63973a4612938284e597df4161571744.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 126

Quality in The Clinical Microbiology Laboratory Microbiology Department KUMS Dr. Mohajeri

Positive Patient outcome in the Microbiology laboratory l Reduced length of stay l Reduced cost of stay l Reduced turn-around time for diagnosis of infection l Change to appropriate antimicrobial therapy l Customer (physician or patients) satisfaction

QC program l The laboratory director is primarily responsible for QC and QA programs. However all laboratory personnel must actively participate in both program
The basic elements of QC l Specimens collection and transport. l Standard operating procedures (SOP) l Personnel Proficiency testing Performance checks Antimicrobial Susceptibility tests (AST) Maintenance of QC stocks Patients reports

SPECIMEN COLLECTION AND TRANSPORT l The laboratory is responsible for providing instructions for the proper collection and transport of specimens. l These instructions should be available to instructions available the clinical staff for use when specimens collected.

Written collection instruction l Test selection criteria l Patients selection criteria l Timing of specimen collection (e. g. , Before antimicrobial are administration) l Optimal specimen collection site l Approved specimen collection method l Specimen transport medium
Continue… l Specimen transport time and temperature l Specimen holding instructions if it cannot be transported immediately (e. g. hold at 4ºC for 24 hours) l Availability of test (on –site or sent to reference laboratory ) l Hours test performed (daily or batch) l Result reporting procedures

Information should be filled l Patient name l Hospital or laboratory number l Ordering physician l Whether the patient receiving antimicrobial therapy l Suspect agent or syndrome

Criteria for unacceptable specimens l Unlabeled or mislabeled specimens Unlabeled mislabeled l Use of improper transport medium l Excessive transport time l Improper temperature during transport or storage Improper temperature l Improper collection site for test request Improper collection site l Specimen leakage out of transport container Specimen leakage l Sera that are excessively hemolyzed , lipemic or contaminated with bacteria
Sections of Standard operating Procedure (SOP) l l l Title (name of procedure) Principle (reason for performing the test) Preferred specimen patient preparation Transport container (need for anticoagulant, preservative or holding medium) Transportation conditions (wet ice, room temperature). Specimen storage in Laboratory (room temperature, 4°C, -20°C, - 10°C) Criteria for unacceptable specimen (delay in transport, leaking container, presence of barium) Special safety precautions (tape plates for AFB or brucellae) Reagents or media required and incubation conditions Examination of cultures Guidelines for identification and susceptibility testing by culture type (respiratory, urine, blood, stool) Required quality control

Continue. . l l l methods for reporting positive, negative and unsatisfactory results Technical notes, including possible sources of error and helpful hints References The SPOM should be available in the work area. It is the definitive laboratory reference and is used often for questions relating to individual test.

Personnel l It is laboratory director's responsibility to employ sufficient qualified personnel for the volume and complexity of the work performed. l Document competency and training twice a year training l Continuing education program should be education program provided l All documentation should maintained in documentation personnel file
Proficiency Testing l Laboratories are required to participate in an external proficiency testing (PT) external proficiency testing l The laboratory must maintain an average score of 80% to maintain licensure in any subspecialty area. l The laboratory's procedures, reagents, equipments and personnel are all checked in the process.

PT or External quality control l Provide laboratory management with an insight into their performance l Improve both local and national standards l Reveals unsuspected area of difficulty l Provides an educational stimulate for improvements l Acts as a check on the efficacy of internal quality control procedures l Demonstrates to colleagues and customers a commitment to quality

Performance Checks l Instrument name, serial number and date nstrument put use l Procedure and periodicity (daily, weekly, monthly) for routine function check l Acceptable performance ranges l Date and time of services requests and response

Continue. . l Maintenance records should be retained in the laboratory for the life of instrument. Specific guidelines regarding periodicity of testing for autoclaves, biological softy testing cabinets, centrifuges, incubators, microscope, refrigerators, freezers, water bathes, heat blocks and other microbiology laboratory can be found in reference books.

Commercially Prepared Culture Media l The CLSI subcommittee on media quality control collected data over several years regarding the incidence of QC failure of commonly used microbiology media Based on its finding the subcommittee published a list of media that did not require retesting in the user's laboratory if purchased from a manufactures who follow CLSI guidelines

User-Prepared and Nonexempt, commercially prepared Media l QC forms for user-prepared media should contain: - The amount of prepared - The source of each ingredient - The lot number - Sterilization methods - The preparation date - The expiration date (Usually 1 month for agar plate and 6 month for tube media) - The name of prepare

All user prepared media also should checked for: - Proper color - Depth - Smoothness - Hemolysis - Excessive bubbles - Contamination

Sterility Check l A representative sample of the lot should be test for sterility; 5% of any lot is tested 5% when a batch of 100 or fewer unit is received and maximum of 10 units are tested in large batches. Sterility is routinely checked by incubating the medium for 48 hours at the temperature at which it will be used.

Performance testing When medium dose need to quality controlled because it was prepared “in house (in the laboratory) or because it is complex, several basic rules must be followed: l QC testing should be performed according to CLSI recommendation l All media must be tested before use

l Each medium must be tested with organisms expected to give positive reaction as well as withy organism expected either not to grow or produce a negative reaction l The medium should be tested for sterility and p. H l The organisms selected for QC should represent the most fastidious organisms for which the medium was designed

l Testing technique should be different for primary plating media that for biochemical or subculture media. Primary plating media should be tested with dilute suspensions of organisms, whereas biochemical media can be tested with undiluted organisms. l Expiration date must be established
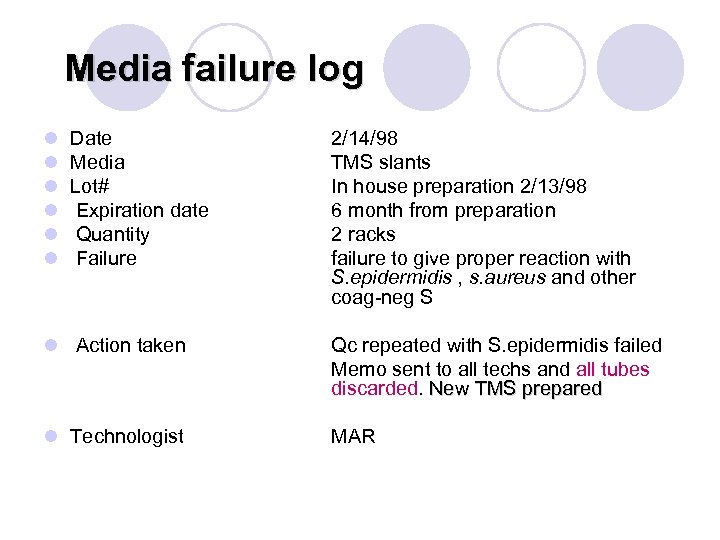
Media failure log l l l Date Media Lot# Expiration date Quantity Failure 2/14/98 TMS slants In house preparation 2/13/98 6 month from preparation 2 racks failure to give proper reaction with S. epidermidis , s. aureus and other coag-neg S l Action taken Qc repeated with S. epidermidis failed Memo sent to all techs and all tubes discarded. New TMS prepared l Technologist MAR

Use of Stock Cultures l To operate a quality control program, stock culture must be maintained by all laboratories. They are available from many sources. l Commercial sources l Proficiency testing l Patients isolates l American Type Culture Collection (ATCC)

l When quality control testing appears have failed, quality control testing appears have failed it is usually the stock culture rather than the test itself that has failed. Organisms may mutate with repeated sub culturing. for best results , a stock culture should be grown in a large volume of broth, then divided among enough small freezer vials to last a year.

l With this technique a new vial can be removed from the freezer weekly so that organism do not have to be continually subcultured l An organism may need to be subcultured twice after thawing to return it to a healthy state. after thawing l Media selection for freezing is at the discretion of selection for freezing individual laboratories but should not contain sugar. l If organism utilize sugar while being maintained, the acid products that result may kill organism with time.

Popular Media for Stock Cultures l Schaeler broth with glycerol l Chopped meat (anaerobes) l Tryptic Soy agar deeps (at room temperature) l Cystein-tryptic agar (CTA) without carbohydrates l Nonfastidious (rapidly growing), aerobic bacterial organisms can be saved up to 1 years on TSA slants.

l Long –term storage of aerobes or anaerobes can be accomplished either by lyophilizartion (freeze drying) or freezing, at -70 C. l Frozen, no fastidious organism should be thawed, reisolated and refrozen every 5 years l fastidious organisms should be thawed reisolated , and refrozen every 3 years. l Stock isolated may be maintained by freezing them in 10% skim milk, Trypticase Soy Broth (TSB) with 15% glycerol.
Stain and Reagents l Containers of stains and reagents should be labeled as to: - contents - concentration - storage requirements - date prepared (or received) - date placed in service - expiration date - source (commercial manufacture or user prepared) and lot number.

- All stains and reagents should be stored according manufacture's recommendations and tested with positive recommendations and negative controls before use.

Antisera l The lot number, date received, condition received, and expiration date must be recorded for all shipments of antisera. l In addition, the antisera should be dated when opened. l New lots must be tested concurrently with previous lots, and testing must include positive and negative controls

Maintence of QC records l All QC results should be recorded on an recorded appropriate QC form l In many laboratories the supervisor reviews and initials all forms weekly and the director then reviews each one monthly. l QC records should be maintained for at least 2 years except those on equipment, which must be saved for the life of instrument.

Patient Report l The laboratory should established a system for supervisory of all laboratory reports. l Reports should be given only authorized by law to receive them.

Continue. . l Clinician should be notified about ‘’panic values’’ immediately. l Panic values are potential-threatening results, for example positive Gram stain for CSF or a positive blood culture. l All patients records should be maintained for least 2 years.

Have a nice time

ANTIBACTERIAL SUSCEPTIBILITY TEST (AST)

Material & Equipment l Antibiotic Disks l 0. 5 Macfarland suspension l Mueller-Hinton Agar l Incubator Also Panel of Antibiotics Zone Diameter Interpretive Standards
Indications The disk diffusion methods are standardized for testing rapidly growing pathogens, which include Staphylococcus spp. , Enterococcus spp. , the Enterobacteriaceae, P. aeruginosa, Acinetobacter spp. , Burkholderia cepacia, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, and Vibrio cholerae, and they have been modified for testing fastidious organisms such as Haemophilus spp. , N. gonorrhoeae, N. meningitidis and streptococci
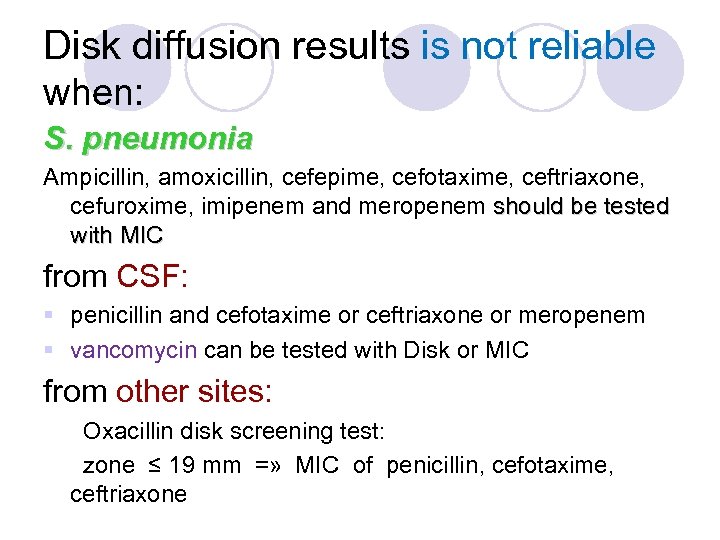
Disk diffusion results is not reliable when: S. pneumonia Ampicillin, amoxicillin, cefepime, cefotaxime, ceftriaxone, cefuroxime, imipenem and meropenem should be tested with MIC from CSF: § penicillin and cefotaxime or ceftriaxone or meropenem § vancomycin can be tested with Disk or MIC from other sites: Oxacillin disk screening test: zone ≤ 19 mm =» MIC of penicillin, cefotaxime, ceftriaxone

