 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Overview
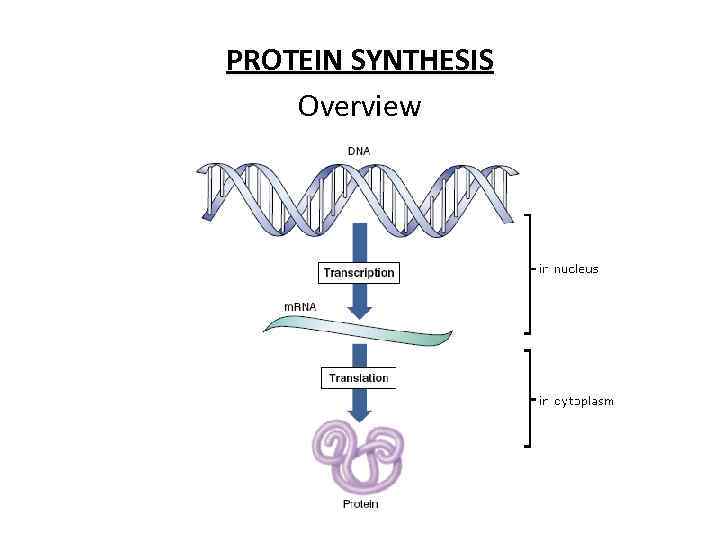
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Overview
 • DNA contain the information needed to make all of the proteins • Eye colour, hair color, and other such traits are visible because of protein synthesis. • DNA does not control protein synthesis directly. It uses RNA.
• DNA contain the information needed to make all of the proteins • Eye colour, hair color, and other such traits are visible because of protein synthesis. • DNA does not control protein synthesis directly. It uses RNA.
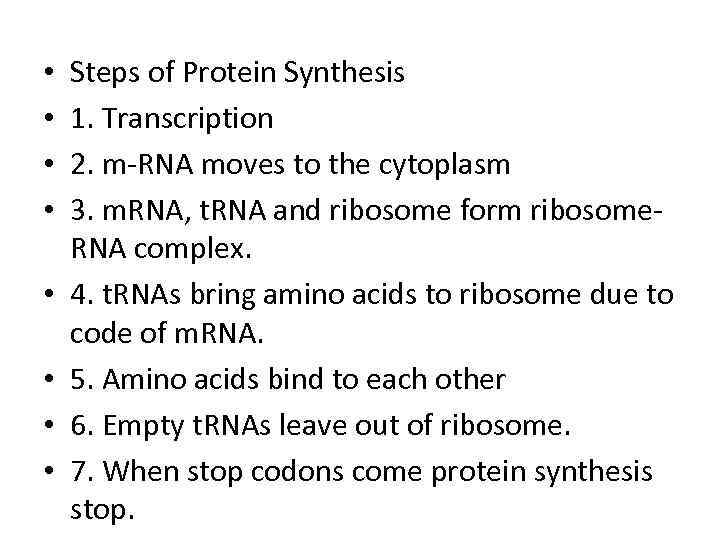 • • Steps of Protein Synthesis 1. Transcription 2. m-RNA moves to the cytoplasm 3. m. RNA, t. RNA and ribosome form ribosome. RNA complex. 4. t. RNAs bring amino acids to ribosome due to code of m. RNA. 5. Amino acids bind to each other 6. Empty t. RNAs leave out of ribosome. 7. When stop codons come protein synthesis stop.
• • Steps of Protein Synthesis 1. Transcription 2. m-RNA moves to the cytoplasm 3. m. RNA, t. RNA and ribosome form ribosome. RNA complex. 4. t. RNAs bring amino acids to ribosome due to code of m. RNA. 5. Amino acids bind to each other 6. Empty t. RNAs leave out of ribosome. 7. When stop codons come protein synthesis stop.
