0edb667590c908144295a9669a61b9b5.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 48

Public-Private Dialogue 4 th PPD Workshop April 2009 Vienna Benjamin Herzberg Sr. Private Sector Development Specialist 1

• • What is it, what does it look like? Why create or support PPDs? How do PPDs work? What is the impact of PPDs? How to implement PPDs? Ten practical tips to get results? How to enter and exit? How to share experiences, get good practice material, tools? 2

What is it, what does it look like? 3

Definition PPDs are structured mechanisms, anchored at the highest level of government, coordinated by a light secretariat, and aimed at facilitating the reform process by involving a balanced range of public and private sector actors in identifying, filtering, accelerating, implementing, and measuring policy reforms. 4
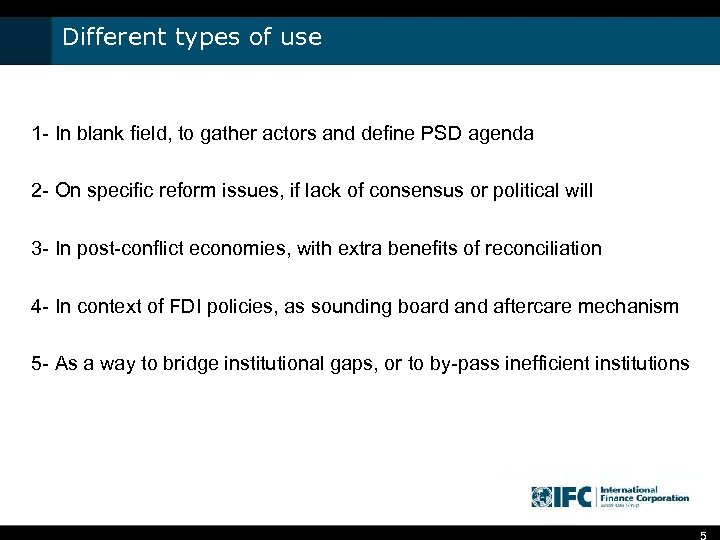
Different types of use 1 - In blank field, to gather actors and define PSD agenda 2 - On specific reform issues, if lack of consensus or political will 3 - In post-conflict economies, with extra benefits of reconciliation 4 - In context of FDI policies, as sounding board and aftercare mechanism 5 - As a way to bridge institutional gaps, or to by-pass inefficient institutions 5

