07b456e48e895bdb7cd79d3c2730ff33.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 87
 Quality Management Prof. Ir. Moses Laksono Singgih, MSc, MReg. Sc, Ph. D, IPU Workshop di UMI Makassar, 11 -12 Mei 2016 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 1
Quality Management Prof. Ir. Moses Laksono Singgih, MSc, MReg. Sc, Ph. D, IPU Workshop di UMI Makassar, 11 -12 Mei 2016 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 1
 SEMANGAT PAGI 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 2
SEMANGAT PAGI 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 2
 QUALITY 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 3
QUALITY 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 3
 Apakah kualitas merupakan kriteria yang penting dalam membeli barang/jasa yang berkualitas? MENGAPA? Barang/jasa berkualitas adalah … 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 4
Apakah kualitas merupakan kriteria yang penting dalam membeli barang/jasa yang berkualitas? MENGAPA? Barang/jasa berkualitas adalah … 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 4
 What is Quality? 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 5
What is Quality? 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 5
 What does the word “quality” mean to you? n Think about your past experiences staying at various hotels. Did you stay at a “quality” hotel? What about the experience made it a “quality” experience for you? n Think about a product you bought. How can you define its “quality”? 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 6
What does the word “quality” mean to you? n Think about your past experiences staying at various hotels. Did you stay at a “quality” hotel? What about the experience made it a “quality” experience for you? n Think about a product you bought. How can you define its “quality”? 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 6
 Dimensions of Quality Garvin (1987) 1. Performance: n Will the product/service do the intended job? 2. Reliability: n How often does the product/service fail? 3. Durability: n How long does the product/service last? 4. Serviceability: n How easy to repair the product / to solve the problems in service? 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 7
Dimensions of Quality Garvin (1987) 1. Performance: n Will the product/service do the intended job? 2. Reliability: n How often does the product/service fail? 3. Durability: n How long does the product/service last? 4. Serviceability: n How easy to repair the product / to solve the problems in service? 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 7
 Dimensions of Quality 5. Aesthetics: n 6. Features: n 7. What does the product do/ service give? Perceived Quality: n 8. What does the product/service look/smell/sound/feel like? What is the reputation of the company or its products/services? Conformance to Standards: n 16/03/2018 Is the product/service made exactly as the designer/standard intended? Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 8
Dimensions of Quality 5. Aesthetics: n 6. Features: n 7. What does the product do/ service give? Perceived Quality: n 8. What does the product/service look/smell/sound/feel like? What is the reputation of the company or its products/services? Conformance to Standards: n 16/03/2018 Is the product/service made exactly as the designer/standard intended? Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 8
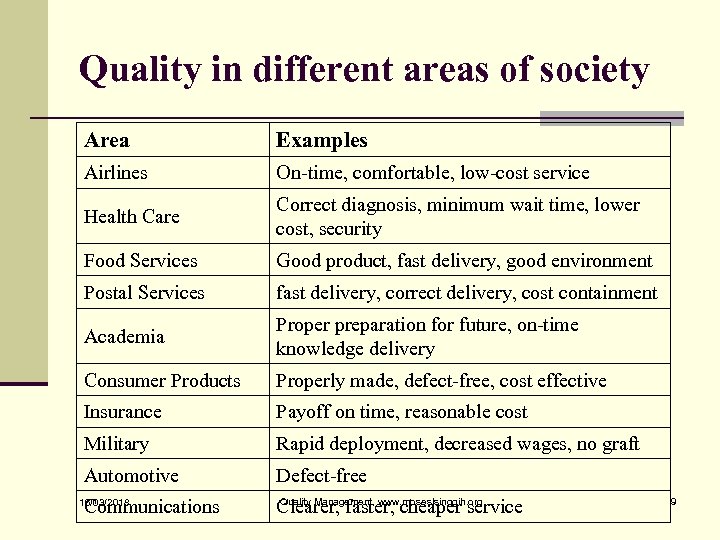 Quality in different areas of society Area Examples Airlines On-time, comfortable, low-cost service Health Care Correct diagnosis, minimum wait time, lower cost, security Food Services Good product, fast delivery, good environment Postal Services fast delivery, correct delivery, cost containment Academia Proper preparation for future, on-time knowledge delivery Consumer Products Properly made, defect-free, cost effective Insurance Payoff on time, reasonable cost Military Rapid deployment, decreased wages, no graft Automotive Defect-free Communications Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org Clearer, faster, cheaper service 16/03/2018 9
Quality in different areas of society Area Examples Airlines On-time, comfortable, low-cost service Health Care Correct diagnosis, minimum wait time, lower cost, security Food Services Good product, fast delivery, good environment Postal Services fast delivery, correct delivery, cost containment Academia Proper preparation for future, on-time knowledge delivery Consumer Products Properly made, defect-free, cost effective Insurance Payoff on time, reasonable cost Military Rapid deployment, decreased wages, no graft Automotive Defect-free Communications Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org Clearer, faster, cheaper service 16/03/2018 9
 What is Quality? n Conformance n n n to specifications (British Defense Industries Quality Assurance Panel) Conformance to requirements (Philip Crosby) Fitness for purpose or use (Juran) A predictable degree of uniformity and dependability, at low cost and suited to the market (Edward Deming) Synonymous with customer needs and expectations (R J Mortiboys) Meeting the (stated) requirements of the customer- now and in the future (Mike Robinson) The total composite product and service characteristics of marketing, engineering, manufacturing and maintenance through which the product and service in use will meet the expectations by the customer (Armand Feigenbaum) 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 10
What is Quality? n Conformance n n n to specifications (British Defense Industries Quality Assurance Panel) Conformance to requirements (Philip Crosby) Fitness for purpose or use (Juran) A predictable degree of uniformity and dependability, at low cost and suited to the market (Edward Deming) Synonymous with customer needs and expectations (R J Mortiboys) Meeting the (stated) requirements of the customer- now and in the future (Mike Robinson) The total composite product and service characteristics of marketing, engineering, manufacturing and maintenance through which the product and service in use will meet the expectations by the customer (Armand Feigenbaum) 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 10
 What is Quality? n “The degree to which a system, component, or process meets (1) specified requirements, and (2) customer or users needs or expectations” – IEEE n The totality of features and characteristics of a product or service that bears on its ability to satisfy stated or implied needs” – ISO 8402 n Degree to which a set of inherent characteristics fulfils requirements – ISO 9000: 2000 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 11
