cb8d68a40d046bfbcfd7eb064ae69be9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 53
 QMD: Waiting-line analysis
QMD: Waiting-line analysis
 Overview Terminology n Characteristics of Waiting-lines n Operating characteristics n M/M/1 model – single channel n • Example: video store n M/M/S model – multi-channel • Example: Multiplex theater n Psychology of waiting
Overview Terminology n Characteristics of Waiting-lines n Operating characteristics n M/M/1 model – single channel n • Example: video store n M/M/S model – multi-channel • Example: Multiplex theater n Psychology of waiting
 You’ve Been There Before! Thank you for holding. ‘The other line Hello. . . are you there? always moves faster. ’ ‘If you change lines, the one you left will start to move faster than the one you’re in. ’ © 1995 Corel Corp.
You’ve Been There Before! Thank you for holding. ‘The other line Hello. . . are you there? always moves faster. ’ ‘If you change lines, the one you left will start to move faster than the one you’re in. ’ © 1995 Corel Corp.
 Waiting Line System o ti opula P n Waiting Line Service Facility
Waiting Line System o ti opula P n Waiting Line Service Facility
 Waiting Line Examples Situation Process Arrivals Servers Service
Waiting Line Examples Situation Process Arrivals Servers Service
 Waiting Line Terminology n n n Queue: Waiting line Arrival: 1 person, machine, part, etc. that arrives and demands service Queue discipline: Rules for determining the order that arrivals receive service n Channel: Number of servers n Phase: Number of steps in service
Waiting Line Terminology n n n Queue: Waiting line Arrival: 1 person, machine, part, etc. that arrives and demands service Queue discipline: Rules for determining the order that arrivals receive service n Channel: Number of servers n Phase: Number of steps in service
 Arrival Characteristics of a Waiting Line System o pulati o Waiting Line P n ¨Pattern of arrivals ¨random ¨scheduled n Service Facility Behavior of the arrivals • join the queue, and wait until served • No balking; refuse to join the line • No reneging; leave the line
Arrival Characteristics of a Waiting Line System o pulati o Waiting Line P n ¨Pattern of arrivals ¨random ¨scheduled n Service Facility Behavior of the arrivals • join the queue, and wait until served • No balking; refuse to join the line • No reneging; leave the line
 Balking Input source Line was too long! Service system Waiting line Service facility © 1995 Corel Corp.
