3747ac61630c4507033741e49d04b75d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26

PUBLIC SERVICE DELIVERY & HUMAN RESOURCES MANAGEMENT TRENDS & CHALLENGES TOWARDS INNOVATIVE PUBLIC SERVICES Current state of the analysis / July 7 th 2015

KEY POINTS OF THE PRESENTATION 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Goal reminder Conceptual Framework: alpha version Work process and data collection Definitions HRM trends, results and corresponding Bundles 6. PSD trends, results and corresponding Bundles 7. Conceptual Framework: beta version 8. Selection and template for the inspiring practices 2 idheap. ch

1. GOAL REMINDER Ø General ambition : identify the main trends and challenges regarding public sector’s innovation capabilities, with a specific focus on HRM (made by IDHEAP) and PSD (made by LIST). Illustration through so-called “inspiring practices” Ø Additional Factors to be considered: trust and transparency as key features of an open government framework Ø Key Deliverables: ? ? ? 1. State of the art : Summary of the main trends and challenges in PSD & HRM, with a specific focus on innovation (first draft end of May) 2. Input for Data collection of inspiring practices (selection criteria and template (end of June) 3. Identification and description of 10 inspiring practices (5 x PSD and 5 x HRM), with prerequisite and success factors (mid-September (EIPA)) 4. List of common & specific priorities in Europe for the next 5 years in terms of recommendations in the two key topics (Full report by end of November) 3 idheap. ch
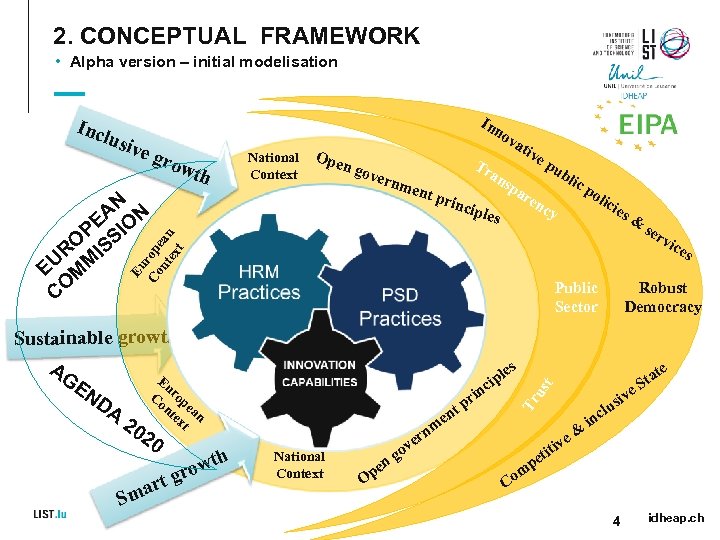
2. CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK • Alpha version – initial modelisation Inc In lusi ve g row th National Context Ope n no v gove r nme AN N PE SIO RO IS EU MM CO ati v Tr nt p rinc ep an sp ub ar en cy iple s po lic ies & ser vic Eu Co rop nt ean ex t Public Sector m en National Context rn ve O go n pe tp es Robust Democracy e e siv lu us t les cip in r Tr Sustainable growth AG Eu EN Co rop DA nt ea ex n t 20 20 h owt r rt g a Sm lic e tiv ti & at St inc e C p om 4 idheap. ch