What is Quality? n “The degree to which a system, component, or process meets (1) specified requirements, and (2) customer or users needs or expectations” – IEEE n The totality of features and characteristics of a product or service that bears on its ability to satisfy stated or implied needs” – ISO 8402 n Degree to which a set of inherent characteristics fulfils requirements – ISO 9000: 2000 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 11
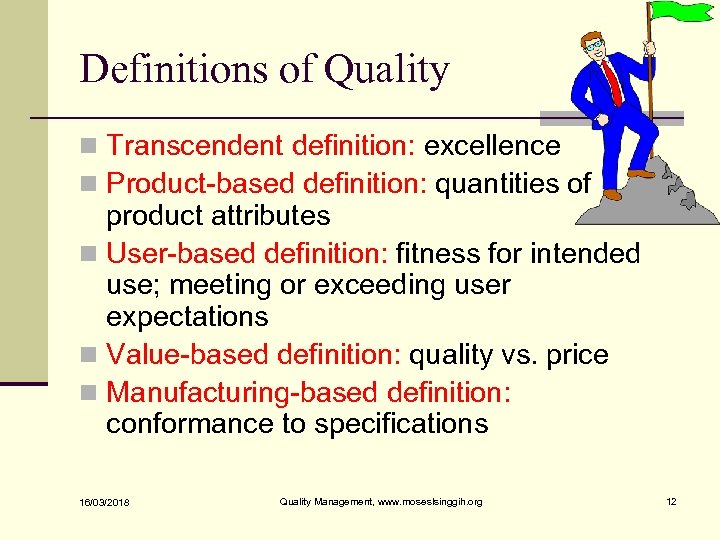 Definitions of Quality n Transcendent definition: excellence n Product-based definition: quantities of product attributes n User-based definition: fitness for intended use; meeting or exceeding user expectations n Value-based definition: quality vs. price n Manufacturing-based definition: conformance to specifications 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 12
Definitions of Quality n Transcendent definition: excellence n Product-based definition: quantities of product attributes n User-based definition: fitness for intended use; meeting or exceeding user expectations n Value-based definition: quality vs. price n Manufacturing-based definition: conformance to specifications 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 12
 More about Quality n Realistic but demanding STANDARDS; n Getting things RIGHT FIRST TIME; ‘It costs less to prevent a problem than it does to correct it’ n Influences the relationship with CUSTOMERS; n Influences how COMPLAINTS are dealt with; n Something to do with how things LOOK and FEEL. 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 13
More about Quality n Realistic but demanding STANDARDS; n Getting things RIGHT FIRST TIME; ‘It costs less to prevent a problem than it does to correct it’ n Influences the relationship with CUSTOMERS; n Influences how COMPLAINTS are dealt with; n Something to do with how things LOOK and FEEL. 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 13
 Kualitas vs harga • Barang/jasa berkualitas harga mahal? • Mengapa konsumen bersedia membeli barang berkualitas yang mahal? 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 14
Kualitas vs harga • Barang/jasa berkualitas harga mahal? • Mengapa konsumen bersedia membeli barang berkualitas yang mahal? 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 14
 History of Quality Methodology Statistical Quality Control 16/03/2018 Quality Assurance Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org Quality Management 15
History of Quality Methodology Statistical Quality Control 16/03/2018 Quality Assurance Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org Quality Management 15
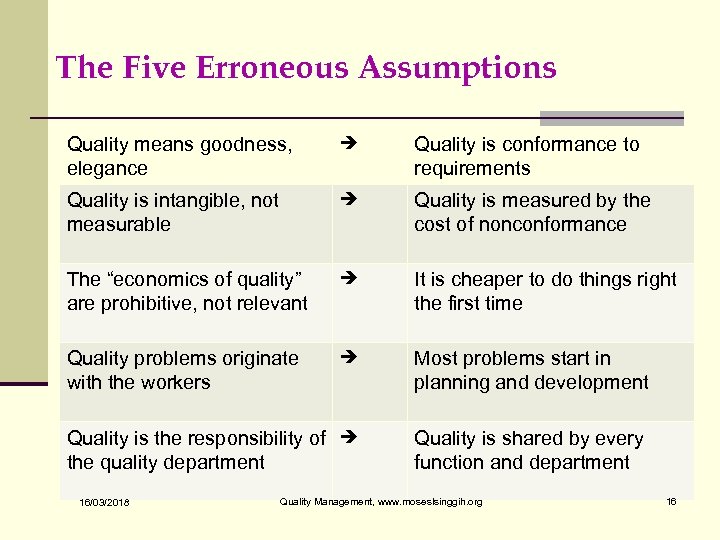 The Five Erroneous Assumptions Quality means goodness, elegance Quality is conformance to requirements Quality is intangible, not measurable Quality is measured by the cost of nonconformance The “economics of quality” are prohibitive, not relevant It is cheaper to do things right the first time Quality problems originate with the workers Most problems start in planning and development Quality is the responsibility of the quality department Quality is shared by every function and department 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 16
The Five Erroneous Assumptions Quality means goodness, elegance Quality is conformance to requirements Quality is intangible, not measurable Quality is measured by the cost of nonconformance The “economics of quality” are prohibitive, not relevant It is cheaper to do things right the first time Quality problems originate with the workers Most problems start in planning and development Quality is the responsibility of the quality department Quality is shared by every function and department 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 16
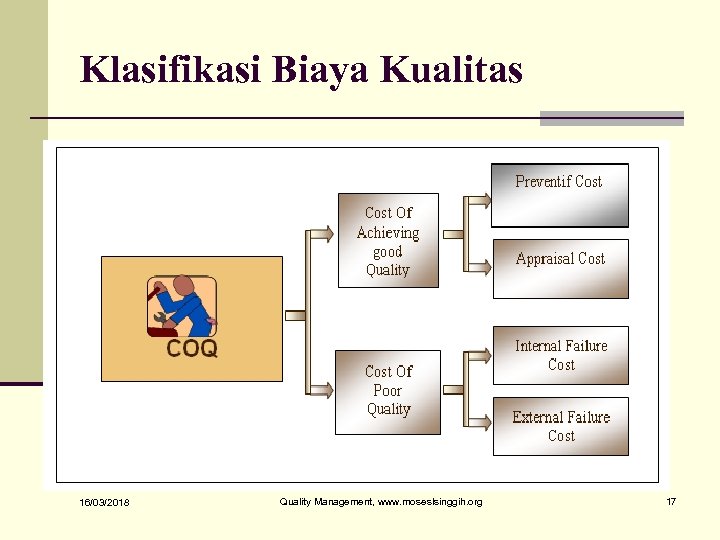 Klasifikasi Biaya Kualitas 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 17
Klasifikasi Biaya Kualitas 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 17
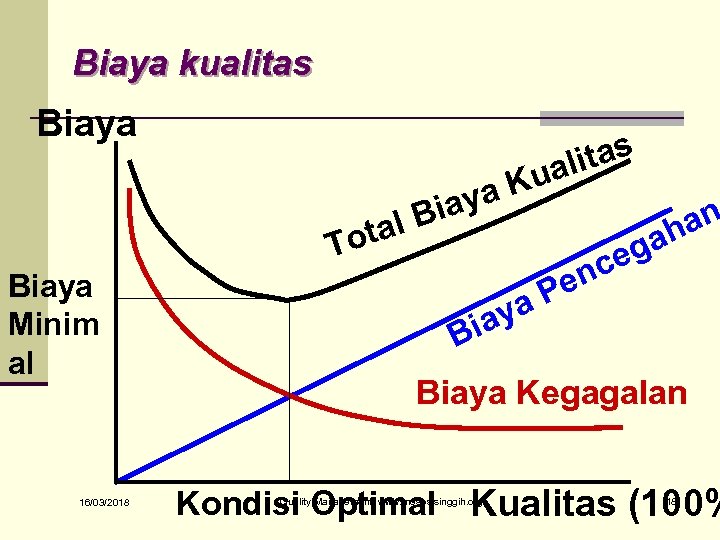 Biaya kualitas Biaya itas ual a. K iay al B ot T Biaya Minim al 16/03/2018 ya ia an h ga ce en P B Biaya Kegagalan Kondisi Optimal Kualitas (100% Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 18
Biaya kualitas Biaya itas ual a. K iay al B ot T Biaya Minim al 16/03/2018 ya ia an h ga ce en P B Biaya Kegagalan Kondisi Optimal Kualitas (100% Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 18
 Slide 6 -2 Dampak terhadap Product Quality Ø Product quality and profitability sangat berhubungan. Ø Bisnis yang menawarkan kualitas produk dan jasa istimewa akan lebih disukai sehingga mendapatkan pangsa pasar yang besar. Ø Kualitas berhubunga positif dengan ROI yang tinggi. 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 19
Slide 6 -2 Dampak terhadap Product Quality Ø Product quality and profitability sangat berhubungan. Ø Bisnis yang menawarkan kualitas produk dan jasa istimewa akan lebih disukai sehingga mendapatkan pangsa pasar yang besar. Ø Kualitas berhubunga positif dengan ROI yang tinggi. 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 19
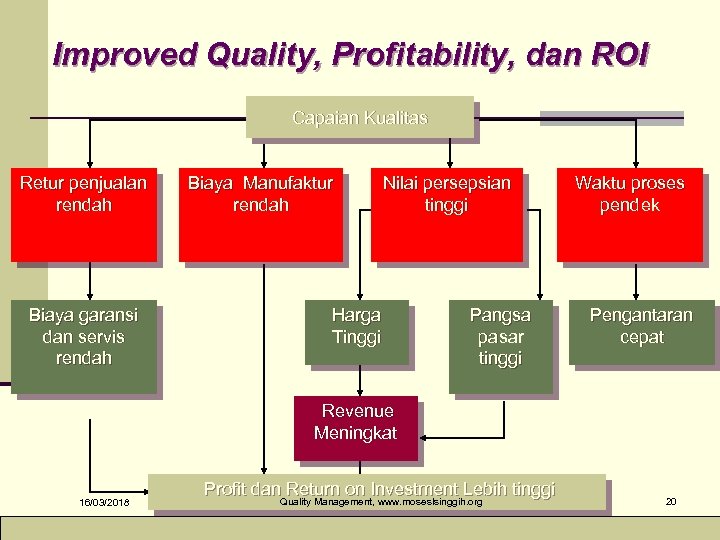 Improved Quality, Profitability, dan ROI Capaian Kualitas Retur penjualan rendah Biaya garansi dan servis rendah Biaya Manufaktur rendah Nilai persepsian tinggi Harga Tinggi Pangsa pasar tinggi Waktu proses pendek Pengantaran cepat Revenue Meningkat 16/03/2018 Profit dan Return on Investment Lebih tinggi Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 20
Improved Quality, Profitability, dan ROI Capaian Kualitas Retur penjualan rendah Biaya garansi dan servis rendah Biaya Manufaktur rendah Nilai persepsian tinggi Harga Tinggi Pangsa pasar tinggi Waktu proses pendek Pengantaran cepat Revenue Meningkat 16/03/2018 Profit dan Return on Investment Lebih tinggi Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 20
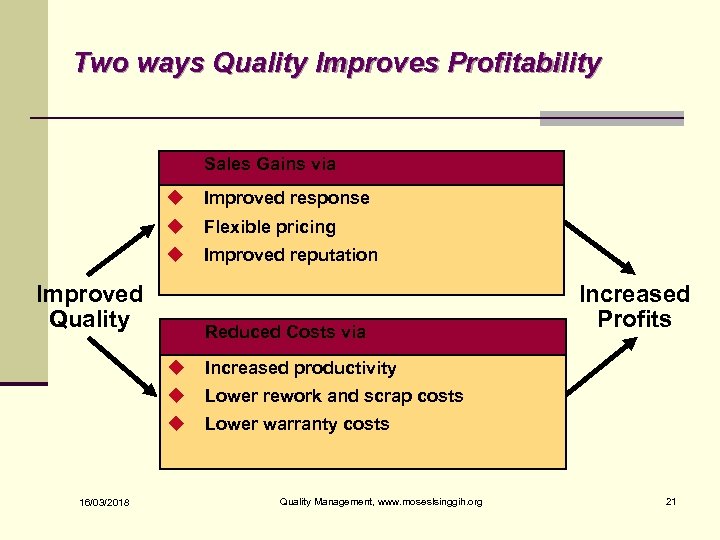 Two ways Quality Improves Profitability Sales Gains via u Improved response u Flexible pricing u Improved reputation Improved Quality Reduced Costs via u Lower rework and scrap costs u 16/03/2018 Increased productivity u Increased Profits Lower warranty costs Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 21
Two ways Quality Improves Profitability Sales Gains via u Improved response u Flexible pricing u Improved reputation Improved Quality Reduced Costs via u Lower rework and scrap costs u 16/03/2018 Increased productivity u Increased Profits Lower warranty costs Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 21
 QUALITY MANAGEMENT 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 22
QUALITY MANAGEMENT 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 22
 Slide 6 -5 Quality Management merupakan peningkatan secara terus menerus yang Dilakukan oleh setiap orang dalam organisasi untuk memahami, memenuhi bahkan melebihi harapan pelanggan. 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 23
