F_L_07-08.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 34

PROTEIN PHYSICS LECTURES 7 -8 Basics of thermodynamics & kinetics

THERMODYNAMISC & STATISTICAL PHYSICS
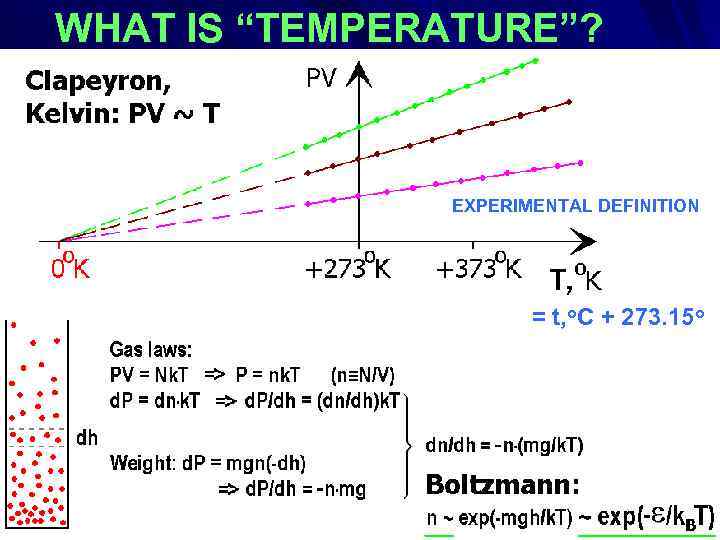
WHAT IS “TEMPERATURE”? EXPERIMENTAL DEFINITION : EXPERIMENTAL DEFINITION = t, o. C + 273. 15 o

Benoît Paul Émile Clapeyron (1799 – 1864) William Thomson, 1 st Baron Kelvin (1824 -1907) Ludwig Eduard Boltzmann (1844 – 1906)
![WHAT IS “TEMPERATURE”? THEORY S ~ ln[M] Closed system: energy E = const CONSIDER: WHAT IS “TEMPERATURE”? THEORY S ~ ln[M] Closed system: energy E = const CONSIDER:](https://present5.com/presentation/180491336_437185164/image-5.jpg)
WHAT IS “TEMPERATURE”? THEORY S ~ ln[M] Closed system: energy E = const CONSIDER: 1 state of “small part” with & all states of thermostat with E-. Mall(E- ) = 1 • Mt(E- ) k • ln[Mt(E- )] St(E- ) St(E) - • (d. St/d. E)|E Mt(E- ) exp[St(E)/k] • exp[- • (d. St/d. E)|E/k] conclusions
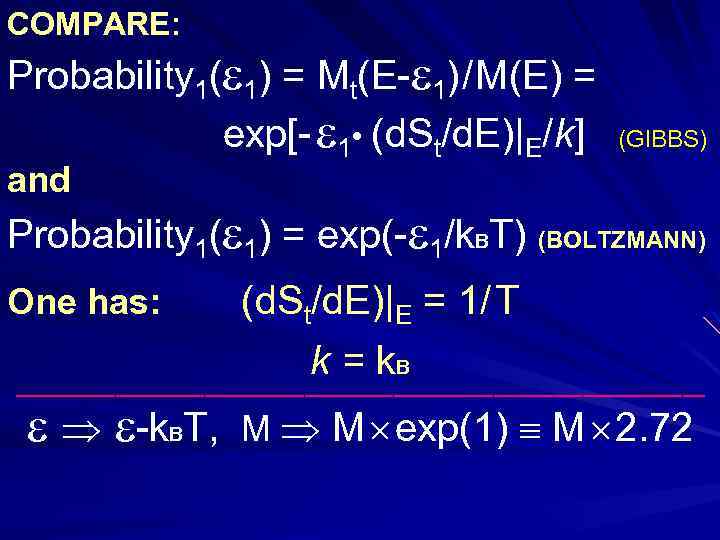
COMPARE: Probability 1( 1) = Mt(E- 1) / M(E) = exp[- 1 • (d. St/d. E)|E/k] (GIBBS) and Probability 1( 1) = exp(- 1/k. BT) (BOLTZMANN) (d. St/d. E)|E = 1/ T k = k. B _______________________________ One has: -k. BT, M M exp(1) M 2. 72

