9e850cb547b4b3172c838d422a8085ff.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 Putting Supply and Demand Together!!! 1
Putting Supply and Demand Together!!! 1
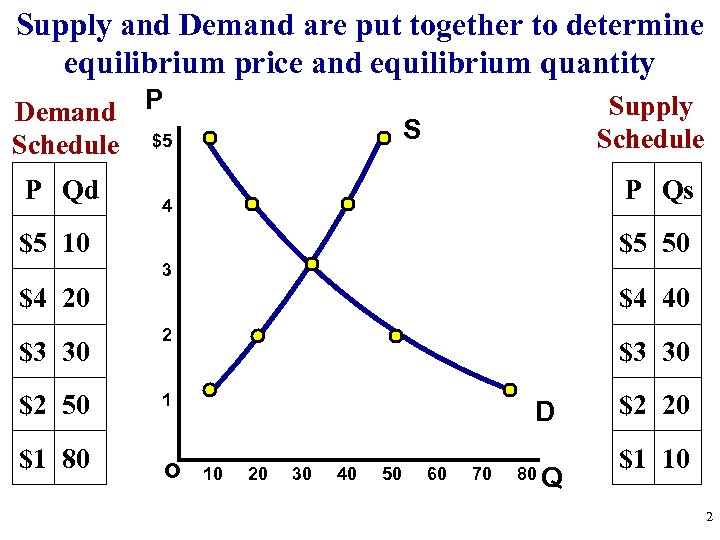 Supply and Demand are put together to determine equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity Demand P Schedule $5 P Qd Supply Schedule S P Qs 4 $5 10 $5 50 3 $4 20 $3 30 $2 50 $1 80 $4 40 2 $3 30 1 o D 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 Q $2 20 $1 10 2
Supply and Demand are put together to determine equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity Demand P Schedule $5 P Qd Supply Schedule S P Qs 4 $5 10 $5 50 3 $4 20 $3 30 $2 50 $1 80 $4 40 2 $3 30 1 o D 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 Q $2 20 $1 10 2
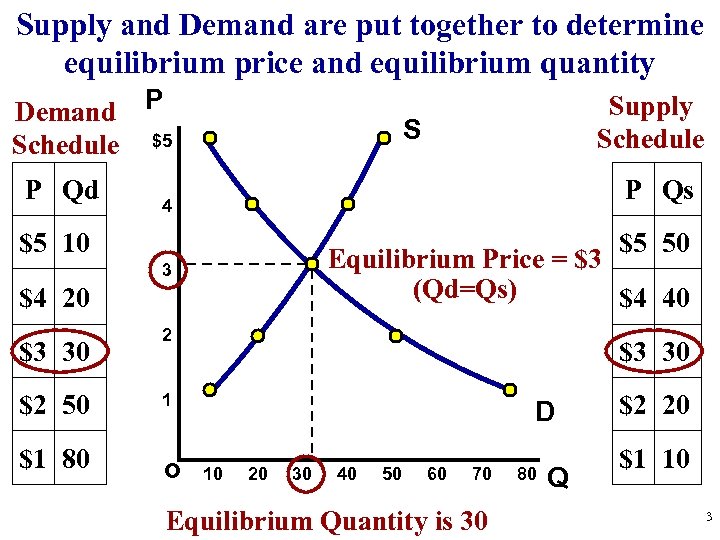 Supply and Demand are put together to determine equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity Demand P Schedule $5 P Qd S P Qs 4 $5 10 $5 50 Equilibrium Price = $3 (Qd=Qs) $4 40 3 $4 20 $3 30 $2 50 $1 80 Supply Schedule 2 $3 30 1 o D 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 Equilibrium Quantity is 30 80 Q $2 20 $1 10 3
Supply and Demand are put together to determine equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity Demand P Schedule $5 P Qd S P Qs 4 $5 10 $5 50 Equilibrium Price = $3 (Qd=Qs) $4 40 3 $4 20 $3 30 $2 50 $1 80 Supply Schedule 2 $3 30 1 o D 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 Equilibrium Quantity is 30 80 Q $2 20 $1 10 3
 Supply and Demand are put together to determine equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity Demand P Schedule $5 P Qd 3 $4 20 $2 50 $1 80 S P Qs 4 $5 10 $3 30 Supply Schedule 2 What if the price increases to $4? 1 o $5 50 $4 40 $3 30 D 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 Q $2 20 $1 10 4
