 Protocols: DNS, TELNET, e-Mail, FTP, WWW, NNTP, SNMP, NTP etc.
Protocols: DNS, TELNET, e-Mail, FTP, WWW, NNTP, SNMP, NTP etc.
 Application layer
Application layer
 DNS - The purpose
DNS - The purpose
 DNS - Historical remarks
DNS - Historical remarks
 DNS design goals
DNS design goals
 DNS design goals (contd. )
DNS design goals (contd. )
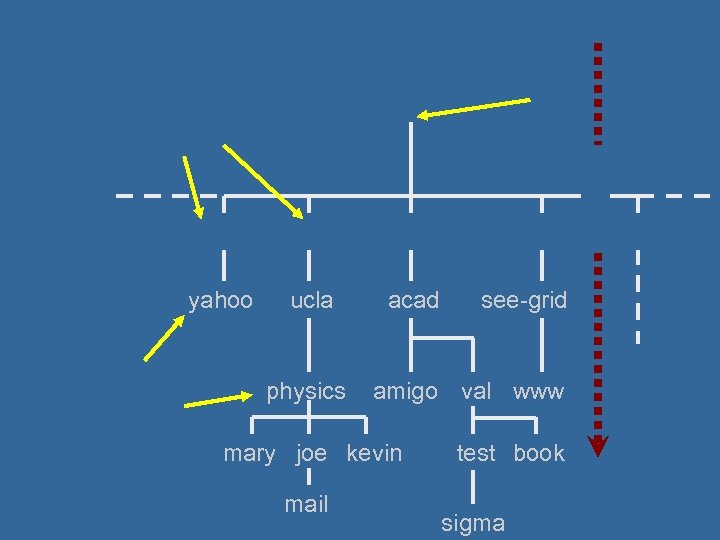 yahoo ucla physics acad amigo val www mary joe kevin mail see-grid test book sigma
yahoo ucla physics acad amigo val www mary joe kevin mail see-grid test book sigma
