F_L_24-25.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 PROTEIN PHYSICS LECTURE 24 -25 PROTEIN STRUCTURE AT ACTION: BIND TRANSFORM RELEASE
PROTEIN PHYSICS LECTURE 24 -25 PROTEIN STRUCTURE AT ACTION: BIND TRANSFORM RELEASE
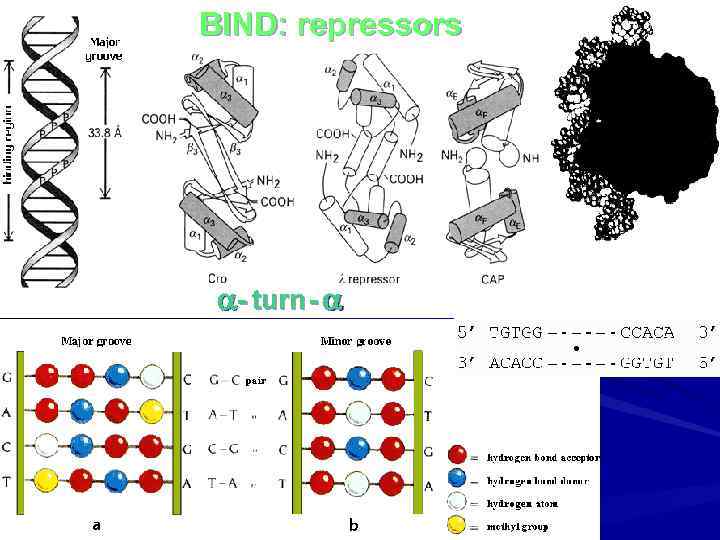 BIND: repressors - turn -
BIND: repressors - turn -
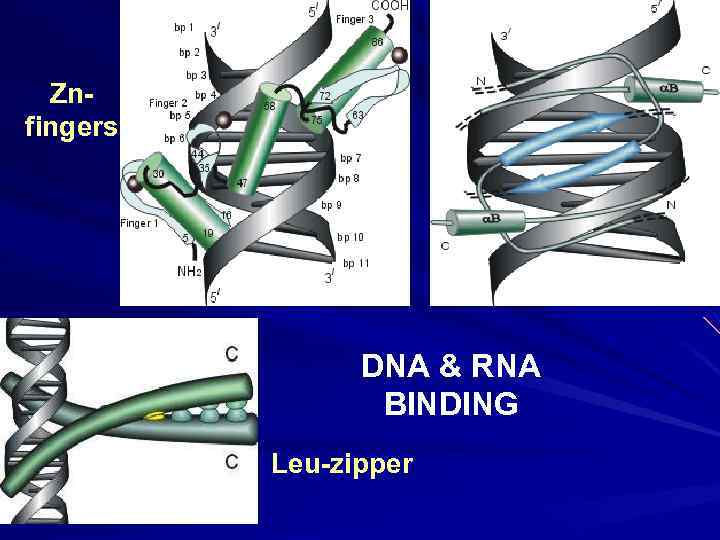 Znfingers DNA & RNA BINDING Leu-zipper
Znfingers DNA & RNA BINDING Leu-zipper
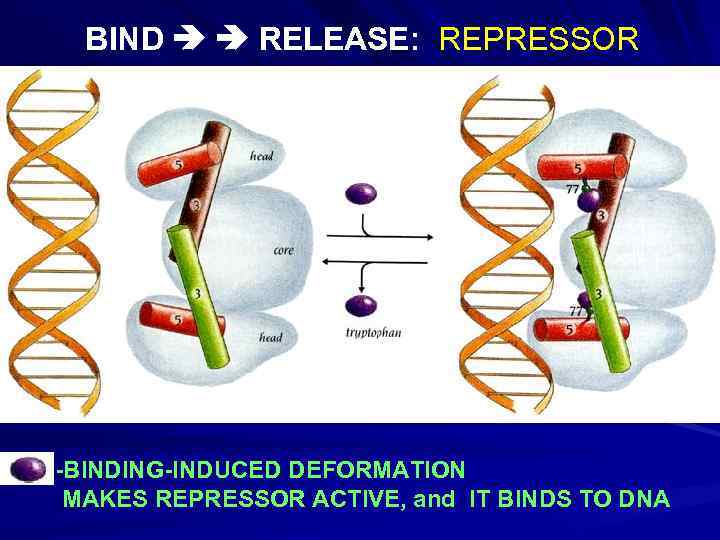 BIND RELEASE: REPRESSOR -BINDING-INDUCED DEFORMATION MAKES REPRESSOR ACTIVE, and IT BINDS TO DNA
BIND RELEASE: REPRESSOR -BINDING-INDUCED DEFORMATION MAKES REPRESSOR ACTIVE, and IT BINDS TO DNA
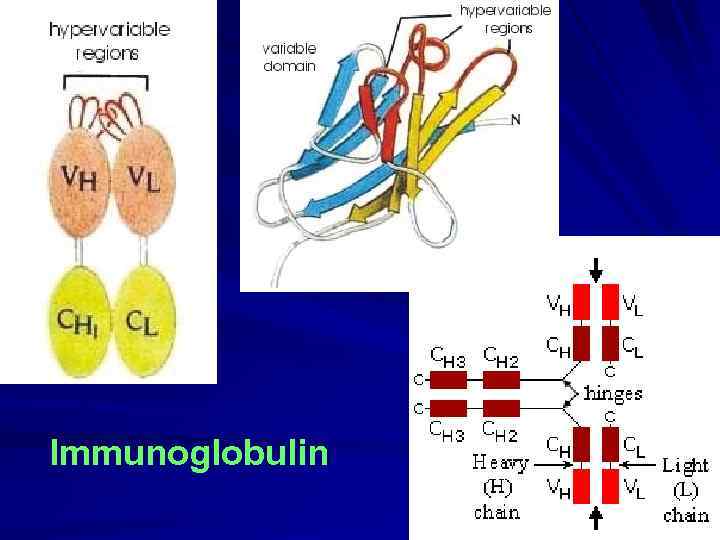 Immunoglobulin
Immunoglobulin
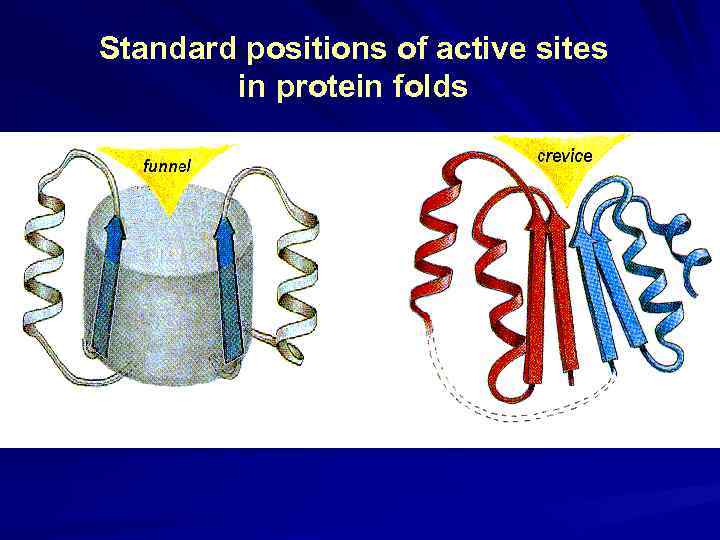 Standard positions of active sites in protein folds
Standard positions of active sites in protein folds
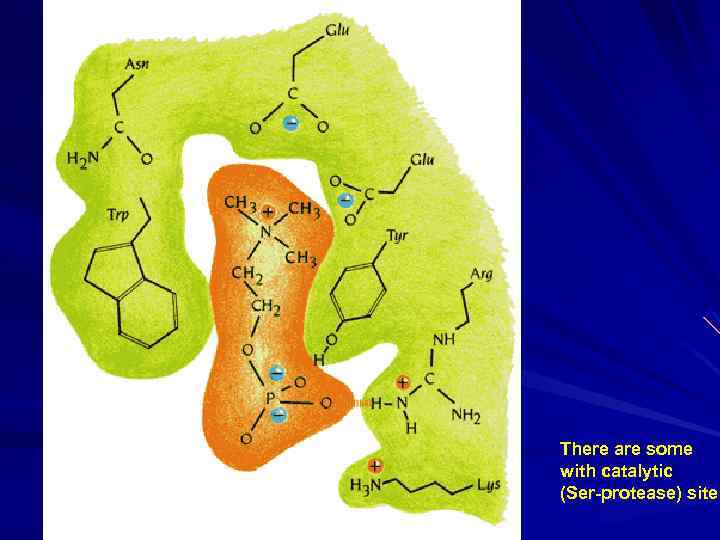 There are some with catalytic (Ser-protease) site
