M01L02_FC_Protocol_Concepts_0424_dsl.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 Protocol Overview FC Protocol Concepts © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. vx. x—L 02 -1
Protocol Overview FC Protocol Concepts © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. vx. x—L 02 -1
 Outline • Fibre Channel Overview • Fibre Channel Performance • Fibre Channel Topologies • Fibre Channel Ports • Fibre Channel HBAs • Classes Of Service • Summary © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. M 01 L 02 vx. x—L 02 -2
Outline • Fibre Channel Overview • Fibre Channel Performance • Fibre Channel Topologies • Fibre Channel Ports • Fibre Channel HBAs • Classes Of Service • Summary © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. M 01 L 02 vx. x—L 02 -2
 Fibre Channel Overview © 2004 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 3
Fibre Channel Overview © 2004 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 3
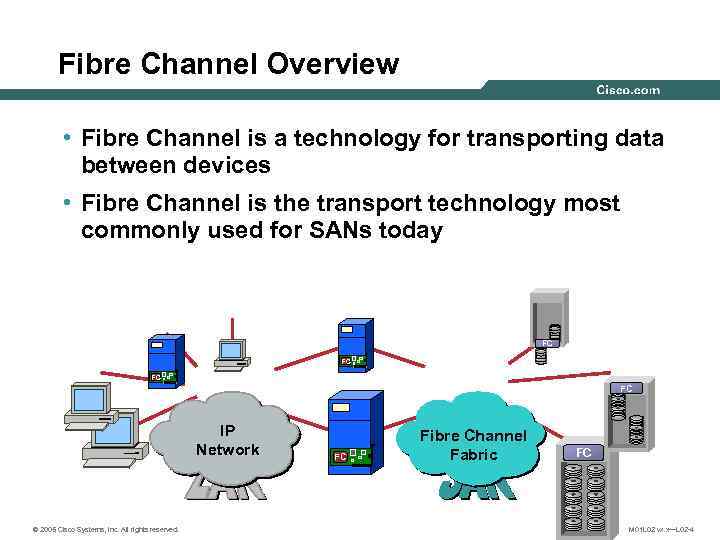 Fibre Channel Overview • Fibre Channel is a technology for transporting data between devices • Fibre Channel is the transport technology most commonly used for SANs today FC FC IP Network © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. FC Fibre Channel Fabric FC M 01 L 02 vx. x—L 02 -4
Fibre Channel Overview • Fibre Channel is a technology for transporting data between devices • Fibre Channel is the transport technology most commonly used for SANs today FC FC IP Network © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. FC Fibre Channel Fabric FC M 01 L 02 vx. x—L 02 -4
