d6f230828528899d1715954ba0457ca9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29
 Quality Management Strategy at the KF University of Graz How change management affects all spheres of a university Mag. a Andrea Bernhard KF University of Graz Institute of Educational Sciences
Quality Management Strategy at the KF University of Graz How change management affects all spheres of a university Mag. a Andrea Bernhard KF University of Graz Institute of Educational Sciences
 Outline Background Information on HE 2. EU experiences in developing university strategies 1. QM Systems in General 3. QM at the KF University of Graz basic idea… implementation… future plans… 2
Outline Background Information on HE 2. EU experiences in developing university strategies 1. QM Systems in General 3. QM at the KF University of Graz basic idea… implementation… future plans… 2
 EU experiences in developing university strategies Starting point „Quality in a product or service is not what the supplier puts in. It is what the customer gets out and is willing to pay for… Customers pay only for what is of use to them and gives them value. Nothing else constitutes quality. “ (Drucker 1986, p. 228) 3
EU experiences in developing university strategies Starting point „Quality in a product or service is not what the supplier puts in. It is what the customer gets out and is willing to pay for… Customers pay only for what is of use to them and gives them value. Nothing else constitutes quality. “ (Drucker 1986, p. 228) 3
 1. Background Information on HE EU experiences in developing university strategies p Loss of monopoly of universities p Autonomy of universities p Marketisation of higher education p Globalisation – internationalisation p planning – controlling – improving Quality Management (QM) 4
1. Background Information on HE EU experiences in developing university strategies p Loss of monopoly of universities p Autonomy of universities p Marketisation of higher education p Globalisation – internationalisation p planning – controlling – improving Quality Management (QM) 4
 2. QM Systems in General Legal requirements p EU experiences in developing university strategies p Quality in research and teaching as well as management & administration p 4 principles for QA systems 1. 2. 3. 4. a coordinating agency for the QA scheme submission of a self-evaluation report by the unit to be evaluated site visit by peers (partly) public report on the evaluation results 5
2. QM Systems in General Legal requirements p EU experiences in developing university strategies p Quality in research and teaching as well as management & administration p 4 principles for QA systems 1. 2. 3. 4. a coordinating agency for the QA scheme submission of a self-evaluation report by the unit to be evaluated site visit by peers (partly) public report on the evaluation results 5
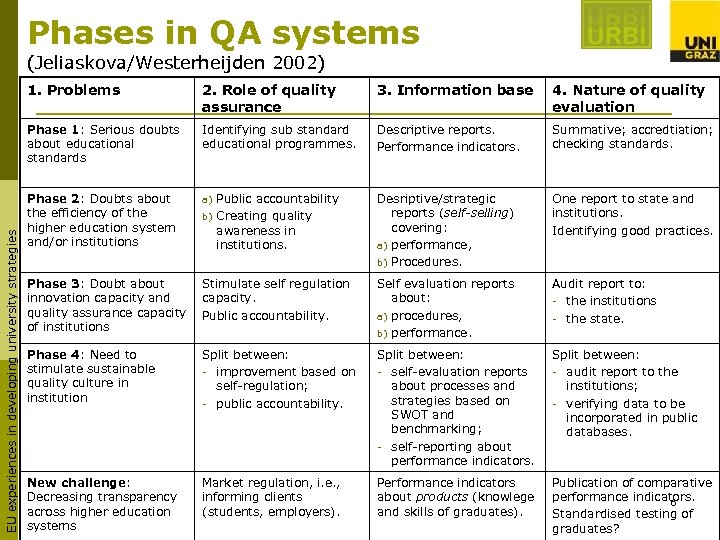 Phases in QA systems (Jeliaskova/Westerheijden 2002) 2. Role of quality assurance 3. Information base 4. Nature of quality evaluation Phase 1: Serious doubts about educational standards EU experiences in developing university strategies 1. Problems Identifying sub standard educational programmes. Descriptive reports. Performance indicators. Summative; accredtiation; checking standards. Phase 2: Doubts about the efficiency of the higher education system and/or institutions a) Public accountability Creating quality awareness in institutions. Desriptive/strategic reports (self-selling) covering: a) performance, b) Procedures. One report to state and institutions. Identifying good practices. Phase 3: Doubt about innovation capacity and quality assurance capacity of institutions Stimulate self regulation capacity. Public accountability. Self evaluation reports about: a) procedures, b) performance. Audit report to: - the institutions - the state. Phase 4: Need to stimulate