cd514f7235fe32e9faec430317d3486f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 48
 PURCHASING & SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT, 4 e The Purchasing Process Chapter 2 CENGAGE LEARNING Monczka – Handfield – Giunipero – Patterson
PURCHASING & SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT, 4 e The Purchasing Process Chapter 2 CENGAGE LEARNING Monczka – Handfield – Giunipero – Patterson
 Chapter Overview § § § Purchasing objectives Responsibilities of purchasing E-procurement and the procure to pay process § Types of purchases § Improving the purchasing process Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 2
Chapter Overview § § § Purchasing objectives Responsibilities of purchasing E-procurement and the procure to pay process § Types of purchases § Improving the purchasing process Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 2
 Elements of the Purchasing Process § § § Identify user requirements Evaluate need effectively and efficiently Identify suppliers Ensure payment occurs promptly Ascertain that the need was effectively met § Drive continuous improvement Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 3
Elements of the Purchasing Process § § § Identify user requirements Evaluate need effectively and efficiently Identify suppliers Ensure payment occurs promptly Ascertain that the need was effectively met § Drive continuous improvement Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 3
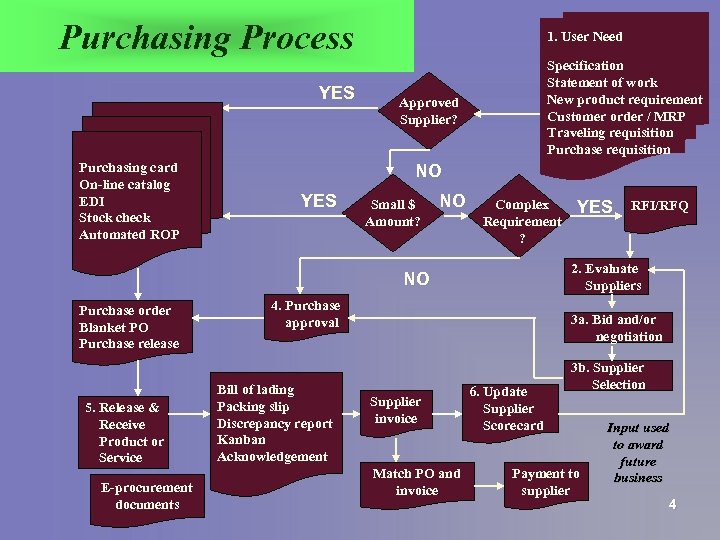 Purchasing Process YES Purchasing card On-line catalog EDI Stock check Automated ROP 1. User Need Specification Statement of work New product requirement Customer order / MRP Traveling requisition Purchase requisition Approved Supplier? NO YES Small $ Amount? NO Complex Requirement ? 5. Release & Receive Product or Service E-procurement documents 4. Purchase approval Bill of lading Packing slip Discrepancy report Kanban Acknowledgement RFI/RFQ 2. Evaluate Suppliers NO Purchase order Blanket PO Purchase release YES 3 a. Bid and/or negotiation Supplier invoice Match PO and invoice 6. Update Supplier Scorecard 3 b. Supplier Selection Payment to supplier Input used to award future business 4
Purchasing Process YES Purchasing card On-line catalog EDI Stock check Automated ROP 1. User Need Specification Statement of work New product requirement Customer order / MRP Traveling requisition Purchase requisition Approved Supplier? NO YES Small $ Amount? NO Complex Requirement ? 5. Release & Receive Product or Service E-procurement documents 4. Purchase approval Bill of lading Packing slip Discrepancy report Kanban Acknowledgement RFI/RFQ 2. Evaluate Suppliers NO Purchase order Blanket PO Purchase release YES 3 a. Bid and/or negotiation Supplier invoice Match PO and invoice 6. Update Supplier Scorecard 3 b. Supplier Selection Payment to supplier Input used to award future business 4
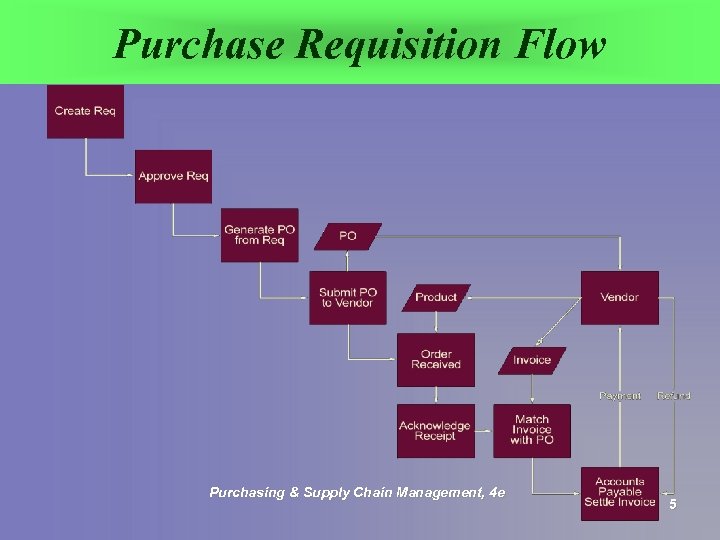 Purchase Requisition Flow Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 5
Purchase Requisition Flow Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 5
 Purchasing Objectives § Supply continuity § Manage the purchasing process efficiently and effectively § Develop supply base management § Develop strong relationships with other functional stakeholders Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 6
Purchasing Objectives § Supply continuity § Manage the purchasing process efficiently and effectively § Develop supply base management § Develop strong relationships with other functional stakeholders Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 6
 Purchasing Objectives § Support organizational goals and objectives § Develop integrated purchasing strategies that support organizational strategies Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 7
Purchasing Objectives § Support organizational goals and objectives § Develop integrated purchasing strategies that support organizational strategies Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 7
 Supply Continuity § § § Buy products/services at the right price Buy them from the right source Buy them at the right specification that meets users’ needs Buy them in the right quantity Arrange for delivery at the right time Require delivery to the right internal customer Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 8