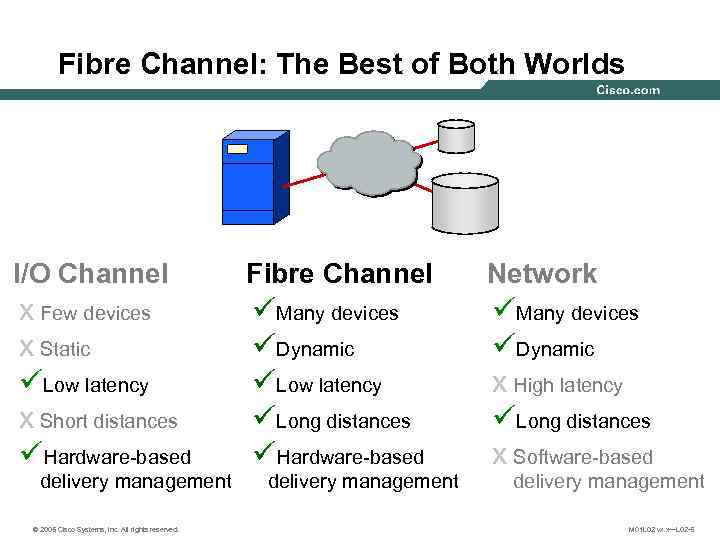 Fibre Channel: The Best of Both Worlds I/O Channel Fibre Channel Network x Few devices x Static üLow latency x Short distances üHardware-based üMany devices üDynamic üLow latency üLong distances üHardware-based üMany devices üDynamic x High latency üLong distances x Software-based delivery management © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. delivery management M 01 L 02 vx. x—L 02 -5
Fibre Channel: The Best of Both Worlds I/O Channel Fibre Channel Network x Few devices x Static üLow latency x Short distances üHardware-based üMany devices üDynamic üLow latency üLong distances üHardware-based üMany devices üDynamic x High latency üLong distances x Software-based delivery management © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. delivery management M 01 L 02 vx. x—L 02 -5
 Fibre Channel Topologies © 2004 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 6
Fibre Channel Topologies © 2004 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 6
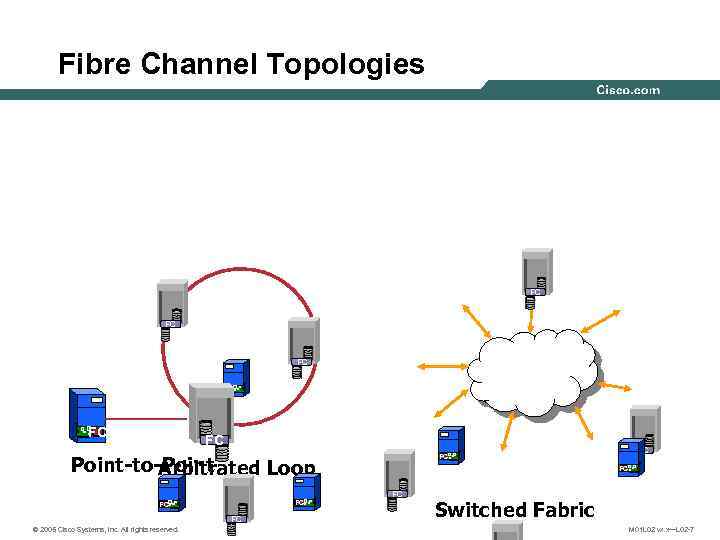 Fibre Channel Topologies FC FC FC Point-to-Point Arbitrated Loop FC FC FC © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. FC FC Switched Fabric M 01 L 02 vx. x—L 02 -7
Fibre Channel Topologies FC FC FC Point-to-Point Arbitrated Loop FC FC FC © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. FC FC Switched Fabric M 01 L 02 vx. x—L 02 -7
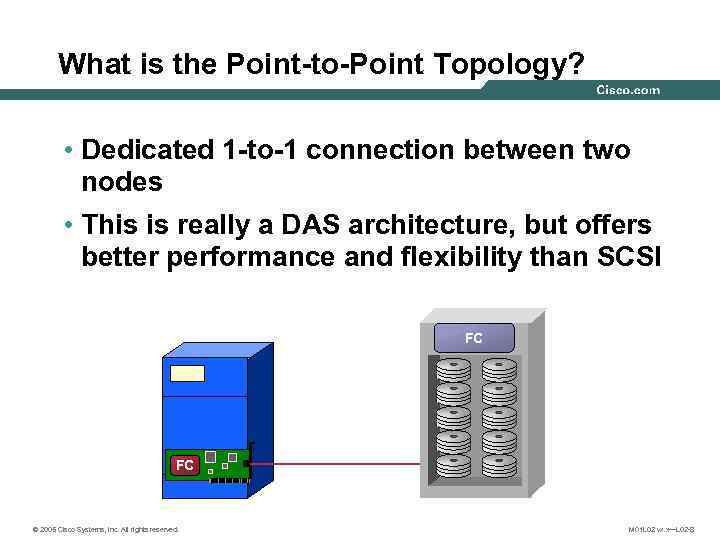 What is the Point-to-Point Topology? • Dedicated 1 -to-1 connection between two nodes • This is really a DAS architecture, but offers better performance and flexibility than SCSI FC FC © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. M 01 L 02 vx. x—L 02 -8
What is the Point-to-Point Topology? • Dedicated 1 -to-1 connection between two nodes • This is really a DAS architecture, but offers better performance and flexibility than SCSI FC FC © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. M 01 L 02 vx. x—L 02 -8