sustainable quality culture in institution Split between: - improvement based on self-regulation; - public accountability. Split between: - self-evaluation reports about processes and strategies based on SWOT and benchmarking; - self-reporting about performance indicators. Split between: - audit report to the institutions; - verifying data to be incorporated in public databases. New challenge: Decreasing transparency across higher education systems Market regulation, i. e. , informing clients (students, employers). Performance indicators about products (knowlege and skills of graduates). Publication of comparative performance indicators. 6 Standardised testing of graduates? b)
Phases in QA systems (Jeliaskova/Westerheijden 2002) 2. Role of quality assurance 3. Information base 4. Nature of quality evaluation Phase 1: Serious doubts about educational standards EU experiences in developing university strategies 1. Problems Identifying sub standard educational programmes. Descriptive reports. Performance indicators. Summative; accredtiation; checking standards. Phase 2: Doubts about the efficiency of the higher education system and/or institutions a) Public accountability Creating quality awareness in institutions. Desriptive/strategic reports (self-selling) covering: a) performance, b) Procedures. One report to state and institutions. Identifying good practices. Phase 3: Doubt about innovation capacity and quality assurance capacity of institutions Stimulate self regulation capacity. Public accountability. Self evaluation reports about: a) procedures, b) performance. Audit report to: - the institutions - the state. Phase 4: Need to stimulate sustainable quality culture in institution Split between: - improvement based on self-regulation; - public accountability. Split between: - self-evaluation reports about processes and strategies based on SWOT and benchmarking; - self-reporting about performance indicators. Split between: - audit report to the institutions; - verifying data to be incorporated in public databases. New challenge: Decreasing transparency across higher education systems Market regulation, i. e. , informing clients (students, employers). Performance indicators about products (knowlege and skills of graduates). Publication of comparative performance indicators. 6 Standardised testing of graduates? b)
 New Challenge EU experiences in developing university strategies Decreasing transparency across higher education systems p Role of QA n p Information base n p Market regulation, i. e. , informing clients (students, employers) Performance indicators about products (knowlege and skills of graduates) Nature of quality evaluation n n publication of comparative performance indicators standardised testing of graduates? 7
New Challenge EU experiences in developing university strategies Decreasing transparency across higher education systems p Role of QA n p Information base n p Market regulation, i. e. , informing clients (students, employers) Performance indicators about products (knowlege and skills of graduates) Nature of quality evaluation n n publication of comparative performance indicators standardised testing of graduates? 7
 QM Systems under Transformation! Challenges p EU experiences in developing university strategies p p bureaucracy intrusion in the primary activities of a HEI control vs. improvement (Middlehurst 2001, Mead/Woodhouse 2000) Recommendations p p avoid fragmentation of the QA organisational structure avoid excessive costs and burdens improve quality information base improve information dissemination (Santiago et al. 2008) 8
QM Systems under Transformation! Challenges p EU experiences in developing university strategies p p bureaucracy intrusion in the primary activities of a HEI control vs. improvement (Middlehurst 2001, Mead/Woodhouse 2000) Recommendations p p avoid fragmentation of the QA organisational structure avoid excessive costs and burdens improve quality information base improve information dissemination (Santiago et al. 2008) 8
