424ccbd6ea6d6df53ec5e96da2a9292c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32

Quality Assurance Strategies: Evaluating Learning Resources Presented by: Karin Lundgren-Cayrol In collaboration with: Gilbert Paquette and Suzanne Lapointe for CICE & GTN-Normétic I 2 LOR WORKSHOP ON REPOSITORIES Montreal, November 8 2006

Overview • Goal and Objectives • Basic Concepts – – Learning Ressources (LR) LR Repository Types Quality Assurance Strategy Quality Dimensions • Integration/Development Processes • LR Life-Cycle and Quality Assurance Strategies • Conclusion

Goals and Objectives Provide a set of Quality Assurance Strategies to ensure LOR sustainability Objectives • Establish quality assurance strategies • Provide pertinent evaluation criteria • Provide guidelines and principles • Repository Managers & Developers • LO designers • LO users

What’s a Learning Resource ? Image Any entity, Electronic digital or non-digital, book which is intended to be, or may be Granularity used for the purpose of learning, education or training Video CDROM SCORM Object Learning Design Software

Quality Assurance Strategy? Organisational and Technical Decisions ISO 9000: 2000 Identify Quality Assurance Stakeholders is the planned and List of Assurance Repository Type systematic activities put in place Strategies User Profile to ensure quality Needs List of requirements for a product or. Metadata Profile be fulfilled. service will Integrating a Repository Document all processes. 1. Design and Produce 2. Integrate into LR 3. Reuse and Revise

Quality Dimensions • • • Instructional Quality Content clarity and conciseness, instructional strategies aligned to the learning objectives, appropriate media according to target audience, etc… Media and Ergonomical Quality User-friendliness, motivating, visually attractive, built-in accessibility features, etc. . Technical Quality Technical interoperability and robustness, metadata schema and tagging procedures, conformance to standards
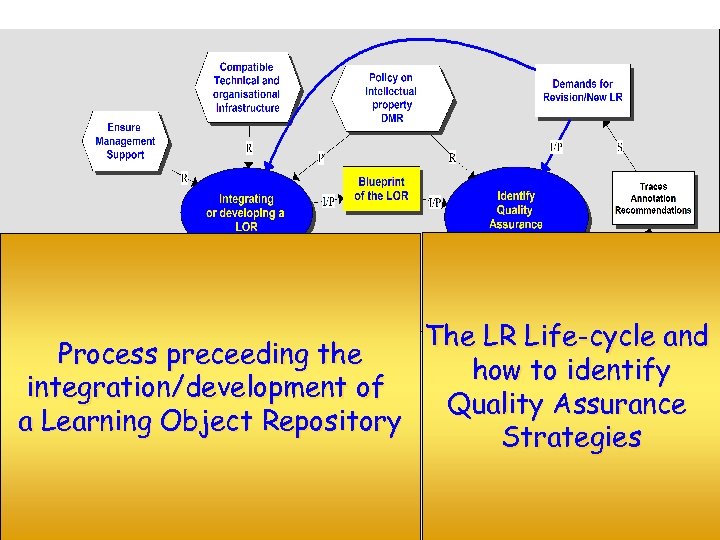
The LR Life-cycle and Process preceeding the how to identify integration/development of Quality Assurance a Learning Object Repository Strategies

Strategies at the Organisational Level • • • Institutional Support Technological Infrastructure Repository Type Policy Stakeholders a on copyrights Integrating LR User Profile List of Needs List of Resource Types Metadata Profile Stakeholder support Define Goal of LR Goal Specify Metadata schema Identify Actors Stakehol der list Identify Needs Specify Resource Types LISTof User Resource Types & Expertise
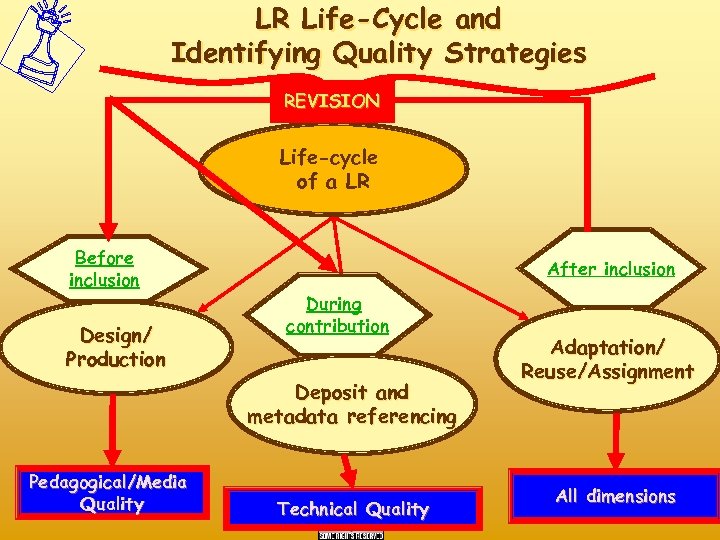
LR Life-Cycle and Identifying Quality Strategies REVISION Life-cycle of a LR Before inclusion Design/ Production After inclusion During contribution Deposit and metadata referencing Pedagogical/Media Quality Technical Quality Adaptation/ Reuse/Assignment All dimensions