There are some with catalytic (Ser-protease) site
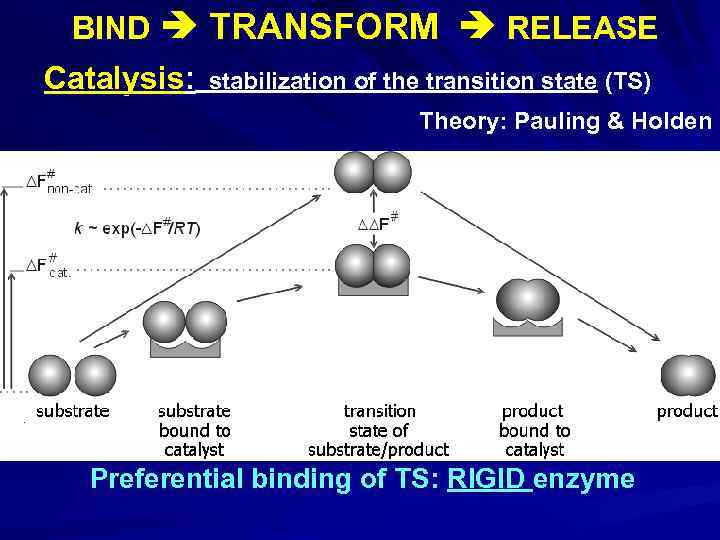 BIND TRANSFORM RELEASE Catalysis: stabilization of the transition state (TS) Theory: Pauling & Holden Preferential binding of TS: RIGID enzyme
BIND TRANSFORM RELEASE Catalysis: stabilization of the transition state (TS) Theory: Pauling & Holden Preferential binding of TS: RIGID enzyme
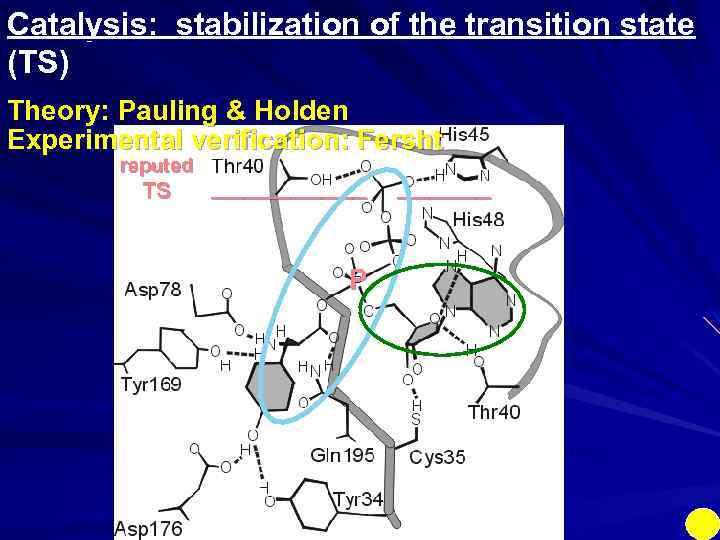 Catalysis: stabilization of the transition state (TS) Theory: Pauling & Holden Experimental verification: Fersht reputed TS _____ P ______
Catalysis: stabilization of the transition state (TS) Theory: Pauling & Holden Experimental verification: Fersht reputed TS _____ P ______
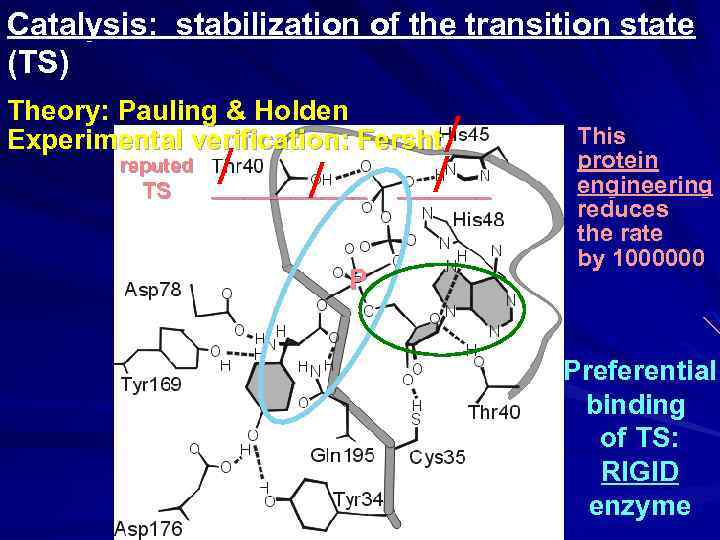 Catalysis: stabilization of the transition state (TS) Theory: Pauling & Holden Experimental verification: Fersht reputed TS / / _____ P / / ______ This protein engineering reduces the rate by 1000000 Preferential binding of TS: RIGID enzyme