PPDs in pictures 6
7

Why create or support PPDs? 8
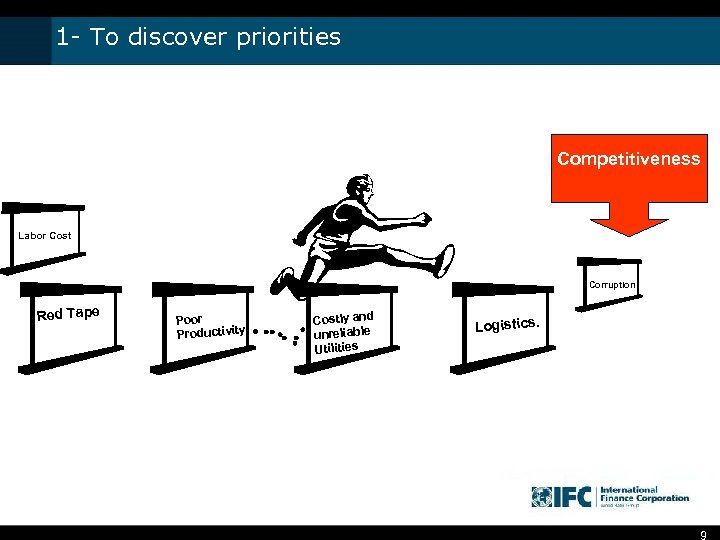
1 - To discover priorities Competitiveness Labor Cost Corruption Red Tape Poor Productivity Costly and unreliable Utilities Logistics. 9
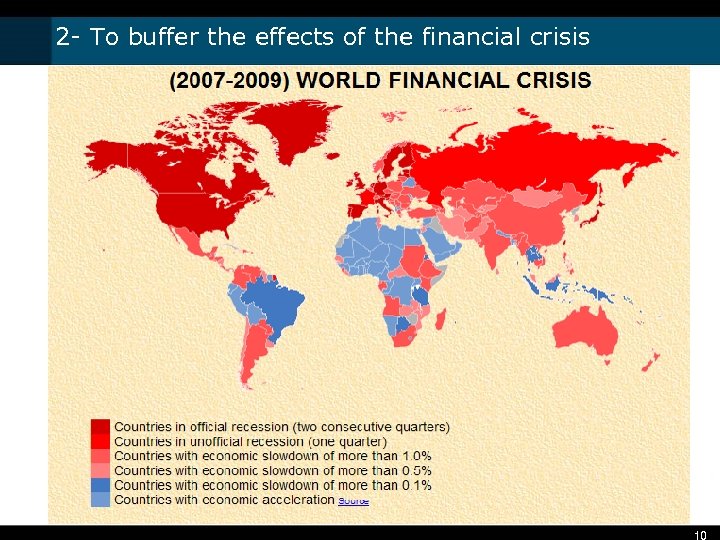
2 - To buffer the effects of the financial crisis 10
3 - To reduce regulatory burden 11
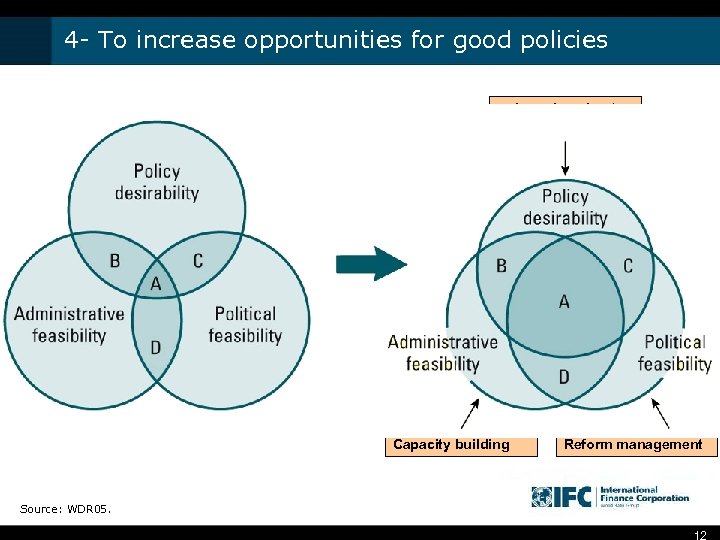
4 - To increase opportunities for good policies Learning about good practice Discovery Institution Capacity building Reform management Source: WDR 05. 12
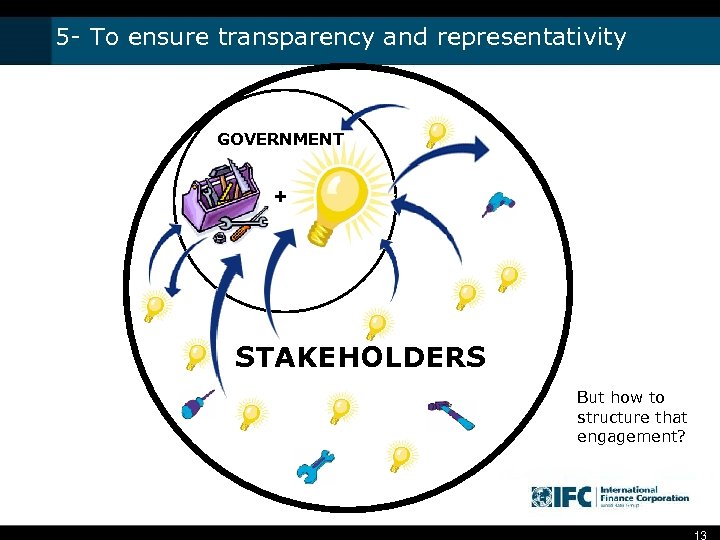
5 - To ensure transparency and representativity GOVERNMENT + STAKEHOLDERS But how to structure that engagement? 13
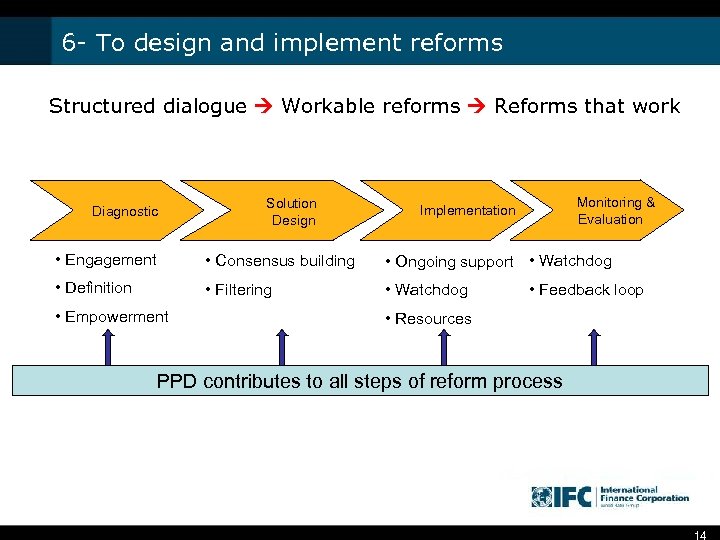
6 - To design and implement reforms Structured dialogue Workable reforms Reforms that work Diagnostic Solution Design Monitoring & Evaluation Implementation • Engagement • Consensus building • Ongoing support • Watchdog • Definition • Filtering • Watchdog • Empowerment • Feedback loop • Resources PPD contributes to all steps of reform process 14