Josiah Willard Gibbs (1839 – 1903) Joseph Liouville (1809 - 1882) Яков Григорьевич Синай, 1935 Abel Prize 2014 “…связь между порядком и хаосом…” 1/r 3
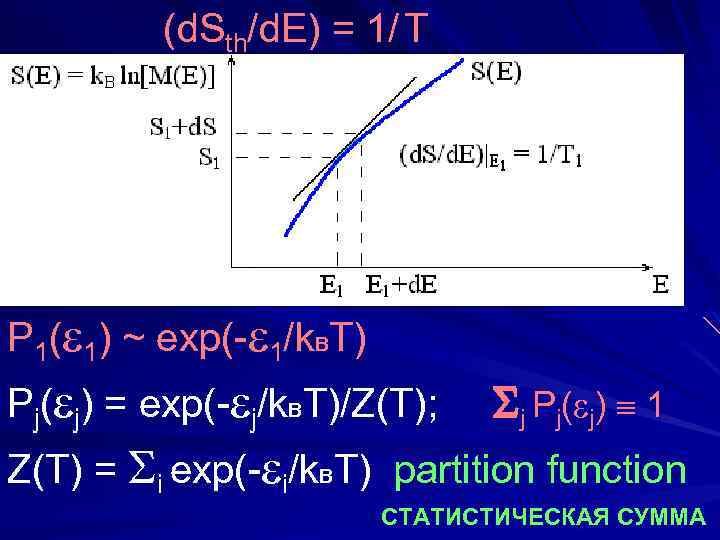
(d. Sth/d. E) = 1/ T P 1( 1) ~ exp(- 1/k. BT) Pj( j) = exp(- j/k. BT)/Z(T); j Pj( j) 1 Z(T) = i exp(- i/k. BT) partition function СТАТИСТИЧЕСКАЯ СУММА
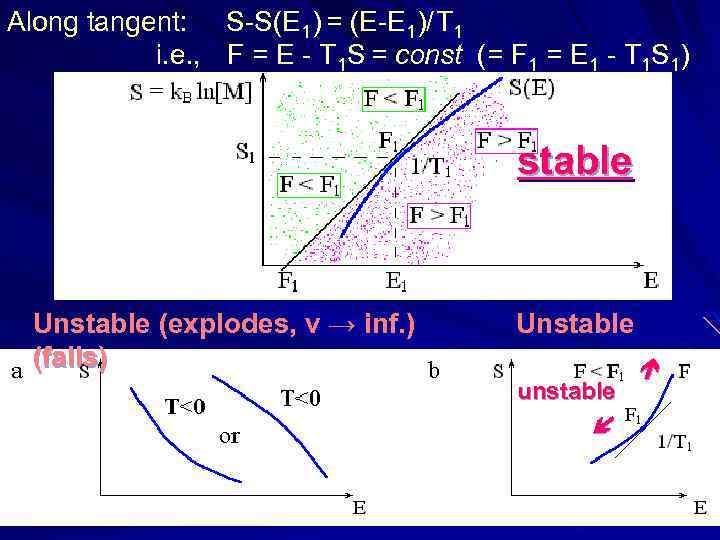
Along tangent: S-S(E 1) = (E-E 1)/ T 1 i. e. , F = E - T 1 S = const (= F 1 = E 1 - T 1 S 1) stable Unstable (explodes, v → inf. ) (falls) Unstable unstable

Separation of potential and kinetic energies in classic (non-quantum) mechanics: P( ) ~ exp(- /k. BT) // Classic: = COORD + KIN = mv 2/2 : does not depend on coordinates Potential energy COORD: depends only on coordinates P( ) ~ exp(- COORD/k. BT) • exp(- KIN/k. BT) Z(T) = ZCOORD(T) • ZKIN(T) F(T) = FCOORD(T)+FKIN(T) ============================================================ Elementary volume: (mv) x ħ ( x)3 (ħ/|mv|)3 = (ħ 2/[mk. BT])3/2 (mv) m|v|, and |mv| (mk T)1/2 B

IN THERMAL EQUILIBRIUM: TCOORD = TKIN = Touter We may consider further only potential energy: E ECOORD M MCOORD S(E) SCOORD(ECOORD ) F(E) FCOORD , etc.

