 PS 134 AA: COMPARATIVE POLITICS OF LATIN AMERICA, or DEMOCRACY AND DEMOCRATIZATION IN LATIN AMERICA Spring 2011
PS 134 AA: COMPARATIVE POLITICS OF LATIN AMERICA, or DEMOCRACY AND DEMOCRATIZATION IN LATIN AMERICA Spring 2011
 Instructor: Peter H. Smith 364 Social Science Building phsmith@dss. ucsd. edu Office hours: Wednesday 11 -1 TA/Grader: Kathryn Dove 320 Social Science Building kdove@ucsd. edu Office hours: Wednesday 3: 30 -4: 30
Instructor: Peter H. Smith 364 Social Science Building phsmith@dss. ucsd. edu Office hours: Wednesday 11 -1 TA/Grader: Kathryn Dove 320 Social Science Building kdove@ucsd. edu Office hours: Wednesday 3: 30 -4: 30
 COURSE WEBSITE http: //weber. ucsd. edu/~phsmith/ps 134 aa. htm OR go to UCSD and then: Political Science Faculty Peter Smith Homepage Teaching PS 134 AA
COURSE WEBSITE http: //weber. ucsd. edu/~phsmith/ps 134 aa. htm OR go to UCSD and then: Political Science Faculty Peter Smith Homepage Teaching PS 134 AA
 REQUIRED READING • Peter H. Smith, Democracy in Latin America: Political Change in Comparative Perspective (2005) • Thomas E. Skidmore, Peter H. Smith, and James N. Green Modern Latin America, 7 th revised edition (2010) • Course Reader: – – www. universityreaders. com “STUDENTS BUY HERE” in “Student Store” Create an account of login Follow instructions
REQUIRED READING • Peter H. Smith, Democracy in Latin America: Political Change in Comparative Perspective (2005) • Thomas E. Skidmore, Peter H. Smith, and James N. Green Modern Latin America, 7 th revised edition (2010) • Course Reader: – – www. universityreaders. com “STUDENTS BUY HERE” in “Student Store” Create an account of login Follow instructions
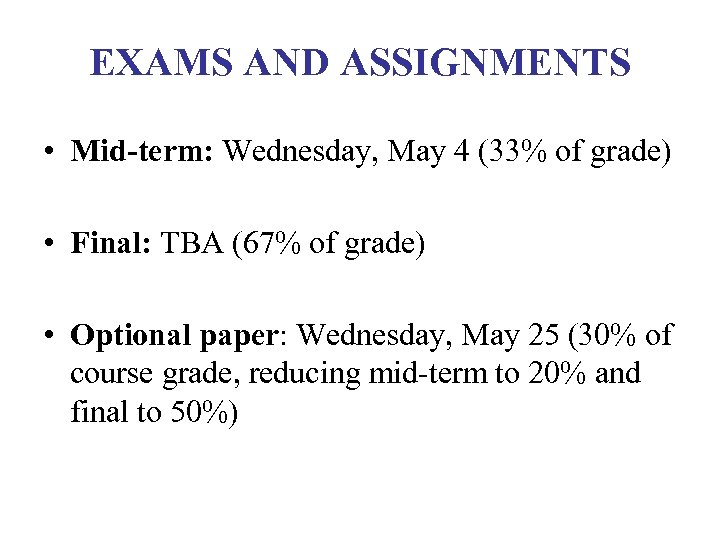 EXAMS AND ASSIGNMENTS • Mid-term: Wednesday, May 4 (33% of grade) • Final: TBA (67% of grade) • Optional paper: Wednesday, May 25 (30% of course grade, reducing mid-term to 20% and final to 50%)
EXAMS AND ASSIGNMENTS • Mid-term: Wednesday, May 4 (33% of grade) • Final: TBA (67% of grade) • Optional paper: Wednesday, May 25 (30% of course grade, reducing mid-term to 20% and final to 50%)
 KEY QUESTIONS • What explains the spread of democracy in Latin America? Given authoritarian past? • What kind of democracy? What quality? • What’s new about the current phase of democratic change? How does it compare to prior periods? • What role (if any) for the United States? • What implications for U. S. relations with Latin America?
KEY QUESTIONS • What explains the spread of democracy in Latin America? Given authoritarian past? • What kind of democracy? What quality? • What’s new about the current phase of democratic change? How does it compare to prior periods? • What role (if any) for the United States? • What implications for U. S. relations with Latin America?
 COURSE SCHEDULE • • Mar 30: Introduction Apr 06: Cycles and Transitions Apr 13: Changing Roles of the Military Apr 20: Presidentialism, Parties, and Legislatures • Apr 27: Economic Policies and Governmental Performance
COURSE SCHEDULE • • Mar 30: Introduction Apr 06: Cycles and Transitions Apr 13: Changing Roles of the Military Apr 20: Presidentialism, Parties, and Legislatures • Apr 27: Economic Policies and Governmental Performance
 SCHEDULE (cont. ) • May 04: MIDTERM • May 11: Liberal and Illiberal Democracy/ Social Class and Satisfaction • May 18: Politics of Gender • May 25: The Rise of the New Left • June 01: What Now? Democracy and U. S. Latin American Relations
SCHEDULE (cont. ) • May 04: MIDTERM • May 11: Liberal and Illiberal Democracy/ Social Class and Satisfaction • May 18: Politics of Gender • May 25: The Rise of the New Left • June 01: What Now? Democracy and U. S. Latin American Relations
 ELECTORAL REGIMES • Democratic = free and fair • Semi-democratic = free but not fair • Oligarchic = fair but not free • Nondemocratic = Nonexistent or openly fraudulent
ELECTORAL REGIMES • Democratic = free and fair • Semi-democratic = free but not fair • Oligarchic = fair but not free • Nondemocratic = Nonexistent or openly fraudulent
 NONDEMOCRATIC TRADITIONS Types of Authoritarian Regime Leadership ________________Power Structure__________ Personalist Institutionalized ___________________ Military Traditional Caudillo or “Man on Horseback” Civilian Technocratic State or Sultanistic Despotism Collective Junta or Bureaucratic-Authoritarian Regime One-Party State or Corporatist Regime
NONDEMOCRATIC TRADITIONS Types of Authoritarian Regime Leadership ________________Power Structure__________ Personalist Institutionalized ___________________ Military Traditional Caudillo or “Man on Horseback” Civilian Technocratic State or Sultanistic Despotism Collective Junta or Bureaucratic-Authoritarian Regime One-Party State or Corporatist Regime
 FRIENDLY ADMONITIONS • 1. Try to put yourself in the place of a Latin American citizen, • 2. Imagine how the world feels, not only how it looks, • 3. View course material as relevant to political change in other regions and parts of the world, • 4. Take videos seriously, and • 5. Have fun!
FRIENDLY ADMONITIONS • 1. Try to put yourself in the place of a Latin American citizen, • 2. Imagine how the world feels, not only how it looks, • 3. View course material as relevant to political change in other regions and parts of the world, • 4. Take videos seriously, and • 5. Have fun!