 Psychology and human development Lecture 2. Prenatal Development. Physical development Perception development Problems: life does not always go to plan Summary of prenatal development.
Psychology and human development Lecture 2. Prenatal Development. Physical development Perception development Problems: life does not always go to plan Summary of prenatal development.
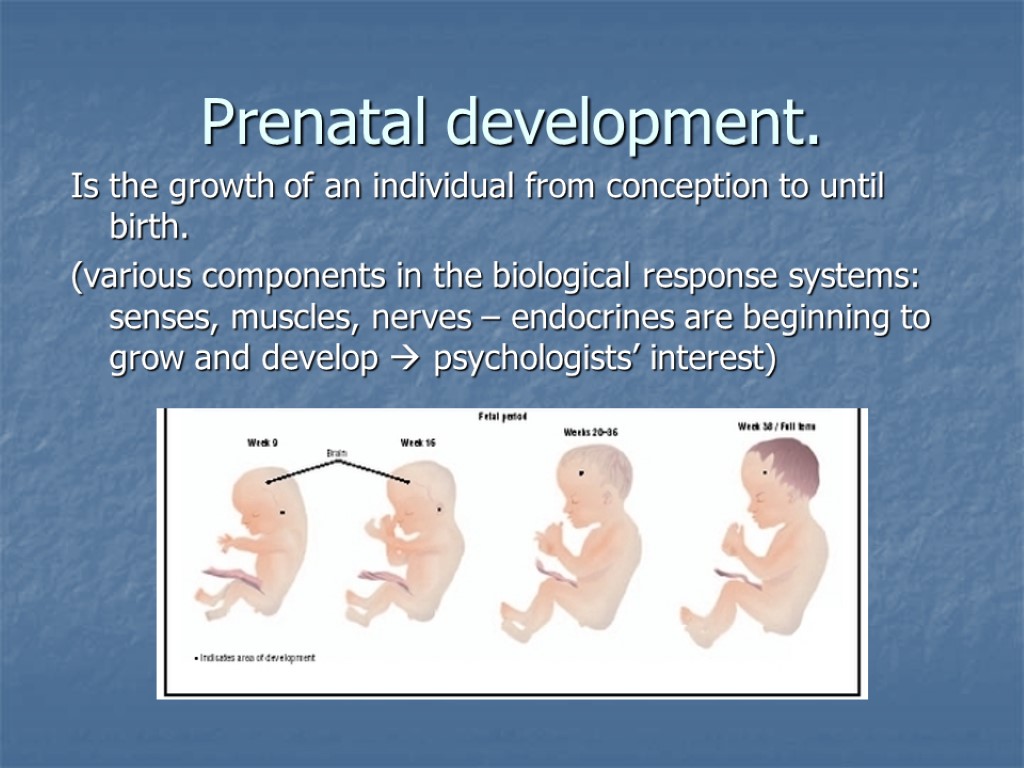 Prenatal development. Is the growth of an individual from conception to until birth. (various components in the biological response systems: senses, muscles, nerves – endocrines are beginning to grow and develop psychologists’ interest)
