20 Pseudomonas&Nonfermenters.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 44

 Pseudomonas and Nonfermenters
Pseudomonas and Nonfermenters
 General Overview Ø Opportunistic Pathogens of Plants, Animals, and Humans Ø Many Taxonomic Changes in Last Decade Ø Clinically Important Aerobic Gram-Negative Bacilli Include: • Aerobic nonfermenters: 10 -15% of clinical isolates ü Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Burkholderia cepacia; Stenotrophomonas maltophilia; Acinetobacter baumannii; Moraxella catarrhalis: Account for >75% of all clinical isolates of aerobic nonfermenters • Facultative anaerobes and microaerophiles: 70 -80% of clinical isolates • Haemophilus & related organisms: 10 -15% of clinical isolates • Unusual bacilli: <1% of clinical isolates Ø Pseudomonads Classified into Five r. RNA Groups
General Overview Ø Opportunistic Pathogens of Plants, Animals, and Humans Ø Many Taxonomic Changes in Last Decade Ø Clinically Important Aerobic Gram-Negative Bacilli Include: • Aerobic nonfermenters: 10 -15% of clinical isolates ü Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Burkholderia cepacia; Stenotrophomonas maltophilia; Acinetobacter baumannii; Moraxella catarrhalis: Account for >75% of all clinical isolates of aerobic nonfermenters • Facultative anaerobes and microaerophiles: 70 -80% of clinical isolates • Haemophilus & related organisms: 10 -15% of clinical isolates • Unusual bacilli: <1% of clinical isolates Ø Pseudomonads Classified into Five r. RNA Groups
 General Characteristics of Nonfermenters Ø Oxidative gram-negative bacilli, including Pseudomonas spp. , produce acid from glucose or other carbohydrates only in the presence of oxygen (nonfermenters). • NOTE: Enterobacteriaceae, Aeromonas and Vibrio are fermentative and can utilize carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. Ø Pseudomonas aeruginosa oxidizes but does not ferment glucose. Alcaligenes faecalis neither ferments nor oxidizes glucose (see Lab Manual).
General Characteristics of Nonfermenters Ø Oxidative gram-negative bacilli, including Pseudomonas spp. , produce acid from glucose or other carbohydrates only in the presence of oxygen (nonfermenters). • NOTE: Enterobacteriaceae, Aeromonas and Vibrio are fermentative and can utilize carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. Ø Pseudomonas aeruginosa oxidizes but does not ferment glucose. Alcaligenes faecalis neither ferments nor oxidizes glucose (see Lab Manual).
 Clinically Important Nonfermentative Gram-Negative Bacilli Lab only Later
Clinically Important Nonfermentative Gram-Negative Bacilli Lab only Later

 Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Family Pseudomonadaceae)
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Family Pseudomonadaceae)
 Characteristics of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Ø Ø Ø Motile (by single or multiple polar flagella) gram-negative rods Obligate (strict) aerobes (most strains) Oxidase (usually) and catalase positive Nonfermentative chemoheterotrophic respiratory metabolism Minimal nutritional reqts. ; Many organic compounds used as C and N sources, but only a few carbohydrates by oxidative metabolism • Glucose used oxidatively • Lactose negative on Mac. Conkey’s agar Ø Some strains produce diffusible pigments: • Pyocyanin (blue); fluorescein (yellow); pyorubin (red) Ø P. aeruginosa produces characteristic grape-like odor and blue-green pus & colonies Ø Broad antibiotic resistance
Characteristics of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Ø Ø Ø Motile (by single or multiple polar flagella) gram-negative rods Obligate (strict) aerobes (most strains) Oxidase (usually) and catalase positive Nonfermentative chemoheterotrophic respiratory metabolism Minimal nutritional reqts. ; Many organic compounds used as C and N sources, but only a few carbohydrates by oxidative metabolism • Glucose used oxidatively • Lactose negative on Mac. Conkey’s agar Ø Some strains produce diffusible pigments: • Pyocyanin (blue); fluorescein (yellow); pyorubin (red) Ø P. aeruginosa produces characteristic grape-like odor and blue-green pus & colonies Ø Broad antibiotic resistance
 Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections Survive where most organisms cannot; e. g. , “oil-eating” bacteria are Pseudomonas. (Slime layer)
Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections Survive where most organisms cannot; e. g. , “oil-eating” bacteria are Pseudomonas. (Slime layer)
 Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections (cont. ) Characteristic grape-like odor. Bluish-green color clinically and in the lab due to presence of two pigments: pyocyanin & fluorescein.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections (cont. ) Characteristic grape-like odor. Bluish-green color clinically and in the lab due to presence of two pigments: pyocyanin & fluorescein.
