 Pythagoras’ Theorem Only works in right angled triangles Nothing to do with angles
Pythagoras’ Theorem Only works in right angled triangles Nothing to do with angles
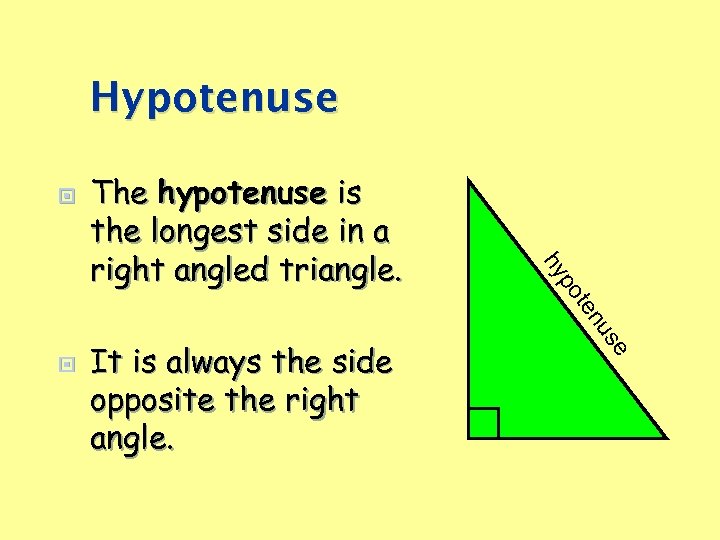 Hypotenuse It is always the side opposite the right angle. se nu te po hy The hypotenuse is the longest side in a right angled triangle.
Hypotenuse It is always the side opposite the right angle. se nu te po hy The hypotenuse is the longest side in a right angled triangle.
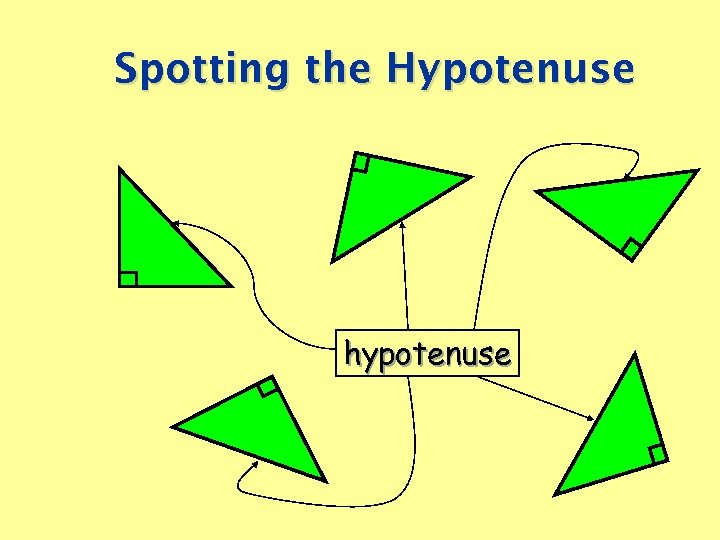 Spotting the Hypotenuse hypotenuse
Spotting the Hypotenuse hypotenuse
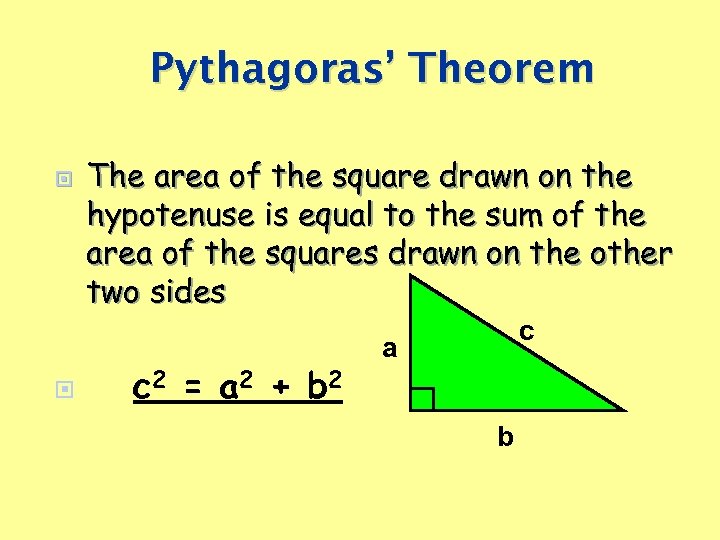 Pythagoras’ Theorem The area of the square drawn on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the area of the squares drawn on the other two sides c 2 = a 2 + b 2 c a b
Pythagoras’ Theorem The area of the square drawn on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the area of the squares drawn on the other two sides c 2 = a 2 + b 2 c a b
