e0880dcc50d8264f5aaaa007db54aeba.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 54
Protein Replacement Therapy for Mitochondrial Diseases Integrative Biology, Berlin, July, 2016 Prof. Haya Lorberboum-Galski Institute for Medical Research (IMRIC) Faculty of Medicine, Hebrew University
Modern medicine offers no cure for mitochondrial disorders….
Treatment is mostly palliative: Vitamins • Co-factors • Oxygen-radical scavengers •
The Approach: Enzyme/Protein Replacement Therapy • The deficient protein/enzyme - artificially manufactured and purified with modifications. • Given to patients regularly. • Current treatment for lysosomal storage diseases. (Gaucher, Fabry, MPS-1) • Not for metabolic deficiencies with CNS involvement.
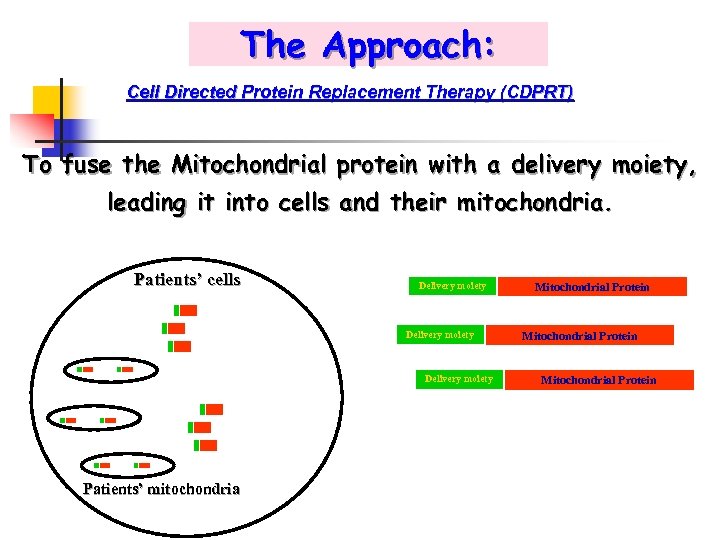
The Approach: Cell Directed Protein Replacement Therapy (CDPRT) To fuse the Mitochondrial protein with a delivery moiety, leading it into cells and their mitochondria. Patients’ cells Delivery moiety Patients’ mitochondria Mitochondrial Protein
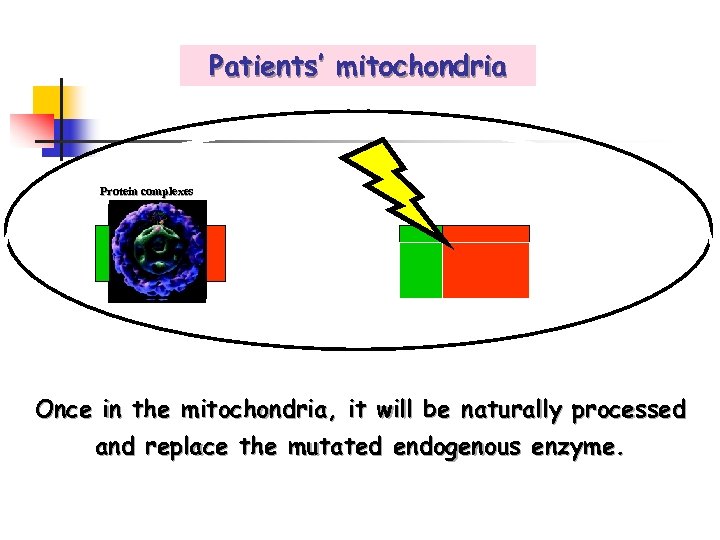
Patients’ mitochondria Protein complexes Once in the mitochondria, it will be naturally processed and replace the mutated endogenous enzyme.
Which delivery moiety to choose? In mitochondrial disorders: Ø Several tissues involved (with different severity). Ø No need for specific targeting.
Protein Transduction Domains (PTDs) * a group of short peptides that serve as delivery vectors for large molecules. * are defined as short, water-soluble and partly hydrophobic, and/or polybasic peptides. * at most 30– 35 amino acids residues. * with a net positive charge at physiological p. H.
PTDs * The main feature of PTDs is that they are able to penetrate biological membranes at low micromolar concentrations in vitro and in vivo without using any chiral receptors and without causing significant membrane damage. * Furthermore, and even more importantly, these peptides are capable of internalizing electrostatically or covalently bound biologically active cargoes such as drugs with high efficiency and low toxicity.
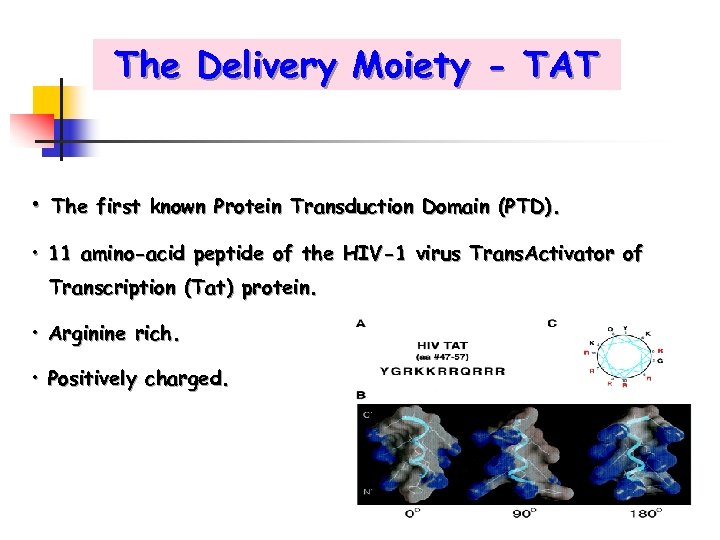
The Delivery Moiety - TAT • The first known Protein Transduction Domain (PTD). • 11 amino-acid peptide of the HIV-1 virus Trans. Activator of Transcription (Tat) protein. • Arginine rich. • Positively charged.
The Delivery Moiety - TAT-fusion proteins cross cell membranes including mitochondrial membranes while retaining their biological activity both in-vitro and in-vivo! The Problem……TAT-fusion proteins are crossing biological membranes: In-Out…!!!
