7fc143a25a4302448b037422f14ea8a1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 'Psychological Rewards' and the First City‘s Command over its National Space: Greater Tel Aviv as a Case in Point Prof. Baruch A. Kipnis The University of Haifa, Israel Presentation the 5 th Bi-National Regional Science Workshop - - UK-Israel Tel Aviv, 29 -30/4/2007 1
'Psychological Rewards' and the First City‘s Command over its National Space: Greater Tel Aviv as a Case in Point Prof. Baruch A. Kipnis The University of Haifa, Israel Presentation the 5 th Bi-National Regional Science Workshop - - UK-Israel Tel Aviv, 29 -30/4/2007 1
 The main Issues üWhat is the notion of a place’s psychological rewards, what are the place’s attributes that foster their development? üWho belongs to a place's creative agencies [who are those who operate the place’s creative industries? ], and how are they linked to the notion of psychological rewards? üWhy is a First City, usually a World City, a place in which psychological rewards meet the wants of the place’s agents of human creativity? üHow does Tel Aviv (the city and metropolis) Israel’s First City and World City, govern Israel’s economy and its social and cultural life? üIs Tel Aviv an exception, or is a leading role of a First City a universal phenomena? üIs there a workable solution to the dominating role of Tel Aviv? 2
The main Issues üWhat is the notion of a place’s psychological rewards, what are the place’s attributes that foster their development? üWho belongs to a place's creative agencies [who are those who operate the place’s creative industries? ], and how are they linked to the notion of psychological rewards? üWhy is a First City, usually a World City, a place in which psychological rewards meet the wants of the place’s agents of human creativity? üHow does Tel Aviv (the city and metropolis) Israel’s First City and World City, govern Israel’s economy and its social and cultural life? üIs Tel Aviv an exception, or is a leading role of a First City a universal phenomena? üIs there a workable solution to the dominating role of Tel Aviv? 2
