performance: time to market, punctual deliveries v. Externally: less nonconformities 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 4
Internal Reasons for Becoming ISO Registered • 100 Italian manufacturing firms were surveyed to find out what improved after certification. – Internal quality: less scrap, rework, nonconformities – Production reliability: less breakdowns, less time with emergencies, downtime – Time performance: time to market, punctual deliveries v. Externally: less nonconformities 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 4
 Negatives • Prevention and appraisal costs increased – Only one negative shown in 100 surveys. – Positives outweigh negatives – Takes time to implement, but worth it in the long run 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 5
Negatives • Prevention and appraisal costs increased – Only one negative shown in 100 surveys. – Positives outweigh negatives – Takes time to implement, but worth it in the long run 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 5
 ISO 9000 • The ISO 9000 series of standards is generic • It is designed to adapt to fit any industry type • Three standards of the 9000 series: – ISO 9000: 2000 - Fundamentals and vocabulary – ISO 9001: 2000 - Requirements – ISO 9004: 2000 - Guidelines for performance improvements 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 6
ISO 9000 • The ISO 9000 series of standards is generic • It is designed to adapt to fit any industry type • Three standards of the 9000 series: – ISO 9000: 2000 - Fundamentals and vocabulary – ISO 9001: 2000 - Requirements – ISO 9004: 2000 - Guidelines for performance improvements 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 6
 Sector-specific Standards • Some industries require special set of ISO rules; not operated the same as most • Three other quality systems: – AS 9100– ISO/TS 16949 – TL 9000 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 7
Sector-specific Standards • Some industries require special set of ISO rules; not operated the same as most • Three other quality systems: – AS 9100– ISO/TS 16949 – TL 9000 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 7
 AS 9100 • This standard is specifically for the aerospace industry • Attempt at unifying the requirements of NASA, DOD, and FAA • At the same time satisfying the industry’s needs 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 8
AS 9100 • This standard is specifically for the aerospace industry • Attempt at unifying the requirements of NASA, DOD, and FAA • At the same time satisfying the industry’s needs 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 8
 ISO/TS 16949 • Standard specifically for automotive suppliers • Merges supplier quality requirements of U. S. with German, French, and Italian automakers • Goal- provide continuous improvement, defect prevention, reduce variation and waste • Is assumed that this standard will show 85% improvement rate in first 5 years 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 9
ISO/TS 16949 • Standard specifically for automotive suppliers • Merges supplier quality requirements of U. S. with German, French, and Italian automakers • Goal- provide continuous improvement, defect prevention, reduce variation and waste • Is assumed that this standard will show 85% improvement rate in first 5 years 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 9
 TL 9000 • Telecommunications Industry • Consolidate various quality systems requirements • Defines design, development, production, delivery, installation and maintenance of telecommunications • Customers receive benefits , worldwide competition, benchmarks, improvement initiatives 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 10
TL 9000 • Telecommunications Industry • Consolidate various quality systems requirements • Defines design, development, production, delivery, installation and maintenance of telecommunications • Customers receive benefits , worldwide competition, benchmarks, improvement initiatives 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 10
 TL 9000 continued • This standard focused on: – Hardware Specific Requirements and Measures – Software Specific Requirements and Measures – Services Specific Requirements and Measures 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 11
TL 9000 continued • This standard focused on: – Hardware Specific Requirements and Measures – Software Specific Requirements and Measures – Services Specific Requirements and Measures 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 11
 ISO 9001 REQUIREMENTS • The standard has 8 clauses 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) Scope Normative Reference Terms and Definitions Quality Management Systems Management Responsibility Resource Management Product Realization Measurement Analysis and Improvement 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 12
ISO 9001 REQUIREMENTS • The standard has 8 clauses 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) Scope Normative Reference Terms and Definitions Quality Management Systems Management Responsibility Resource Management Product Realization Measurement Analysis and Improvement 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 12