ﺷﺮﺍﻳﻂ ﻣﺤﻴﻂ ﻣﻮﻟﺮ ﻫﻴﻨﺘﻮﻥ • • )4. 7 -2. 7( p. H ﻏﻠﻈﺖ ﻛﺎﺗﻴﻮﻥ ﻫﺎ ) ﺑﻪ ﻧﺴﺒﺘﻲ ﺩﺭ ﻧﻈﺮ گﺮﻓﺘﻪ ﺷﺪﻩ ﻛﻪ ﺭﻗﺎﺑﺖ ﺑﺎ آﻨﺘﻲ ﺑﻴﻮﺗﻴﻚ ﻫﺎ ﻛﻪ ﺑﺎﺭ ﻣﺜﺒﺖ ﺩﺍﺭﻧﺪ پﻴﺶ ﻧﻴﺎﻳﺪ ( ﻋﻤﻖ ﻣﺤﻴﻂ ﻧﺴﺒﺖ ﺗﻴﻤﻴﻦ ﻭ ﺗﻴﻤﻴﺪﻳﻦ

p. H l ﺍگﺮ p. H ﻛﻤﺘﺮ ﺍﺯ 2. 7 ﺑﺎﺷﺪ ﺩﺍﺭﻭﻫﺎﻳﻲ ﻣﺎﻧﻨﺪ aminoglycosides, quinolones, macrolides ﺗﻮﺍﻧﺎﻳﻲ ﺧﻮﺩ ﺭﺍ ﺍﺯ ﺩﺳﺖ ﻣﻲ ﺩﻫﻨﺪ ﺩﺭ ﺣﺎﻟﻲ ﻛﻪ ﺗﺘﺮﺍﺳﺎﻳﻜﻠﻴﻦ ﻫﺎ ﻓﻌﺎﻟﻴﺖ ﺷﺎﻥ ﺑﻴﺸﺘﺮ ﻣﻲ ﺷﻮﺩ l ﺍگﺮ p. H ﺑﻴﺸﺘﺮ ﺍﺯ 4. 7 ﺑﺎﺷﺪ ﺍﺛﺮ ﺑﺮﺧﻲ ﺩﺍﺭﻭﻫﺎ ﻣﺘﻀﺎﺩ ﻣﻲ ﺷﻮﺩ

ﺍﺛﺮﺍﺕ ﺗﻐﻴﻴﺮ ﺩﺭ ﻛﺎﺗﻴﻮﻥ ﻫﺎﻱ ﺩﻭﻇﺮﻓﻴﺘﻲ l ﺗﻐﻴﻴﺮ ﺩﺭ ﻣﻘﺪﺍﺭ ﻛﺎﺗﻴﻮﻥ ﻫﺎﻱ ﺩﻭ ﻇﺮﻓﻴﺘﻲ ﺑﺨﺼﻮﺹ ﻛﻠﺴﻴﻢ ﻭ ﻣﻨﻴﺰﻳﻢ ﺩﺭ ﻭﺍﻛﻨﺶ ﺳﻮﺩﻭﻣﻮﻧﺎﺱ آﺌﺮﻭژﻴﻨﻮﺯﺍ ، ﺩﺭ ﻣﻘﺎﺑﻞ آﻤﻴﻨﻮگﻼﻳﻜﻮﺯﻳﺪﻫﺎ ﻭ ﺗﺘﺮﺍﺳﻴﻜﻠﻴﻦ ﺍﻫﻤﻴﺖ ﺩﺍﺭﺩ. ﻛﺎﺗﻴﻮﻥ ﺑﺎﻻ ﺍﻧﺪﺍﺯﻩ ﺯﻭﻥ ﺭﺍ ﻛﻢ ﻛﺮﺩﻩ ﺩﺭ ﺣﺎﻟﻴﻜﻪ ﻛﺎﺗﻴﻮﻥ ﻛﻢ ، ﺯﻭﻥ ﺭﺍ ﺑﺰﺭگﺘﺮ ﻧﺸﺎﻥ ﻣﻲ ﺩﻫﺪ. l ﺑﺮﻋﻜﺲ ﺩﺭ ﻣﻮﺭﺩ ﺩﺍپﺘﻮﻣﺎﻳﺴﻴﻦ، ﻛﻠﺴﻴﻢ پﺎﻳﻴﻦ ﺯﻭﻥ ﺭﺍ ﻛﻢ ﻭ ﻛﻠﺴﻴﻢ ﺑﺎﻻ ﺯﻭﻥ ﺑﺰﺭگﺘﺮﻱ ﻧﺸﺎﻥ ﻣﻲ ﺩﻫﺪ. l ﺩﺭ ﻣﻮﺭﺩ ﻛﺮﺑﺎپﻨﻢ ﺍگﺮ ﻳﻮﻥ ﺭﻭﻱ ﺯﻳﺎﺩ ﺑﺎﺷﺪ ﺯﻭﻥ ﻛﻮچﻚ ﺗﺮﻱ ﺑﻮﺟﻮﺩ ﻣﻲ آﻴﺪ.

ﺍﺛﺮ ﺗﻴﻤﻴﻦ ﻭ ﺗﻴﻤﻴﺪﻳﻦ l ﻣﻮﻟﺮ ﻫﻴﻨﺘﻮﻥ آگﺎﺭ ﺩﺍﺭﺍﻱ ﻣﻘﺪﺍﺭ ﻣﺸﺨﺼﻲ ﺗﻴﻤﻴﻦ ﻭ ﺗﻴﻤﻴﺪﻳﻦ ﺍﺳﺖ ﻛﻪ ﺍﺛﺮ ﻣﻤﺎﻧﻌﺘﻲ ﺗﺮﻱ ﻣﺘﻮپﺮﻳﻢ ﻭ ﺳﻮﻟﻔﻮﻧﺎﻣﻴﺪ ﺭﺍ ﻣﻬﺎﺭ ﻣﻲ ﻛﻨﺪ. l ﺍگﺮ ﺍﻳﻦ ﻣﻮﺍﺩ ﻧﺒﺎﺷﻨﺪ آﻨﺘﻲ ﺑﻴﻮﺗﻴﻚ ﻣﺰﺑﻮﺭ ﺯﻭﻥ ﻛﻢ ﻭ ﻧﺎﻣﺸﺨﺺ ﻳﺎ ﺻﻔﺮ ﺍﻳﺠﺎﺩ ﻣﻲ ﻛﻨﺪ ﻛﻪ ﺳﺒﺐ گﺰﺍﺭﺵ ﻣﻘﺎﻭﻣﺖ ﻛﺎﺫﺏ ﻣﻲ ﺷﻮﺩ.
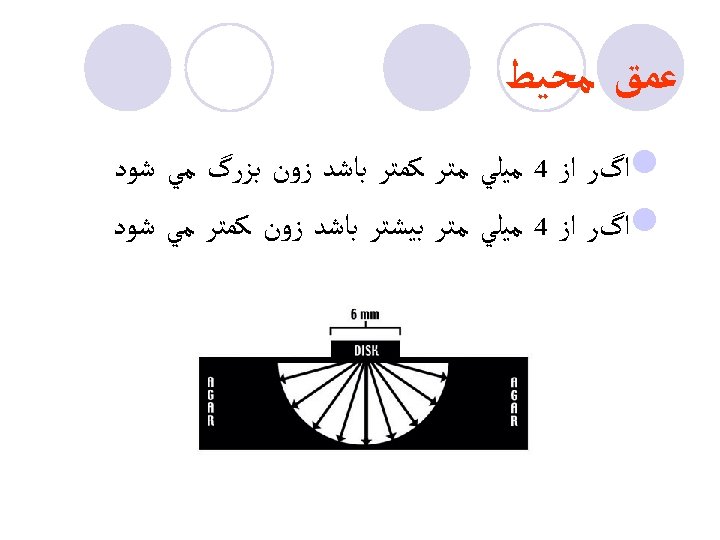
ﻋﻤﻖ ﻣﺤﻴﻂ l ﺍگﺮ ﺍﺯ 4 ﻣﻴﻠﻲ ﻣﺘﺮ ﻛﻤﺘﺮ ﺑﺎﺷﺪ ﺯﻭﻥ ﺑﺰﺭگ ﻣﻲ ﺷﻮﺩ l ﺍگﺮ ﺍﺯ 4 ﻣﻴﻠﻲ ﻣﺘﺮ ﺑﻴﺸﺘﺮ ﺑﺎﺷﺪ ﺯﻭﻥ ﻛﻤﺘﺮ ﻣﻲ ﺷﻮﺩ

ﺭﻭﺵ ﺗﻬﻴﻪ 5. 0 ﻣﻚ ﻓﺎﺭﻟﻨﺪ 0. 5 ml of 0. 048 M Ba. Cl 2 (1. 175% w/v Ba. Cl 2. H 2 O ) to 99. 5 ml of 0. 36 N H 2 SO 4 ( 1% v/v ) Mc. Farland standard, the absorbance at a wavelength of 625 nm should be 0. 08 to 0. 1 ﻣﻚ ﻓﺎﺭﻟﻨﺪ ﺭﺍ ﺩﺭ ﺣﺮﺍﺭﺕ ﺍﺗﺎﻕ ﺩﺭ ﺟﺎﻱ ﺗﺎﺭﻳﻚ ﻗﺮﺍﺭ ﺩﺍﺩﻩ ﻭ ﻫﺮ ﻣﺎﻩ ﻳﻚ ﺑﺎﺭ ﺑﺮﺭﺳﻲ . ﻧﻤﺎﻳﻴﺪ

