lecture 6 27.03.2017.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 74
 QUALITY IN TOURISM AND RECREATION – 27. 03. 2017 Piotr Kociszewski, SGTi. R p. kociszewski@vistula. edu. pl
QUALITY IN TOURISM AND RECREATION – 27. 03. 2017 Piotr Kociszewski, SGTi. R p. kociszewski@vistula. edu. pl
 AGENDA OF LECTURES 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Term QUALITY. Services in tourism and their features. Tourism system – 20. 02. 2017 r. Quality management in tourism. 27. 02. 2017 r. The role of people in creating quality in tourism. 6. 03. 2017 The role of people (2), TQM (1). 13. 03. 2017 r. TQM (2) Complex Quality Management System. 20. 03. 2017 Quality in different types of tourism services. 27. 03. 2017 r. Quality in recreation. 3. 04. 2017 r. Final written credit – OPEN TEST 10. 04. 2017 r. 60% to pass!!! All information from lectures + (? ) literature 2
AGENDA OF LECTURES 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Term QUALITY. Services in tourism and their features. Tourism system – 20. 02. 2017 r. Quality management in tourism. 27. 02. 2017 r. The role of people in creating quality in tourism. 6. 03. 2017 The role of people (2), TQM (1). 13. 03. 2017 r. TQM (2) Complex Quality Management System. 20. 03. 2017 Quality in different types of tourism services. 27. 03. 2017 r. Quality in recreation. 3. 04. 2017 r. Final written credit – OPEN TEST 10. 04. 2017 r. 60% to pass!!! All information from lectures + (? ) literature 2
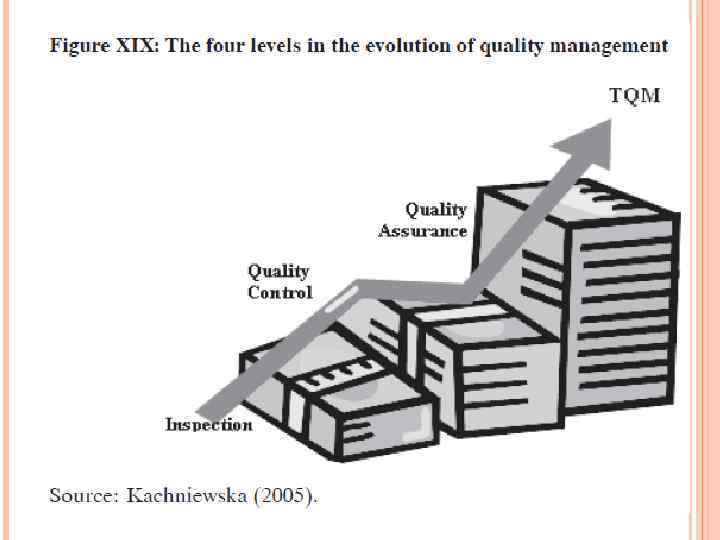 3
3
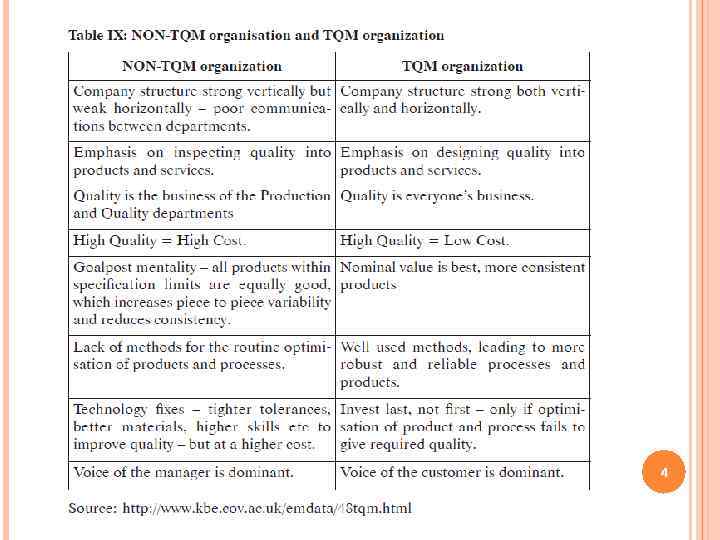 4
4
 IMPORTANT FACTORS • Type of employees: • Skill level • Level of education • Length of employment longer better ? • Age distribution old workforce / young workforce • Level of external customer contact • Shared values: • Attitude towards change SALARY • Business performance • Organization’s age WORKING CONDITIONS • Work methods 5
IMPORTANT FACTORS • Type of employees: • Skill level • Level of education • Length of employment longer better ? • Age distribution old workforce / young workforce • Level of external customer contact • Shared values: • Attitude towards change SALARY • Business performance • Organization’s age WORKING CONDITIONS • Work methods 5
 IMPORTANT FACTORS • Organizational structure: • Number of sites • Stability of organizational structure • Geographic integration • Number of employees • Quality development 6
IMPORTANT FACTORS • Organizational structure: • Number of sites • Stability of organizational structure • Geographic integration • Number of employees • Quality development 6