LR Repository Types and Main Charactersitics • Private Repositories – – – Quality = personal usefulness of the LO Metadata schema Recommendation systems (social/collaborative tagging/folksomy) – – Quality = Member ship and peer reviewed LO’s Domain specific interest, practice or discipline Protects the consumer trough membership May use domain ontology – – Quality = Annotation and Right’s Management Metadata validation system and automatic capturing Propose evaluation criteria for different resources Provide evaluation, recommendation and annotation systems • Community repository • Public Repository
Summary Graphical designer: Julie Aubin, 2006

Give me a chance! Too Much is Overkill Too Little Just Kills Karin Lundgren-Cayrol Suzanne Lapointe Gilbert Paquette CICE, TÉLUQ - UQAM

During Contribution Strategies here could be referring to all types of quality dimensions: - Pedagogical and Ergonomical Quality by enforcing Peer Review Controlled contribution But if Strategies has been applied at the design/production stage, strategies here normally only need to refer to - The quality of the metadata Interoperability of the Learning Resource and its Metadata Record
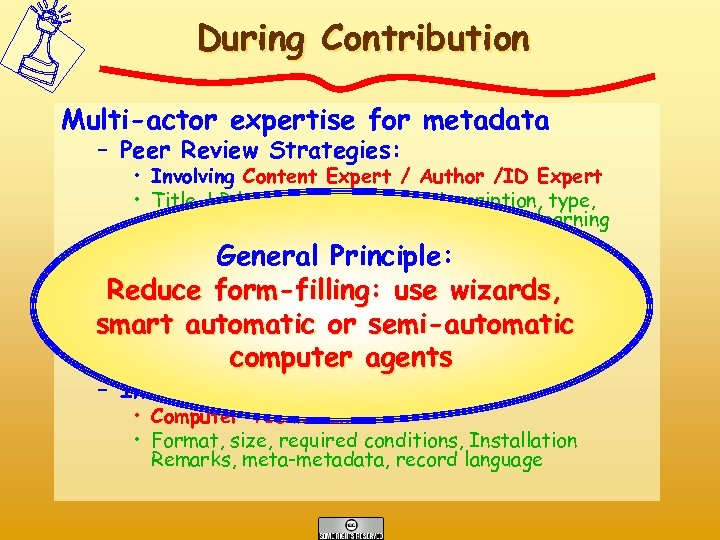
During Contribution Multi-actor expertise for metadata – Peer Review Strategies: • Involving Content Expert / Author /ID Expert • Title, LR language, key words, description, type, version, contributors, intended end user, learning context General Principle: • Text mining algorithms can help –Reduce form-filling: use wizards, Metadata Quality Strategies • Library technician smart automatic or rights, relations metadata semi-automatic • Version, classification, computer standard • Overall respect of the agents used – Interoperability • Computer Technicians • Format, size, required conditions, Installation Remarks, meta-metadata, record language

