 Quality Control: Molecular Diagnostics 1
Quality Control: Molecular Diagnostics 1
 Overview n n Sample Collection, Transport, and Processing ¨ maintain Nucleic acid integrity through these processes Contamination Control ¨ establish a unidirectional work flow from a DNA -free area for reagent preparation, to a sample processing area, to area where amplification and detection occur Positive and Negative Controls Reference: CLSI MM 3 -A (Molecular Diagnostic Methods for Infectious Diseases) Molecular Diagnostics Quality Control - Module 8 2 2
Overview n n Sample Collection, Transport, and Processing ¨ maintain Nucleic acid integrity through these processes Contamination Control ¨ establish a unidirectional work flow from a DNA -free area for reagent preparation, to a sample processing area, to area where amplification and detection occur Positive and Negative Controls Reference: CLSI MM 3 -A (Molecular Diagnostic Methods for Infectious Diseases) Molecular Diagnostics Quality Control - Module 8 2 2
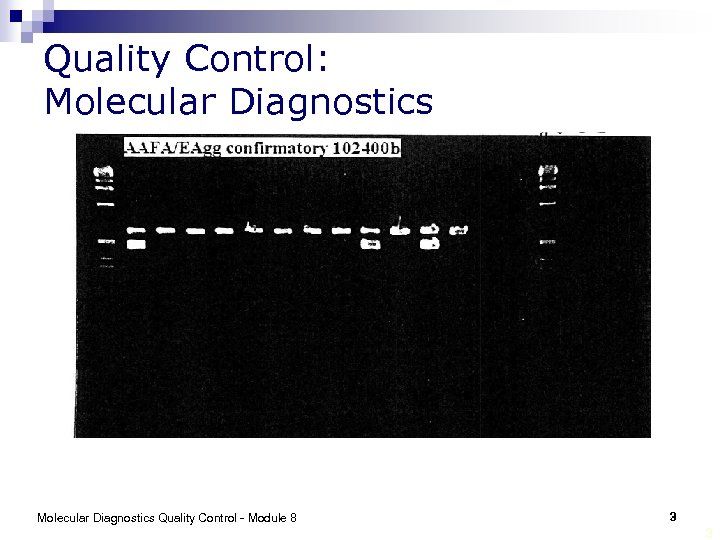 Quality Control: Molecular Diagnostics Quality Control - Module 8 3 3
Quality Control: Molecular Diagnostics Quality Control - Module 8 3 3
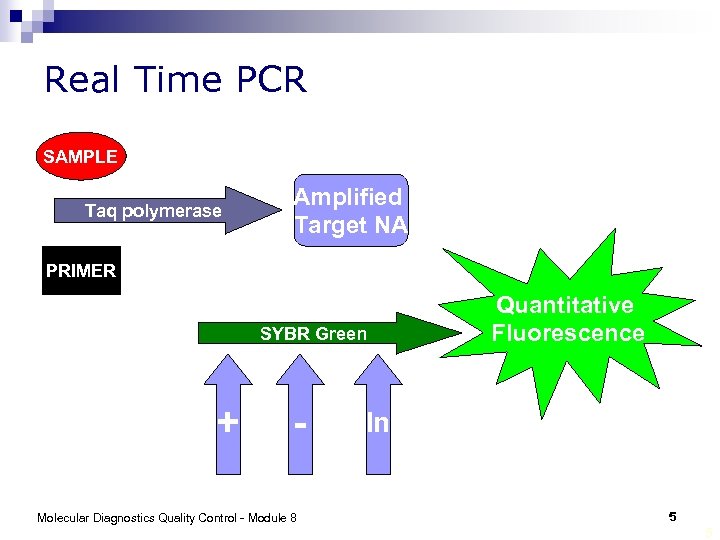 Real Time PCR SAMPLE Taq polymerase Amplified Target NA PRIMER SYBR Green + - Molecular Diagnostics Quality Control - Module 8 Quantitative Fluorescence In 5 5
