998d906a0ba0a3fef4aab16e42fe49b9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 53

PS 1 PSPS Object Data Manager Design PSPS Critical Design Review November 5 -6, 2007 If. A

Outline § § § § § slide 2 ODM Overview Critical Requirements Driving Design Work Completed Detailed Design Spatial Querying [AS] ODM Prototype [MN] Hardware/Scalability [JV] How Design Meets Requirements WBS and Schedule Issues/Risks [AS] = Alex, [MN] = Maria, [JV] = Jan

ODM Overview The Object Data Manager will: § Provide a scalable data archive for the Pan. STARRS data products § Provide query access to the data for Pan-STARRS users § Provide detailed usage tracking and logging slide 3

ODM Driving Requirements § Total size 100 TB, • 1. 5 x 1011 P 2 detections • 8. 3 x 1010 P 2 cumulative-sky (stack) detections • 5. 5 x 109 celestial objects § Nominal daily rate (divide by 3. 5 x 365) • P 2 detections: 120 Million/day • Stack detections: 65 Million/day • Objects: 4. 3 Million/day § Cross-Match requirement: 120 Million / 12 hrs ~ 2800 / s § DB size requirement: • 25 TB / yr • ~100 TB by of PS 1 (3. 5 yrs) slide 4

Work completed so far § Built a prototype § Scoped and built prototype hardware § Generated simulated data • 300 M SDSS DR 5 objects, 1. 5 B Galactic plane objects § Initial Load done – Created 15 TB DB of simulated data • Largest astronomical DB in existence today § Partitioned the data correctly using Zones algorithm § Able to run simple queries on distributed DB § Demonstrated critical steps of incremental loading § It is fast enough • Cross-match > 60 k detections/sec • Required rate is ~3 k/sec slide 5
Detailed Design § § Reuse SDSS software as much as possible Data Transformation Layer (DX) – Interface to IPP Data Loading Pipeline (DLP) Data Storage (DS) • Schema and Test Queries • Database Management System • Scalable Data Architecture • Hardware § Query Manager (QM: Cas. Jobs for prototype) slide 6
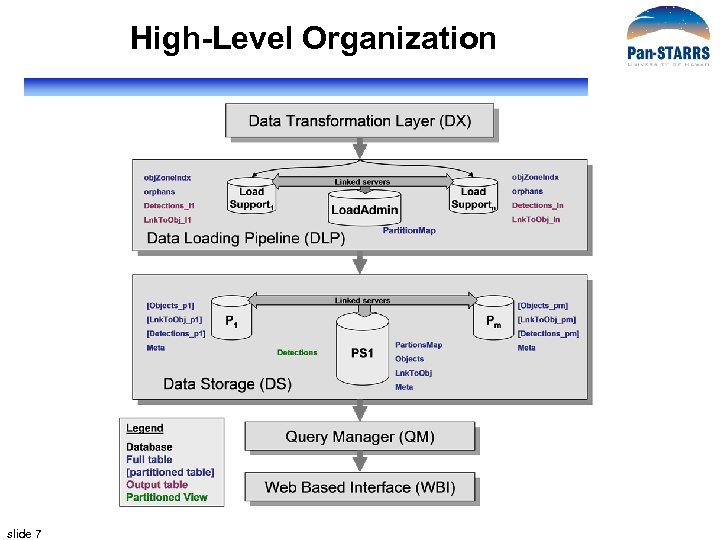
High-Level Organization slide 7