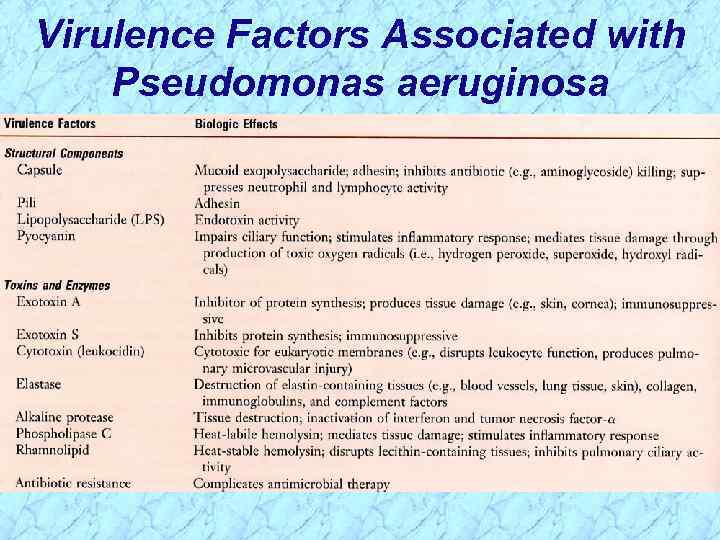 Virulence Factors Associated with Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Virulence Factors Associated with Pseudomonas aeruginosa
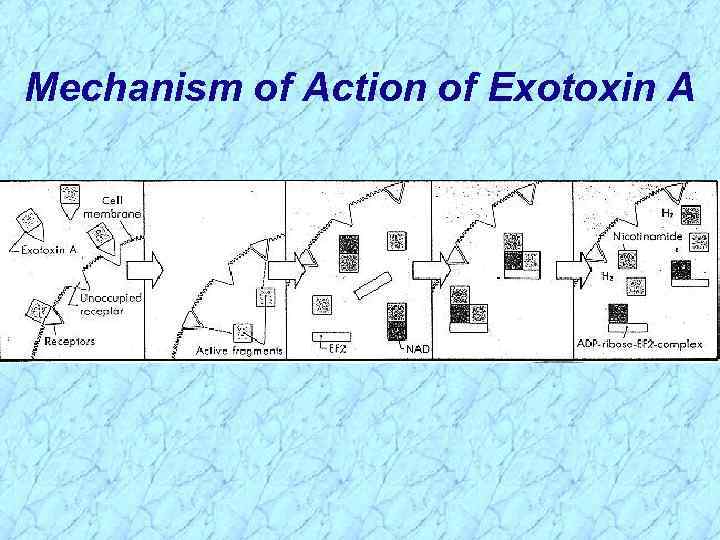 Mechanism of Action of Exotoxin A
Mechanism of Action of Exotoxin A
 Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa

 Burkholderia cepacia
Burkholderia cepacia
 Diseases Associated with Burkholderia spp.
Diseases Associated with Burkholderia spp.
