eff2c8d9aea5abe60b9f9b6661268e8a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35

PRTR & Responsible Care Initiative ® Minsk, 4 November 2011 Bernhard Thier, Cefic Responsible Care Manager 1

Who is Cefic? European Chemical Industry Council: http: //www. cefic. org/ Cefic is the voice of the European chemical industry in the European Union and the world. We represent 27, 000 chemical companies in Europe that produce 24% of the world chemical products and employ over 1. 2 million employees. Staff & network 150 staff members 4000 industry experts from companies & federations (150 Sector Groups, Strategy Implementation Groups and Issue Teams) Members & Affiliates 28 national federations in Europe 50 major international companies Ca. 450 business members Partner of Global sponsor of
Impact of the PRTRs Key factor in public perception of industry’s environmental performance Ø Provides a window through which the public sees industrial operations Ø Easily navigable and immediately accessible to all Ø Shows total releases & transfers from a facility and variability over time Inclusion of diffuse source data will provide a more holistic view Ø Single integrated portal with all available information Ø Large manufacturing industry no longer viewed in isolation Informs environmental decision making Ø Identifies industry sector contribution to overall pollutant load Ø Identifies individual facility contribution to local situation

Challenges Information should be viewed in the appropriate context Ø Shows only a single dimension of a facility’s environmental performance Ø Ø Temptation to assume individual facilities are directly comparable Diffuse source contribution may not be available at local level Ensure difference between Release & Transfer is clearly explained Need to be aware that limitations may not be appreciated by all Importance of data quality Ø Good decisions are based on good data Ø Good implementation of appropriate methodology at facility level is key Ø Improving data quality begins in-house

Improving Data Quality Ensure simple steps are followed Ø Ø Ø Ensure all sources are included Focus data quality effort on the largest contributors to the total Identify and document hidden factors in “black box” calculations Make sure you are applying the method correctly Check your assumptions are still valid Vs your current operation Clear guidance, practically applied is valuable Ø EU Commission PRTR Guidance document Ø ‘Smart’ implementation at facility level Ø Potential role for industry sector associations
Smart Implementation Practical application at facility level minimises impact on industry Reduction of un-necessary testing Ø Plausibility checks for presence of substances Ø Concept of indicative list of substances per industry sector Use of optimal quantification methodology Ø Ø Ø Methods need to best represent individual circumstances Choice of method proportionate to source contribution Use of methodologies agreed with permitting authorities Use of sector specific methodologies Potential role for industry associations to recommend / develop suitable methods

PRTR Reporting Integration with other reporting requirements Ø Focus on simplicity and clarity Ø Easy to follow forms, not overly detailed, clear guidance Ø Clarify exactly which data will make up the PRTR submission Alignment of timing with other reporting mechanisms Ø Verification of emissions under the EU ETS Opportunity to review prior to publication Ø Helps spot transcription errors

Responsible Care® - Initiative of the Global Chemical Industry 8

Responsible Care Ø Global Initiative for the continuous improvement in the chemical industry (launched 1985 in Canada) Ø Involves everybody from top management to plant worker Ø Core Principles: 1. Improve the safety, health and environmental performance 2. Use resources efficiently and minimise waste 3. Report openly on achievements and difficulties 4. Engage in dialogue with stakeholders, in particular with the local communities who live and work around our sites 5. Cooperate with regulators, set standards that go beyond regulation 6. Provide help and advice to foster the responsible management of chemicals throughout the value chain