 TQM Concept in a Tourism Destination Area Tourists’ needs are met not just by one product or service but by three elements of the area’s attraction (3 As): accessibility, attractions, amanities (Holloway, 1996). Quality management of TDA includes the recognition of all the factors, products, services which create the image of quality destination in the eyes of tourists. 7
TQM Concept in a Tourism Destination Area Tourists’ needs are met not just by one product or service but by three elements of the area’s attraction (3 As): accessibility, attractions, amanities (Holloway, 1996). Quality management of TDA includes the recognition of all the factors, products, services which create the image of quality destination in the eyes of tourists. 7
 8
8
 9
9
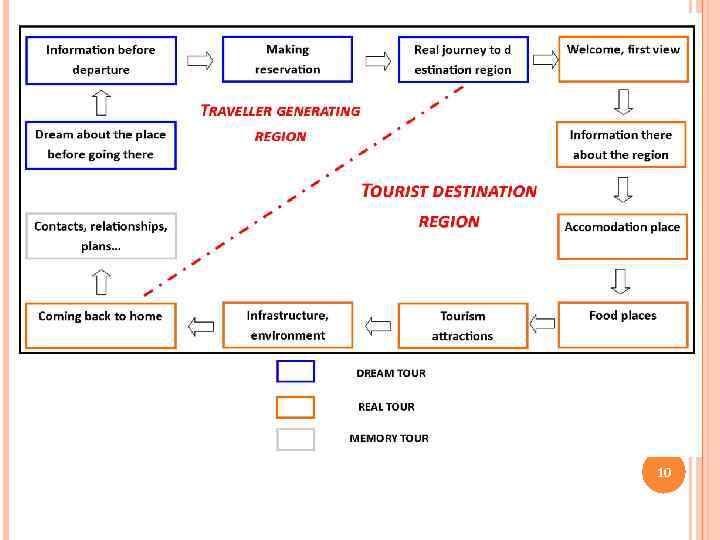 10
10
 11
11
 12
12
 13
13
 14
14
 15
15
 16
16
 17
17
 18
18
 19
19
 20
20
 21
21
 22
22
 23
23
 24
24
 25
25
 26
26
 27
27
 The International organization for standardization (ISO) WHAT IS ISO? At February 2007 156 national members 179 active TCs 3 000 technical bodies 50 000 experts • IT tools • Standards development procedures • Consensus building • Dissemination Central Secretariat in Geneva 150 staff
The International organization for standardization (ISO) WHAT IS ISO? At February 2007 156 national members 179 active TCs 3 000 technical bodies 50 000 experts • IT tools • Standards development procedures • Consensus building • Dissemination Central Secretariat in Geneva 150 staff
 ISO KEY MISSION STATEMENT To be the leading value adding platform and partner for the production of global and market relevant International Standards covering products, services, good conformity assessment, management and organizational practices
ISO KEY MISSION STATEMENT To be the leading value adding platform and partner for the production of global and market relevant International Standards covering products, services, good conformity assessment, management and organizational practices
 WHO IS IOS AND WHAT IS ISO? • The International Organization for Standardization (IOS) is a worldwide federation of national standards bodies. • Working through Technical Committees, it has developed and published over 18, 000 different ISO standards that are used internationally for subjects ranging from film speeds to wine glasses to quality management systems. • The official purpose for the issuance of ISO Standards is to facilitate world trade through standardization.