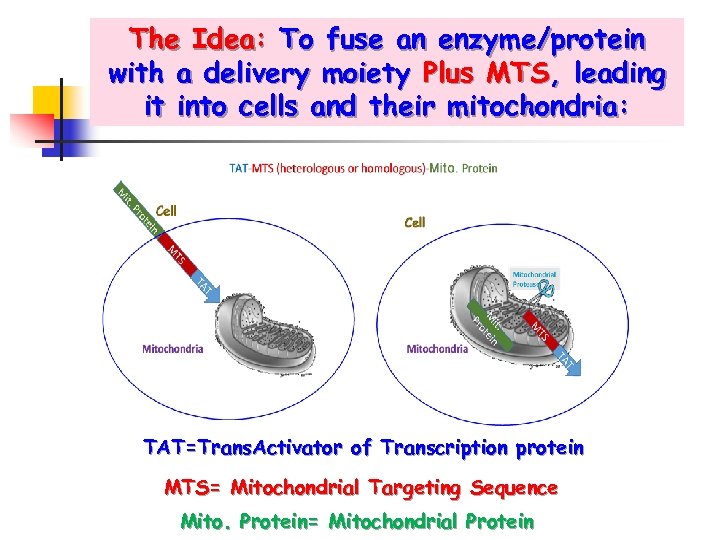
The Idea: To fuse an enzyme/protein with a delivery moiety Plus MTS, leading it into cells and their mitochondria: TAT=Trans. Activator of Transcription protein MTS= Mitochondrial Targeting Sequence Mito. Protein= Mitochondrial Protein
Cell/Organelle-Directed Protein Replacement Therapy for: • Lipoamide Dehydrogenease (LAD) (Rapoport et al 2008, 2011) • C 6 ORF 66 (NDUFAF 4; ORF) (Marcus et al 2013) • Ornitine Transcarbomylase (OTC) • Frataxin (FXN) (Marcus et al, submitted) • Methylmalonyl Co. A mutase (MCM) (Erlich et al, in preparation)
Lipoamide Dehydrogenase (LAD): • The E 3 subunit of the three -ketoacid dehydrogenase complexes: Ø Pyruvate Dehydrogenase (PDHC). Ø -Ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase (KGDHC). Ø Branched-Chain Ketoacid Dehydrogenase (BCKDHC). • The L-protein component in the glycine cleavage system .
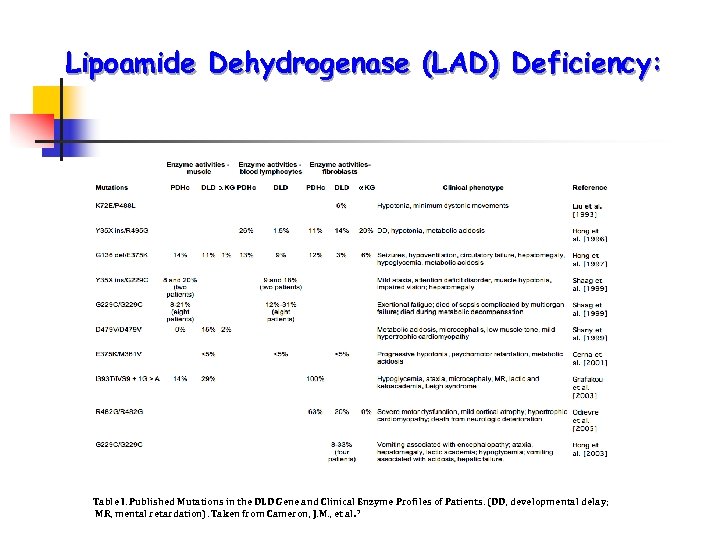
Lipoamide Dehydrogenase (LAD) Deficiency: Table I. Published Mutations in the DLD Gene and Clinical Enzyme Profiles of Patients. (DD, developmental delay; MR, mental retardation). Taken from Cameron, J. M. , et al. 7
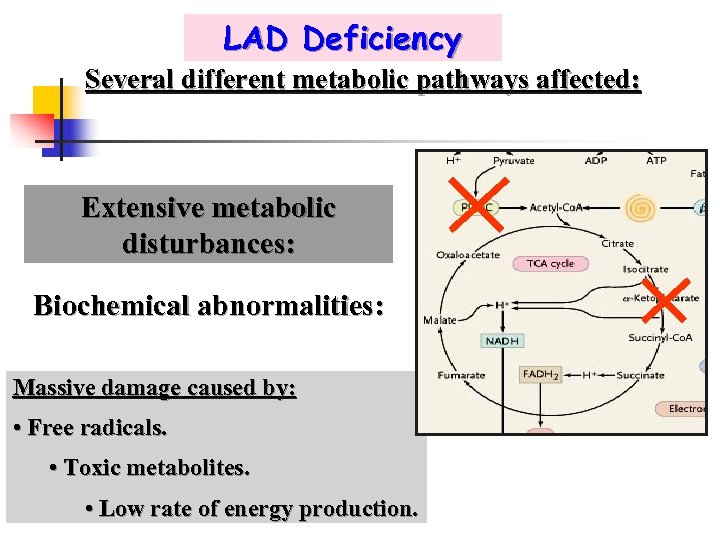
LAD Deficiency Several different metabolic pathways affected: Extensive metabolic disturbances: Biochemical abnormalities: Massive damage caused by: • Free radicals. • Toxic metabolites. • Low rate of energy production.