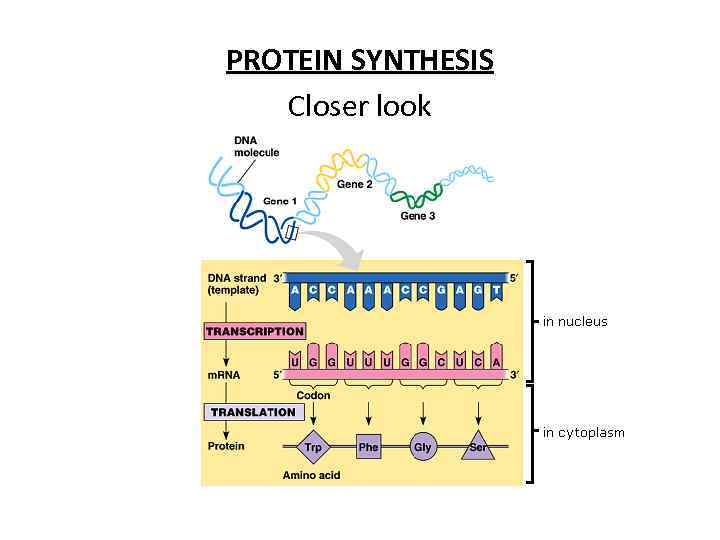 PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Closer look
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Closer look
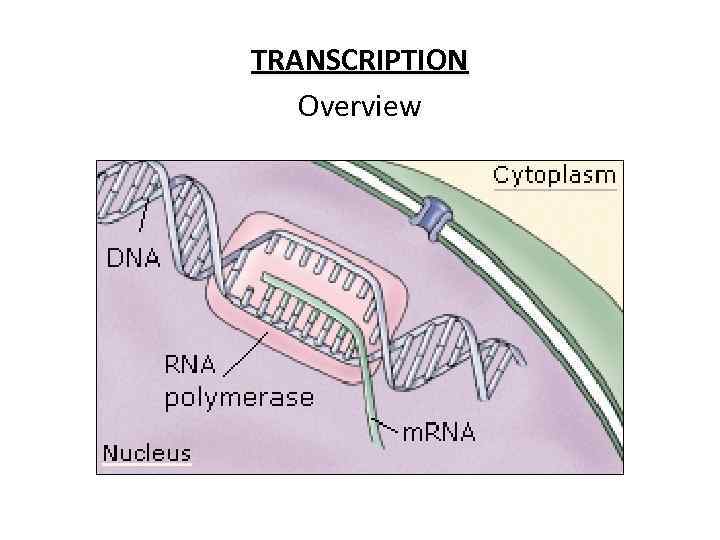 TRANSCRIPTION Overview
TRANSCRIPTION Overview
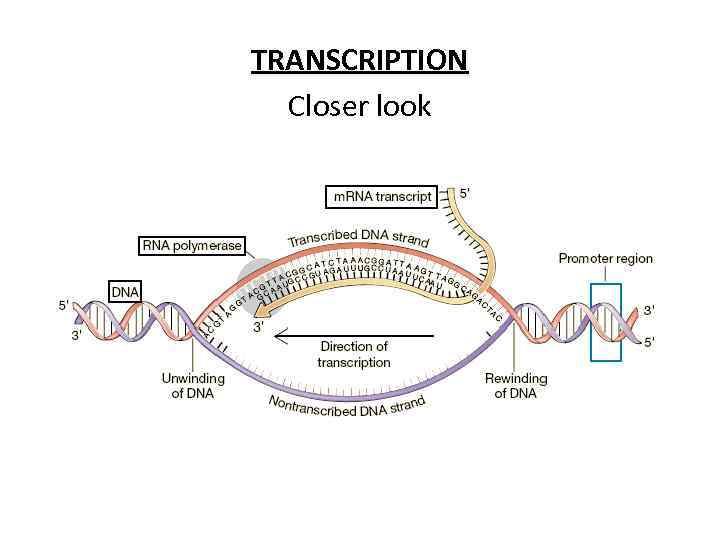 TRANSCRIPTION Closer look
TRANSCRIPTION Closer look
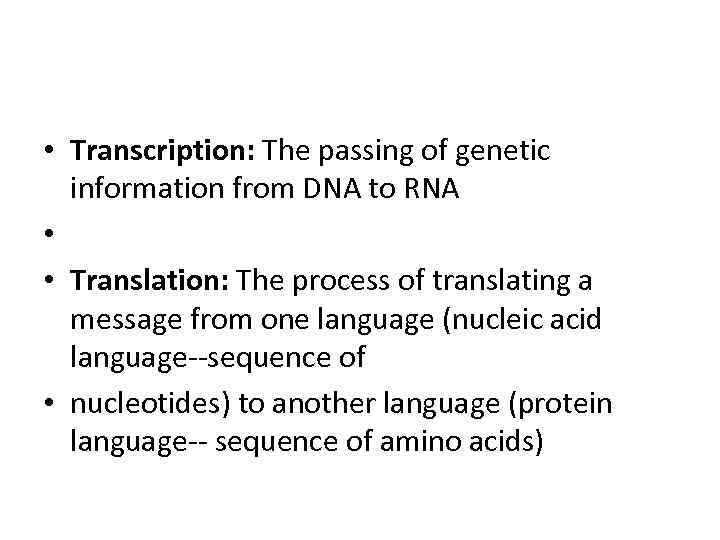 • Transcription: The passing of genetic information from DNA to RNA • • Translation: The process of translating a message from one language (nucleic acid language--sequence of • nucleotides) to another language (protein language-- sequence of amino acids)