 Top Level Domains
Top Level Domains
 Resource Records
Resource Records
 DNS server
DNS server
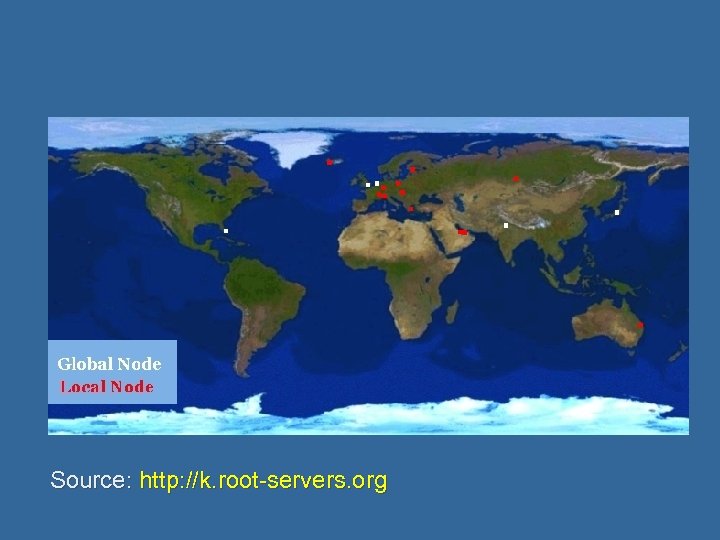 Source: http: //k. root-servers. org
Source: http: //k. root-servers. org
 DNS servers (contd. )
DNS servers (contd. )
 DNS servers (contd. )
DNS servers (contd. )
 Reverse DNS query
Reverse DNS query
 TELNET protocol
TELNET protocol
 TELNET protocol (2)
TELNET protocol (2)
 Electronic mail
Electronic mail