LAD deficiency - Clinical Course • Variable clinical course (type of mutation, homozygosity/compound), Ranging from: Infantile neurodegenerative disease: • Severe psychomotor retardation in infancy. • Lactic acidemia. • Death by early childhood. Episodes of liver failure: • Recurrent vomiting and abdominal pain. • Encephalopathy. • Elevated liver transaminases and prolonged prothrombin time. • Lactic and ketoacidemia.
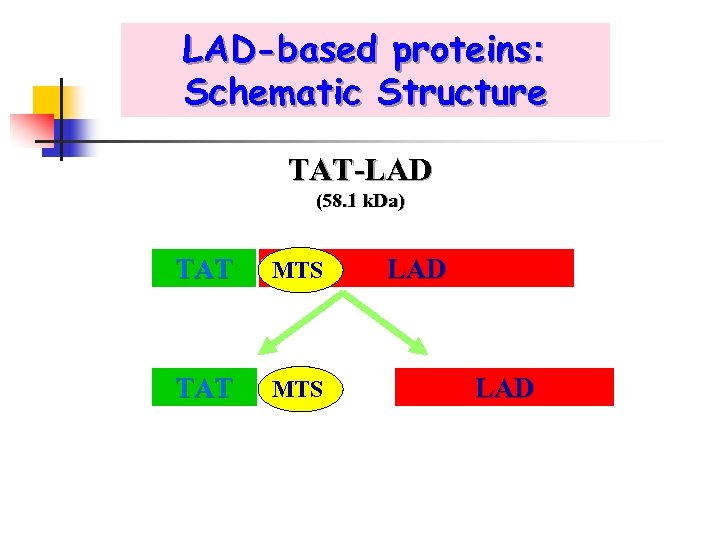
LAD-based proteins: Schematic Structure TAT-LAD (58. 1 k. Da) TAT MTS LAD
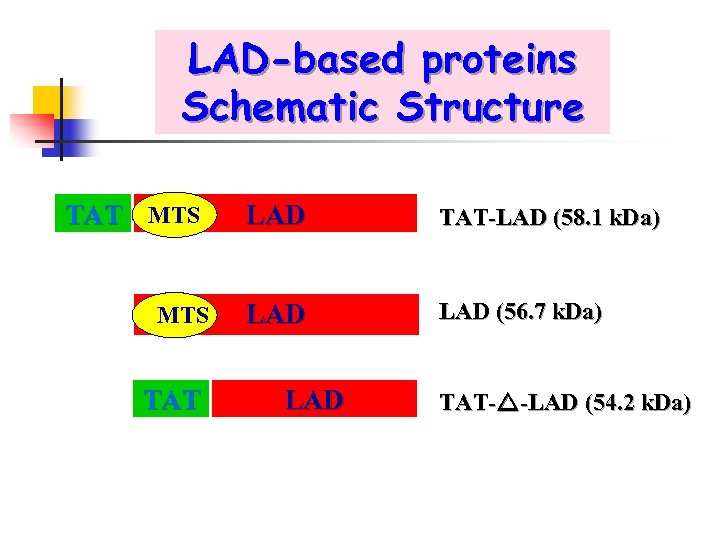
LAD-based proteins Schematic Structure TAT MTS LAD TAT-LAD (58. 1 k. Da) MTS LAD (56. 7 k. Da) TAT LAD TAT- -LAD (54. 2 k. Da)
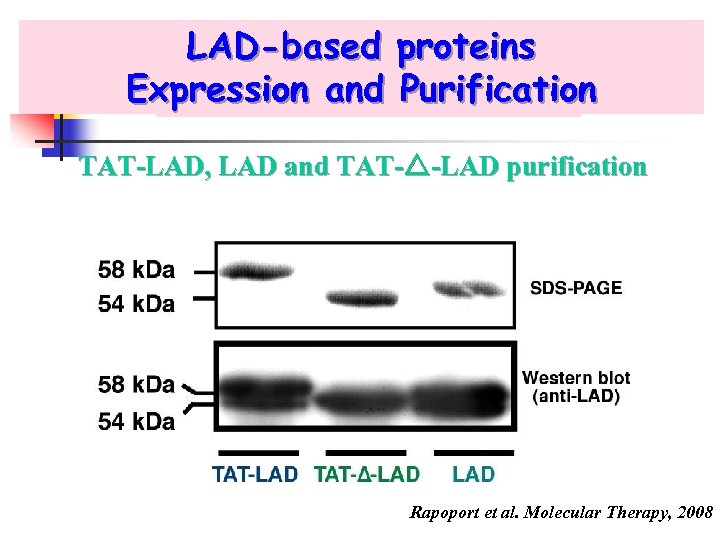
LAD-based proteins Expression and Purification : TAT-LAD, LAD and TAT- -LAD purification Rapoport et al. Molecular Therapy, 2008
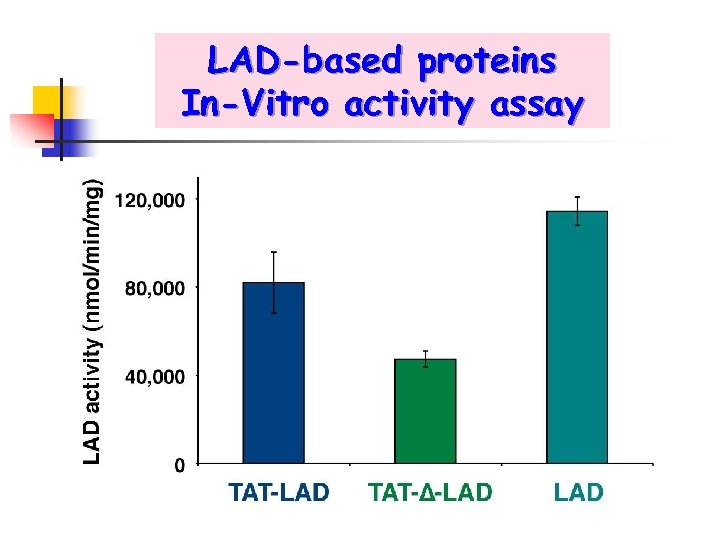
LAD-based proteins In-Vitro activity assay
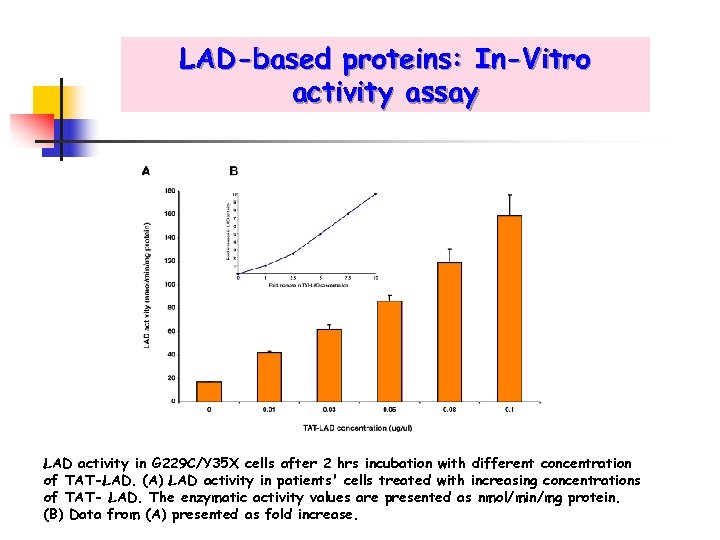
LAD-based proteins: In-Vitro activity assay LAD activity in G 229 C/Y 35 X cells after 2 hrs incubation with different concentration of TAT-LAD. (A) LAD activity in patients' cells treated with increasing concentrations of TAT- LAD. The enzymatic activity values are presented as nmol/min/mg protein. (B) Data from (A) presented as fold increase.