 What do we mean by ‘psychological rewards’ An upgrade of Florida, (2005) ‘creative environment’. In a creative economy, places, shouldn't be measured in terms of GDP – instead, they should be indexed according to the happiness of people who live there. “ …"there are certain things that promote our wellbeing, happiness and personal fulfillment: üThe quality and diversity of our living, work and cultural environment üThe ease of access to our place’s intrinsic opportunities and essential services and infrastructures üThe nature of our job and our personal life This presentation, refers to the above qualities of a place, as the place's 'psychological rewards'. 3
What do we mean by ‘psychological rewards’ An upgrade of Florida, (2005) ‘creative environment’. In a creative economy, places, shouldn't be measured in terms of GDP – instead, they should be indexed according to the happiness of people who live there. “ …"there are certain things that promote our wellbeing, happiness and personal fulfillment: üThe quality and diversity of our living, work and cultural environment üThe ease of access to our place’s intrinsic opportunities and essential services and infrastructures üThe nature of our job and our personal life This presentation, refers to the above qualities of a place, as the place's 'psychological rewards'. 3
 ‘Psychological Rewards’/cont The creativity of a place is a reflection of what Buswell (1983) named [as a metaphor] the place's 'psychological rewards', an asset of a place endeavoring to perform as one labeled by Malecki (1980) as a white collar environment of a postindustrial ambience. Florida's creative environment is a large urban agglomeration, competing for highly mobile talented people by adopting competitive and creative goals, and noticed by its three Ts: ü Talent - the creative human capital, those who engage in creative work. ü Technology - the level of the place's high-tech innovative activity. ü Tolerance - the qualities of a place as liberal and tolerant, both vital for attracting talented people capable of generating new ideas. 4