Balking Input source Line was too long! Service system Waiting line Service facility © 1995 Corel Corp.
 Reneging Input source Service system Waiting line Service facility I give up! © 1995 Corel Corp.
Reneging Input source Service system Waiting line Service facility I give up! © 1995 Corel Corp.
 Line Characteristics of a Waiting Line System - continued o pulati Po n ¨Length of the queue ¨ limited ¨ unlimited Waiting Line Service Facility ¨Service priority ¨ FIFO ¨ other
Line Characteristics of a Waiting Line System - continued o pulati Po n ¨Length of the queue ¨ limited ¨ unlimited Waiting Line Service Facility ¨Service priority ¨ FIFO ¨ other
 Waiting Line Arrangements Service facilities (a) Single line
Waiting Line Arrangements Service facilities (a) Single line
 Waiting Line Arrangements Service facilities (a) Single line Service facilities (b) Multiple lines
Waiting Line Arrangements Service facilities (a) Single line Service facilities (b) Multiple lines
 Waiting Line Arrangements Service facilities (a) Single line Service facilities (b) Multiple lines
Waiting Line Arrangements Service facilities (a) Single line Service facilities (b) Multiple lines
 Service Facility Characteristics of a Waiting Line System - continued ulatio Pop n Waiting Line Service Facility ¨ Number of channels ¨ single ¨ multiple ¨ Number of phases in service system ¨ single
Service Facility Characteristics of a Waiting Line System - continued ulatio Pop n Waiting Line Service Facility ¨ Number of channels ¨ single ¨ multiple ¨ Number of phases in service system ¨ single
 Service Facility Arrangements
Service Facility Arrangements
 Service Facility Arrangements Service facility (a) Single channel, single phase
Service Facility Arrangements Service facility (a) Single channel, single phase
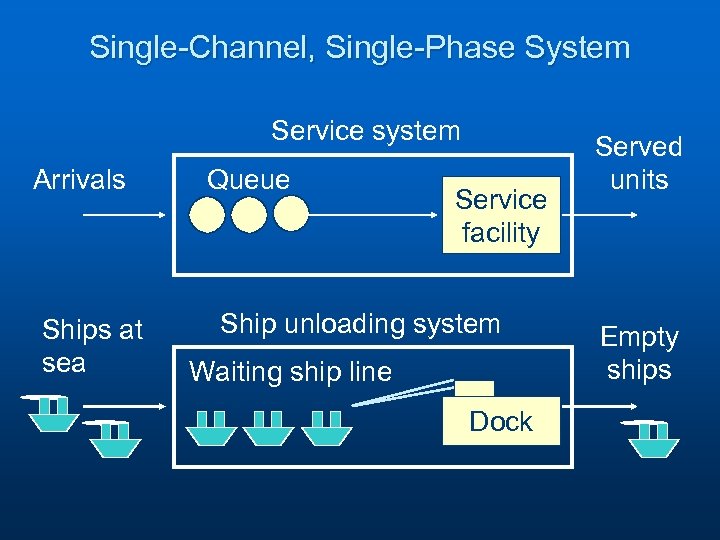 Single-Channel, Single-Phase System Service system Arrivals Ships at sea Queue Service facility Ship unloading system Waiting ship line Dock Served units Empty ships
Single-Channel, Single-Phase System Service system Arrivals Ships at sea Queue Service facility Ship unloading system Waiting ship line Dock Served units Empty ships
 Service Facility Arrangements Service facility 1 (b) Single channel, multiple phase Service facility 2
Service Facility Arrangements Service facility 1 (b) Single channel, multiple phase Service facility 2
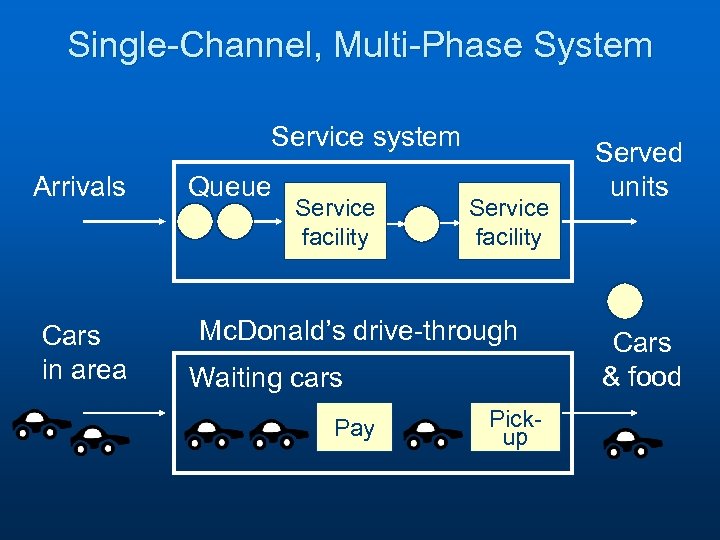 Single-Channel, Multi-Phase System Service system Arrivals Cars in area Queue Service facility Mc. Donald’s drive-through Waiting cars Pay Pickup Served units Cars & food