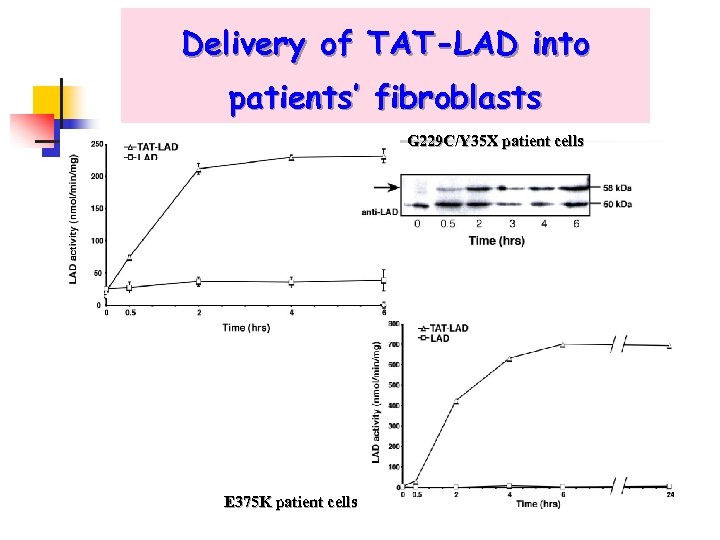
Delivery of TAT-LAD into patients’ fibroblasts G 229 C/Y 35 X patient cells E 375 K patient cells
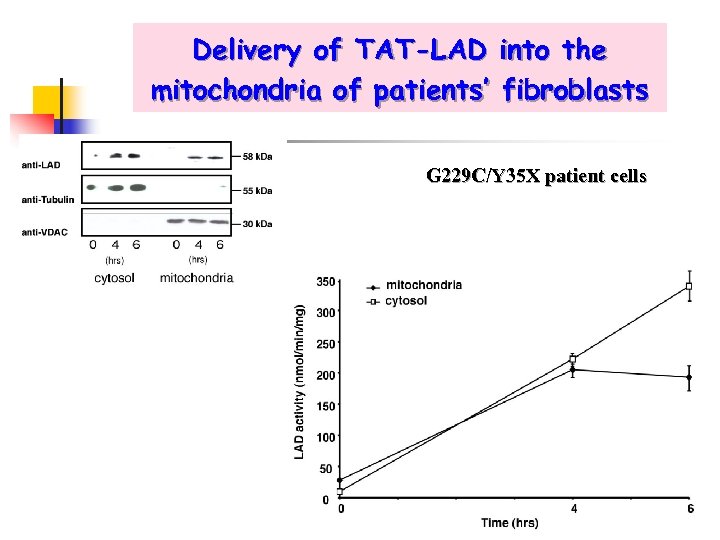
Delivery of TAT-LAD mitochondria of patients’ into the fibroblasts G 229 C/Y 35 X patient cells
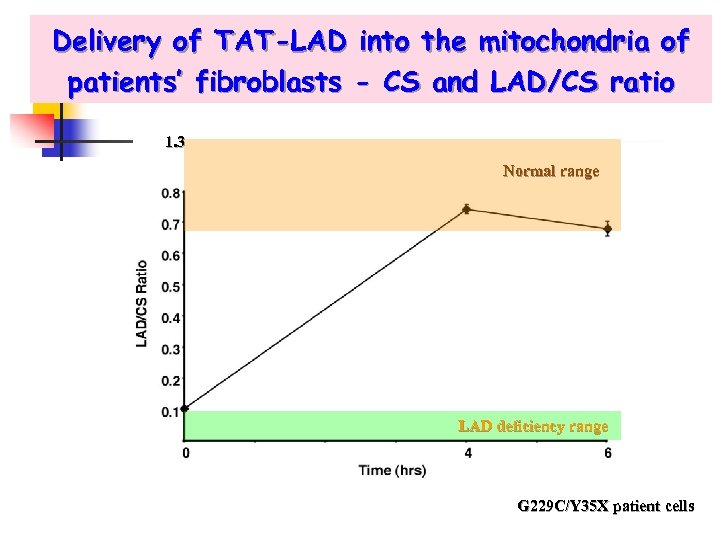
Delivery of TAT-LAD into the mitochondria of patients’ fibroblasts - CS and LAD/CS ratio 1. 3 Normal range LAD deficiency range G 229 C/Y 35 X patient cells
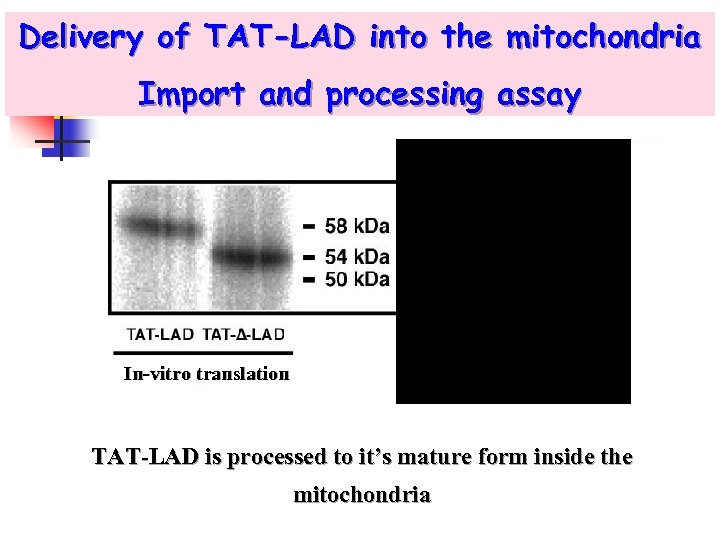
Delivery of TAT-LAD into the mitochondria Import and processing assay In-vitro translation Inside mitochondria TAT-LAD is processed to it’s mature form inside the mitochondria

Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex (PDHC) • 9. 5 x 106 Da “Machine” Ø Core of 60 subunits of E 2. Ø 30 molecules of E 1 (heterodimer of 2 a; 2 b subunits). Ø 6 molecules of the homodimeric E 3. Ø 12 molecules of the E 3 binding protein. • Similar structure to all -ketoacide dehydrogenase complexes.
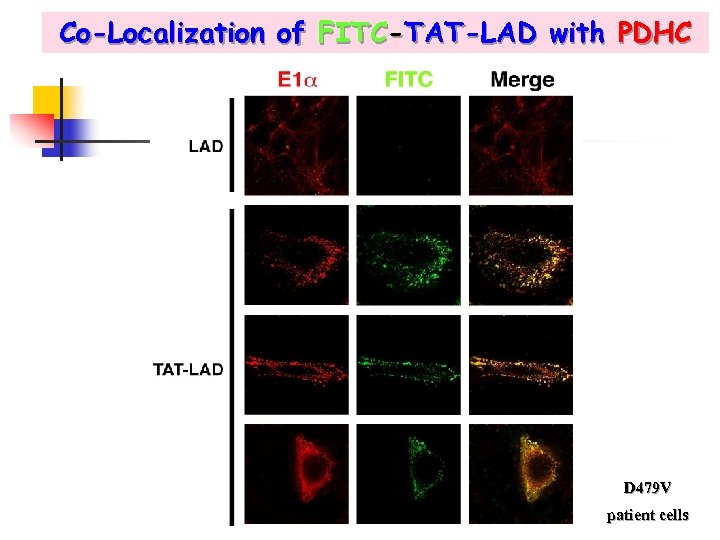
Co-Localization of FITC-TAT-LAD with PDHC D 479 V patient cells
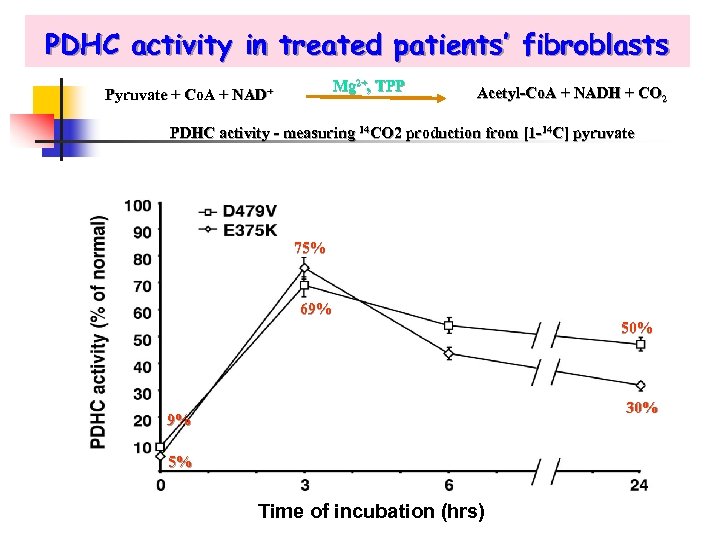
PDHC activity in treated patients’ fibroblasts Mg 2+, TPP Pyruvate + Co. A + NAD+ Acetyl-Co. A + NADH + CO 2 PDHC activity - measuring 14 CO 2 production from [1 -14 C] pyruvate 75% 69% 50% 30% 9% 5% Time of incubation (hrs)
Summary - Patients’ fibroblasts TAT-LAD successfully competes with the endogenous mutated LAD: Dimerization and PDHC integration. Replacement of ONE mutated component is sufficient to restore the activity of a HUGE ENZYMATIC COMPLEX. Rapoport et al. Mol Ther. 2008
The mouse model of LAD deficiency (E 3 Mice) • Heterozygotes to a recessive loss-of-function mutation affecting the Dld gene. • Homozygous mice (Dld-/-) stop developing and die in-utero at early gastrulation. LAD activity: ~50% of WT -ketoacid dehydrogenase complexes: ~50% of WT Heterozygous E 3 mice are phenotipically normal (humans carriers of LAD deficiency present no clinical symptoms).
