94f00ff1f99f975ac1157f4d697bce17.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 Quality Assurance & Standards Mech. Eng SE 3 (non-)lecture 12 Slides by Phil Gray
Quality Assurance & Standards Mech. Eng SE 3 (non-)lecture 12 Slides by Phil Gray
 Where to go for more… l Sommerville » 7 th & 8 th Editions, Chap. 27 » 6 th Edition, Chap. 24 Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 2
Where to go for more… l Sommerville » 7 th & 8 th Editions, Chap. 27 » 6 th Edition, Chap. 24 Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 2
 The Capability Maturity Model Description of the characteristic levels of quality in the software development process l Developed by the Carnegie Mellon Software Engineering Institute l Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 3
The Capability Maturity Model Description of the characteristic levels of quality in the software development process l Developed by the Carnegie Mellon Software Engineering Institute l Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 3
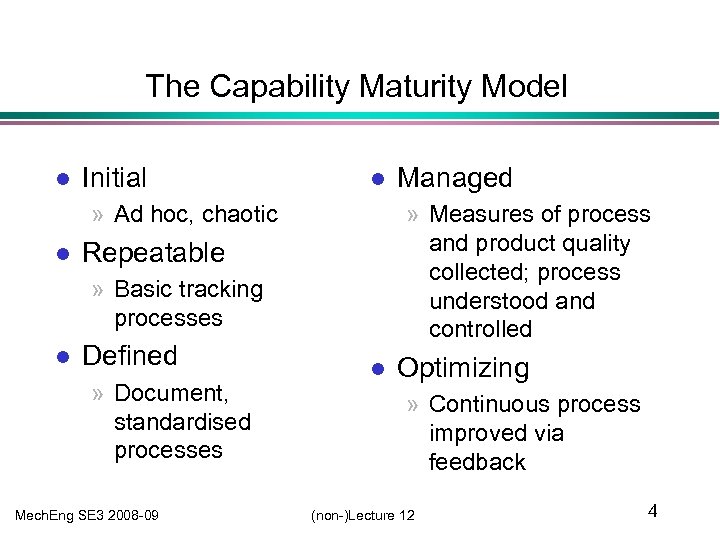 The Capability Maturity Model l Initial l » Ad hoc, chaotic l » Measures of process and product quality collected; process understood and controlled Repeatable » Basic tracking processes l Defined » Document, standardised processes Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 Managed l Optimizing » Continuous process improved via feedback (non-)Lecture 12 4
The Capability Maturity Model l Initial l » Ad hoc, chaotic l » Measures of process and product quality collected; process understood and controlled Repeatable » Basic tracking processes l Defined » Document, standardised processes Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 Managed l Optimizing » Continuous process improved via feedback (non-)Lecture 12 4
 CMM and Quality Key feature of CMM is centrality of process and product quality l How is this achieved? l Answer: Quality Assurance or QA l Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 5
CMM and Quality Key feature of CMM is centrality of process and product quality l How is this achieved? l Answer: Quality Assurance or QA l Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 5
 What is Quality Assurance l From Software QA/Test Resource Center: ". . Software QA involves the entire software development process monitoring and improving the process, making sure that any agreed-upon standards and procedures are followed, and ensuring that problems are found and dealt with. It is oriented to 'prevention'. . “ Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 6
What is Quality Assurance l From Software QA/Test Resource Center: ". . Software QA involves the entire software development process monitoring and improving the process, making sure that any agreed-upon standards and procedures are followed, and ensuring that problems are found and dealt with. It is oriented to 'prevention'. . “ Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 6
 Sommerville on Quality Assurance l for Sommerville: » Quality Assurance – framework of procedures and standards » Quality Plan – selection and adaptation of procedures and standards for a project » Quality Control – carrying out processes that ensure procedures and standards are followed l the term ‘Quality Assurance’ sometimes refers to all of the above Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 7
Sommerville on Quality Assurance l for Sommerville: » Quality Assurance – framework of procedures and standards » Quality Plan – selection and adaptation of procedures and standards for a project » Quality Control – carrying out processes that ensure procedures and standards are followed l the term ‘Quality Assurance’ sometimes refers to all of the above Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 7
 What’s involved in software quality assurance? l At the level of an institution, company or standards body » Develop procedures and standards » Perform certification – to prove that the QA mechanism used is acceptable and effective l At the level of a particular project » Prepare a quality plan – specifying processes, deliverables, measures of quality (metrics, standards) » Carry out quality control – Collect data l l So-called metrics Compared to standards – Conducting reviews l l checking reality against plan and against standards At all levels » Change attitudes – convince staff that quality is important – develop a “quality culture” Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 8
What’s involved in software quality assurance? l At the level of an institution, company or standards body » Develop procedures and standards » Perform certification – to prove that the QA mechanism used is acceptable and effective l At the level of a particular project » Prepare a quality plan – specifying processes, deliverables, measures of quality (metrics, standards) » Carry out quality control – Collect data l l So-called metrics Compared to standards – Conducting reviews l l checking reality against plan and against standards At all levels » Change attitudes – convince staff that quality is important – develop a “quality culture” Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 8
