 Qsort & sort http: //net. pku. edu. cn/~course/cs 101/2014 Hongfei Yan School of EECS, Peking University 12/24/2014
Qsort & sort http: //net. pku. edu. cn/~course/cs 101/2014 Hongfei Yan School of EECS, Peking University 12/24/2014

 qsort function@ void qsort ( void * base, size_t num, size_t size, int ( * comparator ) ( const void *, const void * ) ); Sort elements of array Sorts the num elements of the array pointed by base, each element size bytes long, using the comparator function to determine the order. The sorting algorithm used by this function compares pairs of values by calling the specified comparator function with two pointers to elements of the array. The function does not return any value, but modifies the content of the array pointed by base reordering its elements to the newly sorted order. Parameters base num Pointer to the first element of the array to be sorted. Number of elements in the array pointed by base. size Size in bytes of each element in the array. comparator Function that compares two elements. The function shall follow this prototype: int comparator ( const void * elem 1, const void * elem 2 ); The function must accept two parameters that are pointers to elements, type-casted as void*. These parameters should be cast back to some data type and be compared. The return value of this function should represent whether elem 1 is considered less than, equal, or grater than elem 2 by returning, respectivelly, a negative value, zero or a positive value. Return Value (none) 4
qsort function@ void qsort ( void * base, size_t num, size_t size, int ( * comparator ) ( const void *, const void * ) ); Sort elements of array Sorts the num elements of the array pointed by base, each element size bytes long, using the comparator function to determine the order. The sorting algorithm used by this function compares pairs of values by calling the specified comparator function with two pointers to elements of the array. The function does not return any value, but modifies the content of the array pointed by base reordering its elements to the newly sorted order. Parameters base num Pointer to the first element of the array to be sorted. Number of elements in the array pointed by base. size Size in bytes of each element in the array. comparator Function that compares two elements. The function shall follow this prototype: int comparator ( const void * elem 1, const void * elem 2 ); The function must accept two parameters that are pointers to elements, type-casted as void*. These parameters should be cast back to some data type and be compared. The return value of this function should represent whether elem 1 is considered less than, equal, or grater than elem 2 by returning, respectivelly, a negative value, zero or a positive value. Return Value (none) 4
 Example for qsort
Example for qsort
 sort
sort
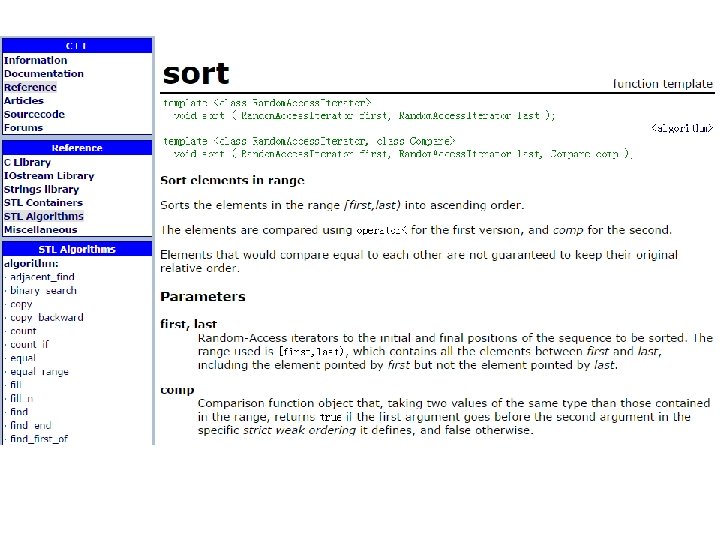
 Sort@ template void sort ( Random. Access. Iterator first, Random. Access. Iterator last ); template void sort ( Random. Access. Iterator first, Random. Access. Iterator last, Compare comp ); Sort elements in range Sorts the elements in the range [first, last) into ascending order. The elements are compared using operator< for the first version, and comp for the second. Elements that would compare equal to each other are not guaranteed to keep their original relative order. Parameters first, last Random-Access iterators to the initial and final positions of the sequence to be sorted. The range used is [first, last), which contains all the elements between first and last, including the element pointed by first but not the element pointed by last. comp Comparison function object that, taking two values of the same type than those contained in the range, returns true if the first argument goes before the second argument in the specific strict weak ordering it defines, and false otherwise.
Sort@ template void sort ( Random. Access. Iterator first, Random. Access. Iterator last ); template void sort ( Random. Access. Iterator first, Random. Access. Iterator last, Compare comp ); Sort elements in range Sorts the elements in the range [first, last) into ascending order. The elements are compared using operator< for the first version, and comp for the second. Elements that would compare equal to each other are not guaranteed to keep their original relative order. Parameters first, last Random-Access iterators to the initial and final positions of the sequence to be sorted. The range used is [first, last), which contains all the elements between first and last, including the element pointed by first but not the element pointed by last. comp Comparison function object that, taking two values of the same type than those contained in the range, returns true if the first argument goes before the second argument in the specific strict weak ordering it defines, and false otherwise.
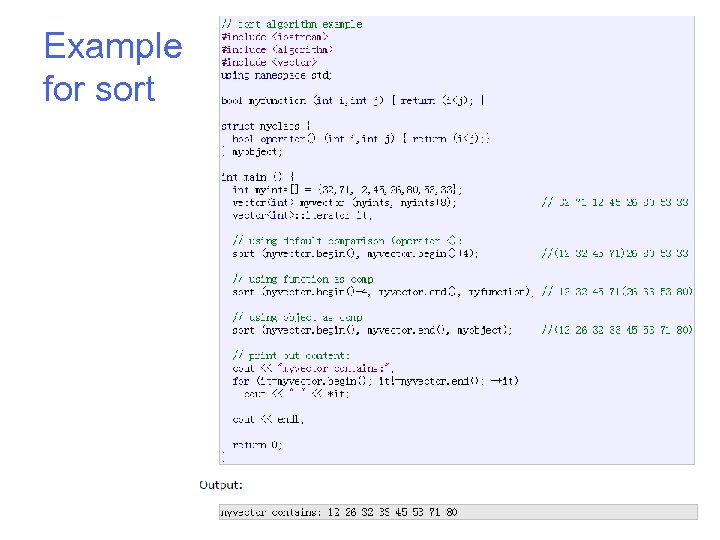 Example for sort
Example for sort
 2915: 字符串排序 描述 先输入你要输入的字符串的个数。然后换行输入该组字符串。每个字 符串以回车结束,每个字符串少于一百个字符。如果在输入过程中输 入的一个字符串为“stop”,也结束输入。 然后将这输入的该组字符串按每个字符串的长度,由小到大排序,按 排序结果输出字符串。 输入 字符串的个数,以及该组字符串。每个字符串以‘n’结束。如果输入字 符串为“stop”,也结束输入. 输出 将输入的所有字符串按长度由小到大排序输出(如果有“stop”,不输出 “stop”)。
2915: 字符串排序 描述 先输入你要输入的字符串的个数。然后换行输入该组字符串。每个字 符串以回车结束,每个字符串少于一百个字符。如果在输入过程中输 入的一个字符串为“stop”,也结束输入。 然后将这输入的该组字符串按每个字符串的长度,由小到大排序,按 排序结果输出字符串。 输入 字符串的个数,以及该组字符串。每个字符串以‘n’结束。如果输入字 符串为“stop”,也结束输入. 输出 将输入的所有字符串按长度由小到大排序输出(如果有“stop”,不输出 “stop”)。
 POJ 2915
POJ 2915