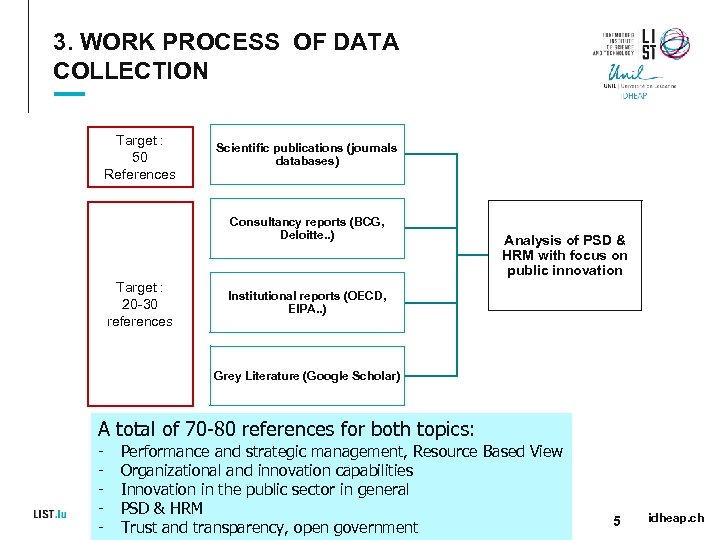
3. WORK PROCESS OF DATA COLLECTION Target : 50 References Scientific publications (journals databases) Consultancy reports (BCG, Deloitte. . ) Target : 20 -30 references Analysis of PSD & HRM with focus on public innovation Institutional reports (OECD, EIPA. . ) Grey Literature (Google Scholar) A total of 70 -80 references for both topics: - Performance and strategic management, Resource Based View Organizational and innovation capabilities Innovation in the public sector in general PSD & HRM Trust and transparency, open government 5 idheap. ch
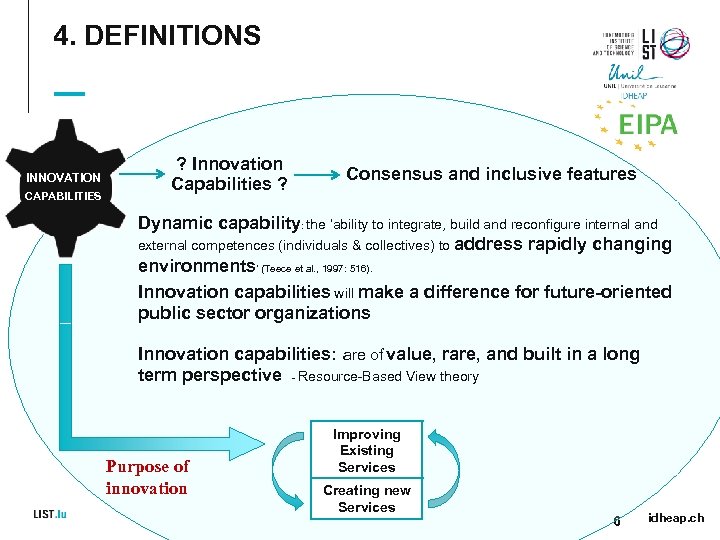
4. DEFINITIONS INNOVATION CAPABILITIES ? Innovation Capabilities ? Consensus and inclusive features Dynamic capability: the ‘ability to integrate, build and reconfigure internal and external competences (individuals & collectives) to address rapidly changing environments’ (Teece et al. , 1997: 516). Innovation capabilities will make a difference for future-oriented public sector organizations Innovation capabilities: are of value, rare, and built in a long term perspective - Resource-Based View theory Purpose of innovation Improving Existing Services Creating new Services 6 idheap. ch

5. HRM TRENDS Themes commonly refered to as future trends in HRM Managing demographics Reskilled HR professionals and business partnerships Talent analytics & management KM becoming a learning organization Flexible work design Performance managemen, rewards & recognition Managing worklife balance Rethinking leadership competences & styles Well being & health management us t Training & employability Managing change & cultural transformation Tr Employer branding to foster attractivity Commitmentenhancing practices 7 idheap. ch
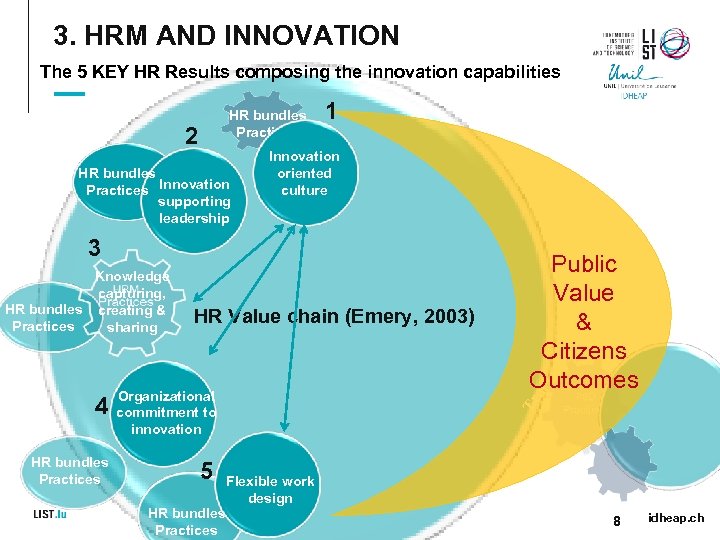