‘Psychological Rewards’/cont The creativity of a place is a reflection of what Buswell (1983) named [as a metaphor] the place's 'psychological rewards', an asset of a place endeavoring to perform as one labeled by Malecki (1980) as a white collar environment of a postindustrial ambience. Florida's creative environment is a large urban agglomeration, competing for highly mobile talented people by adopting competitive and creative goals, and noticed by its three Ts: ü Talent - the creative human capital, those who engage in creative work. ü Technology - the level of the place's high-tech innovative activity. ü Tolerance - the qualities of a place as liberal and tolerant, both vital for attracting talented people capable of generating new ideas. 4
 ‘Psychological Rewards’ and ‘Creative Agencies’ The concept of psychological rewards is more inclusive than that of Florida's tolerance. It contains, in addition to human and social attributes, a variety of physical, cultural, and service attributes. It reflects the diversified qualities of the place’s creative agents including: üThe affluent (the supper rich and TCC) üThe skilled managers and professional experts who form the quinary and the quaternary sectors and run [for the affluent) the nation’s globally oriented economy. üThe providers (human and institutions) of public and private services - - in education, health and community, cultural and leisure services. üThe place’s cultural creators and performers. 5
‘Psychological Rewards’ and ‘Creative Agencies’ The concept of psychological rewards is more inclusive than that of Florida's tolerance. It contains, in addition to human and social attributes, a variety of physical, cultural, and service attributes. It reflects the diversified qualities of the place’s creative agents including: üThe affluent (the supper rich and TCC) üThe skilled managers and professional experts who form the quinary and the quaternary sectors and run [for the affluent) the nation’s globally oriented economy. üThe providers (human and institutions) of public and private services - - in education, health and community, cultural and leisure services. üThe place’s cultural creators and performers. 5