Experimental Design Time (hrs) At different time points Organs removal and analysis (4 -12 mice at each time point) A single injection (i. v. ) of TAT-LAD or LAD (10 units)
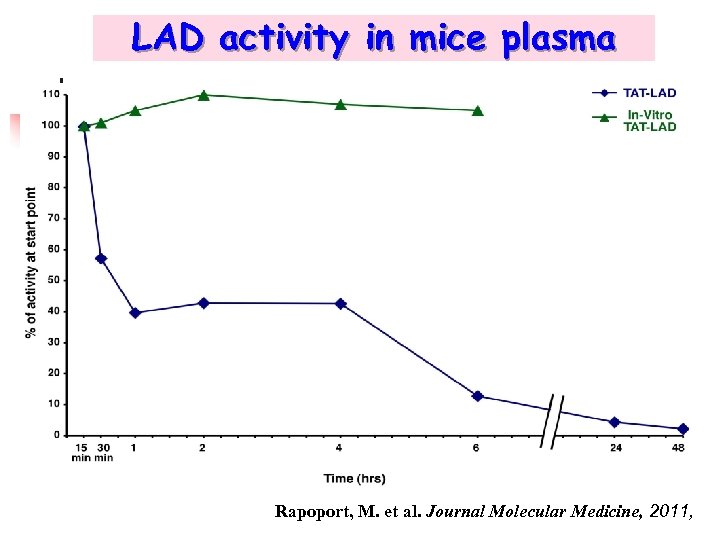
LAD activity in mice plasma Rapoport, M. et al. Journal Molecular Medicine, 2011,
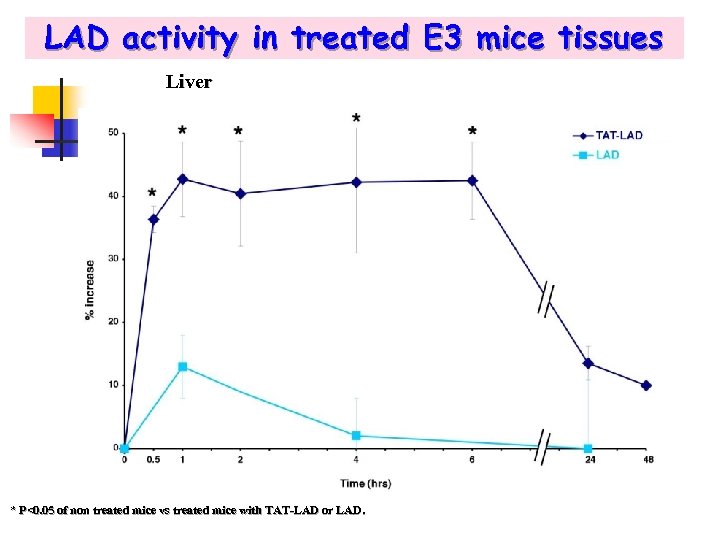
LAD activity in treated E 3 mice tissues Liver * P<0. 05 of non treated mice vs treated mice with TAT-LAD or LAD.
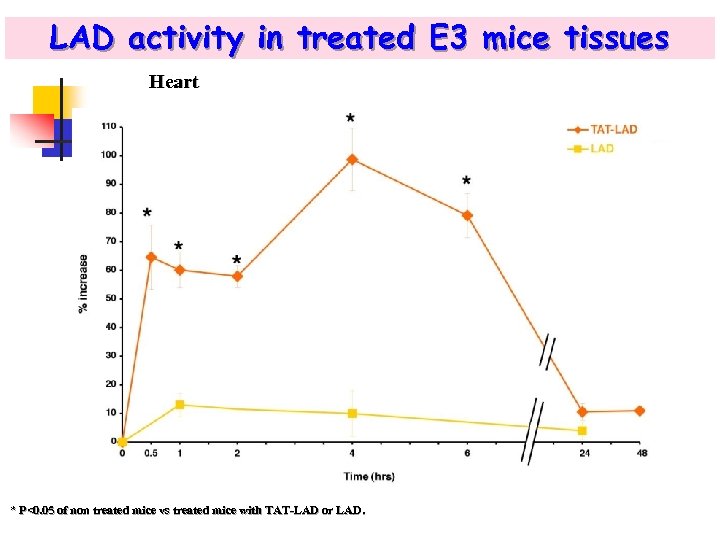
LAD activity in treated E 3 mice tissues Heart * P<0. 05 of non treated mice vs treated mice with TAT-LAD or LAD.
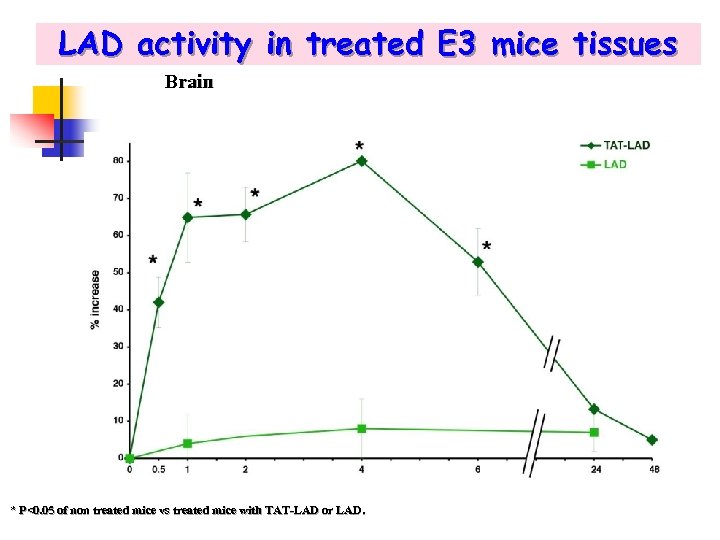
LAD activity in treated E 3 mice tissues Brain * P<0. 05 of non treated mice vs treated mice with TAT-LAD or LAD.