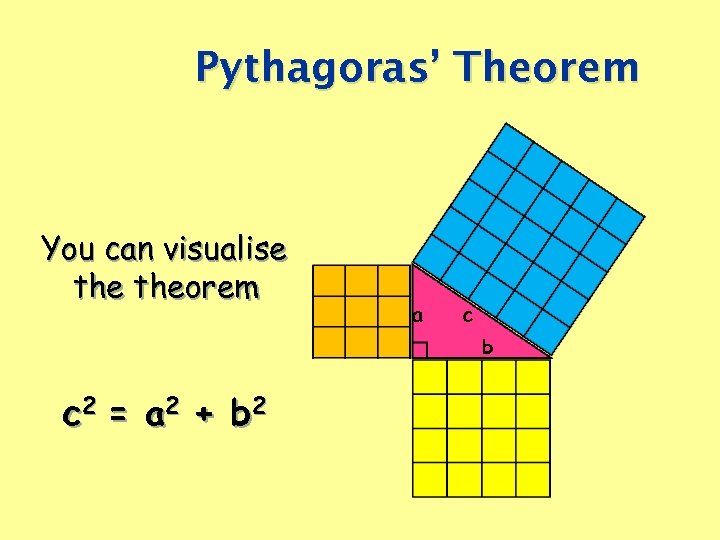 Pythagoras’ Theorem You can visualise theorem a c b c 2 = a 2 + b 2
Pythagoras’ Theorem You can visualise theorem a c b c 2 = a 2 + b 2
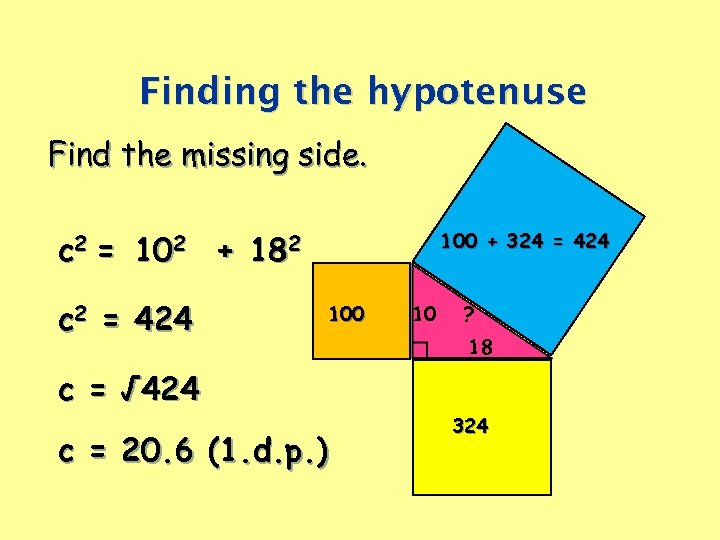 Finding the hypotenuse Find the missing side. c 2 = 102 c 2 = 424 + 100 + 324 = 424 182 100 10 ? 18 c = √ 424 c = 20. 6 (1. d. p. ) 324
Finding the hypotenuse Find the missing side. c 2 = 102 c 2 = 424 + 100 + 324 = 424 182 100 10 ? 18 c = √ 424 c = 20. 6 (1. d. p. ) 324
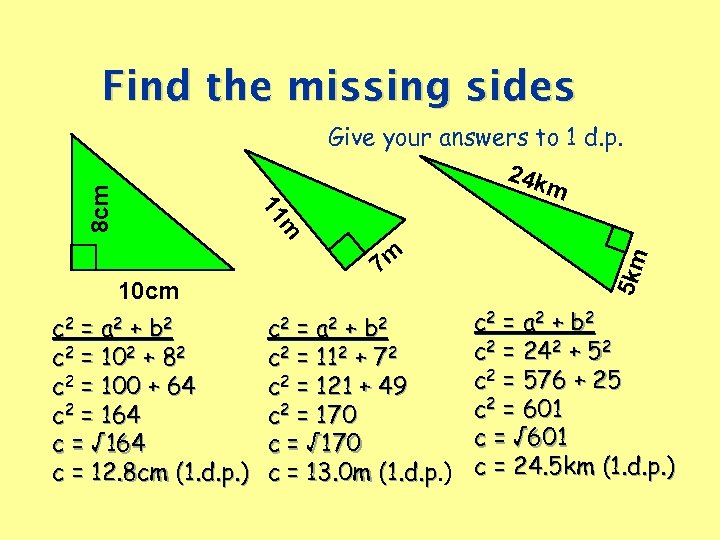 Find the missing sides 11 8 cm Give your answers to 1 d. p. 24 k m 10 cm 5 km m 7 m c 2 = a 2 + b 2 = + 2 = 102 + 82 2 = 112 + 72 c 2 = 242 + 52 c c c 2 = 576 + 25 c 2 = 100 + 64 c 2 = 121 + 49 c 2 = 601 c 2 = 164 c 2 = 170 c = √ 601 c = √ 164 c = √ 170 c = 12. 8 cm (1. d. p. ) c = 13. 0 m (1. d. p. ) c = 24. 5 km (1. d. p. ) (1. d. p c 2 a 2 b 2
Find the missing sides 11 8 cm Give your answers to 1 d. p. 24 k m 10 cm 5 km m 7 m c 2 = a 2 + b 2 = + 2 = 102 + 82 2 = 112 + 72 c 2 = 242 + 52 c c c 2 = 576 + 25 c 2 = 100 + 64 c 2 = 121 + 49 c 2 = 601 c 2 = 164 c 2 = 170 c = √ 601 c = √ 164 c = √ 170 c = 12. 8 cm (1. d. p. ) c = 13. 0 m (1. d. p. ) c = 24. 5 km (1. d. p. ) (1. d. p c 2 a 2 b 2
