0156ed87daa1ffef29f3f61be7aa1f42.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29

Public Policy Update Matt Brow VP, Public Policy & Reimbursement Strategy Mc. Kesson Specialty Health November 14, 2012

2012 Election Results 2
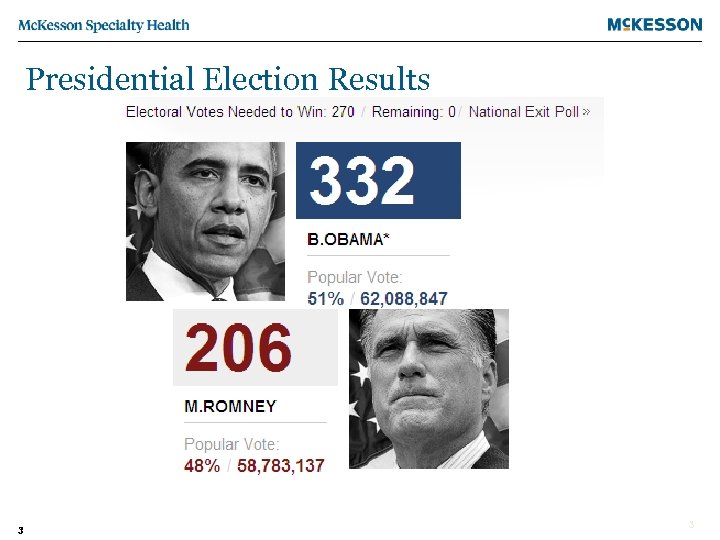
Presidential Election Results 3 3
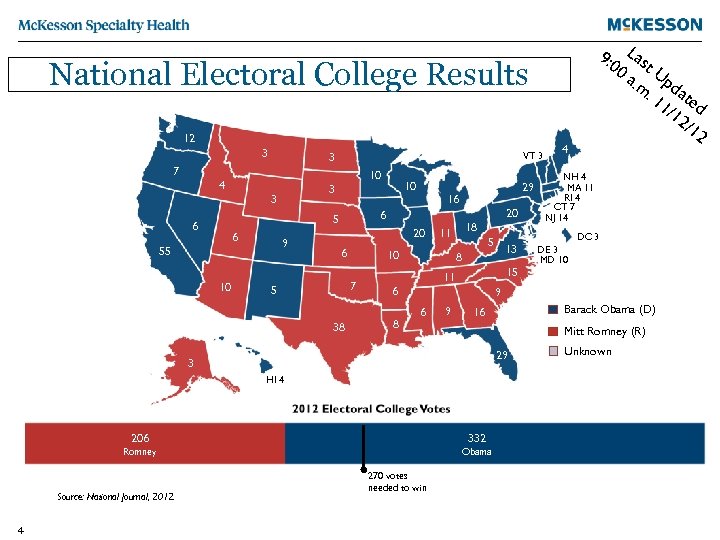
9: 0 Las 0 a t. U. m pda. 1 te 1/1 d 2/1 2 National Electoral College Results 12 3 7 4 VT 3 3 10 3 3 6 55 10 9 29 16 20 6 5 6 10 20 6 38 11 10 7 5 18 5 8 15 11 6 8 6 9 DC 3 DE 3 MD 10 Barack Romney Obama 16 (D) Mitt Romney (R) 29 Unknown Romney Obama HI 4 206 332 Romney 4 NH 4 MA 11 RI 4 CT 7 NJ 14 9 3 Obama Source: National Journal, 2012. 13 4 270 votes needed to win
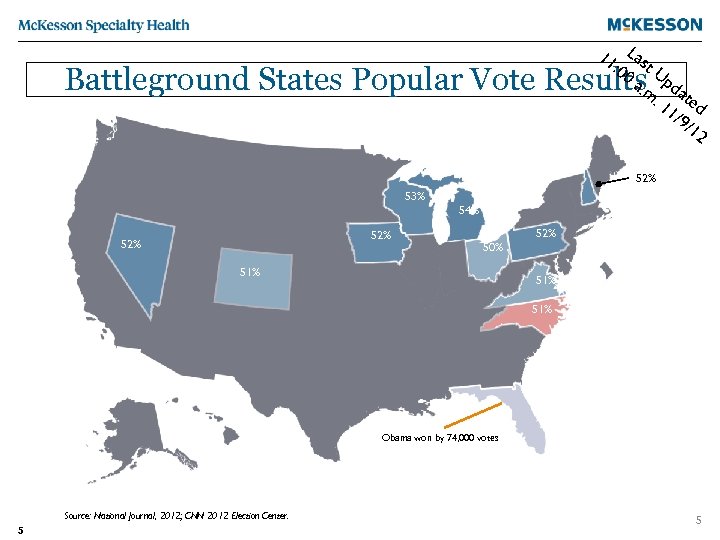
11 Las : 00 t U a. m pda. 1 ted 1/9 /12 Battleground States Popular Vote Results 52% 53% 54% 52% 52% 50% 51% 51% Obama won by 74, 000 votes Source: National Journal, 2012; CNN 2012 Election Center. 5 5
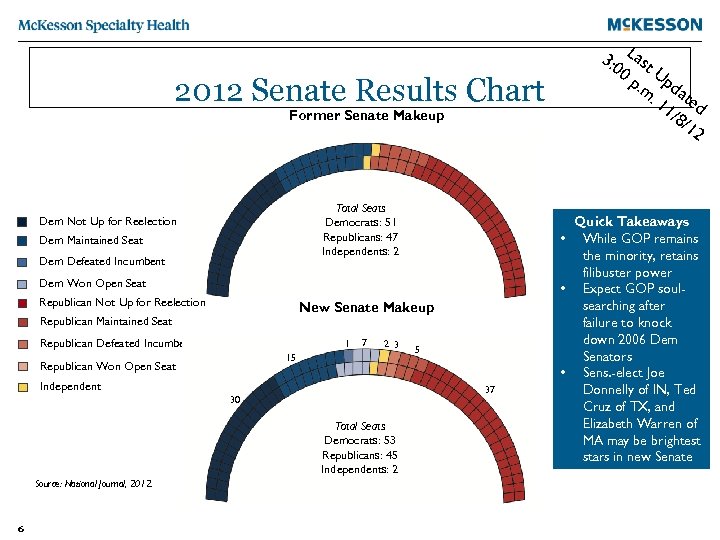
2012 Senate Results Chart Former Senate Makeup Total Seats Democrats: 51 Republicans: 47 Independents: 2 Dem Not Up for Reelection Dem Maintained Seat 51 Dem Defeated Incumbent Dem Won Open Seat Republican Not Up for Reelection New Senate Makeup Republican Maintained Seat Republican Defeated Incumbent 1 173 Romney 2 3 15 Republican Won Open Seat Independent 7 37 30 Total Seats Democrats: 53 Republicans: 45 Independents: 2 Source: National Journal, 2012. 