Ø Consists 10

RC Requirements Ø RC is a commitment from the top of the organization Ø Transparency: reporting on performance indicators defined by national RC programme (Safety & Health; Environment; Transport; Resources) Ø Verification processes of RC compliance e. g. 3 rd party audit of RC management system Ø Active participation in RC network to help build capacity in the sector Ø Use of RC logo only licensed to companies in compliance with local (national) RC requirements Ø Governance of companies at national association Ø Governance of association by International Council of Chemical Associations
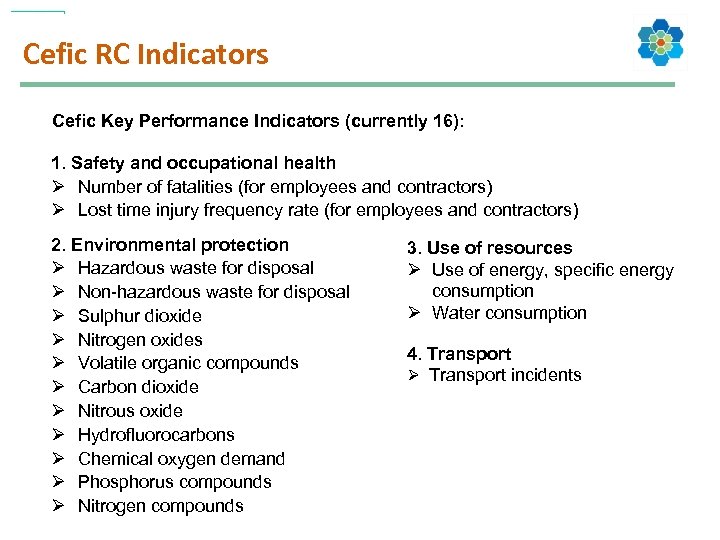
Cefic RC Indicators Cefic Key Performance Indicators (currently 16): 1. Safety and occupational health Ø Number of fatalities (for employees and contractors) Ø Lost time injury frequency rate (for employees and contractors) 2. Environmental protection Ø Hazardous waste for disposal Ø Non-hazardous waste for disposal Ø Sulphur dioxide Ø Nitrogen oxides Ø Volatile organic compounds Ø Carbon dioxide Ø Nitrous oxide Ø Hydrofluorocarbons Ø