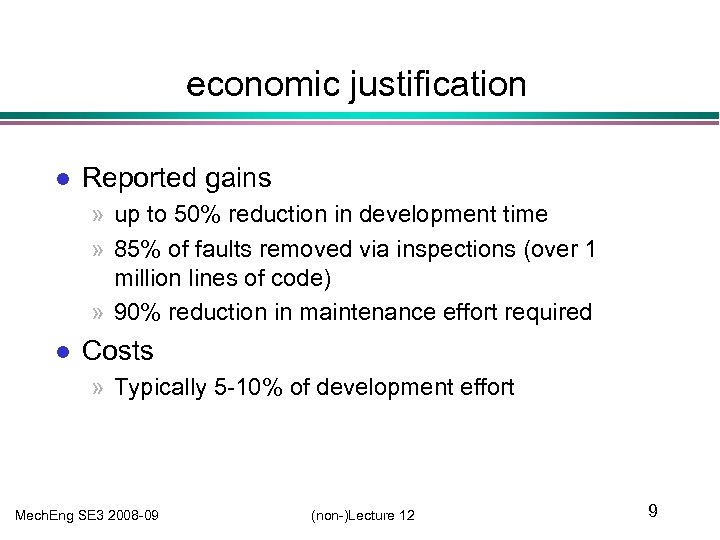 economic justification l Reported gains » up to 50% reduction in development time » 85% of faults removed via inspections (over 1 million lines of code) » 90% reduction in maintenance effort required l Costs » Typically 5 -10% of development effort Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 9
economic justification l Reported gains » up to 50% reduction in development time » 85% of faults removed via inspections (over 1 million lines of code) » 90% reduction in maintenance effort required l Costs » Typically 5 -10% of development effort Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 9
 techniques for quality reviews l Progress review » Examination of progress with respect to plans l Quality review » Examination of project artefacts with respect to attributes of quality l Inspection » an FTR that tries to identify likely areas for faults and to identify lack of conformity to standards » Includes code walkthrough Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 10
techniques for quality reviews l Progress review » Examination of progress with respect to plans l Quality review » Examination of project artefacts with respect to attributes of quality l Inspection » an FTR that tries to identify likely areas for faults and to identify lack of conformity to standards » Includes code walkthrough Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 10
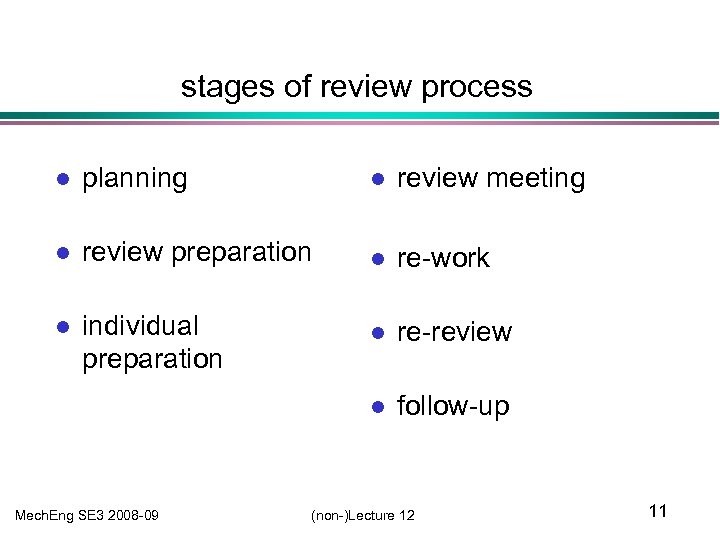 stages of review process l planning l review meeting l review preparation l re-work l individual preparation l re-review l follow-up Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 11
stages of review process l planning l review meeting l review preparation l re-work l individual preparation l re-review l follow-up Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 11
 review team l l minimum 3, maximum 6 roles » author » moderator » reader Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 » plus – scribe – QA staff – specialists – dependent developers – maintainers (non-)Lecture 12 12
review team l l minimum 3, maximum 6 roles » author » moderator » reader Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 » plus – scribe – QA staff – specialists – dependent developers – maintainers (non-)Lecture 12 12
 review dos and don’ts l DO make it peer group review, applicable to all stages of software development » » l method of finding faults cheaply method of training and learning method of control method of encouraging “egoless teamwork” DON’T make it » a problem-solving session – faults should be identified, but solutions should not be patched together ‘in committee’ » a managerial appraisal of personnel Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 13
review dos and don’ts l DO make it peer group review, applicable to all stages of software development » » l method of finding faults cheaply method of training and learning method of control method of encouraging “egoless teamwork” DON’T make it » a problem-solving session – faults should be identified, but solutions should not be patched together ‘in committee’ » a managerial appraisal of personnel Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 13
 standards for assessment l documents » » l structure section numbering and title styles spelling, grammar, style accuracy and appropriateness of content diagrams » semantic correctness » syntactic and lexical correctness (use of symbols, connectivity rules) » number of nodes per page Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 14
standards for assessment l documents » » l structure section numbering and title styles spelling, grammar, style accuracy and appropriateness of content diagrams » semantic correctness » syntactic and lexical correctness (use of symbols, connectivity rules) » number of nodes per page Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 14
 standards for assessment 2 l programs » » » » use of comments indentation style module length completeness consistency cohesion and coupling maintainability N. B. these semantic standards difficult to measure Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 15
standards for assessment 2 l programs » » » » use of comments indentation style module length completeness consistency cohesion and coupling maintainability N. B. these semantic standards difficult to measure Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 15
 code inspection guidelines l l tracing requirements » check off each requirement against piece(s) of code » (possibly) provide a cross-reference of document tracing to the review team » can use code walkthrough questioning assumptions » any assumptions not justified by the requirements? » sizes and volumes of data consistent with requirements Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 16
code inspection guidelines l l tracing requirements » check off each requirement against piece(s) of code » (possibly) provide a cross-reference of document tracing to the review team » can use code walkthrough questioning assumptions » any assumptions not justified by the requirements? » sizes and volumes of data consistent with requirements Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 16