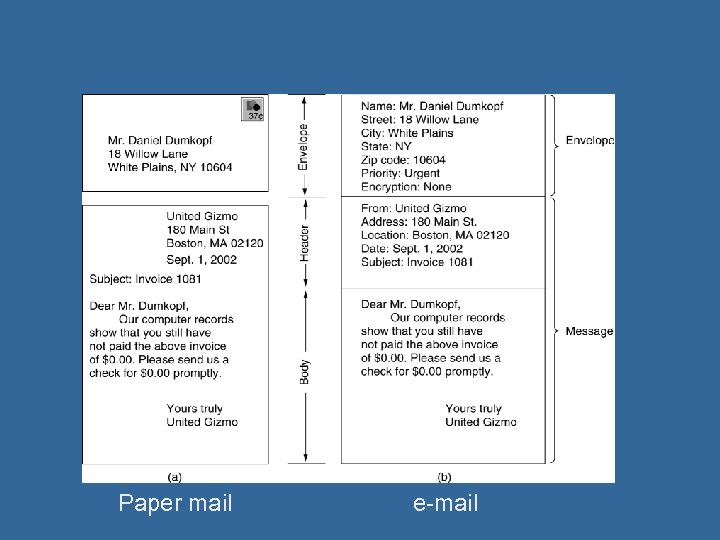 Paper mail e-mail
Paper mail e-mail
 Reading E-mail An example of mailbox
Reading E-mail An example of mailbox
 Message Formats – RFC 822
Message Formats – RFC 822
 MIME – Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions The original e-mail was designed to transfer 7 -bit text (ASCII) characters only, so. . .
MIME – Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions The original e-mail was designed to transfer 7 -bit text (ASCII) characters only, so. . .