Detailed Design § § Reuse SDSS software as much as possible Data Transformation Layer (DX) – Interface to IPP Data Loading Pipeline (DLP) Data Storage (DS) • Schema and Test Queries • Database Management System • Scalable Data Architecture • Hardware § Query Manager (QM: Cas. Jobs for prototype) slide 8
Data Transformation Layer (DX) § Based on SDSS sql. Fits 2 CSV package • LINUX/C++ application • FITS reader driven off header files § Convert IPP FITS files to • ASCII CSV format for ingest (initially) • SQL Server native binary later (3 x faster) § Follow the batch and ingest verification procedure described in ICD • 4 -step batch verification • Notification and handling of broken publication cycle § Deposit CSV or Binary input files in directory structure • Create “ready” file in each batch directory § Stage input data on LINUX side as it comes in from IPP slide 9
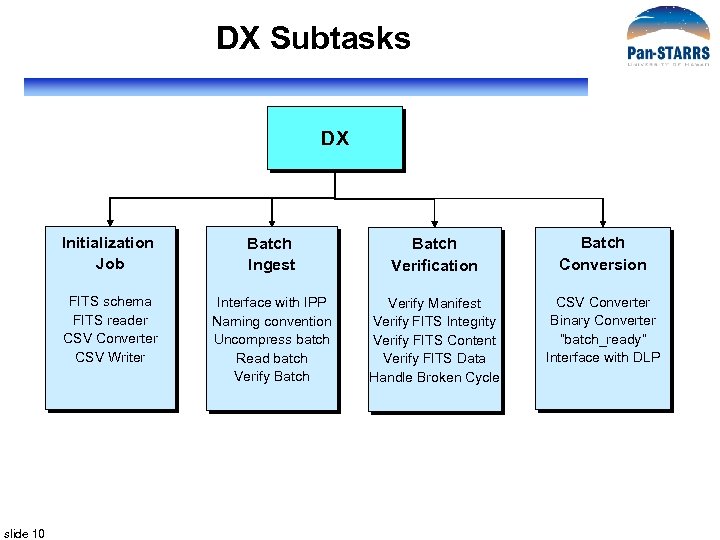
DX Subtasks DX Initialization Job Batch Verification Batch Conversion FITS schema FITS reader CSV Converter CSV Writer slide 10 Batch Ingest Interface with IPP Naming convention Uncompress batch Read batch Verify Batch Verify Manifest Verify FITS Integrity Verify FITS Content Verify FITS Data Handle Broken Cycle CSV Converter Binary Converter “batch_ready” Interface with DLP
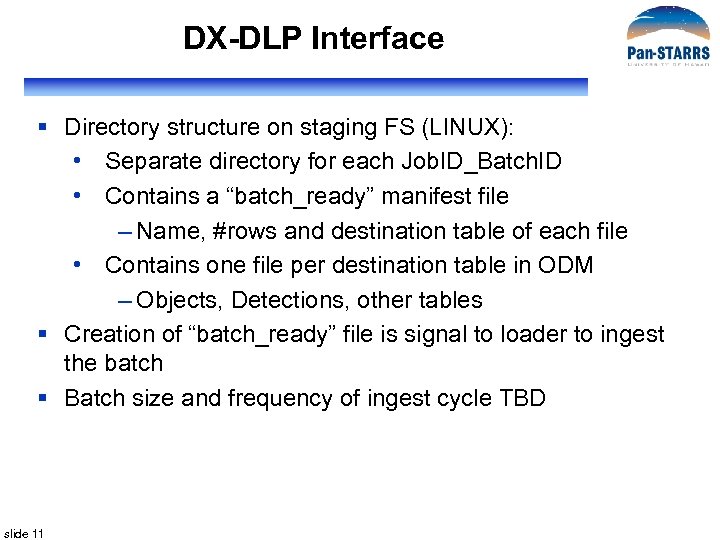
DX-DLP Interface § Directory structure on staging FS (LINUX): • Separate directory for each Job. ID_Batch. ID • Contains a “batch_ready” manifest file – Name, #rows and destination table of each file • Contains one file per destination table in ODM – Objects, Detections, other tables § Creation of “batch_ready” file is signal to loader to ingest the batch § Batch size and frequency of ingest cycle TBD slide 11
Detailed Design § § Reuse SDSS software as much as possible Data Transformation Layer (DX) – Interface to IPP Data Loading Pipeline (DLP) Data Storage (DS) • Schema and Test Queries • Database Management System • Scalable Data Architecture • Hardware § Query Manager (QM: Cas. Jobs for prototype) slide 12