ﺷﺮﺍﻳﻂ ﻛﺸﺖ l l l l l ﺍﻧﺪﺍﺯﻩ ﺗﻠﻘﻴﺢ ﺣﺮﺍﺭﺕ ﺍﻧﻜﻮﺑﺎﺳﻴﻮﻥ ) ﺍﺯ 35 °C ﻛﻤﺘﺮ ﺑﺎﺷﺪ ﺯﻣﺎﻥ ﺭﺷﺪ ﻃﻮﻻﻧﻲ ﻭ ﻫﺎﻟﻪ ﻭﺳﻴﻊ ﻣﻲ ﺷﻮﺩ ، ﺍﺯ °C 53 ﺑﻴﺸﺘﺮ ﺑﺎﺷﺪ ﺭﻭﻱ OX ﺗﺎﺛﻴﺮ ﺩﺍﺭﺩ ( ﺍﺗﻤﺴﻔﺮ ﺍﻧﻜﻮﺑﺎﺳﻴﻮﻥ )ﻛﻨﺪﻝ ﺟﺎﺭ ﻗﺮﺍﺭ ﻧﻤﻲ گﻴﺮﺩ چﻮﻥ 2 CO ﺳﺒﺐ ﻣﻲ ﺷﻮﺩ p. H ﻣﺤﻴﻂ ﺍﺳﻴﺪﻱ ﺷﻮﺩ ﺩﺭ ﺣﺎﻟﻴﻜﻪ ﺑﺎﻳﺪ ﺧﻨﺜﻲ ﺑﺎﺷﺪ ( ﻣﺪﺕ ﺍﻧﻜﻮﺑﺎﺳﻴﻮﻥ 81 ﺳﺎﻋﺖ ) ﺩﺭ ﻣﻮﺍﻗﻊ ﺍﻭﺭژﺎﻧﺲ 6 ﺳﺎﻋﺖ ( ) Supplement ﺧﻮﻥ ، %1 ، Hb ﺍﻳﺰﻭﻭﻳﺘﺎﻝ ، 1% X ﻓﺎﻛﺘﻮﺭ X ﻭ ( V ﺩﻳﺮ ﻗﺮﺍﺭ ﺩﺍﺩﻥ ﺩﻳﺴﻚ ﺭﻭﻱ پﻠﻴﺖ ﺳﺒﺐ ﻣﻲ ﺷﻮﺩ ﺑﺎﻛﺘﺮﻱ ﺭﺷﺪ ﻭ ﻗﻄﺮ ﻫﺎﻟﻪ ﻛﺎﻫﺶ ﻳﺎﺑﺪ ﺗﺎﺭﻳﺦ ﺍﻧﻘﻀﺎﻱ ﺩﻳﺴﻚ : ﺍگﺮ ﺩﻳﺴﻚ ﻛﻬﻨﻪ ﺑﺎﺷﺪ ﺍﺯ ﻗﺪﺭﺕ آﻦ ﻛﻢ ﻭ ﻗﻄﺮ ﻫﺎﻟﻪ ﻛﻢ ﻣﻲ ﺷﻮﺩ ﺟﺪﻭﻝ ﺍﺳﺘﺎﻧﺪﺍﺭﺩ ﻛﺎﺭﺧﺎﻧﻪ ﻭ ﻣﺮﺑﻮﻁ ﺑﻪ ﺑﻴﻤﺎﺭ پﺎﻧﻞ آﻨﺘﻲ ﺑﻴﻮﺗﻴﻚ ﻫﺎ

Streptococcus pneumoniae and Other Streptococcus spp. l Agar Medium The recommended medium for testing S. pneumoniae and other streptococci is Mueller-Hinton agar supplemented with 5% defibrinated sheep blood. 49 Health Reference Laboratory

Pure isolate

In Sailin or Broth

Direct inoculation l ﻣﺴﺘﻘﻴﻢ ﺍﺯ ﺑﺎﻛﺘﺮﻱ 42 ﺳﺎﻋﺖ ﺭﺷﺪ ﻛﺮﺩﻩ ﺗﻌﺪﺍﺩﻱ ﻛﻠﻨﻲ ﺩﺭ ﺳﺎﻟﻴﻦ %58. 0 ﻛﺸﺖ ﺩﺍﺩﻩ ﺗﺎ ﺑﻪ ﻭﺍﺣﺪ 5. 0 ﻣﻚ ﻓﺎﺭﻟﻨﺪ ﺑﺮﺳﺪ l ﺑﺮﺍﻱ ﻫﻤﻪ ﺑﺎﻛﺘﺮﻱ ﻫﺎ ﺧﺼﻮﺻﺎ ﺳﺨﺖ ﺭﺷﺪ ﻫﺎ

Growth Method ﻛﻠﻨﻲ ﻛﻬﻨﻪ ﺷﺪﻩ ﺑﺎﺷﺪ ﺍﺯ ﺭﺍﺱ ﻛﻠﻨﻲ ﺑﺮﻣﻲ ﺩﺍﺭﻳﻢ ﺗﺎ ﺑﻪ ﻓﺎﺯ ﻟگﺎﺭﻳﺘﻤﻲ ﺑﺮﺳﺪ ﻛﻠﻨﻲ ﻛﻢ ﺩﺍﺭﻳﻢ 2 -6 ﺳﺎﻋﺖ ﺩﺭ ﺍﻧﻜﻮﺑﺎﺗﻮﺭ ﺳپﺲ ﺑﺎ ﺷﺎﻫﺪ ﻣﻘﺎﻳﺴﻪ ﻣﻲ ﺷﻮﺩ

ﺳﻨﺠﺶ ﺣﺴﺎﺳﻴﺖ ﺑﺎ ﺭﻭﺵ ﻛﺮﺑﻲ ﺑﺎﺋﺮ l ﺭﺷﺪ ﺑﺎﻛﺘﺮﻱ ﺩﺭﻣﺤﻴﻂ ﻣﺎﻳﻊ ﺑﻪ ﻛﺪﻭﺭﺕ 5. 0 ﻭﺍﺣﺪ ﻣﻚ ﻓﺎﺭﻟﻨﺪ ﺭﺳﻴﺪﻩ ﺑﺎﺷﺪ l پﻠﻴﺖ ﻫﺎﻱ ﻣﻮﻟﺮ ﻫﻴﻨﺘﻮﻥ ﺑﻪ ﻗﻄﺮ 4 ﻣﻴﻠﻴﻤﺘﺮ آﻤﺎﺩﻩ ﺷﻮﻧﺪ l ﺑﻌﺪ ﺍﺯ پﺨﺶ ﺑﺎﻛﺘﺮﻱ چﻨﺪ ﺩﻗﻴﻘﻪ ﺍﻱ ﺻﺒﺮ ﻛﻨﻴﺪ ﺗﺎ ﺭﻃﻮﺑﺖ ﺍﺿﺎﻓﻲ ﺧﺎﺭﺝ ﺷﻮﺩ l ﺩﻳﺴﻚ ﻫﺎ ﺍﺯ ﻳﻚ ﺳﺎﻋﺖ ﻗﺒﻞ ﺍﺯ ﻓﺮﻳﺰﺭ ﺧﺎﺭﺝ ﺷﺪﻩ ﺑﺎﺷﻨﺪ l ﺩﺭ پﻠﻴﺖ 01 ﺳﺎﻧﺘﻴﻤﺘﺮﻱ 5 ﺩﻳﺴﻚ ﺑگﺬﺍﺭﻳﺪ ) ﻓﺎﺻﻠﻪ ﺩﻳﺴﻚ ﻫﺎ ﻣﺮﻛﺰ ﺑﻪ ﻣﺮﻛﺰ 5. 2 ﺳﺎﻧﺘﻴﻤﺘﺮ ﻭ ﺍﺯ ﻟﺒﻪ 1 ﺳﺎﻧﺘﻴﻤﺘﺮ ﺑﺎﺷﺪ (

Storage of Antimicrobial Disks Refrigerate the cartridges at 8 °C or below, or freeze at -14 °C or below until needed. Do not store the disks in a self-defrosting freezer. *** Sealed packages of disks that contain drugs from the β-lactam class should be stored frozen, except for a small working supply, which may be refrigerated for at most one week. *** Some labile agents (e. g. , imipenem, cefaclor, and clavulanic acid combinations) may retain greater stability if stored frozen until the day of use. 58 Health Reference Laboratory

ﻛﻨﺘﺮﻝ ﻛﻴﻔﻲ ﺳﻨﺠﺶ ﺣﺴﺎﺳﻴﺖ National Committee for ﺑﺎ ﺗﻮﺟﻪ ﺑﻪ ﺩﺳﺘﻮﺭﺍﺕ l Clinical Laboratory Standards (NCCLS ) Clinical and Laboratory Standards ﻭ ﺗﻤﺎﻡ ﻣﻮﺍﺭﺩ ﺭﻋﺎﻳﺖ ﻣﻲ گﺮﺩﺩ Institute (CLSI)
Tools of QC l Reference strains l Reagents & Equipments l Chart of acceptable limits for quality control strains l Quality control chart 60 Health Reference Laboratory

Quality Control Reference Strains l Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 l Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853 l Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 l Streptococcus faecalis ATCC 33186 l ATCC =American type culture collection
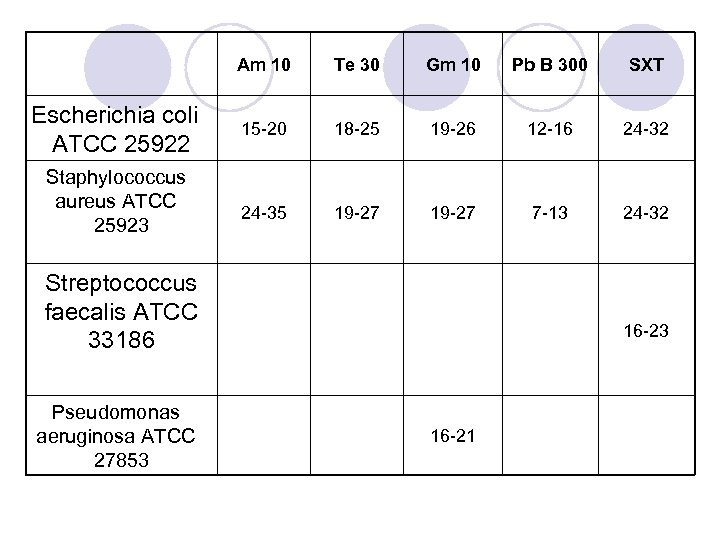
Am 10 Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 Te 30 Gm 10 Pb B 300 SXT 15 -20 18 -25 19 -26 12 -16 24 -32 24 -35 19 -27 7 -13 24 -32 Streptococcus faecalis ATCC 33186 Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853 16 -21

چگﻮﻧﻪ؟ 03 – 02 ﺭﻭﺯ ﻛﺎﺭﻱ ﻗﻄﺮ ﻫﺎﻟﻪ ﻋﺪﻡ ﺭﺷﺪ ﺑﺎ ﺭﻭﺵ ﺍﺳﺘﺎﻧﺪﺍﺭﺩ ﻭ ﺑﺎ ﺳﻮﺵ ﻫﺎﻱ ﺍﺳﺘﺎﻧﺪﺍﺭﺩ ﺑﺮﺭﺳﻲ ﻣﻲ ﺷﻮﺩ SXT ﻛﻨﺘﺮﻝ ﻛﻴﻔﻲ ﻣﺤﻴﻂ ﻣﻮﻟﺮ ﻫﻴﻨﺘﻮﻥ ﺑﺎ ﺍﻧﺘﺮﻭﻛﻮﻙ ﻓﻜﺎﻟﻴﺲ ﻭ ﺑﻪ ﺗﻌﺪﺍﺩ ﺯﻳﺎﺩ ﺩﺭ TSA ﺍﺳﺘﻮﻙ ﺳﻮﺵ ﻫﺎﻱ ﻛﻨﺘﺮﻝ ﻛﻴﻔﻲ ﺩﺭ -41 ﺩﺭﺟﻪ آﻤﺎﺩﻩ ﺑﺎﺷﻨﺪ ﻫﺮ ﻭﻳﺎﻝ ﺭﺍ 3 ﺑﺎﺭ ﻣﻲ ﺗﻮﺍﻥ ﺍﺳﺘﻔﺎﺩﻩ ﻛﺮﺩ ﻣﻮﺟﻮﺩ ﺑﺎﺷﺪ Cl. SI ﺟﺪﻭﻝ ﻛﻨﺘﺮﻝ ﻛﻴﻔﻲ ﻣﺴﺘﻨﺪ ﺳﺎﺯﻱ ) ﻧﺎﻡ ﺳﻮﻳﻪ ، ﻧﺎﻡ ﺩﻳﺴﻚ ، ﺗﺎﺭﻳﺦ ﺍﻧﺠﺎﻡ ﺗﺴﺖ (