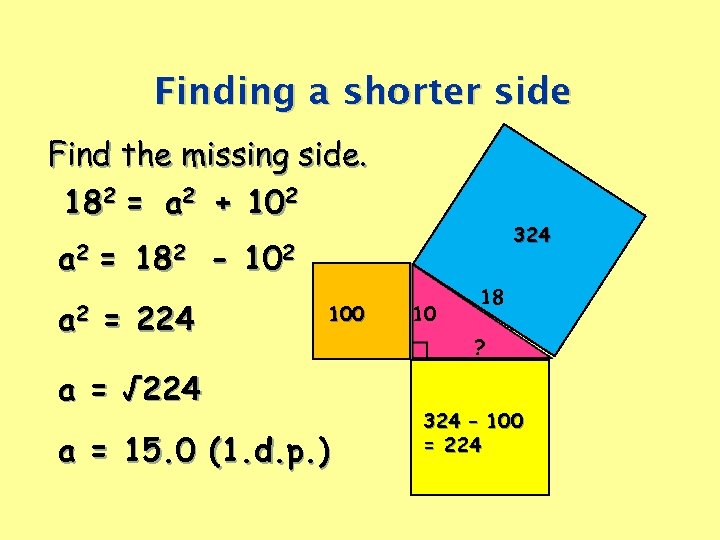 Finding a shorter side Find the missing side. 182 = a 2 + 102 324 a 2 = 182 - 102 a 2 = 224 100 a = √ 224 a = 15. 0 (1. d. p. ) 10 18 ? 324 – 100 = 224
Finding a shorter side Find the missing side. 182 = a 2 + 102 324 a 2 = 182 - 102 a 2 = 224 100 a = √ 224 a = 15. 0 (1. d. p. ) 10 18 ? 324 – 100 = 224
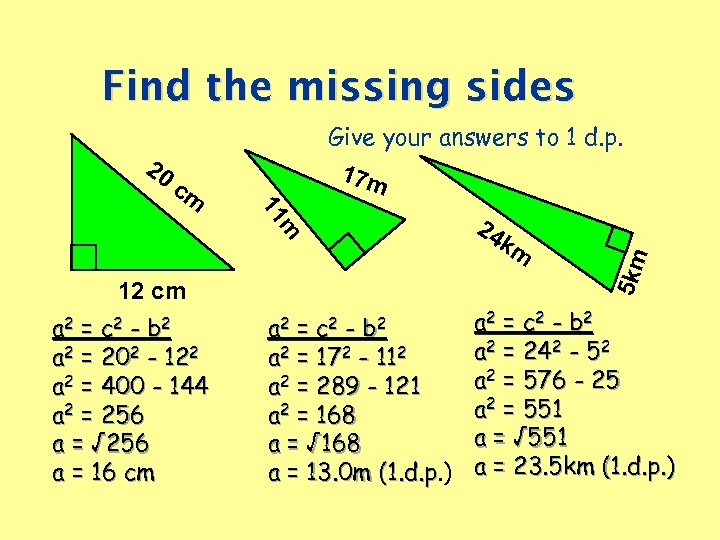 Find the missing sides 11 cm m 24 km 12 cm a 2 c 2 b 2 = a 2 = 202 - 122 a 2 = 400 - 144 a 2 = 256 a = √ 256 a = 16 cm 5 km 20 Give your answers to 1 d. p. 17 m a 2 = c 2 - b 2 = 172 - 112 a 2 = 242 - 52 a a 2 = 576 - 25 a 2 = 289 - 121 a 2 = 551 a 2 = 168 a = √ 551 a = √ 168 a = 13. 0 m (1. d. p. ) a = 23. 5 km (1. d. p. ) (1. d. p a 2 c 2 b 2
Find the missing sides 11 cm m 24 km 12 cm a 2 c 2 b 2 = a 2 = 202 - 122 a 2 = 400 - 144 a 2 = 256 a = √ 256 a = 16 cm 5 km 20 Give your answers to 1 d. p. 17 m a 2 = c 2 - b 2 = 172 - 112 a 2 = 242 - 52 a a 2 = 576 - 25 a 2 = 289 - 121 a 2 = 551 a 2 = 168 a = √ 551 a = √ 168 a = 13. 