Prenatal development. Is the growth of an individual from conception to until birth. (various components in the biological response systems: senses, muscles, nerves – endocrines are beginning to grow and develop psychologists’ interest)
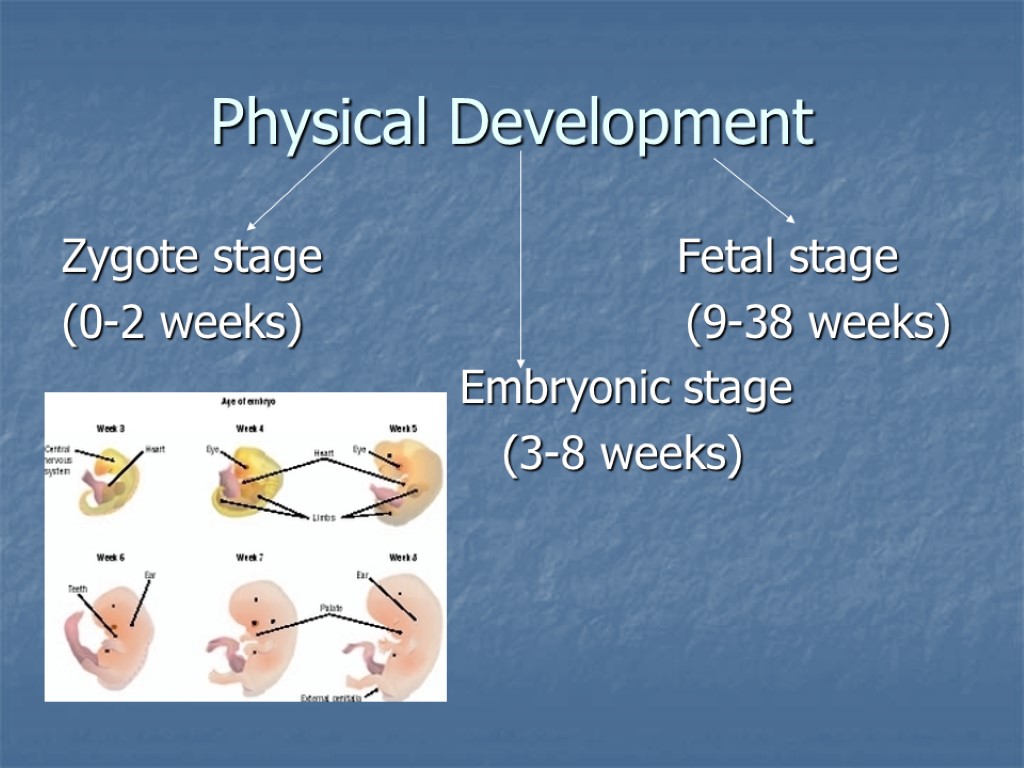 Physical Development Zygote stage Fetal stage (0-2 weeks) (9-38 weeks) Embryonic stage (3-8 weeks)
Physical Development Zygote stage Fetal stage (0-2 weeks) (9-38 weeks) Embryonic stage (3-8 weeks)
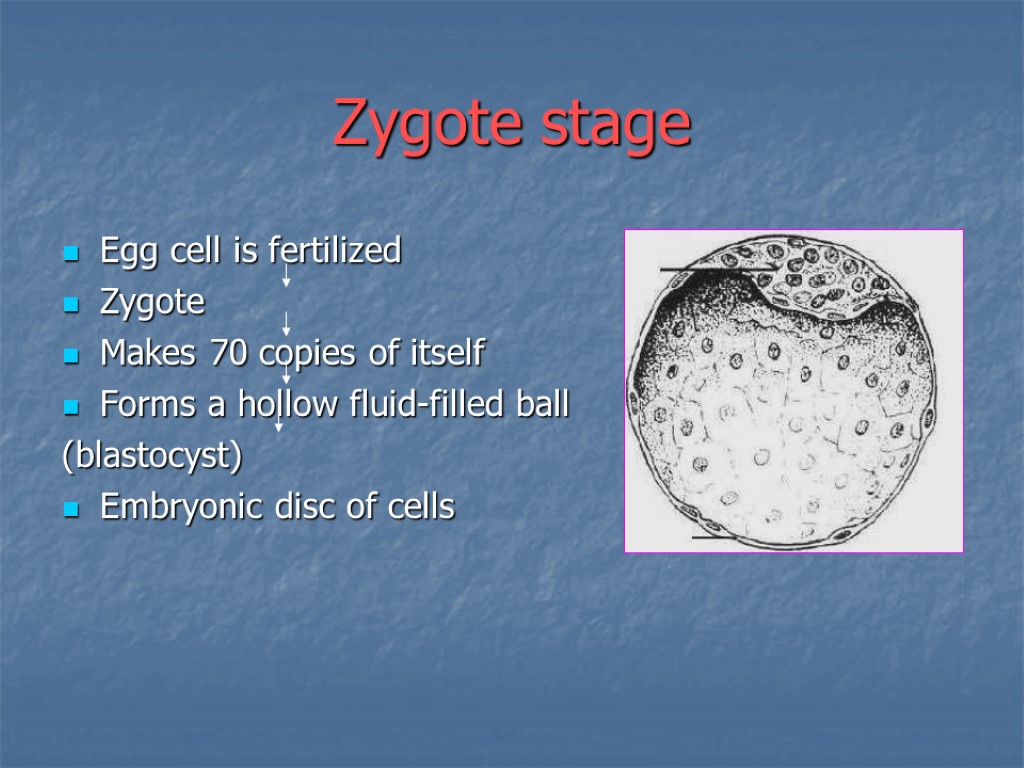 Zygote stage Egg cell is fertilized Zygote Makes 70 copies of itself Forms a hollow fluid-filled ball (blastocyst) Embryonic disc of cells