 Stenotrophomonas maltophilia
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia
 Stenotrophomonas maltophilia
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia
 Stenotrophomonas maltophilia (cont. )
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia (cont. )
 Stenotrophomonas maltophilia (cont. )
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia (cont. )
 Acinetobacter baumanii
Acinetobacter baumanii
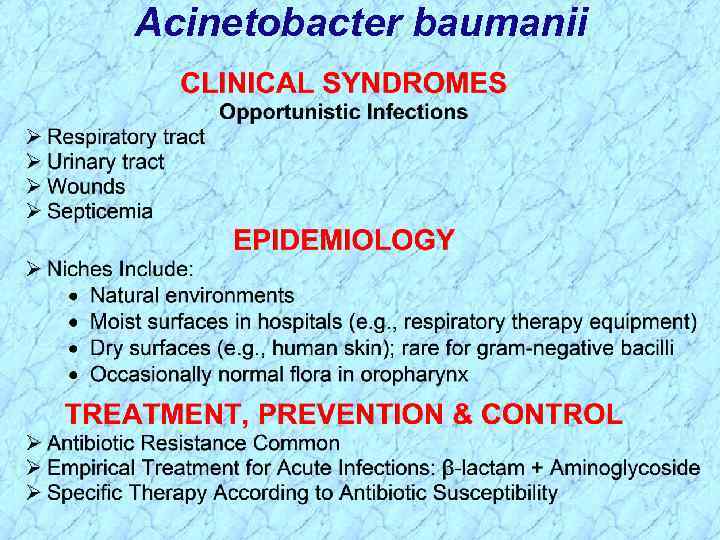 Acinetobacter baumanii
Acinetobacter baumanii
 Moraxella catarrhalis
Moraxella catarrhalis
 Moraxella catarrhalis
Moraxella catarrhalis

 REVIEW Pseudomonas and Nonfermenters
REVIEW Pseudomonas and Nonfermenters
 General Characteristics of Nonfermenters Ø Oxidative gram-negative bacilli, including Pseudomonas spp. , produce acid from glucose or other carbohydrates only in the presence of oxygen (nonfermenters). • NOTE: Enterobacteriaceae, Aeromonas and Vibrio are fermentative and can utilize carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. Ø Pseudomonas aeruginosa oxidizes but does not ferment glucose. Alcaligenes faecalis neither ferments nor oxidizes glucose (see Lab Manual). REVIEW
General Characteristics of Nonfermenters Ø Oxidative gram-negative bacilli, including Pseudomonas spp. , produce acid from glucose or other carbohydrates only in the presence of oxygen (nonfermenters). • NOTE: Enterobacteriaceae, Aeromonas and Vibrio are fermentative and can utilize carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. Ø Pseudomonas aeruginosa oxidizes but does not ferment glucose. Alcaligenes faecalis neither ferments nor oxidizes glucose (see Lab Manual). REVIEW
 Clinically Important Nonfermentative Gram-Negative Bacilli Lab only Later REVIEW
Clinically Important Nonfermentative Gram-Negative Bacilli Lab only Later REVIEW
 Review of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Family Pseudomonadaceae)
Review of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Family Pseudomonadaceae)
 Characteristics of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Ø Ø Ø Motile (by single or multiple polar flagella) gram-negative rods Obligate (strict) aerobes (most strains) Oxidase (usually) and catalase positive Nonfermentative chemoheterotrophic respiratory metabolism Minimal nutritional reqts. ; Many organic compounds used as C and N sources, but only a few carbohydrates by oxidative metabolism • Glucose used oxidatively • Lactose negative on Mac. Conkey’s agar Ø Some strains produce diffusible pigments: • Pyocyanin (blue); fluorescein (yellow); pyorubin (red) Ø P. aeruginosa produces characteristic grape-like odor and blue-green pus & colonies Ø Broad antibiotic resistance REVIEW