 ‘Psychological Rewards’, ‘Creative Ambience’ and the ‘First City’ üplace's psychological rewards, a requisite of aaplace and the A symbiosis between the creative agents for postindustrial 'white collar' environment, is vital for leveraging urban growth. ü(Hall andsymbiosis, is usually a ‘World the context of a 'First City’ Such a best revealed in Pain, 2006), City’, possessing the needed entry thresholds* for a vast range of psychological rewards. üskilled labor offavorable place of activity forsectors, is apt to host A First City, a the affluent and their the quinary and quaternary a creative ambient endowed with ample amounts of ‘Psychological Rewards’. *Other concepts of the Central Place Theory are at work: they are the range of good, nesting, multiple activity, node. 6
‘Psychological Rewards’, ‘Creative Ambience’ and the ‘First City’ üplace's psychological rewards, a requisite of aaplace and the A symbiosis between the creative agents for postindustrial 'white collar' environment, is vital for leveraging urban growth. ü(Hall andsymbiosis, is usually a ‘World the context of a 'First City’ Such a best revealed in Pain, 2006), City’, possessing the needed entry thresholds* for a vast range of psychological rewards. üskilled labor offavorable place of activity forsectors, is apt to host A First City, a the affluent and their the quinary and quaternary a creative ambient endowed with ample amounts of ‘Psychological Rewards’. *Other concepts of the Central Place Theory are at work: they are the range of good, nesting, multiple activity, node. 6
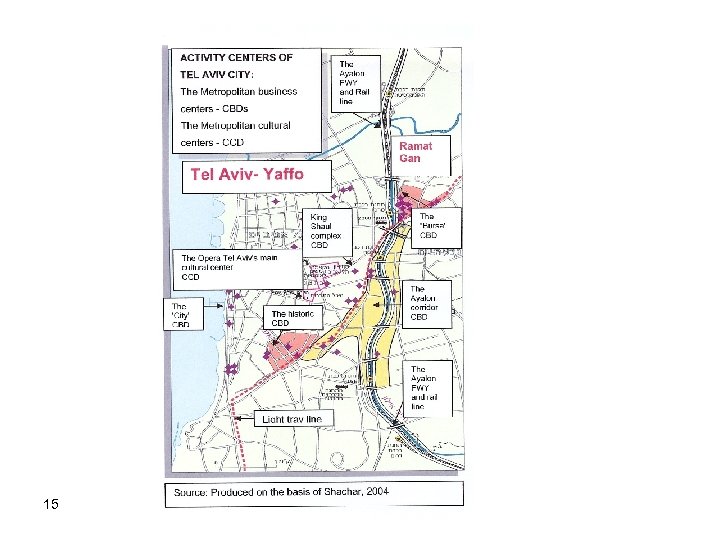
 Greater Tel Aviv, Israel’s ‘First City’ and a “World City’ A syndrome of spatial domination Greater Tel Aviv “a huge head with no mass [body]" [1] 7
Greater Tel Aviv, Israel’s ‘First City’ and a “World City’ A syndrome of spatial domination Greater Tel Aviv “a huge head with no mass [body]" [1] 7