Supply and Demand are put together to determine equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity Demand P Schedule $5 P Qd 3 $4 20 $2 50 $1 80 S P Qs 4 $5 10 $3 30 Supply Schedule 2 What if the price increases to $4? 1 o $5 50 $4 40 $3 30 D 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 Q $2 20 $1 10 4
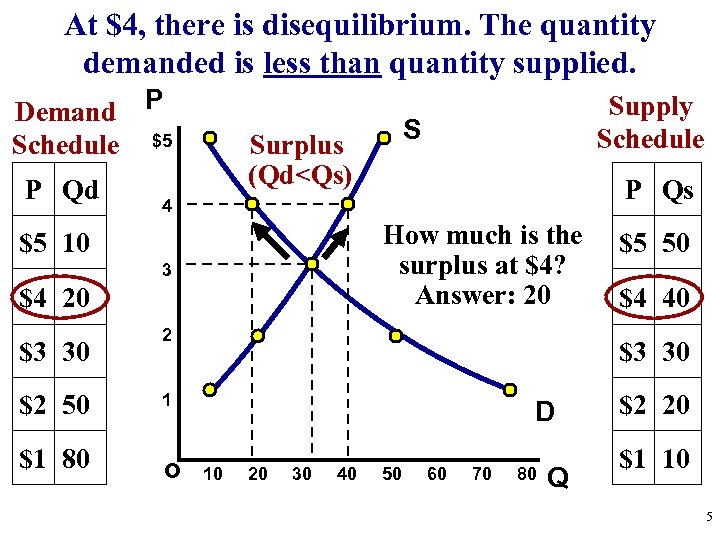 At $4, there is disequilibrium. The quantity demanded is less than quantity supplied. Demand P Schedule $5 P Qd How much is the surplus at $4? Answer: 20 $4 20 $1 80 P Qs 4 3 $2 50 S Surplus (Qd
At $4, there is disequilibrium. The quantity demanded is less than quantity supplied. Demand P Schedule $5 P Qd How much is the surplus at $4? Answer: 20 $4 20 $1 80 P Qs 4 3 $2 50 S Surplus (Qd
 How much is the surplus if the price is $5? Demand P Schedule $5 P Qd 3 $4 20 $2 50 $1 80 S P Qs 4 $5 10 $3 30 Supply Schedule 2 What if the Answer: 40 price decreases to $2? 1 o D 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 Q $5 50 $4 40 $3 30 $2 20 $1 10 6
How much is the surplus if the price is $5? Demand P Schedule $5 P Qd 3 $4 20 $2 50 $1 80 S P Qs 4 $5 10 $3 30 Supply Schedule 2 What if the Answer: 40 price decreases to $2? 1 o D 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 Q $5 50 $4 40 $3 30 $2 20 $1 10 6
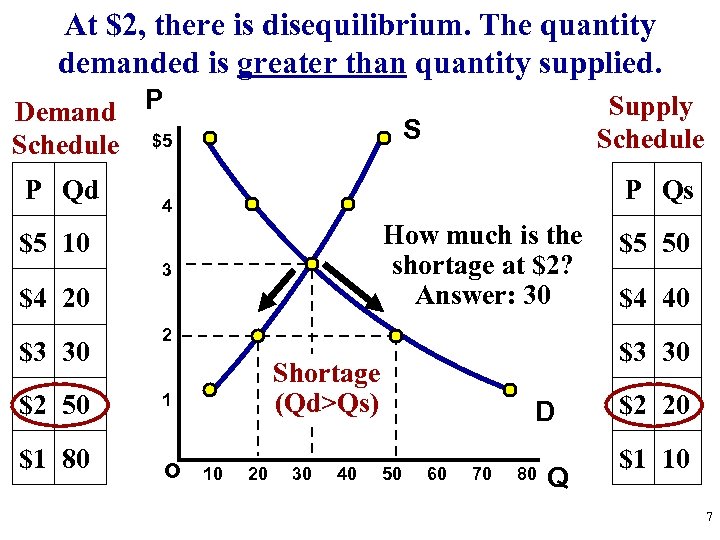 At $2, there is disequilibrium. The quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied. Demand P Schedule $5 P Qd S P Qs 4 How much is the shortage at $2? Answer: 30 $5 10 3 $4 20 $3 30 $2 50 $1 80 Supply Schedule 2 o 10 20 30 40 $4 40 $3 30 Shortage (Qd>Qs) 1 $5 50 D 50 60 70 80 Q $2 20 $1 10 7
At $2, there is disequilibrium. The quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied. Demand P Schedule $5 P Qd S P Qs 4 How much is the shortage at $2? Answer: 30 $5 10 3 $4 20 $3 30 $2 50 $1 80 Supply Schedule 2 o 10 20 30 40 $4 40 $3 30 Shortage (Qd>Qs) 1 $5 50 D 50 60 70 80 Q $2 20 $1 10 7