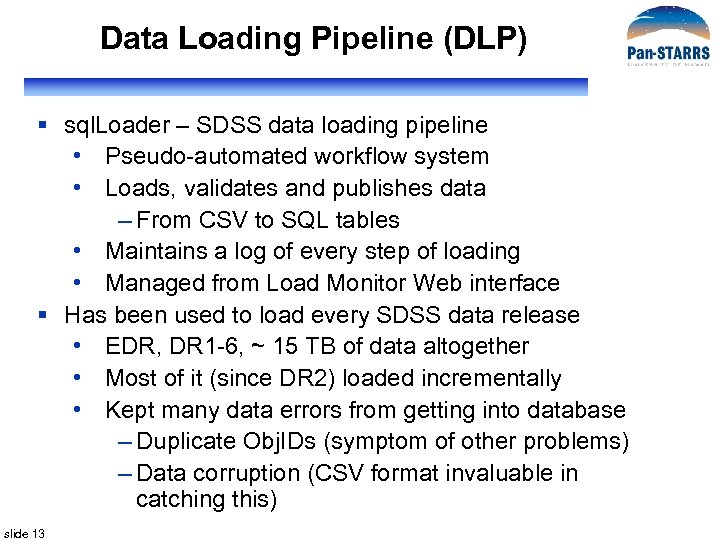
Data Loading Pipeline (DLP) § sql. Loader – SDSS data loading pipeline • Pseudo-automated workflow system • Loads, validates and publishes data – From CSV to SQL tables • Maintains a log of every step of loading • Managed from Load Monitor Web interface § Has been used to load every SDSS data release • EDR, DR 1 -6, ~ 15 TB of data altogether • Most of it (since DR 2) loaded incrementally • Kept many data errors from getting into database – Duplicate Obj. IDs (symptom of other problems) – Data corruption (CSV format invaluable in catching this) slide 13

sql. Loader Design § Existing functionality • Shown for SDSS version • Workflow, distributed loading, Load Monitor § New functionality • Schema changes • Workflow changes • Incremental loading – Cross-match and partitioning slide 14
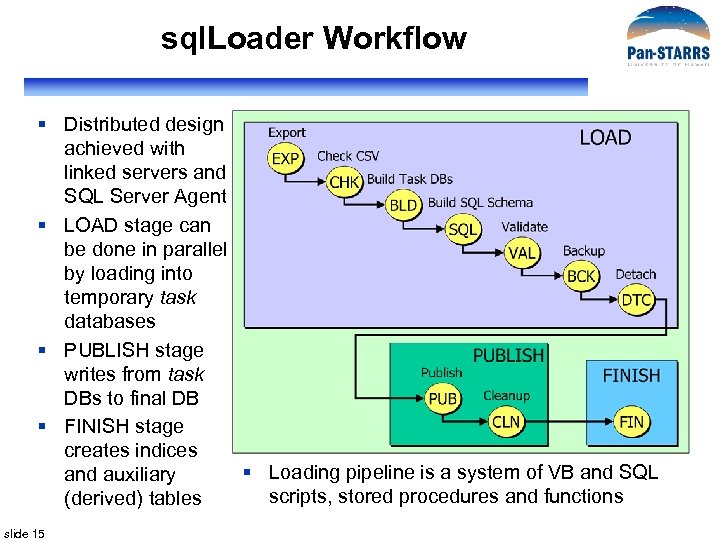
sql. Loader Workflow § Distributed design achieved with linked servers and SQL Server Agent § LOAD stage can be done in parallel by loading into temporary task databases § PUBLISH stage writes from task DBs to final DB § FINISH stage creates indices § Loading pipeline is a system of VB and SQL and auxiliary scripts, stored procedures and functions (derived) tables slide 15
Load Monitor Tasks Page slide 16
Load Monitor Active Tasks slide 17
Load Monitor Statistics Page slide 18
Load Monitor – New Task(s) slide 19
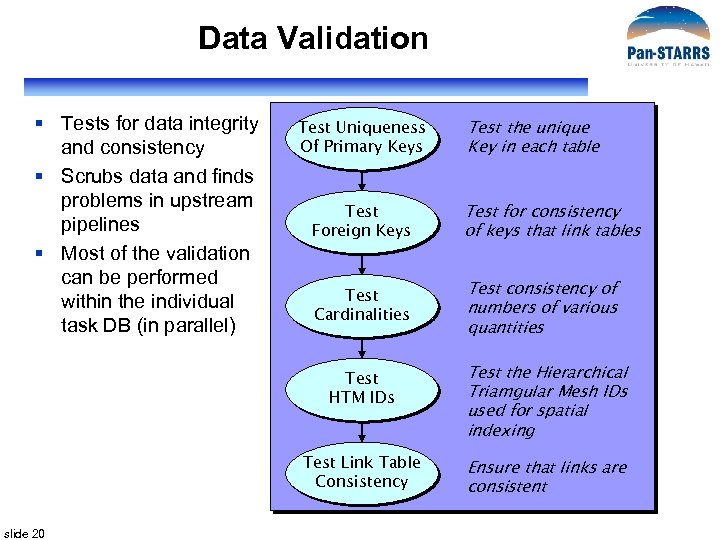
Data Validation § Tests for data integrity and consistency § Scrubs data and finds problems in upstream pipelines § Most of the validation can be performed within the individual task DB (in parallel) Test Uniqueness Of Primary Keys Test the unique Key in each table Test Foreign Keys Test for consistency of keys that link tables Test Cardinalities Test consistency of numbers of various quantities Test HTM IDs Test Link Table Consistency slide 20 Test the Hierarchical Triamgular Mesh IDs used for spatial indexing Ensure that links are consistent