Supply Continuity § § § Buy products/services at the right price Buy them from the right source Buy them at the right specification that meets users’ needs Buy them in the right quantity Arrange for delivery at the right time Require delivery to the right internal customer Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 8
 Manage the Purchasing Process § § § Determining staff levels Developing and adhering to budgets Providing professional training and growth opportunities § Introducing procure to pay systems Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 9
Manage the Purchasing Process § § § Determining staff levels Developing and adhering to budgets Providing professional training and growth opportunities § Introducing procure to pay systems Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 9
 Procure to Pay Systems § § § Improved spending visibility Efficient invoicing and payment User satisfaction Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 10
Procure to Pay Systems § § § Improved spending visibility Efficient invoicing and payment User satisfaction Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 10
 Develop Supply Base Management § Select competitive suppliers § Identify new suppliers with high potential and build closer relationships § Improve existing suppliers § Develop new suppliers who are not currently competitive Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 11
Develop Supply Base Management § Select competitive suppliers § Identify new suppliers with high potential and build closer relationships § Improve existing suppliers § Develop new suppliers who are not currently competitive Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 11
 Develop Strong Internal Relationships § § § Internal customers as stakeholders Strong two-way communication Cross-functional coordination and collaboration § Positive, problem-solving relationships Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 12
Develop Strong Internal Relationships § § § Internal customers as stakeholders Strong two-way communication Cross-functional coordination and collaboration § Positive, problem-solving relationships Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 12
 Support Goals and Objectives § Congruency of functional goals with organizational goals § Mutually-supportive, not counterproductive § Purchasing’s substantial impact on the organization’s bottom line § Purchasing as a strategic core competency Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 13
Support Goals and Objectives § Congruency of functional goals with organizational goals § Mutually-supportive, not counterproductive § Purchasing’s substantial impact on the organization’s bottom line § Purchasing as a strategic core competency Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 13
 Supply Market Intelligence § Monitoring supply markets and trends § Identifying critical materials and services § Supporting new product development § Developing supply options and contingency plans § Supporting a diverse and globally competitive supply base Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 14
Supply Market Intelligence § Monitoring supply markets and trends § Identifying critical materials and services § Supporting new product development § Developing supply options and contingency plans § Supporting a diverse and globally competitive supply base Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 14
 Reasons for Not Being Strategic § Purchasing personnel have not historically participated in senior-level corporate planning § Executive management has not always recognized the benefits of world-class purchasing Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 15
Reasons for Not Being Strategic § Purchasing personnel have not historically participated in senior-level corporate planning § Executive management has not always recognized the benefits of world-class purchasing Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 15
 Purchasing Responsibilities § § § Evaluate and select suppliers Review specifications Act as primary contact with suppliers Forecast and plan requirements Clarify requisitioner’s needs Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 16