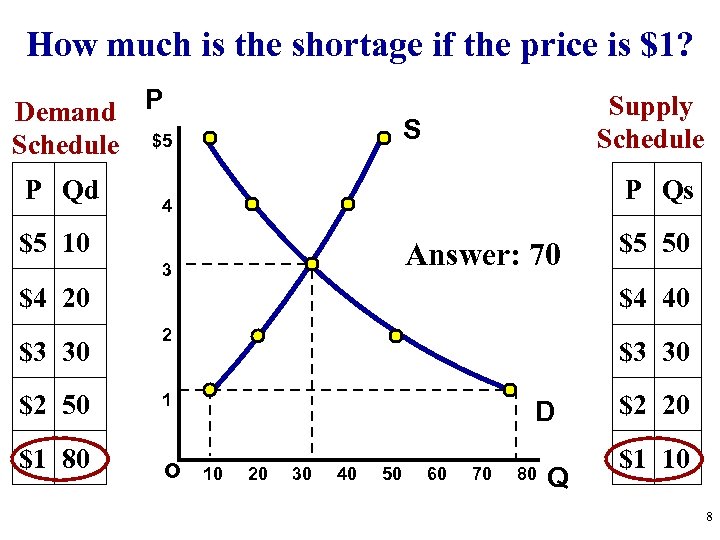 How much is the shortage if the price is $1? Demand P Schedule $5 P Qd Supply Schedule S P Qs 4 $5 10 Answer: 70 3 $4 20 $3 30 $2 50 $1 80 $5 50 $4 40 2 $3 30 1 o D 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 Q $2 20 $1 10 8
How much is the shortage if the price is $1? Demand P Schedule $5 P Qd Supply Schedule S P Qs 4 $5 10 Answer: 70 3 $4 20 $3 30 $2 50 $1 80 $5 50 $4 40 2 $3 30 1 o D 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 Q $2 20 $1 10 8
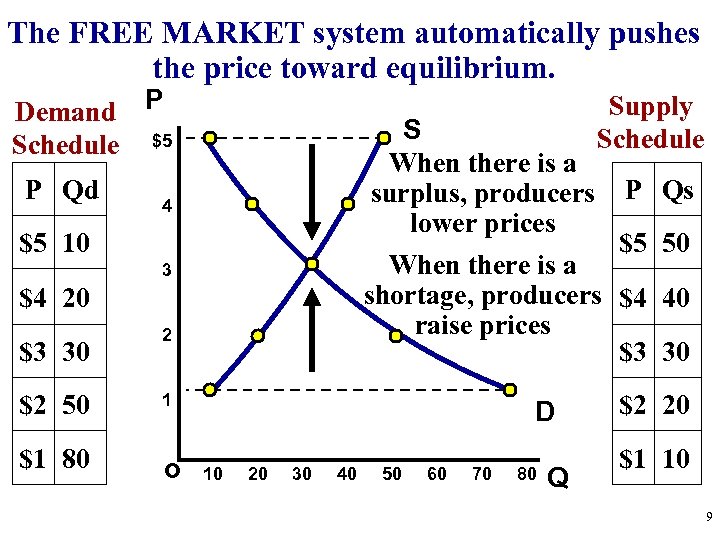 The FREE MARKET system automatically pushes the price toward equilibrium. Demand P Schedule $5 P Qd Supply Schedule S When there is a surplus, producers P Qs lower prices $5 50 When there is a shortage, producers $4 40 raise prices $3 30 4 $5 10 3 $4 20 $3 30 $2 50 $1 80 2 1 o D 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 Q $2 20 $1 10 9
The FREE MARKET system automatically pushes the price toward equilibrium. Demand P Schedule $5 P Qd Supply Schedule S When there is a surplus, producers P Qs lower prices $5 50 When there is a shortage, producers $4 40 raise prices $3 30 4 $5 10 3 $4 20 $3 30 $2 50 $1 80 2 1 o D 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 Q $2 20 $1 10 9
 Use a S&D to explain this shift 10
Use a S&D to explain this shift 10
 Voluntary Exchange In the free-market, buyers and sellers voluntarily come together to seek mutual benefits. 11
Voluntary Exchange In the free-market, buyers and sellers voluntarily come together to seek mutual benefits. 11
 Voluntary Exchange In the free-market, buyers and sellers voluntarily come together to seek mutual benefits. 12
Voluntary Exchange In the free-market, buyers and sellers voluntarily come together to seek mutual benefits. 12
 Voluntary Exchange In the free-market, buyers and sellers voluntarily come together to seek mutual benefits. 13