 1. Scope To provide a product that meets a) Customer Requirement b) Regulatory Requirements c) 3/18/2018 Customers Satisfaction SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 13
1. Scope To provide a product that meets a) Customer Requirement b) Regulatory Requirements c) 3/18/2018 Customers Satisfaction SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 13
 2. Normative Reference: Fundamentals and vocabulary 3. Terms and Definitions: Supplier Organization Customers 4. Quality Management System: a) General Requirements b) Documentation * General Documentation * Quality Manual * Control of Documents * Control of Records 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 14
2. Normative Reference: Fundamentals and vocabulary 3. Terms and Definitions: Supplier Organization Customers 4. Quality Management System: a) General Requirements b) Documentation * General Documentation * Quality Manual * Control of Documents * Control of Records 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 14
 5) Management Responsibility: a) Management commitment b) Customer Focus c) Quality policy d)Planning * Quality Objectives * Quality Management System Planning e) Responsibility, Authority, And Communication * Responsibility and Authority * Management Representative * Internal Communication f) Management Review * General Management * Review Input * Review Output 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 15
5) Management Responsibility: a) Management commitment b) Customer Focus c) Quality policy d)Planning * Quality Objectives * Quality Management System Planning e) Responsibility, Authority, And Communication * Responsibility and Authority * Management Representative * Internal Communication f) Management Review * General Management * Review Input * Review Output 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 15
 6) Resource Management : a) Provision of Resources b) Human Resources * General * Competence, Awareness and Training c) Infrastructure d) Work Environment 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 16
6) Resource Management : a) Provision of Resources b) Human Resources * General * Competence, Awareness and Training c) Infrastructure d) Work Environment 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 16
 7) Product Realization a) Planning of product Realization b) Customer Related Processes * Determination Of Requirement Related to the Product * Review Of Requirement Related to the Product *Customer Communication c) Design And Development * Design And Development Planning * Design And Development Inputs * Design And Development Outputs * Design And Development Review * Design And Development Verification * Design And Development Validation * Control of Design And Development Changes 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 17
7) Product Realization a) Planning of product Realization b) Customer Related Processes * Determination Of Requirement Related to the Product * Review Of Requirement Related to the Product *Customer Communication c) Design And Development * Design And Development Planning * Design And Development Inputs * Design And Development Outputs * Design And Development Review * Design And Development Verification * Design And Development Validation * Control of Design And Development Changes 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 17
 d) Purchasing * Purchasing Process * Purchasing Information * Verification Of Purchased Product e)Production And service Provision * Control Of Production And service Provision * Validation Of Processes For Production And service Provision *Identification And Traceability * Customer Property * Preservation of Product f) Control Of Monitoring And Measuring Devices 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 18
d) Purchasing * Purchasing Process * Purchasing Information * Verification Of Purchased Product e)Production And service Provision * Control Of Production And service Provision * Validation Of Processes For Production And service Provision *Identification And Traceability * Customer Property * Preservation of Product f) Control Of Monitoring And Measuring Devices 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 18
 8) Measurement , Analysis, And Improvement a) General b) Monitoring And Measurement * Customer Satisfaction * Internal Audit * Monitoring And Measurement Of Processes * Monitoring And Measurement of Product and Service c) Control Of Nonconforming Product d) Analysis Of Data e) Improvement * continual improvement * corrective Action * preventive Action 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 19
8) Measurement , Analysis, And Improvement a) General b) Monitoring And Measurement * Customer Satisfaction * Internal Audit * Monitoring And Measurement Of Processes * Monitoring And Measurement of Product and Service c) Control Of Nonconforming Product d) Analysis Of Data e) Improvement * continual improvement * corrective Action * preventive Action 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 19
 IMPLEMENTATION 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) 10) Top Management Commitment Appoint the Management Representative Awareness Appoint an Implementation Team Training Time Schedule Select Element Owners Review the Present System Write the Documents Install the New System 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 20