 Important questions, that have to be raised… (Newton 2007) can quality be managed effectively? p EU experiences in developing university strategies p does accountability provide a basis for delivering quality improvement? p can accountability and enhancement be reconciled? p can external and internal requirements be balanced? p how were academics receiving, responding to, and coping with quality and quality policy? The University of Graz tries to find suitable answers! 9
Important questions, that have to be raised… (Newton 2007) can quality be managed effectively? p EU experiences in developing university strategies p does accountability provide a basis for delivering quality improvement? p can accountability and enhancement be reconciled? p can external and internal requirements be balanced? p how were academics receiving, responding to, and coping with quality and quality policy? The University of Graz tries to find suitable answers! 9
 3. QM System of the KF University of Graz The Austrian Experience 1. Legal Framework 2. QM Model itself 3. Barriers and Problems during Implementation 4. Lessons Learned 5. Success in the Implementation Phase 6. Future Plans
3. QM System of the KF University of Graz The Austrian Experience 1. Legal Framework 2. QM Model itself 3. Barriers and Problems during Implementation 4. Lessons Learned 5. Success in the Implementation Phase 6. Future Plans
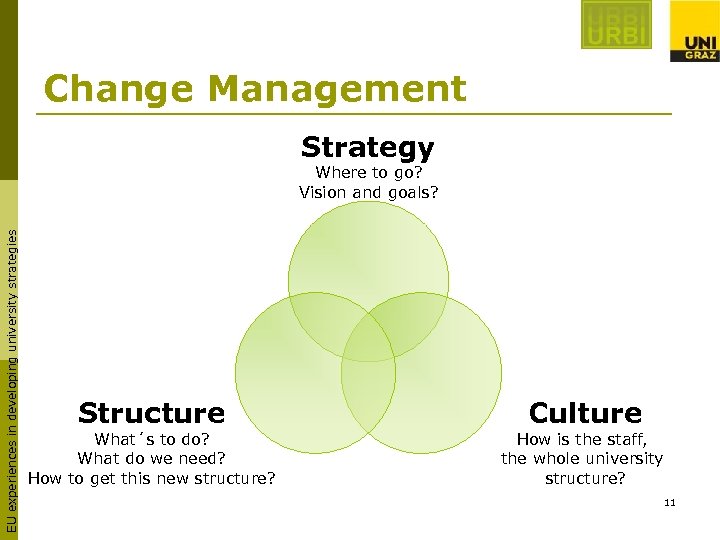 Change Management Strategy EU experiences in developing university strategies Where to go? Vision and goals? Structure What´s to do? What do we need? How to get this new structure? Culture How is the staff, the whole university structure? 11
Change Management Strategy EU experiences in developing university strategies Where to go? Vision and goals? Structure What´s to do? What do we need? How to get this new structure? Culture How is the staff, the whole university structure? 11
 1. Legal Framework p UOG 1993 n first systematic and comprehensive programme evaluation 1993 non-university sector p 1999 private higher education sector p n p ex-ante accreditation UG 2002 n n high degree of autonomy for universities public universities have to adopt QM (§ 14) no explicit regulation for compulsory external QA 12
1. Legal Framework p UOG 1993 n first systematic and comprehensive programme evaluation 1993 non-university sector p 1999 private higher education sector p n p ex-ante accreditation UG 2002 n n high degree of autonomy for universities public universities have to adopt QM (§ 14) no explicit regulation for compulsory external QA 12
 AQA – Austrian Agency for QA www. aqa. ac. at p founded in 2003 p as an independent non-governmental organisation p Scope of authority n n n assists and monitors HEIs to implement QA procedures coordinates evaluations elaborates QA standards 13
AQA – Austrian Agency for QA www. aqa. ac. at p founded in 2003 p as an independent non-governmental organisation p Scope of authority n n n assists and monitors HEIs to implement QA procedures coordinates evaluations elaborates QA standards 13
 2. QM System at the KF University of Graz p QM = various implemented instruments p QM system = closed circle that is tightly linked to university steering p Elements of the QM system n n n Strategic, goal-oriented steering instrument Integrated in all performance areas Communication and transparency Low and purpose-oriented ressources Feedback and learning-oriented (Raggautz 2009) 14
2. QM System at the KF University of Graz p QM = various implemented instruments p QM system = closed circle that is tightly linked to university steering p Elements of the QM system n n n Strategic, goal-oriented steering instrument Integrated in all performance areas Communication and transparency Low and purpose-oriented ressources Feedback and learning-oriented (Raggautz 2009) 14