 2783: Holiday Hotel 描述 Mr. and Mrs. Smith are going to the seaside for their holiday. Before they start off, they need to choose a hotel. They got a list of hotels from the Internet, and want to choose some candidate hotels which are cheap and close to the seashore. A candidate hotel M meets two requirements: Any hotel which is closer to the seashore than M will be more expensive than M. Any hotel which is cheaper than M will be farther away from the seashore than M. 输入 There are several test cases. The first line of each test case is an integer N (1 <= N <= 10000), which is the number of hotels. Each of the following N lines describes a hotel, containing two integers D and C (1 <= D, C <= 10000). D means the distance from the hotel to the seashore, and C means the cost of staying in the hotel. You can assume that there are no two hotels with the same D and C. A test case with N = 0 ends the input, and should not be processed. 输出 For each test case, you should output one line containing an integer, which is the number of all the candidate hotels.
2783: Holiday Hotel 描述 Mr. and Mrs. Smith are going to the seaside for their holiday. Before they start off, they need to choose a hotel. They got a list of hotels from the Internet, and want to choose some candidate hotels which are cheap and close to the seashore. A candidate hotel M meets two requirements: Any hotel which is closer to the seashore than M will be more expensive than M. Any hotel which is cheaper than M will be farther away from the seashore than M. 输入 There are several test cases. The first line of each test case is an integer N (1 <= N <= 10000), which is the number of hotels. Each of the following N lines describes a hotel, containing two integers D and C (1 <= D, C <= 10000). D means the distance from the hotel to the seashore, and C means the cost of staying in the hotel. You can assume that there are no two hotels with the same D and C. A test case with N = 0 ends the input, and should not be processed. 输出 For each test case, you should output one line containing an integer, which is the number of all the candidate hotels.