3. HRM AND INNOVATION The 5 KEY HR Results composing the innovation capabilities HR bundles Practices 2 HR bundles Practices Innovation supporting leadership 1 Innovation oriented culture 3 HR Value chain (Emery, 2003) Organizational commitment to innovation HR bundles Practices 5 HR bundles Practices Tr 4 Public Value & Citizens Outcomes us t Knowledge capturing, HR bundles creating & Practices sharing Flexible work design 8 idheap. ch

HR RESULT 1: INNOVATION-ORIENTED CULTURE, AND HR BUNDLE 1 • The culture of public sector organizations is not innovation-oriented: due to (among other factors): restrictive and rigid legal framework, absence of competition, routine-oriented, low risk and experimentation adverse culture, absence of rewards and recognition • The following HR bundle may foster an innovation-oriented culture: Staffing for innovation (competencies and motivation, diversity) of leaders and employees *IOS = innovation-oriented strategy of the organization HR policy & Chart (creativity, openness and receptiveness to new ideas), & strategic lignement with IOS* HR-Bundle 1 Collective appraisal/rewards and recognition for innovation Organizational slack and experimentation Distributed heroism towards innovation 9 idheap. ch
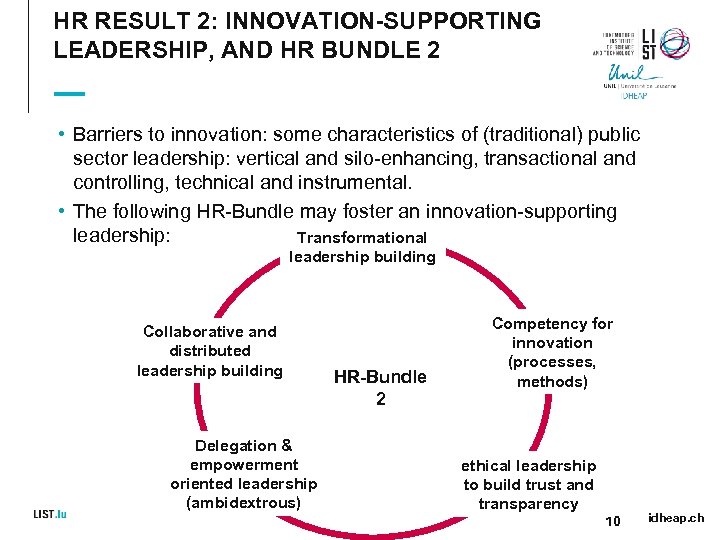
HR RESULT 2: INNOVATION-SUPPORTING LEADERSHIP, AND HR BUNDLE 2 • Barriers to innovation: some characteristics of (traditional) public sector leadership: vertical and silo-enhancing, transactional and controlling, technical and instrumental. • The following HR-Bundle may foster an innovation-supporting leadership: Transformational leadership building Collaborative and distributed leadership building Delegation & empowerment oriented leadership (ambidextrous) HR-Bundle 2 Competency for innovation (processes, methods) ethical leadership to build trust and transparency 10 idheap. ch
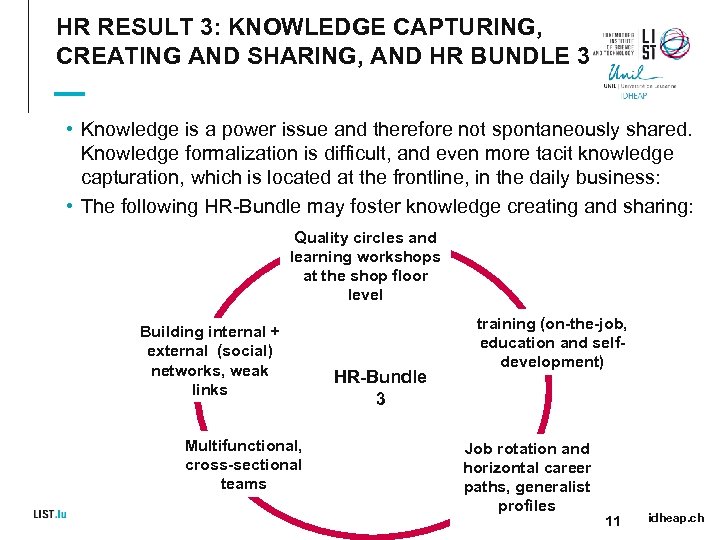