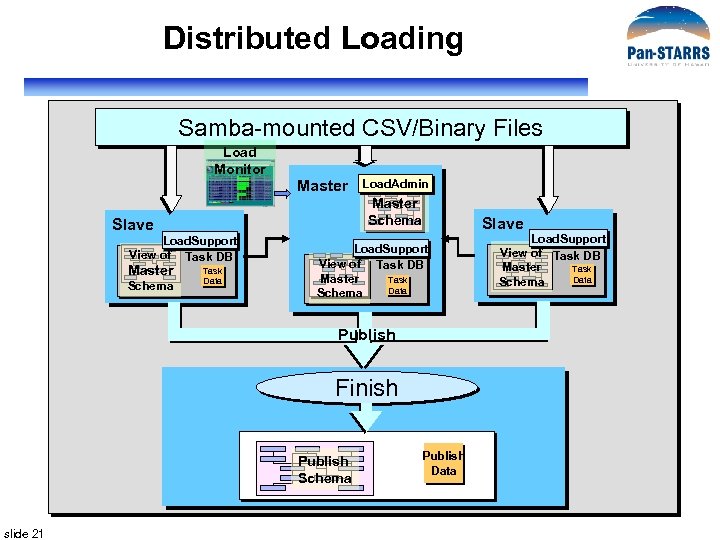
Distributed Loading Samba-mounted CSV/Binary Files Load Monitor Master Schema Slave Load. Support View of Task DB Master Schema Load. Admin Task Data Slave Load. Support View of Task DB Master Task Data Schema Publish Finish Publish Schema slide 21 Publish Data Load. Support View of Task DB Master Task Data Schema
Schema Changes § Schema in task and publish DBs is driven off a list of schema DDL files to execute (xschema. txt) § Requires replacing DDL files in schema/sql directory and updating xschema. txt with their names § PS 1 schema DDL files have already been built § Index definitions have also been created § Metadata tables will be automatically generated using metadata scripts already in the loader slide 22
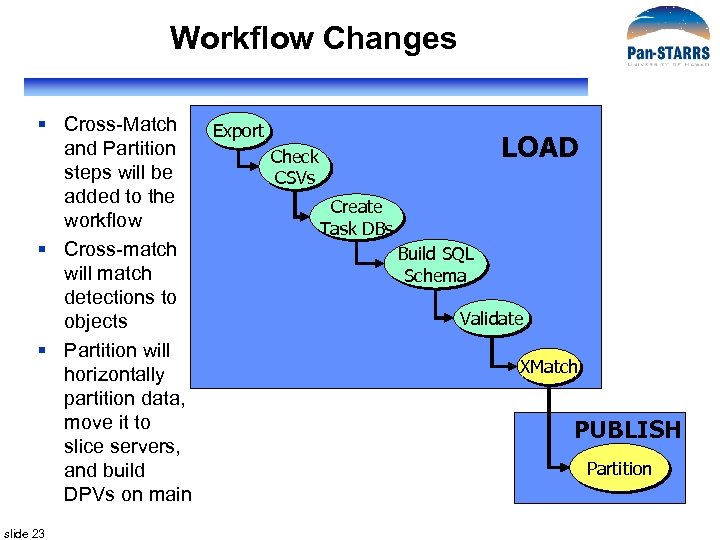
Workflow Changes § Cross-Match and Partition steps will be added to the workflow § Cross-match will match detections to objects § Partition will horizontally partition data, move it to slice servers, and build DPVs on main slide 23 Export LOAD Check CSVs Create Task DBs Build SQL Schema Validate XMatch PUBLISH Partition
Matching Detections with Objects § Algorithm described fully in prototype section § Stored procedures to cross-match detections will be part of the LOAD stage in loader pipeline § Vertical partition of Objects table kept on load server for matching with detections § Zones cross-match algorithm used to do 1” and 2” matches § Detections with no matches saved in Orphans table slide 24
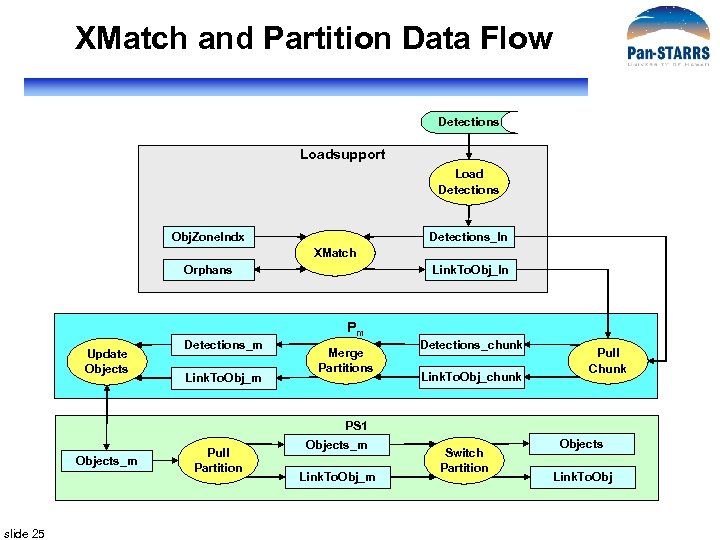
XMatch and Partition Data Flow Detections Loadsupport Load Detections Obj. Zone. Indx Detections_In XMatch Orphans Update Objects Detections_m Link. To. Obj_In Pm Merge Partitions Detections_chunk Link. To. Obj_chunk Pull Chunk PS 1 Objects_m slide 25 Pull Partition Objects_m Link. To. Obj_m Switch Partition Objects Link. To. Obj