![]()
 Qsort & sort http: //net. pku. edu. cn/~course/cs 101/2014 Hongfei Yan School of EECS, Peking University 12/24/2014
Qsort & sort http: //net. pku. edu. cn/~course/cs 101/2014 Hongfei Yan School of EECS, Peking University 12/24/2014 
 qsort function@
qsort function@ Example for qsort
Example for qsort 


 sort
sort  Sort@
Sort@ Example for sort
Example for sort  2915: 字符串排序 描述 先输入你要输入的字符串的个数。然后换行输入该组字符串。每个字 符串以回车结束,每个字符串少于一百个字符。如果在输入过程中输 入的一个字符串为“stop”,也结束输入。 然后将这输入的该组字符串按每个字符串的长度,由小到大排序,按 排序结果输出字符串。 输入 字符串的个数,以及该组字符串。每个字符串以‘n’结束。如果输入字 符串为“stop”,也结束输入. 输出 将输入的所有字符串按长度由小到大排序输出(如果有“stop”,不输出 “stop”)。
2915: 字符串排序 描述 先输入你要输入的字符串的个数。然后换行输入该组字符串。每个字 符串以回车结束,每个字符串少于一百个字符。如果在输入过程中输 入的一个字符串为“stop”,也结束输入。 然后将这输入的该组字符串按每个字符串的长度,由小到大排序,按 排序结果输出字符串。 输入 字符串的个数,以及该组字符串。每个字符串以‘n’结束。如果输入字 符串为“stop”,也结束输入. 输出 将输入的所有字符串按长度由小到大排序输出(如果有“stop”,不输出 “stop”)。  POJ 2915
POJ 2915 

 2783: Holiday Hotel 描述 Mr. and Mrs. Smith are going to the seaside for their holiday. Before they start off, they need to choose a hotel. They got a list of hotels from the Internet, and want to choose some candidate hotels which are cheap and close to the seashore. A candidate hotel M meets two requirements: Any hotel which is closer to the seashore than M will be more expensive than M. Any hotel which is cheaper than M will be farther away from the seashore than M. 输入 There are several test cases. The first line of each test case is an integer N (1 <= N <= 10000), which is the number of hotels. Each of the following N lines describes a hotel, containing two integers D and C (1 <= D, C <= 10000). D means the distance from the hotel to the seashore, and C means the cost of staying in the hotel. You can assume that there are no two hotels with the same D and C. A test case with N = 0 ends the input, and should not be processed. 输出 For each test case, you should output one line containing an integer, which is the number of all the candidate hotels.
2783: Holiday Hotel 描述 Mr. and Mrs. Smith are going to the seaside for their holiday. Before they start off, they need to choose a hotel. They got a list of hotels from the Internet, and want to choose some candidate hotels which are cheap and close to the seashore. A candidate hotel M meets two requirements: Any hotel which is closer to the seashore than M will be more expensive than M. Any hotel which is cheaper than M will be farther away from the seashore than M. 输入 There are several test cases. The first line of each test case is an integer N (1 <= N <= 10000), which is the number of hotels. Each of the following N lines describes a hotel, containing two integers D and C (1 <= D, C <= 10000). D means the distance from the hotel to the seashore, and C means the cost of staying in the hotel. You can assume that there are no two hotels with the same D and C. A test case with N = 0 ends the input, and should not be processed. 输出 For each test case, you should output one line containing an integer, which is the number of all the candidate hotels. 