Slide 6 -5 Quality Management merupakan peningkatan secara terus menerus yang Dilakukan oleh setiap orang dalam organisasi untuk memahami, memenuhi bahkan melebihi harapan pelanggan. 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 23
 • Apakah keinginan semua konsumen dipenuhi? • Kalau tidak semua konsumen, bagaimana memilihnya? Customer profitability analysis = pilih konsumen yang berani membayar mahal tetapi tidak terlalu menuntut 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 24
• Apakah keinginan semua konsumen dipenuhi? • Kalau tidak semua konsumen, bagaimana memilihnya? Customer profitability analysis = pilih konsumen yang berani membayar mahal tetapi tidak terlalu menuntut 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 24
 Quality Management þ Focus thd pemenuhan pelanggan þ Mengarahkan pada continuous improvement þ Keterlibatan Gugus tugas (work force) 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 25
Quality Management þ Focus thd pemenuhan pelanggan þ Mengarahkan pada continuous improvement þ Keterlibatan Gugus tugas (work force) 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 25
 Quality Management Activities: n Quality assurance n Establish organisational procedures and standards for quality. n Quality planning n Select applicable procedures and standards for a particular project and modify these as required. n Quality control n 16/03/2018 Ensure that procedures and standards are followed by the software development team. Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 26
Quality Management Activities: n Quality assurance n Establish organisational procedures and standards for quality. n Quality planning n Select applicable procedures and standards for a particular project and modify these as required. n Quality control n 16/03/2018 Ensure that procedures and standards are followed by the software development team. Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 26
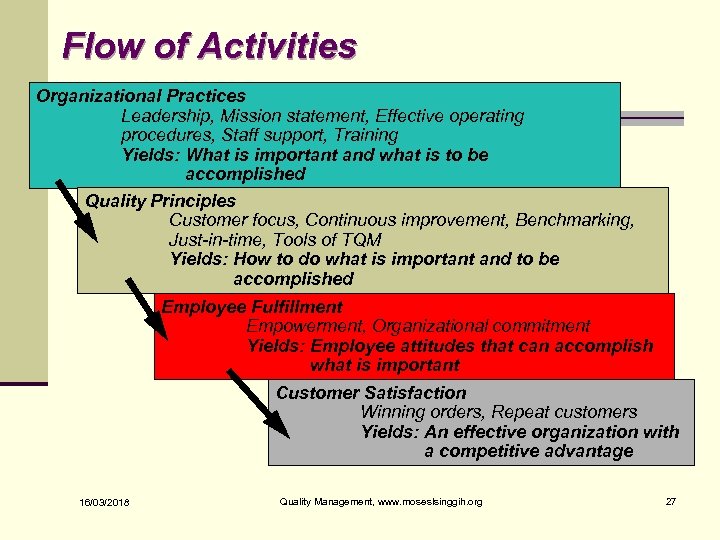 Flow of Activities Organizational Practices Leadership, Mission statement, Effective operating procedures, Staff support, Training Yields: What is important and what is to be accomplished Quality Principles Customer focus, Continuous improvement, Benchmarking, Just-in-time, Tools of TQM Yields: How to do what is important and to be accomplished Employee Fulfillment Empowerment, Organizational commitment Yields: Employee attitudes that can accomplish what is important Customer Satisfaction Winning orders, Repeat customers Yields: An effective organization with a competitive advantage 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 27
Flow of Activities Organizational Practices Leadership, Mission statement, Effective operating procedures, Staff support, Training Yields: What is important and what is to be accomplished Quality Principles Customer focus, Continuous improvement, Benchmarking, Just-in-time, Tools of TQM Yields: How to do what is important and to be accomplished Employee Fulfillment Empowerment, Organizational commitment Yields: Employee attitudes that can accomplish what is important Customer Satisfaction Winning orders, Repeat customers Yields: An effective organization with a competitive advantage 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 27
 Process and Product Quality: n The quality of a developed product is influenced by the quality of the production process. n This is important in software development as some product quality attributes are hard to assess. n However, there is a very complex and poorly understood relationship between software processes and product quality. 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 28
Process and Product Quality: n The quality of a developed product is influenced by the quality of the production process. n This is important in software development as some product quality attributes are hard to assess. n However, there is a very complex and poorly understood relationship between software processes and product quality. 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 28
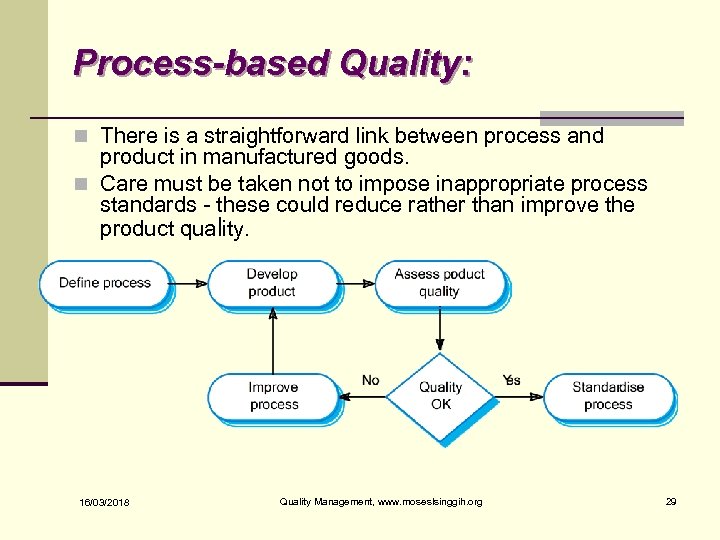 Process-based Quality: n There is a straightforward link between process and product in manufactured goods. n Care must be taken not to impose inappropriate process standards - these could reduce rather than improve the product quality. 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 29
Process-based Quality: n There is a straightforward link between process and product in manufactured goods. n Care must be taken not to impose inappropriate process standards - these could reduce rather than improve the product quality. 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 29
 Practical Process-based Quality: n Define process standards such as how reviews should be conducted, configuration, management, etc. n Monitor the development process to ensure that standards are being followed. n Don’t use inappropriate practices simply because standards have been established. 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 30
Practical Process-based Quality: n Define process standards such as how reviews should be conducted, configuration, management, etc. n Monitor the development process to ensure that standards are being followed. n Don’t use inappropriate practices simply because standards have been established. 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 30
 Quality Assurance and Standards: n Standards are the key to effective quality management. n They may be international, organizational or project standards. n Product standards define characteristics that all components should exhibit e. g. a common programming style. n Process standards define how the software process should be enacted. 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 31
Quality Assurance and Standards: n Standards are the key to effective quality management. n They may be international, organizational or project standards. n Product standards define characteristics that all components should exhibit e. g. a common programming style. n Process standards define how the software process should be enacted. 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 31
 Importance of Standards: n Encapsulation of best practice- avoids repetition of past mistakes. n They are a framework for quality assurance processes - they involve checking compliance to standards. n They provide continuity - new staff can understand the organisation by understanding the standards that are used. 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 32
Importance of Standards: n Encapsulation of best practice- avoids repetition of past mistakes. n They are a framework for quality assurance processes - they involve checking compliance to standards. n They provide continuity - new staff can understand the organisation by understanding the standards that are used. 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 32