During Contribution • Demand Membership for contributors: – Gives responsability and motivation; – Make contributors visible by ‘Business Card’ portfolio, chat groups etc. – Suggest domain specific Community of Practices • Make sure that the author provides the following infos: – Degree of Pedagogical Reusability (Rights) Rights – Content quality indications (Method, checklist, evaluation used etc) – Interface quality (idem) – How it might be an efficient learning or teaching tool
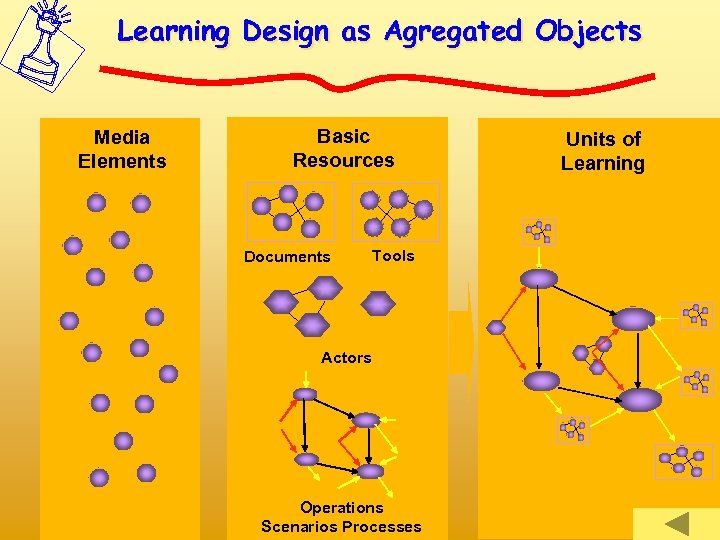
Learning Design as Agregated Objects Media Elements Basic Resources Documents Tools Actors Operations Scenarios Processes Units of Learning

Before Inclusion Strategies that refers to Instructional Design of the Learning Resource and aims at: - Pedagogical Quality - Ergonomical Quality Demands specilized ID methods if LR is a Unit of Learning compliant with : - IMS LD - SCORM - Other like WEBCT, Black. Board etc. .

Some Guidance Principles • Design and Production Strategies – Use a solid and adapted ID method – Support Collaborative design, that is let specialists apply their expertise – Clearly identify knowledge and user competencies – Favor pedagogical strategies putting the learner in the center – Apply evaluation criteria during development and implement at least one learner/peer evaluation cycle – Be informed about Access 4 All production principles
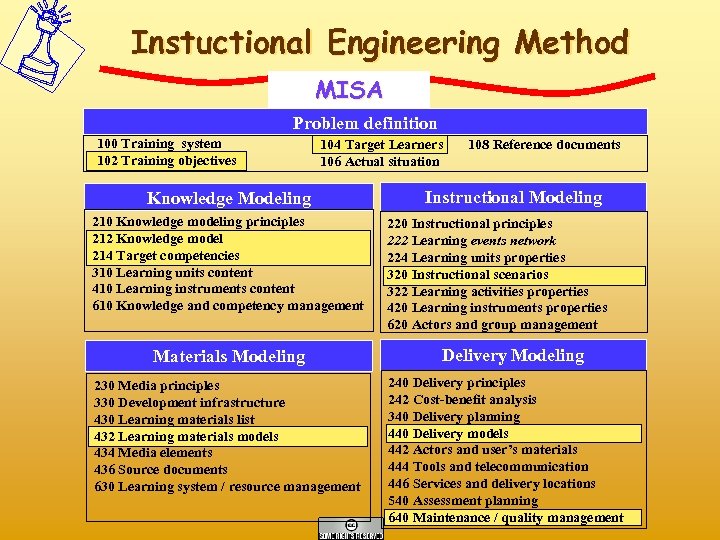
Instuctional Engineering Method MISA Problem definition 100 Training system 102 Training objectives 104 Target Learners 106 Actual situation Knowledge Modeling 210 Knowledge modeling principles 212 Knowledge model 214 Target competencies 310 Learning units content 410 Learning instruments content 610 Knowledge and competency management Materials Modeling 230 Media principles 330 Development infrastructure 430 Learning materials list 432 Learning materials models 434 Media elements 436 Source documents 630 Learning system / resource management 108 Reference documents Instructional Modeling 220 Instructional principles 222 Learning events network 224 Learning units properties 320 Instructional scenarios 322 Learning activities properties 420 Learning instruments properties 620 Actors and group management Delivery Modeling 240 Delivery principles 242 Cost-benefit analysis 340 Delivery planning 440 Delivery models 442 Actors and user’s materials 444 Tools and telecommunication 446 Services and delivery locations 540 Assessment planning 640 Maintenance / quality management