TRANSITIONS: THERMODYNAMICS
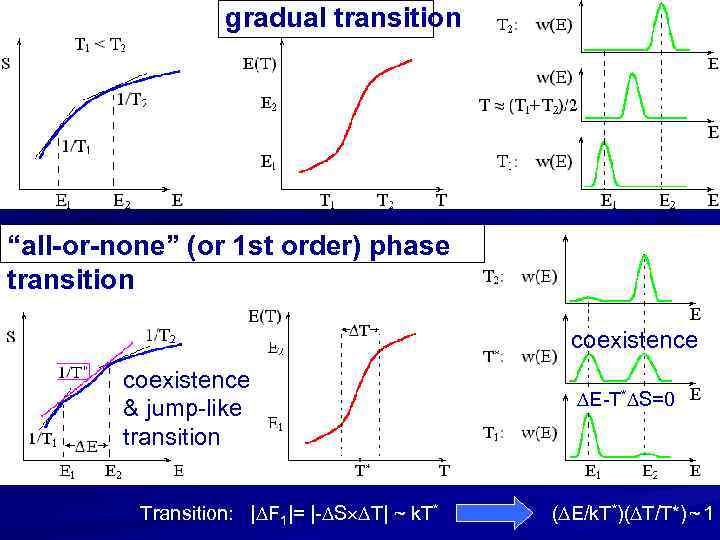
gradual transition “all-or-none” (or 1 st order) phase transition coexistence & jump-like transition Transition: | F 1|= |- S T| ~ k. T* E-T* S=0 ( E/k. T*)( T/T*) ~ 1
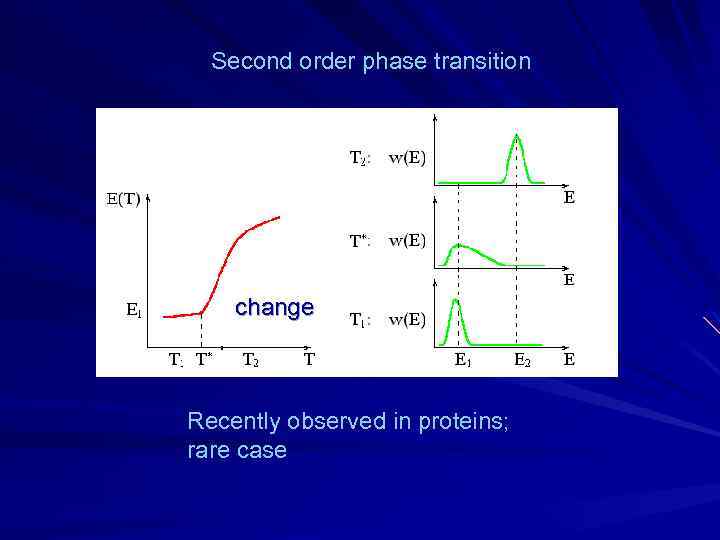
Second order phase transition change Recently observed in proteins; rare case
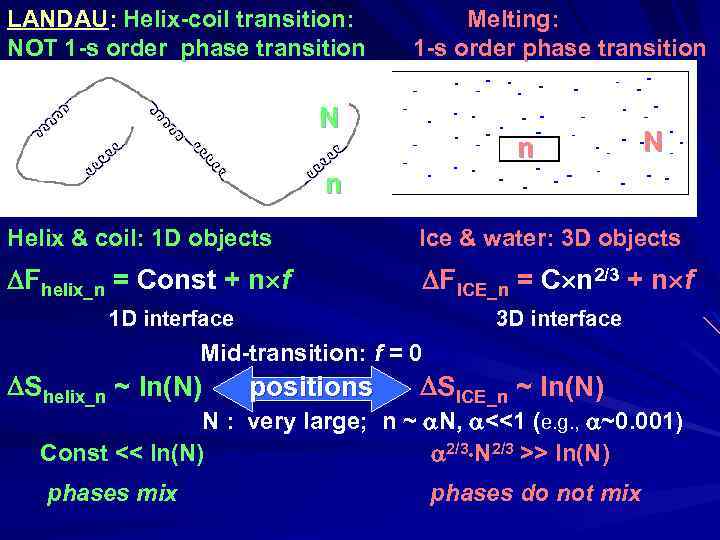
LANDAU: Helix-coil transition: NOT 1 -s order phase transition Melting: 1 -s order phase transition N n Helix & coil: 1 D objects Ice & water: 3 D objects Fhelix_n = Const + n f FICE_n = C n 2/3 + n f 1 D interface 3 D interface Mid-transition: f = 0 Shelix_n ~ ln(N) positions SICE_n ~ ln(N) N : very large; n ~ N, <<1 (e. g. , ~0. 001) Const << ln(N) 2/3 N 2/3 >> ln(N) phases mix phases do not mix

Лев Давидович Ландау (1908 - 1968) Нобелевская Премия 1962