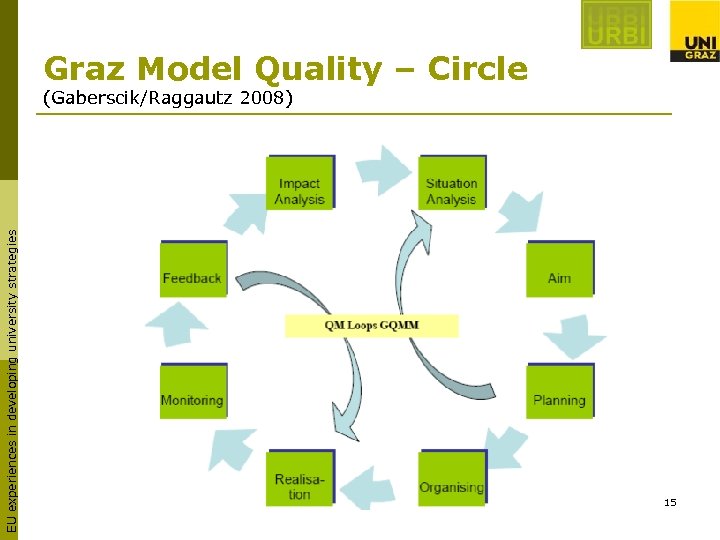 Graz Model Quality – Circle EU experiences in developing university strategies (Gaberscik/Raggautz 2008) 15
Graz Model Quality – Circle EU experiences in developing university strategies (Gaberscik/Raggautz 2008) 15
 Department for Performance and Quality Management (LQM) www. uni-graz. at/lqm p EU experiences in developing university strategies p Under the Rectorate p Responsible for n n n p Performance agreements (ZLV) Quality management (QM) Knowledge survey (WB) Main targets: n n n Strategic steering QM Reporting system Data Analysis: strategic and in-depth 16
Department for Performance and Quality Management (LQM) www. uni-graz. at/lqm p EU experiences in developing university strategies p Under the Rectorate p Responsible for n n n p Performance agreements (ZLV) Quality management (QM) Knowledge survey (WB) Main targets: n n n Strategic steering QM Reporting system Data Analysis: strategic and in-depth 16
 Graz QM Model EU experiences in developing university strategies „theoretical basis“ (Gaberscik/Raggautz 2008) 17
Graz QM Model EU experiences in developing university strategies „theoretical basis“ (Gaberscik/Raggautz 2008) 17
 Map of QM Processes http: //www. uni-graz. at/prozesslandkarte Performance Agreements Quality Management Processes Etc. Teaching Performance Processes Research Further Education Infrastructure Management Monitoring Information Management Financial Planning Personnel Management EU experiences in developing university strategies Strategy Assisting Processes 18 Work in progress…
Map of QM Processes http: //www. uni-graz. at/prozesslandkarte Performance Agreements Quality Management Processes Etc. Teaching Performance Processes Research Further Education Infrastructure Management Monitoring Information Management Financial Planning Personnel Management EU experiences in developing university strategies Strategy Assisting Processes 18 Work in progress…
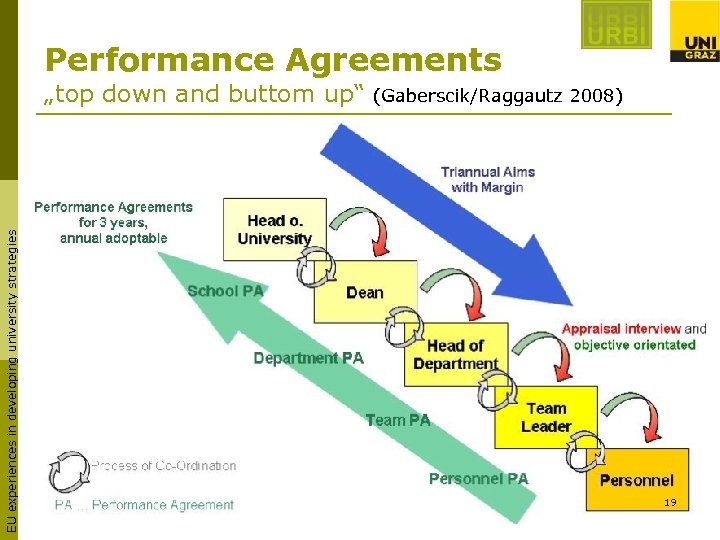 Performance Agreements EU experiences in developing university strategies „top down and buttom up“ (Gaberscik/Raggautz 2008) 19
Performance Agreements EU experiences in developing university strategies „top down and buttom up“ (Gaberscik/Raggautz 2008) 19
 Tool Box of Graz QM Model EU experiences in developing university strategies (Gaberscik/Raggautz 2008) 20
Tool Box of Graz QM Model EU experiences in developing university strategies (Gaberscik/Raggautz 2008) 20
 Selected Instruments with External Experts p Evaluation of research p Appointment procedures p New curricula p Process accreditation for study and teaching (ACQUIN) p Strategic analysis labour market p Internationalisation (AQA audit) (Raggautz 2009) 21
Selected Instruments with External Experts p Evaluation of research p Appointment procedures p New curricula p Process accreditation for study and teaching (ACQUIN) p Strategic analysis labour market p Internationalisation (AQA audit) (Raggautz 2009) 21
 Student Involvement Designing new curricula p Student information service „ 4 students“ p Basic module p Quality assurance and involvement p n n Course evaluation Evaluation of students’ workload Accreditation of processes Several strategic analysis Working experience p General involvement p (Salmhofer 2008) 22
Student Involvement Designing new curricula p Student information service „ 4 students“ p Basic module p Quality assurance and involvement p n n Course evaluation Evaluation of students’ workload Accreditation of processes Several strategic analysis Working experience p General involvement p (Salmhofer 2008) 22