Chemical oxygen demand Ø Phosphorus compounds Ø Nitrogen compounds 3. Use of resources Ø Use of energy, specific energy consumption Ø Water consumption 4. Transport Ø Transport incidents
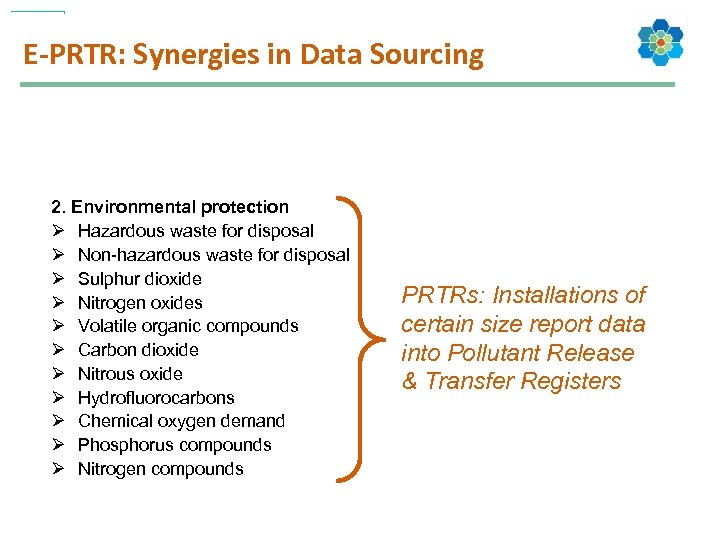
E-PRTR: Synergies in Data Sourcing 2. Environmental protection Ø Hazardous waste for disposal Ø Non-hazardous waste for disposal Ø Sulphur dioxide Ø Nitrogen oxides Ø Volatile organic compounds Ø Carbon dioxide Ø Nitrous oxide Ø Hydrofluorocarbons Ø Chemical oxygen demand Ø Phosphorus compounds Ø Nitrogen compounds PRTRs: Installations of certain size report data into Pollutant Release & Transfer Registers
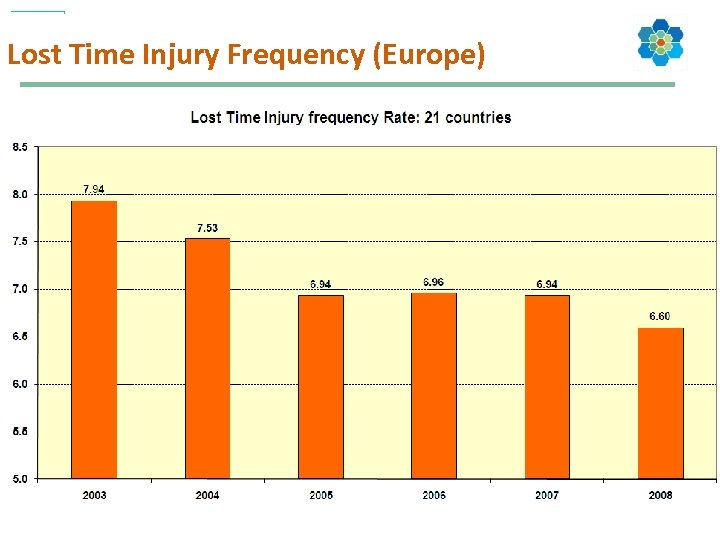
Lost Time Injury Frequency (Europe) 14
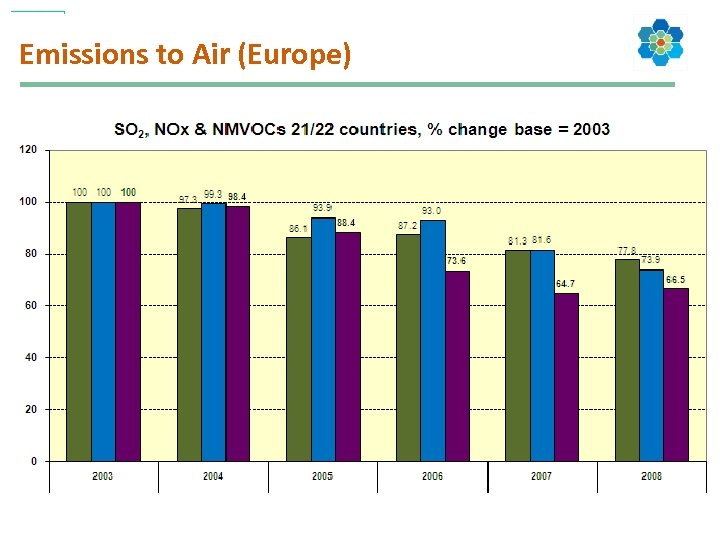
Emissions to Air (Europe)
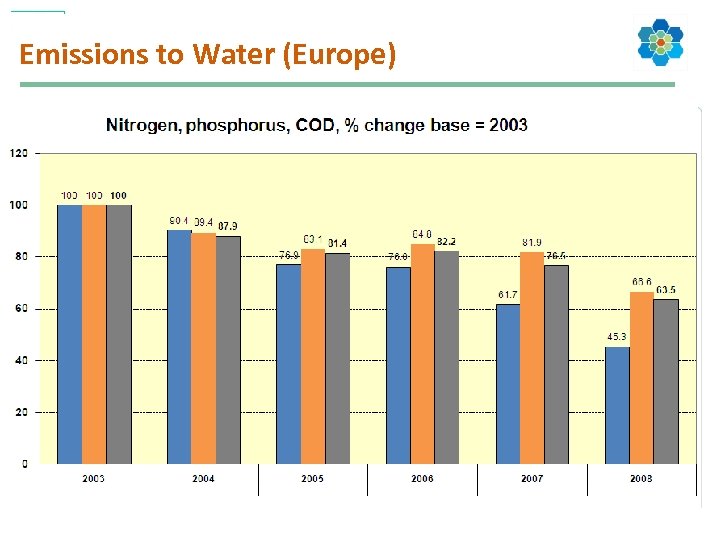
Emissions to Water (Europe)
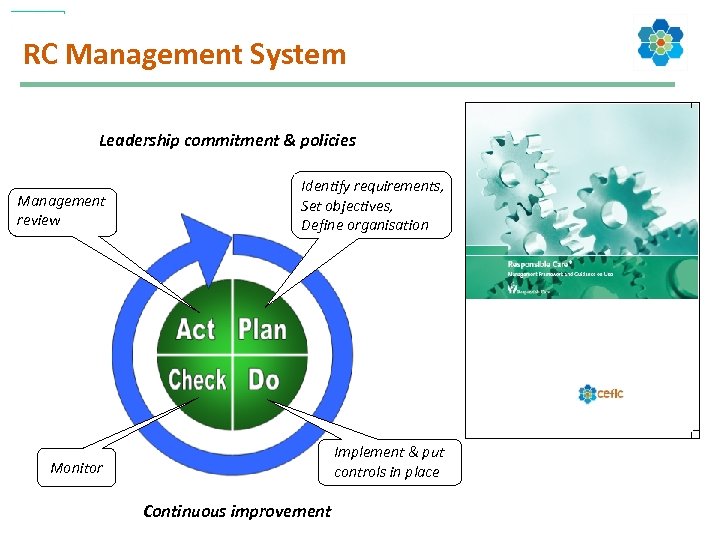
RC Management System Leadership commitment & policies Management review Identify requirements, Set objectives, Define organisation Monitor Implement & put controls in place Continuous improvement

