80a81a456da6cda6aaa3902b81d3f0fe.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
Pulmonary Surfactant Metabolism Dysfunction types 1, 2 and 3 Caroline Archer NE Thames Regional Molecular Genetics 03 -Apr-2008

Outline • Clinical overview • Physiological Role of the three genes • Phenotype of each gene • Service need • Methodology • Results • Case studies
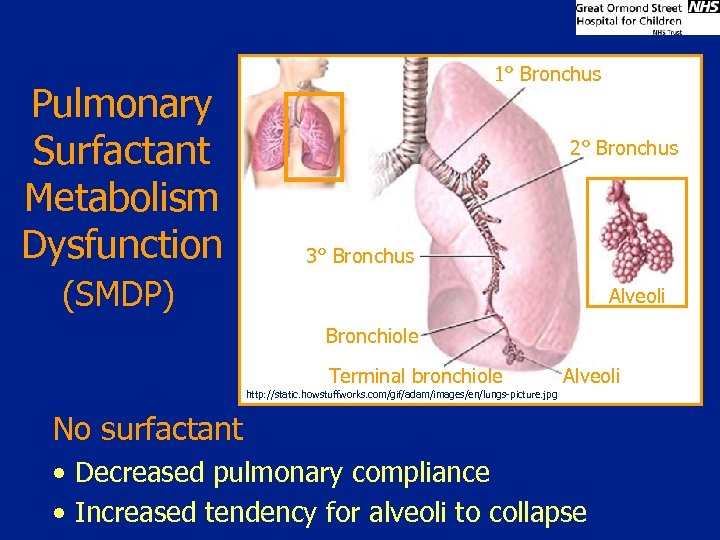
Pulmonary Surfactant Metabolism Dysfunction 1° Bronchus 2° Bronchus 3° Bronchus (SMDP) Alveoli Bronchiole Terminal bronchiole Alveoli http: //static. howstuffworks. com/gif/adam/images/en/lungs-picture. jpg No surfactant • Decreased pulmonary compliance • Increased tendency for alveoli to collapse
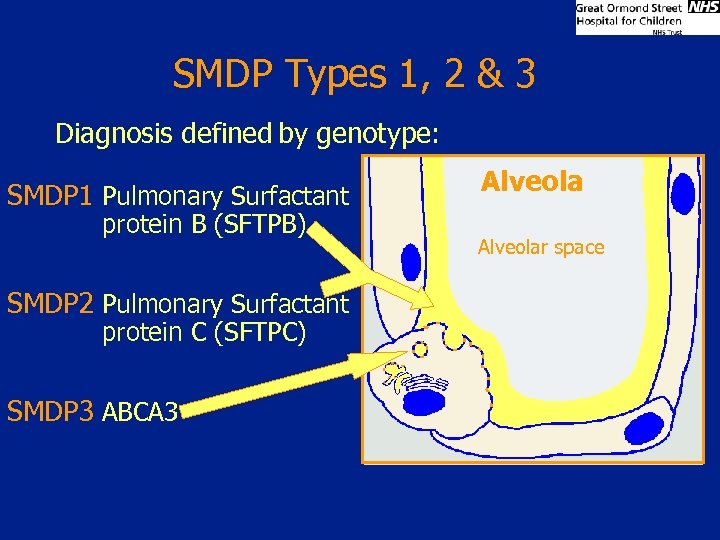
SMDP Types 1, 2 & 3 Diagnosis defined by genotype: SMDP 1 Pulmonary Surfactant protein B (SFTPB) SMDP 2 Pulmonary Surfactant protein C (SFTPC) SMDP 3 ABCA 3 Alveolar space
SMDP type 1 Autosomal Recessive mutations SFTPB • 1 per million live births • Term neonates with severe respiratory distress presenting within hours of birth • Refractory to ventilation & synthetic surfactant replacement therapy • Fatal in first three months of life - lung transplant is the only successful intervention • Partial deficiencies may be less severe
SMDP type 2 Autosomal Dominant mutations SFTPC • Incidence unknown • Familial and sporadic (55%) • Highly variable clinical course & severity • Later onset tachypnoea & cyanosis with interstitial lung disease • Rarely acute neonatal lung disease