• Transcription: The passing of genetic information from DNA to RNA • • Translation: The process of translating a message from one language (nucleic acid language--sequence of • nucleotides) to another language (protein language-- sequence of amino acids)
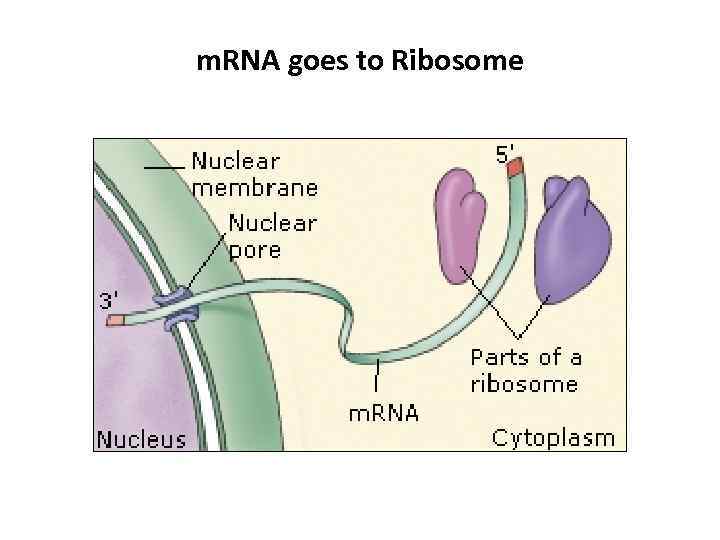 m. RNA goes to Ribosome
m. RNA goes to Ribosome
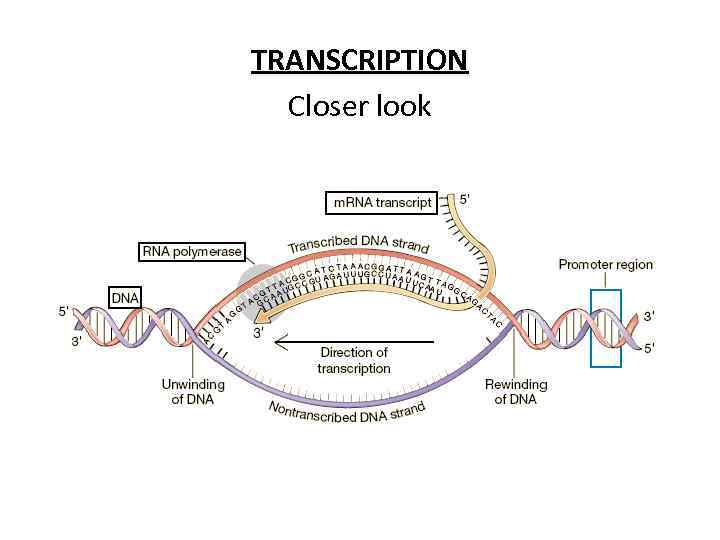 TRANSCRIPTION Closer look
TRANSCRIPTION Closer look
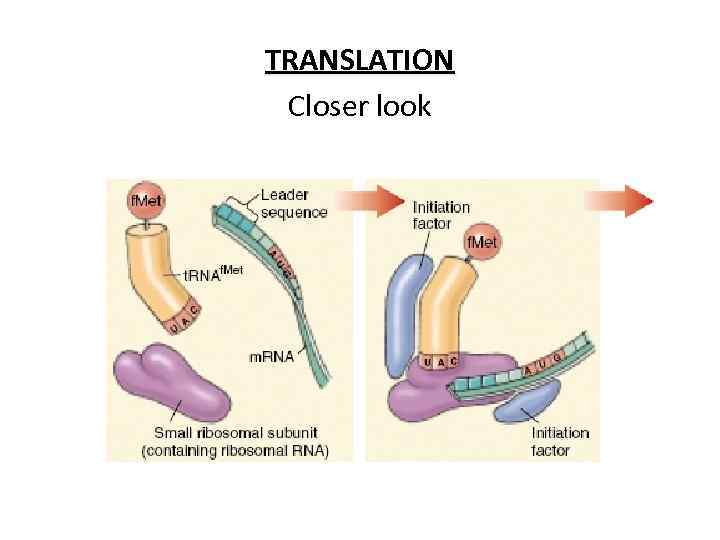 TRANSLATION Closer look
TRANSLATION Closer look
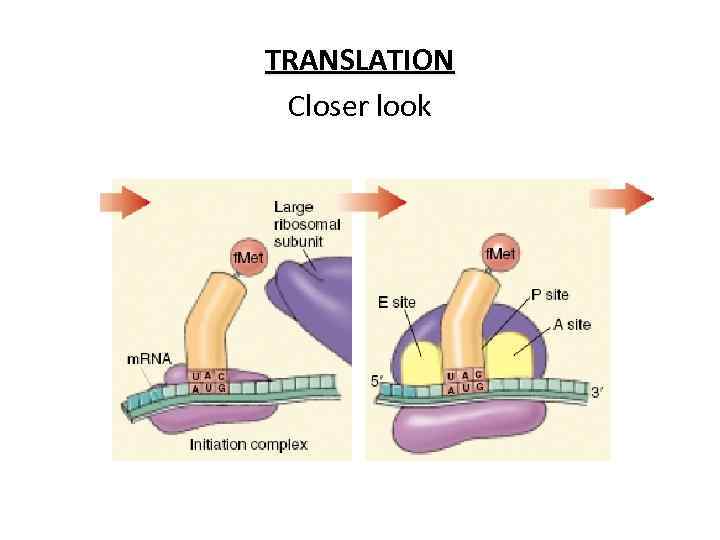 TRANSLATION Closer look
TRANSLATION Closer look
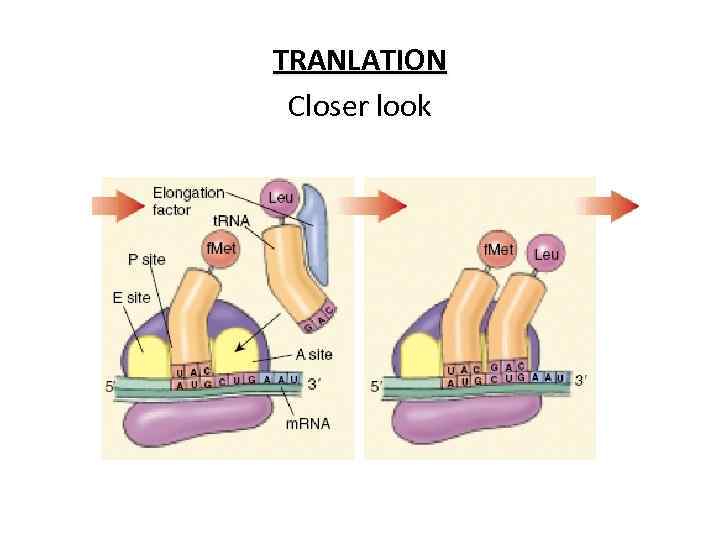 TRANLATION Closer look