Purchasing Responsibilities § § § Evaluate and select suppliers Review specifications Act as primary contact with suppliers Forecast and plan requirements Clarify requisitioner’s needs Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 16
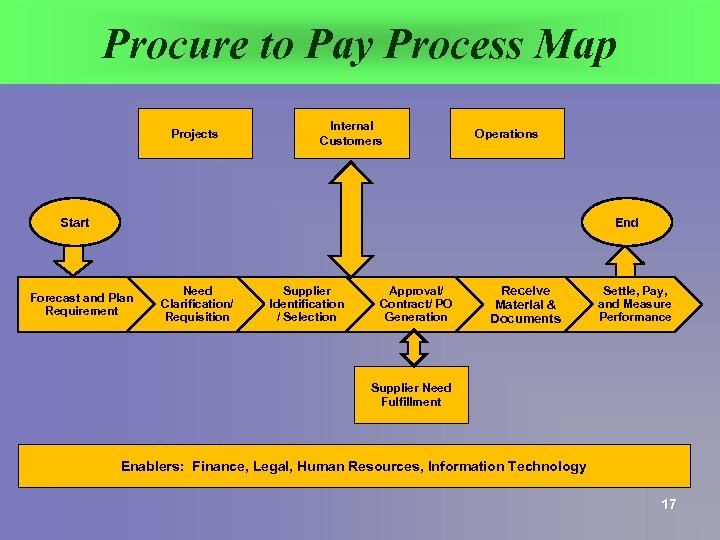 Procure to Pay Process Map Projects Internal Customers Operations Start End Forecast and Plan Requirement Need Clarification/ Requisition Supplier Identification / Selection Approval/ Contract/ PO Generation Receive Material & Documents Settle, Pay, and Measure Performance Supplier Need Fulfillment Enablers: Finance, Legal, Human Resources, Information Technology 17
Procure to Pay Process Map Projects Internal Customers Operations Start End Forecast and Plan Requirement Need Clarification/ Requisition Supplier Identification / Selection Approval/ Contract/ PO Generation Receive Material & Documents Settle, Pay, and Measure Performance Supplier Need Fulfillment Enablers: Finance, Legal, Human Resources, Information Technology 17
 Benefits of Electronic Documents § Virtual elimination of paperwork § Reduced time between need recognition and order release and receipt § Improved communication § Reduced errors § Reduced overhead costs § Reduced order and invoice processing Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 18
Benefits of Electronic Documents § Virtual elimination of paperwork § Reduced time between need recognition and order release and receipt § Improved communication § Reduced errors § Reduced overhead costs § Reduced order and invoice processing Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 18
 Needs Clarification – Requisitioning § Purchase requisition and/or statement of work § Forecasts and actual customer orders § Reorder point system § Stock checks (cycle counts) § New product development teams Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 19
Needs Clarification – Requisitioning § Purchase requisition and/or statement of work § Forecasts and actual customer orders § Reorder point system § Stock checks (cycle counts) § New product development teams Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 19
 Elements of a Purchase Requisition § Description of required material or service § Quantity required § Estimated unit cost § Operating account to be charged § Date of requisition § Date required § Authorized signature Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 20
Elements of a Purchase Requisition § Description of required material or service § Quantity required § Estimated unit cost § Operating account to be charged § Date of requisition § Date required § Authorized signature Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 20
 Traveling Purchase Requisition § Printed card or barcode § Description of item § List of approved suppliers § Prices paid to suppliers § Reorder point § Record of usage § Conserves time for handling routine materials and supplies Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 21
Traveling Purchase Requisition § Printed card or barcode § Description of item § List of approved suppliers § Prices paid to suppliers § Reorder point § Record of usage § Conserves time for handling routine materials and supplies Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 21
 Description § § Market grade or industry standard Brand Specification Performance characteristics Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 22
Description § § Market grade or industry standard Brand Specification Performance characteristics Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 22
 Supplier Identification and Selection § Existing supplier § Familiarity and track record § List of preferred suppliers § New supplier § Problem of maverick spending § Need to identify potential suppliers § Need to evaluate and qualify § Negotiate or competitive bidding? Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 23
Supplier Identification and Selection § Existing supplier § Familiarity and track record § List of preferred suppliers § New supplier § Problem of maverick spending § Need to identify potential suppliers § Need to evaluate and qualify § Negotiate or competitive bidding? Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 23