SMDP type 3 Autosomal Recessive mutations in ABCA 3 • Incidence unknown • Phenotypic overlap with SMPD 1 and SMDP 2 • Severe hypoxic respiratory disease with death in the first three months • Milder paediatric lung disease with survival past infancy • Mutations in ABCA 3 modifies phenotype of SMDP 2 (SFTPC)
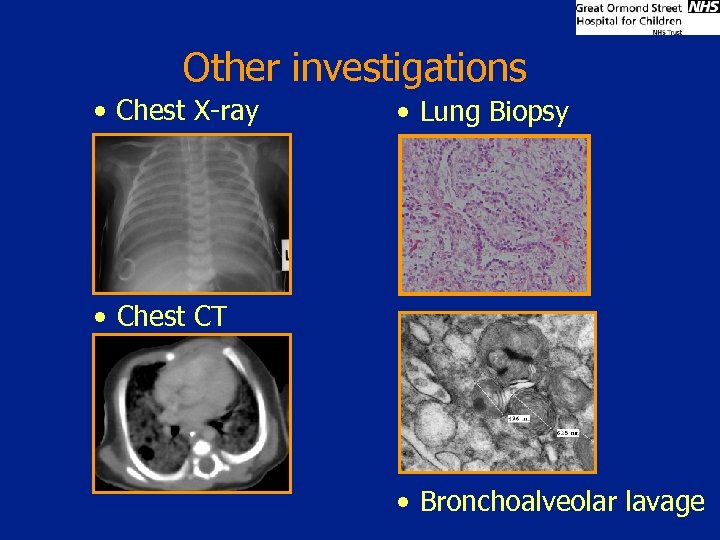
Other investigations • Chest X-ray • Lung Biopsy • Chest CT • Bronchoalveolar lavage

• • Clinical Utility Supportive care Consider lung transplantation No rapid diagnostic test Genotype critical for parental counselling Clinical Overlap • Transient symptoms in premature infants respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) • Short term treatment with synthetic surfactant Proforma • Clinical information required • Clinical queries to an in-house Consultant Intensivist

Diagnostic service • 2002 SFTPB ‘common’ mutation service: pick up 0% • 2006 Full screen: SFTPB - 10 exons SFTPC - 5 exons ABCA 3 - 30 exons • SFTPB linkage – six markers Strategy Considerations • • • Turnaround Times Low DNA requirement Very low referral numbers expected RNA not possible Polymorphisms – known susceptibility to RDS Mutations reported throughout coding region