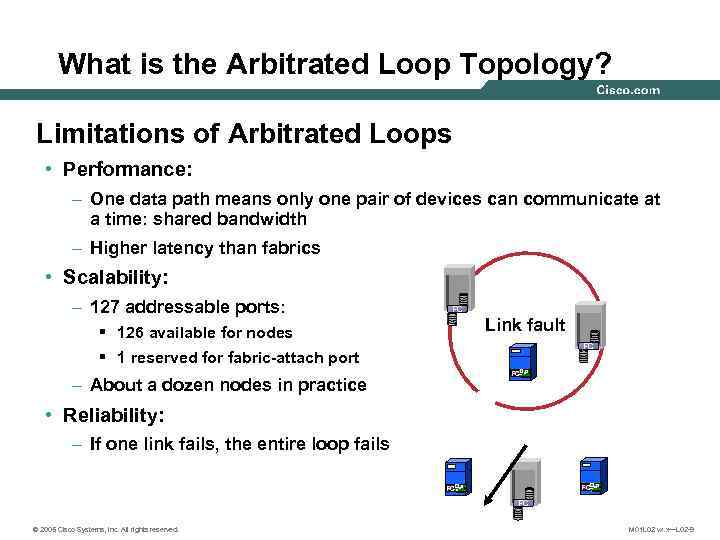 What is the Arbitrated Loop Topology? Limitations of Arbitrated Loops • Performance: – One data path means only one pair of devices can communicate at a time: shared bandwidth – Higher latency than fabrics • Scalability: – 127 addressable ports: FC Link fault § 126 available for nodes FC § 1 reserved for fabric-attach port FC – About a dozen nodes in practice • Reliability: – If one link fails, the entire loop fails FC FC FC © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. M 01 L 02 vx. x—L 02 -9
What is the Arbitrated Loop Topology? Limitations of Arbitrated Loops • Performance: – One data path means only one pair of devices can communicate at a time: shared bandwidth – Higher latency than fabrics • Scalability: – 127 addressable ports: FC Link fault § 126 available for nodes FC § 1 reserved for fabric-attach port FC – About a dozen nodes in practice • Reliability: – If one link fails, the entire loop fails FC FC FC © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. M 01 L 02 vx. x—L 02 -9
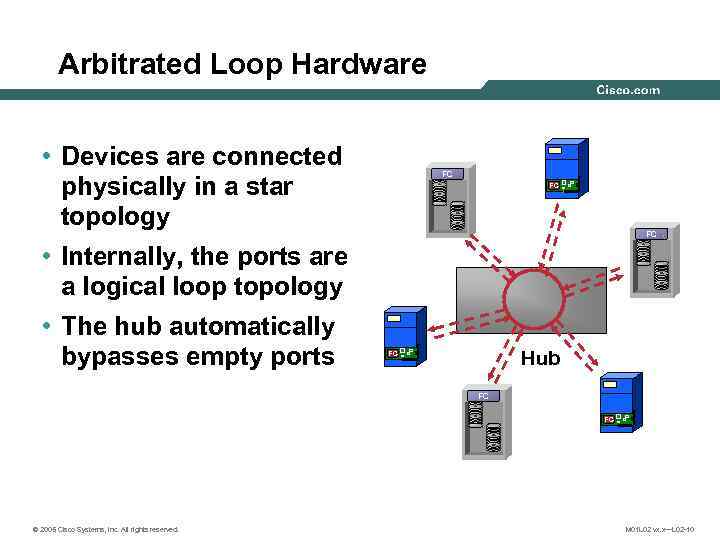 Arbitrated Loop Hardware • Devices are connected physically in a star topology FC FC FC • Internally, the ports are a logical loop topology • The hub automatically bypasses empty ports Hub FC FC FC © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. M 01 L 02 vx. x—L 02 -10
Arbitrated Loop Hardware • Devices are connected physically in a star topology FC FC FC • Internally, the ports are a logical loop topology • The hub automatically bypasses empty ports Hub FC FC FC © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. M 01 L 02 vx. x—L 02 -10