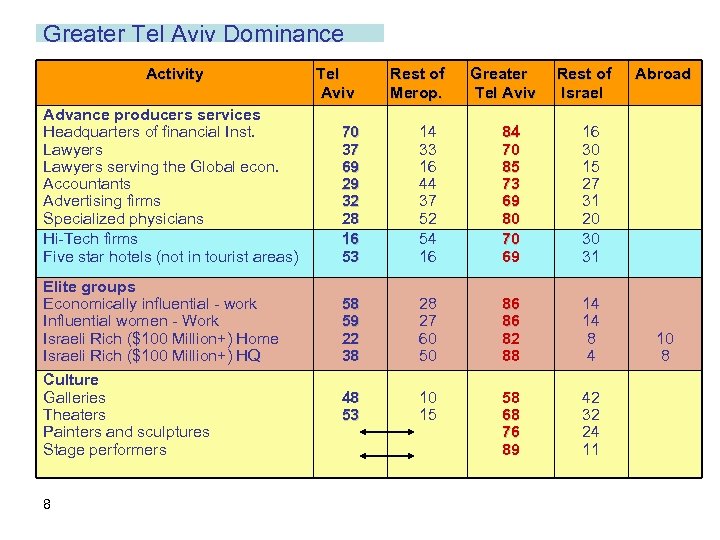 Greater Tel Aviv Dominance Activity Tel Aviv Rest of Merop. Greater Tel Aviv Rest of Israel Advance producers services Headquarters of financial Inst. Lawyers serving the Global econ. Accountants Advertising firms Specialized physicians Hi-Tech firms Five star hotels (not in tourist areas) 70 37 69 29 32 28 16 53 14 33 16 44 37 52 54 16 84 70 85 73 69 80 70 69 16 30 15 27 31 20 30 31 Elite groups Economically influential - work Influential women - Work Israeli Rich ($100 Million+) Home Israeli Rich ($100 Million+) HQ 58 59 22 38 28 27 60 50 86 86 82 88 14 14 8 4 48 53 10 15 58 68 76 89 42 32 24 11 Abroad Culture Galleries Theaters Painters and sculptures Stage performers 8 10 8
Greater Tel Aviv Dominance Activity Tel Aviv Rest of Merop. Greater Tel Aviv Rest of Israel Advance producers services Headquarters of financial Inst. Lawyers serving the Global econ. Accountants Advertising firms Specialized physicians Hi-Tech firms Five star hotels (not in tourist areas) 70 37 69 29 32 28 16 53 14 33 16 44 37 52 54 16 84 70 85 73 69 80 70 69 16 30 15 27 31 20 30 31 Elite groups Economically influential - work Influential women - Work Israeli Rich ($100 Million+) Home Israeli Rich ($100 Million+) HQ 58 59 22 38 28 27 60 50 86 86 82 88 14 14 8 4 48 53 10 15 58 68 76 89 42 32 24 11 Abroad Culture Galleries Theaters Painters and sculptures Stage performers 8 10 8
 The Skyline of Tel Aviv 9
The Skyline of Tel Aviv 9
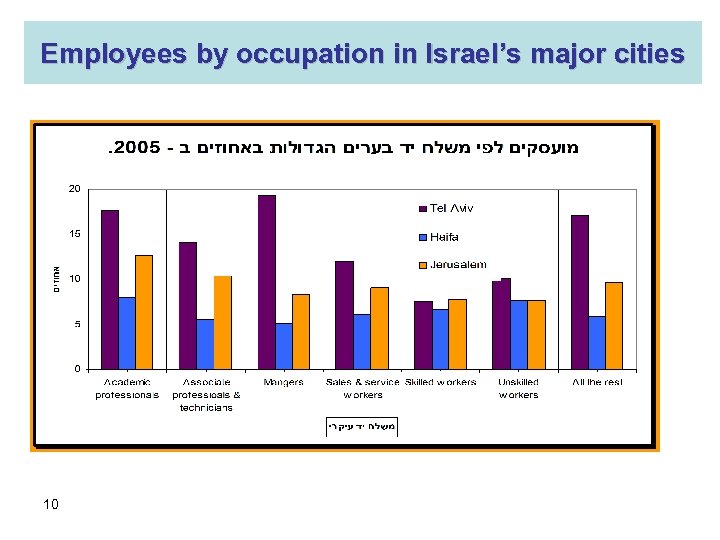 Employees by occupation in Israel’s major cities 10
Employees by occupation in Israel’s major cities 10
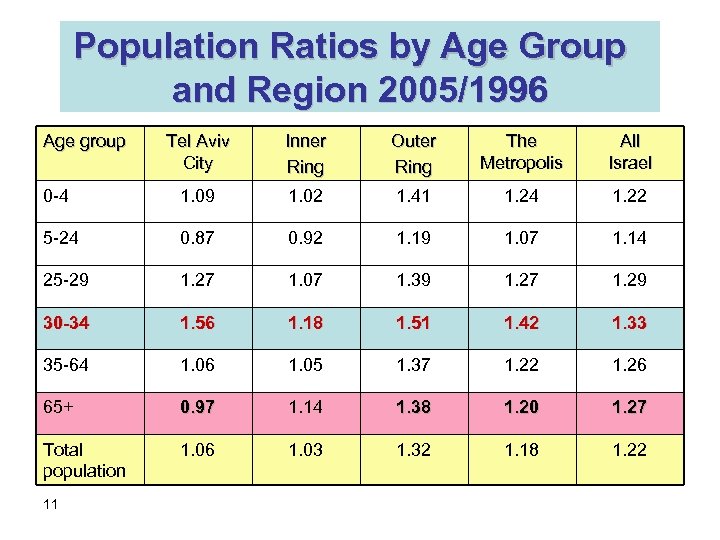 Population Ratios by Age Group and Region 2005/1996 Age group Tel Aviv City Inner Ring Outer Ring The Metropolis All Israel 0 -4 1. 09 1. 02 1. 41 1. 24 1. 22 5 -24 0. 87 0. 92 1. 19 1. 07 1. 14 25 -29 1. 27 1. 07 1. 39 1. 27 1. 29 30 -34 1. 56 1. 18 1. 51 1. 42 1. 33 35 -64 1. 06 1. 05 1. 37 1. 22 1. 26 65+ 0. 97 1. 14 1. 38 1. 20 1. 27 Total population 1. 06 1. 03 1. 32 1. 18 1. 22 11
Population Ratios by Age Group and Region 2005/1996 Age group Tel Aviv City Inner Ring Outer Ring The Metropolis All Israel 0 -4 1. 09 1. 02 1. 41 1. 24 1. 22 5 -24 0. 87 0. 92 1. 19 1. 07 1. 14 25 -29 1. 27 1. 07 1. 39 1. 27 1. 29 30 -34 1. 56 1. 18 1. 51 1. 42 1. 33 35 -64 1. 06 1. 05 1. 37 1. 22 1. 26 65+ 0. 97 1. 14 1. 38 1. 20 1. 27 Total population 1. 06 1. 03 1. 32 1. 18 1. 22 11