HR RESULT 3: KNOWLEDGE CAPTURING, CREATING AND SHARING, AND HR BUNDLE 3 • Knowledge is a power issue and therefore not spontaneously shared. Knowledge formalization is difficult, and even more tacit knowledge capturation, which is located at the frontline, in the daily business: • The following HR-Bundle may foster knowledge creating and sharing: Quality circles and learning workshops at the shop floor level Building internal + external (social) networks, weak links Multifunctional, cross-sectional teams HR-Bundle 3 training (on-the-job, education and selfdevelopment) Job rotation and horizontal career paths, generalist profiles 11 idheap. ch

HR RESULT 4: ORGANIZATIONAL COMMITMENT (TO INNOVATION), AND HR BUNDLE 4 • Innovation is mainly an extra-role behaviour, which cannot be ordered. It is about capturing, sharing ideas, experimenting and risk-taking, as innovation challenges routines. It’s about autonomous extrinsic and intrinsic motivation • The following HR-Bundle may foster organization commitment (to innovation): Information sharing and communication Developmental feedback and performance appraisal Participative and non-controlling leadership style training and development in a long-term perspective HR-Bundle 4 Participatorycontrol practices Job security and organizational support 12 idheap. ch
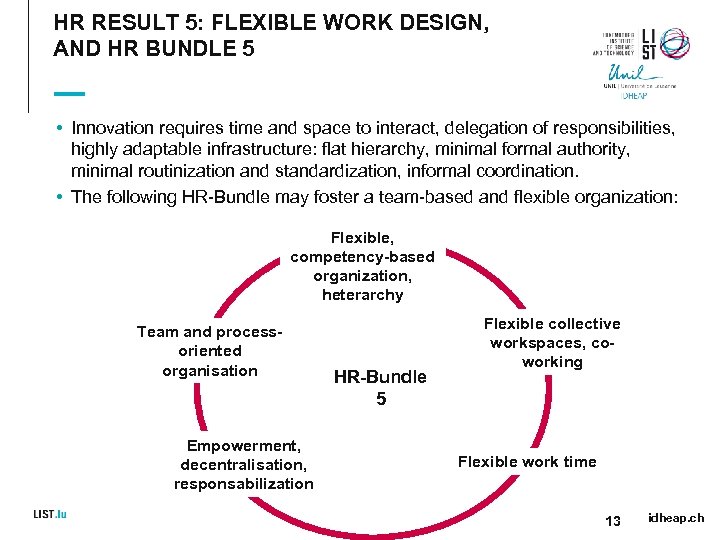
HR RESULT 5: FLEXIBLE WORK DESIGN, AND HR BUNDLE 5 • Innovation requires time and space to interact, delegation of responsibilities, highly adaptable infrastructure: flat hierarchy, minimal formal authority, minimal routinization and standardization, informal coordination. • The following HR-Bundle may foster a team-based and flexible organization: Flexible, competency-based organization, heterarchy Team and processoriented organisation Empowerment, decentralisation, responsabilization HR-Bundle 5 Flexible collective workspaces, coworking Flexible work time 13 idheap. ch