What is the impact of PPDs? 15
Evidence of development effectiveness 2005: Independent evaluation of 5 Investors Advisory Councils in Africa 2007: Independent evaluation of 3 Business Forums in Mekong 2009: Independent evaluation of 30 WBG-sponsored PPDs 16
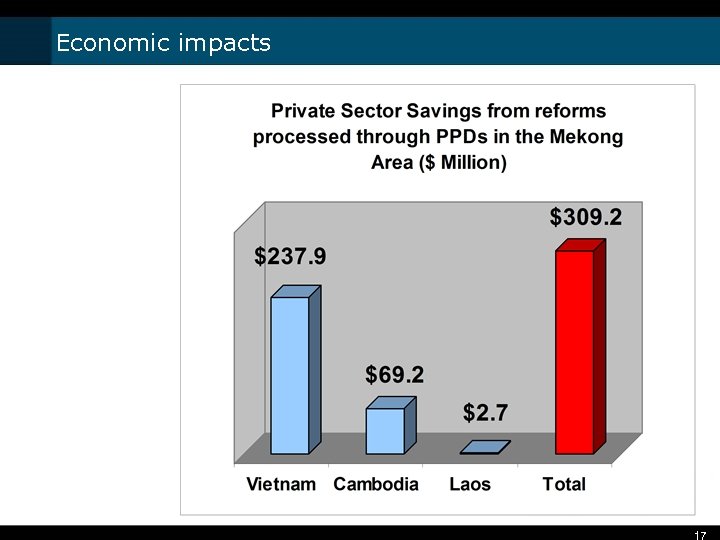
Economic impacts 17
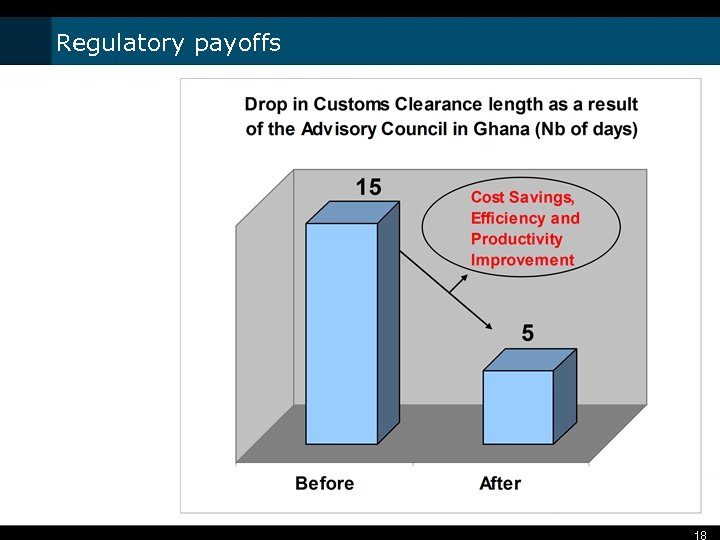
Regulatory payoffs 18
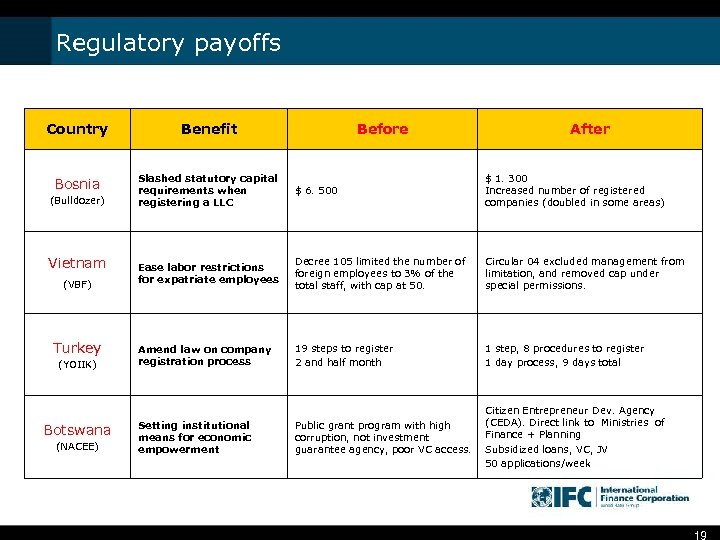
Regulatory payoffs Country Benefit Bosnia Slashed statutory capital requirements when registering a LLC $ 6. 500 $ 1. 300 Increased number of registered companies (doubled in some areas) Ease labor restrictions for expatriate employees Decree 105 limited the number of foreign employees to 3% of the total staff, with cap at 50. Circular 04 excluded management from limitation, and removed cap under special permissions. Amend law on company registration process 19 steps to register 2 and half month 1 step, 8 procedures to register 1 day process, 9 days total Public grant program with high corruption, not investment guarantee agency, poor VC access. Citizen Entrepreneur Dev. Agency (CEDA). Direct link to Ministries of Finance + Planning Subsidized loans, VC, JV 50 applications/week (Bulldozer) Vietnam (VBF) Turkey (YOIIK) Botswana (NACEE) Setting institutional means for economic empowerment Before After 19
How to implement PPDs? 20
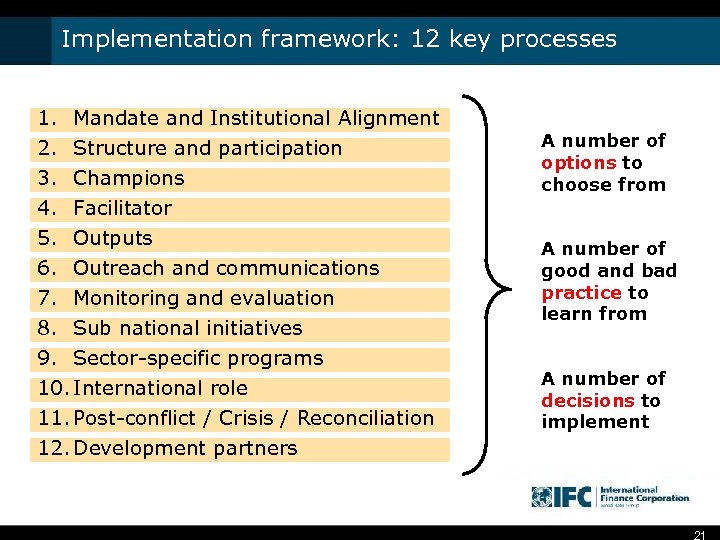
Implementation framework: 12 key processes 1. Mandate and Institutional Alignment 2. Structure and participation 3. Champions 4. Facilitator 5. Outputs 6. Outreach and communications 7. Monitoring and evaluation 8. Sub national initiatives 9. Sector-specific programs 10. International role 11. Post-conflict / Crisis / Reconciliation 12. Development partners A number of options to choose from A number of good and bad practice to learn from A number of decisions to implement 21
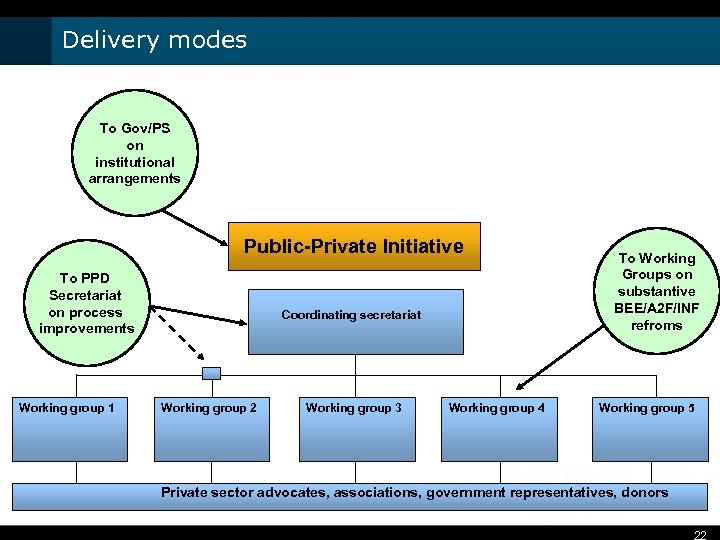
Delivery modes To Gov/PS on institutional arrangements Public-Private Initiative To PPD Secretariat on process improvements Working group 1 Coordinating secretariat Working group 2 Working group 3 Working group 4 To Working Groups on substantive BEE/A 2 F/INF refroms Working group 5 Private sector advocates, associations, government representatives, donors 22