TRANLATION Closer look
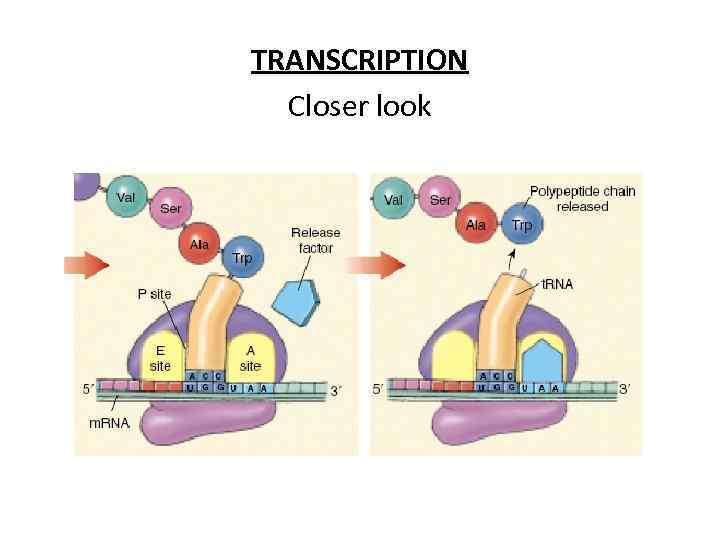 TRANSCRIPTION Closer look
TRANSCRIPTION Closer look
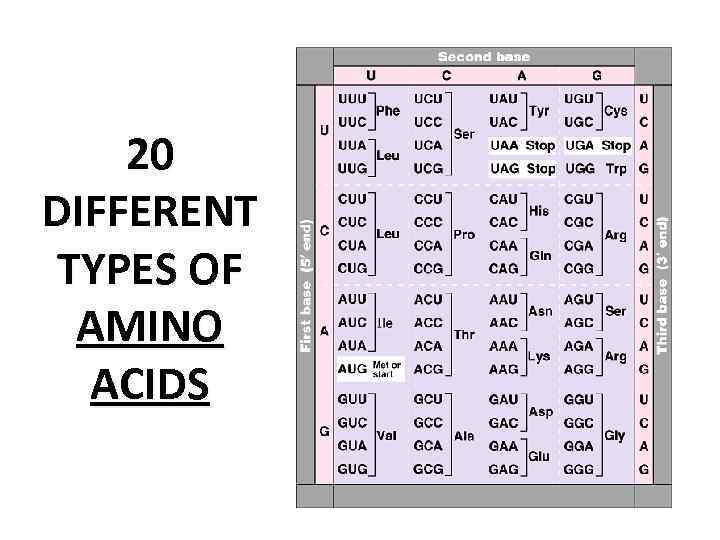 20 DIFFERENT TYPES OF AMINO ACIDS
20 DIFFERENT TYPES OF AMINO ACIDS
 REVIEW TEST: 1. When RNA is being made, the RNA base ____ always pairs with the base _____ in DNA. A) B) C) D) E) U. . . T T. . . G U. . . A A. . . U T. . . A
REVIEW TEST: 1. When RNA is being made, the RNA base ____ always pairs with the base _____ in DNA. A) B) C) D) E) U. . . T T. . . G U. . . A A. . . U T. . . A
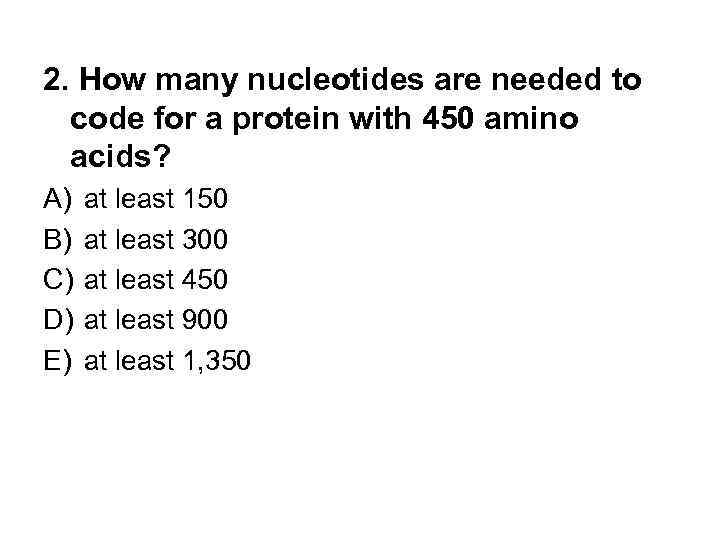 2. How many nucleotides are needed to code for a protein with 450 amino acids? A) B) C) D) E) at least 150 at least 300 at least 450 at least 900 at least 1, 350