WHO IS IOS AND WHAT IS ISO? • The International Organization for Standardization (IOS) is a worldwide federation of national standards bodies. • Working through Technical Committees, it has developed and published over 18, 000 different ISO standards that are used internationally for subjects ranging from film speeds to wine glasses to quality management systems. • The official purpose for the issuance of ISO Standards is to facilitate world trade through standardization.
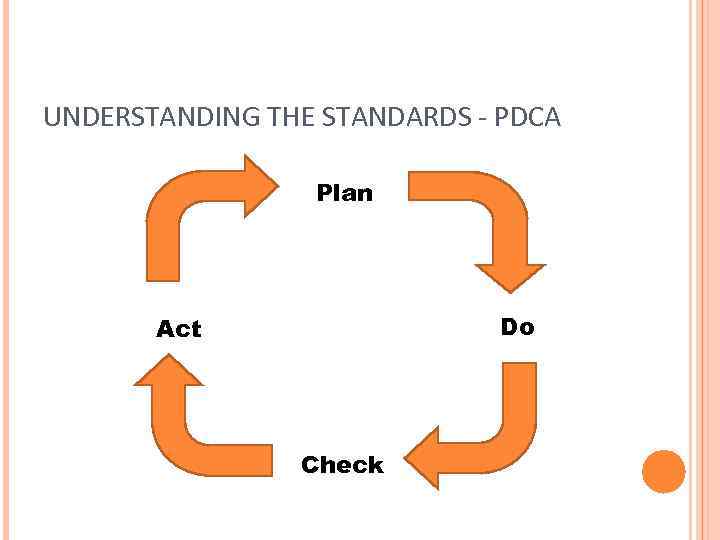 UNDERSTANDING THE STANDARDS - PDCA Plan Do Act Check
UNDERSTANDING THE STANDARDS - PDCA Plan Do Act Check
 32
32
 33
33
 34
34
 35
35
 36
36
 37
37
 38
38
 39
39
 40
40
 41
41
 42
42
 43
43
 44
44
 45
45
 46
46
 47
47
 48
48
 49
49
 50
50
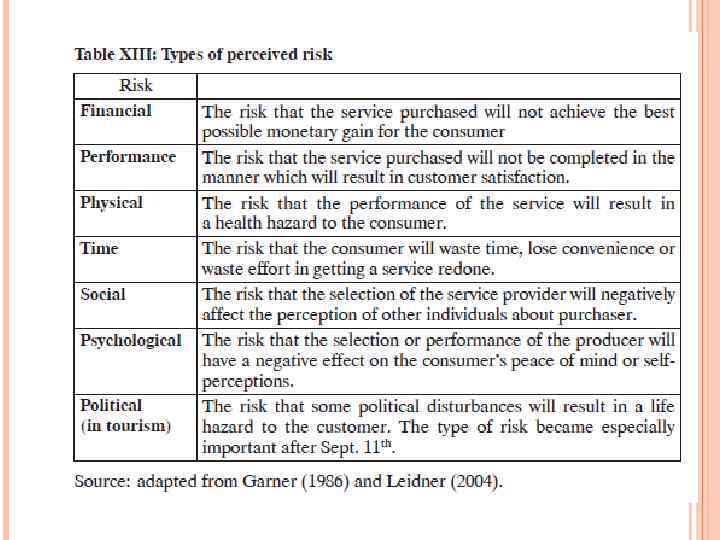
 To minimize these risks, consumers seek to reduce the uncertainty surrounding the purchase decision (Mangan and Collins, 2002). Different forms of information can be used by enterprises as risk reducing strategy. They include the use of brands, symbols, quality levels etc. 51
To minimize these risks, consumers seek to reduce the uncertainty surrounding the purchase decision (Mangan and Collins, 2002). Different forms of information can be used by enterprises as risk reducing strategy. They include the use of brands, symbols, quality levels etc. 51
