d19ad991c66a874bb4ac7957cfcb231b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 PSSIG Scoping Session Chris Foye Information Architect National Patient Safety Agency, UK 28 th September 2004
PSSIG Scoping Session Chris Foye Information Architect National Patient Safety Agency, UK 28 th September 2004
 Overview • San Antonio – Revisit PSSIG’s scope – Decision tree • Ensure efficient working of PSSIG – Set priorities • Aim – Ensure paper is truly representative – Finalise paper
Overview • San Antonio – Revisit PSSIG’s scope – Decision tree • Ensure efficient working of PSSIG – Set priorities • Aim – Ensure paper is truly representative – Finalise paper
 Agenda • • Assumptions Patient safety / patient safety incident definitions Principles Vision statement / mission statement WHO’s International Patient Safety Alliance Reporting systems Prioritisation Decision tree
Agenda • • Assumptions Patient safety / patient safety incident definitions Principles Vision statement / mission statement WHO’s International Patient Safety Alliance Reporting systems Prioritisation Decision tree
 Assumptions Goal – improve patient safety Derive PS messages which have universal applicability. Financial, resourcing and time considerations out of scope No consistent view of patient safety and what constitutes a PSI Cannot operate disconnected from the realities of modern health care
Assumptions Goal – improve patient safety Derive PS messages which have universal applicability. Financial, resourcing and time considerations out of scope No consistent view of patient safety and what constitutes a PSI Cannot operate disconnected from the realities of modern health care
 Patient safety & patient safety incident definitions Patient safety: The processes by which an organisation reduces the risk and occurrence of harm to patients as a result of their healthcare Patient safety incident: Any unintended or unexpected incident(s) that could have or did lead to harm for one or more persons receiving healthcare services
Patient safety & patient safety incident definitions Patient safety: The processes by which an organisation reduces the risk and occurrence of harm to patients as a result of their healthcare Patient safety incident: Any unintended or unexpected incident(s) that could have or did lead to harm for one or more persons receiving healthcare services
 Principles • Provide context • Unearth assumptions about patient safety – Translate into modelling assumptions • Identify potential work streams – Activities – Prioritisation • Formulate vision statement – Mission statement – Scope
Principles • Provide context • Unearth assumptions about patient safety – Translate into modelling assumptions • Identify potential work streams – Activities – Prioritisation • Formulate vision statement – Mission statement – Scope
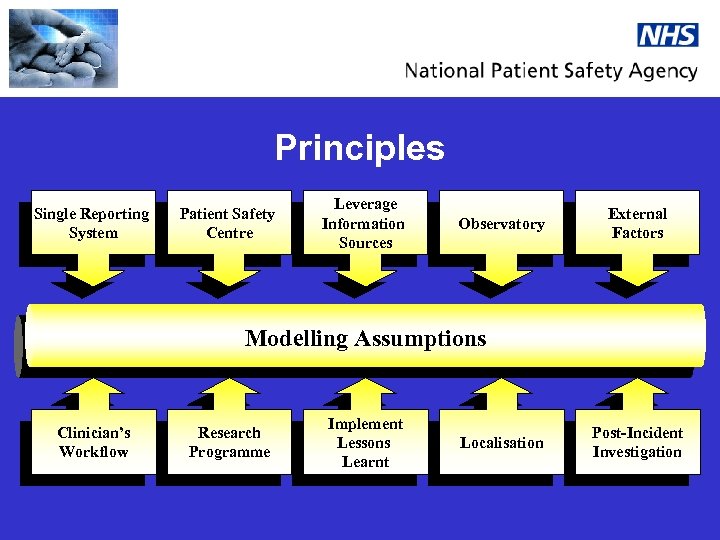 Principles Single Reporting System Patient Safety Centre Leverage Information Sources Observatory External Factors Modelling Assumptions Messaging Assumptions Clinician’s Workflow Research Programme Implement Lessons Learnt Localisation Post-Incident Investigation
Principles Single Reporting System Patient Safety Centre Leverage Information Sources Observatory External Factors Modelling Assumptions Messaging Assumptions Clinician’s Workflow Research Programme Implement Lessons Learnt Localisation Post-Incident Investigation
 Vision statement • Ensure patients receive the safest care possible • Encourage a systemic view • Establish a message model for capturing and transmitting PSI data • Ensure complementary information is directed to the appropriate organisations: – Aid understanding – Provide context – Assist in the analysis and identification of areas of concern. • Embed patient safety related clinical decision support systems to reduce overall system risk.