Voluntary Exchange In the free-market, buyers and sellers voluntarily come together to seek mutual benefits. 13
 Voluntary Exchange In the free-market, buyers and sellers voluntarily come together to seek mutual benefits. 14
Voluntary Exchange In the free-market, buyers and sellers voluntarily come together to seek mutual benefits. 14
 Example of Voluntary Exchange Ex: You want to buy a truck so you go to the local dealership. You are willing to spend up to $20, 000 for a new 4 x 4. The seller is willing to sell this truck for no less than $15, 000. After some negotiation you buy the truck for $18, 000. Analysis: Buyer’ Maximum- $20, 000 Sellers Minimum- $15, 000 Price- $18, 000 Consumer’s Surplus-$2, 000 Producer’s Surplus- $3, 000 15
Example of Voluntary Exchange Ex: You want to buy a truck so you go to the local dealership. You are willing to spend up to $20, 000 for a new 4 x 4. The seller is willing to sell this truck for no less than $15, 000. After some negotiation you buy the truck for $18, 000. Analysis: Buyer’ Maximum- $20, 000 Sellers Minimum- $15, 000 Price- $18, 000 Consumer’s Surplus-$2, 000 Producer’s Surplus- $3, 000 15
 Voluntary Exchange Terms Consumer Surplus is the difference between what you are willing to pay and what you actually pay. CS = Buyer’s Maximum – Price Producer’s Surplus is the difference between the price the seller received and how much they were willing to sell it for. PS = Price – Seller’s Minimum 16
Voluntary Exchange Terms Consumer Surplus is the difference between what you are willing to pay and what you actually pay. CS = Buyer’s Maximum – Price Producer’s Surplus is the difference between the price the seller received and how much they were willing to sell it for. PS = Price – Seller’s Minimum 16
 Pearl Exchange Activity 17
Pearl Exchange Activity 17
 Voluntary Exchange Activity 18
Voluntary Exchange Activity 18