6. PSD TRENDS IN THE EU Tr us t Themes commonly referred to as future trends in PSD 14 idheap. ch
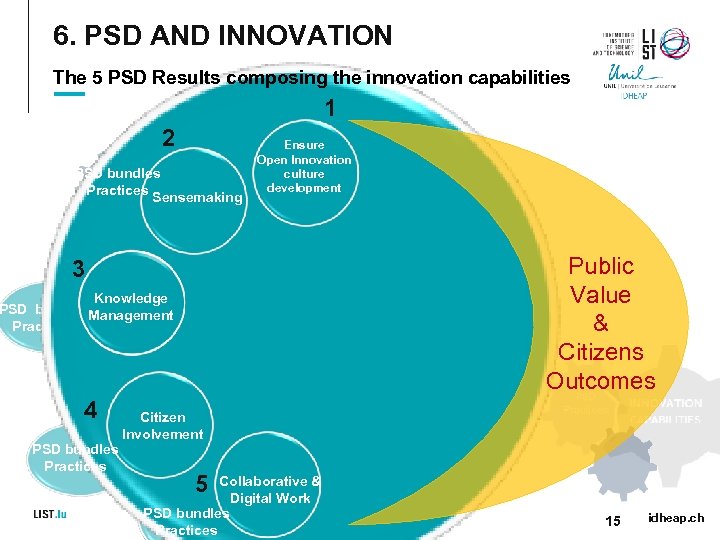
6. PSD AND INNOVATION The 5 PSD Results composing the innovation capabilities PSD bundles Practices 2 PSD bundles Practices Sensemaking 1 Ensure Open Innovation culture development Public Value & Citizens Outcomes 3 PSD bundles Practices Citizen Involvement Tr 4 us t Knowledge PSD bundles. Management Practices 5 Collaborative & Digital Work PSD bundles Practices 15 idheap. ch

PSD RESULT 1: ENSURE OPEN INNOVATION CULTURE DEVELOPMENT AND PSD BUNDLE 1 • Many public administrations have an innovative culture. They have developed this culture through (transversal) projects dedicated to improve and/or digitalize some public services. The challenge for public organizations is to develop a culture that supports Service Innovation. • The following PSD bundle may foster the development of such an Innovation Culture: State organizational values consistent to Innovation PSD-Bundle 1 Promote & manage a risk culture Build parternship with innovation lab/hub/factory, … 16 idheap. ch
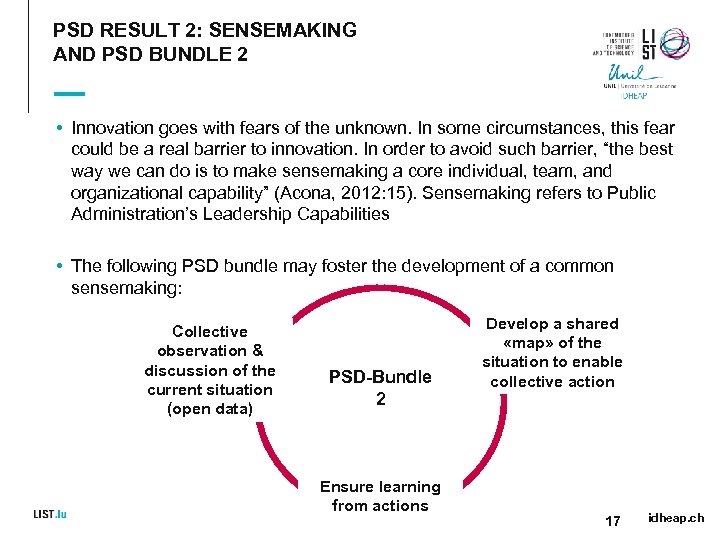
PSD RESULT 2: SENSEMAKING AND PSD BUNDLE 2 • Innovation goes with fears of the unknown. In some circumstances, this fear could be a real barrier to innovation. In order to avoid such barrier, “the best way we can do is to make sensemaking a core individual, team, and organizational capability” (Acona, 2012: 15). Sensemaking refers to Public Administration’s Leadership Capabilities • The following PSD bundle may foster the development of a common sensemaking: Collective observation & discussion of the current situation (open data) PSD-Bundle 2 Ensure learning from actions Develop a shared «map» of the situation to enable collective action 17 idheap. ch