 Problems with Standards: n They may not be seen as relevant and up-to- date by software engineers. n They often involve too much bureaucratic form filling. n If they are unsupported by software tools, tedious manual work is often involved to maintain the documentation associated with the standards. 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 33
Problems with Standards: n They may not be seen as relevant and up-to- date by software engineers. n They often involve too much bureaucratic form filling. n If they are unsupported by software tools, tedious manual work is often involved to maintain the documentation associated with the standards. 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 33
 Standards development: n Involve practitioners in development. Engineers should understand the rationale underlying a standard. n Review standards and their usage regularly. Standards can quickly become outdated and this reduces their credibility amongst practitioners. n Detailed standards should have associated tool support. Excessive clerical work is the most significant complaint against standards. 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 34
Standards development: n Involve practitioners in development. Engineers should understand the rationale underlying a standard. n Review standards and their usage regularly. Standards can quickly become outdated and this reduces their credibility amongst practitioners. n Detailed standards should have associated tool support. Excessive clerical work is the most significant complaint against standards. 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 34
 ISO 9000: n An international set of standards for quality management. n Applicable to a range of organisations from manufacturing to service industries. n ISO 9001 applicable to organisations which design, develop and maintain products. n ISO 9001 is a generic model of the quality process that must be instantiated for each organisation using the standard. 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 35
ISO 9000: n An international set of standards for quality management. n Applicable to a range of organisations from manufacturing to service industries. n ISO 9001 applicable to organisations which design, develop and maintain products. n ISO 9001 is a generic model of the quality process that must be instantiated for each organisation using the standard. 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 35
 Apakah barang/jasa berkualitas terjadi dengan sendirinya atau perlu diusahakan? 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 36
Apakah barang/jasa berkualitas terjadi dengan sendirinya atau perlu diusahakan? 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 36
 QUALITY MANAGEMENT TOOLS !!! 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 37
QUALITY MANAGEMENT TOOLS !!! 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 37
 QUALITY DOES NOT OCCUR BY ACCIDENT n What does the customer actually want? n Identify, understand agree customer requirements n How are you going to meet those requirements? n Plan to achieve them 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 38
QUALITY DOES NOT OCCUR BY ACCIDENT n What does the customer actually want? n Identify, understand agree customer requirements n How are you going to meet those requirements? n Plan to achieve them 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 38
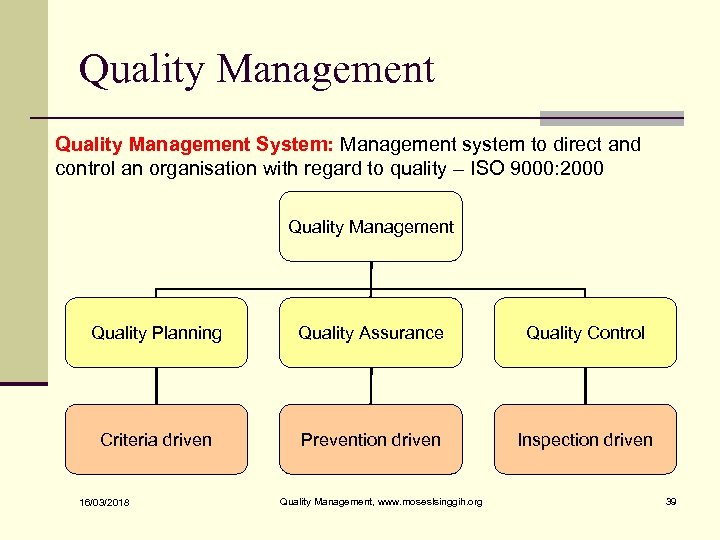 Quality Management System: Management system to direct and control an organisation with regard to quality – ISO 9000: 2000 Quality Management Quality Planning Quality Assurance Quality Control Criteria driven Prevention driven Inspection driven 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 39
Quality Management System: Management system to direct and control an organisation with regard to quality – ISO 9000: 2000 Quality Management Quality Planning Quality Assurance Quality Control Criteria driven Prevention driven Inspection driven 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 39
 Quality Management Components n Quality Planning n It identifies the standards and determines how to satisfy those standards. n It lays out the roles and responsibilities, resources, procedures, and processes to be utilized for quality control and quality assurance. n Quality Assurance n It is the review to ensure aligning with the quality standards. An assessment will be provided here. n Planned and systematic quality activities. n Provide the confidence that the standards will be met. 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 40
Quality Management Components n Quality Planning n It identifies the standards and determines how to satisfy those standards. n It lays out the roles and responsibilities, resources, procedures, and processes to be utilized for quality control and quality assurance. n Quality Assurance n It is the review to ensure aligning with the quality standards. An assessment will be provided here. n Planned and systematic quality activities. n Provide the confidence that the standards will be met. 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 40
 Quality Control – Inspection Driven n Quality Control n It addresses the assessment conducted during Quality Assurance for corrective actions. n Measure specific results to determine that they match the standards. n Use of Statistical Process Control (SPC) : a methodology for monitoring a process to identify special causes of variation and signal the need to take corrective action when appropriate. n SPC relies on control charts. 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 41
Quality Control – Inspection Driven n Quality Control n It addresses the assessment conducted during Quality Assurance for corrective actions. n Measure specific results to determine that they match the standards. n Use of Statistical Process Control (SPC) : a methodology for monitoring a process to identify special causes of variation and signal the need to take corrective action when appropriate. n SPC relies on control charts. 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 41
 What is a Control Chart? n A control chart is a presentation of data in which the control values are plotted against time. n Control charts have a central line, upper and lower warning limits, and upper and lower action limits. n Immediate visualisation of problems. 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 42
What is a Control Chart? n A control chart is a presentation of data in which the control values are plotted against time. n Control charts have a central line, upper and lower warning limits, and upper and lower action limits. n Immediate visualisation of problems. 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 42