6 5 3: 0 Last 0 p Up. m da. 1 ted 1/8 /12 Quick Takeaways • While GOP remains the minority, retains filibuster power • Expect GOP soulsearching after failure to knock down 2006 Dem Senators • Sens. -elect Joe Donnelly of IN, Ted Cruz of TX, and Elizabeth Warren of MA may be brightest stars in new Senate
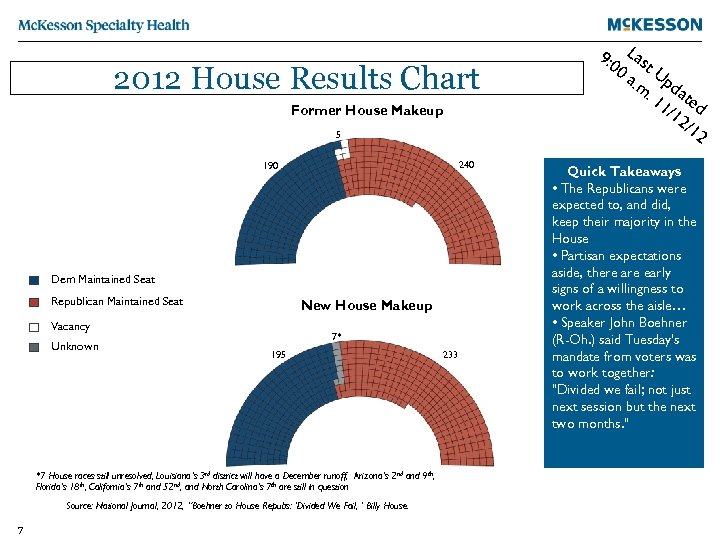
2012 House Results Chart Former House Makeup 5 240 190 Dem Maintained Seat Republican Maintained Seat New House Makeup Vacancy 7* Unknown 195 173 Romney *7 House races still unresolved, Louisiana’s 3 rd district will have a December runoff, Arizona’s 2 nd and 9 th, Florida’s 18 th, California’s 7 th and 52 nd, and North Carolina’s 7 th are still in question Source: National Journal, 2012, “Boehner to House Repubs: ‘Divided We Fail, ’ Billy House. 7 233 9: 0 Las 0 a t. U. m pda. 1 te 1/1 d 2/1 2 Quick Takeaways • The Republicans were expected to, and did, keep their majority in the House • Partisan expectations aside, there are early signs of a willingness to work across the aisle… • Speaker John Boehner (R-Oh. ) said Tuesday's mandate from voters was to work together: "Divided we fail; not just next session but the next two months. "