0 m (1. d. p. ) a = 23. 5 km (1. d. p. ) (1. d. p a 2 c 2 b 2
 Navigation N Navigation problems are often solved W using Pythagoras’ Theorem. E S
Navigation N Navigation problems are often solved W using Pythagoras’ Theorem. E S
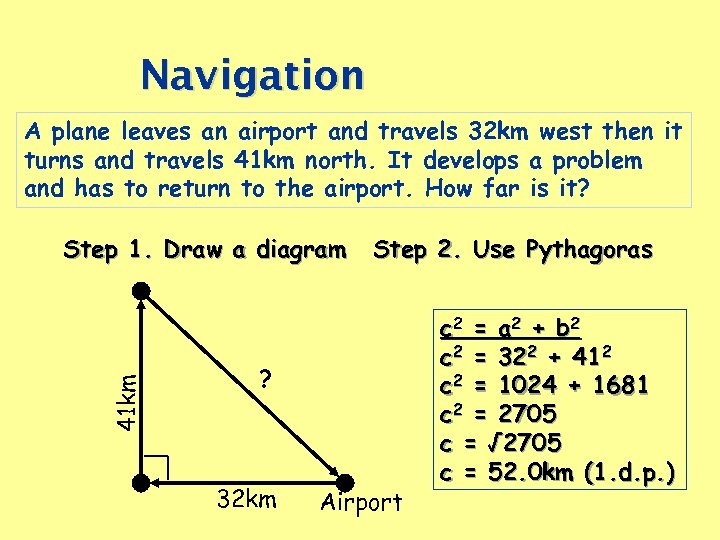 Navigation A plane leaves an airport and travels 32 km west then it turns and travels 41 km north. It develops a problem and has to return to the airport. How far is it? 41 km Step 1. Draw a diagram Step 2. Use Pythagoras ? 32 km Airport c 2 = a 2 + b 2 c 2 = 322 + 412 c 2 = 1024 + 1681 c 2 = 2705 c = √ 2705 c = 52. 0 km (1. d. p. )
Navigation A plane leaves an airport and travels 32 km west then it turns and travels 41 km north. It develops a problem and has to return to the airport. How far is it? 41 km Step 1. Draw a diagram Step 2. Use Pythagoras ? 32 km Airport c 2 = a 2 + b 2 c 2 = 322 + 412 c 2 = 1024 + 1681 c 2 = 2705 c = √ 2705 c = 52. 0 km (1. d. p. )