Catalysis: stabilization of the transition state (TS) Theory: Pauling & Holden Experimental verification: Fersht reputed TS / / _____ P / / ______ This protein engineering reduces the rate by 1000000 Preferential binding of TS: RIGID enzyme
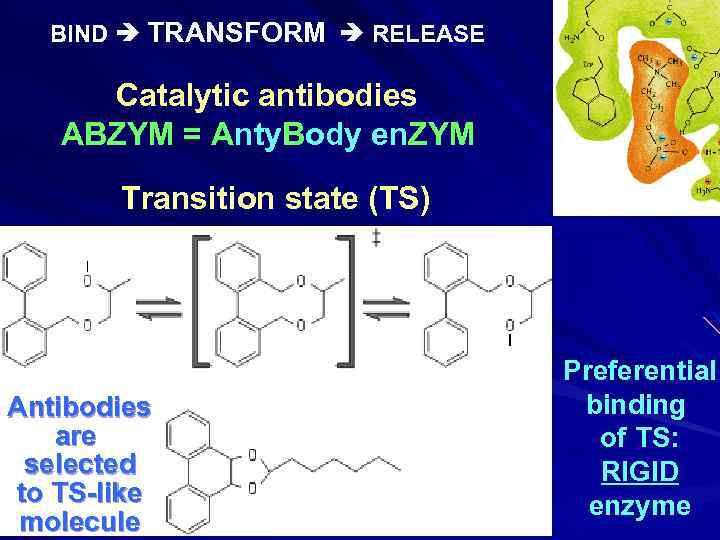 BIND TRANSFORM RELEASE Catalytic antibodies ABZYM = Anty. Body en. ZYM Transition state (TS) Antibodies are selected to TS-like molecule Preferential binding of TS: RIGID enzyme
BIND TRANSFORM RELEASE Catalytic antibodies ABZYM = Anty. Body en. ZYM Transition state (TS) Antibodies are selected to TS-like molecule Preferential binding of TS: RIGID enzyme
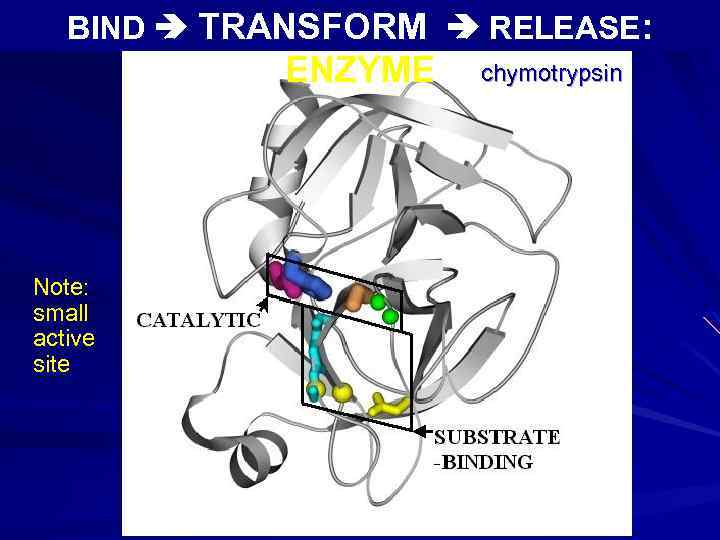 BIND TRANSFORM RELEASE: ENZYME Note: small active site chymotrypsin
BIND TRANSFORM RELEASE: ENZYME Note: small active site chymotrypsin
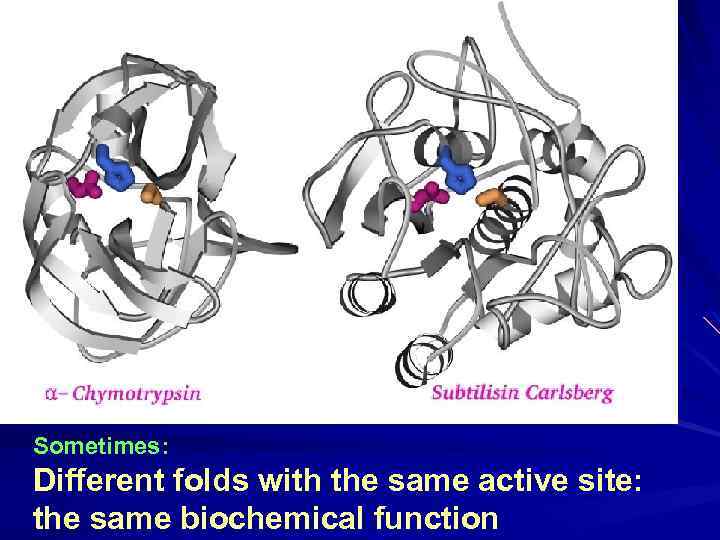 Sometimes: Different folds with the same active site: the same biochemical function