Ten practical tips to get results 23

How to get results ? -1 A lot of work Huge coordination and mediation business 24
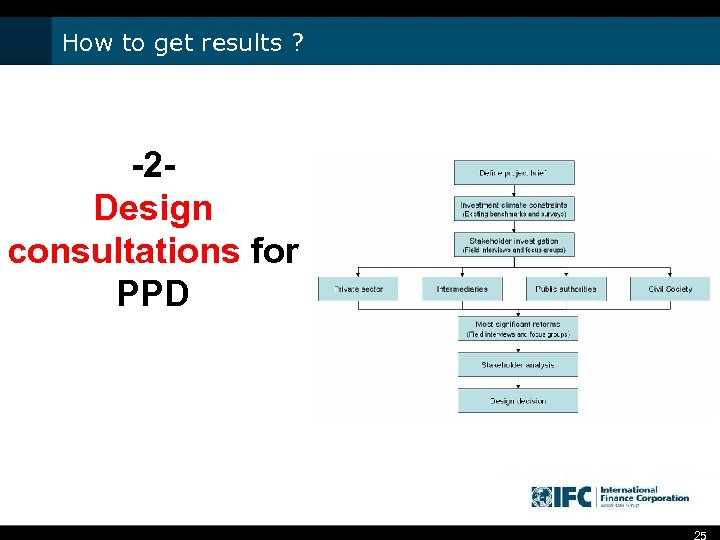
How to get results ? -2 Design consultations for PPD 25