 code inspection guidelines 2 l l program structure » program structure sensible? » data structures updated properly (wrt DFDs) scoping » variables as tightly scoped as possible? » global variables used only where absolutely necessary? » local subprograms used where appropriate? Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 17
code inspection guidelines 2 l l program structure » program structure sensible? » data structures updated properly (wrt DFDs) scoping » variables as tightly scoped as possible? » global variables used only where absolutely necessary? » local subprograms used where appropriate? Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 17
 code inspection guidelines 3 l l optimisation / factoring » overlapping subprograms which can be combined? » opportunities for code re-use? » code optimised where needed to satisfy efficiency requirements? algorithms » algorithm efficiency appropriate for data volume assumptions » standard algorithms / libraries used where appropriate Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 18
code inspection guidelines 3 l l optimisation / factoring » overlapping subprograms which can be combined? » opportunities for code re-use? » code optimised where needed to satisfy efficiency requirements? algorithms » algorithm efficiency appropriate for data volume assumptions » standard algorithms / libraries used where appropriate Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 18
 code inspection guidelines 4 l description of functionality » links from requirements to code via design documents » adequate embedded comments Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 19
code inspection guidelines 4 l description of functionality » links from requirements to code via design documents » adequate embedded comments Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 19
 reviewing the inspection process l statistics collected on » » l details of items inspected list of faults found & classification resources required for re-working number of people involved & time analysis provides » fault checklists » management reports on effectiveness of inspections l it’s the process being assessed, not the authors or inspectors Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 20
reviewing the inspection process l statistics collected on » » l details of items inspected list of faults found & classification resources required for re-working number of people involved & time analysis provides » fault checklists » management reports on effectiveness of inspections l it’s the process being assessed, not the authors or inspectors Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 20
 What is a Standard? "A standard is a document approved by a recognized body, that provides, for common and repeated use, rules, guidelines, or characteristics for products, processes or services with which compliance is not mandatory. ” A Guide to Project Management Body of Knowledge, 1996 Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 21
What is a Standard? "A standard is a document approved by a recognized body, that provides, for common and repeated use, rules, guidelines, or characteristics for products, processes or services with which compliance is not mandatory. ” A Guide to Project Management Body of Knowledge, 1996 Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 21
 Standards Organisations l International Organization for Standardization (ISO) » » » non-governmental develops standards for various technical fields (more than 11000) 120 national members, which are themselves standards organisations Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 22
Standards Organisations l International Organization for Standardization (ISO) » » » non-governmental develops standards for various technical fields (more than 11000) 120 national members, which are themselves standards organisations Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 22
 Standards Organisations l l l BSI (UK) ANSI (USA) DIN (Germany) ETSI (European) IEC (International) Other standard setting bodies » » » IET BCS EU W 3 C OMG Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 23
Standards Organisations l l l BSI (UK) ANSI (USA) DIN (Germany) ETSI (European) IEC (International) Other standard setting bodies » » » IET BCS EU W 3 C OMG Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 23
 Software Engineering/IT Standards l l ISO/IET/EU have specific standards that can be used for measuring product and process quality E. g. , » ISO/IEC TR 14471: 1999 : Information Technology – Software Engineering – Guidelines for the adoption of CASE tools » ISO 9241 -1 Ergonomic requirements for office work with visual display terminals » W 3 C – Standard = “recommendation” – E. g. , XML 1. 1 Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 24
Software Engineering/IT Standards l l ISO/IET/EU have specific standards that can be used for measuring product and process quality E. g. , » ISO/IEC TR 14471: 1999 : Information Technology – Software Engineering – Guidelines for the adoption of CASE tools » ISO 9241 -1 Ergonomic requirements for office work with visual display terminals » W 3 C – Standard = “recommendation” – E. g. , XML 1. 1 Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 24