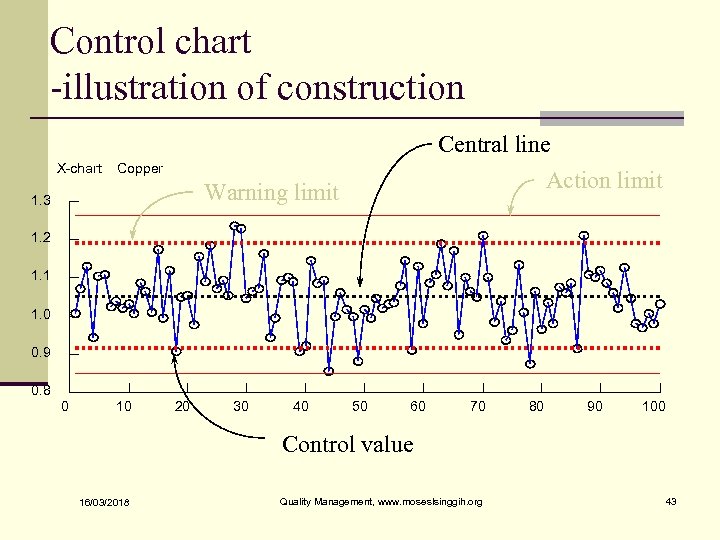 Control chart -illustration of construction Central line X-chart Copper Action limit Warning limit 1. 3 1. 2 1. 1 1. 0 0. 9 0. 8 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Control value 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 43
Control chart -illustration of construction Central line X-chart Copper Action limit Warning limit 1. 3 1. 2 1. 1 1. 0 0. 9 0. 8 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Control value 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 43
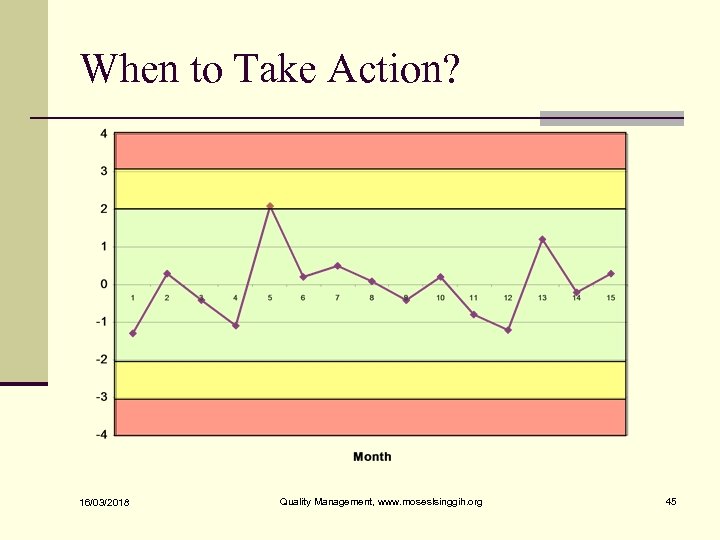
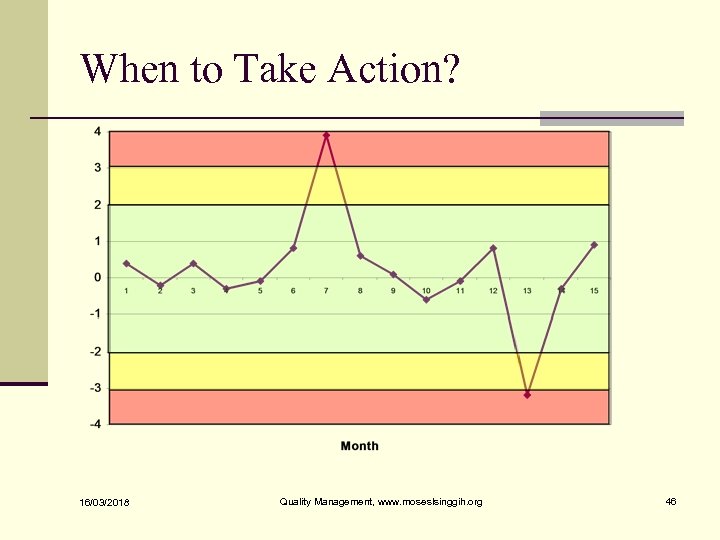
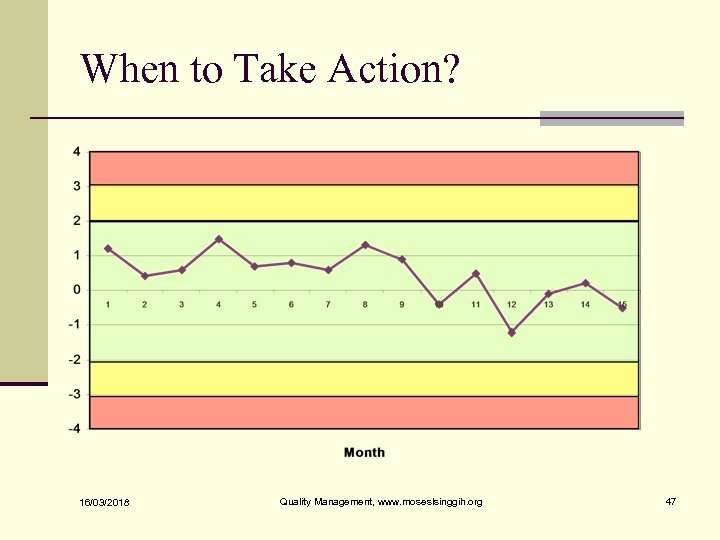
 When to Take Action? n One point plots outside the Action Limits. n Two consecutive points plots between the Warning and Action Limits n Eight consecutive points plot on one side of the Center Line n Six points plots steadily increasing or decreasing n When an unusual or nonrandom pattern is observed 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 44
When to Take Action? n One point plots outside the Action Limits. n Two consecutive points plots between the Warning and Action Limits n Eight consecutive points plot on one side of the Center Line n Six points plots steadily increasing or decreasing n When an unusual or nonrandom pattern is observed 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 44
 When to Take Action? 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 45
When to Take Action? 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 45
 When to Take Action? 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 46
When to Take Action? 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 46
 When to Take Action? 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 47
When to Take Action? 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 47
 Quality Improvement Tools Brainstorming Nominal Group Technique 16/03/2018 Cause & Effect Flow Diagram Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 48
Quality Improvement Tools Brainstorming Nominal Group Technique 16/03/2018 Cause & Effect Flow Diagram Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 48
 Brainstorming n Everyone participates n Go round and only one person speaks n n n 16/03/2018 at a time No discussion of ideas There is no such thing as a dumb idea Pass when necessary Use “BIG” yellow sticky notes and write only 1 idea per sticky note One person assigned as scribe For a complicated issue, the session could last 30 -45 minutes…or longer! Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 49
Brainstorming n Everyone participates n Go round and only one person speaks n n n 16/03/2018 at a time No discussion of ideas There is no such thing as a dumb idea Pass when necessary Use “BIG” yellow sticky notes and write only 1 idea per sticky note One person assigned as scribe For a complicated issue, the session could last 30 -45 minutes…or longer! Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 49
 Nominal Group Technique Use a Nominal Group Technique To focus brainstorming results An internet search on “Nominal Group Technique” 16/03/2018 Will yield many examples and methods to apply this technique Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 50
Nominal Group Technique Use a Nominal Group Technique To focus brainstorming results An internet search on “Nominal Group Technique” 16/03/2018 Will yield many examples and methods to apply this technique Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 50
 Flow Diagrams Why is flow diagramming helpful? n Build a common understanding of a whole process n Develop process thinking n Improve a process n Standardize a process 16/03/2018 Week 4_4 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 51
Flow Diagrams Why is flow diagramming helpful? n Build a common understanding of a whole process n Develop process thinking n Improve a process n Standardize a process 16/03/2018 Week 4_4 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 51
 16/03/2018 Week 4_5 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 52
16/03/2018 Week 4_5 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 52
 Investigate the Root Causes Understand the root causes of a problem BEFORE you put a “solution” into place 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 53
Investigate the Root Causes Understand the root causes of a problem BEFORE you put a “solution” into place 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 53
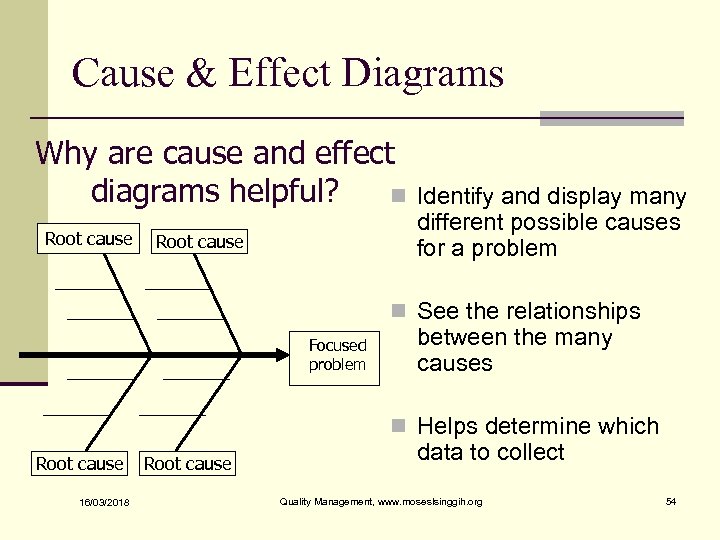 Cause & Effect Diagrams Why are cause and effect diagrams helpful? n Root cause Identify and display many different possible causes for a problem n See the relationships Focused problem between the many causes n Helps determine which Root cause 16/03/2018 Root cause data to collect Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 54
Cause & Effect Diagrams Why are cause and effect diagrams helpful? n Root cause Identify and display many different possible causes for a problem n See the relationships Focused problem between the many causes n Helps determine which Root cause 16/03/2018 Root cause data to collect Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 54
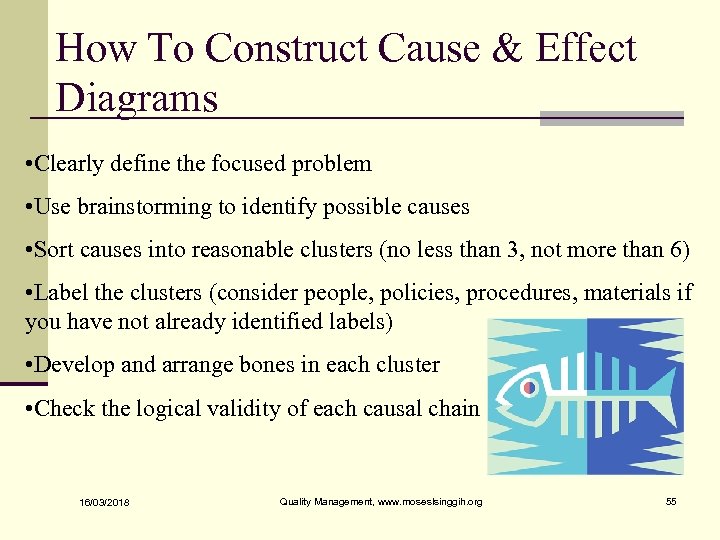 How To Construct Cause & Effect Diagrams • Clearly define the focused problem • Use brainstorming to identify possible causes • Sort causes into reasonable clusters (no less than 3, not more than 6) • Label the clusters (consider people, policies, procedures, materials if you have not already identified labels) • Develop and arrange bones in each cluster • Check the logical validity of each causal chain 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 55
How To Construct Cause & Effect Diagrams • Clearly define the focused problem • Use brainstorming to identify possible causes • Sort causes into reasonable clusters (no less than 3, not more than 6) • Label the clusters (consider people, policies, procedures, materials if you have not already identified labels) • Develop and arrange bones in each cluster • Check the logical validity of each causal chain 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 55
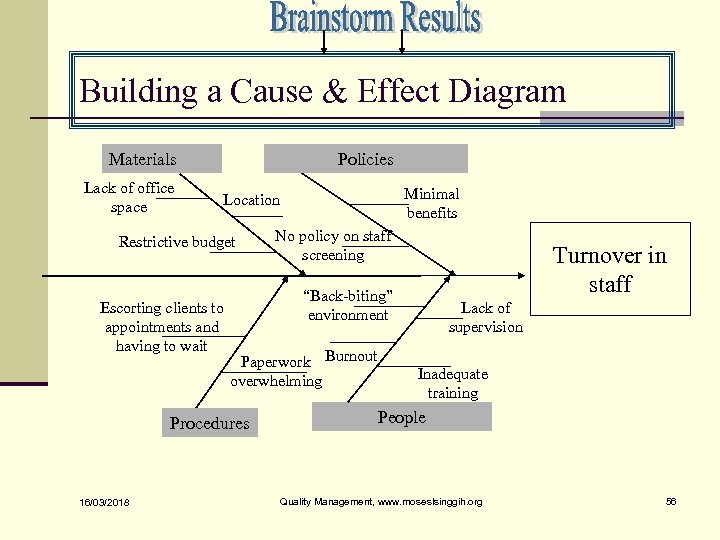 Building a Cause & Effect Diagram Materials Lack of office space Policies Restrictive budget Escorting clients to appointments and having to wait No policy on staff screening Turnover in staff “Back-biting” environment Paperwork Burnout overwhelming Procedures 16/03/2018 Minimal benefits Location Lack of supervision Inadequate training People Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 56