Sometimes: Different folds with the same active site: the same biochemical function
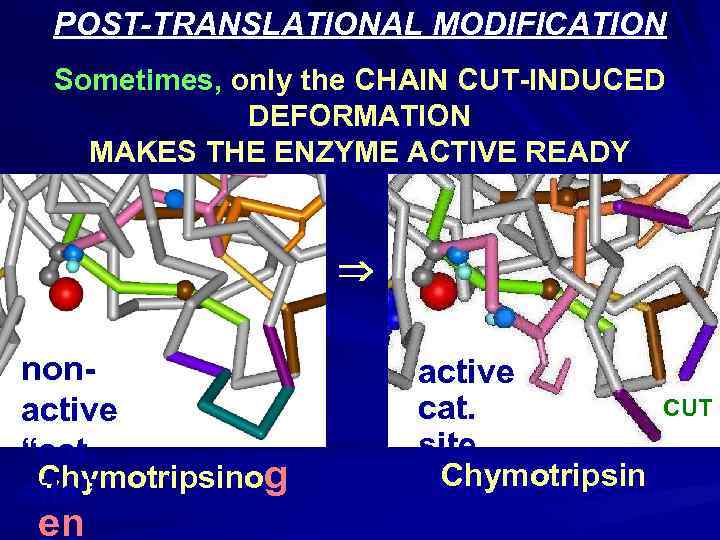 POST-TRANSLATIONAL MODIFICATION Sometimes, only the CHAIN CUT-INDUCED DEFORMATION MAKES THE ENZYME ACTIVE READY nonactive “cat. Chymotripsinog site” en active cat. site Chymotripsin CUT
POST-TRANSLATIONAL MODIFICATION Sometimes, only the CHAIN CUT-INDUCED DEFORMATION MAKES THE ENZYME ACTIVE READY nonactive “cat. Chymotripsinog site” en active cat. site Chymotripsin CUT
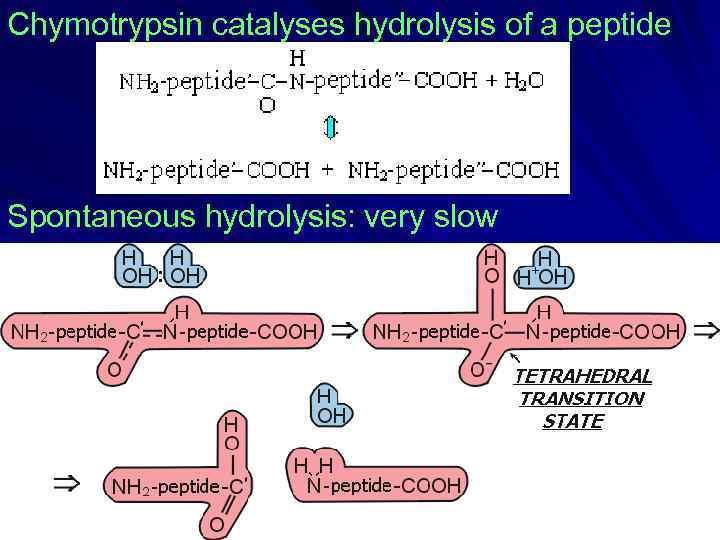 Chymotrypsin catalyses hydrolysis of a peptide Spontaneous hydrolysis: very slow
Chymotrypsin catalyses hydrolysis of a peptide Spontaneous hydrolysis: very slow
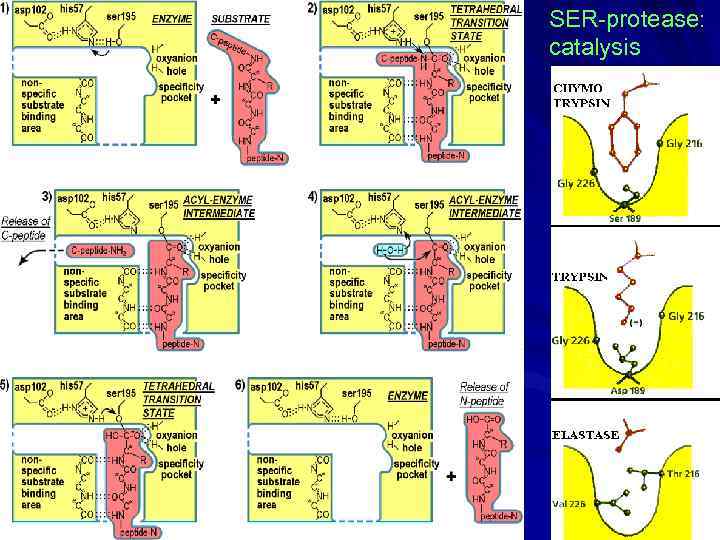 SER-protease: catalysis
SER-protease: catalysis
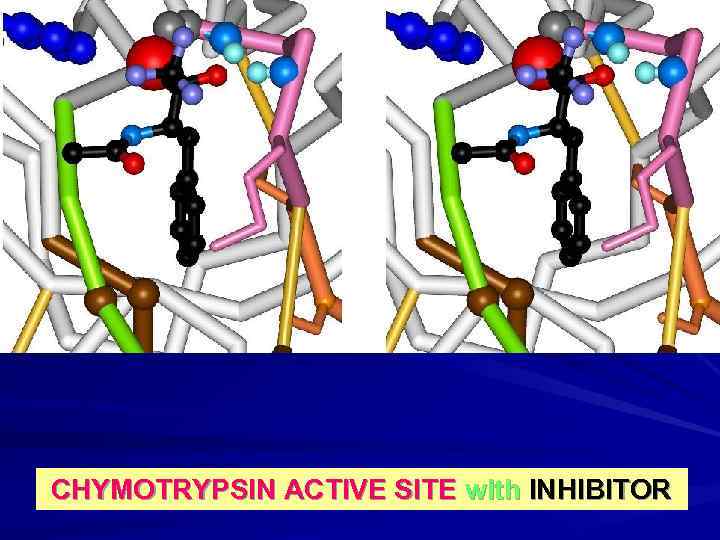 CHYMOTRYPSIN ACTIVE SITE with INHIBITOR
CHYMOTRYPSIN ACTIVE SITE with INHIBITOR