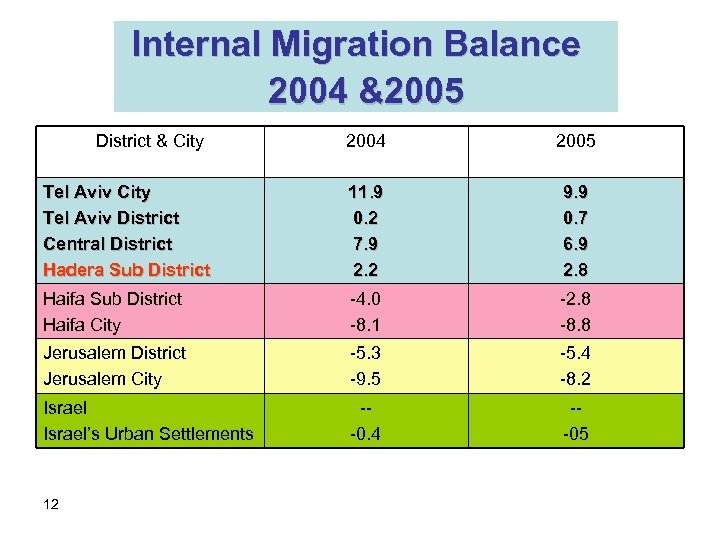 Internal Migration Balance 2004 &2005 District & City 2004 2005 Tel Aviv City Tel Aviv District Central District Hadera Sub District 11. 9 0. 2 7. 9 2. 2 9. 9 0. 7 6. 9 2. 8 Haifa Sub District Haifa City -4. 0 -8. 1 -2. 8 -8. 8 Jerusalem District Jerusalem City -5. 3 -9. 5 -5. 4 -8. 2 Israel’s Urban Settlements --0. 4 --05 12
Internal Migration Balance 2004 &2005 District & City 2004 2005 Tel Aviv City Tel Aviv District Central District Hadera Sub District 11. 9 0. 2 7. 9 2. 2 9. 9 0. 7 6. 9 2. 8 Haifa Sub District Haifa City -4. 0 -8. 1 -2. 8 -8. 8 Jerusalem District Jerusalem City -5. 3 -9. 5 -5. 4 -8. 2 Israel’s Urban Settlements --0. 4 --05 12
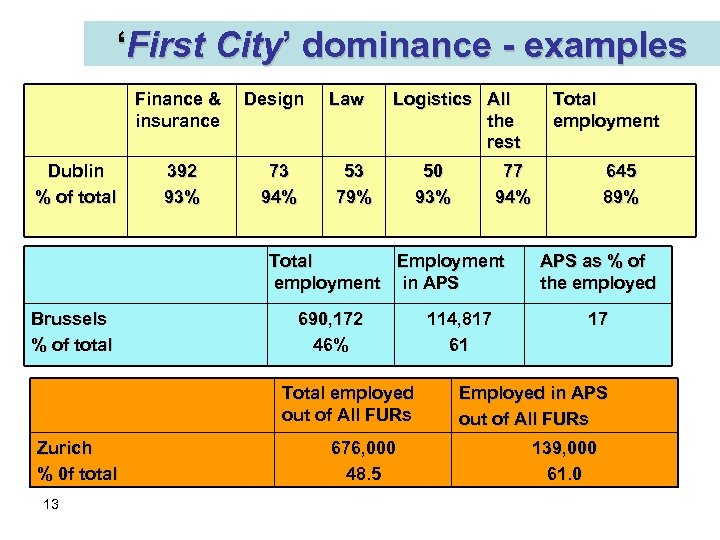 ‘First City’ dominance - examples Finance & insurance Dublin % of total 392 93% Design 73 94% Law Logistics All the rest 53 79% 50 93% 77 94% Total Employment employment in APS Brussels % of total 690, 172 46% Total employed out of All FURs Zurich % 0 f total 13 676, 000 48. 5 Total employment 114, 817 61 645 89% APS as % of the employed 17 Employed in APS out of All FURs 139, 000 61. 0
‘First City’ dominance - examples Finance & insurance Dublin % of total 392 93% Design 73 94% Law Logistics All the rest 53 79% 50 93% 77 94% Total Employment employment in APS Brussels % of total 690, 172 46% Total employed out of All FURs Zurich % 0 f total 13 676, 000 48. 5 Total employment 114, 817 61 645 89% APS as % of the employed 17 Employed in APS out of All FURs 139, 000 61. 0
 First City’ dominance – examples/ cont. Population as % of total Holland Amsterdam + suburbs For major Randstad Cities Paris City Percent of Employed in APS Yeary increase of employment in APS 1982 -1999 14 Global firms as % of total Holland 5. 4 14. 7 68. 0 88. 0 Inner Ring Second Ring Employed in APS as % of total Holland 11. 1 21. 9 Third Ring All Paris Region 42 41 31 22 32 - 0. 3 4. 1 5. 3 2. 2 2. 1
