c846ba275393946d4f2e7e6e51b6470e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 46

QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM ISO 9001: 2000 SHIP BUILDING AND SHIP REPAIR INDUSTRY 16. 03. 2018 1
QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM * What is Quality, Quality Management System * Product Certification/ System Certification * What other standards are available, Who made these standards? * Main Changes from 1994 to 2000 Standards * Transition Steps * Appreciation of some clauses as applied to Shipbuilding and Ship repair Industry 16. 03. 2018 2
QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM Quality ( ISO 9000 ) Degree to which a set of inherent characteristics fulfils requirements 16. 03. 2018 3

QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM MAJOR QUALITY PROBLEMS (RESULTS SURVEY OF ENGINEERING INDUSTRIES IN BRITAIN IN 1970) * Human Error………………. . 12% * Bad Inspection Method…………………. 10% * Lack of and/or wrong specification……. 16% * Lack of Proving (new design, materials, manufacturing processes) ………………. 36% * Poor Planning………………. 14% * Unforeseeable & other…………………. . 12% 16. 03. 2018 4

QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM Quality Management System ( ISO 9000 ) Coordinated activities to direct and control an organization with regard to quality 16. 03. 2018 5

QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM * Product Certification Vs Management System Certification * - Management System Certification Schemes Quality Management ( ISO 9000/AS 9000/QS 9000/Tick. IT etc) Environmental Management ( Greenhouse Gas Services/ ISO 14000: 1996 etc ) Safety Management ( OHSMS/SSC or VCA ) Food Safety ( HACCP/GHP/GMP/BRC) Information Security Management ( BS 7799 ) Social Accountability ( SA 8000 ) Integrated Management Systems 16. 03. 2018 6

QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM What is this ISO…… ? * ISO is an International Standards Organization having office at Geneva, Switzerland * ISO (The International Organisation for Standardisation is a World- wide Federation of National Standard Bodies (ISO -Member Bodies e. g. IS BIS) 16. 03. 2018 7

QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM Who Makes Standards? * International Standards are Prepared through ISO Technical Committees * Each Member Body interested in a Subject for which a Technical Committee is established has the Right to be Represented on that Committee * International Organisations, Government and Non-Governmental, in liaison with ISO, also Take Part in Work 16. 03. 2018 8

QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM How Standards are made……? * Draft International Standards adopted by the Technical committee are circulated to the member bodies for comments/approval before their acceptance as International Standards by the ISO council. * They are approved in accordance with ISO procedures requiring at least 75% approval by the member bodies voting * ISO 9000 series International standards is the responsibility of ISO Technical Committee 176, Quality Management & Quality Assurance. * ISO/TC 176 adopted in 1990 a strategy for revision of the ISO 9000 series originally published in 1987. The present standard was released in 1994 which is again revised/released now in Dec’ 2000 16. 03. 2018 9
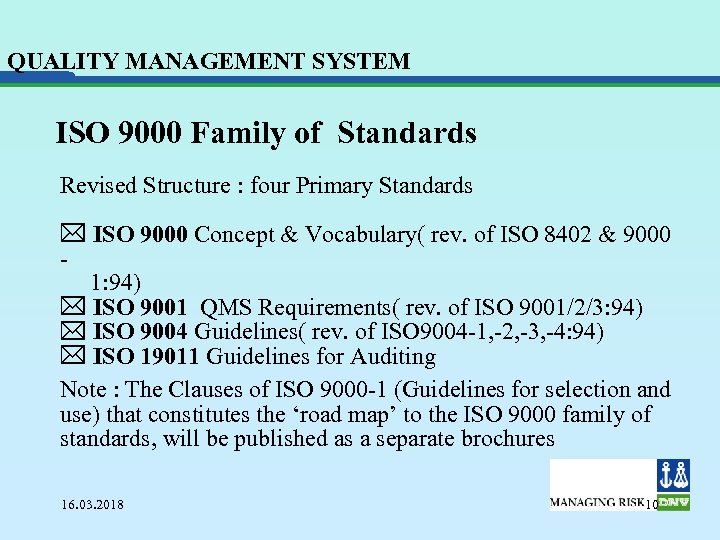
QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM ISO 9000 Family of Standards Revised Structure : four Primary Standards * ISO 9000 Concept & Vocabulary( rev. of ISO 8402 & 9000 1: 94) * ISO 9001 QMS Requirements( rev. of ISO 9001/2/3: 94) * ISO 9004 Guidelines( rev. of ISO 9004 -1, -2, -3, -4: 94) * ISO 19011 Guidelines for Auditing Note : The Clauses of ISO 9000 -1 (Guidelines for selection and use) that constitutes the ‘road map’ to the ISO 9000 family of standards, will be published as a separate brochures 16. 03. 2018 10

QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM ADVANTAGES OF QMS * A systematic, methodical approach in way business is done * A tool for consistent delivery * Continuous improvement in quality * System dependent regime instead of person dependent * Efficiency in sub-processes * Positive impact on customer satisfaction 16. 03. 2018 11
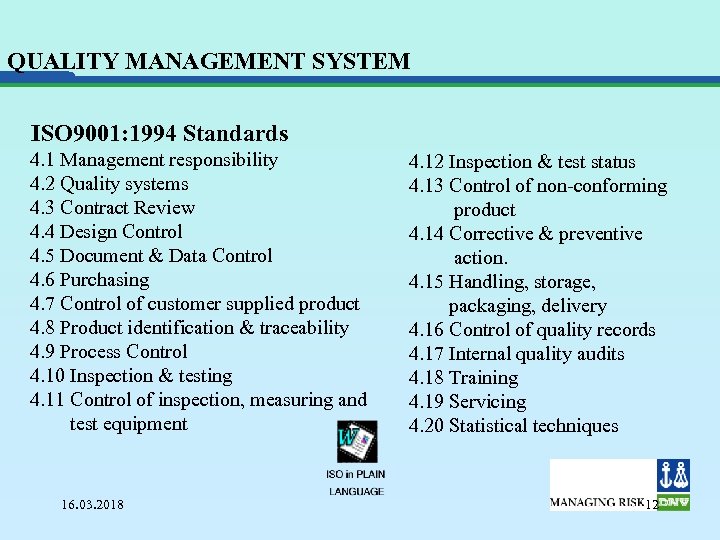
QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM ISO 9001: 1994 Standards 4. 1 Management responsibility 4. 2 Quality systems 4. 3 Contract Review 4. 4 Design Control 4. 5 Document & Data Control 4. 6 Purchasing 4. 7 Control of customer supplied product 4. 8 Product identification & traceability 4. 9 Process Control 4. 10 Inspection & testing 4. 11 Control of inspection, measuring and test equipment 16. 03. 2018 4. 12 Inspection & test status 4. 13 Control of non-conforming product 4. 14 Corrective & preventive action. 4. 15 Handling, storage, packaging, delivery 4. 16 Control of quality records 4. 17 Internal quality audits 4. 18 Training 4. 19 Servicing 4. 20 Statistical techniques 12

QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM ISO 9001: 2000 Standards 4 Quality Management System ( Documentation/Manual/Records ) 5 Management Responsibility ( Commitment/ Customer Focus/ Quality Policy/ Objectives/ Planning/Responsibility/MR/ Internal Communication/ Reviews ) 6 Resource Management ( Human Resources/Infrastructure ) 7 Product Realization ( Planning/Customer requirements & review/ Communication/Design & Development/Purchasing/Production and Service Provision ie Validation of Processes/ Identification & Traceability/ Care of Customer Property and Preservation/ Control of Monitoring & Measuring Devices ) 16. 03. 2018 13

QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM ISO 9001: 2000 8 Measurement, Analysis and Improvement ( Customer Satisfaction/Internal Audit/ M&M of Processes and Product/ Control of Non - confirming product/ Analysis/ Continual Improvement/ Corrective & Preventive Actions ) 16. 03. 2018 14
QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM Changes from ISO 9001: 1994 to ISO 9001: 2000 * Another Creation of Trade Barrier ? * Consultants and Certification Bodies Continue to Make Money ? * To Confuse the Organisation Using the Standards ? * Additional Investments with No Returns ? 16. 03. 2018 15

QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM ISO 9001: 2000 Need of Changes ? “ NOTHING IS CONSTANT IN THE WORLD EXCEPT CHANGES. ” ISO Rules require the review of all standards every 5 year, to ensure that they reflect the best practices, and take into account the lessons learnt OUTCOME Standards confirmed, revised or withdrawn ? In 1990, TC 176 adopted a two-phase revision process : First Phase completed in 1994 : Minor Changes pertaining to Tidying up, clarified ambiguity and better use of English Second Phase undergone now : Has significant number of changes both in style and content 16. 03. 2018 16

QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM ISO 9001: 2000 Need of Changes ? In 1997, TC 176 undertook a global survey of ISO 9000 users and the need of significant changes was felt as a result of analysis of responses : Revised standards should have increased compatibility with ISO 14000 Revised standard should have a common structure based on a process model Provision should be made for tailoring the requirements to omit elements not applicable Requirements should include demonstration of continuous improvement and prevention of non conformity ISO 9001 should address effectiveness while ISO 9004 should address efficiency and effectiveness ISO 9004 should help achieve benefits for all interested parties, e. g. Customers, Owners, Employees, Suppliers & Society Revised standard should be simple to use, easy to understand use clear language and terminology Revised standards should facilitate self - evaluation Manufacturing orientation of current standards be removed 16. 03. 2018 17
QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM ISO 9001: 2000 Need of Changes ? In 1997, TC 176 issued a document entitled “Quality Management Principles and Guidelines on their Application” ( ref. ISO/TC 176/SC 2/N 130 ) This document formed one of the other design inputs to the ISO Working Group responsible for the development of a consistent pair of standards i. e. ISO 9001: 2000 and ISO 9004: 2000 A Quality Management Principle(QMP) is defined as: “ a comprehensive and fundamental rule or belief, for leading and operating an organisation, aimed at continually improving performance over the long term by focusing on customers while addressing the needs of all other stakeholders” 16. 03. 2018 18

QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM ISO 9001: 2000 What are Changes ? • Change in Management System Philosophy itself • Changes reflect an approach which is more complete and consider management principles that go towards Total Management Main Changes * Customer Focus * Use of Demming’s ( Process Approach ) PLAN- DO-CHECK-ACT Cycle 16. 03. 2018 Check 19
QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM ISO 9001: 2000 Summary of Changes : • Continual Improvement of the System is Mandatory • Approach is based on “Input”, “process” and “Out Put” • Competency of Personnel requirement made more elaborate • Quality Objectives - SMART ( specific, measurable, achievable, result oriented and time bound ) • QM to define the SCOPE of certification • Product requirements to include specified & intended use • Proactive customer satisfaction measures • Requirements for Effective Communication defined • Internal Audits to confirm compliance to ISO 9001 • More complete as a Management System Specification 16. 03. 2018 20
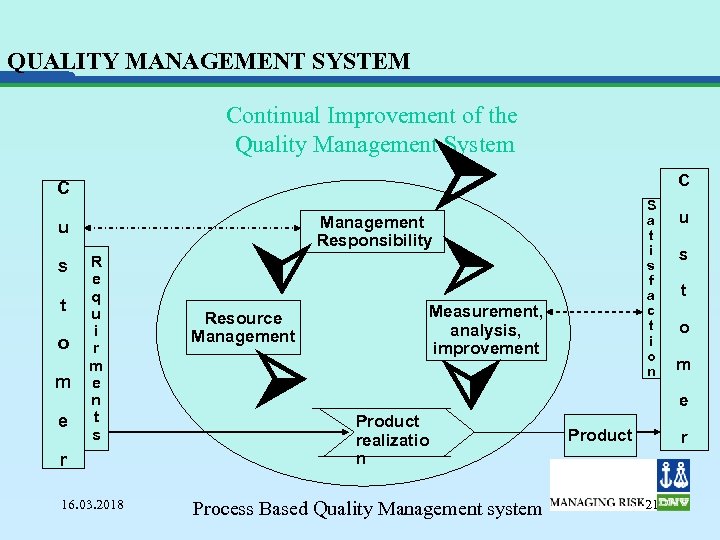
QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM C o m e R e q u i r m e n t s r 16. 03. 2018 t C S a t i s f a c t i o n Management Responsibility u s Continual Improvement of the Quality Management System Measurement, analysis, improvement Resource Management Product realizatio n Process Based Quality Management system u s t o m e Product r 21
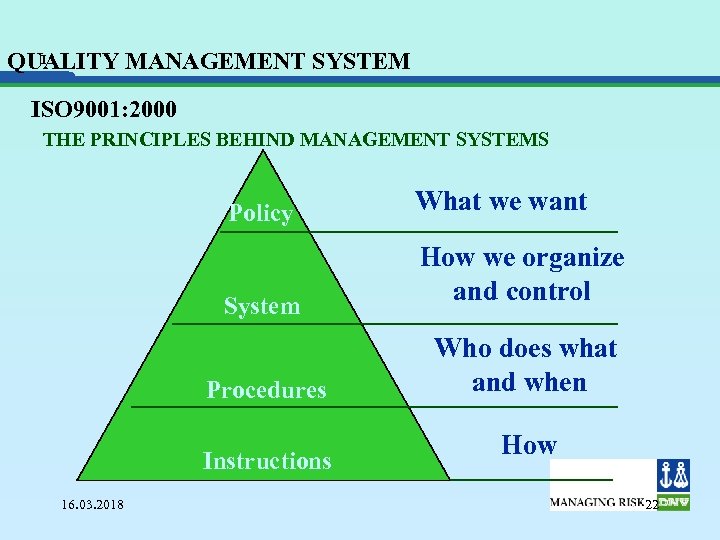
I QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM ISO 9001: 2000 THE PRINCIPLES BEHIND MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS Policy System Procedures Instructions 16. 03. 2018 What we want How we organize and control Who does what and when How 22
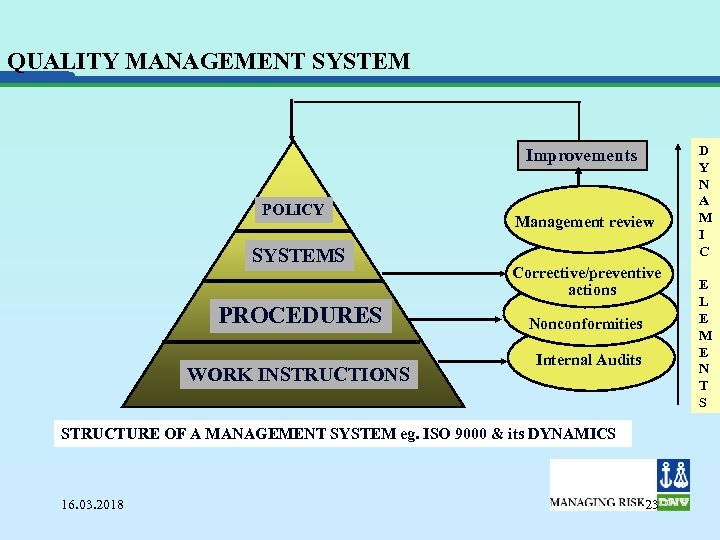
QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM Improvements POLICY SYSTEMS PROCEDURES WORK INSTRUCTIONS Management review Corrective/preventive actions Nonconformities Internal Audits STRUCTURE OF A MANAGEMENT SYSTEM eg. ISO 9000 & its DYNAMICS 16. 03. 2018 23 D Y N A M I C E L E M E N T S

QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM ISO 9001: 2000 Basic principles in system development • Utilise existing documentation and routines • Limit the System to what is vital • Limit the documentation ( Documented Procedure needed for SIX activities only : Control of Documents, Control of Records, Internal Audits, Control of Non conforming Products, Corrective Actions and Preventive Actions ) • Organise the System to get ADEQUATE control • Avoid overlapping systems/instructions/routines 16. 03. 2018 24

QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM ISO 9001: 2000 Conditions for success • • • Management commitment Information and training Motivation and involvement of employees Project organisation and management A detailed and strict project plan 16. 03. 2018 25

QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM ISO 9001: 2000 Steps in writing procedures • Describe the main steps in a flow diagram • • • Analyse the need for more details Add necessary details Make references Benefits: þ Employees can start to contribute at any given time þ No QA knowledge and experience are needed þ Easy control with format and style 16. 03. 2018 26
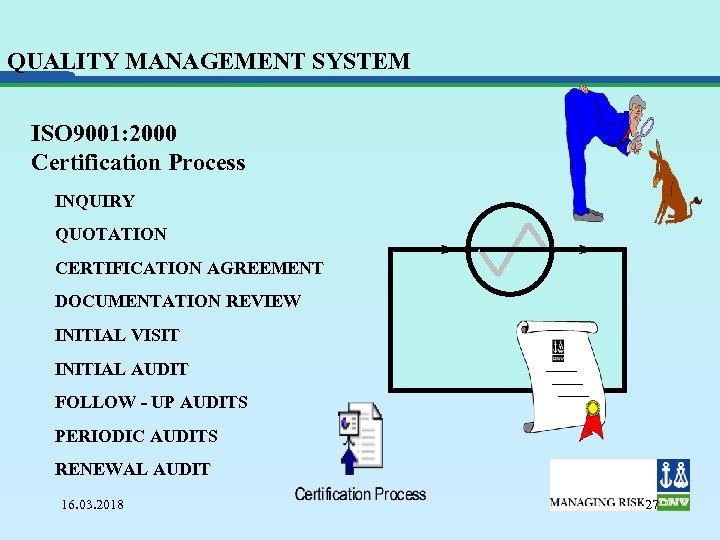
QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM ISO 9001: 2000 Certification Process INQUIRY QUOTATION CERTIFICATION AGREEMENT DOCUMENTATION REVIEW INITIAL VISIT INITIAL AUDIT FOLLOW - UP AUDITS PERIODIC AUDITS RENEWAL AUDIT 16. 03. 2018 27
QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM ISO 9001: 2000 IMPLEMENTATION/ TRANSITION 16. 03. 2018 28
QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM ISO 9001: 2000 AUDIT ( a systematic and independent verification ) Why quality audits? • health of unit • compliance to a standard • to determine effectiveness of system • identify and prioritize area of improvement What auditor looks for? • Existence of system • operation of system • effectiveness 16. 03. 2018 29

QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM ISO 9001: 2000 SHIPBUILDING and SHIP REPAIR Industry ( Where these slides do not refer to ISO elements, the standard interpretation is applicable ) Process Description • Hull Processes Pre - treatment/ Marking and Cutting/ Bending( cold or hot )/ Block Assembly/ Pre erection and Erection • Outfitting Production/ Installation Process Covers all outfitting to be installed on hull e. g. Piping, fittings, equipment and Cable etc - Manufacturing ( marking, cutting, bending, fit up, welding and painting and galvanizing) - Installation ( fit up and welding, bolting and bushing ) • Painting Process Cleaning, pre treatment ( blasting and shop priming ) and coating • Repair and/or Reconditioning of machinery 16. 03. 2018 30

QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM ISO 9001: 2000 SHIPBUILDING and SHIP REPAIR Industry 4. 2. 3 Control of Documents * Drawing control is the key area of document control * Other documents e. g. WPS, Quality Plans, Inspection Procedures including NDT, Calibration and Qualification records * External documents to be checked are : • class rules, legislations, regulations • industrial standards/ codes e. g. AWS, ASME 16. 03. 2018 31

QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM ISO 9001: 2000 SHIPBUILDING and SHIP REPAIR Industry 5. 4. 2 Quality Planning should focus on identifying processes needed to meet effectively and efficiently the organizations quality objectives and requirements Input : Strategies, Objectives, Need & Expectations, statutory & regulatory requirements, evaluation of performance data, lessons learnt from previous experiences, related risk assessments etc Output: Need for skill, resources, responsibilities, improvement in process/tools, records etc A quality plan is normally prepared for a new ship or a series of ships ( ships with same design ), coverage of the plan may vary depending upon experience In case of repair units, a quality plan is to be made for each product and/ or process QUALITY PLAN may be in the form of ITP, traveller’s card , control 16. 03. 2018 plan etc 32

QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM ISO 9001: 2000 SHIPBUILDING and SHIP REPAIR Industry 6. 2. 2 Competence, Awareness and Training For each position job description and qualification to be defined. Welding, heat treatment, NDT and painting are special processes which normally require specific qualification of personnel 7. 2. 1 Identification of Customer Requirements Specified : Ship Building: Contract Documents normally include commercial terms, contract specifications and the basic drawings Ship Repairs : is carried out as per Class rules and/or suppliers’ standards based on the industrial standards Not specified: Supplies to EC countries, special requirements for particular flag vessel. 16. 03. 2018 33

QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM ISO 9001: 2000 SHIPBUILDING and SHIP REPAIR Industry 7. 2. 1 Identification of Customer Requirements The process shall consider: • extent to which customers have specified requirements • requirements not specified by the customer • product and/or service obligations, including regulatory and legal requirements ( e. g. API, ASME, ASTM, IBR, CE etc) • requirements for availability, delivery and support The object of this process is to develop a clear picture of what are the customer needs and expectations, both in terms of the product/ service itself and its delivery. 16. 03. 2018 34

QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM ISO 9001: 2000 SHIPBUILDING and SHIP REPAIR Industry 7. 3 Design and/or Development • Ship design function are hull, hull outfitting, machinery, electrical etc • Design stages can be grouped as basic design, detailed design and production design. They can be conducted by separate or in the same organization ( depending upon the size of shipyard ) • Design input shall consider class rules, customer requirements and statutory and/or regulatory requirements • Design verification includes design reviews, ship’s model test, drawing review against design input checklist etc • Design validation normally includes inclined test and sea trial Verification: Confirmation by examination and provision of objective evidence that specified requirements have been fulfilled Validation: 16. 03. 2018 by examination and provision of objective evidence that the particular requirements Confirmation for a specific intended usage are fulfilled 35

QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM ISO 9001: 2000 SHIPBUILDING and SHIP REPAIR Industry 7. 4. 1 Purchasing Control • Check if supplier evaluation includes the suppliers capability to get the supplied product certified by the Class (e. g. , DNV), when required ( steel plates, welding fillers, machinery & spares etc ) • Purchasing documents should be checked at both design & purchasing functions. • Purchasing documents shall include requirements of product certification by the class, and verification requirements of shipyard and/or ship owner's inspectors at source. 16. 03. 2018 36

QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM ISO 9001: 2000 SHIPBUILDING and SHIP REPAIR Industry 7. 4. 3 Verification of Purchased Product • Receiving inspection shall include that all applicable class certificates and/or manufacturer’s certificates have been received. (When not received with the product, positive recall procedure shall apply. 16. 03. 2018 37

QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM ISO 9001: 2000 SHIPBUILDING and SHIP REPAIR Industry 7. 5. 1 Operations Control • In the process of block assembly, pre-erection and erection, fit-up and welding processes are most important. • Monitoring and control should include following process. Material Identification, Dimensions for hull and piping, during marking, cutting, bending and assembly (fit-up and welding) process. Welding being a special process need following controls: • Procedure should comply with the reference standards/codes e. g. AWS codes, ASME codes, Class rules etc. • Qualification test results should be recorded in PQR Contd…. . 16. 03. 2018 38

QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM ISO 9001: 2000 SHIPBUILDING and SHIP REPAIR Industry 7. 5. 1 Operations Control • Procedure may be documented in WPS and shall normally include specifications of welding materials, welding equipment, welding parameters ( voltage, current, speed ) , welding environment ( temp, wind speed, pre heat ) and criteria for workmanship ( e. g. groove angle, root gap etc ) • Externally qualified WPS may also be used, such as customer supplied WPS, manufacturer’s WPS or WPS in the reference standard/ code. • Monitoring and/or operating criteria ( this is a special process ) - monitoring as per quality plan and WPS. Shall cover welding consumable, welding parameters and environment and criteria for workmanship • Qualification requirements for welders shall be specified and maintained as quality records 16. 03. 2018 39

QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM ISO 9001: 2000 SHIPBUILDING and SHIP REPAIR Industry 7. 5. 2 Identification & Traceability Identification and/or traceability of the structural plates and shapes, and of pipes are critical, during the process of marking, cutting and assembly. • Identification of machinery and components are important, during storage and installation onboard. • Check if inspection (including NDT) status is identified when hull blocks and pipe spools are painted, erected and/or installed. 16. 03. 2018 40

QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM ISO 9001: 2000 SHIPBUILDING and SHIP REPAIR Industry 7. 5. 3 Customer Property It is normal that ship owners are supplying some equipment to be installed onboard • Inventories are partly supplied by the ship owners 16. 03. 2018 41

QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM ISO 9001: 2000 SHIPBUILDING and SHIP REPAIR Industry 7. 5. 4 Preservation of Product Storage conditions should be suitable to prevent rust, pitting, etc and prevent grits and dirt's contaminating the inside of piping. 16. 03. 2018 42

QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM ISO 9001: 2000 SHIPBUILDING and SHIP REPAIR Industry 7. 6 Control of Measuring & Monitoring Devices Equipment to be calibrated included welding equipment (except SMAW ( shielded metal arc welding ) equipment), temperature gauges of drying ovens for welding consumables, temperature gauges and recorders of heat treatment equipment. • Equipment used for hull inspection, painting inspection, outfitting inspection including inclining test, deadweight measurement and sea trial also requires to be calibrated and cover Non destructive, mechanical and chemical testing. 16. 03. 2018 43

QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM ISO 9001: 2000 SHIPBUILDING and SHIP REPAIR Industry 8. 2. 3 Measurement and Monitoring of Process • Welding, heat treatment (sometimes following welding) and painting are special process. -They normally require qualification of process and personnel. • Process monitoring is also required specifically for these activities. 16. 03. 2018 44

QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM ISO 9001: 2000 SHIPBUILDING and SHIP REPAIR Industry 8. 2. 4 Measurement and Monitoring of Product • Inspection and test plans are prepared for each (series of) ship(s). The plans shall cover hull inspection, painting inspection, outfitting inspection (including inclining test, deadweight measurement and sea trial) and NDT (non-destructive testing). • NDT activities should adhere to class rule requirements. • At the final stage inspections shall include inclining test, deadweight measurement and sea trial. 16. 03. 2018 45

QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM HAPPY ISO 9000 16. 03. 2018 46
c846ba275393946d4f2e7e6e51b6470e.ppt