Single-Channel, Multi-Phase System Service system Arrivals Cars in area Queue Service facility Mc. Donald’s drive-through Waiting cars Pay Pickup Served units Cars & food
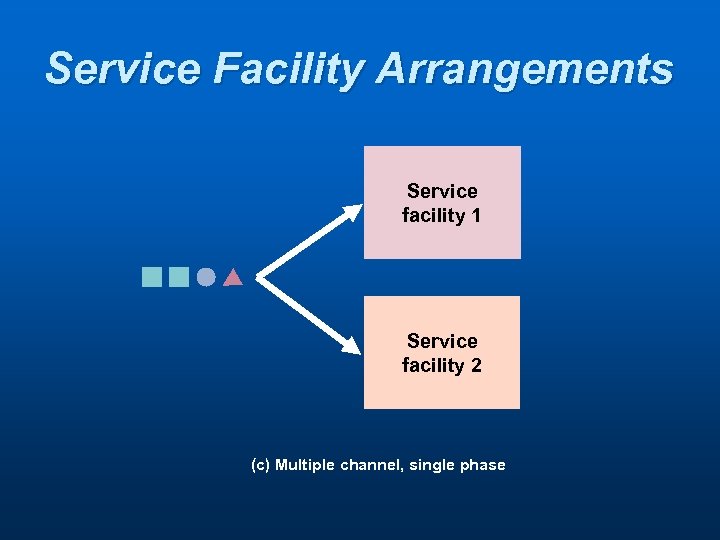 Service Facility Arrangements Service facility 1 Service facility 2 (c) Multiple channel, single phase
Service Facility Arrangements Service facility 1 Service facility 2 (c) Multiple channel, single phase
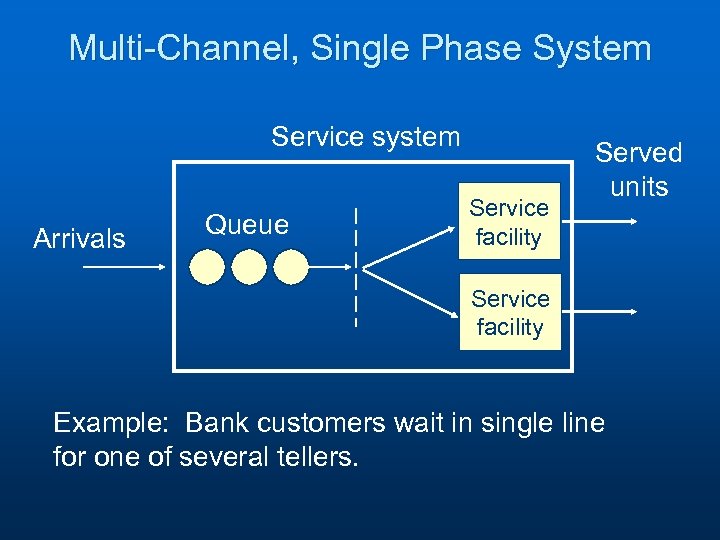 Multi-Channel, Single Phase System Service system Arrivals Queue Service facility Served units Service facility Example: Bank customers wait in single line for one of several tellers.
Multi-Channel, Single Phase System Service system Arrivals Queue Service facility Served units Service facility Example: Bank customers wait in single line for one of several tellers.
 Decision Areas · · · Arrival rates Number of service channels Number of phases Service time Priority rule Line arrangement
Decision Areas · · · Arrival rates Number of service channels Number of phases Service time Priority rule Line arrangement
 Performance Measures or Operating Characteristics n Average queue length, Lq n Average number in system, Ls n Average queue time, Wq n Average time in system, Ws n System utilization,
Performance Measures or Operating Characteristics n Average queue length, Lq n Average number in system, Ls n Average queue time, Wq n Average time in system, Ws n System utilization,
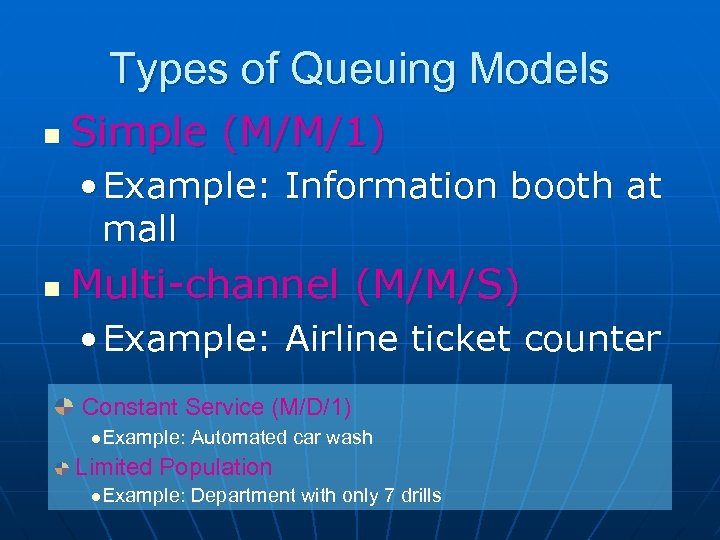 Types of Queuing Models n Simple (M/M/1) • Example: Information booth at mall n Multi-channel (M/M/S) • Example: Airline ticket counter Constant Service (M/D/1) l. Example: Automated car wash Limited Population l. Example: Department with only 7 drills
Types of Queuing Models n Simple (M/M/1) • Example: Information booth at mall n Multi-channel (M/M/S) • Example: Airline ticket counter Constant Service (M/D/1) l. Example: Automated car wash Limited Population l. Example: Department with only 7 drills
 Simple (M/M/1) Model Characteristics n Type: Single-channel, singlephase system n Queue: Unlimited; single line n Queue discipline: FIFO (FCFS) n Service rate > arrival rate
Simple (M/M/1) Model Characteristics n Type: Single-channel, singlephase system n Queue: Unlimited; single line n Queue discipline: FIFO (FCFS) n Service rate > arrival rate
 Queuing Models n - ‘lambda’ • arrival rate of the customers n - ‘mu’ • service rate for a single server • If the service time is 15 minutes per customer, what is the service rate? ?