How to get results ? -3 Strong focus on targeted, measurable refroms 26
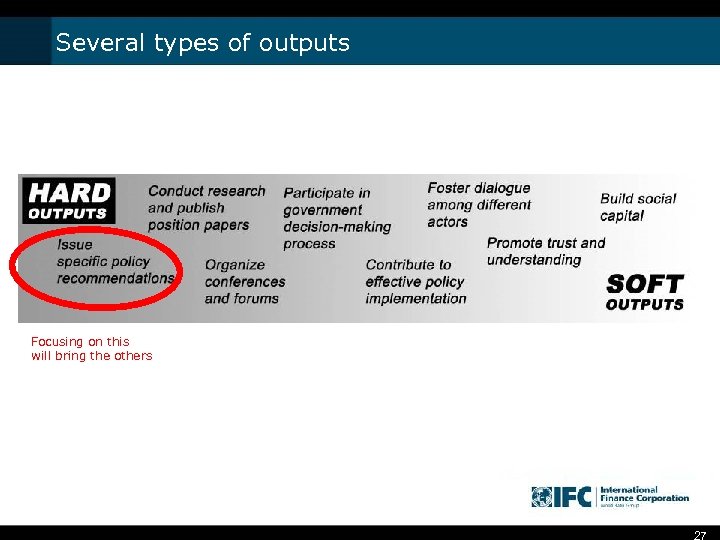
Several types of outputs Focusing on this will bring the others 27
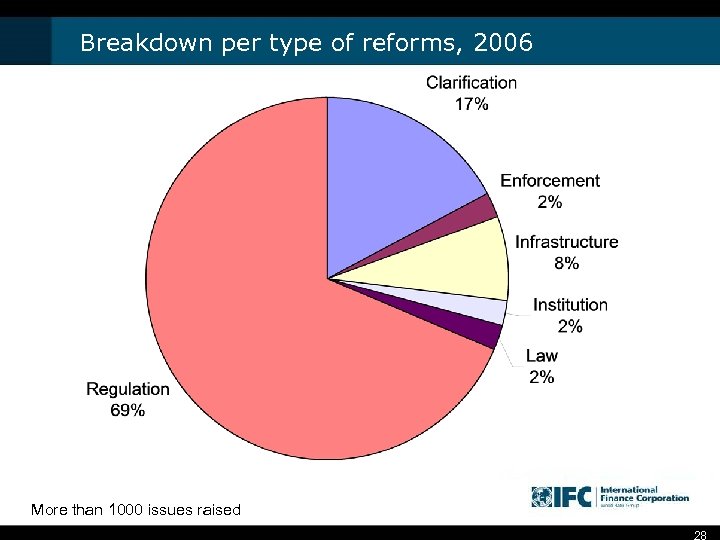
Breakdown per type of reforms, 2006 More than 1000 issues raised 28
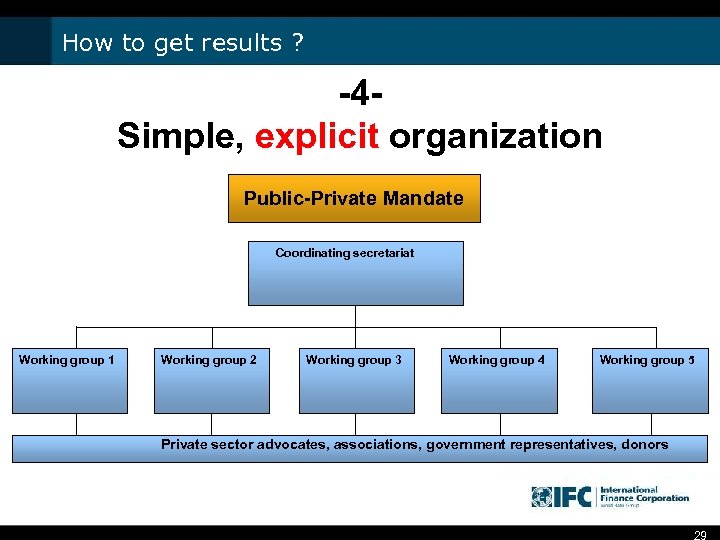
How to get results ? -4 Simple, explicit organization Public-Private Mandate Coordinating secretariat Working group 1 Working group 2 Working group 3 Working group 4 Working group 5 Private sector advocates, associations, government representatives, donors 29