 Supplier Identification and Selection § § Bidding vs. negotiating Request for quotation Specifications or blueprints Supplier evaluation Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 24
Supplier Identification and Selection § § Bidding vs. negotiating Request for quotation Specifications or blueprints Supplier evaluation Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 24
 When to Use Competitive Bidding § Volume is sufficiently high § Specifications or requirements are clear to the supplier § Marketplace is competitive § Buyers receive bids only from technically qualified suppliers § Adequate time is available § Buyer does not have preferred supplier Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 25
When to Use Competitive Bidding § Volume is sufficiently high § Specifications or requirements are clear to the supplier § Marketplace is competitive § Buyers receive bids only from technically qualified suppliers § Adequate time is available § Buyer does not have preferred supplier Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 25
 When to Use Negotiation § Any criteria for competitive bidding are missing § The purchase requires agreement on wide range of performance factors other than price alone § The buyer requires early supplier involvement Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 26
When to Use Negotiation § Any criteria for competitive bidding are missing § The purchase requires agreement on wide range of performance factors other than price alone § The buyer requires early supplier involvement Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 26
 When to Use Negotiation § The supplier cannot determine risks and costs before contract is awarded § The supplier requires substantial lead time to develop and product the requested items Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 27
When to Use Negotiation § The supplier cannot determine risks and costs before contract is awarded § The supplier requires substantial lead time to develop and product the requested items Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 27
 The Purchase Order § Quantity § Material specification § Quality requirements § Price § Delivery date § Method of delivery § Ship-to address § P. O. number § Order due date Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 28
The Purchase Order § Quantity § Material specification § Quality requirements § Price § Delivery date § Method of delivery § Ship-to address § P. O. number § Order due date Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 28
 P. O. Form Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 29
P. O. Form Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 29
 P. O. Visibility § § § Accounts payable Requisitioner Receiving Traffic management Purchasing Quality control Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 30
P. O. Visibility § § § Accounts payable Requisitioner Receiving Traffic management Purchasing Quality control Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 30
 Blanket P. O. § Used for ongoing purchases of an item § Release materials as needed vs. issuing a new P. O. each time § P. O. remains open during the time specified Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 31
Blanket P. O. § Used for ongoing purchases of an item § Release materials as needed vs. issuing a new P. O. each time § P. O. remains open during the time specified Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 31
 Blanket P. O. Form Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 32
Blanket P. O. Form Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 32
 Types of P. O. s § Fixed-price contracts § Financial risk – market fluctuations § Competition § Technology risk § Cost-based contracts § Risk of large contingency fee § Need to identify and monitor relevant supplier costs Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 33
Types of P. O. s § Fixed-price contracts § Financial risk – market fluctuations § Competition § Technology risk § Cost-based contracts § Risk of large contingency fee § Need to identify and monitor relevant supplier costs Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 33
 Receipt and Inspection § § § § Electronic vs. paper documents Material packing slip Bill of lading Receiving discrepancy report Issues with just-in-time purchasing Backflush accounting Impact of change notices Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 34