Collaborative Design • • • Content Expert Instructional Designer Media Specialist Delivery Specialist Project Leader Basic principle: Build or integrate objects that you can quality certify Note: Interactive Objets are Software and answers to software quality criteria
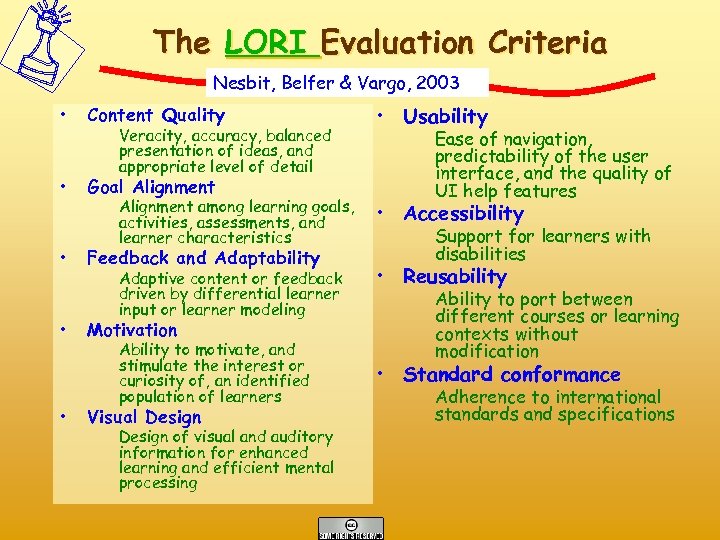
The LORI Evaluation Criteria Nesbit, Belfer & Vargo, 2003 • Content Quality • Goal Alignment • • • Veracity, accuracy, balanced presentation of ideas, and appropriate level of detail • Usability Ease of navigation, predictability of the user interface, and the quality of UI help features Alignment among learning goals, activities, assessments, and learner characteristics • Accessibility Adaptive content or feedback driven by differential learner input or learner modeling • Reusability Feedback and Adaptability Motivation Ability to motivate, and stimulate the interest or curiosity of, an identified population of learners Visual Design of visual and auditory information for enhanced learning and efficient mental processing Support for learners with disabilities Ability to port between different courses or learning contexts without modification • Standard conformance Adherence to international standards and specifications

LORI instrument Adding: General quality or the rate (X/45) or % ? Other criteria ?

Accessibility 4 All Checklist of Checkpoints for Web Content Accessibility Guidelines 1. 0 The TILE PROJECT : http: //barrierfree. ca/tile/index. htm

After Inclusion in the Repository Refers to strategies that provide: • Retrieval quality • • – – – Free text search Browsing by Classification Schemes or Typologies Ontological search Federated search Easy display of information Descriptive resumé Full meta data record How many used it What do they think Peer reviews and evaluations from actual users/reusers. Simple Annotation systems Social tagging/bookmarking and Folksomy Collaborative filtering techniques Recommendation algorithms