Real Time PCR SAMPLE Taq polymerase Amplified Target NA PRIMER SYBR Green + - Molecular Diagnostics Quality Control - Module 8 Quantitative Fluorescence In 5 5
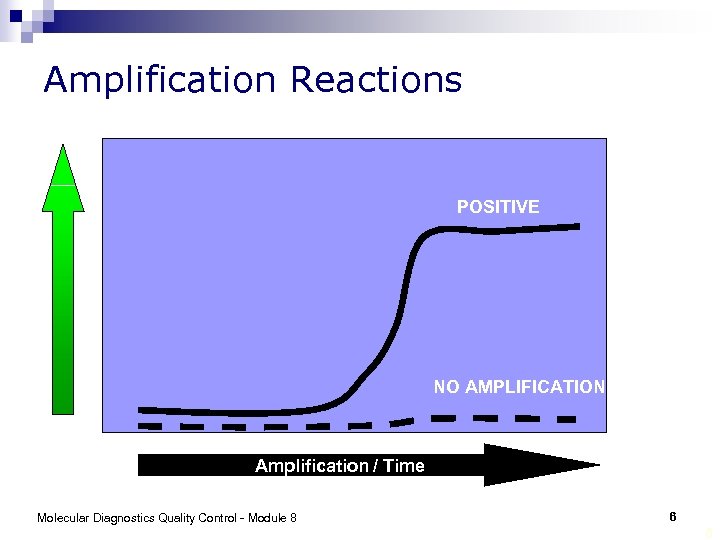 Amplification Reactions POSITIVE NO AMPLIFICATION Amplification / Time Molecular Diagnostics Quality Control - Module 8 6 6
Amplification Reactions POSITIVE NO AMPLIFICATION Amplification / Time Molecular Diagnostics Quality Control - Module 8 6 6
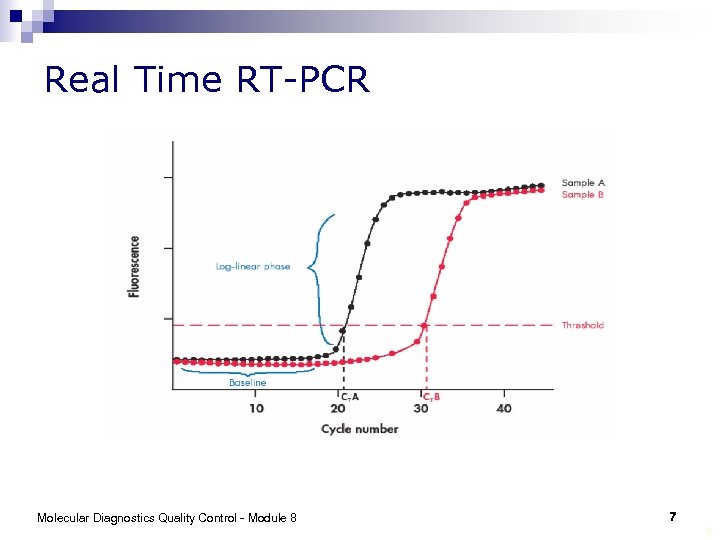 Real Time RT-PCR Molecular Diagnostics Quality Control - Module 8 7 7
Real Time RT-PCR Molecular Diagnostics Quality Control - Module 8 7 7
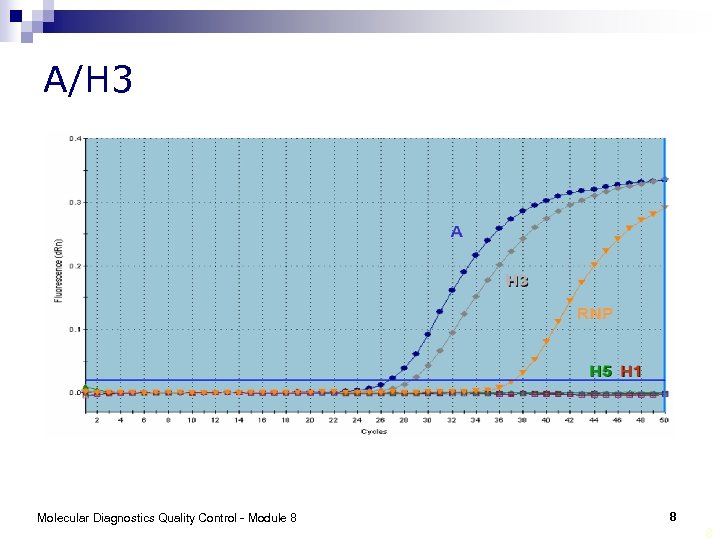 A/H 3 Molecular Diagnostics Quality Control - Module 8 8 8
A/H 3 Molecular Diagnostics Quality Control - Module 8 8 8
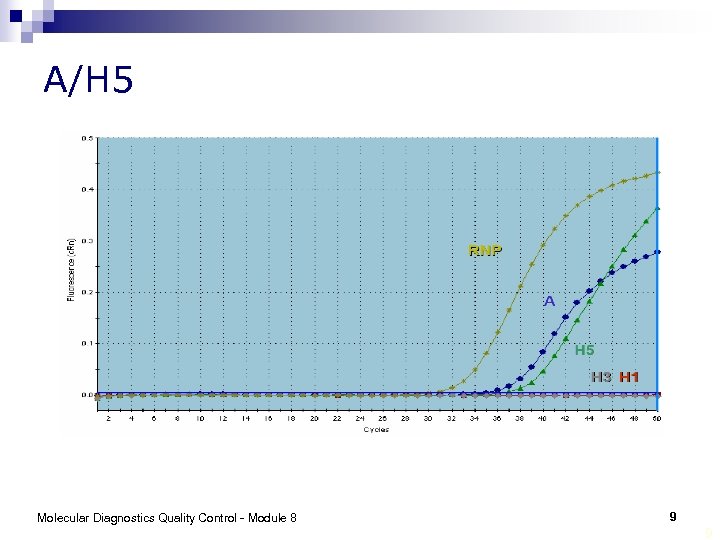 A/H 5 Molecular Diagnostics Quality Control - Module 8 9 9
A/H 5 Molecular Diagnostics Quality Control - Module 8 9 9
 Risks with PCR n most RT-PCR is still done as “inhouse” or “home-brew” ¨ primers are not necessarily optimized to test ¨ positive controls are “in-house” ¨ negative controls are “in-house” n interpretation of tests need to be done with caution Molecular Diagnostics Quality Control - Module 8 11 11
Risks with PCR n most RT-PCR is still done as “inhouse” or “home-brew” ¨ primers are not necessarily optimized to test ¨ positive controls are “in-house” ¨ negative controls are “in-house” n interpretation of tests need to be done with caution Molecular Diagnostics Quality Control - Module 8 11 11