PSD RESULT 3: KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT AND PSD BUNDLE 3 • Innovation is Knowledge-based. Hence, Public Administrations have to be able to manage knowledge. Managing Knowledge consists in supporting Knowledge sharing, creation and learning. • The following PSD bundle may foster the development of public administration capability to manage knowledge. Ensure knowledge exchange between stakeholders Collecting stakeholders knowledge (citizens, community, …) PSD-Bundle 3 Accessibility of public information & Knowledge Organizational support to create a Common Knowledge 18 idheap. ch
PSD RESULT 4: CITIZEN INVOLVEMENT AND PSD BUNDLE 4 • Stakeholders engagement appears as the main trend in the literature dedicated to Public Administration, especially Citizens. To design new services and to ensure their efficiency, citizen participation is required as well as the implication of other stakeholders. • The following PSD bundle may foster the involvement of citizens: 19 idheap. ch
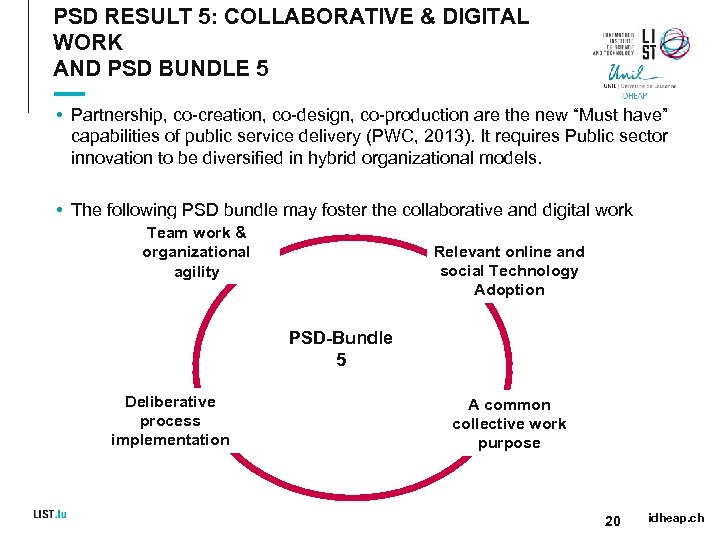
PSD RESULT 5: COLLABORATIVE & DIGITAL WORK AND PSD BUNDLE 5 • Partnership, co-creation, co-design, co-production are the new “Must have” capabilities of public service delivery (PWC, 2013). It requires Public sector innovation to be diversified in hybrid organizational models. • The following PSD bundle may foster the collaborative and digital work Team work & organizational agility Relevant online and social Technology Adoption PSD-Bundle 5 Deliberative process implementation A common collective work purpose 20 idheap. ch
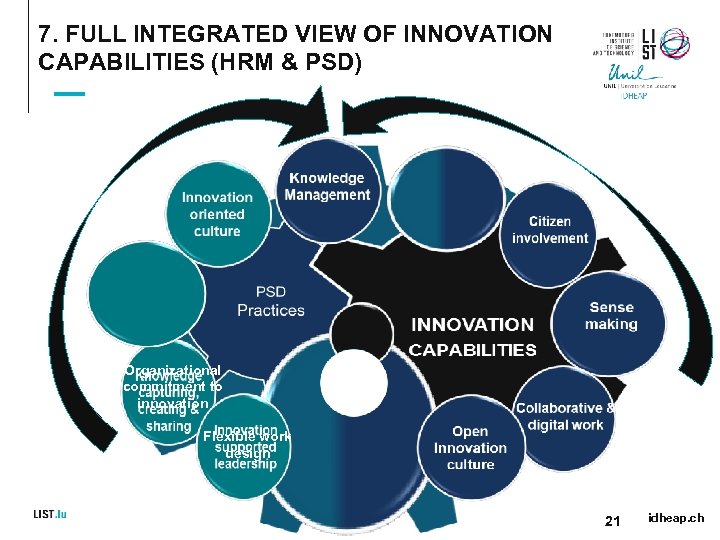
7. FULL INTEGRATED VIEW OF INNOVATION CAPABILITIES (HRM & PSD) Organizational commitment to innovation PSD-Bundle 1 Flexible work design 21 idheap. ch
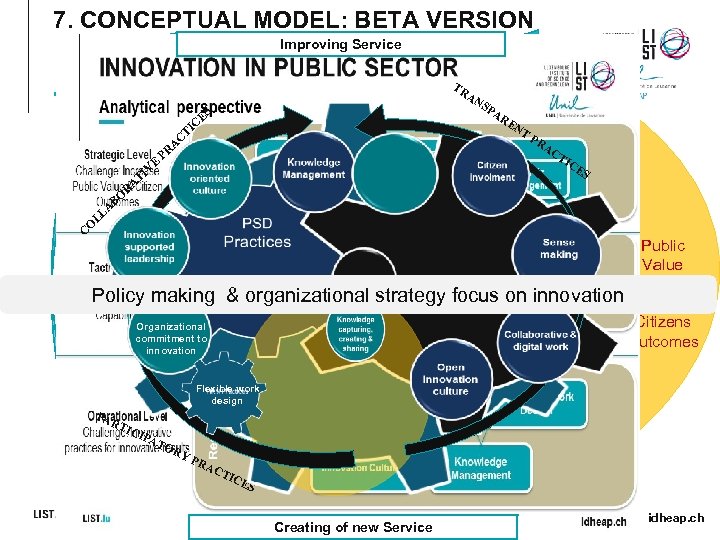
7. CONCEPTUAL MODEL: BETA VERSION Improving Service T C TR AN SP AR ES IC EN T A E PR AC TI V TI A R BO PR CE S A LL O C Public Value Policy making & organizational strategy focus on innovation Citizens Outcomes Organizational commitment to innovation Flexible work design PA RT ICI PA TO RY PR AC T ICE S Creating of new Service 22 idheap. ch