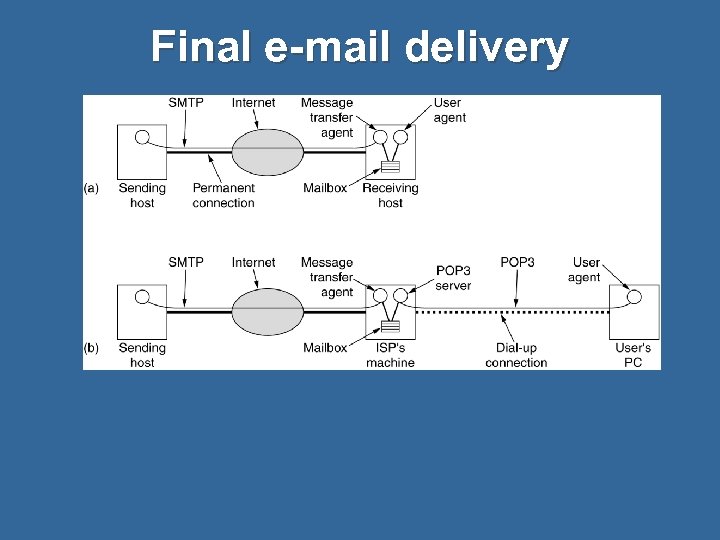 Final e-mail delivery
Final e-mail delivery
 Post Office Protocol (POP 3)
Post Office Protocol (POP 3)
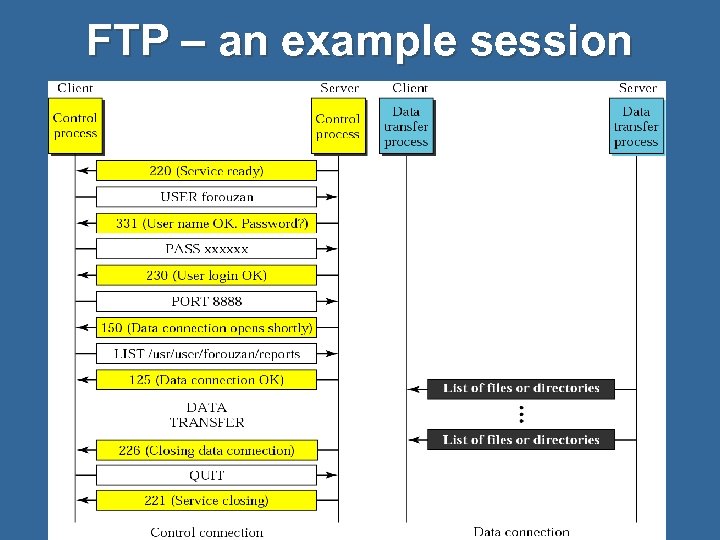 FTP – an example session
FTP – an example session
 FTP pros and cons
FTP pros and cons
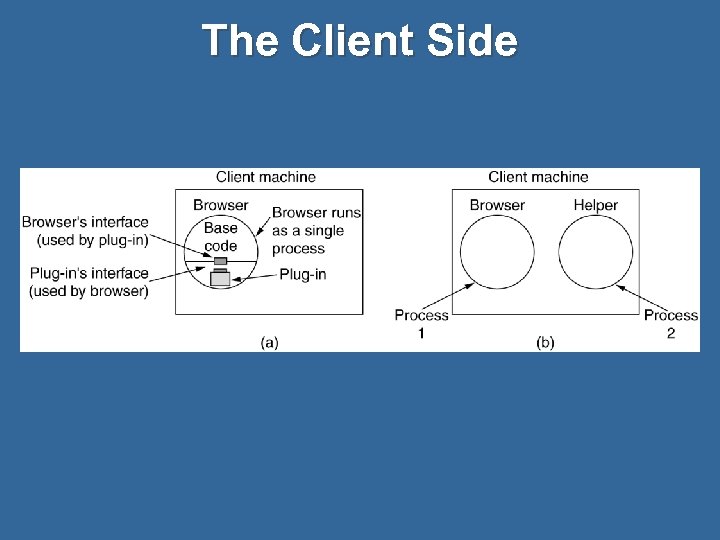 The Client Side
The Client Side
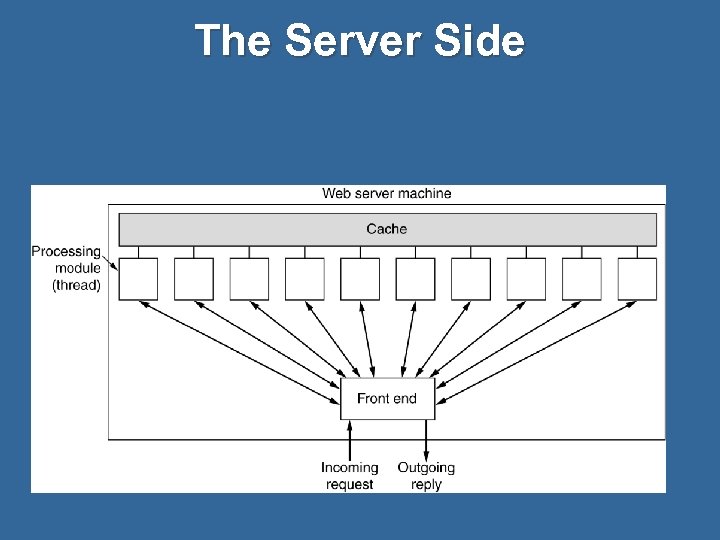 The Server Side
The Server Side
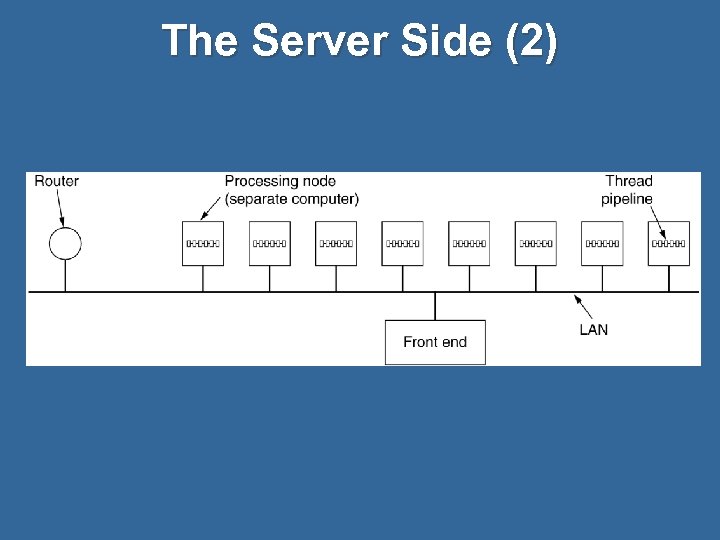 The Server Side (2)
The Server Side (2)
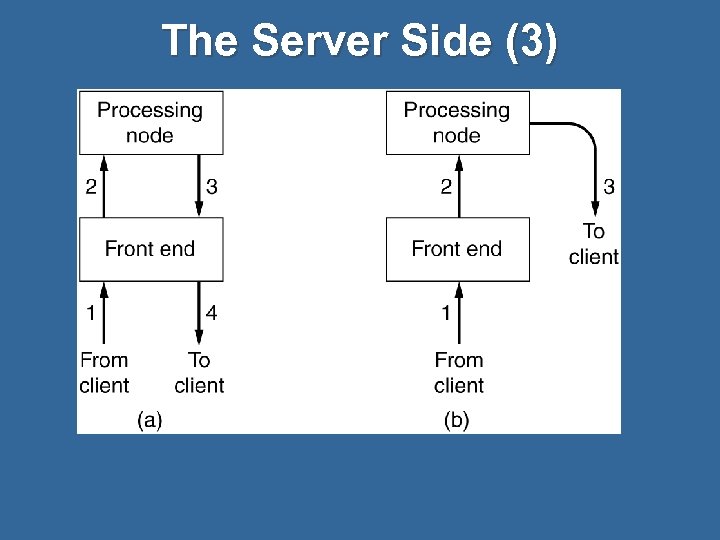 The Server Side (3)