Daily Testing Performance is satisfactory for daily QC testing when no more than 3 out of 30 consecutive results for each antimicrobial agent/organism combination are outside the acceptable limit Corrective action by the laboratory is required when this frequency is exceeded. 64 Health Reference Laboratory

Weekly Testing Test all applicable control strains for 20 or 30 consecutive test days and document results. To convert from daily to weekly quality control testing, no more than 1 out of 20 or 3 out of 30 zone diameters for each antimicrobial agent/organism combination may be outside the acceptable zone diameter limits. 65 Health Reference Laboratory

Error l. Random l. Systematic

Obvious reasons l use of the wrong disk; l use of the wrong control strain; l obvious contamination of the strain; or l inadvertent use of the wrong incubation temperature or conditions. 67 Health Reference Laboratory

Selecting Antimicrobial Agents for Testing and Reporting

ﺗﺴﺖ ﺣﺴﺎﺳﻴﺖ ﺩﺍﺭﻭﻳﻲ l ﺣﺴﺎﺱ : ﺑﻪ ﺍﺭگﺎﻧﻴﺰﻣﻲ ﺣﺴﺎﺱ ﺑﻪ ﺩﺍﺭﻭ گﻔﺘﻪ ﻣﻲ ﺷﻮﺩﻛﻪ ﻋﻔﻮﻧﺖ ﻧﺎﺷﻲ ﺍﺯ ﺍﻳﻦ ﺍﺭگﺎﻧﻴﺰﻡ ﺑﻪ ﺩﻭﺯ ﻗﺎﺑﻞ ﻗﺒﻮﻝ ﻭ ﺗﻮﺻﻴﻪ ﺷﺪﻩ آﻦ ﺩﺍﺭﻭ ﺑﻪ ﺧﻮﺑﻲ پﺎﺳﺦ ﺩﻫﺪ l ﺣﺴﺎﺳﻴﺖ ﻣﺘﻮﺳﻂ ﻳﺎ : Moderatly ﻳﻌﻨﻲ ﺑﻪ ﻃﻮﺭ ﻣﺘﻮﺳﻂ ﺑﻪ ﻣﺎﺩﻩ ﺿﺪ ﻣﻴﻜﺮﻭﺑﻲ ﺣﺴﺎﺳﻴﺖ ﻧﺸﺎﻥ ﺩﻫﺪ ﺩﺍﺭﻭﻫﺎﻳﻲ ﻣﺜﻞ ﺑﺘﺎﻻﻛﺘﺎﻡ ﻛﻪ ﺳﻤﻴﺖ پﺎﻳﻴﻨﻲ ﺩﺍﺭﻧﺪ ﺑﺎ ﺩﻭﺯ ﺑﺎﻻ ﻣﻲ ﺗﻮﺍﻧﻨﺪ ﺑﻜﺎﺭ ﺭﻭﻧﺪ l ﺣﺴﺎﺳﻴﺖ ﻧﺴﺒﻲ ﻳﺎ : Intermediate ﻣﺜﻞ آﻤﻴﻨﻮگﻼﻳﻜﻮﺯﻳﺪﻫﺎ ﻛﻪ ﺳﻤﻴﺖ ﺷﺪﻳﺪ ﺩﺍﺭﻧﺪ ﺑﺎ ﺩﻭﺯ ﺑﺎﻻ ﻧﻤﻲ ﺗﻮﺍﻥ ﺍﺳﺘﻔﺎﺩﻩ ﻛﺮﺩ ﻭ ﺩﺭ ﺍﻳﻦ ﺣﺎﻟﺖ ﻣﻘﺎﻭﻡ گﺰﺍﺭﺵ ﻣﻲ ﺷﻮﺩ l ﻣﻘﺎﻭﻡ : ﺑﺎ ﺗﻮﺟﻪ ﺑﻪ Range ﻛﻨﺘﺮﻝ ﻣﻘﺎﻭﻡ ﺍﺳﺖ ﺍﻣﺎ گﺎﻫﻲ پﺰﺷﻚ ﺑﺎ ﺩﺭ ﻧﻈﺮ گﺮﻓﺘﻦ ﻓﺎﻛﺘﻮﺭ ﻫﺎﻳﻲ آﻦ ﺩﺍﺭﻭ ﺭﺍ ﺗﺠﻮﻳﺰ ﻣﻲ ﻧﻤﺎﻳﺪ ) ﺍﻫﻤﻴﺖ ﺑﻴﻤﺎﺭﻱ ﺯﺍﻳﻲ ﺑﺎﻛﺘﺮﻱ ، ﺍﺛﺮﺍﺕ ﺳﺎﺧﺘﻤﺎﻧﻲ ﺩﺍﺭﻭ، ﻧﻔﻮﺫ ﻭ ﺍﻧﺘﺸﺎﺭ ﺩﺍﺭﻭ ﺩﺭ ﻗﺴﻤﺘﻬﺎﻱ ﻣﺨﺘﻠﻒ ﺑﺪﻥ ﻭ ﻭﺿﻌﻴﺖ ﺳﻴﺴﺘﻢ ﺍﻳﻤﻨﻲ ﺑﻴﻤﺎﺭ (
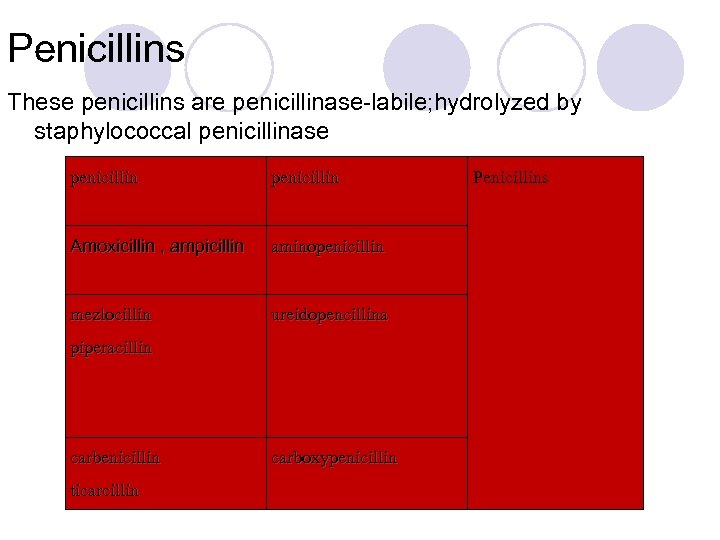
Penicillins These penicillins are penicillinase-labile; hydrolyzed by staphylococcal penicillinase penicillin Amoxicillin , ampicillin aminopenicillin mezlocillin ureidopencillina piperacillin carbenicillin ticarcillin carboxypenicillin Penicillins

Penicillinase-stable penicillin Cloxacillin Dicloxacillin Meticillin Nafcillin oxacillin
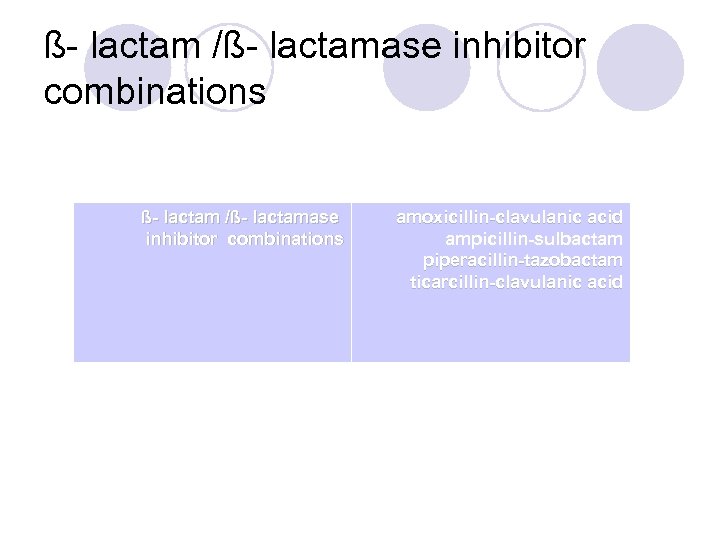
ß- lactam /ß- lactamase inhibitor combinations ß- lactam /ß- lactamase inhibitor combinations amoxicillin-clavulanic acid ampicillin-sulbactam piperacillin-tazobactam ticarcillin-clavulanic acid

Cephems

“Warning”: The following antimicrobial agents should not be routinely reported for bacteria isolated from CSF . These antimicrobial agents are not the drugs of choice and may not be effective for treating CSF infections caused by these organisms ü agents administered by oral route only ü 1 st- and 2 nd-generation cephalosporins (except cefuroxime sodium) üClindamycin - macrolides - tetracyclines - fluoroquinolones
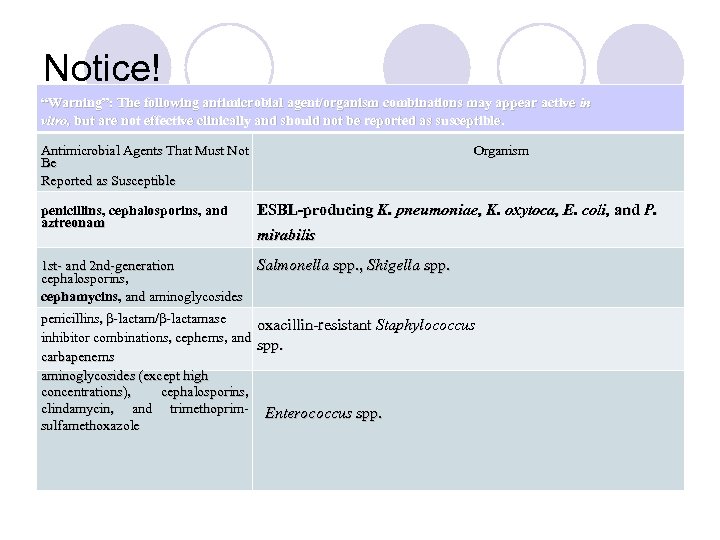
Notice! “Warning”: The following antimicrobial agent/organism combinations may appear active in vitro, but are not effective clinically and should not be reported as susceptible. Antimicrobial Agents That Must Not Be Reported as Susceptible penicillins, cephalosporins, and aztreonam Organism ESBL-producing K. pneumoniae, K. oxytoca, E. coli, and P. mirabilis 1 st- and 2 nd-generation Salmonella spp. , Shigella spp. cephalosporins, cephamycins, and aminoglycosides penicillins, β-lactam/β-lactamase oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus inhibitor combinations, cephems, and spp. carbapenems aminoglycosides (except high concentrations), cephalosporins, clindamycin, and trimethoprim- Enterococcus spp. sulfamethoxazole
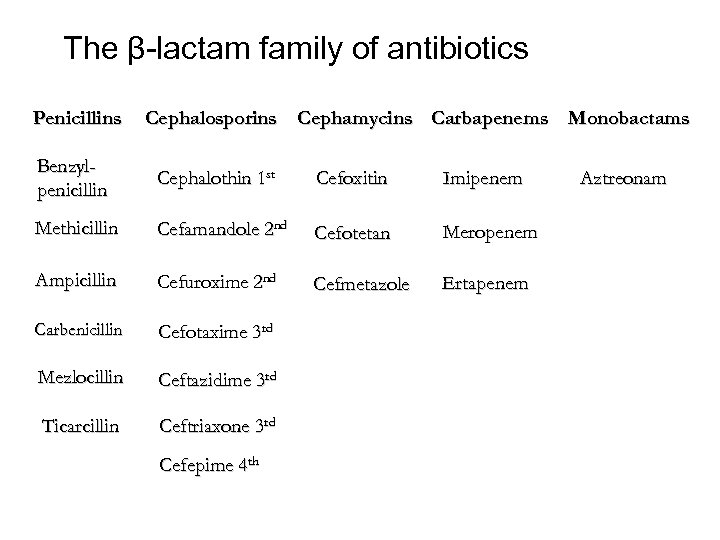
The β-lactam family of antibiotics Penicillins Cephalosporins Cephamycins Carbapenems Monobactams Benzylpenicillin Cephalothin 1 st Cefoxitin Imipenem Methicillin Cefamandole 2 nd Cefotetan Meropenem Ampicillin Cefuroxime 2 nd Cefmetazole Ertapenem Carbenicillin Cefotaxime 3 rd Mezlocillin Ceftazidime 3 rd Ticarcillin Ceftriaxone 3 rd Cefepime 4 th Aztreonam