How to get results ? -5 A unique, transparent and disciplined way to collect reform proposals 30
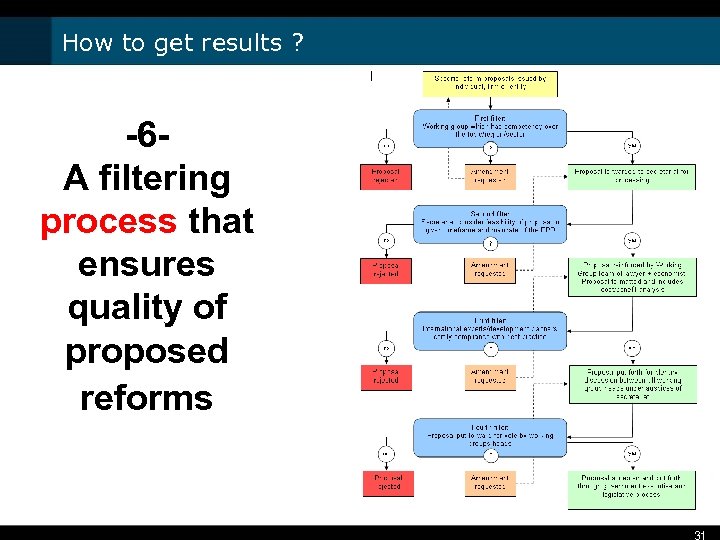
How to get results ? -6 A filtering process that ensures quality of proposed reforms 31

How to get results ? 32
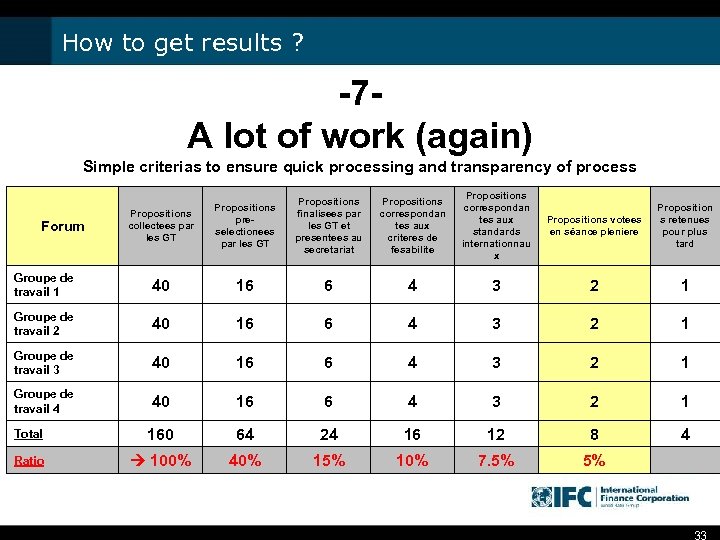
How to get results ? -7 A lot of work (again) Simple criterias to ensure quick processing and transparency of process Propositions collectees par les GT Propositions preselectionees par les GT Propositions finalisees par les GT et presentees au secretariat Propositions correspondan tes aux criteres de fesabilite Propositions correspondan tes aux standards internationnau x Propositions votees en séance pleniere Proposition s retenues pour plus tard Groupe de travail 1 40 16 6 4 3 2 1 Groupe de travail 2 40 16 6 4 3 2 1 Groupe de travail 3 40 16 6 4 3 2 1 Groupe de travail 4 40 16 6 4 3 2 1 Total 160 64 24 16 12 8 4 Ratio 100% 40% 15% 10% 7. 5% 5% Forum 33
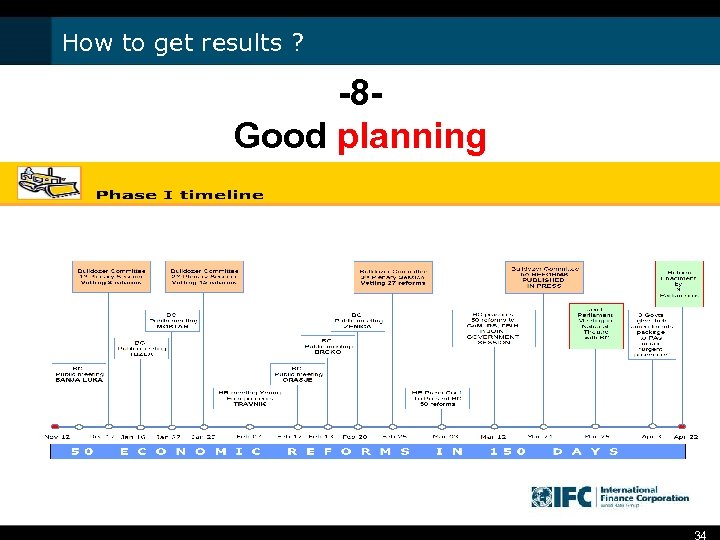
How to get results ? -8 Good planning 34