 ISO 9000 l international standard for quality management and quality assurance » » » l states what must be in a quality management system first established in 1987 derived from BS 5750, a British standard ISO 9001 » » » applies to products involving design Latest version is ISO 9001: 2000 9001 -3 interprets 9001 for software development Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 25
ISO 9000 l international standard for quality management and quality assurance » » » l states what must be in a quality management system first established in 1987 derived from BS 5750, a British standard ISO 9001 » » » applies to products involving design Latest version is ISO 9001: 2000 9001 -3 interprets 9001 for software development Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 25
 ISO 9000 (cont’d) l certification is not carried out by ISO » » carried out by independent certification bodies organisation is awarded a Certificate of Conformity Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 26
ISO 9000 (cont’d) l certification is not carried out by ISO » » carried out by independent certification bodies organisation is awarded a Certificate of Conformity Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 26
 What’s in ISO 9000? l covers 20 topics, including » » » » Quality System Design Control Process Control Inspection & Testing Contract Review Quality Records Internal Quality Audits Training Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 27
What’s in ISO 9000? l covers 20 topics, including » » » » Quality System Design Control Process Control Inspection & Testing Contract Review Quality Records Internal Quality Audits Training Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 27
 What’s in ISO 9000? (cont’d) standard is abstract; it sets ends not means l for example, l “The supplier shall establish and maintain a documented quality system as a means of ensuring that product confirms to specified requirements. ” [from Section 4. 2 of ISO 9001] Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 28
What’s in ISO 9000? (cont’d) standard is abstract; it sets ends not means l for example, l “The supplier shall establish and maintain a documented quality system as a means of ensuring that product confirms to specified requirements. ” [from Section 4. 2 of ISO 9001] Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 28
 Tick. It developed by DTI l provides a nationally accredited certification body l interpretation of ISO 9000 l » related to ISO 9001 -3 Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 29
Tick. It developed by DTI l provides a nationally accredited certification body l interpretation of ISO 9000 l » related to ISO 9001 -3 Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 29
 Tick. It (cont’d) l gives concrete guidelines on how software development should conform to the standard » » based on developing a scheme of internal audits related to standards compliance auditors require training audits involve document reviews and staff interviews Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 30
Tick. It (cont’d) l gives concrete guidelines on how software development should conform to the standard » » based on developing a scheme of internal audits related to standards compliance auditors require training audits involve document reviews and staff interviews Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 30
 QA Standards: A Good Thing? l pro » » » makes quality assurance assessable as of 1993, 40 000 organisations in 93 countries have adopted the standard US survey – – 89% reported greater operational efficiency 48% reported increased profitability Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 31
QA Standards: A Good Thing? l pro » » » makes quality assurance assessable as of 1993, 40 000 organisations in 93 countries have adopted the standard US survey – – 89% reported greater operational efficiency 48% reported increased profitability Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 31
 QA Standards: A Good Thing? l con » fosters “command & control” style of management – » emphasises inflexible compliance with a set of rigid written rules standards rely heavily on assessors’ judgements – standards are not completely objective Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 32
QA Standards: A Good Thing? l con » fosters “command & control” style of management – » emphasises inflexible compliance with a set of rigid written rules standards rely heavily on assessors’ judgements – standards are not completely objective Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 32
 QA Standards: A Good Thing? » staff will pay attention to controls, not the things affected by the controls – – attention to quality inspection and monitoring can deflect from attention to quality itself like the problem of exams distorting education Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 33
QA Standards: A Good Thing? » staff will pay attention to controls, not the things affected by the controls – – attention to quality inspection and monitoring can deflect from attention to quality itself like the problem of exams distorting education Mech. Eng SE 3 2008 -09 (non-)Lecture 12 33