ACA is the Law of the Land 8
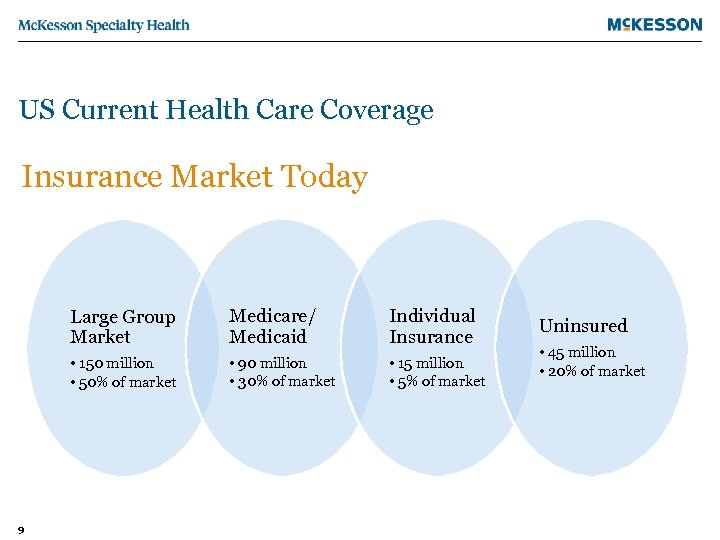
US Current Health Care Coverage Insurance Market Today Large Group Market Individual Insurance • 150 million • 50% of market 9 Medicare/ Medicaid • 90 million • 30% of market • 15 million • 5% of market Uninsured • 45 million • 20% of market

Affordable Care Act Expansions Uninsured Reduced by 30 Million § 15 million more covered under streamlined Medicaid program open to all with incomes up to 133% of FPL • Pending state expansion decisions § 15 million covered under reformed commercial market for individuals and small groups • Guarantee issue, community rating, individual mandate with limited exceptions, tax credits to help with premiums up to 400% of FPL • Exchanges to make coverage more accessible 10

Affordable Care Act Insurance Expansions Insurance Requirements § Community Rating • Rates may only vary by age (3: 1 ratio), tobacco use, self or family, and rating area § Guaranteed Issue • Eligibility for coverage may not be based on health factors § Employer-sponsored coverage waiting periods = < 90 days § Coverage must include “essential benefits package” § Limit annual cost sharing, eliminate benefit maximums § Medical Loss Ratio § HAS and FSA caps 11