IMPLEMENTATION 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) 10) Top Management Commitment Appoint the Management Representative Awareness Appoint an Implementation Team Training Time Schedule Select Element Owners Review the Present System Write the Documents Install the New System 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 20
 11) Internal Audit 12) Management Review 13) Preassessment 14) Registration 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 21
11) Internal Audit 12) Management Review 13) Preassessment 14) Registration 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 21
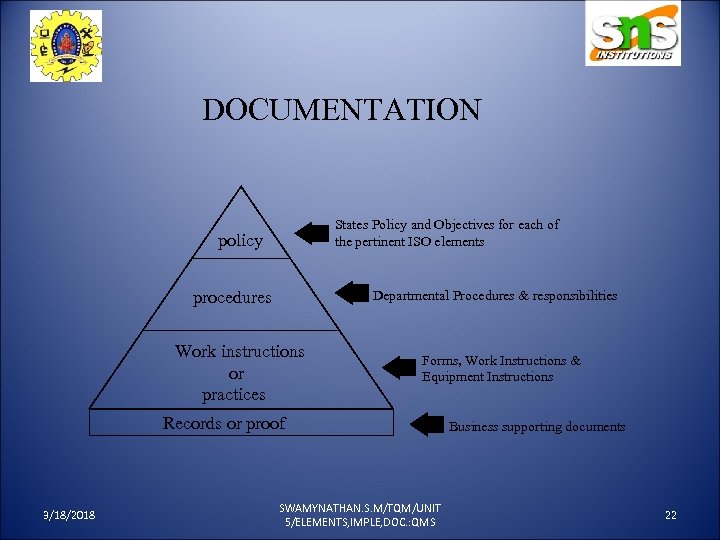 DOCUMENTATION States Policy and Objectives for each of the pertinent ISO elements policy procedures Departmental Procedures & responsibilities Work instructions or practices Forms, Work Instructions & Equipment Instructions Records or proof 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS Business supporting documents 22
DOCUMENTATION States Policy and Objectives for each of the pertinent ISO elements policy procedures Departmental Procedures & responsibilities Work instructions or practices Forms, Work Instructions & Equipment Instructions Records or proof 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS Business supporting documents 22
 POLICY: • This is a document that defines what will be done and why. • A quality policy manual should be written so it is clear, precise, practical, and easy to understand. 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 23
POLICY: • This is a document that defines what will be done and why. • A quality policy manual should be written so it is clear, precise, practical, and easy to understand. 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 23
 PROCEDURE: • The procedures define 1) who should perform specific tasks 2) when the task should be done 3) Where documentation will be made showing that the task was performed. 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 24
PROCEDURE: • The procedures define 1) who should perform specific tasks 2) when the task should be done 3) Where documentation will be made showing that the task was performed. 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 24
 WORK INSTRUCTIONS: • Work instructions are usually department, machine, task, or product oriented and spell out how a job will be done. • The writing of a work instruction is best carried out by the employee who performs the task. 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 25
WORK INSTRUCTIONS: • Work instructions are usually department, machine, task, or product oriented and spell out how a job will be done. • The writing of a work instruction is best carried out by the employee who performs the task. 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 25
 RECORDS: • Records are a way of documenting that the polices, procedures, and work instructions have been followed. • Records provide data for corrective action and a way of recalling products. 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 26
RECORDS: • Records are a way of documenting that the polices, procedures, and work instructions have been followed. • Records provide data for corrective action and a way of recalling products. 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 26
 DOCUMENT DEVELOPMENT: • To begin creating the documentation system, the implementation team should gather all the existing policies, procedures, work instructions, and forms that are presently in use. • When the documents have been completed, they should be formatted in a manner that will allow for simple and effective document control. 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 27
DOCUMENT DEVELOPMENT: • To begin creating the documentation system, the implementation team should gather all the existing policies, procedures, work instructions, and forms that are presently in use. • When the documents have been completed, they should be formatted in a manner that will allow for simple and effective document control. 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 27
 WRITING THE DOCUMENTS • When writing the document it should be simple rather than complex. • Use flow chart and check sheets where ever possible wherever possible rather than lengthy verbiage. 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 28
WRITING THE DOCUMENTS • When writing the document it should be simple rather than complex. • Use flow chart and check sheets where ever possible wherever possible rather than lengthy verbiage. 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 28
 INTERNAL AUDITS Objectives: 1) Determine that actual performance conforms to the documented QMS. 2) Initiate corrective action activities in response deficiencies. 3) Follow up on noncompliance items from previous audits. 4) Provide continued improvement in the system through feedback to management. 5) Cause the auditee to think about the process, thereby encouraging possible improvement. 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 29