TRANSITIONS: KINETICS
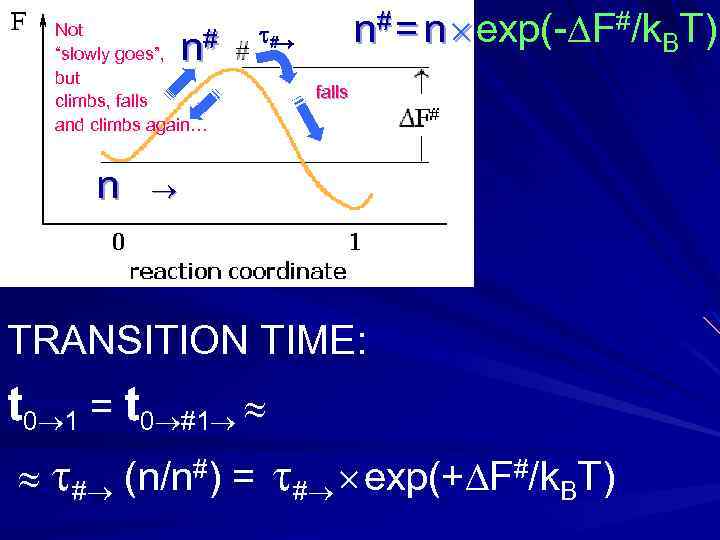
Not # “slowly goes”, but climbs, falls and climbs again… n n n# = n exp(- F#/k. BT) # falls TRANSITION TIME: t 0 1 = t 0 #1 # (n/n#) = # exp(+ F#/k. BT)
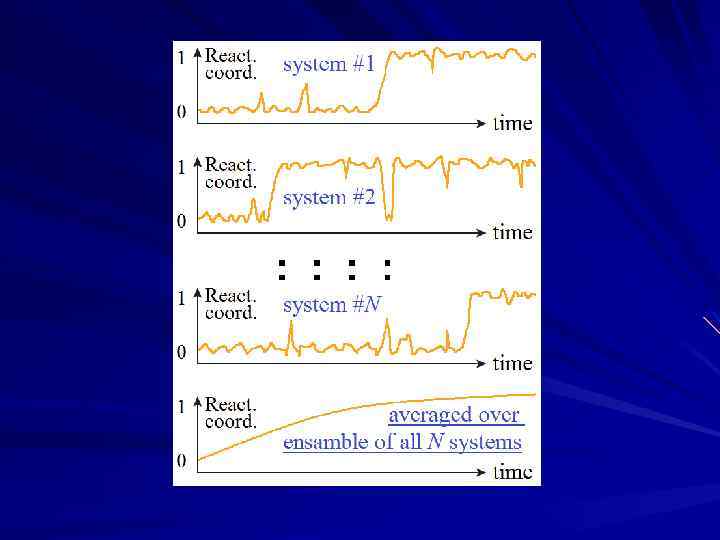
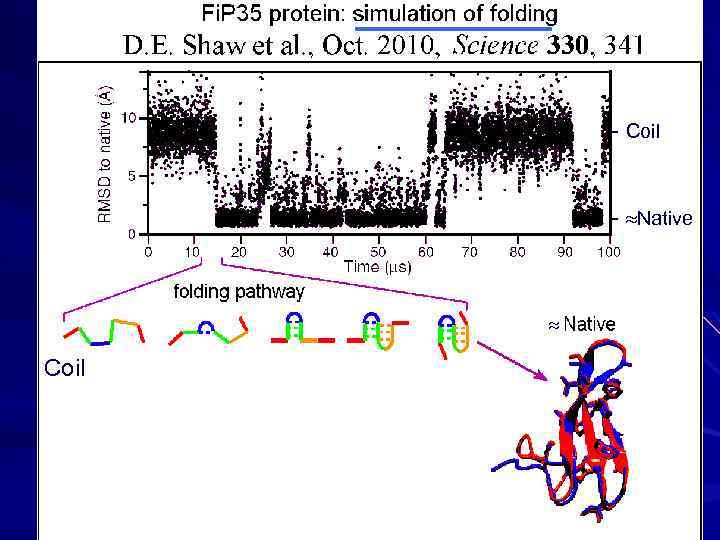
- Coil - Native Coil phase separation
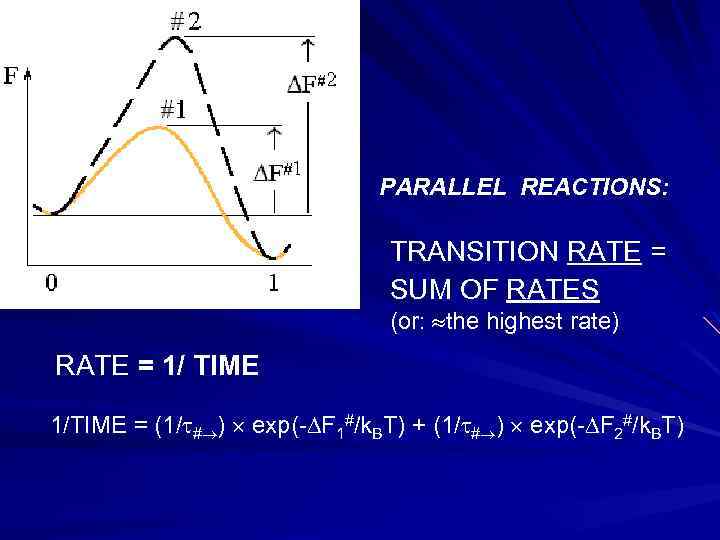
PARALLEL REACTIONS: TRANSITION RATE = SUM OF RATES (or: the highest rate) RATE = 1/ TIME 1/TIME = (1/ # ) exp(- F 1#/k. BT) + (1/ # ) exp(- F 2#/k. BT)
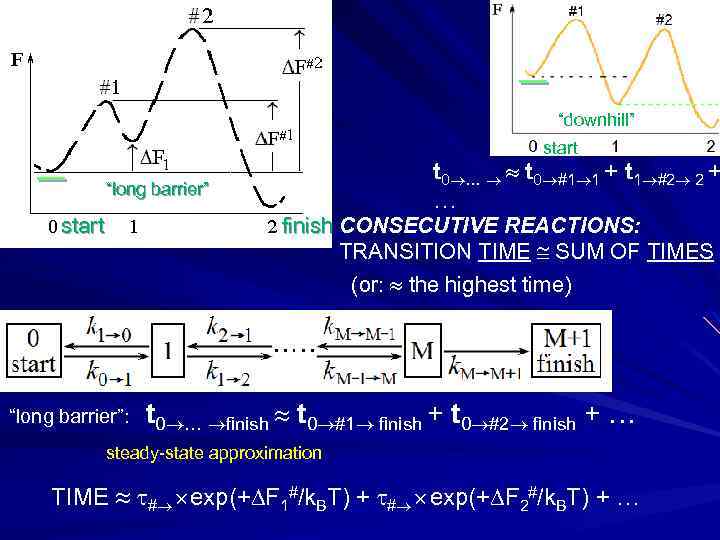
# _ _# “downhill” start t 0 … t 0 #1 1 + t 1 #2 2 + … “long barrier” finish CONSECUTIVE REACTIONS: TRANSITION TIME SUM OF TIMES (or: the highest time) start “long barrier”: t 0 … finish t 0 #1 finish + t 0 #2 finish + … steady-state approximation TIME # exp(+ F 1#/k. BT) + # exp(+ F 2#/k. BT) + …
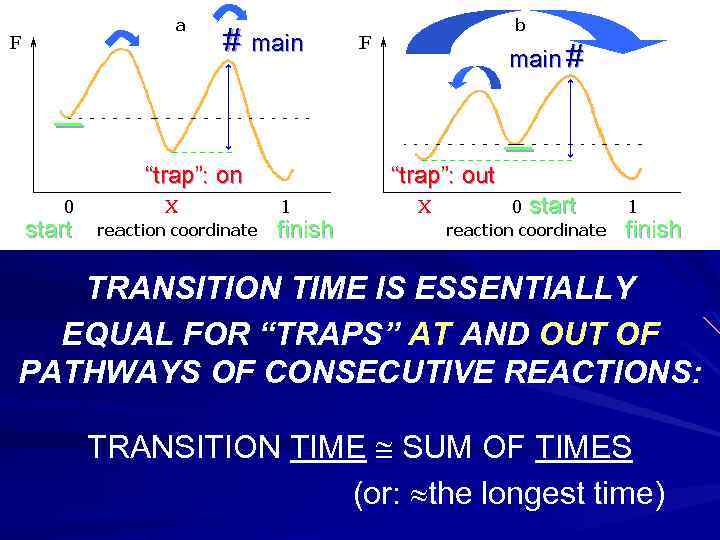