Queuing Models n - ‘lambda’ • arrival rate of the customers n - ‘mu’ • service rate for a single server • If the service time is 15 minutes per customer, what is the service rate? ?
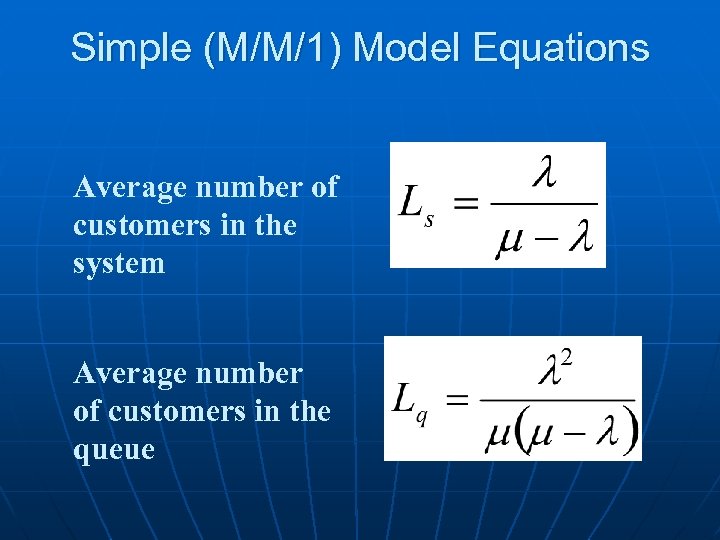 Simple (M/M/1) Model Equations Average number of customers in the system Average number of customers in the queue
Simple (M/M/1) Model Equations Average number of customers in the system Average number of customers in the queue
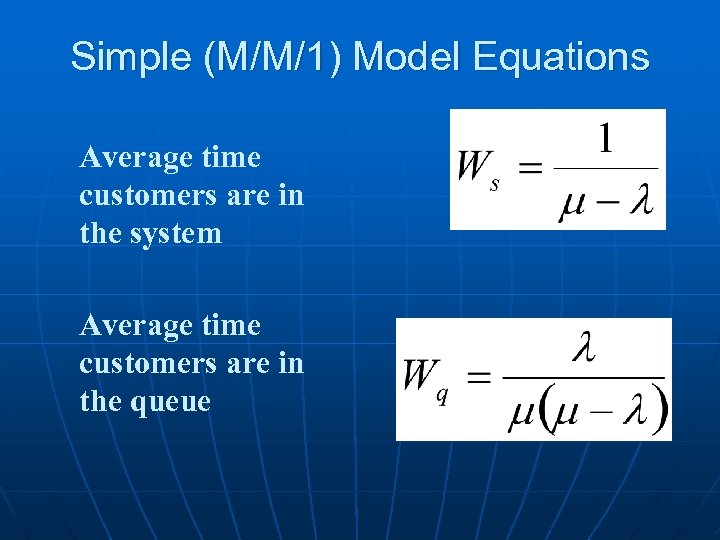 Simple (M/M/1) Model Equations Average time customers are in the system Average time customers are in the queue
Simple (M/M/1) Model Equations Average time customers are in the system Average time customers are in the queue
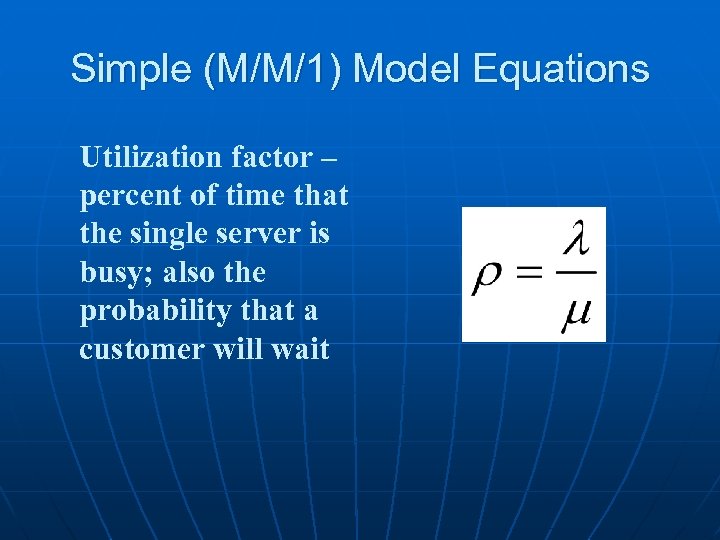 Simple (M/M/1) Model Equations Utilization factor – percent of time that the single server is busy; also the probability that a customer will wait
Simple (M/M/1) Model Equations Utilization factor – percent of time that the single server is busy; also the probability that a customer will wait
 Example: Video Store n The manager of a video store is interested in providing good service. On a Friday or Saturday night, on average 30 customers per hour arrive at the counter to check out a video. The customers are served at an average rate of 35 customers per hour from a single cash register.