First City’ dominance – examples/ cont. Population as % of total Holland Amsterdam + suburbs For major Randstad Cities Paris City Percent of Employed in APS Yeary increase of employment in APS 1982 -1999 14 Global firms as % of total Holland 5. 4 14. 7 68. 0 88. 0 Inner Ring Second Ring Employed in APS as % of total Holland 11. 1 21. 9 Third Ring All Paris Region 42 41 31 22 32 - 0. 3 4. 1 5. 3 2. 2 2. 1
 15
15
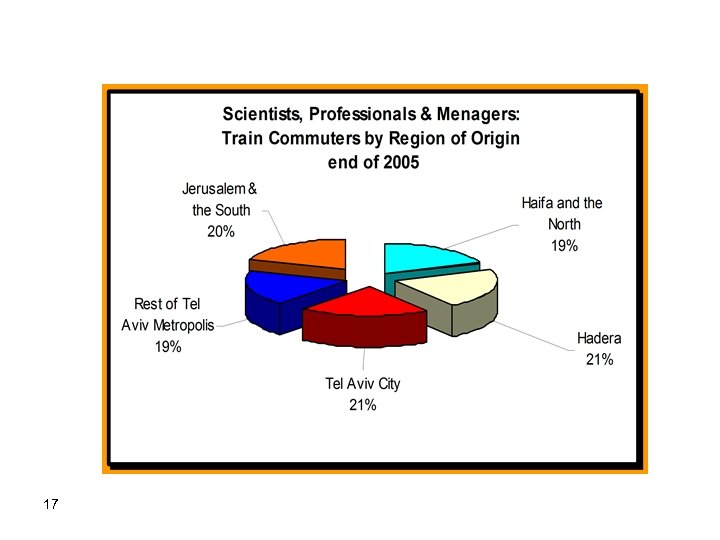
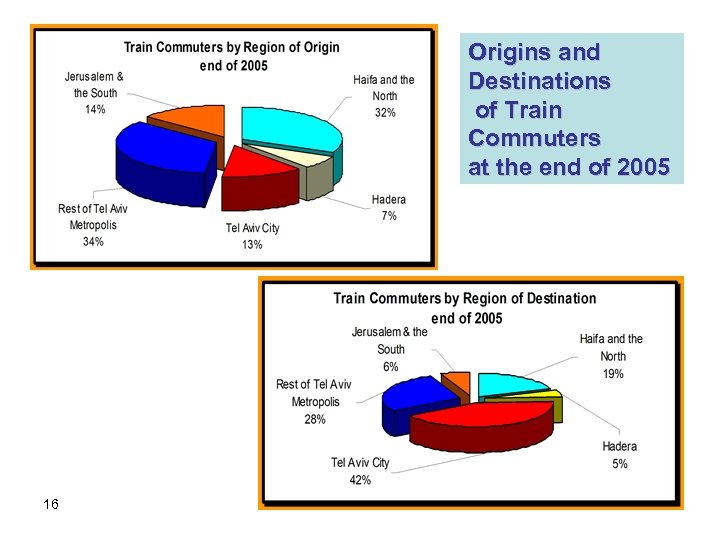 Origins and Destinations of Train Commuters at the end of 2005 16
Origins and Destinations of Train Commuters at the end of 2005 16
 17
17
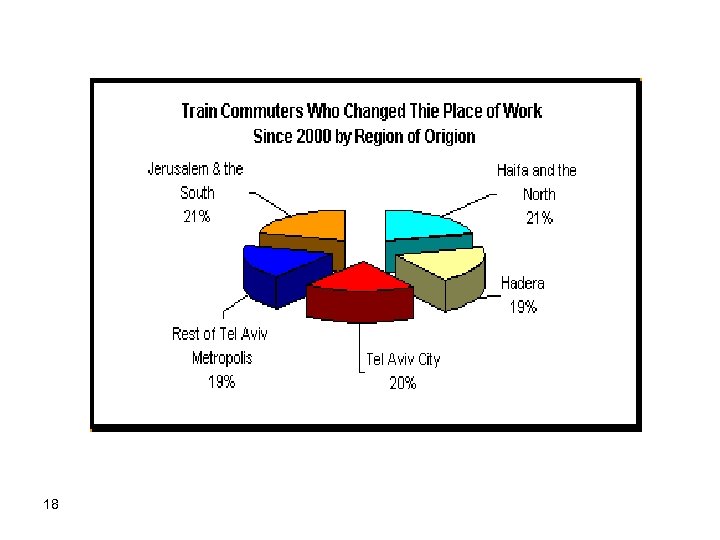 18
18
 Schematic layout for a City Dyads structure along Israel’s coast üExtended hinterlands- labor catchment areas of Tel Aviv and Haifa - - the anchors of a possible City Dyads structure of a World City üGreater Tel Aviv the hard core of Israel’s advanced labor market üFeeder bus stations and the rail line are the backbones of the City Dyads structure üGreater Haifa, is viewed as an ‘opportunity absorber’ anchor of the coastal ‘World City’ structure. üBeer Sheva, a second stage candidate 19
Schematic layout for a City Dyads structure along Israel’s coast üExtended hinterlands- labor catchment areas of Tel Aviv and Haifa - - the anchors of a possible City Dyads structure of a World City üGreater Tel Aviv the hard core of Israel’s advanced labor market üFeeder bus stations and the rail line are the backbones of the City Dyads structure üGreater Haifa, is viewed as an ‘opportunity absorber’ anchor of the coastal ‘World City’ structure. üBeer Sheva, a second stage candidate 19
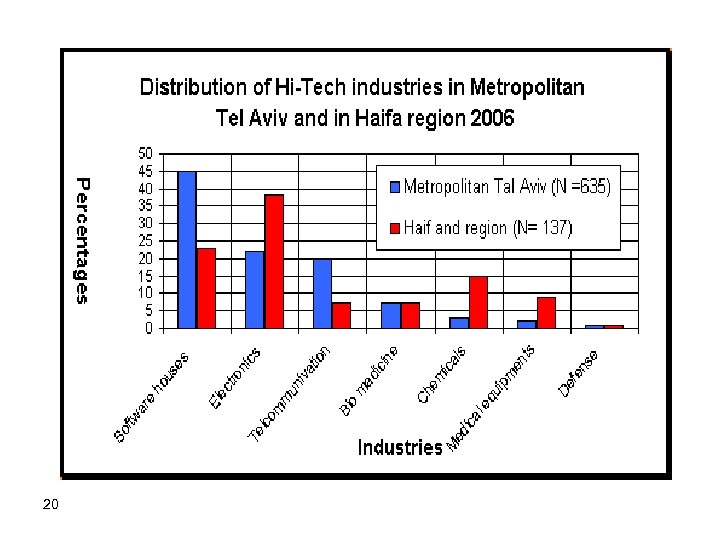 20
20
 The Inherent Potentials of Haifa to Evolve into a Second Anchor of Israel’s World City Recearch Centers Energy Academic Institutions Industry Hi-Tech 21 A Port Health Centers
The Inherent Potentials of Haifa to Evolve into a Second Anchor of Israel’s World City Recearch Centers Energy Academic Institutions Industry Hi-Tech 21 A Port Health Centers
 Thanks for your Attention 22
Thanks for your Attention 22