Receipt and Inspection § § § § Electronic vs. paper documents Material packing slip Bill of lading Receiving discrepancy report Issues with just-in-time purchasing Backflush accounting Impact of change notices Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 34
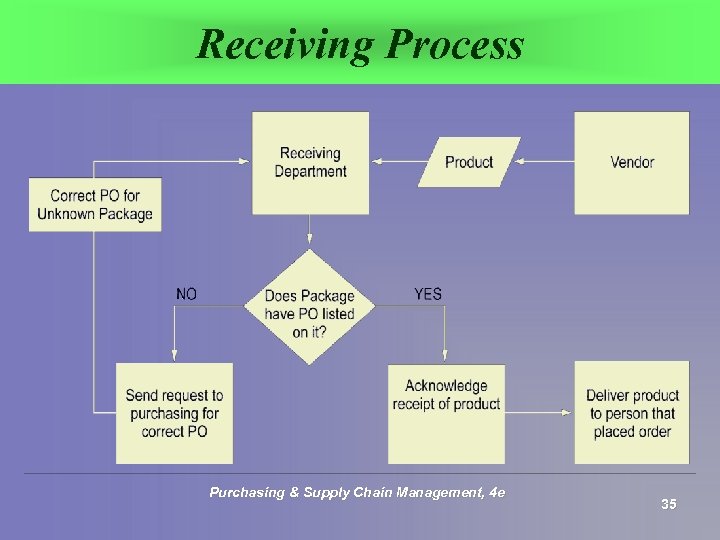 Receiving Process Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 35
Receiving Process Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 35
 Invoice Settlement and Payment § Three-way match required § P. O. § Invoice § Receiving report § Electronic funds transfer (EFT) § Summarized monthly payments vs. paying for each P. O. individually § Mostly done electronically now Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 36
Invoice Settlement and Payment § Three-way match required § P. O. § Invoice § Receiving report § Electronic funds transfer (EFT) § Summarized monthly payments vs. paying for each P. O. individually § Mostly done electronically now Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 36
 Reengineering Procure to Pay § Secure top management support § Map existing processes, highlighting difficulties and challenges § Understand the needs and requirements of user groups § Utilize a cross-functional team, including users Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 37
Reengineering Procure to Pay § Secure top management support § Map existing processes, highlighting difficulties and challenges § Understand the needs and requirements of user groups § Utilize a cross-functional team, including users Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 37
 Reengineering Procure to Pay § Explore technology solutions § Define new process and conduct pilot test § Train and deploy other users (rollout) § Monitor, update, and improve the system Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 38
Reengineering Procure to Pay § Explore technology solutions § Define new process and conduct pilot test § Train and deploy other users (rollout) § Monitor, update, and improve the system Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 38
 Types of Purchases § § Raw materials Semifinished products and components Finished products Maintenance, repair, and operating supplies (MRO) Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 39
Types of Purchases § § Raw materials Semifinished products and components Finished products Maintenance, repair, and operating supplies (MRO) Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 39
 Types of Purchases § § Production support items Services Capital equipment Transportation and third-party logistics providers Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 40
Types of Purchases § § Production support items Services Capital equipment Transportation and third-party logistics providers Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 40
 MRO Purchasing § Most organizations do not track MRO items like they do production items § There are typically too many MRO suppliers § There are too many small orders which take up too much time Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 41
MRO Purchasing § Most organizations do not track MRO items like they do production items § There are typically too many MRO suppliers § There are too many small orders which take up too much time Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 41
 Improving the Purchasing Process § § § Online requisitioning systems Procurement cards issued to users E-commerce using the Internet Longer-term purchase agreements Online ordering systems Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 42
Improving the Purchasing Process § § § Online requisitioning systems Procurement cards issued to users E-commerce using the Internet Longer-term purchase agreements Online ordering systems Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 42
 Improving the Purchasing Process § § § Purchasing process redesign Electronic data interchange (EDI) Online ordering using electronic catalogs § Direct user-supplier contact Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 43
Improving the Purchasing Process § § § Purchasing process redesign Electronic data interchange (EDI) Online ordering using electronic catalogs § Direct user-supplier contact Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 43