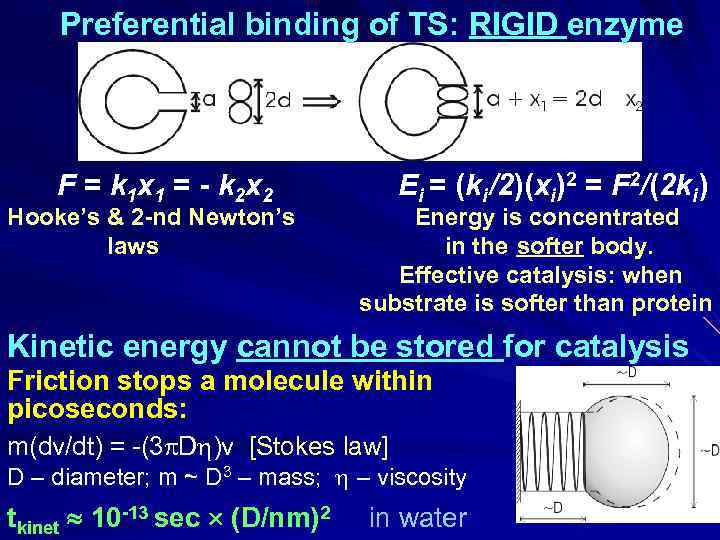 Preferential binding of TS: RIGID enzyme F = k 1 x 1 = - k 2 x 2 Hooke’s & 2 -nd Newton’s laws Ei = (ki /2)(xi)2 = F 2/(2 ki ) Energy is concentrated in the softer body. Effective catalysis: when substrate is softer than protein Kinetic energy cannot be stored for catalysis Friction stops a molecule within picoseconds: m(dv/dt) = -(3 D )v [Stokes law] D – diameter; m ~ D 3 – mass; – viscosity tkinet 10 -13 sec (D/nm)2 in water
Preferential binding of TS: RIGID enzyme F = k 1 x 1 = - k 2 x 2 Hooke’s & 2 -nd Newton’s laws Ei = (ki /2)(xi)2 = F 2/(2 ki ) Energy is concentrated in the softer body. Effective catalysis: when substrate is softer than protein Kinetic energy cannot be stored for catalysis Friction stops a molecule within picoseconds: m(dv/dt) = -(3 D )v [Stokes law] D – diameter; m ~ D 3 – mass; – viscosity tkinet 10 -13 sec (D/nm)2 in water
 PROTEIN STRUCTURE AT ACTION: BIND TRANSFORM RELEASE RIGID CATALITIC SITE INDEPENDENT ON OVERALL CHAIN FOLD