The Server Side (3)
 The World Wide Web - HTTP
The World Wide Web - HTTP
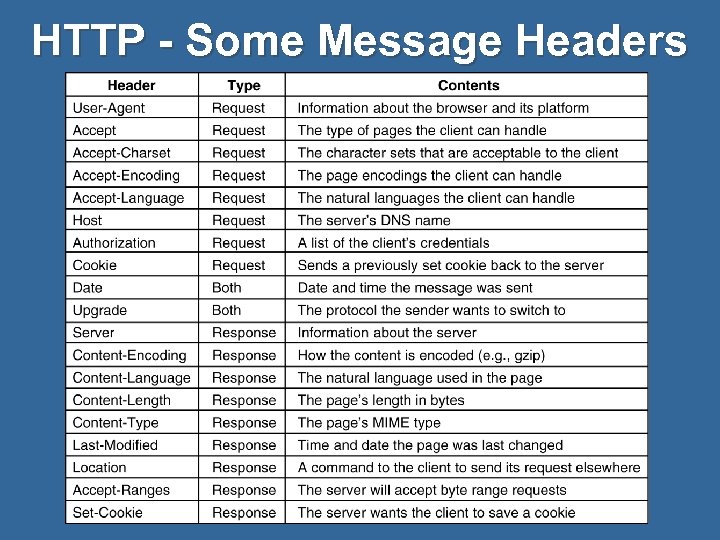 HTTP - Some Message Headers
HTTP - Some Message Headers
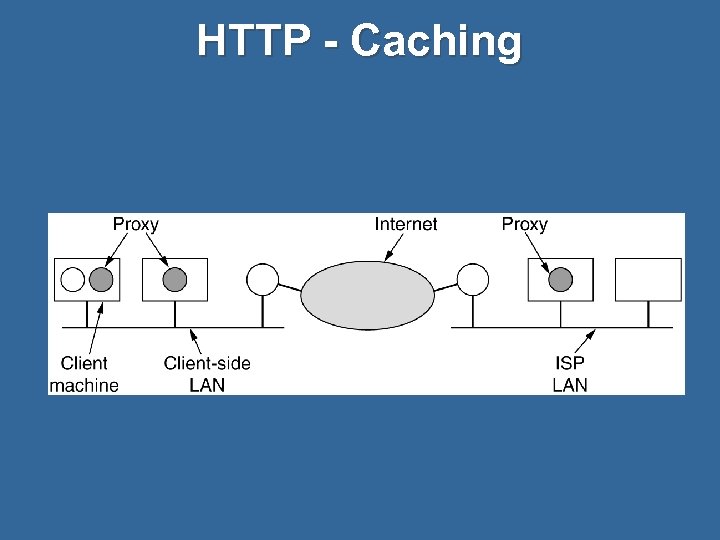 HTTP - Caching
HTTP - Caching
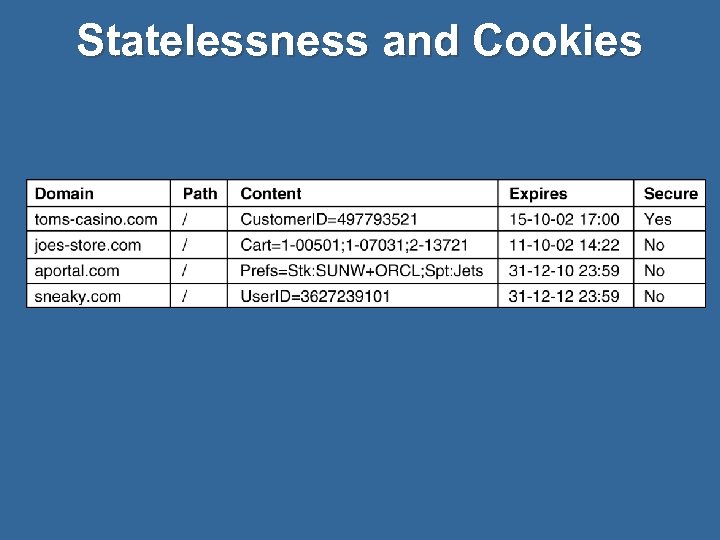 Statelessness and Cookies
Statelessness and Cookies
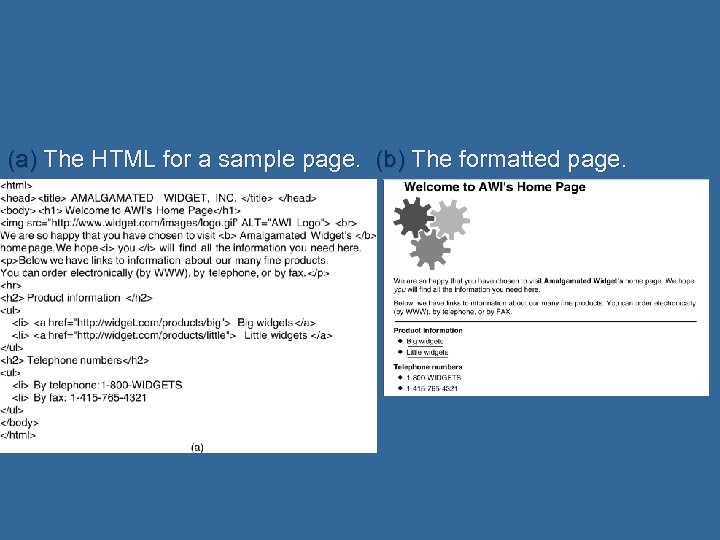 (a) The HTML for a sample page. (b) The formatted page.
(a) The HTML for a sample page. (b) The formatted page.