Detailed Design § § Reuse SDSS software as much as possible Data Transformation Layer (DX) – Interface to IPP Data Loading Pipeline (DLP) Data Storage (DS) • Schema and Test Queries • Database Management System • Scalable Data Architecture • Hardware § Query Manager (QM: Cas. Jobs for prototype) slide 26
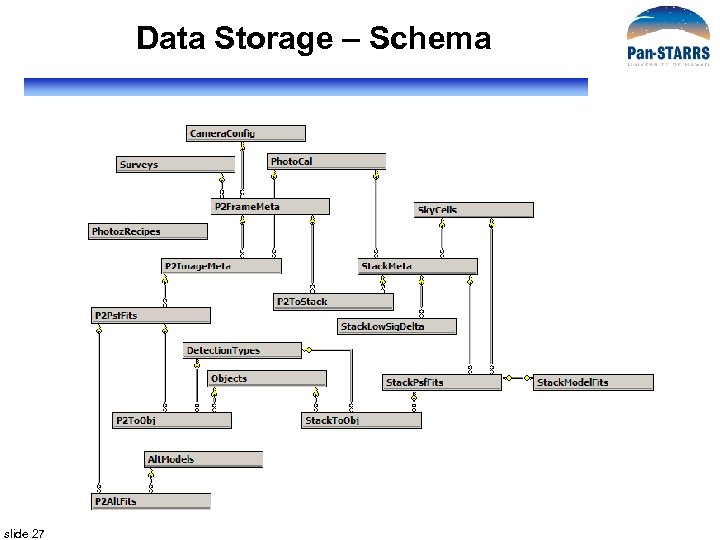
Data Storage – Schema slide 27
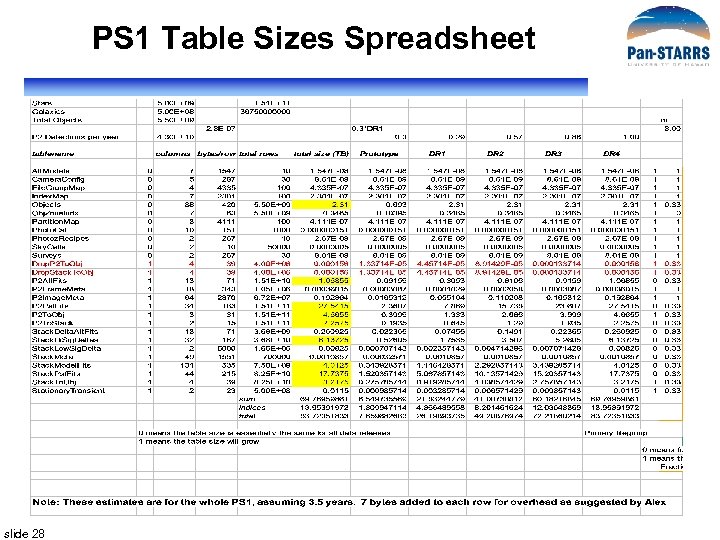
PS 1 Table Sizes Spreadsheet slide 28
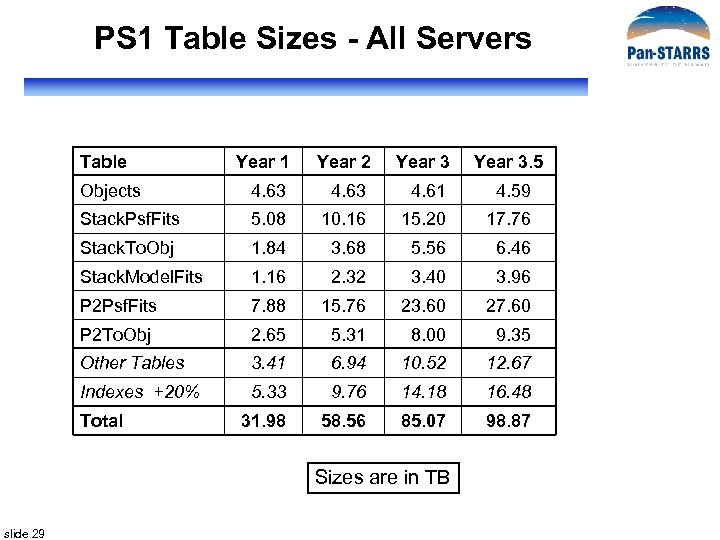
PS 1 Table Sizes - All Servers Table Year 1 Year 2 Year 3. 5 Objects 4. 63 4. 61 4. 59 Stack. Psf. Fits 5. 08 10. 16 15. 20 17. 76 Stack. To. Obj 1. 84 3. 68 5. 56 6. 46 Stack. Model. Fits 1. 16 2. 32 3. 40 3. 96 P 2 Psf. Fits 7. 88 15. 76 23. 60 27. 60 P 2 To. Obj 2. 65 5. 31 8. 00 9. 35 Other Tables 3. 41 6. 94 10. 52 12. 67 Indexes +20% 5. 33 9. 76 14. 18 16. 48 31. 98 58. 56 85. 07 98. 87 Total Sizes are in TB slide 29
Data Storage – Test Queries § Drawn from several sources • Initial set of SDSS 20 queries • SDSS Sky. Server Sample Queries • Queries from PS scientists (Monet, Howell, Kaiser, Heasley) § Two objectives • Find potential holes/issues in schema • Serve as test queries – Test DBMS iintegrity – Test DBMS performance § Loaded into Cas. Jobs (Query Manager) as sample queries for prototype slide 30
Data Storage – DBMS § Microsoft SQL Server 2005 • Relational DBMS with excellent query optimizer § Plus • Spherical/HTM (C# library + SQL glue) – Spatial index (Hierarchical Triangular Mesh) • Zones (SQL library) – Alternate spatial decomposition with dec zones • Many stored procedures and functions – From coordinate conversions to neighbor search functions • Self-extracting documentation (metadata) and diagnostics slide 31
Documentation and Diagnostics slide 32
Data Storage – Scalable Architecture § Monolithic database design (a la SDSS) will not do it § SQL Server does not have cluster implementation • Do it by hand § Partitions vs Slices • Partitions are file-groups on the same server – Parallelize disk accesses on the same machine • Slices are data partitions on separate servers • We use both! § Additional slices can be added for scale-out § For PS 1, use SQL Server Distributed Partition Views (DPVs) slide 33