 POSSIBILITIES OF SYMBOLIZING QUALITY Classification (category, class, grade, rating) – which relates basically to physical attributes of the establishment. Brands (trademarks) – can replace classification whereby each brand may stand for a specific class and include a series of quality attributes. Accordingly, a brand may be representative of a certain service idiom and level of quality. Commercial brands are protected by intellectual property rights. 52
POSSIBILITIES OF SYMBOLIZING QUALITY Classification (category, class, grade, rating) – which relates basically to physical attributes of the establishment. Brands (trademarks) – can replace classification whereby each brand may stand for a specific class and include a series of quality attributes. Accordingly, a brand may be representative of a certain service idiom and level of quality. Commercial brands are protected by intellectual property rights. 52
 53
53
 54
54
 55
55
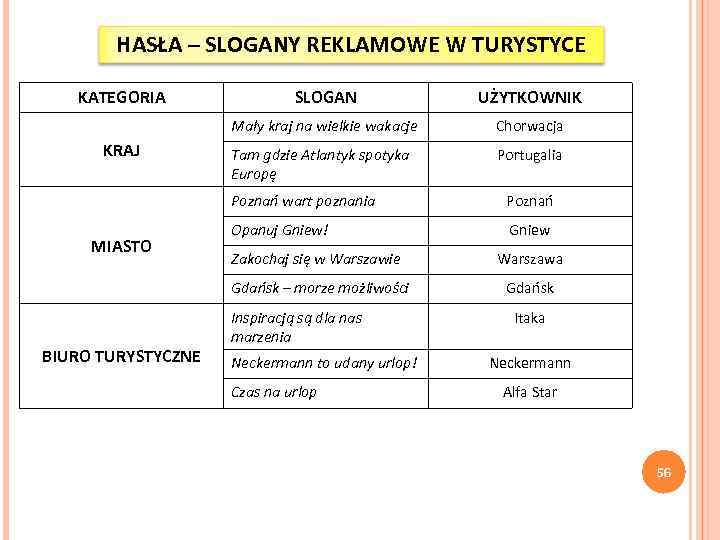 HASŁA – SLOGANY REKLAMOWE W TURYSTYCE KATEGORIA UŻYTKOWNIK Mały kraj na wielkie wakacje KRAJ SLOGAN Chorwacja Tam gdzie Atlantyk spotyka Europę Portugalia Poznań wart poznania MIASTO Poznań Opanuj Gniew! Gniew Warszawa Gdańsk – morze możliwości BIURO TURYSTYCZNE Zakochaj się w Warszawie Gdańsk Inspiracją są dla nas marzenia Neckermann to udany urlop! Czas na urlop Itaka Neckermann Alfa Star 56