Zygote stage Egg cell is fertilized Zygote Makes 70 copies of itself Forms a hollow fluid-filled ball (blastocyst) Embryonic disc of cells
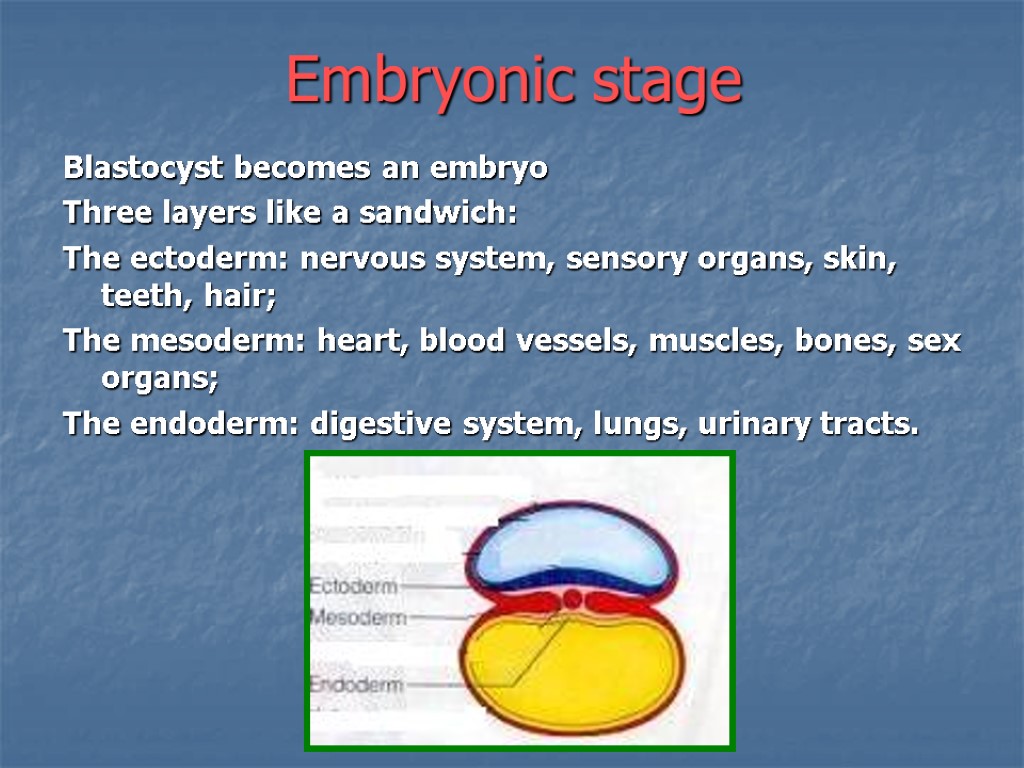 Embryonic stage Blastocyst becomes an embryo Three layers like a sandwich: The ectoderm: nervous system, sensory organs, skin, teeth, hair; The mesoderm: heart, blood vessels, muscles, bones, sex organs; The endoderm: digestive system, lungs, urinary tracts.
Embryonic stage Blastocyst becomes an embryo Three layers like a sandwich: The ectoderm: nervous system, sensory organs, skin, teeth, hair; The mesoderm: heart, blood vessels, muscles, bones, sex organs; The endoderm: digestive system, lungs, urinary tracts.