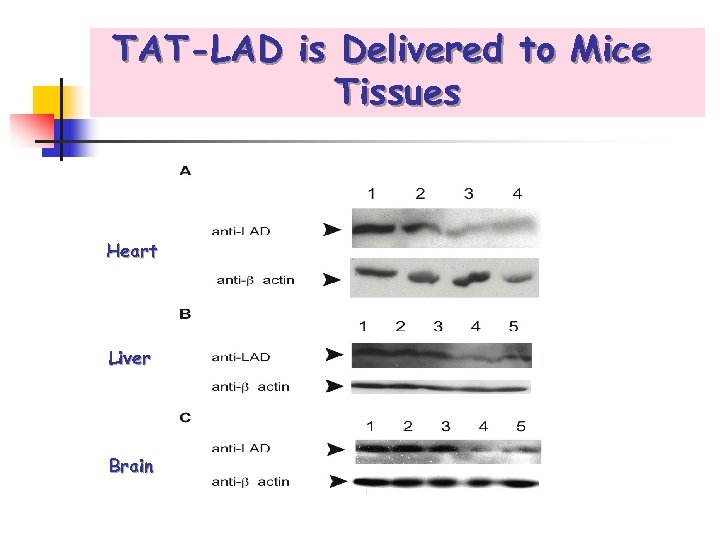
TAT-LAD is Delivered to Mice Tissues Heart Liver Brain
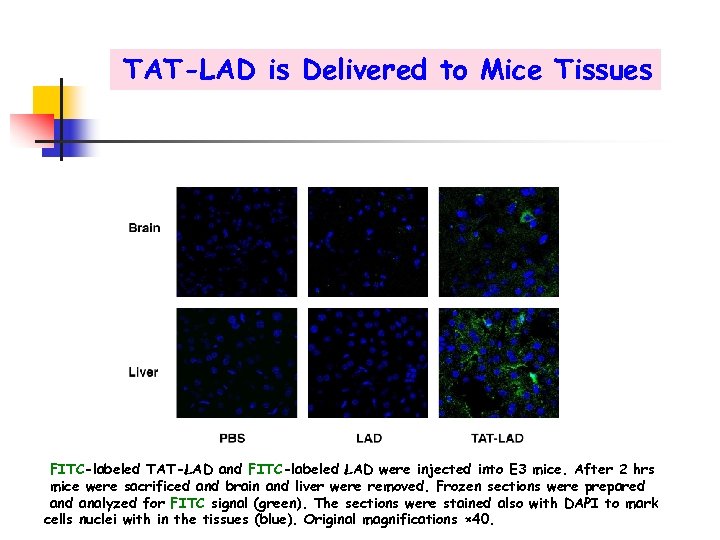
TAT-LAD is Delivered to Mice Tissues FITC-labeled TAT-LAD and FITC-labeled LAD were injected into E 3 mice. After 2 hrs mice were sacrificed and brain and liver were removed. Frozen sections were prepared analyzed for FITC signal (green). The sections were stained also with DAPI to mark cells nuclei with in the tissues (blue). Original magnifications × 40.
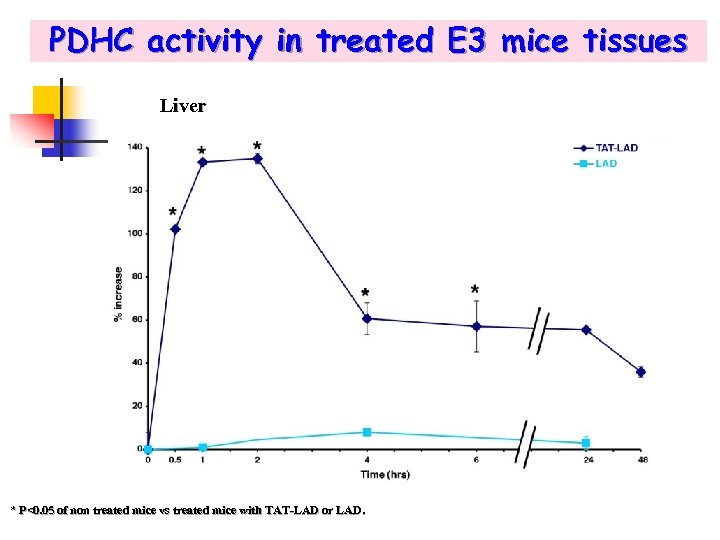
PDHC activity in treated E 3 mice tissues Liver * P<0. 05 of non treated mice vs treated mice with TAT-LAD or LAD.
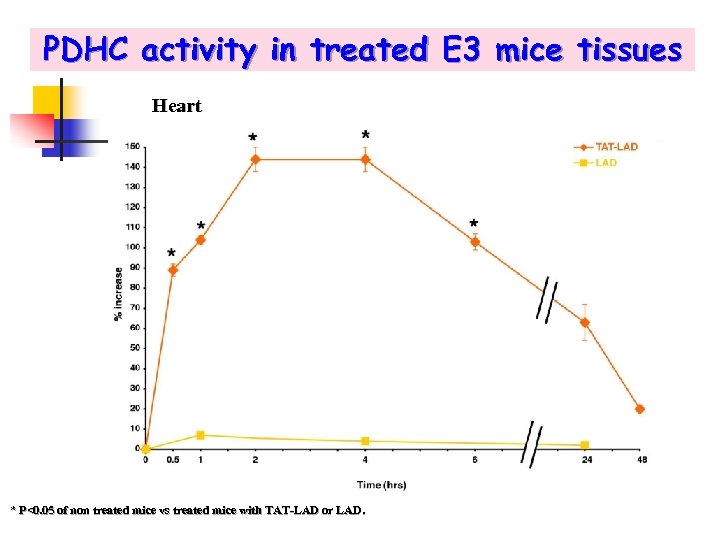
PDHC activity in treated E 3 mice tissues Heart * P<0. 05 of non treated mice vs treated mice with TAT-LAD or LAD.
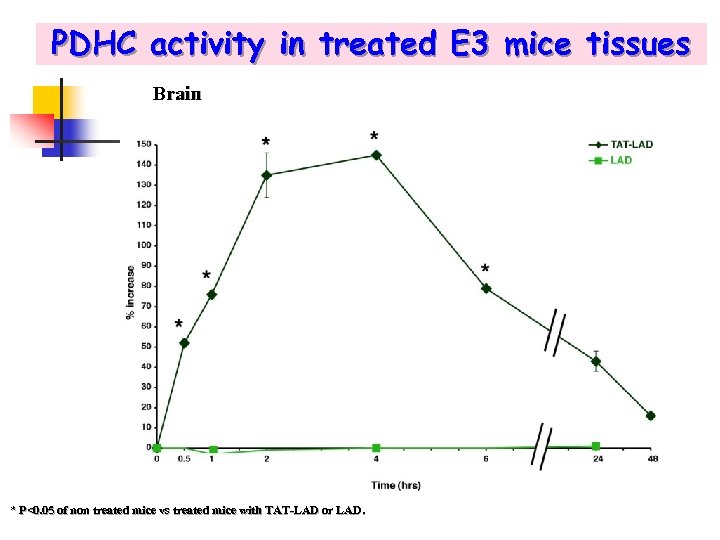
PDHC activity in treated E 3 mice tissues Brain * P<0. 05 of non treated mice vs treated mice with TAT-LAD or LAD.