Favorite Mid-Year Pastime 12

Decision is a Win for Patients & Specialty Physicians § > 30 million newly insured Americans (half Medicaid and half private insurance purchased with government subsidies through exchanges) § Elimination pre-existing conditions exclusions and rescissions § Elimination of lifetime and annual benefits maximums § Creation of a new mandate to cover the routine costs of care associated with participation in cancer clinical trials • Applied to all coverage not just fully insured § New patient out of pocket caps that will limit patient financial responsibility and associated bad debt for practices 13

What’s Next with the ACA? 14 | For internal use only/proprietary and confidential.
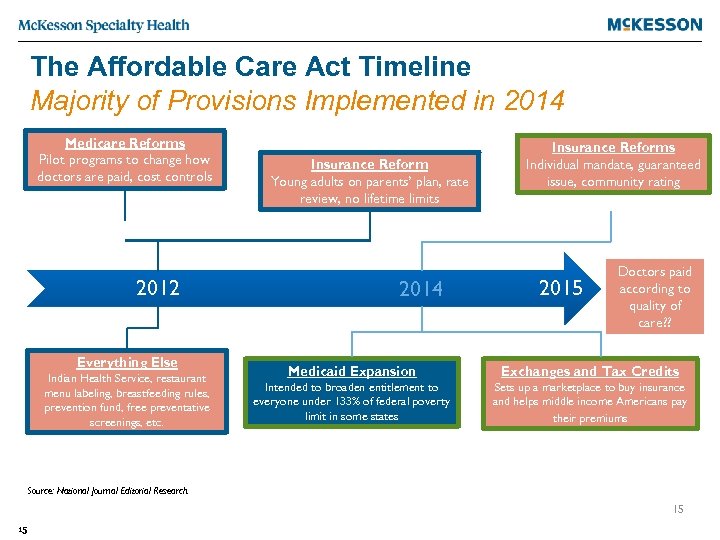
The Affordable Care Act Timeline Majority of Provisions Implemented in 2014 Medicare Reforms Pilot programs to change how doctors are paid, cost controls 2012 Everything Else Indian Health Service, restaurant menu labeling, breastfeeding rules, prevention fund, free preventative screenings, etc. Insurance Reform Young adults on parents’ plan, rate review, no lifetime limits 2014 Insurance Reforms Individual mandate, guaranteed issue, community rating 2015 Doctors paid according to quality of care? ? Medicaid Expansion Exchanges and Tax Credits Intended to broaden entitlement to everyone under 133% of federal poverty limit in some states Sets up a marketplace to buy insurance 15 and helps middle income Americans pay their premiums Source: National Journal Editorial Research. 15 15

Implementation Will Be Anything But a Cakewalk Many states were gambling that Supreme Court would invalidate law – have done nothing to set up exchanges HHS implementation is incomplete and diverse funding sources are subject to vagaries of Congress – unlikely law will roll out on time 2017 16 2017 and beyond, states will be held accountable for a greater share of the Medicaid funding – states may have to cut other programs or raise taxes to fund
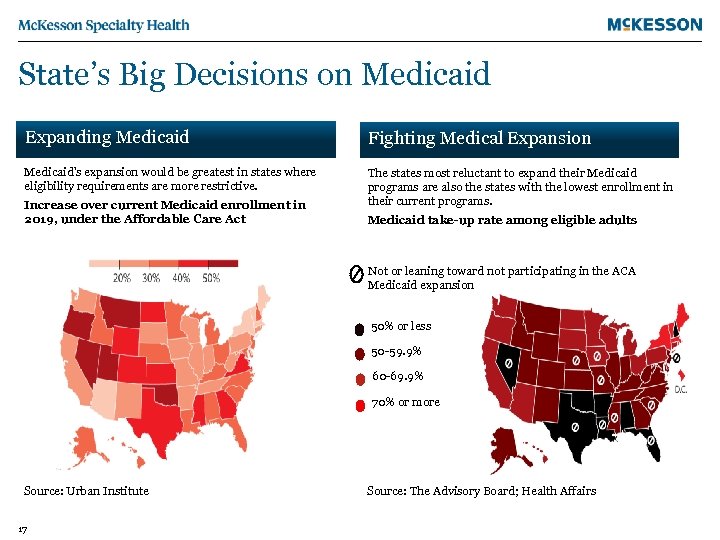
State’s Big Decisions on Medicaid Expanding Medicaid Fighting Medical Expansion Medicaid’s expansion would be greatest in states where eligibility requirements are more restrictive. The states most reluctant to expand their Medicaid programs are also the states with the lowest enrollment in their current programs. Increase over current Medicaid enrollment in 2019, under the Affordable Care Act Medicaid take-up rate among eligible adults Not or leaning toward not participating in the ACA Medicaid expansion 50% or less 50 -59. 9% 60 -69. 9% 70% or more Source: Urban Institute 17 Source: The Advisory Board; Health Affairs