Company Example (BASF) Responsible Care Management System (RCMS) Example Transportation & Distribution Safety (TDS) RCMS Code TDS (“Compliance with the transport security requirements”) BASF Group Directives BASF Group Directive TDS (“appropriate action to reduce risks”) Functional Requirements TDS Requirements: (Chapter 8, “Filling of bulk goods”) Successful Practices TDS Successful Practice (Loading Checklist “Bulk”)
RC tools for SMEs

EU-OHSA Campaign on Maintenance Ø Target: 25% reduction of accidents rate by 2012 Ø Maintenance workers at increased risk: Ø 10 -15% of all fatal accidents at work and 15 -20% of all accidents related to maintenance Ø The EU-OSHA campaign messages: 1. Maintenance = essential to keep the working environment safe & healthy 2. Maintenance = high-risk activity that has to be performed in a safe way Ø Higher exposure of maintenance workers to dangerous substances Ø Higher exposure to noise, vibration and radiation Ø Maintenance workers often perform physically demanding work Ø Indications of higher risk of occupational diseases (e. g. musculoskeletal disorders)

Maintenance: Risks & Subcontracting Maintenance-specific risks Ø Working alongside a running process and in close contact with machinery Ø Involves disassembly and reassembly of complicated machinery Ø Non-routine tasks & exceptional conditions Ø Changing tasks and working environments Ø Working under time-pressure Subcontracting (maintenance is very often subcontracted) Ø Aggravating factor in terms of safety and health Ø Maintenance operations are often carried out on customer sites which are unfamiliar to the workers Ø Workers carry out operations very independently, making decisions by themselves Ø Working alone, working during the nights Ø Many subcontracting companies to operate simultaneously on sites
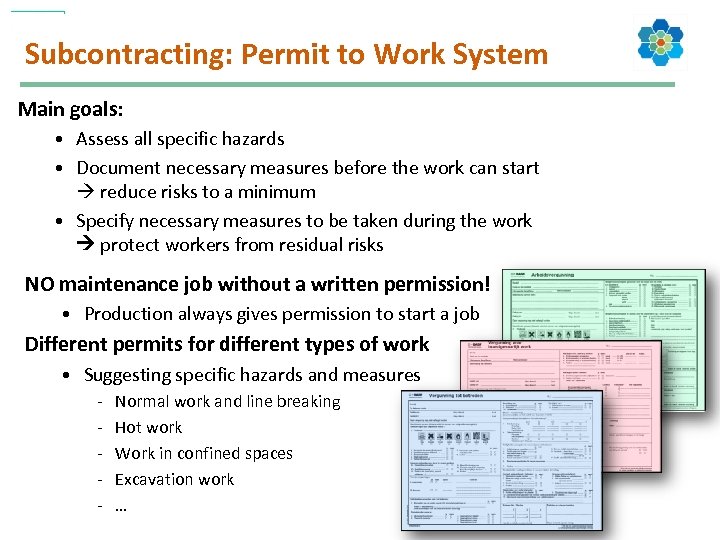
Subcontracting: Permit to Work System Main goals: • Assess all specific hazards • Document necessary measures before the work can start reduce risks to a minimum • Specify necessary measures to be taken during the work protect workers from residual risks NO maintenance job without a written permission! • Production always gives permission to start a job Different permits for different types of work • Suggesting specific hazards and measures - Normal work and line breaking Hot work Work in confined spaces Excavation work …