7. CONCEPTUAL MODEL, BETA VERSION ANALYTICAL PERSPECTIVE Analytical perspective 23 idheap. ch

8. WORK PROCESS OF DATA COLLECTION FOR INSPIRING PRACTICES Selection criteria & template for the inspiring practices Notion of “Bundles” as a key lever of innovation (capabilities) • HR or PSD practices have to be considered as bundles, not individually • HR or PSD bundles are composed of mutually reinforcing HR or PSD practices which, as a whole, represent a unique set (configuration) leading to increased HR or PSD results Each HRM bundle has to be related to a PSD counterpart so as to address the corresponding result: • Both have to work in close connection in order to developp the organization’s innovation capabilitites, • One HRM bundle with the “corresponding” PSD bundle; According to the underlying idea that a specific set of HRM practices aligned to a set of PSD practices is intended to boost innovation and ultimately deliver public value and citizen outcomes THE 10 INSPIRING PRACTICES should cover all 10 bundles: • Each of them is first to be illustrative of one specific bundle, • It should consider the corresponding counterpart, • It should check for potential links to the eight remaining bundles 24 idheap. ch

8. TEMPLATE FOR THE INSPIRING PRACTICES 25 idheap. ch

8. WORK PROCESS OF DATA COLLECTION FOR INSPIRING PRACTICES Additional criteria Inspiring, creative and displaying uncommon ideas Proven impact/results Sustainable; Specifically the propensity of the practice to be long lasting instead of being a short-term, one shot, change. Cost/ return on Investment (ROI). Implementation scope: the whole organization should be (ideally) targeted and not only one team or subunit. Adaptable/transferable. The possibility for the project to be considered as a good example for other organizations 26 idheap. ch
3747ac61630c4507033741e49d04b75d.ppt