Example: Video Store n The manager of a video store is interested in providing good service. On a Friday or Saturday night, on average 30 customers per hour arrive at the counter to check out a video. The customers are served at an average rate of 35 customers per hour from a single cash register.
 Example: Video Store n Determine the operating characteristics for the video store. • Average number of customers in line • Average number of customers in the system • Average wait time in line • Average time in the system • Server utilization
Example: Video Store n Determine the operating characteristics for the video store. • Average number of customers in line • Average number of customers in the system • Average wait time in line • Average time in the system • Server utilization
 Average number of customers in line
Average number of customers in line
 Average number of customers in the system
Average number of customers in the system
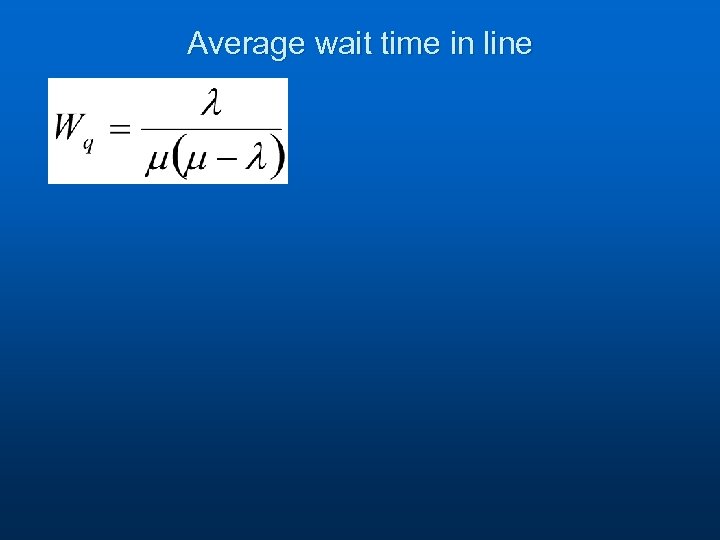 Average wait time in line
Average wait time in line
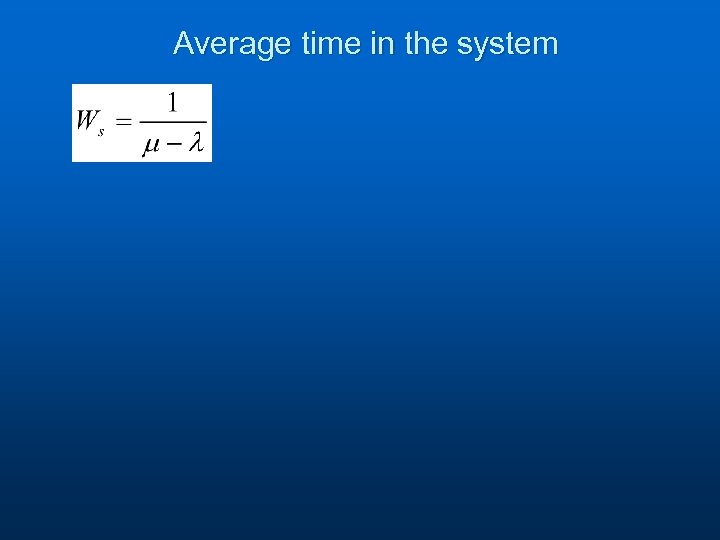 Average time in the system
Average time in the system
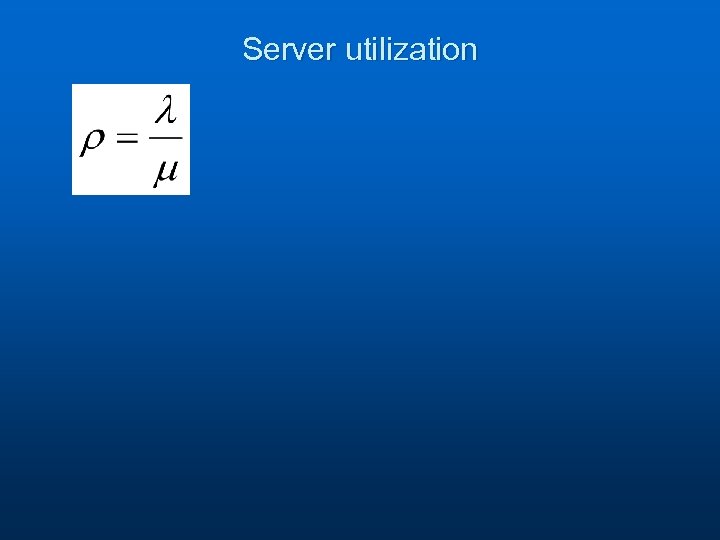 Server utilization
Server utilization
 Example: Video Store • What service rate would be required to have customers average only 5 minutes in the system?
Example: Video Store • What service rate would be required to have customers average only 5 minutes in the system?
