aaa15c1a470ba3560da88f053603d60d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19

Public Private Partnerships in the Baltics and Europe Vilnius, 22 -23 November 2006 DAY I, TOPIC IV Structuring and Implementing PPPs: Risk Allocation and Mitigation 1. UK/European PPP Experience and Lessons 2. Risks in PPP Projects Scott Dickson Senior Associate, Projects Group Berwin Leighton Paisner LLP, London 22 November 2006 [5440725] 1

1. UK/European PPP Experience and Lessons 2

History of PFI in the UK 1992: Launch of the Private Finance Initiative by the Conservative Government 1997 to date: changes introduced by the Labour Government, including relaunch as Public Private Partnerships (PPPs) Policy development now rests with HM Treasury, including standardisation 3

European takeup and globalisation Includes Italy, France, Portugal, Germany, Spain, Greece, Austria, Ireland, Netherlands, Scandinavia, Hungary, Poland Early projects – Finland (roads) Increasing deal pipeline Keep an eye on experience further away: Canada, Australia, Central/South America, South Africa, Japan 4

Key drivers for PFI Neglected and crumbling infrastructure and public assets Need for investment, avoiding the public balance sheet Failures of public procurement Political consistency – move from public to private Utilisation of private sector expertise Promotion of value for money and more efficient of use of resources Promotion of innovation (especially design) 5

Tested benefits/success of PFI Transferred risk from the public authority to private sector Harnessed private sector skills and expertise Introduced competition into procurement of public assets Payment linked to performance – deductions for unavailability and poor performance – incentive for private sector to deliver 6
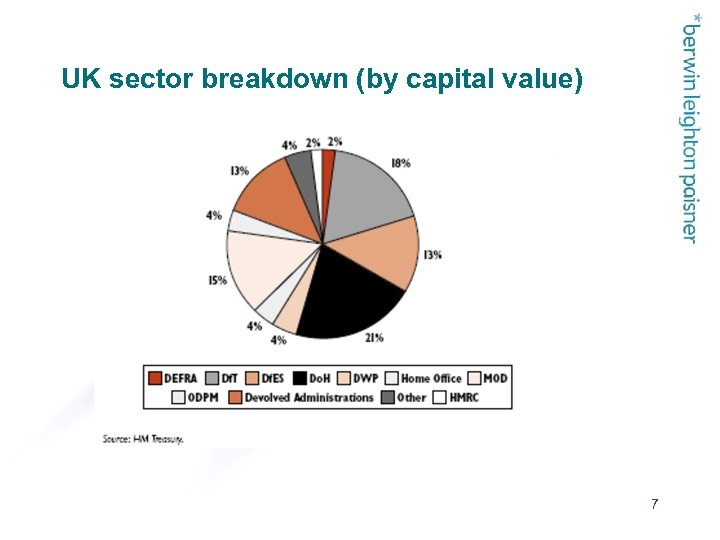
UK sector breakdown (by capital value) 7

UK sectors (by capital value) – in figures Health (21%) Transport (18%) Defence (15%) Education (13%) Scotland/Wales (13%) Other accommodation projects (government buildings, prisons) (12%) Housing (4%) 8

UK position today…. 700 signed projects worth £ 46 bn 500 operational projects Standard contractual/risk positions Commoditised market Pipeline: Health, Defence, Transport, Education, Housing, Waste Market uncertainty – health projects Growth of other sectors – defence, housing, waste 9

Consequences of UK commoditised market…. Tight returns Interest moved to the margins: – – – bundling long-term relationships new structures, including not-for-profit funding competitions secondary market Opportunities in Europe 10

Lessons (1): development aide-mémoire Choosing projects - sectors/assets Assemble the right public sector team Robust business case Analysis and allocation of risks Learn from early projects Project planning and management Legal framework in place Standardisation/co-ordination 11

Lessons (2): general Understand the private sector Take long term approach and sell project flow to attract private sector Communication with stakeholders Deal with opposition Promote innovation Limit transaction costs 12

2. Risks in PPP Projects 13

Thinking about project risks Risk transfer/balance sheet vs Value for money Analysis of risks Specifics: Sectoral/Geographical Funder expectations/bankability Always open for negotiation? vs Transaction costs UK settled risk allocation Private sector: risk mitigation 14

Public sector – scoping the project Full risk transfer Pricing/Value for money considerations – – example: condition of existing buildings impossibility of rational pricing? risk premium too high? consider competitive bidding environment Approach – – – methodical analysis justifiable risk transfer consider value for money bankable consistent 15

Categorisation of risks, with examples Construction – – – failure of design cost of materials delay/incorrect time estimate condition of site/existing buildings change in law Operational – – failure of perform incorrect cost estimates change in public authority requirements change in law Pure financial risks – tax – inflation – insurance costs 16

Risk mitigation/management Contractual/negotiation (inc ringfencing) Private sector passdown SPV management Insurance Senior funding Equity funding Decreasing Sponsor Appeal Effects of secondary market/ portfolio risk spreading 17

Recommendations Public authority Early analysis of the project risk matrix Take soundings from funding market Private sector Work on risks register/internal compliance Pricing/mitigation issues Early discussions with insurance advisers 18

Vilnius, 22 November 2006 1. UK/European PPP Experience and Lessons 2. Risks in PPP Projects Scott Dickson Senior Associate, Projects Group t: +44 (0)20 7760 4392 e: scott. dickson@blplaw. com Berwin Leighton Paisner LLP Adelaide House London Bridge London EC 4 R 9 HA t: +44 (0)20 7760 1000 f: +44 (0)20 7760 1111 www. blplaw. com 19
aaa15c1a470ba3560da88f053603d60d.ppt