 Isosceles Triangle Problems involving isosceles triangles are often solved using Pythagoras’ Theorem.
Isosceles Triangle Problems involving isosceles triangles are often solved using Pythagoras’ Theorem.
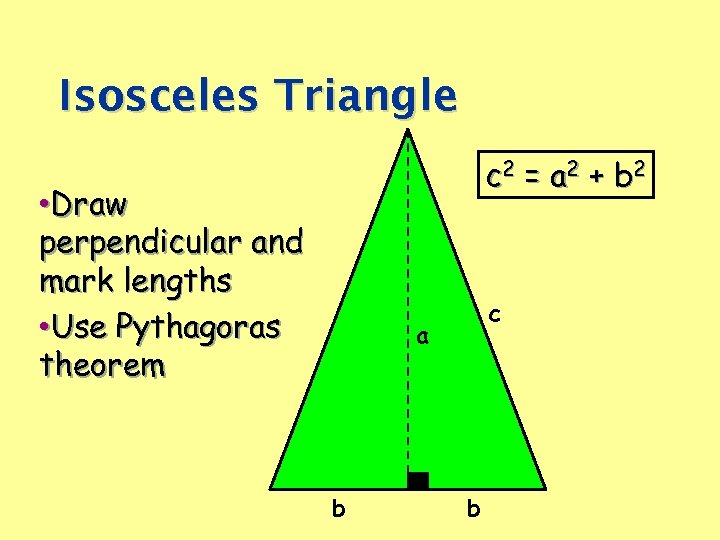 Isosceles Triangle c 2 = a 2 + b 2 • Draw perpendicular and mark lengths • Use Pythagoras theorem c a b b
Isosceles Triangle c 2 = a 2 + b 2 • Draw perpendicular and mark lengths • Use Pythagoras theorem c a b b
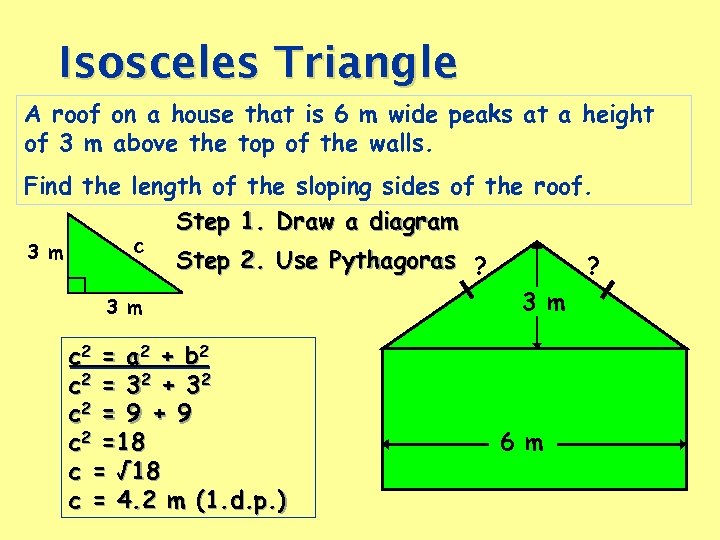 Isosceles Triangle A roof on a house that is 6 m wide peaks at a height of 3 m above the top of the walls. Find the length of the sloping sides of the roof. Step 1. Draw a diagram 3 m c Step 2. Use Pythagoras ? 3 m c 2 = a 2 + b 2 c 2 = 3 2 + 3 2 c 2 = 9 + 9 c 2 =18 c = √ 18 c = 4. 2 m (1. d. p. ) ? 3 m 6 m
Isosceles Triangle A roof on a house that is 6 m wide peaks at a height of 3 m above the top of the walls. Find the length of the sloping sides of the roof. Step 1. Draw a diagram 3 m c Step 2. Use Pythagoras ? 3 m c 2 = a 2 + b 2 c 2 = 3 2 + 3 2 c 2 = 9 + 9 c 2 =18 c = √ 18 c = 4. 2 m (1. d. p. ) ? 3 m 6 m