# main # _ _ “trap”: on start “trap”: out finish start finish TRANSITION TIME IS ESSENTIALLY EQUAL FOR “TRAPS” AT AND OUT OF PATHWAYS OF CONSECUTIVE REACTIONS: TRANSITION TIME SUM OF TIMES (or: the longest time)

DIFFUSION: KINETICS
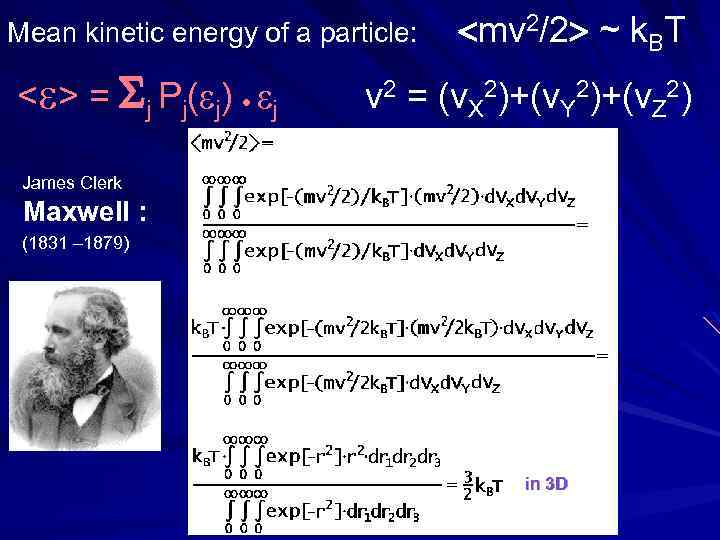
Mean kinetic energy of a particle: mv 2/2 ~ k. BT < > = j Pj( j) j v 2 = (v. X 2)+(v. Y 2)+(v. Z 2) James Clerk Maxwell : (1831 – 1879) in 3 D
![Friction stops a molecule within picoseconds: m(dv/dt) = -(3 D )v [Stokes law], or Friction stops a molecule within picoseconds: m(dv/dt) = -(3 D )v [Stokes law], or](https://present5.com/presentation/180491336_437185164/image-26.jpg)
Friction stops a molecule within picoseconds: m(dv/dt) = -(3 D )v [Stokes law], or m(dv/dt) = -(k. BT/Ddiff)v [Einstein-Stokes] D – diameter; m ~ D 3 1 g/cm 3 – mass; – viscosity tkinet 10 -13 sec (D/nm)2 in water Sir George Gabriel Stokes Albert Einstein (1819 -1903) (1879 -1995) DIFFUSION: During tkinet the molecule moves by Lkinet ~ v • tkinet Then it restores its kinetic energy mv 2/2 ~ k. BT from thermal kicks of other molecules, and moves in another random side CHARACTERISTIC DIFFUSION TIME: nanoseconds
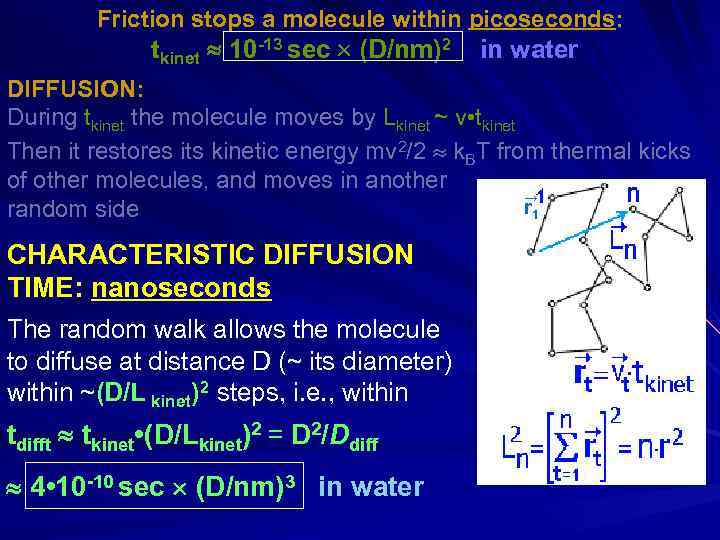
Friction stops a molecule within picoseconds: tkinet 10 -13 sec (D/nm)2 in water DIFFUSION: During tkinet the molecule moves by Lkinet ~ v • tkinet Then it restores its kinetic energy mv 2/2 k. BT from thermal kicks of other molecules, and moves in another → r 1 random side CHARACTERISTIC DIFFUSION TIME: nanoseconds The random walk allows the molecule to diffuse at distance D (~ its diameter) within ~(D/L kinet)2 steps, i. e. , within tdifft tkinet • (D/Lkinet)2 = D 2/Ddiff 4 • 10 -10 sec (D/nm)3 in water