Beta-lactamase inhibitors l Resemble β-lactam antibiotic structure l Bind to β-lactamase and protect the antibiotic from destruction l Most successful when they bind the βlactamase irreversibly l Three important in medicine ¡Clavulanic acid ¡Sulbactam ¡Tazobactam
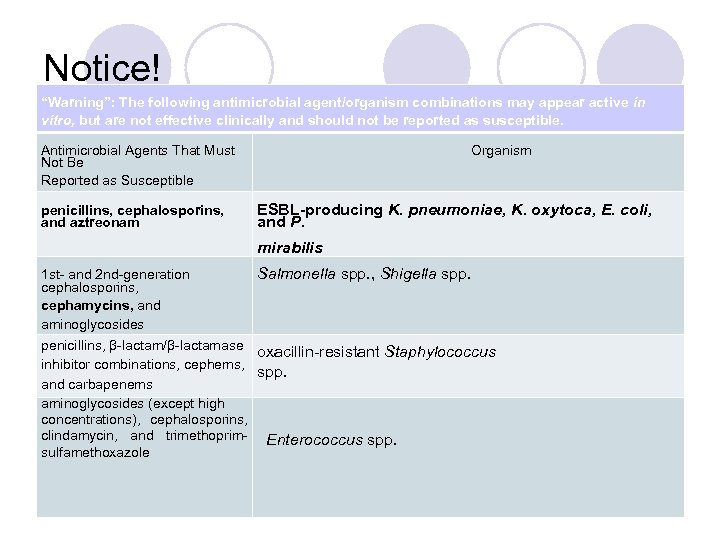
Notice! “Warning”: The following antimicrobial agent/organism combinations may appear active in vitro, but are not effective clinically and should not be reported as susceptible. Antimicrobial Agents That Must Not Be Reported as Susceptible penicillins, cephalosporins, and aztreonam Organism ESBL-producing K. pneumoniae, K. oxytoca, E. coli, and P. mirabilis 1 st- and 2 nd-generation cephalosporins, cephamycins, and aminoglycosides penicillins, β-lactam/β-lactamase inhibitor combinations, cephems, and carbapenems aminoglycosides (except high concentrations), cephalosporins, clindamycin, and trimethoprim- sulfamethoxazole Salmonella spp. , Shigella spp. oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus spp. Enterococcus spp.

Misleading Results Dangerously misleading results can occur when certain antimicrobial agents are tested and reported as susceptible against specific organisms. These combinations include, but may not be limited to, the following: • first- and second-generation cephalosporins and aminoglycosides against. Salmonella and Shigella spp. ; • all β-lactam antimicrobial agents (except oxacillin, methicillin, and nafcillin) against smethicillin-resistant staphylococci; • cephalosporins, aminoglycosides (except testing for high-level resistance), clindamycin, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole against enterococci; • cephalosporins and aztreonam against ESBL-producing K. pneumoniae, K. oxytoca, E. coli, and P. mirabilis.
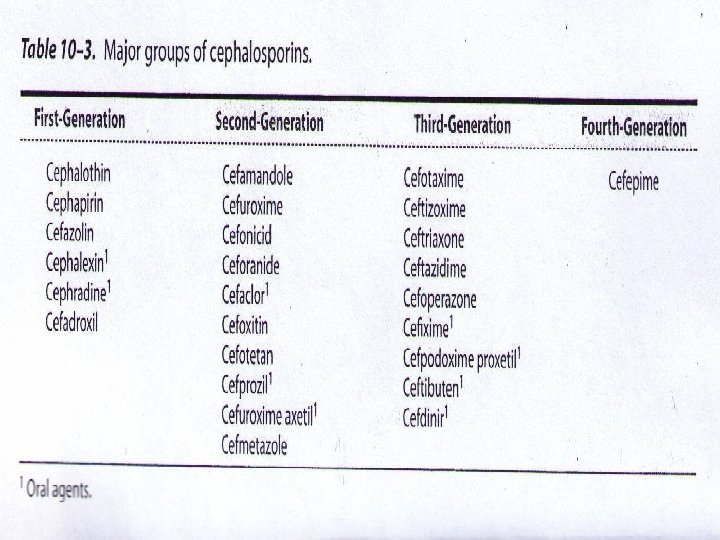
Pseudomona s aeroginosa Suggested panel for routine testing & reporting Uri ne Imipenem meropene m Ofloxaci n gentamyci n piperacili n Amikaci n cefepim e ceftazidi me Ciprofloxaci n levofloxacin
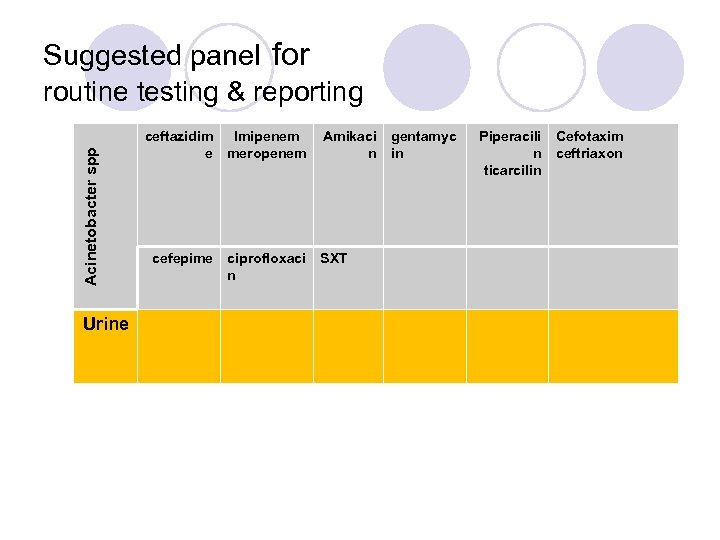
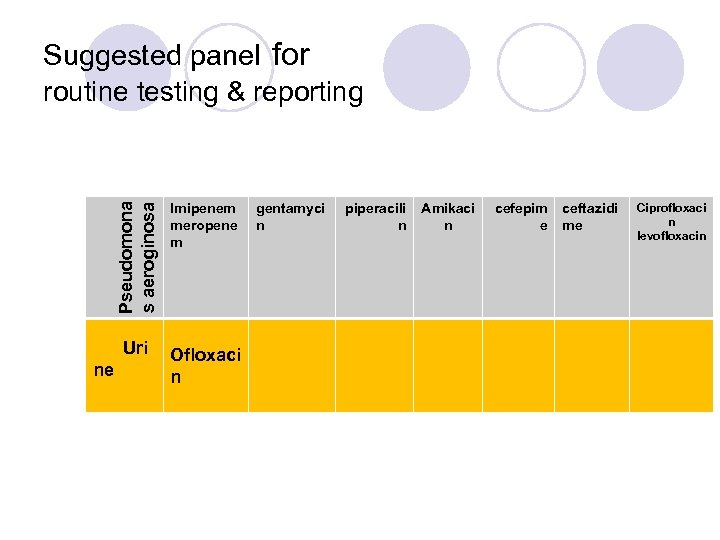
Acinetobacter spp Suggested panel for routine testing & reporting Urine ceftazidim Imipenem e meropenem cefepime ciprofloxaci n Amikaci n SXT gentamyc in Piperacili n ticarcilin Cefotaxim ceftriaxon

Salmonella and Shigella When fecal isolates of Salmonella and Shigella spp. are tested, only ampicillin, a quinolone, and trimethoprimsulfamethoxazole should be reported routinely. In addition, chloramphenicol and a third- generation cephalosporin should be tested and reported for extraintestinal isolates of Salmonella spp.
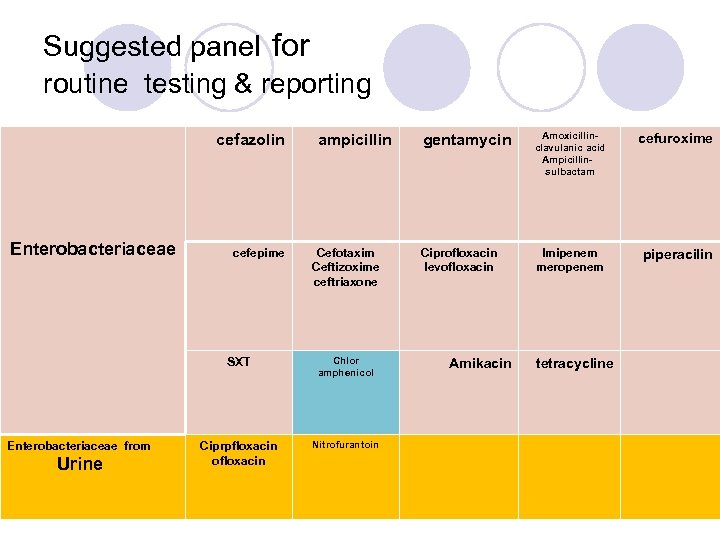
Suggested panel for routine testing & reporting cefazolin Enterobacteriaceae cefepime ampicillin Cefotaxim Ceftizoxime ceftriaxone SXT Enterobacteriaceae from Urine Chlor amphenicol Ciprpfloxacin ofloxacin Nitrofurantoin gentamycin Amoxicillinclavulanic acid Ampicillin- sulbactam cefuroxime Ciprofloxacin levofloxacin Imipenem meropenem piperacilin Amikacin tetracycline