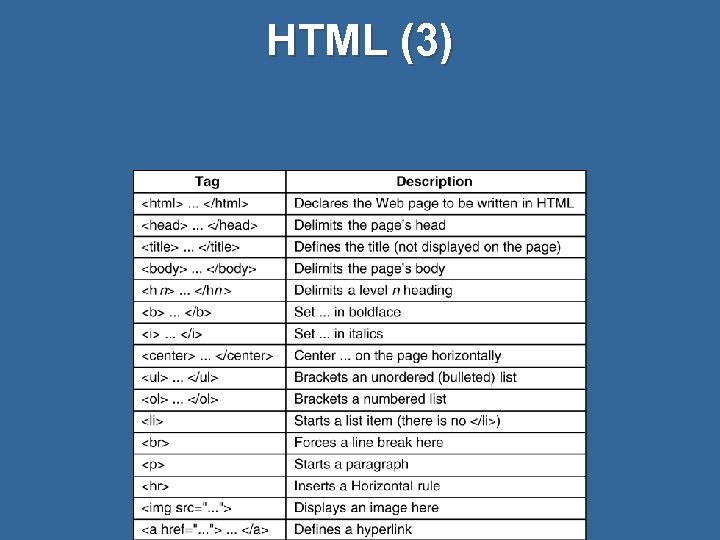 HTML (3)
HTML (3)
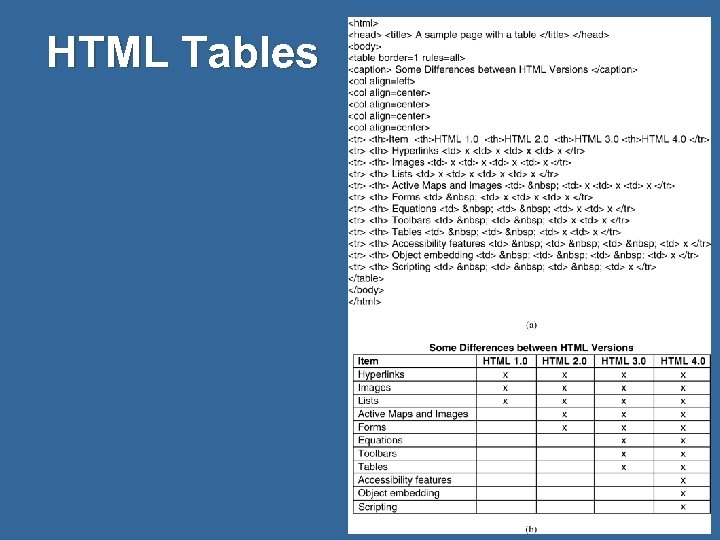 HTML Tables
HTML Tables
 HTML Forms
HTML Forms
 HTML Forms (2)
HTML Forms (2)
 A simple Web page in XML.
A simple Web page in XML.
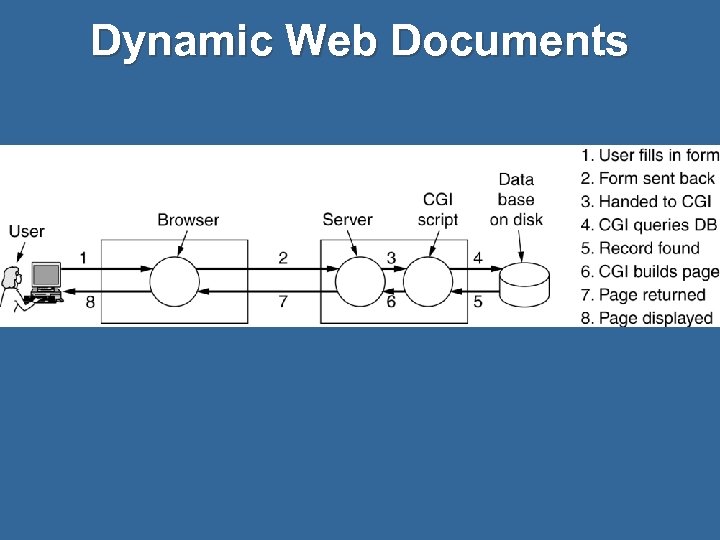 Dynamic Web Documents
Dynamic Web Documents
 Dynamic Web Documents (2)
Dynamic Web Documents (2)
 “Web Services”
“Web Services”
 NNTP (2)
NNTP (2)
 SNMP – some history
SNMP – some history