The End
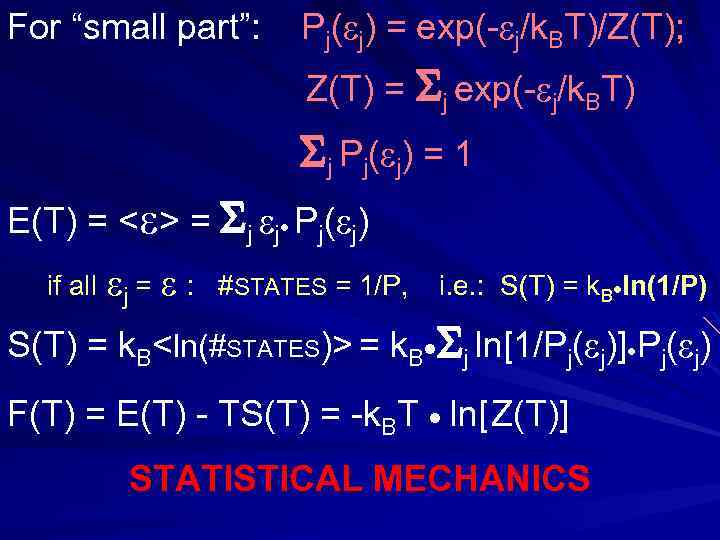
For “small part”: Pj( j) = exp(- j/k. BT)/Z(T); Z(T) = j exp(- j/k. BT) j Pj( j) = 1 E(T) = < > = j j Pj( j) if all j = : #STATES = 1/P, i. e. : S(T) = k. B ln(1/P) S(T) = k. B<ln(#STATES)> = k. B j ln[1/Pj( j)] Pj( j) F(T) = E(T) - TS(T) = -k. BT ln[ Z(T)] STATISTICAL MECHANICS
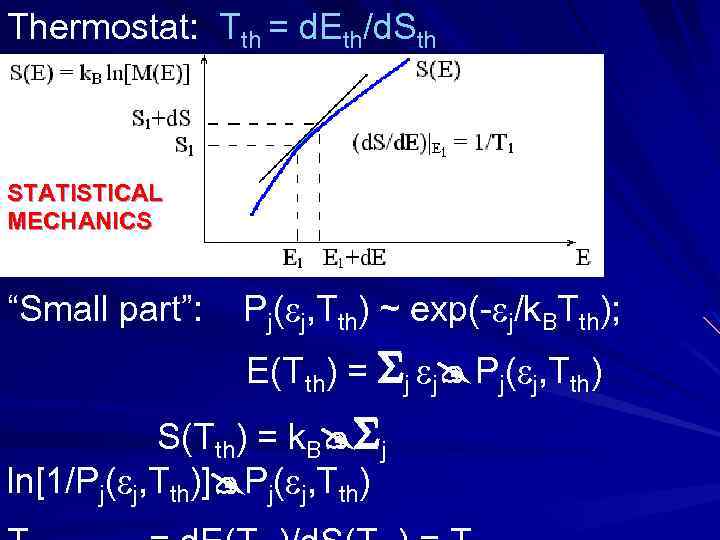
Thermostat: Tth = d. Eth/d. Sth STATISTICAL MECHANICS “Small part”: Pj( j, Tth) ~ exp(- j/k. BTth); E(Tth) = j j Pj( j, Tth) S(Tth) = k. B j ln[1/Pj( j, Tth)] Pj( j, Tth)
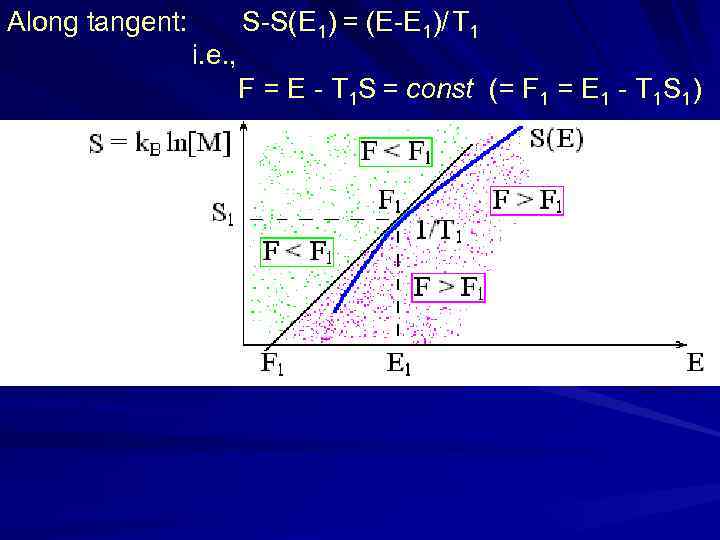
Along tangent: S-S(E 1) = (E-E 1)/ T 1 i. e. , F = E - T 1 S = const (= F 1 = E 1 - T 1 S 1)