INTERNAL AUDITS Objectives: 1) Determine that actual performance conforms to the documented QMS. 2) Initiate corrective action activities in response deficiencies. 3) Follow up on noncompliance items from previous audits. 4) Provide continued improvement in the system through feedback to management. 5) Cause the auditee to think about the process, thereby encouraging possible improvement. 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 29
 AUDITOR: A qualified individual who have received training in auditing principles and procedures should perform audits. 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 30
AUDITOR: A qualified individual who have received training in auditing principles and procedures should perform audits. 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 30
 TECHNIQUES: During the auditor should employee three methods: 1) Examination of documents 2) Observation of activates 3) Interviews 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 31
TECHNIQUES: During the auditor should employee three methods: 1) Examination of documents 2) Observation of activates 3) Interviews 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 31
 Examination of Documents: The auditor should examine the documents in a systematic manner 1) Documents are identified with a title, revision date, and responsible owner. 2) Documents are readily available to users 3) A master list by departments or function for procedures, work instructions, and records is appropriately located. 4) There are no obsolete documents at workstations. 5) Changes follow a prescribed procedure. 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 32
Examination of Documents: The auditor should examine the documents in a systematic manner 1) Documents are identified with a title, revision date, and responsible owner. 2) Documents are readily available to users 3) A master list by departments or function for procedures, work instructions, and records is appropriately located. 4) There are no obsolete documents at workstations. 5) Changes follow a prescribed procedure. 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 32
 Observation Activity: It requires an aptitude for details. Interviews: 1) Place the auditee in a nonthreathing environment 2) Encourage employees to talk about the process. 3) Focus on the system not on the auditee. 4) Discuss the major issues informally with the auditee first. 5) Use the appropriate type of questions. 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 33
Observation Activity: It requires an aptitude for details. Interviews: 1) Place the auditee in a nonthreathing environment 2) Encourage employees to talk about the process. 3) Focus on the system not on the auditee. 4) Discuss the major issues informally with the auditee first. 5) Use the appropriate type of questions. 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 33
 PROCEDURE: • Before the audit takes place an audit plan and check list should be prepared. • The audit itself has three parts 1) The preaudit meeting 2) The audit 3) A closing meeting 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 34
PROCEDURE: • Before the audit takes place an audit plan and check list should be prepared. • The audit itself has three parts 1) The preaudit meeting 2) The audit 3) A closing meeting 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 34
 REGISTRATION It is the assessment and audit of a quality system by a third party, known as a registrar. Two parts: 1) Selecting a registrar. 2) The registration process. 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 35
REGISTRATION It is the assessment and audit of a quality system by a third party, known as a registrar. Two parts: 1) Selecting a registrar. 2) The registration process. 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 35
 SELECTING A REGISTRAR • Qualifications And Experience • • 3/18/2018 Certificate Recognition The Registration Process Time And Cost Constraints Auditor Qualifications SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 36
SELECTING A REGISTRAR • Qualifications And Experience • • 3/18/2018 Certificate Recognition The Registration Process Time And Cost Constraints Auditor Qualifications SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 36
 REGISTRATION PROCESS The process has six basic steps: 1) Application for registration. 2) Document review. 3) Preassessment 4) Assessment 5) Registration 6) Follow-up surveillance 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 37
REGISTRATION PROCESS The process has six basic steps: 1) Application for registration. 2) Document review. 3) Preassessment 4) Assessment 5) Registration 6) Follow-up surveillance 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 37
 CLOSING COMMENTS • The standards are written for contractual compliance to the standard. • Before entering into a contract for registration, management must be able to justify the cost versus the potential gains in continued or increased business. 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 38
CLOSING COMMENTS • The standards are written for contractual compliance to the standard. • Before entering into a contract for registration, management must be able to justify the cost versus the potential gains in continued or increased business. 3/18/2018 SWAMYNATHAN. S. M/TQM/UNIT 5/ELEMENTS, IMPLE, DOC. : QMS 38