After Inclusion Strategies • List of new and innovative high quality LRs • Suggestions for: – Revisions to authors/designers for improvements – Renewal of resource – New resource
MERLOT
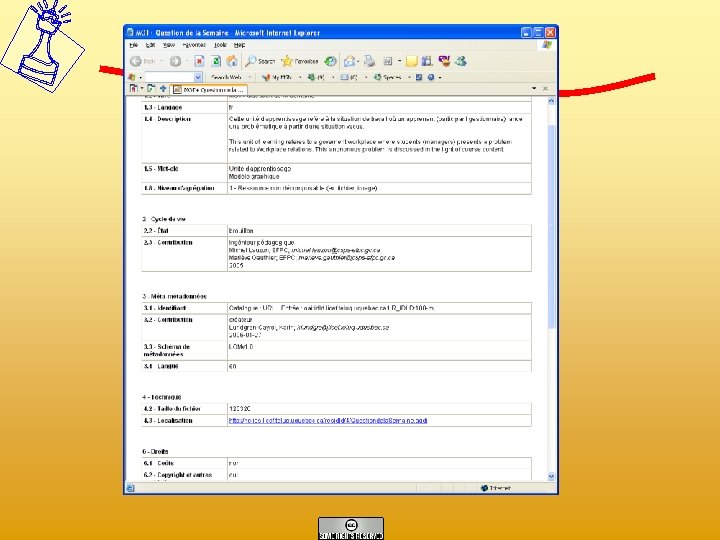
Metadata display
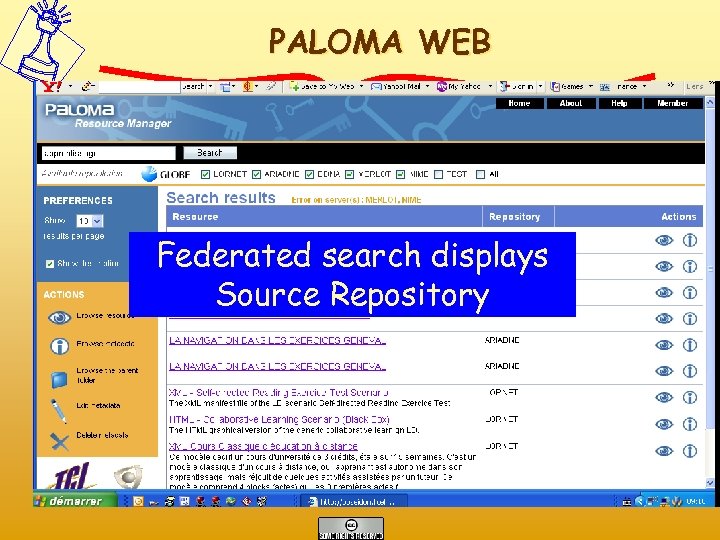
PALOMA WEB Federated search displays Source Repository
EDNA Online
SEARCH ARIADNE DISPLAY
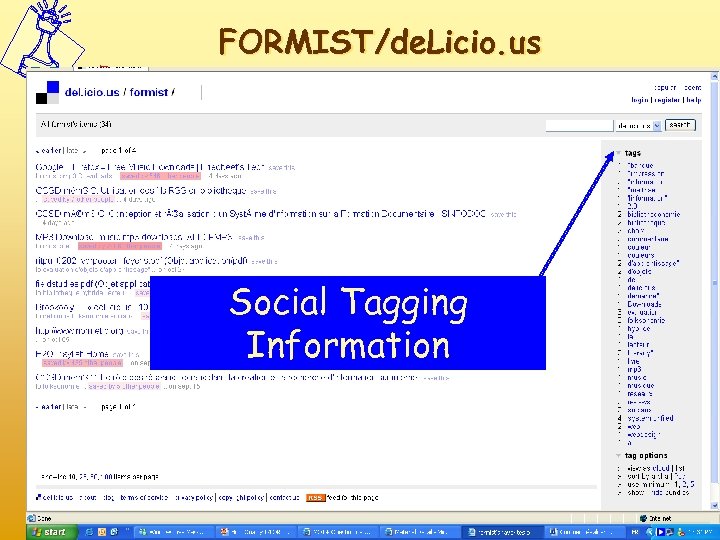
FORMIST/de. Licio. us Social Tagging Information
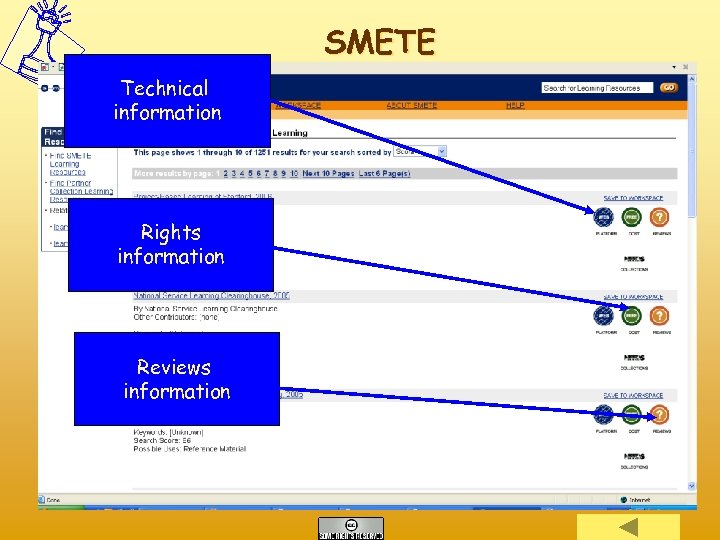
SMETE Technical information Rights information Reviews information
424ccbd6ea6d6df53ec5e96da2a9292c.ppt