 Advantages of Online Ordering § § § Immediate visibility to backorders Faster order input time Reduced ordering errors Order tracking capability Order acknowledgement from supplier Ability to batch multiple items into a single order § Faster order cycle time Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 44
Advantages of Online Ordering § § § Immediate visibility to backorders Faster order input time Reduced ordering errors Order tracking capability Order acknowledgement from supplier Ability to batch multiple items into a single order § Faster order cycle time Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 44
 The Fed. Ex Sourcing Process § § § Requisition item Select sourcing strategy Conduct in-depth research on potential suppliers § Confirm and reevaluate strategy and need Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 45
The Fed. Ex Sourcing Process § § § Requisition item Select sourcing strategy Conduct in-depth research on potential suppliers § Confirm and reevaluate strategy and need Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 45
 The Fed. Ex Sourcing Process § Conduct supplier selection and negotiation process § Integrate supplier with e-procurement tools and other Fed. Ex systems § Benchmark the supply market using Fed. Ex Supplier Scorecard system Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 46
The Fed. Ex Sourcing Process § Conduct supplier selection and negotiation process § Integrate supplier with e-procurement tools and other Fed. Ex systems § Benchmark the supply market using Fed. Ex Supplier Scorecard system Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 46
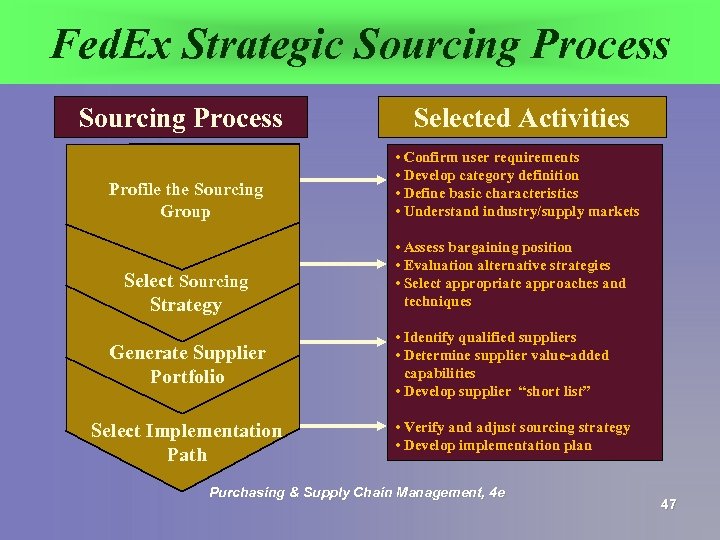 Fed. Ex Strategic Sourcing Process Profile the Sourcing Group Select Sourcing Strategy Generate Supplier Portfolio Select Implementation Path Selected Activities • Confirm user requirements • Develop category definition • Define basic characteristics • Understand industry/supply markets • Assess bargaining position • Evaluation alternative strategies • Select appropriate approaches and techniques • Identify qualified suppliers • Determine supplier value-added capabilities • Develop supplier “short list” • Verify and adjust sourcing strategy • Develop implementation plan Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 47
Fed. Ex Strategic Sourcing Process Profile the Sourcing Group Select Sourcing Strategy Generate Supplier Portfolio Select Implementation Path Selected Activities • Confirm user requirements • Develop category definition • Define basic characteristics • Understand industry/supply markets • Assess bargaining position • Evaluation alternative strategies • Select appropriate approaches and techniques • Identify qualified suppliers • Determine supplier value-added capabilities • Develop supplier “short list” • Verify and adjust sourcing strategy • Develop implementation plan Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 47
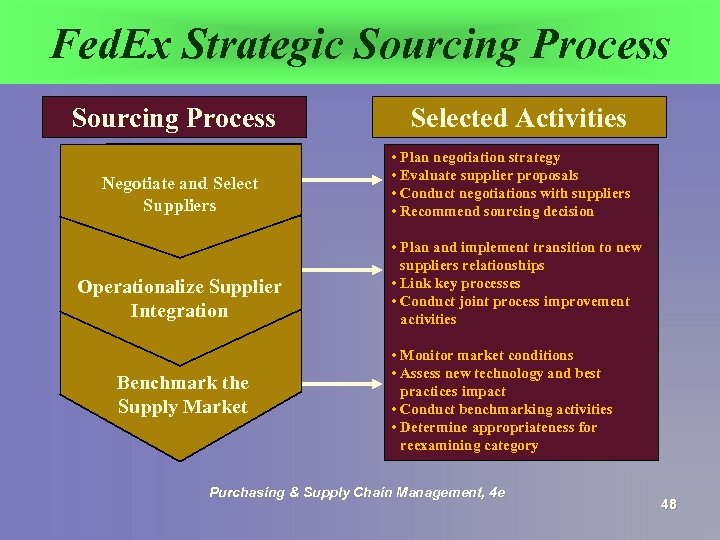 Fed. Ex Strategic Sourcing Process Negotiate and Select Suppliers Operationalize Supplier Integration Benchmark the Supply Market Selected Activities • Plan negotiation strategy • Evaluate supplier proposals • Conduct negotiations with suppliers • Recommend sourcing decision • Plan and implement transition to new suppliers relationships • Link key processes • Conduct joint process improvement activities • Monitor market conditions • Assess new technology and best practices impact • Conduct benchmarking activities • Determine appropriateness for reexamining category Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 48
Fed. Ex Strategic Sourcing Process Negotiate and Select Suppliers Operationalize Supplier Integration Benchmark the Supply Market Selected Activities • Plan negotiation strategy • Evaluate supplier proposals • Conduct negotiations with suppliers • Recommend sourcing decision • Plan and implement transition to new suppliers relationships • Link key processes • Conduct joint process improvement activities • Monitor market conditions • Assess new technology and best practices impact • Conduct benchmarking activities • Determine appropriateness for reexamining category Purchasing & Supply Chain Management, 4 e 48