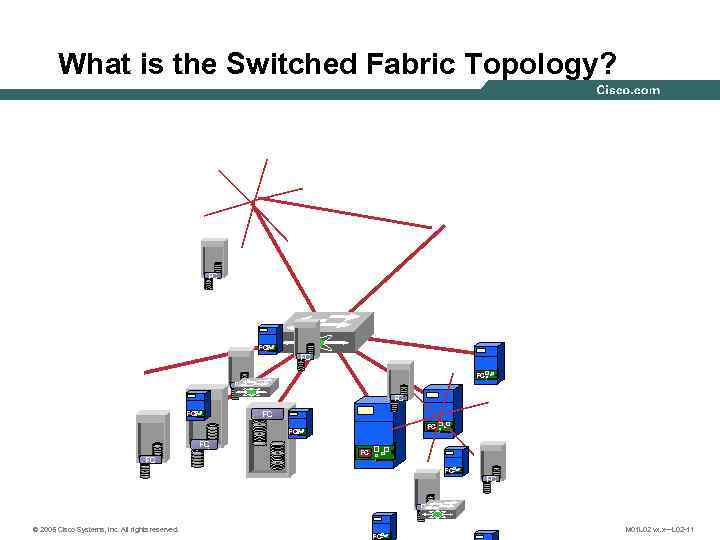 What is the Switched Fabric Topology? FC FC FC FC © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. FC M 01 L 02 vx. x—L 02 -11
What is the Switched Fabric Topology? FC FC FC FC © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. FC M 01 L 02 vx. x—L 02 -11
 What is the Switched Fabric Topology? (cont. ) • Supports multiple “conversations” at full link speed • Allows over 16, 000 device addresses • Enhanced management capabilities: – Security services – Multicast and broadcast – Remote management • The majority of modern organizations choose to implement a fabric © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. M 01 L 02 vx. x—L 02 -12
What is the Switched Fabric Topology? (cont. ) • Supports multiple “conversations” at full link speed • Allows over 16, 000 device addresses • Enhanced management capabilities: – Security services – Multicast and broadcast – Remote management • The majority of modern organizations choose to implement a fabric © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. M 01 L 02 vx. x—L 02 -12
 Fibre Channel Ports © 2004 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 13
Fibre Channel Ports © 2004 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 13
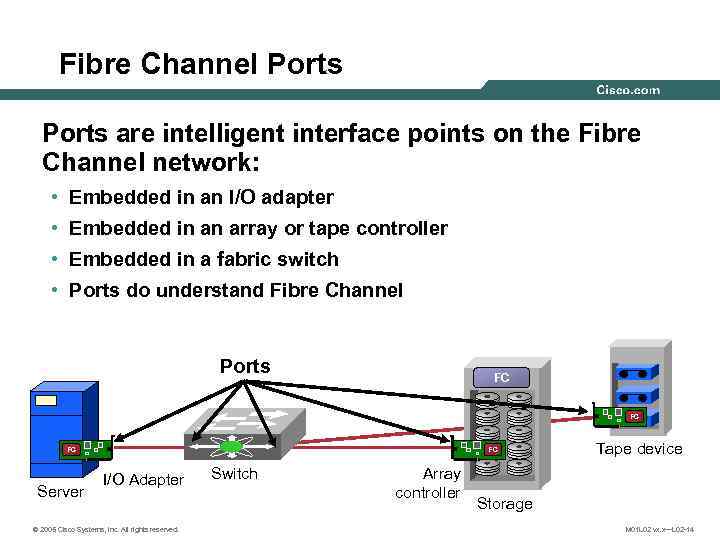 Fibre Channel Ports are intelligent interface points on the Fibre Channel network: • Embedded in an I/O adapter • Embedded in an array or tape controller • Embedded in a fabric switch • Ports do understand Fibre Channel Ports FC FC FC Server FC I/O Adapter © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Switch Array controller Tape device Storage M 01 L 02 vx. x—L 02 -14