2. How many nucleotides are needed to code for a protein with 450 amino acids? A) B) C) D) E) at least 150 at least 300 at least 450 at least 900 at least 1, 350
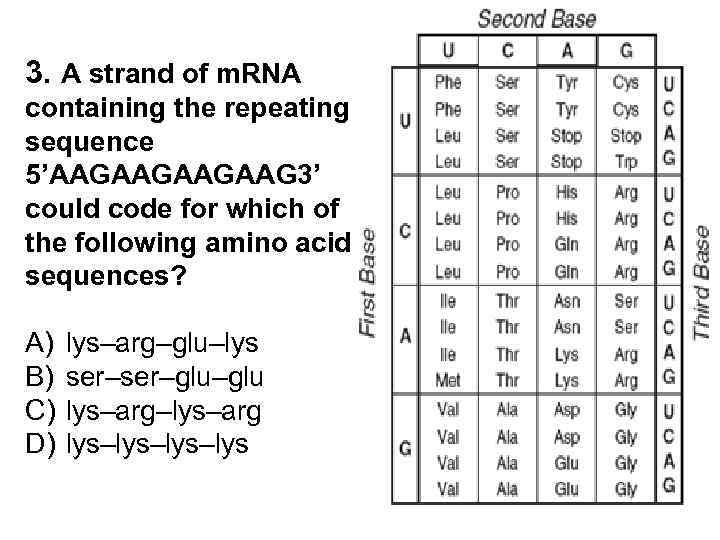 3. A strand of m. RNA containing the repeating sequence 5’AAGAAG 3’ could code for which of the following amino acid sequences? A) B) C) D) lys–arg–glu–lys ser–glu–glu lys–arg–lys–arg lys–lys–lys
3. A strand of m. RNA containing the repeating sequence 5’AAGAAG 3’ could code for which of the following amino acid sequences? A) B) C) D) lys–arg–glu–lys ser–glu–glu lys–arg–lys–arg lys–lys–lys