State Leadership 18
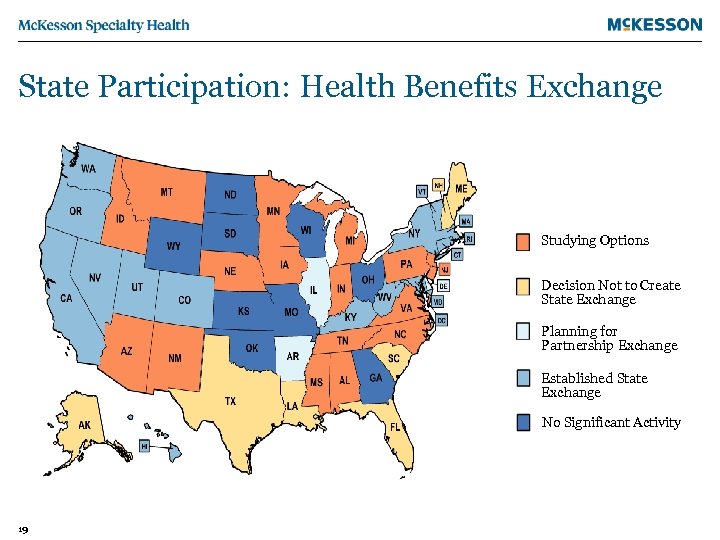
State Participation: Health Benefits Exchange Studying Options Decision Not to Create State Exchange Planning for Partnership Exchange Established State Exchange No Significant Activity 19

2013 Medicare Physician Fee Schedule 20
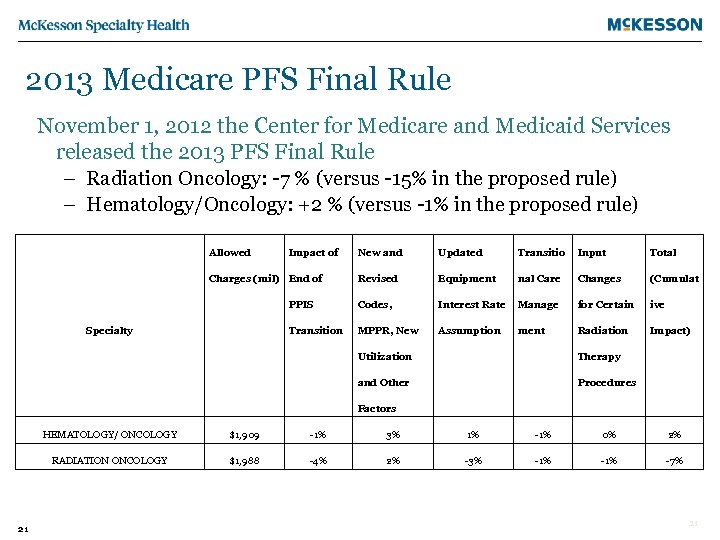
2013 Medicare PFS Final Rule November 1, 2012 the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services released the 2013 PFS Final Rule – Radiation Oncology: -7 % (versus -15% in the proposed rule) – Hematology/Oncology: +2 % (versus -1% in the proposed rule) Allowed Impact of New and Updated Transitio Input Total Revised Equipment nal Care Changes (Cumulat PPIS Codes, Interest Rate Manage for Certain ive Transition MPPR, New Assumption Radiation Impact) Charges (mil) End of Specialty ment Utilization Therapy and Other Procedures Factors HEMATOLOGY/ ONCOLOGY -1% 3% 1% -1% 0% 2% RADIATION ONCOLOGY 21 $1, 909 $1, 988 -4% 2% -3% -1% -7% 21

Lame Duck / Fiscal Cliff 22 | For internal use only/proprietary and confidential.