 Involvement of other Stakeholders p No explicit stakeholder management until recently p Rather unstructured, ad hoc and based on short-term considerations p Main challenge identify all relevant target groups & establish stakeholder management n n n Prospective students Alumni Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) (Salmhofer 2008) 23
Involvement of other Stakeholders p No explicit stakeholder management until recently p Rather unstructured, ad hoc and based on short-term considerations p Main challenge identify all relevant target groups & establish stakeholder management n n n Prospective students Alumni Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) (Salmhofer 2008) 23
 3. Barriers and Problems during Implementation inertia against change p EU experiences in developing university strategies p brownfields p Academic freedom n n Academic staff ≠ managers or employers with responsibilities for achieving aims or leading staff I can´t tell a professor what s/he should do in his/her research p Misunderstanding of QM p Unique constitution of universities (Gaberscik/Raggautz 2008) 24
3. Barriers and Problems during Implementation inertia against change p EU experiences in developing university strategies p brownfields p Academic freedom n n Academic staff ≠ managers or employers with responsibilities for achieving aims or leading staff I can´t tell a professor what s/he should do in his/her research p Misunderstanding of QM p Unique constitution of universities (Gaberscik/Raggautz 2008) 24
 4. Lessons Learned EU experiences in developing university strategies p Formulate valid facts about staff performance! p Do not start with explicit aim to create the best system! p Consider the time frame for developing and implementing a QM model! p Do not use too many different QM tools! p Use an iterative approach to develop indicators! (Gaberscik/Raggautz 2008) 25
4. Lessons Learned EU experiences in developing university strategies p Formulate valid facts about staff performance! p Do not start with explicit aim to create the best system! p Consider the time frame for developing and implementing a QM model! p Do not use too many different QM tools! p Use an iterative approach to develop indicators! (Gaberscik/Raggautz 2008) 25
 5. Success in the Implementation Phase EU experiences in developing university strategies p Effective definition of a principle QM model as a base p Streamlining of all the QM tools already used in the university p Long and broad discussion process is needed p Has to be continued after implementation to fulfill the specific demands of ALL stakeholders Maintain regular communication and take action as soon as difficulties arise! 26
5. Success in the Implementation Phase EU experiences in developing university strategies p Effective definition of a principle QM model as a base p Streamlining of all the QM tools already used in the university p Long and broad discussion process is needed p Has to be continued after implementation to fulfill the specific demands of ALL stakeholders Maintain regular communication and take action as soon as difficulties arise! 26
 6. Future Plans Flexibility and Adaptibility p EU experiences in developing university strategies p Comparable, reliable & valid performance indicators p Changing legal regulation concerning QM p Quality system audits p Critical view on the whole QA sector n n development of only one QAA? coordination between different sectors QA at the public sector still lax university courses (further education) 27
6. Future Plans Flexibility and Adaptibility p EU experiences in developing university strategies p Comparable, reliable & valid performance indicators p Changing legal regulation concerning QM p Quality system audits p Critical view on the whole QA sector n n development of only one QAA? coordination between different sectors QA at the public sector still lax university courses (further education) 27