PROTEIN STRUCTURE AT ACTION: BIND TRANSFORM RELEASE RIGID CATALITIC SITE INDEPENDENT ON OVERALL CHAIN FOLD
 MOTIONS
MOTIONS
 Double sieve: movement of substrate from one active site to another t. RNAIle
Double sieve: movement of substrate from one active site to another t. RNAIle
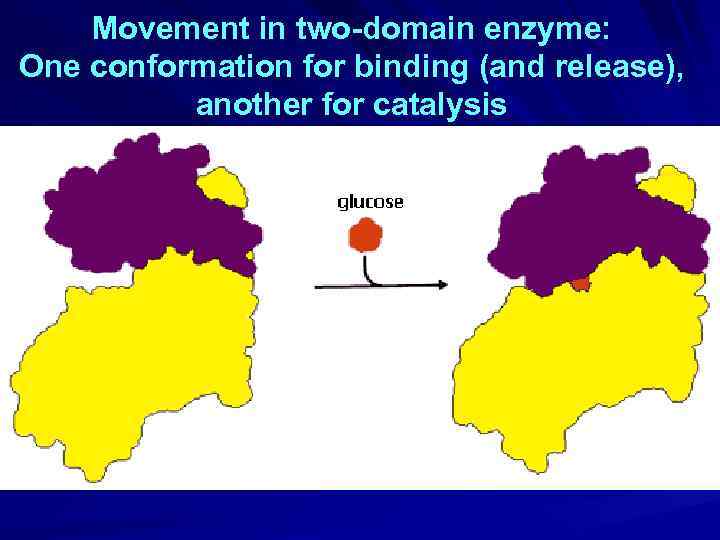 Movement in two-domain enzyme: One conformation for binding (and release), another for catalysis
Movement in two-domain enzyme: One conformation for binding (and release), another for catalysis
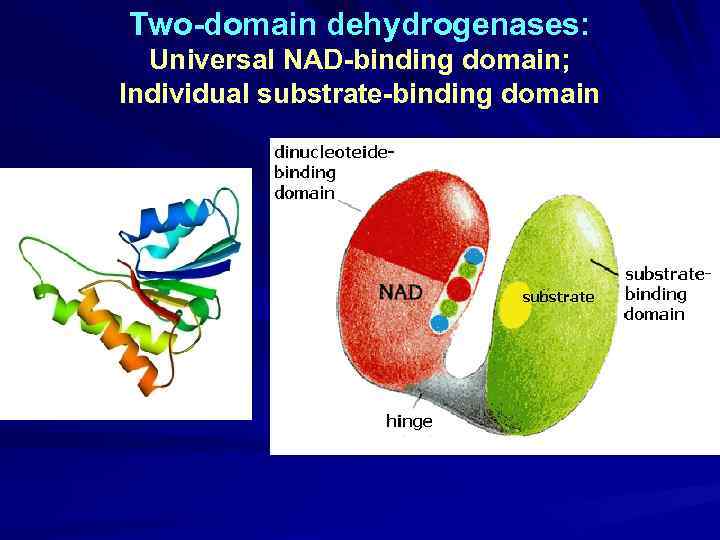 Two-domain dehydrogenases: Universal NAD-binding domain; Individual substrate-binding domain
Two-domain dehydrogenases: Universal NAD-binding domain; Individual substrate-binding domain
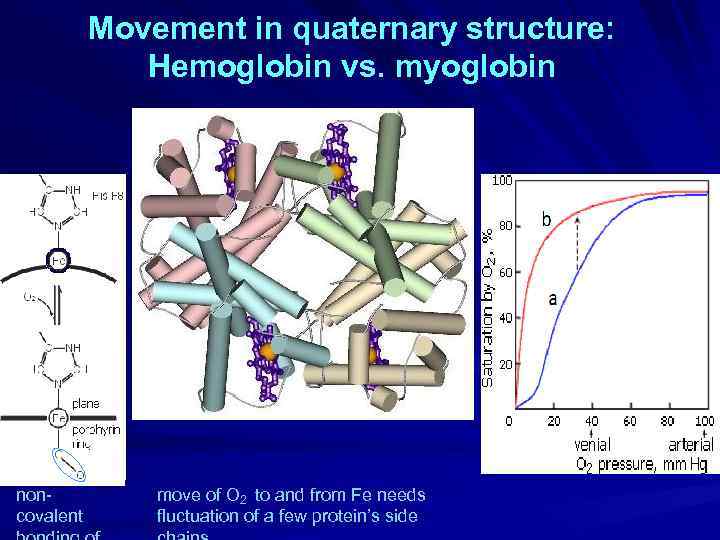 Movement in quaternary structure: Hemoglobin vs. myoglobin noncovalent move of O 2 to and from Fe needs fluctuation of a few protein’s side