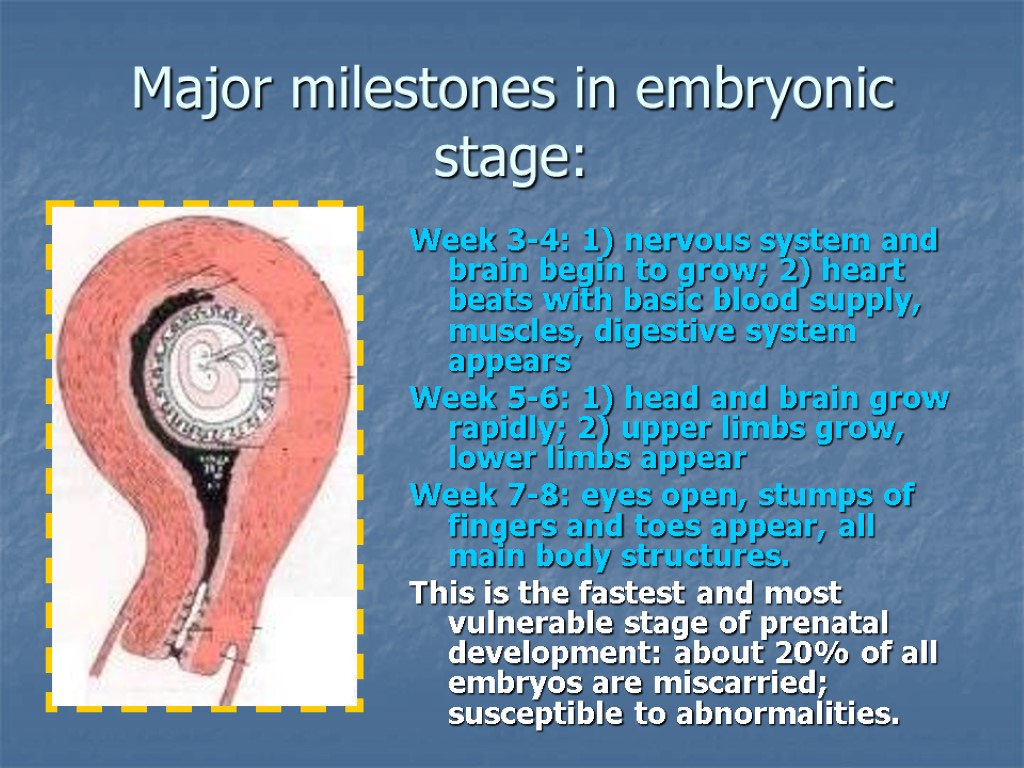 Major milestones in embryonic stage: Week 3-4: 1) nervous system and brain begin to grow; 2) heart beats with basic blood supply, muscles, digestive system appears Week 5-6: 1) head and brain grow rapidly; 2) upper limbs grow, lower limbs appear Week 7-8: eyes open, stumps of fingers and toes appear, all main body structures. This is the fastest and most vulnerable stage of prenatal development: about 20% of all embryos are miscarried; susceptible to abnormalities.
Major milestones in embryonic stage: Week 3-4: 1) nervous system and brain begin to grow; 2) heart beats with basic blood supply, muscles, digestive system appears Week 5-6: 1) head and brain grow rapidly; 2) upper limbs grow, lower limbs appear Week 7-8: eyes open, stumps of fingers and toes appear, all main body structures. This is the fastest and most vulnerable stage of prenatal development: about 20% of all embryos are miscarried; susceptible to abnormalities.
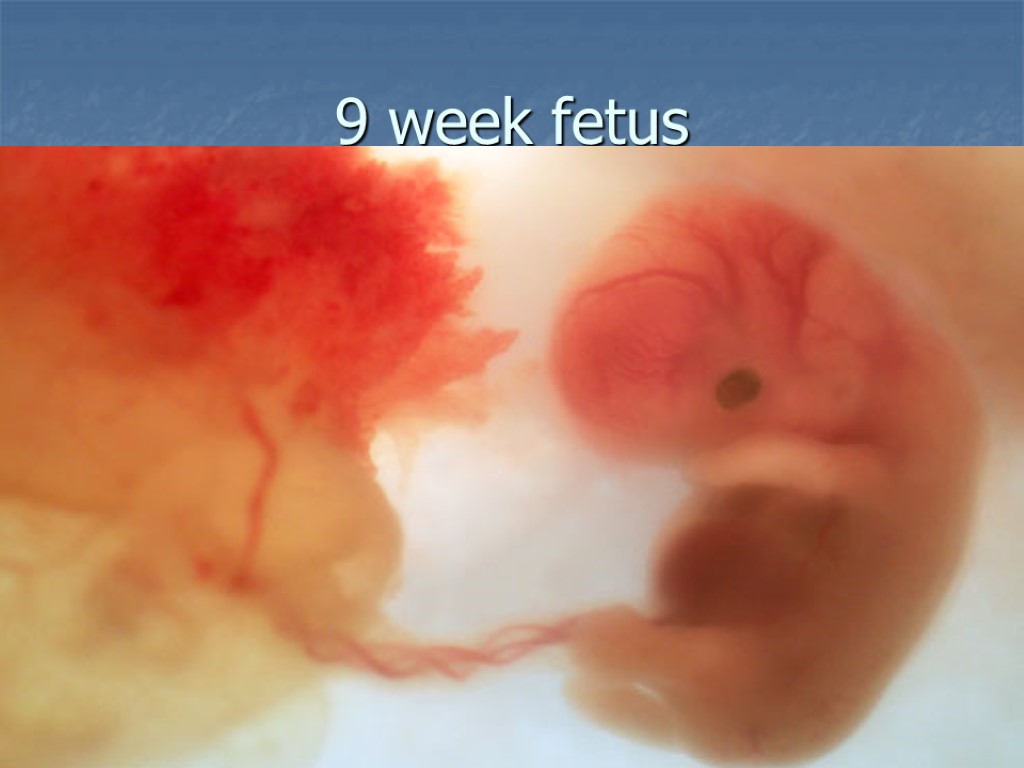 9 week fetus
9 week fetus
 Fetal stage By week 9 major organs and structures of the body are formed and in place. The main purpose: to grow bigger and more complex. Most babies survive this stage. The most remarkable changes in this period: increasing responsiveness to external stimulation and the ability to remember or learn about information from the outside world.