staphylococcus Penicillin-susceptible staphylococci are also susceptible to other penicillins, cephems, and carbapenems approved for use by the FDA for staphylococcal infections. Penicillin-resistant, oxacillin- susceptible strains are resistant to penicillinaselabile penicillins, but susceptible to other penicillinase-stable penicillins, β-lactam/β-lactamase inhibitor combinations, relevant cephems, and carbapenems. Oxacillin-resistant staphylococci are resistant to all currently available β-lactam antibiotics. Thus, susceptibility or resistance to a wide array of β-lactam antibiotics may be deduced from testing only penicillin and oxacillin. Routine testing of other penicillins, β-lactamase inhibitor combinations, cephems, and carbapenems is not advised.
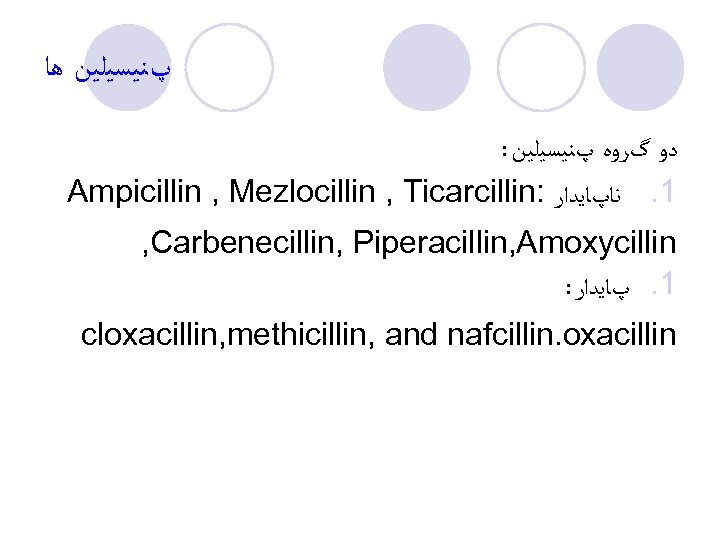
پﻨﻴﺴﻴﻠﻴﻦ ﻫﺎ : ﺩﻭ گﺮﻭﻩ پﻨﻴﺴﻴﻠﻴﻦ Ampicillin , Mezlocillin , Ticarcillin: 1. ﻧﺎپﺎﻳﺪﺍﺭ , Carbenecillin, Piperacillin, Amoxycillin : 1. پﺎﻳﺪﺍﺭ cloxacillin, methicillin, and nafcillin. oxacillin
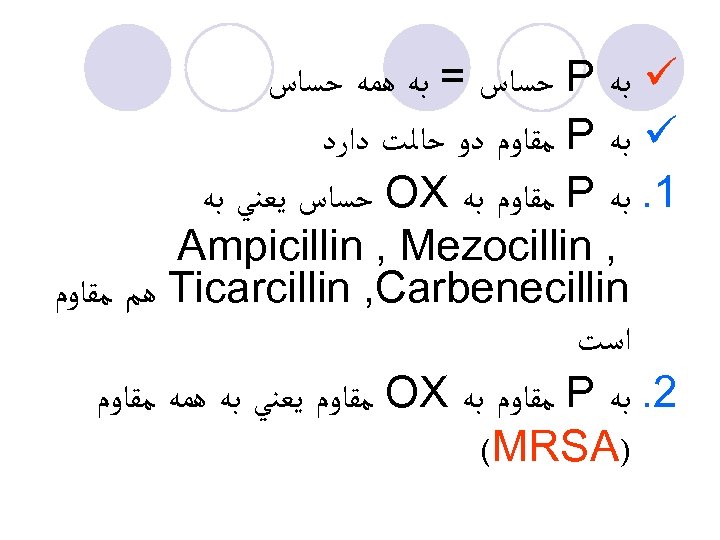
ü ﺑﻪ P ﺣﺴﺎﺱ = ﺑﻪ ﻫﻤﻪ ﺣﺴﺎﺱ ü ﺑﻪ P ﻣﻘﺎﻭﻡ ﺩﻭ ﺣﺎﻟﺖ ﺩﺍﺭﺩ 1. ﺑﻪ P ﻣﻘﺎﻭﻡ ﺑﻪ OX ﺣﺴﺎﺱ ﻳﻌﻨﻲ ﺑﻪ , Ampicillin , Mezocillin Ticarcillin , Carbenecillin ﻫﻢ ﻣﻘﺎﻭﻡ ﺍﺳﺖ 2. ﺑﻪ P ﻣﻘﺎﻭﻡ ﺑﻪ OX ﻣﻘﺎﻭﻡ ﻳﻌﻨﻲ ﺑﻪ ﻫﻤﻪ ﻣﻘﺎﻭﻡ ) (MRSA

MRSA l Penicillin-resistant, oxacillin- susceptible strains are resistant to penicillinaselabile penicillins, but susceptible to other penicillinase-stable penicillins, βlactam/β-lactamase inhibitor combinations, relevant cephems, and carbapenems.

MRSA Oxacillin-resistant staphylococci are resistant to all currently available βlactam antibiotics.

cefoxitin disk test The cefoxitin disk test is the preferred method for testing S. aureus, S. lugdunensis, and coagulase-negative staphylococci for resistance to the penicillinase-stable penicillins. Cefoxitin is used as a surrogate for detecting oxacillin resistance; report oxacillin as susceptible or resistant based on the cefoxitin result.

Vancomycin All staphylococcal isolates for which vancomycin zone diameters are 14 mm or less should be tested by a reference MIC method.
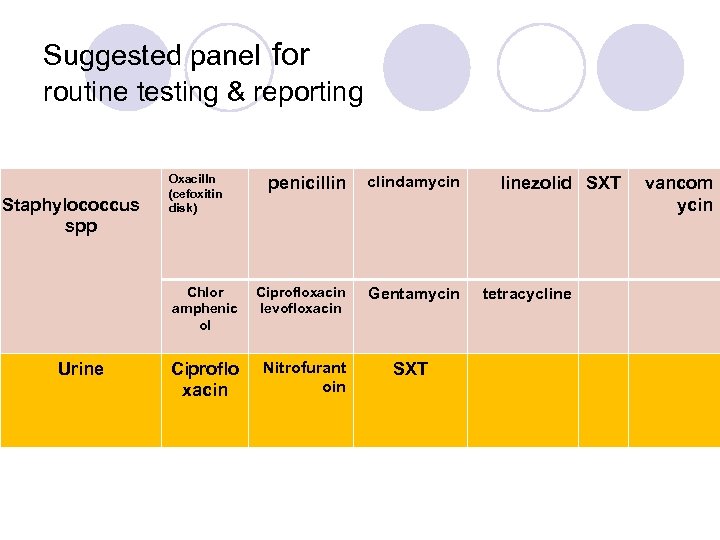
Suggested panel for routine testing & reporting Oxacilln (cefoxitin disk) Urine clindamycin Chlor amphenic ol Staphylococcus spp penicillin Ciprofloxacin levofloxacin Gentamycin Ciproflo xacin Nitrofurant oin SXT linezolid SXT tetracycline vancom ycin

Warning For Enterococcus spp. , cephalosporins, aminoglycosides (except for high-level resistance screening), clindamycin, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole may appear active in vitro, but are not effective clinically, and isolates should not be reported as susceptible.
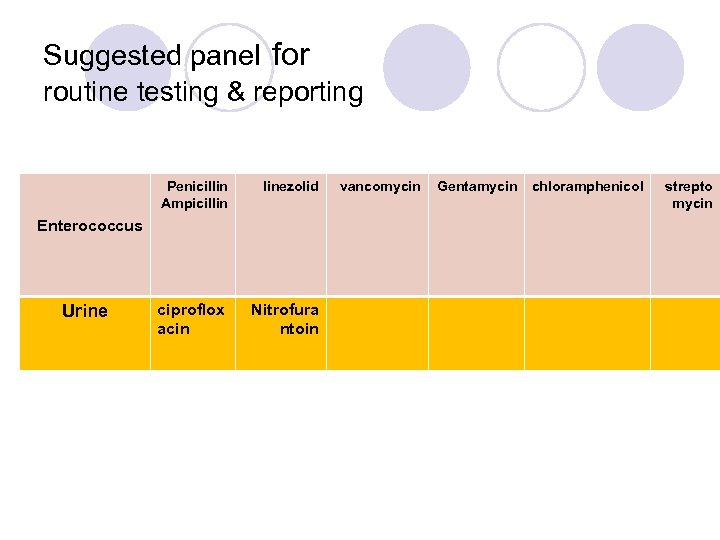
Suggested panel for routine testing & reporting Penicillin Ampicillin linezolid ciproflox acin Nitrofura ntoin Enterococcus Urine vancomycin Gentamycin chloramphenicol strepto mycin

Enterococcus ß lactamase - enterococcus : susceptible to penicillin, ampicillin, amoxicillin, ampicillin sulbactam, amoxicillin-clavulanic acid, piperacillin tazobactam Prediction with: penicillin disk test ß lactamase + enterococcus : Resistant to penicillin, ampicillin, amoxicillin, ampicillin sulbactam, amoxicillin-clavulanic acid, piperacillin tazobactam a β-lactamase test is the only reliable test for detecting β-lactamase-producing Enterococcus spp.

Alternative drugs for VRE Because of limited alternatives, chloramphenicol, erythromycin, tetracycline (or doxycycline or minocycline), and rifampin may be tested for vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE), And consultation with an infectious disease practitioner is recommended.

Pneumococcus from CSF =MIC penicillin and cefotaxime or ceftriaxone or meropenem Vancomycin (MIC or Disk)

Pneumococcus from other sites: Oxacillin Disk Screening Test zone ≤ 19 mm =» MIC of penicillin, cefotaxime, ceftriaxone
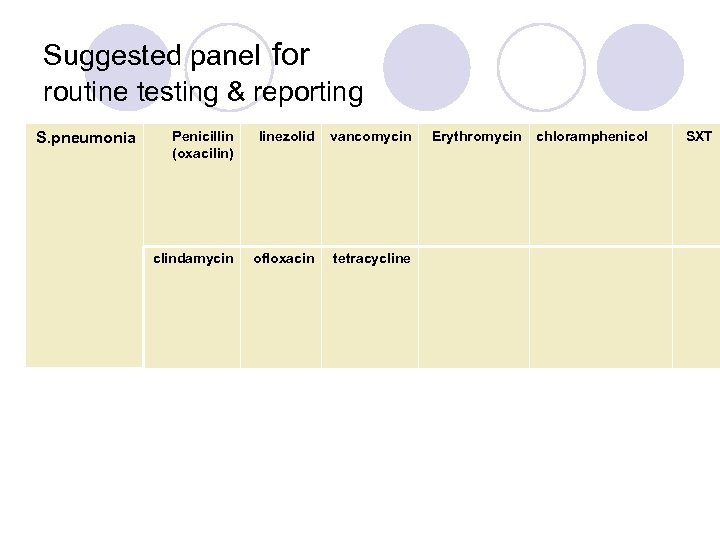
Suggested panel for routine testing & reporting S. pneumonia Penicillin (oxacilin) linezolid vancomycin clindamycin ofloxacin tetracycline Erythromycin chloramphenicol SXT

Extended-Spectrum-β Lactamase ESBLs Strains of Klebsiella spp. E. coli, and P. mirabilis that produce ESBLs may be clinically resistant to therapy with penicillins, cephalosporins, or aztreonam, despite apparent in vitro susceptibility to some of these agents.

l Some of these strains will show zones of inhibition below the normal susceptible population, but above the standard breakpoints for certain extended-spectrum cephalosporins or aztreonam; such strains may be screened for potential ESBL production by using the screening breakpoints. Other strains may test intermediate or resistant by standard breakpoints to one or more of these agents.