How to get results ? -9 Strong convincing power 35
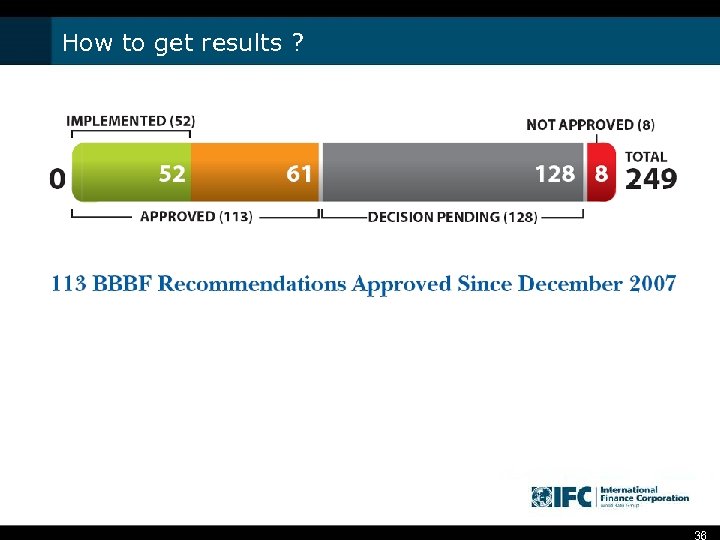
How to get results ? 36
How to get results ? 37
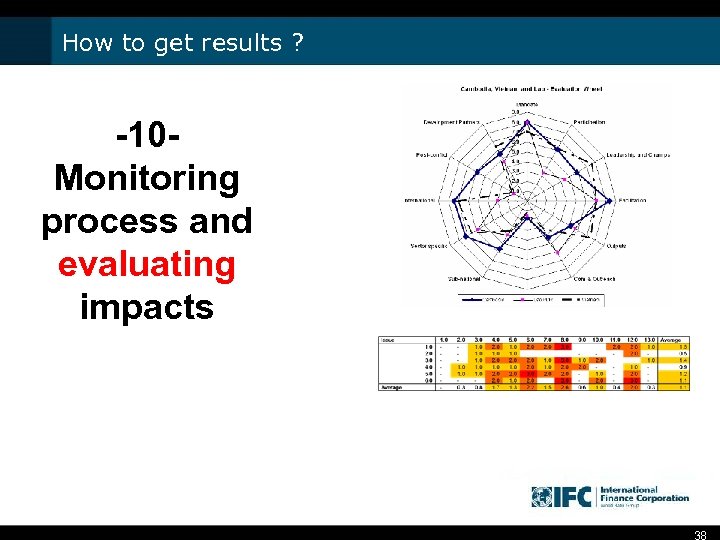
How to get results ? -10 Monitoring process and evaluating impacts 38
Tools and techniques for monitoring + evaluation 39
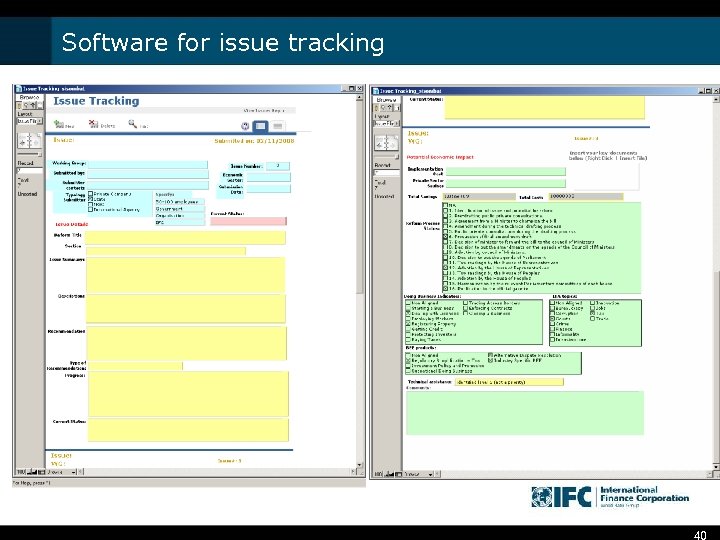
Software for issue tracking 40