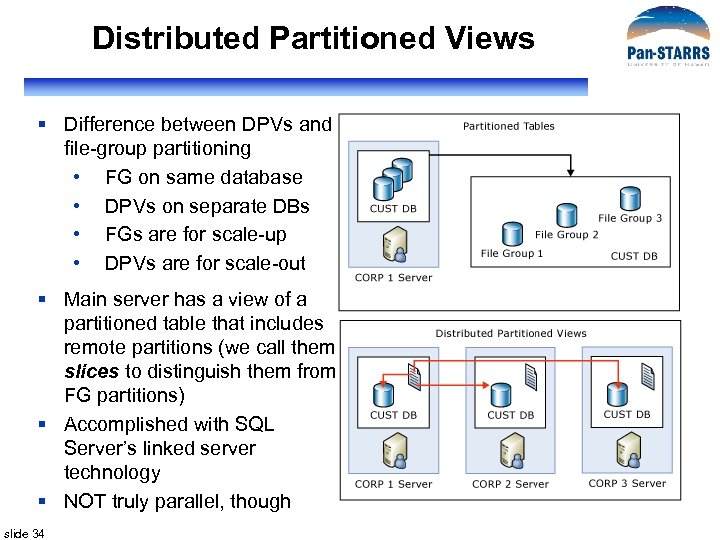
Distributed Partitioned Views § Difference between DPVs and file-group partitioning • FG on same database • DPVs on separate DBs • FGs are for scale-up • DPVs are for scale-out § Main server has a view of a partitioned table that includes remote partitions (we call them slices to distinguish them from FG partitions) § Accomplished with SQL Server’s linked server technology § NOT truly parallel, though slide 34
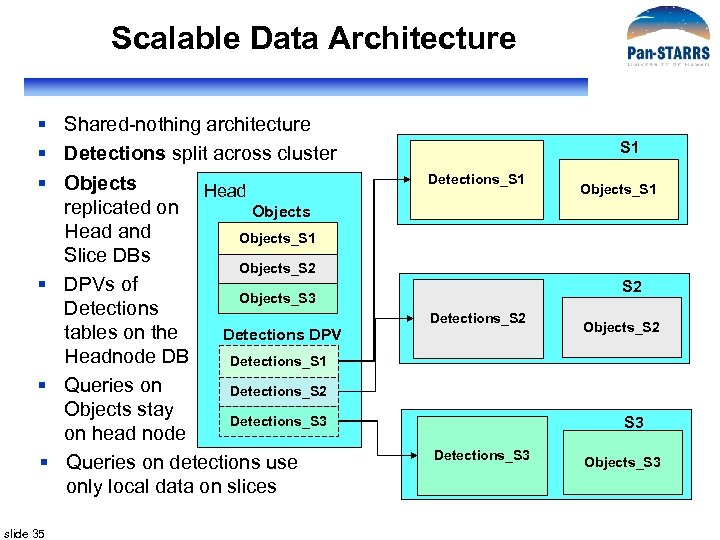
Scalable Data Architecture § Shared-nothing architecture § Detections split across cluster § Objects Head replicated on Objects Head and Objects_S 1 Slice DBs Objects_S 2 § DPVs of Objects_S 3 Detections tables on the Detections DPV Headnode DB Detections_S 1 § Queries on Detections_S 2 Objects stay Detections_S 3 on head node § Queries on detections use only local data on slices slide 35 S 1 Detections_S 1 Objects_S 1 S 2 Detections_S 2 Objects_S 2 S 3 Detections_S 3 Objects_S 3
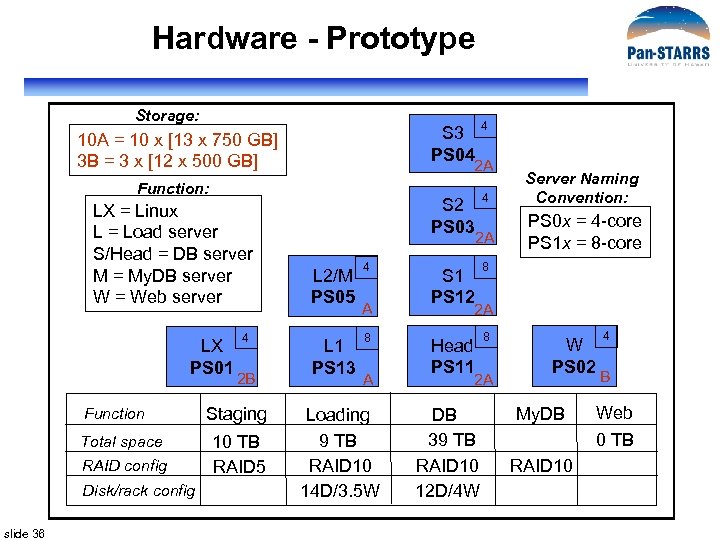
Hardware - Prototype Storage: S 3 PS 04 10 A = 10 x [13 x 750 GB] 3 B = 3 x [12 x 500 GB] 2 A Function: LX = Linux L = Load server S/Head = DB server M = My. DB server W = Web server LX PS 01 Function Total space RAID config Disk/rack config slide 36 4 2 B Staging 10 TB RAID 5 4 S 2 PS 03 4 S 1 PS 12 8 Head PS 11 8 2 A L 2/M PS 05 L 1 PS 13 4 A 8 A Loading 9 TB RAID 10 14 D/3. 5 W Server Naming Convention: PS 0 x = 4 -core PS 1 x = 8 -core 2 A 2 A DB 39 TB RAID 10 12 D/4 W W PS 02 My. DB 4 B Web 0 TB RAID 10
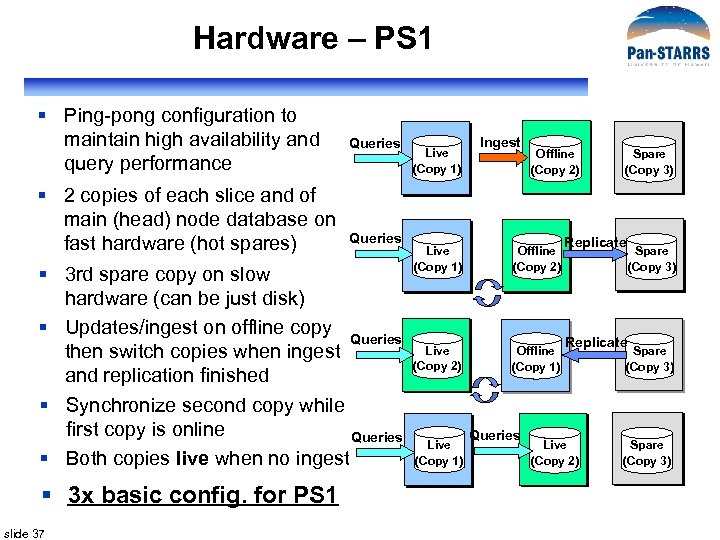