Building a Cause & Effect Diagram Materials Lack of office space Policies Restrictive budget Escorting clients to appointments and having to wait No policy on staff screening Turnover in staff “Back-biting” environment Paperwork Burnout overwhelming Procedures 16/03/2018 Minimal benefits Location Lack of supervision Inadequate training People Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 56
 Cause & Effect Diagrams n Bones should not include solutions n Bones should not include lists of process steps n Bones include the possible causes Better understand the current situation…. . Now begin to develop a change. 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 57
Cause & Effect Diagrams n Bones should not include solutions n Bones should not include lists of process steps n Bones include the possible causes Better understand the current situation…. . Now begin to develop a change. 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 57
 To Summarize…. n Brainstorming n Nominal Group Technique n Flow Diagram n Cause & Effect Diagram 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 58
To Summarize…. n Brainstorming n Nominal Group Technique n Flow Diagram n Cause & Effect Diagram 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 58
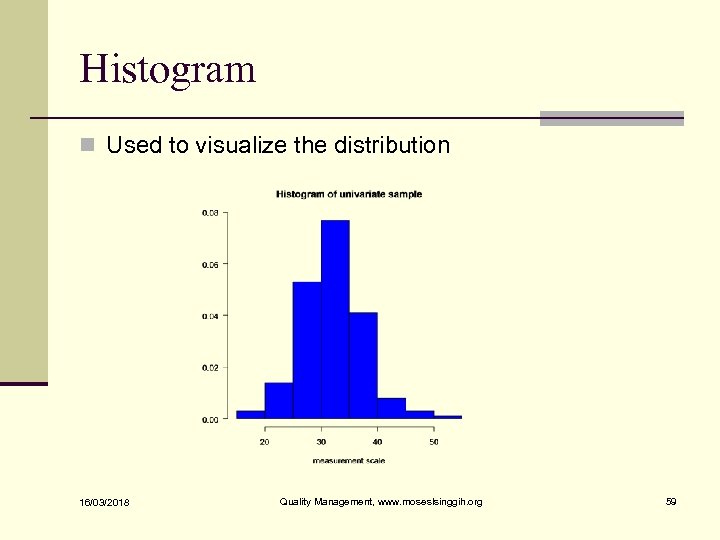 Histogram n Used to visualize the distribution 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 59
Histogram n Used to visualize the distribution 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 59
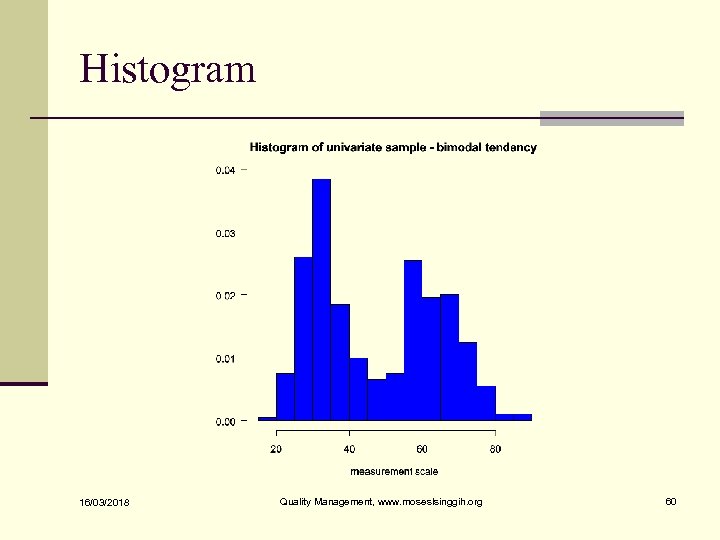 Histogram 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 60
Histogram 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 60
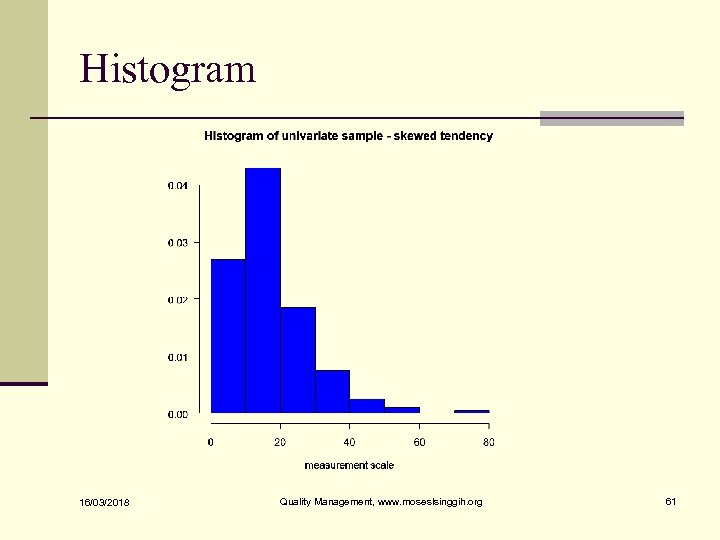 Histogram 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 61
Histogram 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 61
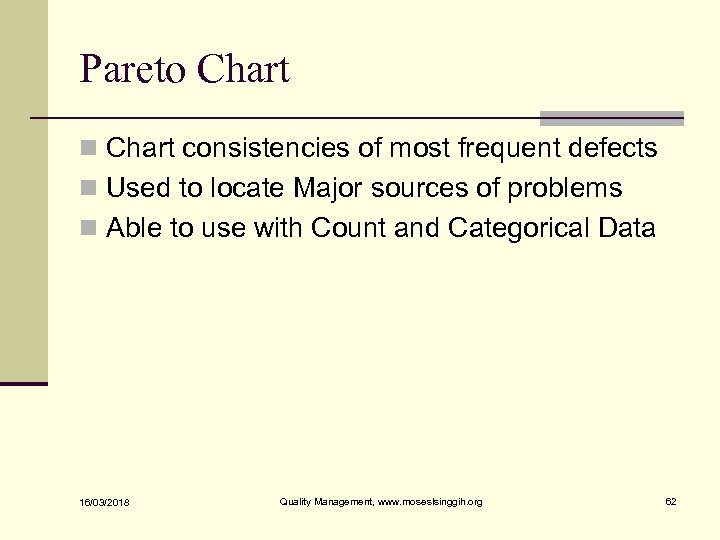 Pareto Chart n Chart consistencies of most frequent defects n Used to locate Major sources of problems n Able to use with Count and Categorical Data 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 62
Pareto Chart n Chart consistencies of most frequent defects n Used to locate Major sources of problems n Able to use with Count and Categorical Data 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 62
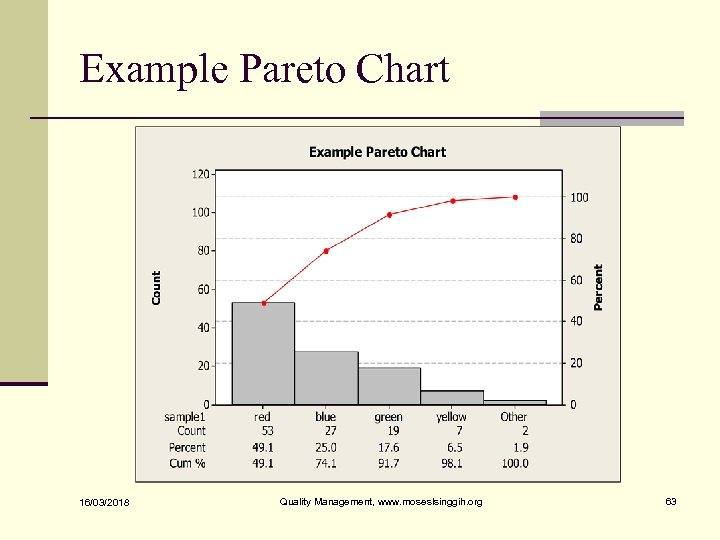 Example Pareto Chart 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 63
Example Pareto Chart 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 63
 Control Charts n Used to determine if variation is chance or assignable cause n Good for measuring control of variation n Control needed before Change n More appropriately applied to process rather than product 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 64
Control Charts n Used to determine if variation is chance or assignable cause n Good for measuring control of variation n Control needed before Change n More appropriately applied to process rather than product 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 64
 Quality-related costs n Prevention costs n activities to keep unacceptable products from being generated and to keep track of the process n Appraisal costs n activities to maintain control of the system n Correction costs n activities to correct conditions out of control, including errors 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 65
Quality-related costs n Prevention costs n activities to keep unacceptable products from being generated and to keep track of the process n Appraisal costs n activities to maintain control of the system n Correction costs n activities to correct conditions out of control, including errors 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 65
 Prevention costs n Quality planning and engineering n New products review n Product/process design n Process control n Burn-in n Training n Quality data acquisition and analysis 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 66
Prevention costs n Quality planning and engineering n New products review n Product/process design n Process control n Burn-in n Training n Quality data acquisition and analysis 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 66
 Appraisal costs n Inspection and test of incoming material n Product inspection and test n Materials and services consumed n Maintaining accuracy of test equipment 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 67
Appraisal costs n Inspection and test of incoming material n Product inspection and test n Materials and services consumed n Maintaining accuracy of test equipment 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 67
 Correction costs 1. Internal Failure Costs: n Scrap n Rework n Retest n Failure analysis n Downtime n Yield losses n Downgrading (off-specing) 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 68
Correction costs 1. Internal Failure Costs: n Scrap n Rework n Retest n Failure analysis n Downtime n Yield losses n Downgrading (off-specing) 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 68
 Correction costs 2. External Failure Costs: n Complaint adjustment n Returned product/material n Warranty charges n Liability costs n Indirect costs 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 69
Correction costs 2. External Failure Costs: n Complaint adjustment n Returned product/material n Warranty charges n Liability costs n Indirect costs 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 69
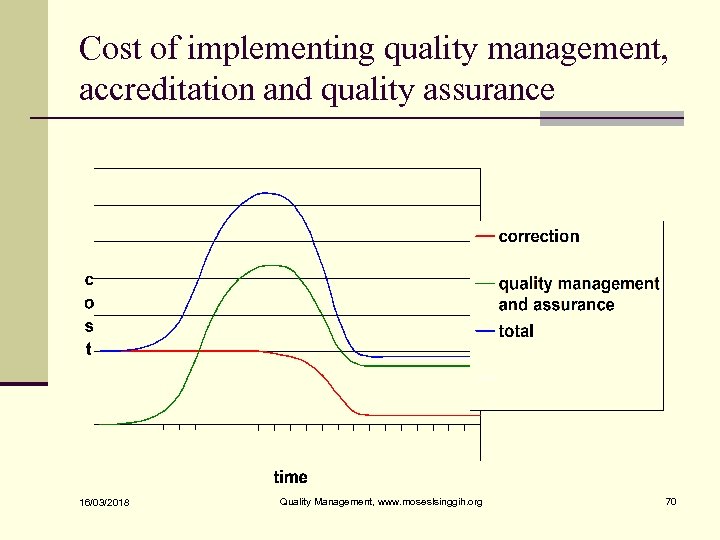 Cost of implementing quality management, accreditation and quality assurance 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 70
Cost of implementing quality management, accreditation and quality assurance 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 70
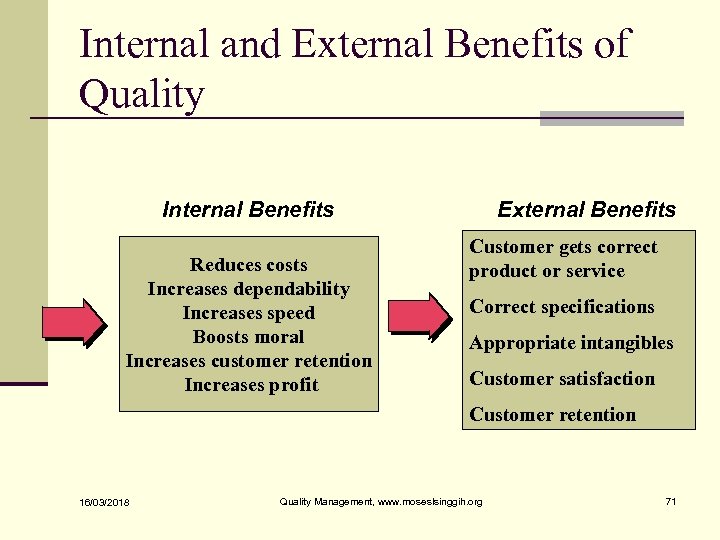 Internal and External Benefits of Quality Internal Benefits Reduces costs Increases dependability Increases speed Boosts moral Increases customer retention Increases profit External Benefits Customer gets correct product or service Correct specifications Appropriate intangibles Customer satisfaction Customer retention 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 71
Internal and External Benefits of Quality Internal Benefits Reduces costs Increases dependability Increases speed Boosts moral Increases customer retention Increases profit External Benefits Customer gets correct product or service Correct specifications Appropriate intangibles Customer satisfaction Customer retention 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 71
 Drawbacks n Long way to establish in the organisation n QM design not always fit for purpose (loss of cost effectiveness) n Substantial efforts n Maintain system, otherwise reject it. 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 72
Drawbacks n Long way to establish in the organisation n QM design not always fit for purpose (loss of cost effectiveness) n Substantial efforts n Maintain system, otherwise reject it. 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 72