Direct Sequencing • 45 exons (all 3 genes) • Robotic PCR set up using 8 span robot • Each gene separate • Touch-down PCR program for all three genes • Direct sequencing using 8 & 96 span robots 1. Robotic Exosap-IT or Ampure beads 2. Robotic sequencing set-up 3. Tailed primers 4. Robotic clean-up using clean seq beads
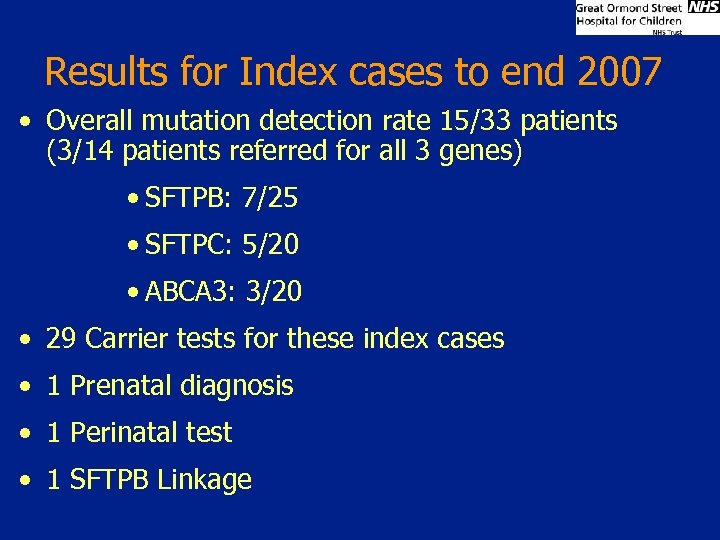
Results for Index cases to end 2007 • Overall mutation detection rate 15/33 patients (3/14 patients referred for all 3 genes) • SFTPB: 7/25 • SFTPC: 5/20 • ABCA 3: 3/20 • 29 Carrier tests for these index cases • 1 Prenatal diagnosis • 1 Perinatal test • 1 SFTPB Linkage
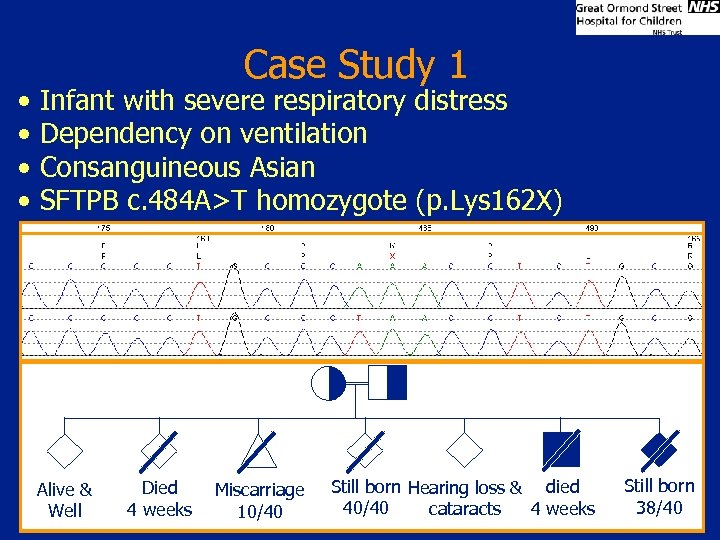
• • Case Study 1 Infant with severe respiratory distress Dependency on ventilation Consanguineous Asian SFTPB c. 484 A>T homozygote (p. Lys 162 X) Alive & Well Died 4 weeks Miscarriage 10/40 Still born Hearing loss & died 40/40 4 weeks cataracts Still born 38/40
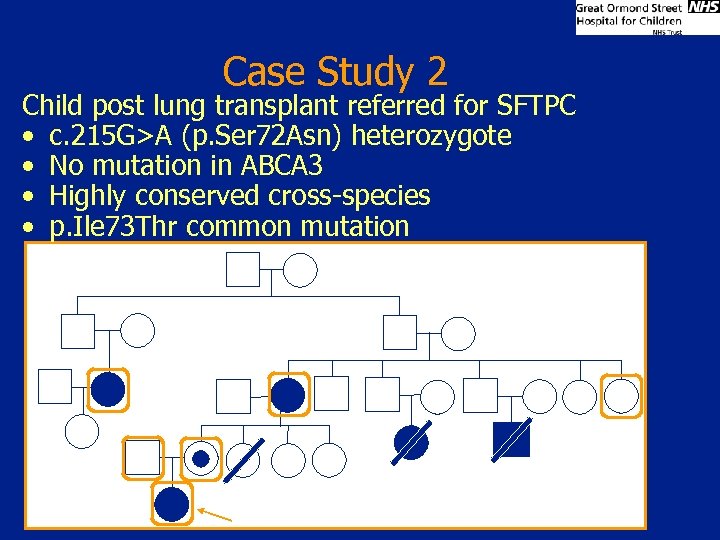
Case Study 2 Child post lung transplant referred for SFTPC • c. 215 G>A (p. Ser 72 Asn) heterozygote • No mutation in ABCA 3 • Highly conserved cross-species • p. Ile 73 Thr common mutation
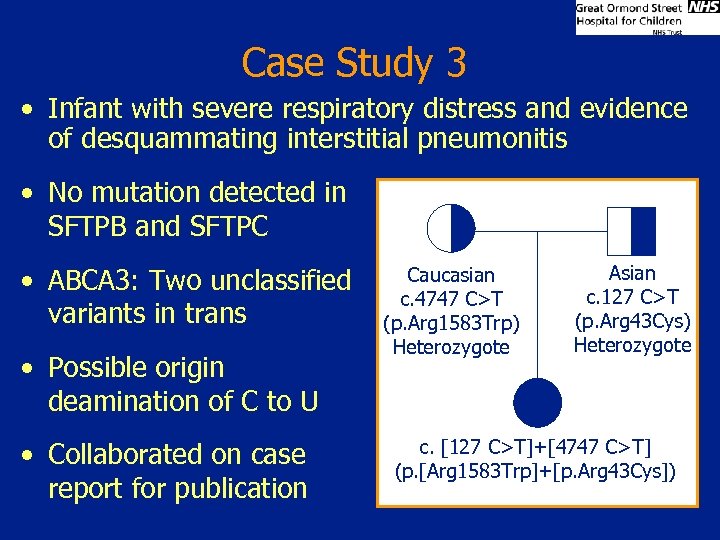
Case Study 3 • Infant with severe respiratory distress and evidence of desquammating interstitial pneumonitis • No mutation detected in SFTPB and SFTPC • ABCA 3: Two unclassified variants in trans • Possible origin deamination of C to U • Collaborated on case report for publication Caucasian c. 4747 C>T (p. Arg 1583 Trp) Heterozygote Asian c. 127 C>T (p. Arg 43 Cys) Heterozygote c. [127 C>T]+[4747 C>T] (p. [Arg 1583 Trp]+[p. Arg 43 Cys])