Hardware – PS 1 § Ping-pong configuration to maintain high availability and query performance § 2 copies of each slice and of main (head) node database on fast hardware (hot spares) Queries § 3 rd spare copy on slow hardware (can be just disk) § Updates/ingest on offline copy Queries then switch copies when ingest and replication finished § Synchronize second copy while first copy is online Queries § Both copies live when no ingest § 3 x basic config. for PS 1 slide 37 Live (Copy 1) Ingest Offline (Copy 2) Live (Copy 1) Offline (Copy 2) Live (Copy 2) Offline (Copy 1) Live (Copy 1) Queries Spare (Copy 3) Replicate Live (Copy 2) Spare (Copy 3)
Detailed Design § § Reuse SDSS software as much as possible Data Transformation Layer (DX) – Interface to IPP Data Loading Pipeline (DLP) Data Storage (DS) • Schema and Test Queries • Database Management System • Scalable Data Architecture • Hardware § Query Manager (QM: Cas. Jobs for prototype) slide 38
Query Manager § Based on SDSS Cas. Jobs § Configure to work with distributed database, DPVs § Direct links (contexts) to slices can be added later if necessary § Segregates quick queries from long ones § Saves query results server-side in My. DB § Gives users a powerful query workbench § Can be scaled out to meet any query load § PS 1 Sample Queries available to users § PS 1 Prototype QM demo slide 39
ODM Prototype Components § Data Loading Pipeline § Data Storage § Cas. Jobs • Query Manager (QM) • Web Based Interface (WBI) § Testing slide 40
Spatial Queries (Alex) slide 41

Prototype (Maria) slide 42
Hardware/Scalability (Jan) slide 43

How Design Meets Requirements § Cross-matching detections with objects • Zone cross-match part of loading pipeline • Already exceeded requirement with prototype § Query performance • Ping-pong configuration for query during ingest • Spatial indexing and distributed queries • Query manager can be scaled out as necessary § Scalability • Shared-nothing architecture • Scale out as needed • Beyond PS 1 we will need truly parallel query plans slide 44
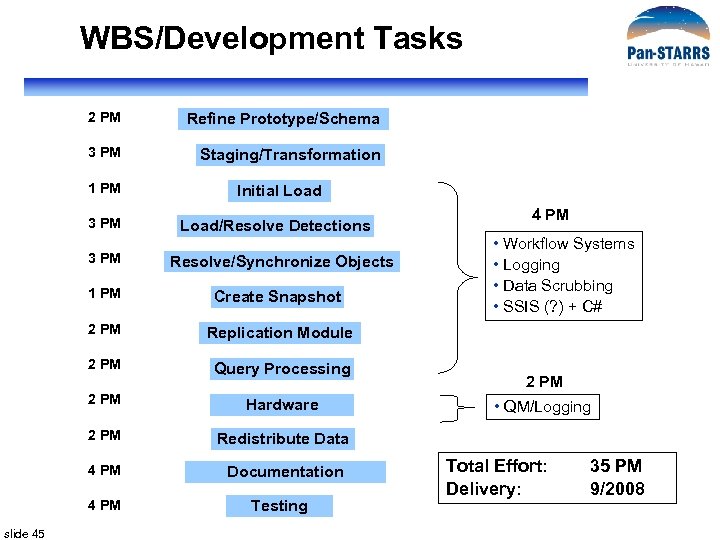