Movement in quaternary structure: Hemoglobin vs. myoglobin noncovalent move of O 2 to and from Fe needs fluctuation of a few protein’s side
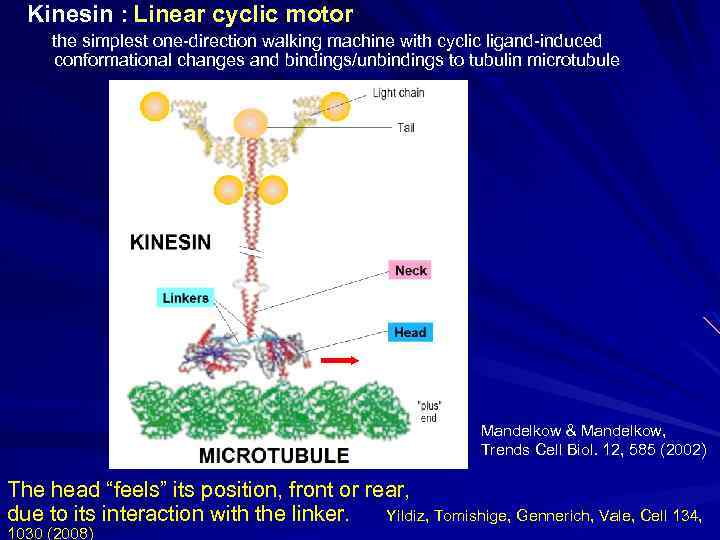 Kinesin : Linear cyclic motor the simplest one-direction walking machine with cyclic ligand-induced conformational changes and bindings/unbindings to tubulin microtubule Mandelkow & Mandelkow, Trends Cell Biol. 12, 585 (2002) The head “feels” its position, front or rear, due to its interaction with the linker. Yildiz, Tomishige, Gennerich, Vale, Cell 134, 1030 (2008)
Kinesin : Linear cyclic motor the simplest one-direction walking machine with cyclic ligand-induced conformational changes and bindings/unbindings to tubulin microtubule Mandelkow & Mandelkow, Trends Cell Biol. 12, 585 (2002) The head “feels” its position, front or rear, due to its interaction with the linker. Yildiz, Tomishige, Gennerich, Vale, Cell 134, 1030 (2008)