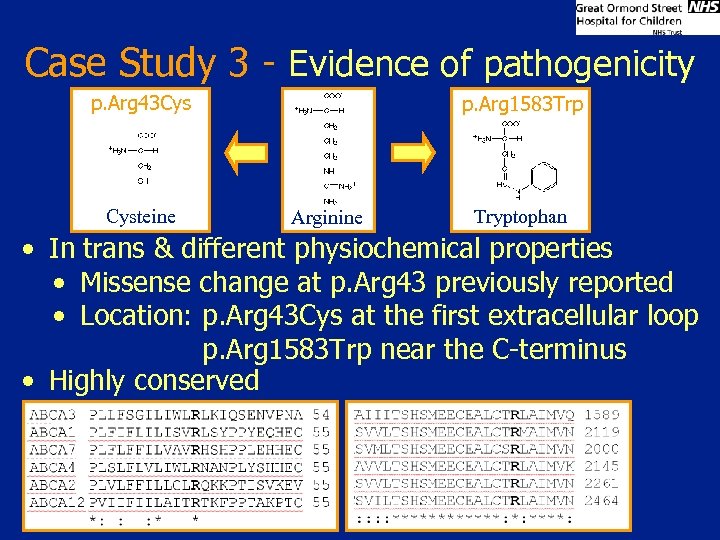
Case Study 3 - Evidence of pathogenicity p. Arg 43 Cys Cysteine p. Arg 1583 Trp Arginine Tryptophan • In trans & different physiochemical properties • Missense change at p. Arg 43 previously reported • Location: p. Arg 43 Cys at the first extracellular loop p. Arg 1583 Trp near the C-terminus • Highly conserved

• • • Further Work SFTPC linkage for de novo cases Use proforma to develop a tiered strategy based on genetic & clinical data. Now charging for testing - Gene Dossier May 2008 Summary • • NE Thames RMG offers screening of SFTPB, SFTPC, ABCA 3 for SMDP 1, 2 and 3. This is a group of rare chronic respiratory disorders typically seen in full term neonates and younger children.

Acknowledgements Gail Norbury, Lucy Jenkins, Vicky Aldridge, & All Staff Quen Mok Paediatric Intensive Care Unit NE Thames Regional Molecular Genetics laboratory Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children London WC 1 N 3 JH http: //www. ich. ucl. ac. uk/gosh/clinicalservices/Molecular_Genetics Sian Jenkins Evelina Children's Hospital St Thomas' Hospital Lambeth Palace Road London SE 1 7 EH Larry Nogee Department of Paediatrics Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Baltimore USA
80a81a456da6cda6aaa3902b81d3f0fe.ppt