 Solving Problems Using Pythagoras’ Theorem • draw a diagram for the problem that includes a right-angled triangle • label the triangle with the length of its sides from the question • label the unknown side ‘x’ • if it’s the hypotenuse, then “SQUARE, ADD, SQUARE ROOT” • if it’s one of the shorter sides, then “SQUARE, SUBTRACT, SQUARE ROOT” • round your answer to a suitable degree of accuracy
Solving Problems Using Pythagoras’ Theorem • draw a diagram for the problem that includes a right-angled triangle • label the triangle with the length of its sides from the question • label the unknown side ‘x’ • if it’s the hypotenuse, then “SQUARE, ADD, SQUARE ROOT” • if it’s one of the shorter sides, then “SQUARE, SUBTRACT, SQUARE ROOT” • round your answer to a suitable degree of accuracy
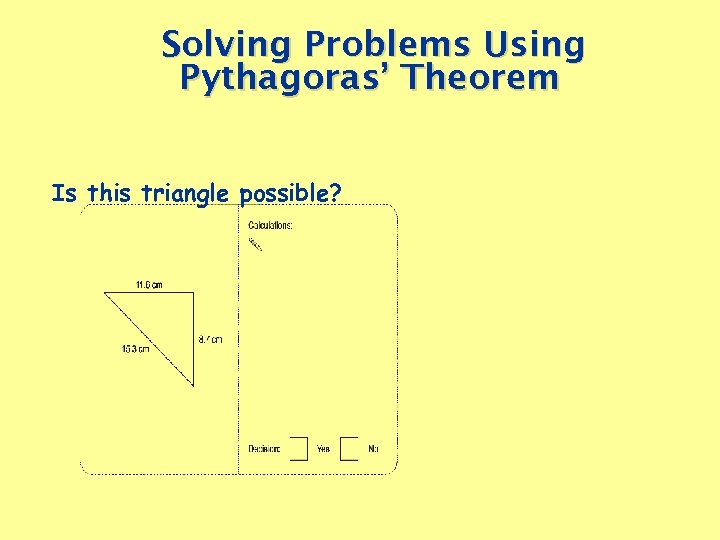 Solving Problems Using Pythagoras’ Theorem Is this triangle possible?
Solving Problems Using Pythagoras’ Theorem Is this triangle possible?