Fibre Channel Ports are intelligent interface points on the Fibre Channel network: • Embedded in an I/O adapter • Embedded in an array or tape controller • Embedded in a fabric switch • Ports do understand Fibre Channel Ports FC FC FC Server FC I/O Adapter © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Switch Array controller Tape device Storage M 01 L 02 vx. x—L 02 -14
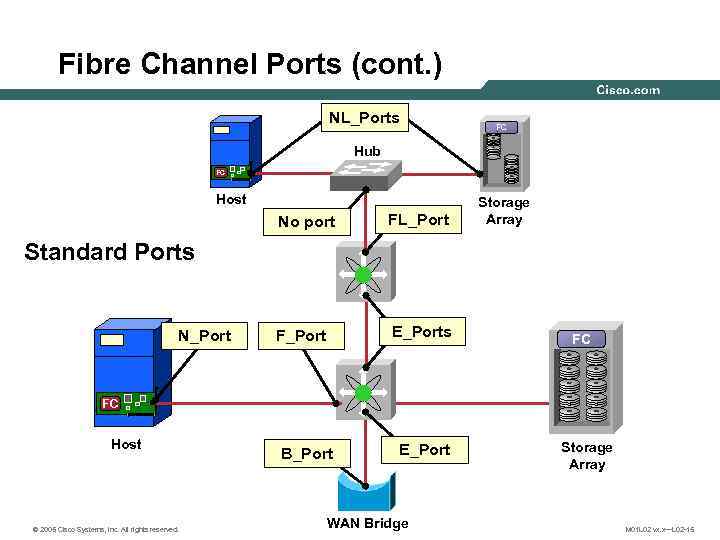 Fibre Channel Ports (cont. ) NL_Ports NL_Port FC Hub FC Host (No port) No port FL_Port F_Port E_Ports Storage Array Standard Ports N_Port FC FC Host © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. B_Port E_Port WAN Bridge Storage Array M 01 L 02 vx. x—L 02 -15
Fibre Channel Ports (cont. ) NL_Ports NL_Port FC Hub FC Host (No port) No port FL_Port F_Port E_Ports Storage Array Standard Ports N_Port FC FC Host © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. B_Port E_Port WAN Bridge Storage Array M 01 L 02 vx. x—L 02 -15
 Fibre Channel HBAs © 2004 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 16
Fibre Channel HBAs © 2004 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 16
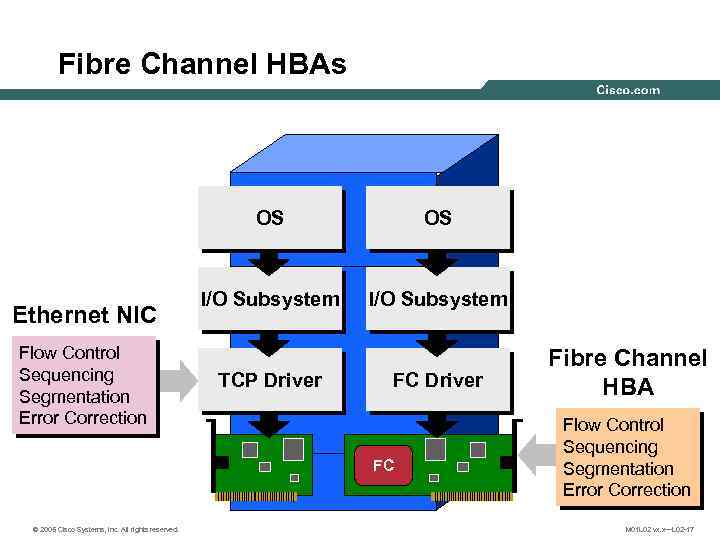 Fibre Channel HBAs OS Ethernet NIC Flow Control Sequencing Segmentation Error Correction OS I/O Subsystem TCP Driver FC © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Fibre Channel HBA Flow Control Sequencing Segmentation Error Correction M 01 L 02 vx. x—L 02 -17
Fibre Channel HBAs OS Ethernet NIC Flow Control Sequencing Segmentation Error Correction OS I/O Subsystem TCP Driver FC © 2005 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. Fibre Channel HBA Flow Control Sequencing Segmentation Error Correction M 01 L 02 vx. x—L 02 -17