 EU experiences in developing university strategies Literature Drucker, P. F. (1986): Innovation and Entrepreneurship: Practice and Principles. New York: Harper Row. Gaberscik, G. /Raggautz, A. (2008): Graz Quality Management Model for Universities. Paper presented at the 3 rd Quality Assurance Forum in Budapest, 20 -22 November 2008. Jeliazkova, Margarita/Westerheijden, Don F. (2002): Systemic Adaption to a Changing Environment: Towards a Next Generation of Quality Assurance Models. In: Higher Education, Vol. 44, No. 3/4. pp. 433 -449. Meade, P. /Woodhouse, D. (2000): Evaluating the effectiveness of the New Zealand Academic Audit Unit: review and outcomes. In: Quality in Higher Education, Vol. 6, No. 1. pp. 19 -29. Middlehurst, R. (2001): Quality Assurance Implications of New Forms of Higher Education. Part 1: A Typology. Helsinki: ENQA. (ENQA Occasional Papers, Vol. 3) Newton, Jethro (2007): What is quality? In: Bollaert, Lucien et al. (Eds. ): Embedding Quality Culture in Higher Education. A Selection of Papers from the 1 st European Forum for Quality Assurance. Munich, 23 -25 November 2006. pp. 14 -20. Raggautz, A. (2009): Qualitätsmanagementsystem und externe Qualitätssicherung. In: AQA: Trends of Quality Assurance and Quality Management in Higher Education Systems. Vienna: Facultas. pp. 112 -116. Santiago et al. (2008): Tertiary Education for Knowledge Society. OECD Thematic Review of Tertiary Education: Synthesis Report. Vol. 2 -3. Salmhofer, G. (2008): Quality Assurance for Higher Education Change Area (QAHECA). Online in Internet: http: //www. eua. be/index. php? id=529 28 Van Vught, F. A. /Westerheijden, D. F. (1994): Towards a general model of quality assessment in higher education. In: Higher Education, Vol. 28, No. 3. pp. 355 -371.
EU experiences in developing university strategies Literature Drucker, P. F. (1986): Innovation and Entrepreneurship: Practice and Principles. New York: Harper Row. Gaberscik, G. /Raggautz, A. (2008): Graz Quality Management Model for Universities. Paper presented at the 3 rd Quality Assurance Forum in Budapest, 20 -22 November 2008. Jeliazkova, Margarita/Westerheijden, Don F. (2002): Systemic Adaption to a Changing Environment: Towards a Next Generation of Quality Assurance Models. In: Higher Education, Vol. 44, No. 3/4. pp. 433 -449. Meade, P. /Woodhouse, D. (2000): Evaluating the effectiveness of the New Zealand Academic Audit Unit: review and outcomes. In: Quality in Higher Education, Vol. 6, No. 1. pp. 19 -29. Middlehurst, R. (2001): Quality Assurance Implications of New Forms of Higher Education. Part 1: A Typology. Helsinki: ENQA. (ENQA Occasional Papers, Vol. 3) Newton, Jethro (2007): What is quality? In: Bollaert, Lucien et al. (Eds. ): Embedding Quality Culture in Higher Education. A Selection of Papers from the 1 st European Forum for Quality Assurance. Munich, 23 -25 November 2006. pp. 14 -20. Raggautz, A. (2009): Qualitätsmanagementsystem und externe Qualitätssicherung. In: AQA: Trends of Quality Assurance and Quality Management in Higher Education Systems. Vienna: Facultas. pp. 112 -116. Santiago et al. (2008): Tertiary Education for Knowledge Society. OECD Thematic Review of Tertiary Education: Synthesis Report. Vol. 2 -3. Salmhofer, G. (2008): Quality Assurance for Higher Education Change Area (QAHECA). Online in Internet: http: //www. eua. be/index. php? id=529 28 Van Vught, F. A. /Westerheijden, D. F. (1994): Towards a general model of quality assessment in higher education. In: Higher Education, Vol. 28, No. 3. pp. 355 -371.
 Thank you for your attention! andrea. bernhard@uni-graz. at The floor is open for discussion! What is required by universities? Which kind of agencies are needed? Beside agencies – further demands?
Thank you for your attention! andrea. bernhard@uni-graz. at The floor is open for discussion! What is required by universities? Which kind of agencies are needed? Beside agencies – further demands?