How to start and exit? 41

PPDs are risky business but risk is manageable Reinforcing vested interest (e. g. Mongolia) Be open and transparent – Publicize quality control – Broad based Over and under representation (e. g. Tanzania, 18%) Strengthening BMOS – Equal representation – Periodic review Sustainability issues (e. g. Bolivia) Clear agenda and proposals – Manage expectations – Live and let die One man shows (e. g. Botswana) Foster bottom-up support – Secure written commitment – Prepare transition Political risks (e. g. Bosnia) Depoliticize through outreach – Woo parliamentarians – Go local Institutional misalignments (e. g. Uganda NF) embrace institutions – Use technical ministerial staff – Transfer competencies 42
Initiative or institution? Public authorities Private sector 43
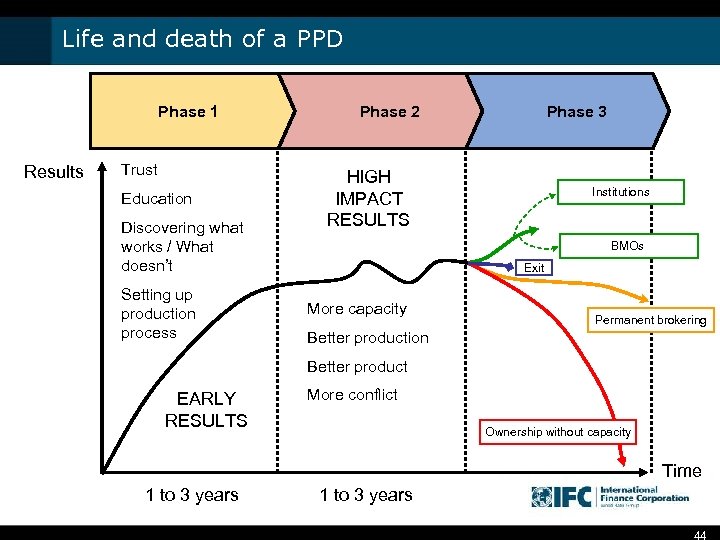
Life and death of a PPD Phase 1 Results Trust Education Discovering what works / What doesn’t Setting up production process Phase 2 Phase 3 HIGH IMPACT RESULTS Institutions BMOs Exit More capacity Permanent brokering Better production Better product EARLY RESULTS More conflict Ownership without capacity Time 1 to 3 years 44
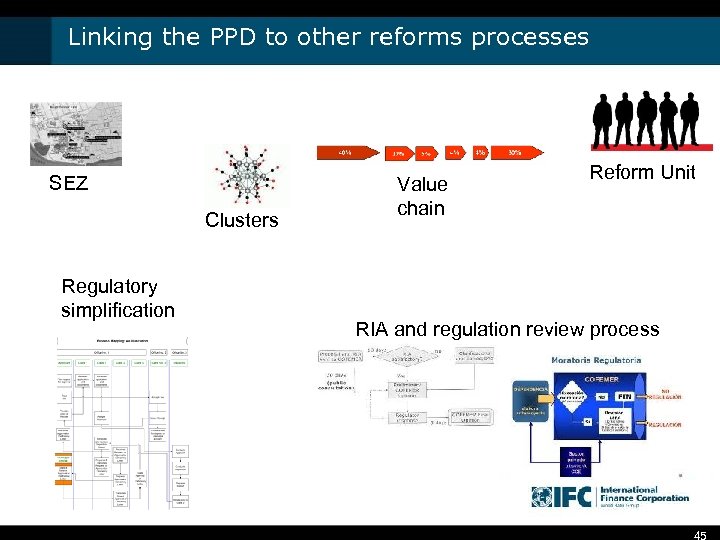
Linking the PPD to other reforms processes SEZ Clusters Regulatory simplification Value chain Reform Unit RIA and regulation review process 45

How to share experiences, get good practice material, tools? 46
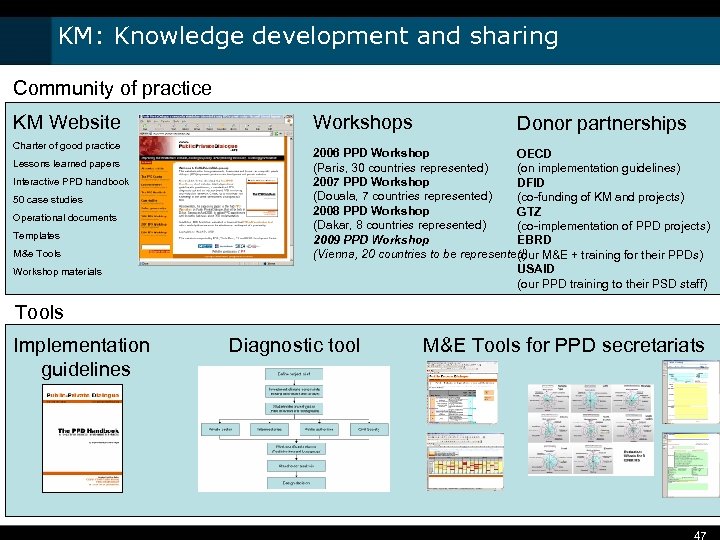
KM: Knowledge development and sharing Community of practice KM Website Charter of good practice Lessons learned papers Interactive PPD handbook 50 case studies Operational documents Templates M&e Tools Workshop materials Workshops Donor partnerships 2006 PPD Workshop OECD (Paris, 30 countries represented) (on implementation guidelines) 2007 PPD Workshop DFID (Douala, 7 countries represented) (co-funding of KM and projects) 2008 PPD Workshop GTZ (Dakar, 8 countries represented) (co-implementation of PPD projects) 2009 PPD Workshop EBRD (Vienna, 20 countries to be represented) M&E + training for their PPDs) (our USAID (our PPD training to their PSD staff) Tools Implementation guidelines Diagnostic tool M&E Tools for PPD secretariats 47

Thank you! Benjamin Herzberg World Bank Group bherzberg@worldbank. org 48
0edb667590c908144295a9669a61b9b5.ppt