Process Safety Incidents with huge impact 2005 Texas, USA: 15 killed, 170 injured 2005 Buncefield, UK: Biggest explosion in peacetime

Cefic Guidance on Process Safety Keep the hazard potentials contained! Handle inevitable hazard potentials professionally that the likelyhood of their activation and adverse effects to environment, people and assets is as low as practicable
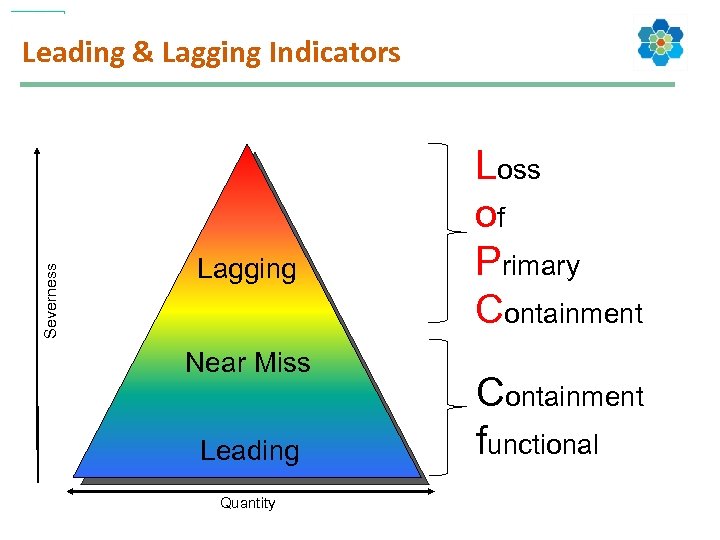
Severness Leading & Lagging Indicators Lagging Near Miss Leading Quantity Loss of Primary Containment functional
Reportable Process Safety incident Unintended release of substance or energy (= Loss of Primary Containment, Lo. PC) in production, distribution, storage, utilities or pilot plants and laboratories with a) Employee / contractor lost time injury (≥ 1 d) and/or fatality or hospital admission and/or fatality of a third party or b) Fires or explosions resulting ≥ € 20, 000 of direct cost or c) Substance release ≥ defined release threshold quantities from primary containment (i. e. , vessel or pipe)

ICCA Global Product Strategy (GPS) Committed to have by 2020: Ø Established a base-set of hazard and exposure information adequate to conduct safety assessments for chemicals in commerce Ø Provided global capacity to implement best assessment practices and management procedures, especially in developing countries Ø Shared relevant product information with co-producers, governments and the public Ø Worked across the value chain so suppliers and customers can effectively evaluate the risks and enhance their performance Ø Made information on chemicals publicly available via ICCA GPS IT Portal