 Deming’s 14 Principles. “Create Constancy of Purpose” 1. Ø Ø Define the problems of today and the future Allocate resources for long-term planning Allocate resources for research and education Constantly improve design of product and service “Adopt A New Philosophy” 2. Ø Ø Quality costs less not more Superstitious learning The call for major change Stop looking at your competition and look at your customer instead “Cease Dependence On Inspection For Quality” 3. Ø Ø 16/03/2018 Quality does not come from inspection Mass inspection is unreliable, costly, and ineffective Inspectors fail to agree with each other Inspection should be used to collect data for process control Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 73
Deming’s 14 Principles. “Create Constancy of Purpose” 1. Ø Ø Define the problems of today and the future Allocate resources for long-term planning Allocate resources for research and education Constantly improve design of product and service “Adopt A New Philosophy” 2. Ø Ø Quality costs less not more Superstitious learning The call for major change Stop looking at your competition and look at your customer instead “Cease Dependence On Inspection For Quality” 3. Ø Ø 16/03/2018 Quality does not come from inspection Mass inspection is unreliable, costly, and ineffective Inspectors fail to agree with each other Inspection should be used to collect data for process control Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 73
 Deming’s 14 Principles. “End Proactive Awarding Of Business Based On Price. Alone” 4. Ø Ø Price alone has no meaning Change focus from lowest inital cost to lowest cost Work toward a single source and long term relationship Establish a mutual confidence and aid between purchaser and vendor “Improve Every Process Constantly / Forever” 5. Ø Ø Quality starts qith the intend of management Teamwork in design is fundamental Forever continue to reduce waste and continue to improve Putting out fires is not improvement of the process “Institute Training” 6. Ø Ø 16/03/2018 Management must provide the setting where workers can be succesful Management must remove the inhibitors to good work Management needs an appreciation of variation This is management’s new www. moseslsinggih. org Quality Management, role 74
Deming’s 14 Principles. “End Proactive Awarding Of Business Based On Price. Alone” 4. Ø Ø Price alone has no meaning Change focus from lowest inital cost to lowest cost Work toward a single source and long term relationship Establish a mutual confidence and aid between purchaser and vendor “Improve Every Process Constantly / Forever” 5. Ø Ø Quality starts qith the intend of management Teamwork in design is fundamental Forever continue to reduce waste and continue to improve Putting out fires is not improvement of the process “Institute Training” 6. Ø Ø 16/03/2018 Management must provide the setting where workers can be succesful Management must remove the inhibitors to good work Management needs an appreciation of variation This is management’s new www. moseslsinggih. org Quality Management, role 74
 Deming’s 14 Principles. “Adopt And Institute Leadership” 7. Ø Ø Ø Remove barriers to pride of workmanship Know the work they supervise Know the difference between special and common cause of variation “Drive Out Fear” 8. Ø Ø The common denominator of fear: Fear of knowledge Performance appraisals Management by fear or numbers “Break Barriers Between Staff Areas” 9. Ø Ø Know your internal suppliers and customers Promote team work “Eliminate Slogans, Exhortations And Targets” 10. Ø Ø 16/03/2018 They generate frustration and resentment Use posters that explain what management is doing to improve Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 75 the work environment
Deming’s 14 Principles. “Adopt And Institute Leadership” 7. Ø Ø Ø Remove barriers to pride of workmanship Know the work they supervise Know the difference between special and common cause of variation “Drive Out Fear” 8. Ø Ø The common denominator of fear: Fear of knowledge Performance appraisals Management by fear or numbers “Break Barriers Between Staff Areas” 9. Ø Ø Know your internal suppliers and customers Promote team work “Eliminate Slogans, Exhortations And Targets” 10. Ø Ø 16/03/2018 They generate frustration and resentment Use posters that explain what management is doing to improve Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 75 the work environment
 Deming’s 14 Principles. “Eliminate Numerical Quotas” 11. Ø Ø Ø They impede quality They reduce production The person’s job becomes meeting a quota “Remove Barriers That Rob Pride Of Workmanship” 12. Ø Ø Performance appraisal systems Production rates Financial management systems Allow people to take pride in their workmanship “Institute Programs For Education And Self Improvement” 13. Ø Ø Ø Commitment to lifelong employment Work with higher education needs Develop team building skills “Put Everybody In The Company To Work For This Transformation” 14. Ø Ø 16/03/2018 Ø Struggle over the 14 points Take pride in new philosophy Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org Include the critical mass of people in the change 76
Deming’s 14 Principles. “Eliminate Numerical Quotas” 11. Ø Ø Ø They impede quality They reduce production The person’s job becomes meeting a quota “Remove Barriers That Rob Pride Of Workmanship” 12. Ø Ø Performance appraisal systems Production rates Financial management systems Allow people to take pride in their workmanship “Institute Programs For Education And Self Improvement” 13. Ø Ø Ø Commitment to lifelong employment Work with higher education needs Develop team building skills “Put Everybody In The Company To Work For This Transformation” 14. Ø Ø 16/03/2018 Ø Struggle over the 14 points Take pride in new philosophy Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org Include the critical mass of people in the change 76
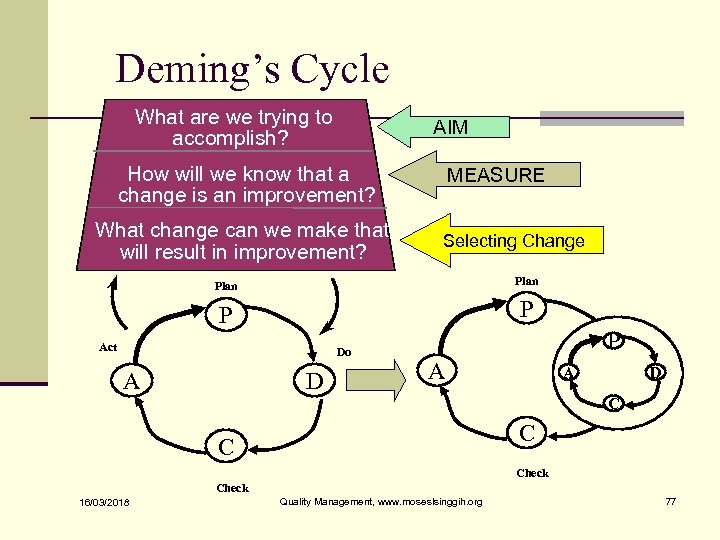 Deming’s Cycle What are we trying to accomplish? AIM How will we know that a change is an improvement? What change can we make that will result in improvement? MEASURE Selecting Change Plan P P Act Do A D A A P D Do D C Check 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 77
Deming’s Cycle What are we trying to accomplish? AIM How will we know that a change is an improvement? What change can we make that will result in improvement? MEASURE Selecting Change Plan P P Act Do A D A A P D Do D C Check 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 77