The Fiscal Cliff 23 23

Fiscal Cliff 24

Expiring 2001 & 2003 Tax Cuts § Higher taxes for every American who pays income taxes, including small business owners – The 10% bracket disappears, – All other brackets increase by 3% – Top tier at 39. 6% or above § Higher taxes if you are married (marriage penalties reinstated) – Penalties in 2013 at least $2, 087 § Higher taxes if you are a parent (child credit cut in half) – Credit goes from $1000 to $500 § Higher taxes on investments – Capital Gains goes from 15% to 20% – Qualified Dividends goes from 15% to 39. 6% (44. 6% with 3. 8% Obama. Care surtax) 25 25

Expiring 2001 & 2003 Tax Cuts § Higher Death Taxes – % Exemption drops from $5. 12 million to $1 million – Top rate will rise from 35% to 55% § Higher taxes for 31 million households due to Alternative Minimum Tax – Exemptions fall from $74, 450 to $45, 000 for couples – Average of about $4, 200 per affected taxpayer 26 26

Sequestration on the Horizon If Congress does not reduce the deficit by $1. 2 trillion by January 1, 2013, automatic spending cuts (sequestration) begin. If Sequestration Is Enforced Budget Defense Non-Defense Cuts 2013 to 2021 $493. 2 B Interest TOTAL 27 $216 B $1. 2 T 27
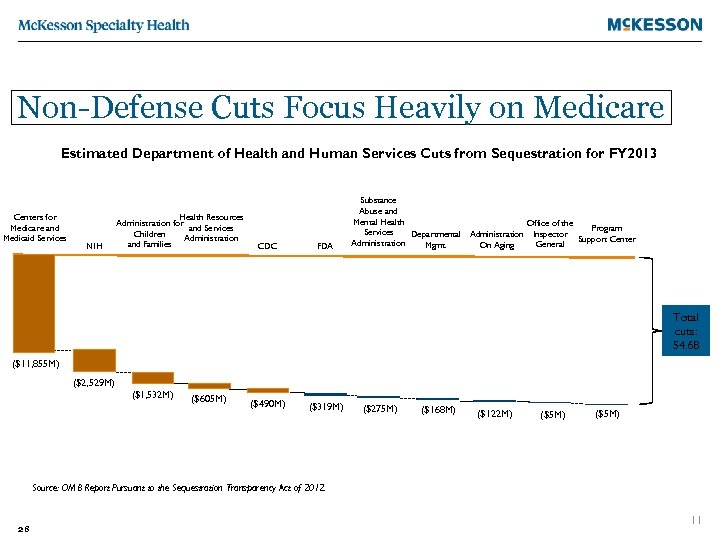
Non-Defense Cuts Focus Heavily on Medicare Estimated Department of Health and Human Services Cuts from Sequestration for FY 2013 Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services NIH Health Resources Administration for and Services Children Administration and Families CDC FDA Substance Abuse and Mental Health Office of the Program Services Departmental Administration Inspector Support Center Administration General Mgmt. On Aging Total cuts: 54. 6 B ($11, 855 M) ($2, 529 M) ($1, 532 M) ($605 M) ($490 M) ($319 M) ($275 M) ($168 M) ($122 M) ($5 M) Source: OMB Report Pursuant to the Sequestration Transparency Act of 2012. 28 11

Discussion 29 | For internal use only/proprietary and confidential.
0156ed87daa1ffef29f3f61be7aa1f42.ppt