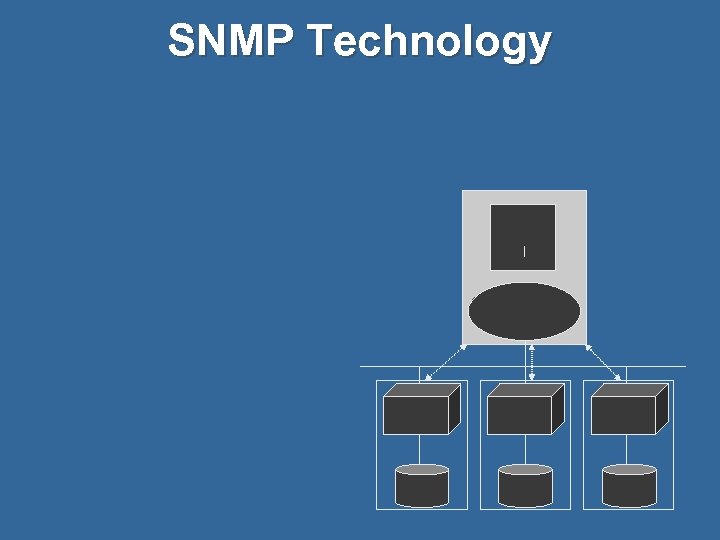 SNMP Technology
SNMP Technology
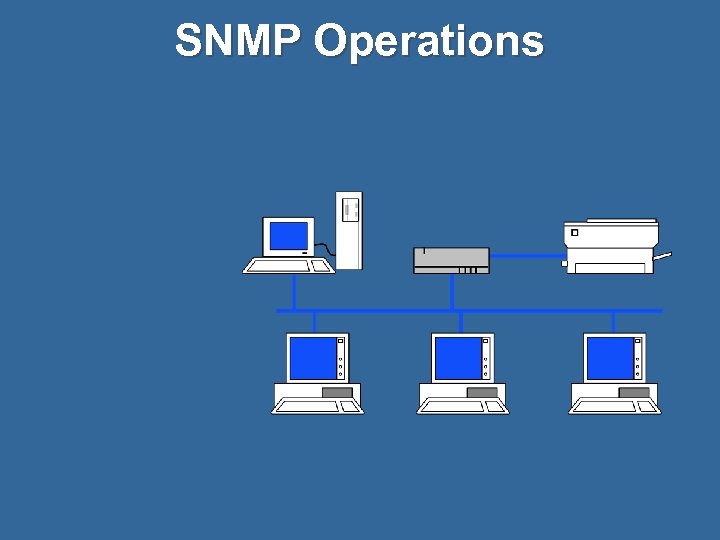 SNMP Operations
SNMP Operations
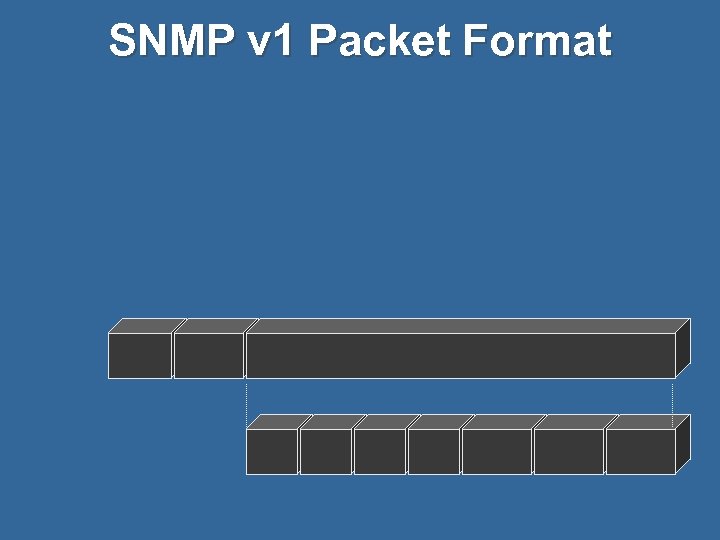 SNMP v 1 Packet Format
SNMP v 1 Packet Format
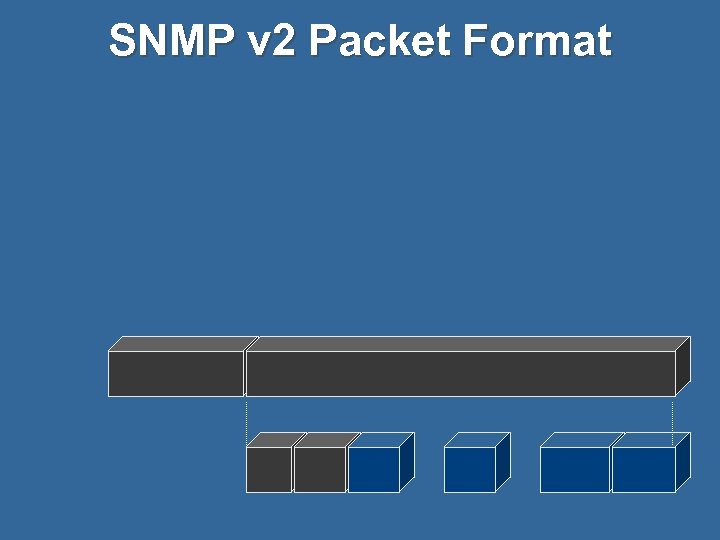 SNMP v 2 Packet Format
SNMP v 2 Packet Format
 The new SNMP v 3
The new SNMP v 3
 SNMP Conclusion
SNMP Conclusion
 NTP - Introduction
NTP - Introduction
 Needs for precision time
Needs for precision time