 What service rate would be required to have customers average only 5 minutes in the system? GO TO EXCEL OM
What service rate would be required to have customers average only 5 minutes in the system? GO TO EXCEL OM
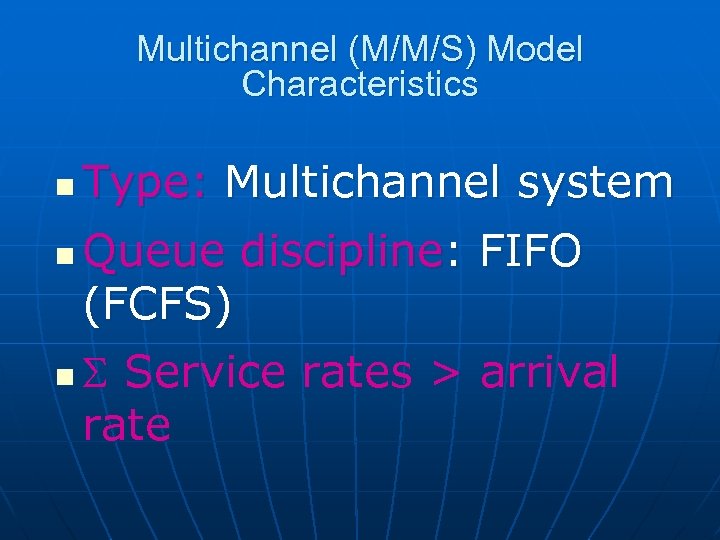 Multichannel (M/M/S) Model Characteristics n n n Type: Multichannel system Queue discipline: FIFO (FCFS) Service rates > arrival rate
Multichannel (M/M/S) Model Characteristics n n n Type: Multichannel system Queue discipline: FIFO (FCFS) Service rates > arrival rate
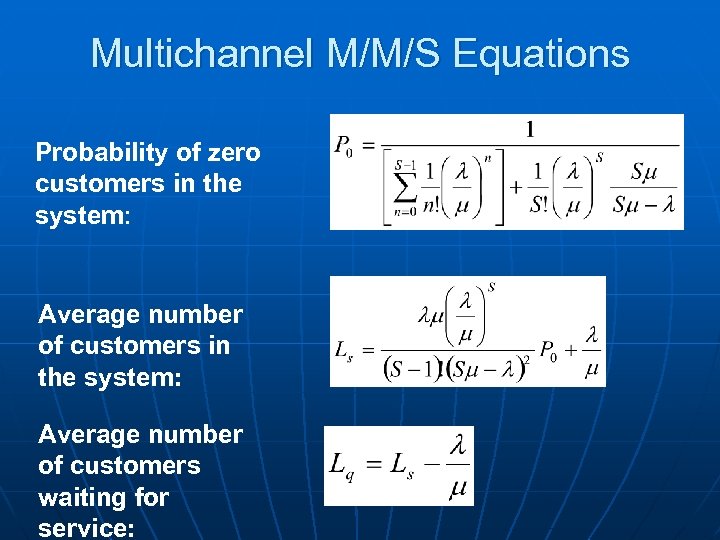 Multichannel M/M/S Equations Probability of zero customers in the system: Average number of customers in the system: Average number of customers waiting for service:
Multichannel M/M/S Equations Probability of zero customers in the system: Average number of customers in the system: Average number of customers waiting for service:
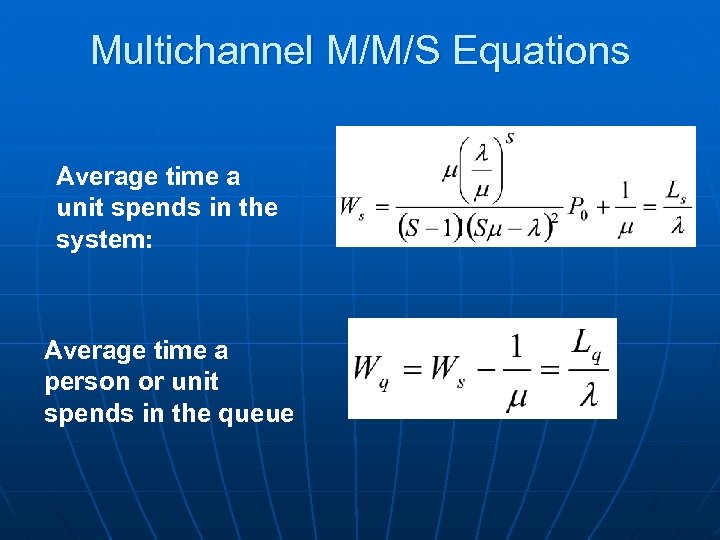 Multichannel M/M/S Equations Average time a unit spends in the system: Average time a person or unit spends in the queue
Multichannel M/M/S Equations Average time a unit spends in the system: Average time a person or unit spends in the queue
 Example: Movie Theater n A multiplex movie theater has 3 concession clerks serving customers on a first come, first served basis. The service time per customer is exponentially distributed with an average of 2 minutes per customer. Concession customers arrive at a rate of 81 customers per hour. 10 minutes of previews run in the lobby. If the average time in the concession area exceed 10 minutes, customers become dissatisfied.
Example: Movie Theater n A multiplex movie theater has 3 concession clerks serving customers on a first come, first served basis. The service time per customer is exponentially distributed with an average of 2 minutes per customer. Concession customers arrive at a rate of 81 customers per hour. 10 minutes of previews run in the lobby. If the average time in the concession area exceed 10 minutes, customers become dissatisfied.
 Example: Movie theater n What is the average number of customers in the concession area?
Example: Movie theater n What is the average number of customers in the concession area?
 What is the average number of customers in the concession area? GO TO EXCEL OM
What is the average number of customers in the concession area? GO TO EXCEL OM
 Multiplex Movie Theater n The distribution is reducing the length of the previews to 8 minutes. How many servers will be required to so that the average wait is no longer than 8 minutes?
Multiplex Movie Theater n The distribution is reducing the length of the previews to 8 minutes. How many servers will be required to so that the average wait is no longer than 8 minutes?