Vision statement • Ensure patients receive the safest care possible • Encourage a systemic view • Establish a message model for capturing and transmitting PSI data • Ensure complementary information is directed to the appropriate organisations: – Aid understanding – Provide context – Assist in the analysis and identification of areas of concern. • Embed patient safety related clinical decision support systems to reduce overall system risk.
 Mission statement • Standard message model for patient safety – Facilitate reporting and investigation • Work with other SIGs – Ensure messages do not adversely affect patient safety – Decision support mechanisms • Complementary information
Mission statement • Standard message model for patient safety – Facilitate reporting and investigation • Work with other SIGs – Ensure messages do not adversely affect patient safety – Decision support mechanisms • Complementary information
 WHO’s International Patient Safety Alliance • Recognise need for international representation • PSA recognises that “…no single player has the expertise, funding or research and delivery capabilities to tackle the full range of patient safety issues on a worldwide scale. An international alliance would provide a mechanism to decrease duplication of investment and activities. ” • PSSIG should work with the PSA to: – Raise awareness of the group’s activities – Disseminate key deliverables for review – Seek guidance – Ensure the needs of the international community are catered for
WHO’s International Patient Safety Alliance • Recognise need for international representation • PSA recognises that “…no single player has the expertise, funding or research and delivery capabilities to tackle the full range of patient safety issues on a worldwide scale. An international alliance would provide a mechanism to decrease duplication of investment and activities. ” • PSSIG should work with the PSA to: – Raise awareness of the group’s activities – Disseminate key deliverables for review – Seek guidance – Ensure the needs of the international community are catered for
 Reporting systems • Review of Central Returns Committee (ROCR) – Over 97 different requests for non-financial information. – “Year-on-year impact on the NHS of supplying nonfinancial data in 2000/2001 was an increase of 74 person years. ” • Unnecessary burden on frontline staff – Double entry – Information silos
Reporting systems • Review of Central Returns Committee (ROCR) – Over 97 different requests for non-financial information. – “Year-on-year impact on the NHS of supplying nonfinancial data in 2000/2001 was an increase of 74 person years. ” • Unnecessary burden on frontline staff – Double entry – Information silos
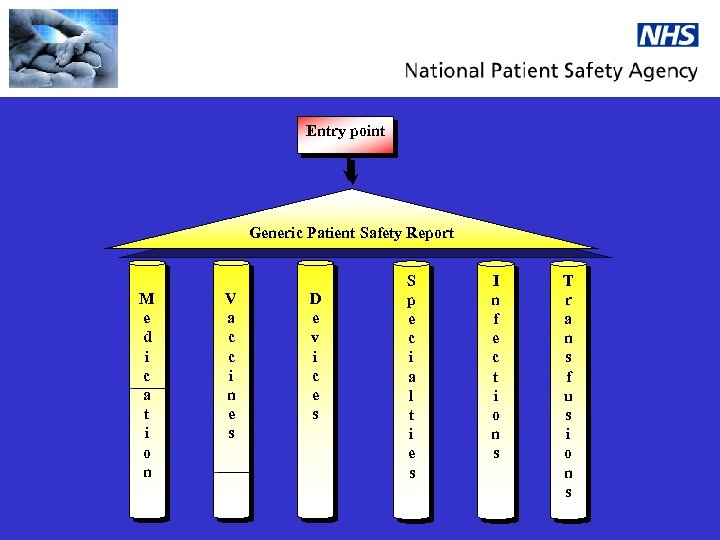 Entry point Generic Patient Safety Report M e d i c a t i o n V a c c i n e s D e v i c e s S p e c i a l t i e s I n f e c t i o n s T r a n s f u s i o n s
Entry point Generic Patient Safety Report M e d i c a t i o n V a c c i n e s D e v i c e s S p e c i a l t i e s I n f e c t i o n s T r a n s f u s i o n s
 Prioritisation 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Individual Case Safety Report Generic Patient Safety Report Sub-Domain Development Incident Investigation Decision Support Complementary Information
Prioritisation 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Individual Case Safety Report Generic Patient Safety Report Sub-Domain Development Incident Investigation Decision Support Complementary Information
 chris. foye@npsa. nhs. uk
chris. foye@npsa. nhs. uk