CAZ ﺳﻔﺘﺎﺯﻳﺪﻳﻢ CTX ﺳﻔﻮﺗﺎﻛﺴﻴﻢ ﺳﻔﻮﺭﻭﻛﺴﻴﻢ
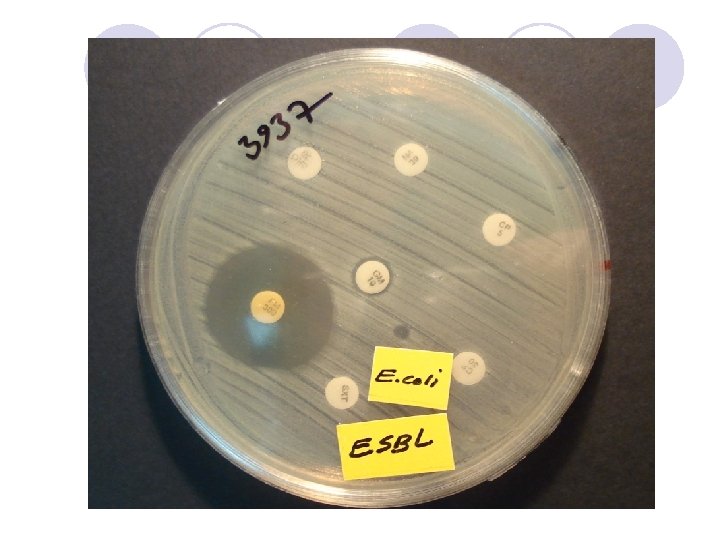
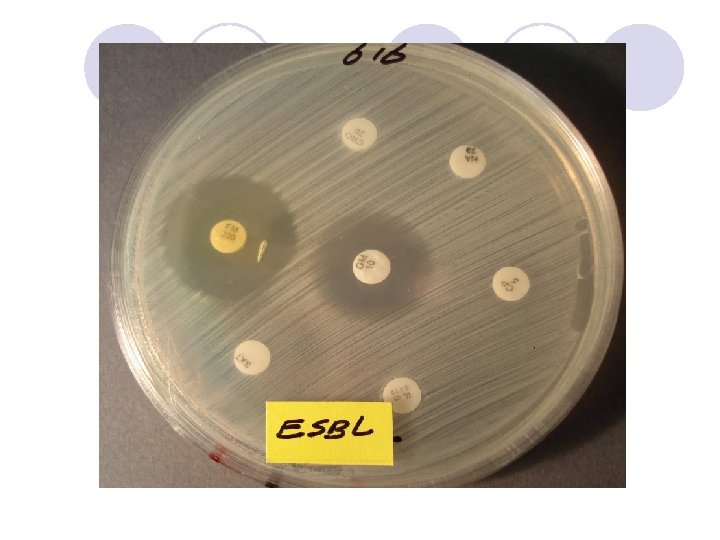
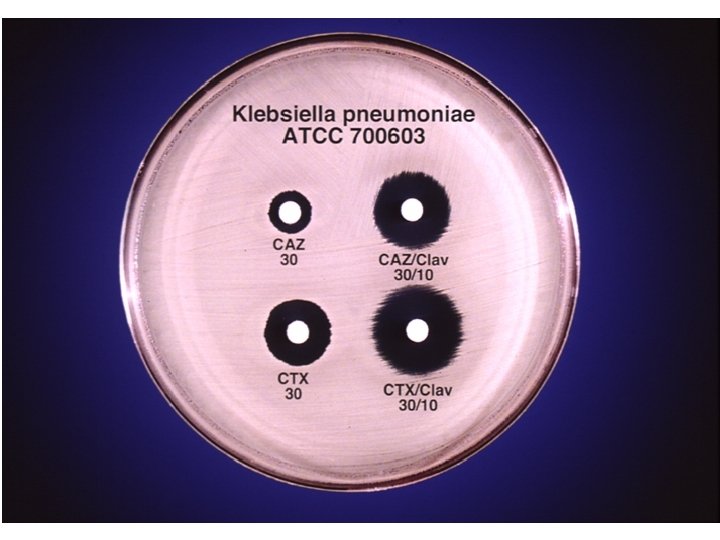
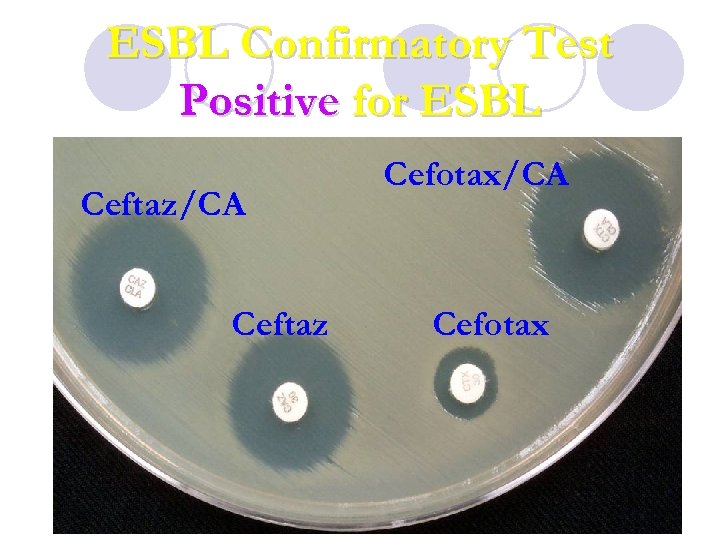
ESBL Confirmatory Test Positive for ESBL Ceftaz/CA Ceftaz Cefotax/CA Cefotax

E-test for detection of ESBLs AB Biodisk (Solna, Sweden) has introduced a two sided ESBL E-test strip that contain either a combination of ceftazidime and ceftazidime/clavulanic acid or cefotaxime and cefotaxime /clavulanic acid
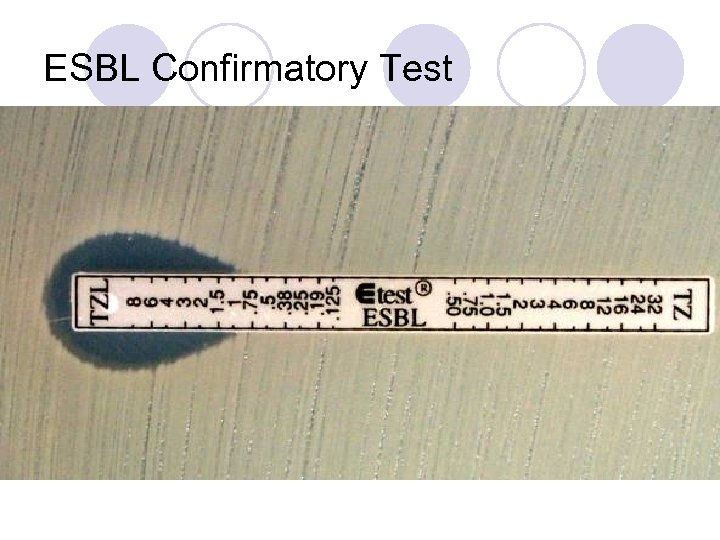
ESBL Confirmatory Test

l In all strains with ESBLs, the zone diameters for one or more of the extended-spectrum cephalosporins should increase in the presence of clavulanic acid.

آﻴﺎ ﻛﺮﺑﻲ ﺑﺎﺋﺮ پﺎﺳﺨگﻮﻱ ﻫﻤﻪ ﺑﺎﻛﺘﺮﻱ ﻫﺎﻣﻲ ﺑﺎﺷﺪ ؟ l The disk diffusion methods are standardized for testing rapidly growing pathogens, which include Staphylococcus spp. , Enterococcus spp. , the Enterobacteriaceae, aeruginosa, Acinetobacter spp. , Burkholderia cepacia, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, and Vibrio cholerae, and they have been modified for testing fastidious organisms such as Haemophilus spp. , N. gonorrhoeae, N. meningitidis, and streptococci

Disk diffusion results is not reliable when: S. Pneumonia ampicillin, amoxicillin, cefepime, cefotaxime, ceftriaxone, cefuroxime, imi penem and meropenem should be tested with MIC from CSF: § penicillin and cefotaxime or ceftriaxone or meropenem § vancomycin can be tested with Disk or MIC from other sites Oxacillin disk screening test: zone ≤ 19 mm =» MIC of penicillin, cefotaxime, ceftriaxone

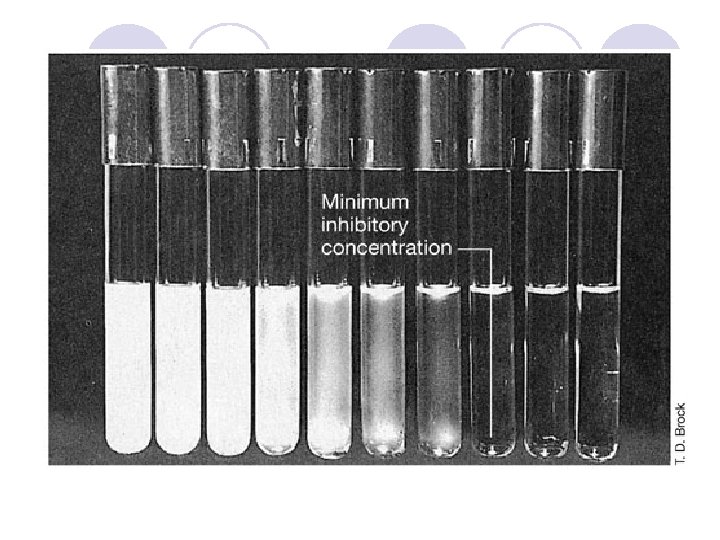
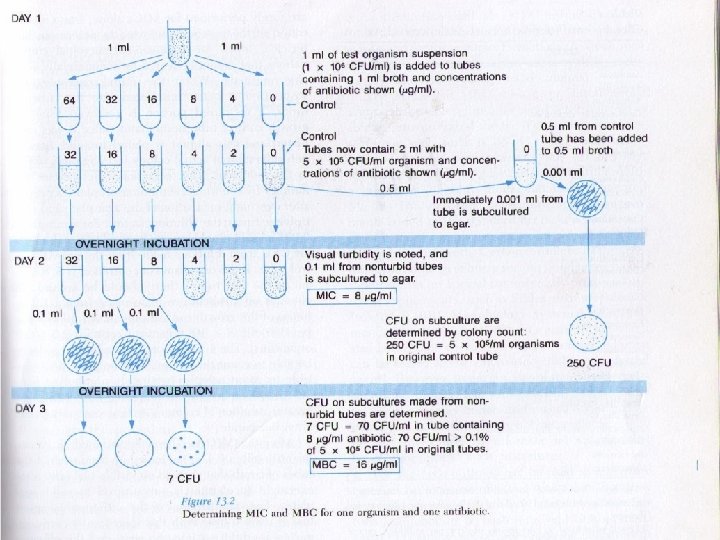
Tube dilution ﻣﻘﺪﺍﺭ ﻛﻢ ﻭ ﻣﺸﺨﺼﻲ ﺍﺯ ﺣﺠﻢ ﺑﺎﻛﺘﺮﻱ ﺑﻪ ﻟﻮﻟﻪ ﻫﺎ ﺍﺿﺎﻓﻪ ﺷﺪﻩ ﻭ پﺲ ﺍﺯ 42 ﺑﻪ ﻋﻨﻮﺍﻥ ﻛﻤﺘﺮﻳﻦ ﻏﻠﻈﺘﻲ ﺍﺯ آﻨﺘﻲ ﺑﻴﻮﺗﻴﻚ ﻛﻪ ﺳﺒﺐ ﻣﻤﺎﻧﻌﺖ MIC ﺳﺎﻋﺖ ﺍﺯ ﺭﺷﺪ ﻣﻲ ﺷﻮﺩ ﺩﺭ ﻧﻈﺮ گﺮﻓﺘﻪ ﻣﻲ ﺷﻮﺩ ﻫﻤﺎﻥ ﻛﻤﺘﺮﻳﻦ ﻏﻠﻈﺖ ﻛﺸﻨﺪﻩ ﺑﺎﻛﺘﺮﻱ ﺍﺳﺖ MBC ﺍﻃﻼﻋﺎﺕ MBC ﺑﻴﺎﻥ ﻣﻲ ﺷﻮﺩ ﺍﻣﺎ MIC ﺩﺭ ﺭﻭﺵ ﻛﺮﺑﻲ ﺑﺎﺋﺮ ﺣﺴﺎﺳﻴﺖ ﺑﺎ ﻣﻲ ﺗﻮﺍﻧﺪ پﻴﺸﺒﻴﻨﻲ ﻛﻨﺪ ﺳﻄﺢ آﻨﺘﻲ MBC ﻛﻤﻲ ﺑﻪ ﺩﺳﺖ ﻣﺎ ﻣﻲ ﺩﻫﺪ ﺑﻴﻮﺗﻴﻚ ﺩﺭ ﺧﻮﻥ ﻭ ﺑﺎﻓﺖ ﺗﺎ چﻪ ﺣﺪ ﺑﺎﻳﺪ ﺑﺮﺳﺪ ﺗﺎ ﺑﺎﻛﺘﺮﻱ ﻛﺸﺘﻪ ﺷﻮﺩ