Characteristics of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Ø Ø Ø Motile (by single or multiple polar flagella) gram-negative rods Obligate (strict) aerobes (most strains) Oxidase (usually) and catalase positive Nonfermentative chemoheterotrophic respiratory metabolism Minimal nutritional reqts. ; Many organic compounds used as C and N sources, but only a few carbohydrates by oxidative metabolism • Glucose used oxidatively • Lactose negative on Mac. Conkey’s agar Ø Some strains produce diffusible pigments: • Pyocyanin (blue); fluorescein (yellow); pyorubin (red) Ø P. aeruginosa produces characteristic grape-like odor and blue-green pus & colonies Ø Broad antibiotic resistance REVIEW
 Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections Survive where most organisms cannot; e. g. , “oil-eating” bacteria are Pseudomonas. REVIEW (Slime layer)
Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections Survive where most organisms cannot; e. g. , “oil-eating” bacteria are Pseudomonas. REVIEW (Slime layer)
 Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections (cont. ) Characteristic grape-like odor. Bluish-green color clinically and in the lab due to presence of two pigments: pyocyanin & fluorescein. REVIEW
Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections (cont. ) Characteristic grape-like odor. Bluish-green color clinically and in the lab due to presence of two pigments: pyocyanin & fluorescein. REVIEW
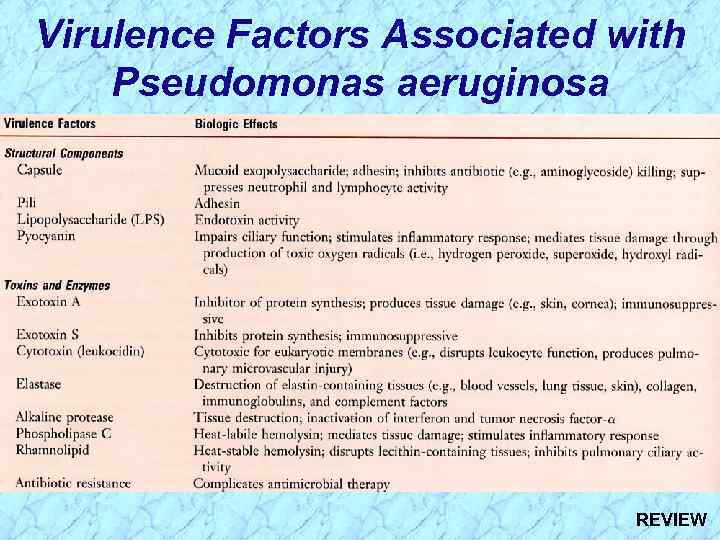 Virulence Factors Associated with Pseudomonas aeruginosa REVIEW
Virulence Factors Associated with Pseudomonas aeruginosa REVIEW
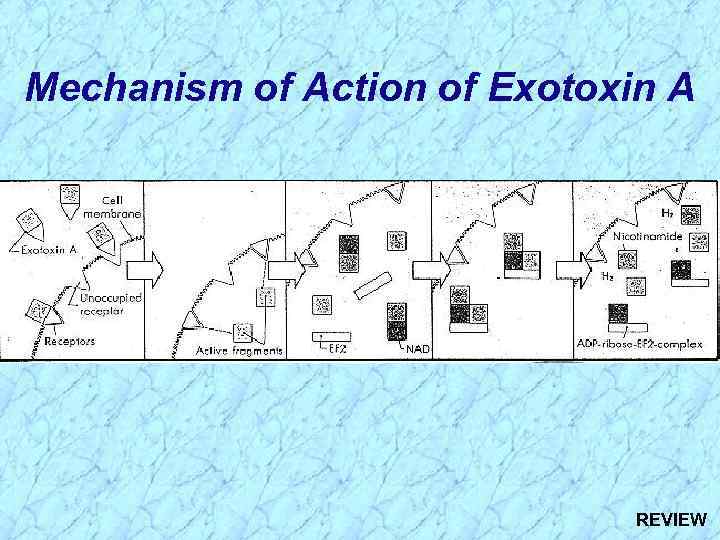 Mechanism of Action of Exotoxin A REVIEW
Mechanism of Action of Exotoxin A REVIEW
 Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa REVIEW
Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa REVIEW
 Review of Burkholderia cepacia
Review of Burkholderia cepacia
 Diseases Associated with Burkholderia spp. REVIEW
Diseases Associated with Burkholderia spp. REVIEW
 Review of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia
Review of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia
 Stenotrophomonas maltophilia (cont. ) REVIEW
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia (cont. ) REVIEW
 Review of Acinetobacter baumanii
Review of Acinetobacter baumanii
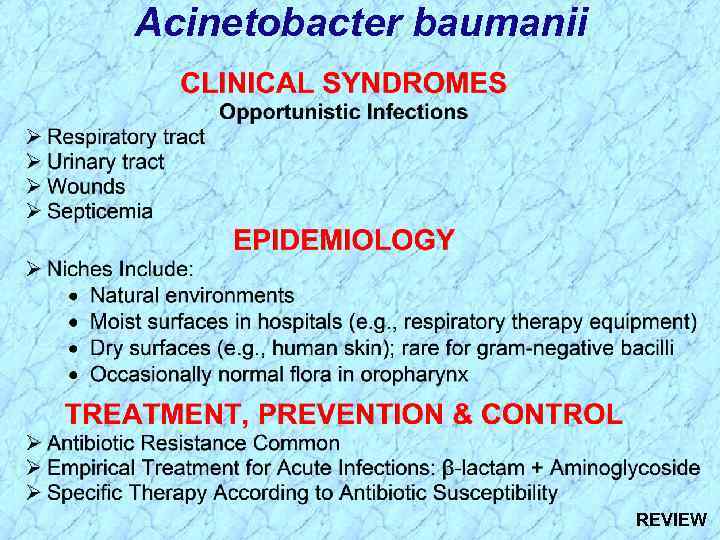 Acinetobacter baumanii REVIEW
Acinetobacter baumanii REVIEW
 Review of Moraxella catarrhalis
Review of Moraxella catarrhalis
 Moraxella catarrhalis REVIEW
Moraxella catarrhalis REVIEW