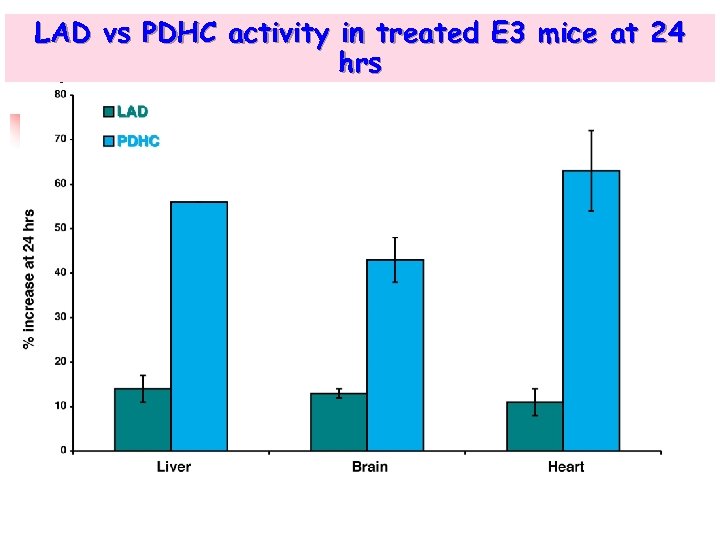
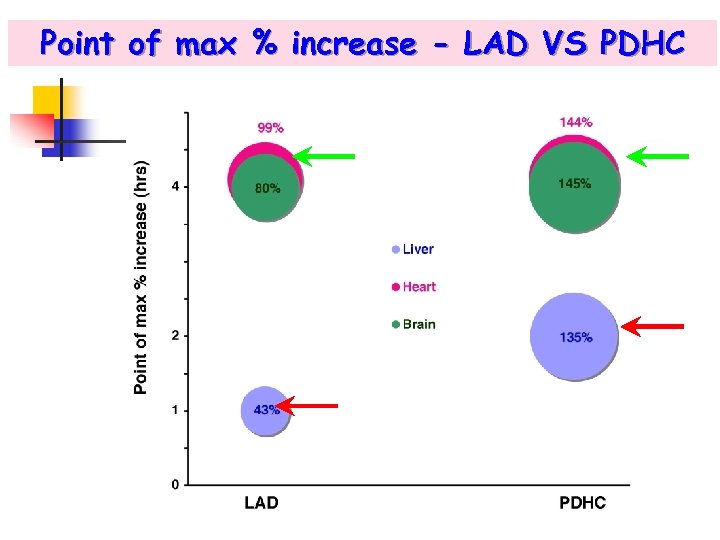
LAD vs PDHC activity in treated E 3 mice at 24 hrs
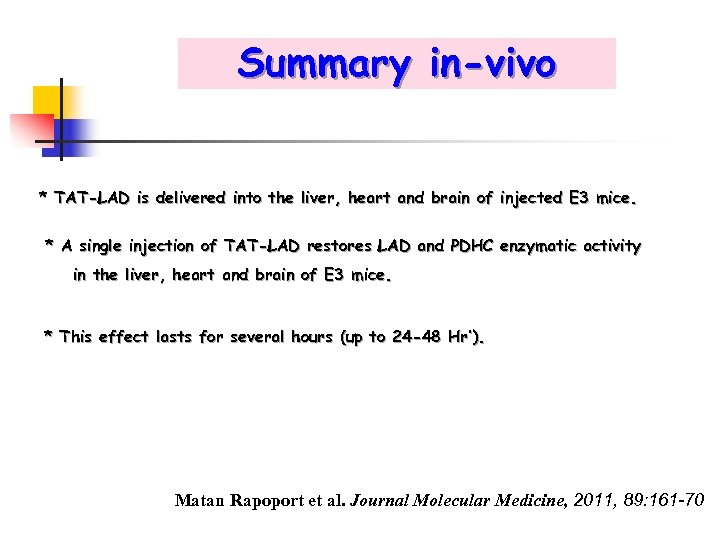
Summary in-vivo * TAT-LAD is delivered into the liver, heart and brain of injected E 3 mice. * A single injection of TAT-LAD restores LAD and PDHC enzymatic activity in the liver, heart and brain of E 3 mice. * This effect lasts for several hours (up to 24 -48 Hr’). Matan Rapoport et al. Journal Molecular Medicine, 2011, 89: 161 -70
Cell/Organelle-Directed Protein Replacement Therapy for: • Lipoamide Dehydrogenease (LAD) (Rapoport et al 2008, 2011) • C 6 ORF 66 (NDUFAF 4; ORF) (Marcus et al 2013) • Ornitine Transcarbomylase (OTC) • Frataxin (FXN) (Marcus et al, submitted) • Methylmalonyl Co. A mutase (MCM) (Erlich et al, in preparation)
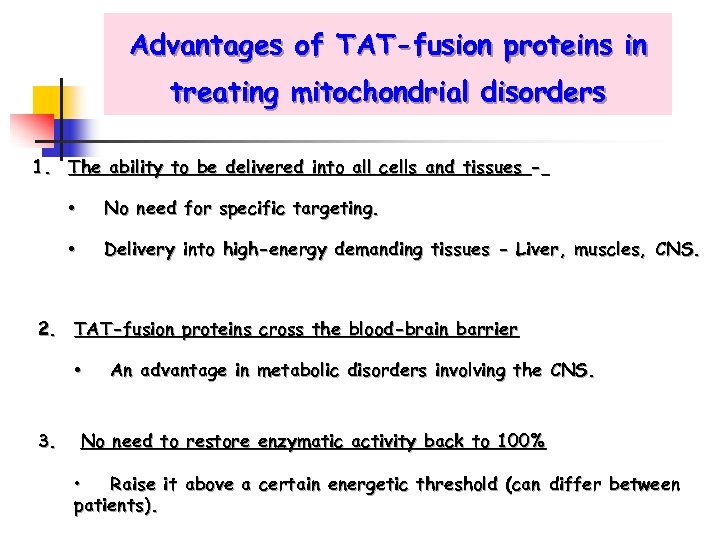
Advantages of TAT-fusion proteins in treating mitochondrial disorders 1. The ability to be delivered into all cells and tissues • No need for specific targeting. • Delivery into high-energy demanding tissues - Liver, muscles, CNS. 2. TAT-fusion proteins cross the blood-brain barrier • 3. An advantage in metabolic disorders involving the CNS. No need to restore enzymatic activity back to 100% • Raise it above a certain energetic threshold (can differ between patients).