GPS IT Portal Ø Accessible to all stakeholders but provides secure upload functions for ICCA members only. Ø Companies have provided > 1000 GPS safety summaries ICCA website GPS info search
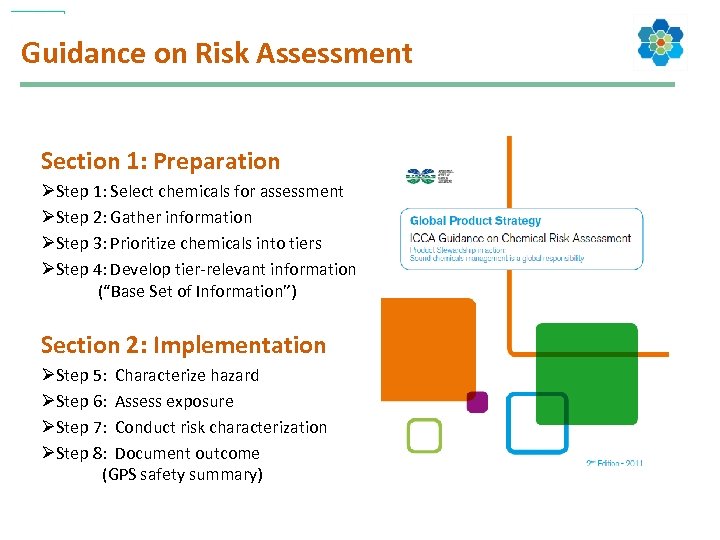
Guidance on Risk Assessment Section 1: Preparation ØStep 1: Select chemicals for assessment ØStep 2: Gather information ØStep 3: Prioritize chemicals into tiers ØStep 4: Develop tier-relevant information (“Base Set of Information”) Section 2: Implementation ØStep 5: Characterize hazard ØStep 6: Assess exposure ØStep 7: Conduct risk characterization ØStep 8: Document outcome (GPS safety summary)

Responsible Care Global Charter ”An inspiring model of self-regulation that other industries should consider following. ” (K. Annan, 2006) Global Charter Key Elements Ø Ø Ø Commit to advancing Sustainable Development Continuously improve and report performance Enhance the safe management of chemicals worldwide Facilitate the extension of RC along the value chain Actively support national and global RC governance processes Provide appropriate resources to effectively implement RC ü 55 associations worldwide ü 90% of largest chemical companies
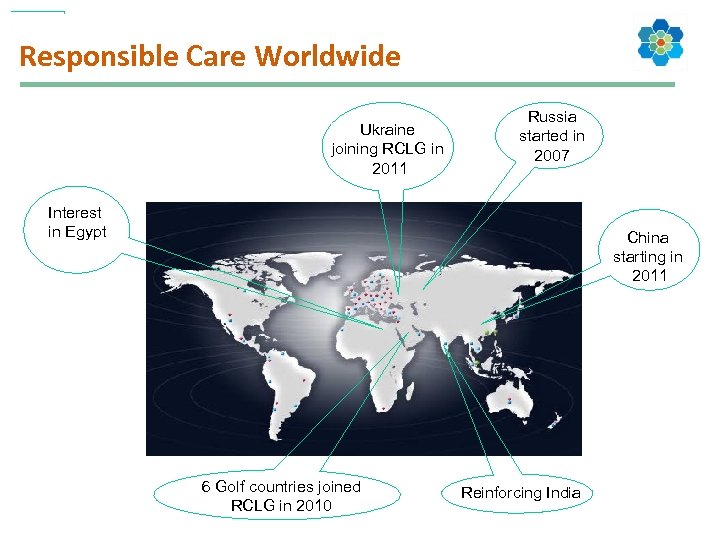
Responsible Care Worldwide Ukraine joining RCLG in 2011 Russia started in 2007 Interest in Egypt China starting in 2011 6 Golf countries joined RCLG in 2010 Reinforcing India

Responsible Care at the Gulf Ø Gulf Petrochemical & Chemical Association (Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, UAE, Qatar, Bahrain, Oman) Ø Supported by Cefic & American Chemistry Council Ø 54 th RCLG member association (approved in 2010)

Responsible Care in the Ukraine Ø Ukraine Chemists Union (UCU) Ø Mo. U with Cefic since 2010 Ø 2010 workshops in Kiev, Yuzhne, Cherkassy, Severodonetsk Ø 55 th ICCA RCLG member association (approved in 2011) UCU General Assembly Odessa Port Plant, Yuzhne

Start of Responsible Care in Egypt Ø Egyptian Chamber of Chemical Industries Ø Mo. U signed with Cefic in 4/2011 Ø Egyptian RC Board established 8/2011 Cefic DG Mandery with Sherif Al Gabaly, Chair of ECCI

Many Thanks for Your Attention! Questions? (contact: bth@cefic. be) 35
eff2c8d9aea5abe60b9f9b6661268e8a.ppt