Fetal stage By week 9 major organs and structures of the body are formed and in place. The main purpose: to grow bigger and more complex. Most babies survive this stage. The most remarkable changes in this period: increasing responsiveness to external stimulation and the ability to remember or learn about information from the outside world.

 Early cognitive in foetal phase: 1. By week 20 the foetus responds to most external sounds, especially if loud enough: sounds of mother’s voice and tunes of TV pr. It can retain such auditory info in memory. 2. It is possible to train or condition the foetus to associate 2 separate stimuli (classical conditioning) – tone + tactile stimulus. It can be retained after birth. (Mothers watched neighbors during pregnancy, neonates became more alert and stopped moving when the program started. 3. Foetus reacts to touch and has a sense of taste, showing more swallowing if a sweet substance is introduced. Also, visual sense – reaction to light- by closing eyes.
Early cognitive in foetal phase: 1. By week 20 the foetus responds to most external sounds, especially if loud enough: sounds of mother’s voice and tunes of TV pr. It can retain such auditory info in memory. 2. It is possible to train or condition the foetus to associate 2 separate stimuli (classical conditioning) – tone + tactile stimulus. It can be retained after birth. (Mothers watched neighbors during pregnancy, neonates became more alert and stopped moving when the program started. 3. Foetus reacts to touch and has a sense of taste, showing more swallowing if a sweet substance is introduced. Also, visual sense – reaction to light- by closing eyes.
 Problems Though the foetus goes from strength to strengths, 6-7% of all newborn have congenital defects due to a) genetic factors or b) teratogens ( harmful environmental factors)
Problems Though the foetus goes from strength to strengths, 6-7% of all newborn have congenital defects due to a) genetic factors or b) teratogens ( harmful environmental factors)
 Genetic defects are due to Errors resulting in chromosomal or genetic aberrations in the new cells. (Down’s Syndrome- children are born with an extra chromosome in Pair 21) Environmental defects are due to Infections diseases ( Rubella measles results in blindness, hearing loss, heart abnormalities, brain damage) Effects from drugs (alcohol results in foetus alcohol syndrome, poor growth, facial abnormalities, small head size, cognitive disabilities. Dangerous factors from environment (mercury pollution in Japan resulted in mental and physical abnormalities in children. Poor diet (malnutrition) - especially on development of brain in the last few months.
Genetic defects are due to Errors resulting in chromosomal or genetic aberrations in the new cells. (Down’s Syndrome- children are born with an extra chromosome in Pair 21) Environmental defects are due to Infections diseases ( Rubella measles results in blindness, hearing loss, heart abnormalities, brain damage) Effects from drugs (alcohol results in foetus alcohol syndrome, poor growth, facial abnormalities, small head size, cognitive disabilities. Dangerous factors from environment (mercury pollution in Japan resulted in mental and physical abnormalities in children. Poor diet (malnutrition) - especially on development of brain in the last few months.
 Summary of the development:
Summary of the development:
 Seminar overview questions: Describe the main developmental events in the period of embryonic development. Summarize the main developmental events in the foetal period of life. Describe some of the main teratogens that may affect prenatal development.
Seminar overview questions: Describe the main developmental events in the period of embryonic development. Summarize the main developmental events in the foetal period of life. Describe some of the main teratogens that may affect prenatal development.













