The Future… This approach could be applied to the many other known mitochondrial and metabolic disorders Revolutionize the management of these types of disorders in modern medicine TAT open the Door……
Acknowledgements…. . Lab members: Dr. Matan Rapoport Lina Salman Dr. Michal Lichtenstein Prof. Orly Elpeleg Dana Marcus Prof. Ann Saada Natali Cohen Metabolic Disease Unit, Hadassah University Hospital, Jerusalem, Israel Dr. Tal Erlich-Hadad Rita Hadad Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology IMRIC, Faculty of Medicine, Hebrew University Bio. Blast - Pharma Ltd. Prof. Patel MS Department of Biochemistry, School of Medicine, State University of New York, Buffalo, USA

Point of max % increase - LAD VS PDHC
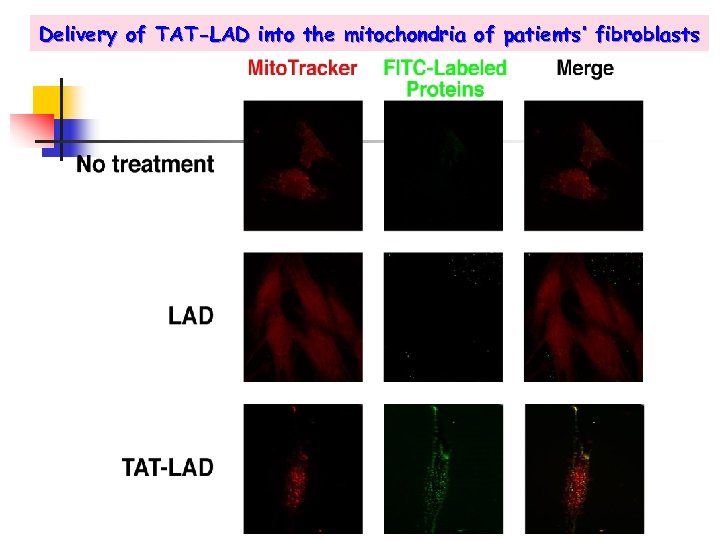
Delivery of TAT-LAD into the mitochondria of patients’ fibroblasts
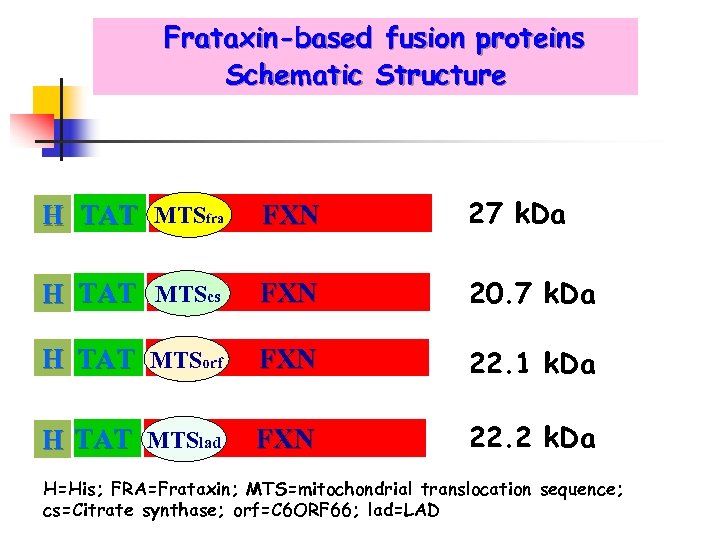
Frataxin-based fusion proteins Schematic Structure Hi s H TAT MTSfra FXN 27 k. Da H TAT MTScs FXN 20. 7 k. Da H TAT MTSorf FXN 22. 1 k. Da H TAT MTSlad FXN 22. 2 k. Da H=His; FRA=Frataxin; MTS=mitochondrial translocation sequence; cs=Citrate synthase; orf=C 6 ORF 66; lad=LAD
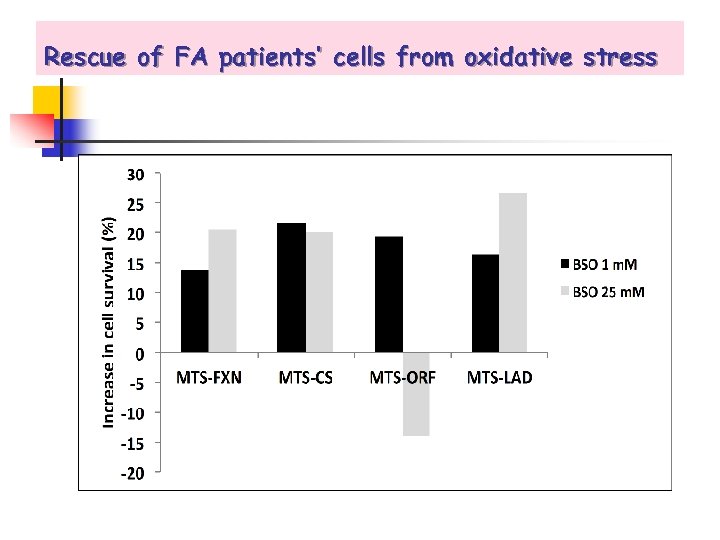
Rescue of FA patients’ cells from oxidative stress
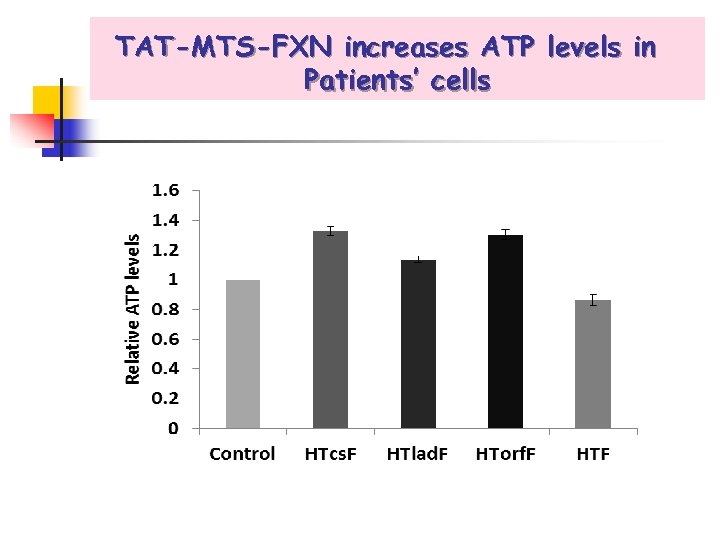
TAT-MTS-FXN increases ATP levels in Patients’ cells
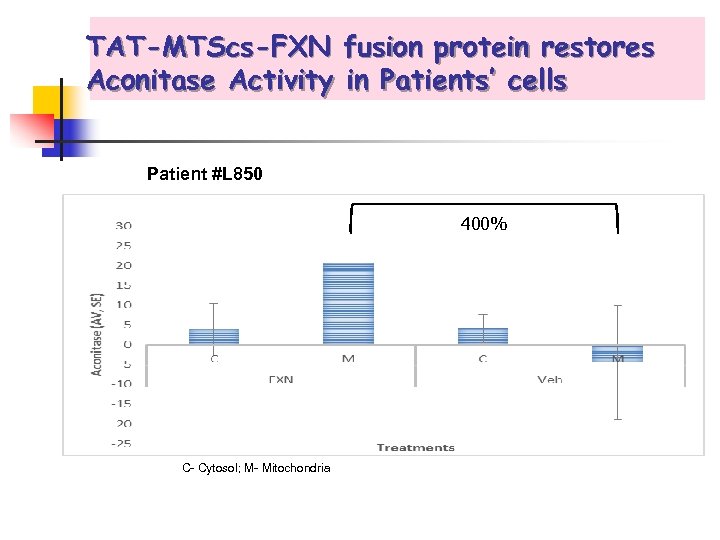
TAT-MTScs-FXN fusion protein restores Aconitase Activity in Patients’ cells Patient #L 850 400% C- Cytosol; M- Mitochondria
e0880dcc50d8264f5aaaa007db54aeba.ppt