 Taguchi’s Contribution n In the early 1980 s, Prof. Genechi Taguchi introduced his approach to using experimental design for 1) 2) 3) Designing products or processes so that they are robust to environmental conditions. Designing/developing products so that they are robust to component variation. Minimizing variation around a target value. n By robust, we mean that the product or process performs consistently on target and is relatively insensitive to factors that are difficult to control. 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 78
Taguchi’s Contribution n In the early 1980 s, Prof. Genechi Taguchi introduced his approach to using experimental design for 1) 2) 3) Designing products or processes so that they are robust to environmental conditions. Designing/developing products so that they are robust to component variation. Minimizing variation around a target value. n By robust, we mean that the product or process performs consistently on target and is relatively insensitive to factors that are difficult to control. 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 78
 Taguchi Philosophy n 3 stages in a product’s (or process’s) development: 1) 2) 3) 16/03/2018 System design: uses scientific and engineering principles to determine the basic configuration. Parameter design: specific values for the system parameters are determined. Tolerance design: determine the best tolerances for the parameters. Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 79
Taguchi Philosophy n 3 stages in a product’s (or process’s) development: 1) 2) 3) 16/03/2018 System design: uses scientific and engineering principles to determine the basic configuration. Parameter design: specific values for the system parameters are determined. Tolerance design: determine the best tolerances for the parameters. Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 79
 Taguchi Philosophy n Recommends: statistical experimental design methods have to be used for quality improvement, particularly during parameter and tolerance design phases. n Key component: reduce the variability around the target (nominal) value. 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 80
Taguchi Philosophy n Recommends: statistical experimental design methods have to be used for quality improvement, particularly during parameter and tolerance design phases. n Key component: reduce the variability around the target (nominal) value. 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 80
 MANAGEMENT 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 81
MANAGEMENT 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 81
 What is management n The art of getting things done through the others – (Mary Parker Follet) n Is the process directing and facilitating the work of people organized in formal group to achieve a desired end (John D Millet) n Proses perencanaan, pengorganisasian, pengarahan dan pengendalian kegiatan anggota organisasi dgn menggunakan sumber daya organisasi untuk mencapai tujuan yg telah ditetapkan (James AF Stoner) 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 1– 82
What is management n The art of getting things done through the others – (Mary Parker Follet) n Is the process directing and facilitating the work of people organized in formal group to achieve a desired end (John D Millet) n Proses perencanaan, pengorganisasian, pengarahan dan pengendalian kegiatan anggota organisasi dgn menggunakan sumber daya organisasi untuk mencapai tujuan yg telah ditetapkan (James AF Stoner) 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 1– 82
 Proses: cara sistematis untuk melakukan sesuatu 1. 2. 3. 4. Perencanaan (Planning) : sebelum melakukan sesuatu manajer memikirkan apa tujuan organisasinya, bagaimana mencapainya, bagaimana sumber dayanya, kapan selesainya. Pengorganisasian (Organizing): bagaimanajer mengelompokkan kegiatan-kegiatan yang ada dlm organisasinya, menempatkan orang-orang dan mengalokasi sumber daya Kepemimpinan /mengarahkan (Leading) : bagaimanajer mempengaruhi bawahan agar mau bekerja dlm mancapai tujuan organisasi Pengendalian (Controlling) : bagaimanajer mengawal seluruh aktivitas dlm organisasinya agar tetap berada pada jalur yang benar (on the right track) 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 1– 83
Proses: cara sistematis untuk melakukan sesuatu 1. 2. 3. 4. Perencanaan (Planning) : sebelum melakukan sesuatu manajer memikirkan apa tujuan organisasinya, bagaimana mencapainya, bagaimana sumber dayanya, kapan selesainya. Pengorganisasian (Organizing): bagaimanajer mengelompokkan kegiatan-kegiatan yang ada dlm organisasinya, menempatkan orang-orang dan mengalokasi sumber daya Kepemimpinan /mengarahkan (Leading) : bagaimanajer mempengaruhi bawahan agar mau bekerja dlm mancapai tujuan organisasi Pengendalian (Controlling) : bagaimanajer mengawal seluruh aktivitas dlm organisasinya agar tetap berada pada jalur yang benar (on the right track) 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 1– 83
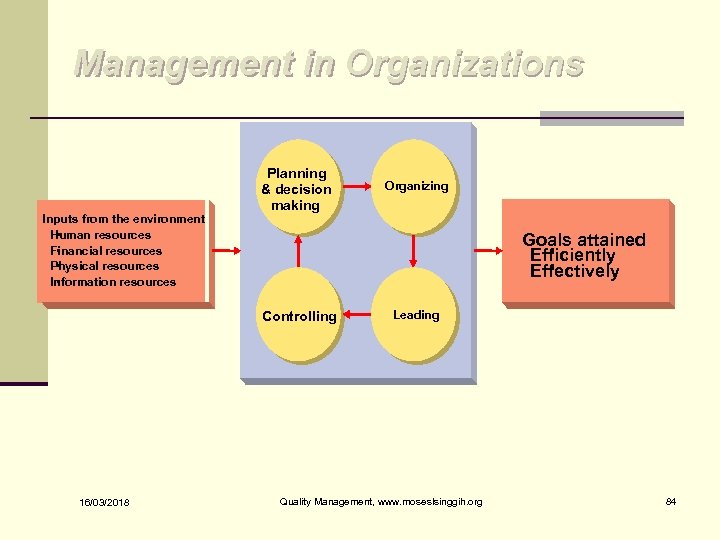 Management in Organizations Inputs from the environment • Human resources • Financial resources Physical resources • Information resources • Planning & decision making Goals attained • Efficiently • Effectively Controlling 16/03/2018 Organizing Leading Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 84
Management in Organizations Inputs from the environment • Human resources • Financial resources Physical resources • Information resources • Planning & decision making Goals attained • Efficiently • Effectively Controlling 16/03/2018 Organizing Leading Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 84
 Resources in Organizations n Human resources n Managerial talent and labor n Financial resources n Capital investments to support ongoing and long-term operations n Physical Assets n Raw materials; office and production facilities, and equipment n Information n 16/03/2018 Usable data, information linkages Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 1– 85
Resources in Organizations n Human resources n Managerial talent and labor n Financial resources n Capital investments to support ongoing and long-term operations n Physical Assets n Raw materials; office and production facilities, and equipment n Information n 16/03/2018 Usable data, information linkages Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 1– 85
 Goals: EFFICIENTLY Using resources wisely and in a cost-effective way And EFFECTIVELY Making the right decisions and successfully implementing them 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 86
Goals: EFFICIENTLY Using resources wisely and in a cost-effective way And EFFECTIVELY Making the right decisions and successfully implementing them 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 86
 Materi yang dibahas: n Quality Management n Quality n Management n Quality Management tools 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 87
Materi yang dibahas: n Quality Management n Quality n Management n Quality Management tools 16/03/2018 Quality Management, www. moseslsinggih. org 87