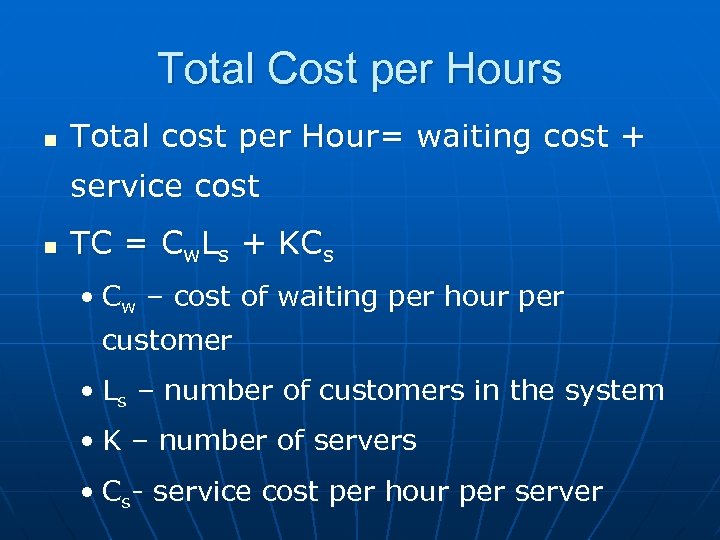 Total Cost per Hours n Total cost per Hour= waiting cost + service cost n TC = Cw. Ls + KCs • Cw – cost of waiting per hour per customer • Ls – number of customers in the system • K – number of servers • Cs- service cost per hour per server
Total Cost per Hours n Total cost per Hour= waiting cost + service cost n TC = Cw. Ls + KCs • Cw – cost of waiting per hour per customer • Ls – number of customers in the system • K – number of servers • Cs- service cost per hour per server
 Total Cost: Video Store n Considering adding another cashier for Friday and Saturday nights. n Part-time cashier will cost $6. 00 per hour n Customers waiting time (cost of goodwill, etc) is $10. 00 per hour. n Is it cost effective to hire the cashier?
Total Cost: Video Store n Considering adding another cashier for Friday and Saturday nights. n Part-time cashier will cost $6. 00 per hour n Customers waiting time (cost of goodwill, etc) is $10. 00 per hour. n Is it cost effective to hire the cashier?
 Total Cost: Video Store M/M/1 TC = Cw. Ls + KC Cw = $10/hour Ls = 6 K=1 CS = $6. 00/hr TC = 10(6) + 1(6) = $66/hour
Total Cost: Video Store M/M/1 TC = Cw. Ls + KC Cw = $10/hour Ls = 6 K=1 CS = $6. 00/hr TC = 10(6) + 1(6) = $66/hour
 Total Cost: Video Store M/M/2 TC = Cw. L + KC Cw = $10/hour Ls = 1. 05 K=2 Cs = $6. 00/hr TC = 10(1. 05) + 2(6) = $22. 50/hr
Total Cost: Video Store M/M/2 TC = Cw. L + KC Cw = $10/hour Ls = 1. 05 K=2 Cs = $6. 00/hr TC = 10(1. 05) + 2(6) = $22. 50/hr
 Remember: n & Are Rates = Mean number of arrivals per time period • e. g. , 3 units/hour n If average service time is 15 minutes, then μ is 4 customers/hour = Mean number of people or items served per time period • e. g. , 4 units/hour n 1/ = 15 minutes/unit © 1984 -1994 T/Maker Co.
Remember: n & Are Rates = Mean number of arrivals per time period • e. g. , 3 units/hour n If average service time is 15 minutes, then μ is 4 customers/hour = Mean number of people or items served per time period • e. g. , 4 units/hour n 1/ = 15 minutes/unit © 1984 -1994 T/Maker Co.
 The Psychology of Waiting n Maister’s (1985) Propositions of customer satisfaction in queues • Unoccupied time feels longer than occupied time • Pre-process wait feels longer than in-process waits. • Anxiety makes waits feel longer
The Psychology of Waiting n Maister’s (1985) Propositions of customer satisfaction in queues • Unoccupied time feels longer than occupied time • Pre-process wait feels longer than in-process waits. • Anxiety makes waits feel longer
 The Psychology of Waiting • Uncertain waits seem longer than certain waits • Unexplained waits seem longer than explained waits • Unfair waits seem longer than equitable waits
The Psychology of Waiting • Uncertain waits seem longer than certain waits • Unexplained waits seem longer than explained waits • Unfair waits seem longer than equitable waits
 Psychology of Waiting • More valuable the service, the longer people will wait. • Solo waiting feels longer than group waiting.
Psychology of Waiting • More valuable the service, the longer people will wait. • Solo waiting feels longer than group waiting.