Separation of potential energy in classic (non-quantum) mechanics: P( ) ~ exp(- /k. BT) Classic: = COORD + KIN = mv 2/2 : does not depend on coordinates Potential energy COORD: depends only on coordinates P( ) ~ exp(- COORD/k. BT) • exp(- KIN/k. BT) ZKIN(T) = K exp(- K/k. BT): don’t depend on coord. ZCOORD(T) = Cexp(- C/k. BT): depends on coord. Z(T) = ZCOORD(T) • ZKIN(T) F(T) = FCOORD(T)+FKIN(T) ============================================================ Elementary volume: (mv) x = ħ ( x)3 =(ħ/|mv|)3
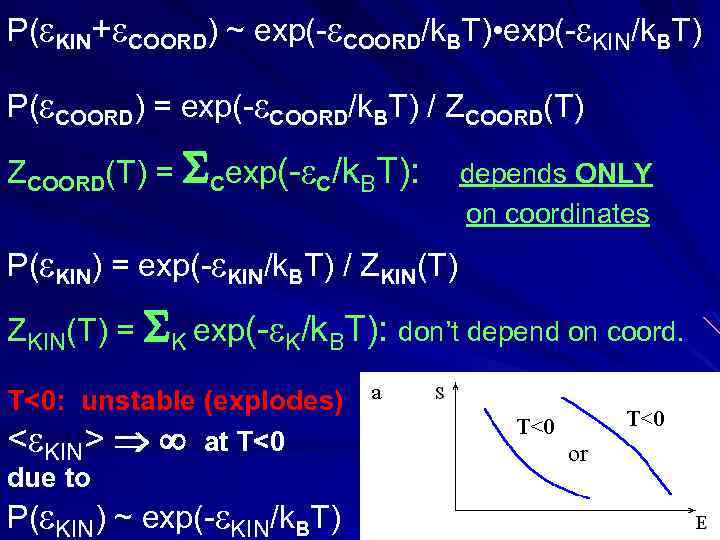
P( KIN+ COORD) ~ exp(- COORD/k. BT) • exp(- KIN/k. BT) P( COORD) = exp(- COORD/k. BT) / ZCOORD(T) = Cexp(- C/k. BT): depends ONLY on coordinates P( KIN) = exp(- KIN/k. BT) / ZKIN(T) = K exp(- K/k. BT): don’t depend on coord. T<0: unstable (explodes) < KIN> at T<0 due to P( KIN) ~ exp(- KIN/k. BT)
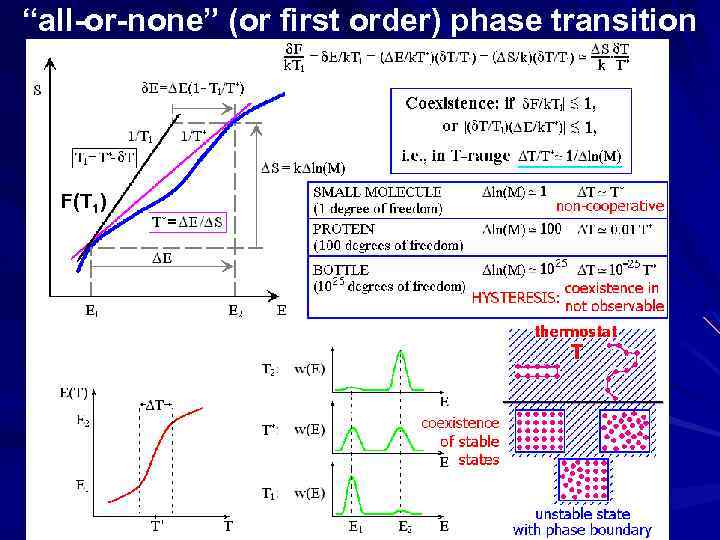
“all-or-none” (or first order) phase transition F(T 1) ________
F_L_07-08.ppt