WBS/Development Tasks 2 PM Refine Prototype/Schema 3 PM Staging/Transformation 1 PM Initial Load 3 PM Load/Resolve Detections 3 PM Resolve/Synchronize Objects 1 PM Create Snapshot 2 PM Query Processing 2 PM Hardware 2 PM Documentation 2 PM Redistribute Data 4 PM slide 45 • Workflow Systems • Logging • Data Scrubbing • SSIS (? ) + C# Replication Module 2 PM 4 PM Testing • QM/Logging Total Effort: Delivery: 35 PM 9/2008

Personnel Available § § § § § slide 46 2 new hires (SW Engineers) 100% Maria 80% Ani 20% Jan 10% Alainna 15% Nolan Li 25% Sam Carliles 25% George Fekete 5% Laszlo Dobos 50% (for 6 months)

Issues/Risks § Versioning • Do we need to preserve snapshots of monthly versions? • How will users reproduce queries on subsequent versions? • Is it ok that a new version of the sky replaces the previous one every month? § Backup/recovery • Will we need 3 local copies rather than 2 for safety • Is restoring from offsite copy feasible? § Handoff to If. A beyond scope of WBS shown • This will involve several PMs slide 47

Mahalo!
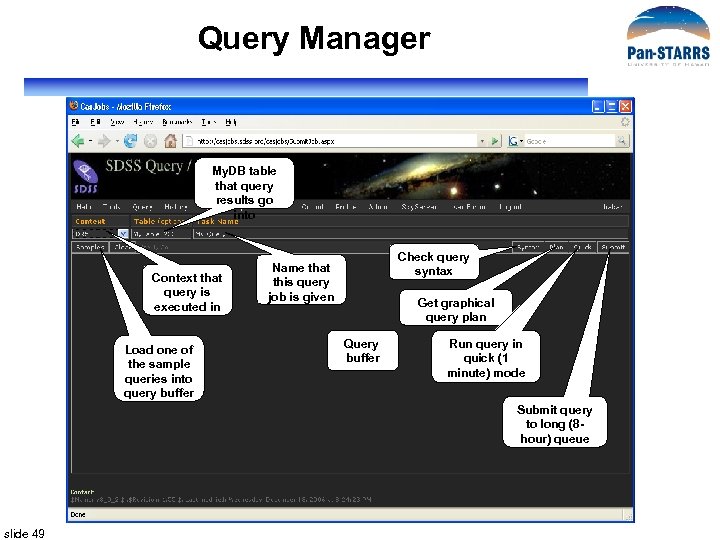
Query Manager My. DB table that query results go into Context that query is executed in Load one of the sample queries into query buffer Check query syntax Name that this query job is given Get graphical query plan Query buffer Run query in quick (1 minute) mode Submit query to long (8 hour) queue slide 49
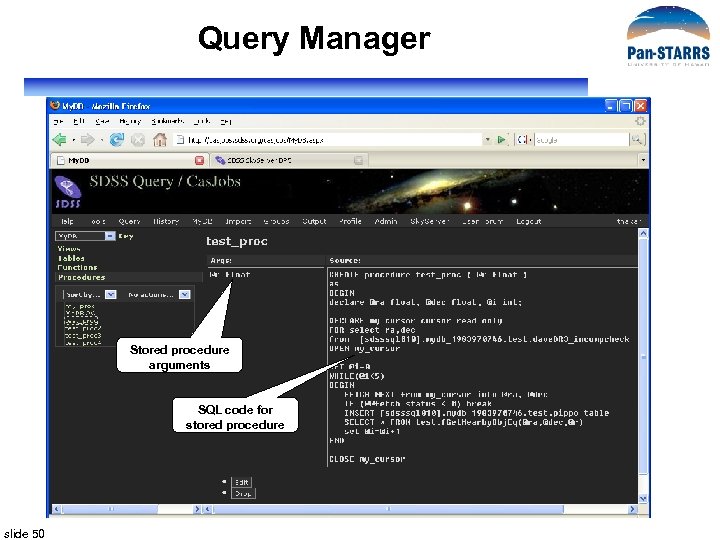
Query Manager Stored procedure arguments SQL code for stored procedure slide 50
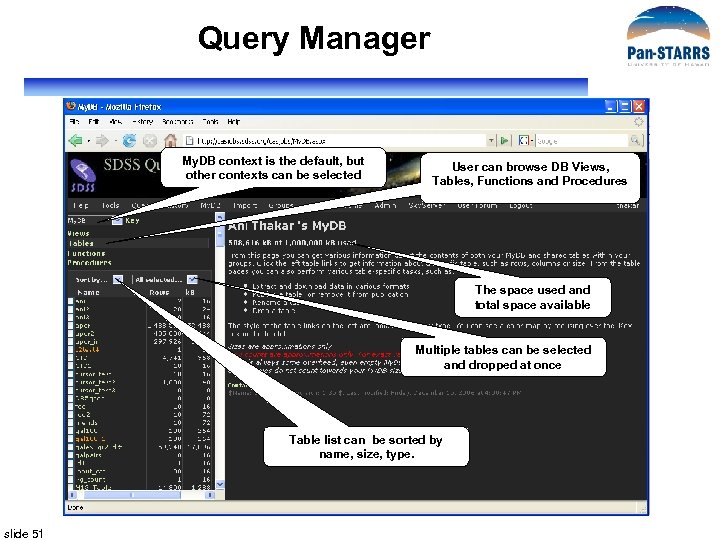
Query Manager My. DB context is the default, but other contexts can be selected User can browse DB Views, Tables, Functions and Procedures The space used and total space available Multiple tables can be selected and dropped at once Table list can be sorted by name, size, type. slide 51
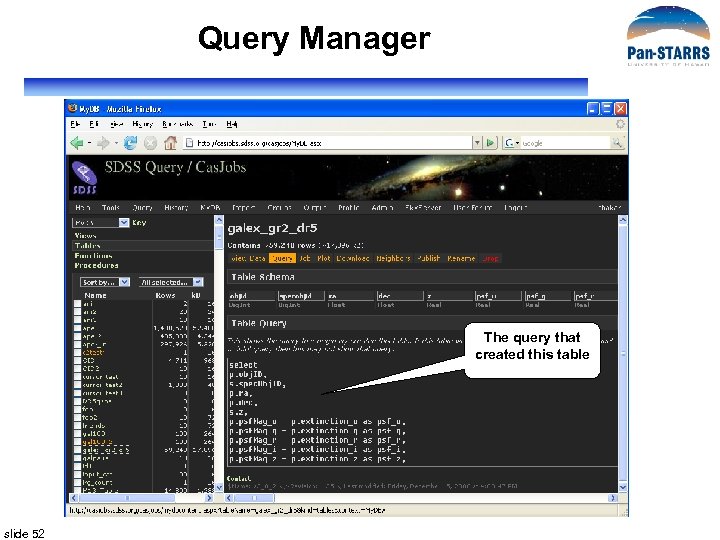
Query Manager The query that created this table slide 52
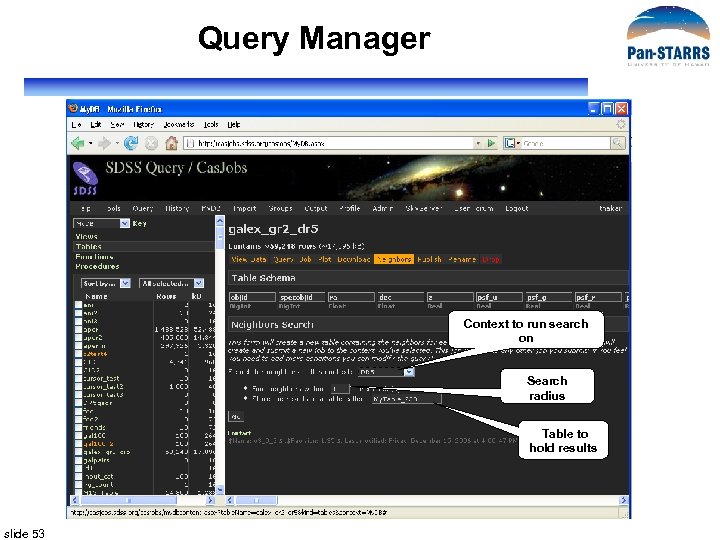
Query Manager Context to run search on Search radius Table to hold results slide 53
998d906a0ba0a3fef4aab16e42fe49b9.ppt