HASŁA – SLOGANY REKLAMOWE W TURYSTYCE KATEGORIA UŻYTKOWNIK Mały kraj na wielkie wakacje KRAJ SLOGAN Chorwacja Tam gdzie Atlantyk spotyka Europę Portugalia Poznań wart poznania MIASTO Poznań Opanuj Gniew! Gniew Warszawa Gdańsk – morze możliwości BIURO TURYSTYCZNE Zakochaj się w Warszawie Gdańsk Inspiracją są dla nas marzenia Neckermann to udany urlop! Czas na urlop Itaka Neckermann Alfa Star 56
 57
57
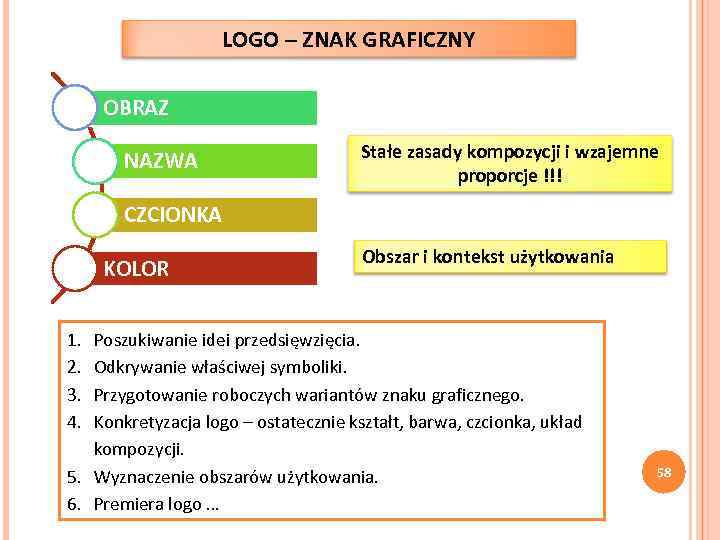 LOGO – ZNAK GRAFICZNY OBRAZ NAZWA Stałe zasady kompozycji i wzajemne proporcje !!! CZCIONKA KOLOR Obszar i kontekst użytkowania 1. 2. 3. 4. Poszukiwanie idei przedsięwzięcia. Odkrywanie właściwej symboliki. Przygotowanie roboczych wariantów znaku graficznego. Konkretyzacja logo – ostatecznie kształt, barwa, czcionka, układ kompozycji. 5. Wyznaczenie obszarów użytkowania. 6. Premiera logo … 58
LOGO – ZNAK GRAFICZNY OBRAZ NAZWA Stałe zasady kompozycji i wzajemne proporcje !!! CZCIONKA KOLOR Obszar i kontekst użytkowania 1. 2. 3. 4. Poszukiwanie idei przedsięwzięcia. Odkrywanie właściwej symboliki. Przygotowanie roboczych wariantów znaku graficznego. Konkretyzacja logo – ostatecznie kształt, barwa, czcionka, układ kompozycji. 5. Wyznaczenie obszarów użytkowania. 6. Premiera logo … 58
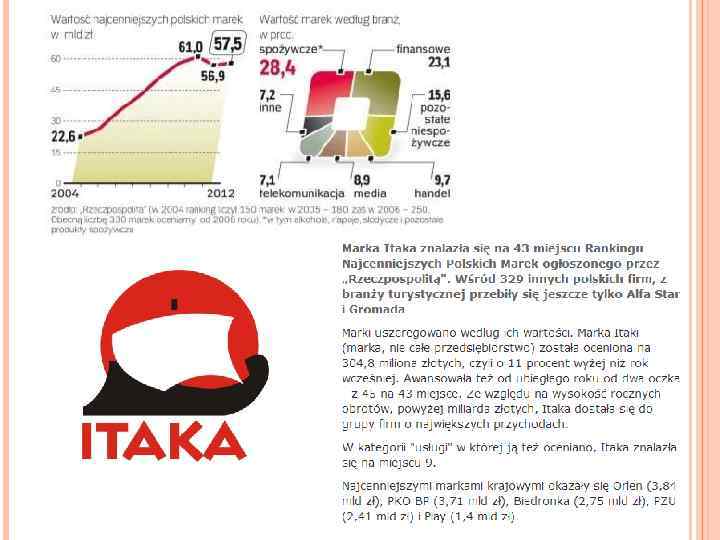 59
59
 60
60
 61
61
 62
62
 63
63
 64
64
 65
65
 66
66
 67
67
 68
68
 69
69
 70
70
 71
71
 72
72
 73
73
 74
74