 NTP summary
NTP summary
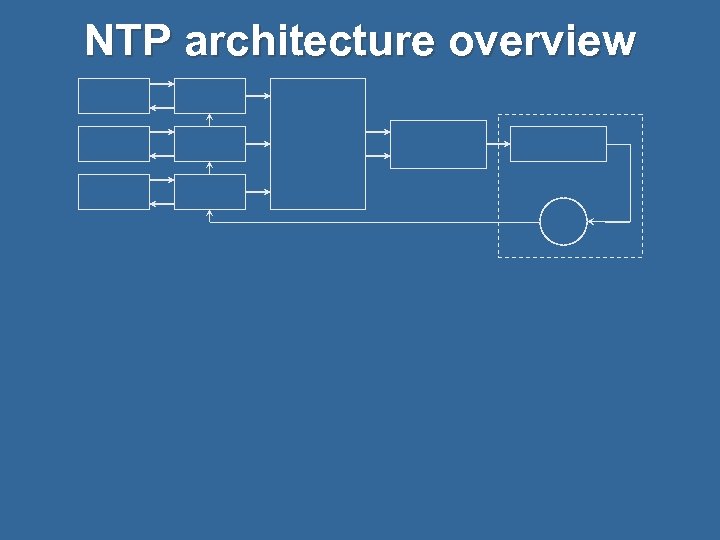 NTP architecture overview
NTP architecture overview
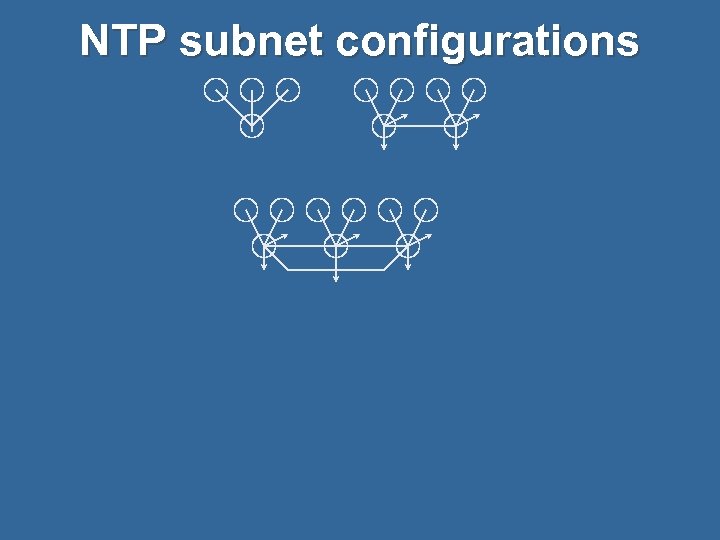 NTP subnet configurations
NTP subnet configurations
 NTP - Goals and non-goals
NTP - Goals and non-goals
 NTP Version 4
NTP Version 4
 Squeezing the nanoseconds
Squeezing the nanoseconds
 NTP resources
NTP resources
 Miscellaneous Application Protocols (2)
Miscellaneous Application Protocols (2)