Tube dilution ﻣﻘﺪﺍﺭ ﻣﺸﺨﺼﻲ ﺍﺯ ﺑﺎﻛﺘﺮﻱ ﺑﻪ ﻟﻮﻟﻪ ﻫﺎ ﺍﺿﺎﻓﻪ ﺷﺪﻩ ﻭ پﺲ ﺍﺯ 42 ﺳﺎﻋﺖ ﺑﻪ ﻋﻨﻮﺍﻥ ﻛﻤﺘﺮﻳﻦ ﻏﻠﻈﺘﻲ ﺍﺯ آﻨﺘﻲ ﺑﻴﻮﺗﻴﻚ ﻛﻪ ﺳﺒﺐ ﻣﻤﺎﻧﻌﺖ ﺍﺯ ﺭﺷﺪ MIC ﻣﻲ ﺷﻮﺩ ﺩﺭ ﻧﻈﺮ گﺮﻓﺘﻪ ﻣﻲ ﺷﻮﺩ ﻫﻤﺎﻥ ﻛﻤﺘﺮﻳﻦ ﻏﻠﻈﺖ ﻛﺸﻨﺪﻩ ﺑﺎﻛﺘﺮﻱ ﺍﺳﺖ MBC ﺍﻃﻼﻋﺎﺕ MBC ﺑﻴﺎﻥ ﻣﻲ ﺷﻮﺩ ﺍﻣﺎ MIC ﺩﺭ ﺭﻭﺵ ﻛﺮﺑﻲ ﺑﺎﺋﺮ ﺣﺴﺎﺳﻴﺖ ﺑﺎ ﻣﻲ ﺗﻮﺍﻧﺪ پﻴﺸﺒﻴﻨﻲ ﻛﻨﺪ ﺳﻄﺢ آﻨﺘﻲ MBC ﻛﻤﻲ ﺑﻪ ﺩﺳﺖ ﻣﺎ ﻣﻲ ﺩﻫﺪ ﺑﻴﻮﺗﻴﻚ ﺩﺭ ﺧﻮﻥ ﻭ ﺑﺎﻓﺖ ﺗﺎ چﻪ ﺣﺪ ﺑﺎﻳﺪ ﺑﺮﺳﺪ ﺗﺎ ﺑﺎﻛﺘﺮﻱ ﻛﺸﺘﻪ ﺷﻮﺩ

ﺭﻗﺖ ﻟﻮﻟﻪ ﺍﻱ ﺑﻪ ﻧﺴﺒﺖ ﺧﺎﺻﻲ ﻋﻮﺍﻣﻞ ﺿﺪ ﻣﻴﻜﺮﻭﺑﻲ ﺭﻗﻴﻖ ﻣﻲ ﺷﻮﻧﺪ ﻣﺜﻞ 0/52 ، l 0/5 ، 1 ، 2 ، 4 ، 8 ، 61 ، 23 ، 46. . .


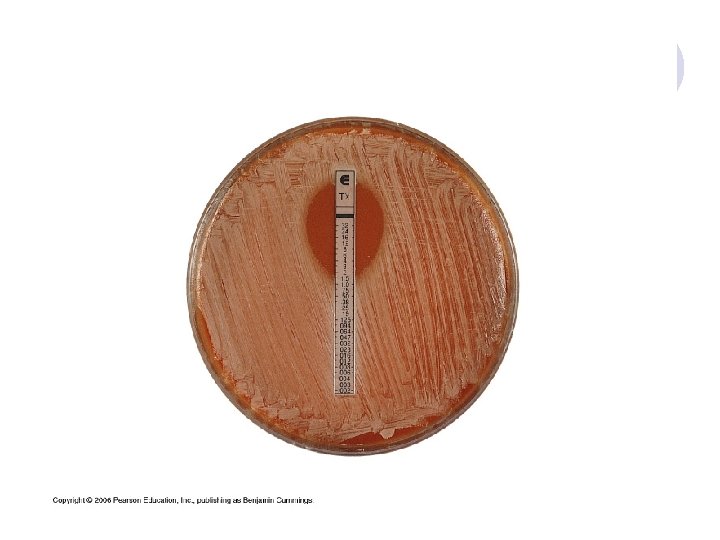
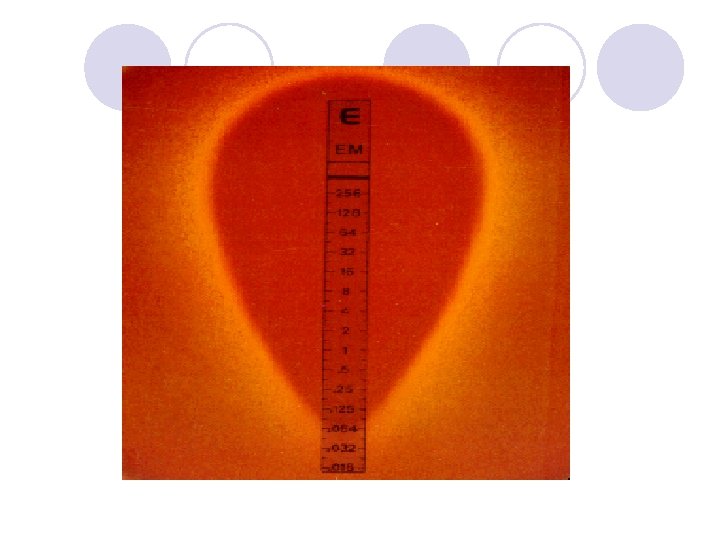
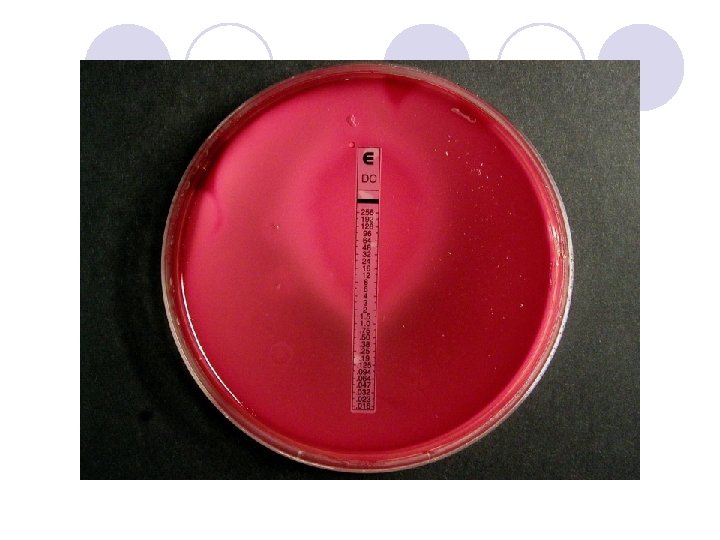
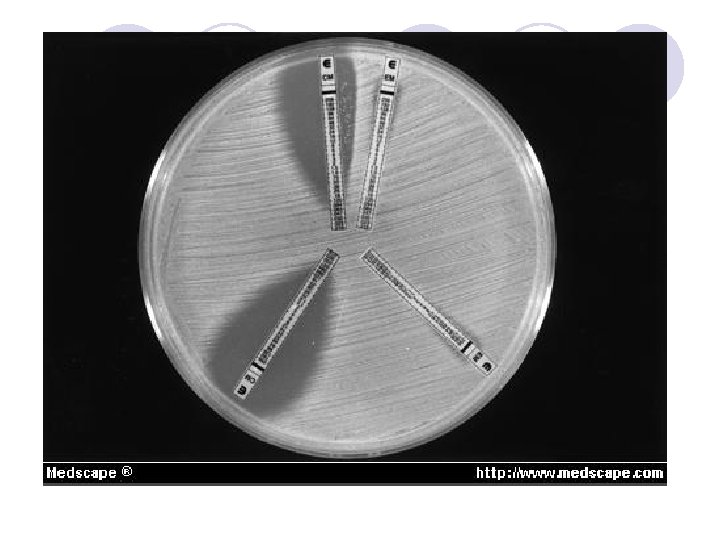
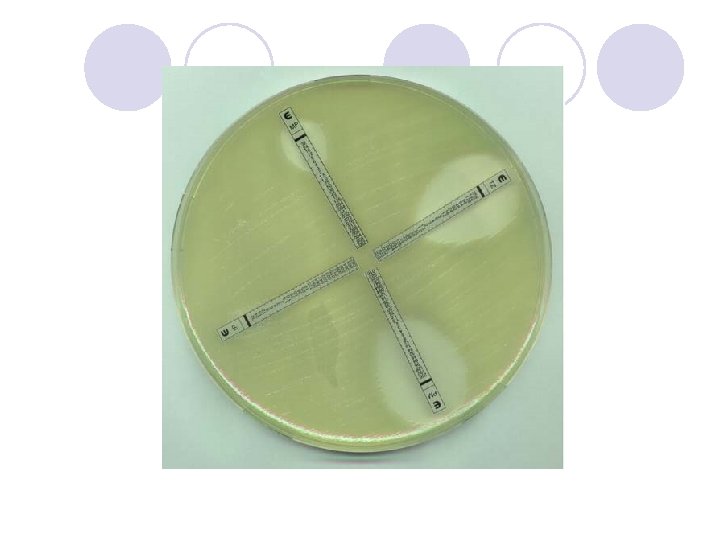
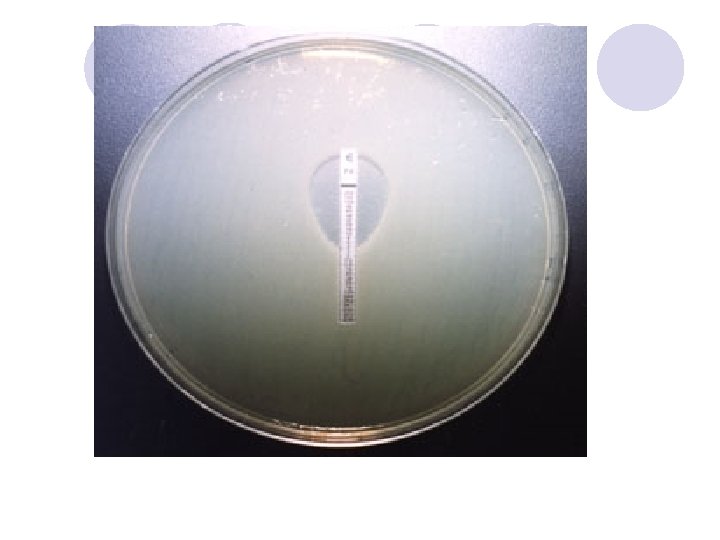
DIFFUSION IN AGAR DERIVATION Commercial E. TEST

E. TEST l. Uses plastic strip l. One side of strip contains antimicrobial concentration gradient and the other a numeric scale that indicate drug concentration

Method l. After incubation MIC is read where the growth inhibition edge intersects the strip graduated with an MIC scale across no. dilutions l. Several antibiotic strips can be tested on a plate

63973a4612938284e597df4161571744.ppt