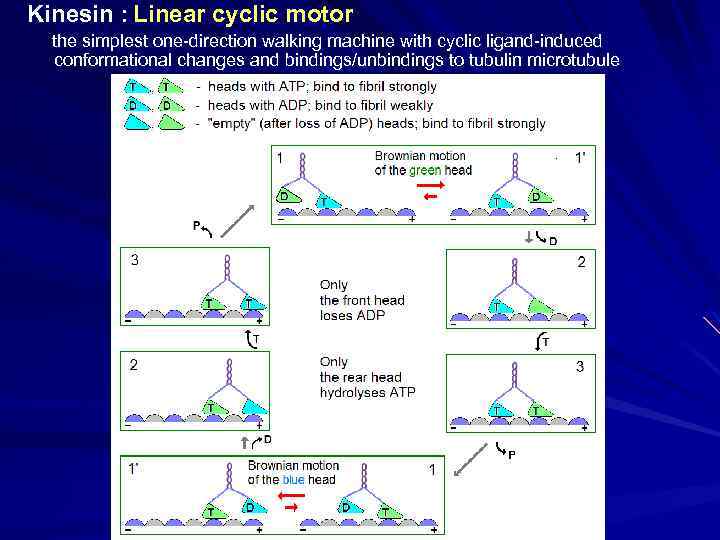 Kinesin : Linear cyclic motor the simplest one-direction walking machine with cyclic ligand-induced conformational changes and bindings/unbindings to tubulin microtubule
Kinesin : Linear cyclic motor the simplest one-direction walking machine with cyclic ligand-induced conformational changes and bindings/unbindings to tubulin microtubule
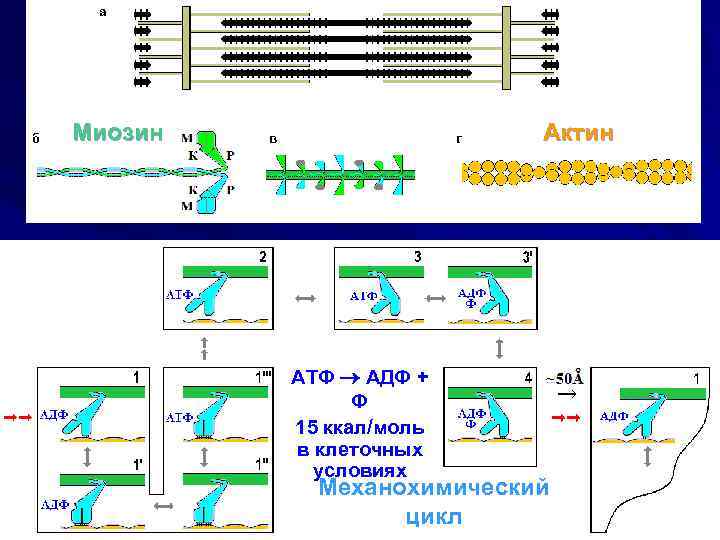 Миозин Актин АТФ АДФ + Ф 15 ккал/моль в клеточных условиях Механохимический цикл
Миозин Актин АТФ АДФ + Ф 15 ккал/моль в клеточных условиях Механохимический цикл
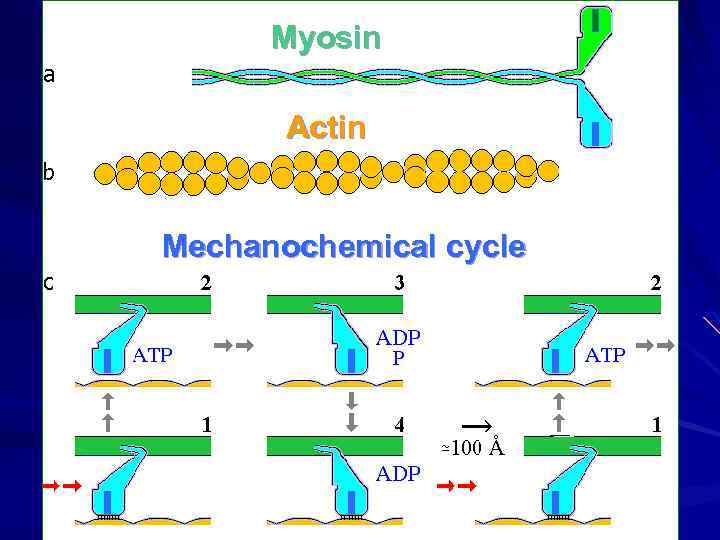 Myosin Actin Mechanochemical cycle
Myosin Actin Mechanochemical cycle
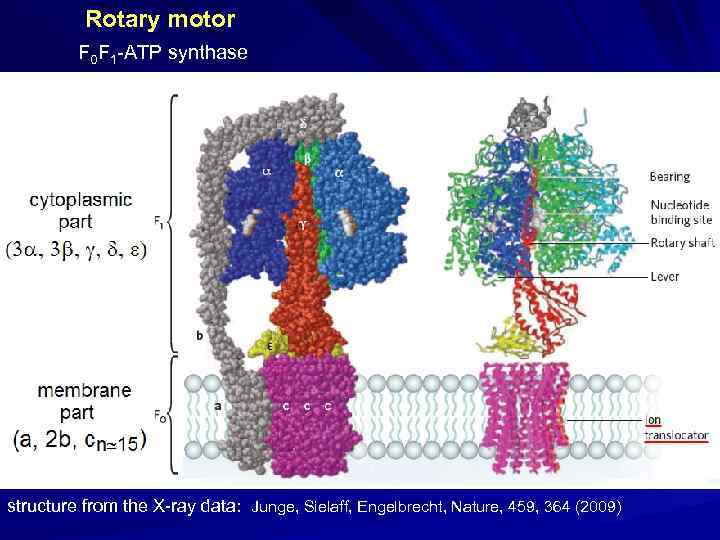 Rotary motor F 0 F 1 -ATP synthase structure from the X-ray data: Junge, Sielaff, Engelbrecht, Nature, 459, 364 (2009)
Rotary motor F 0 F 1 -ATP synthase structure from the X-ray data: Junge, Sielaff, Engelbrecht, Nature, 459, 364 (2009)
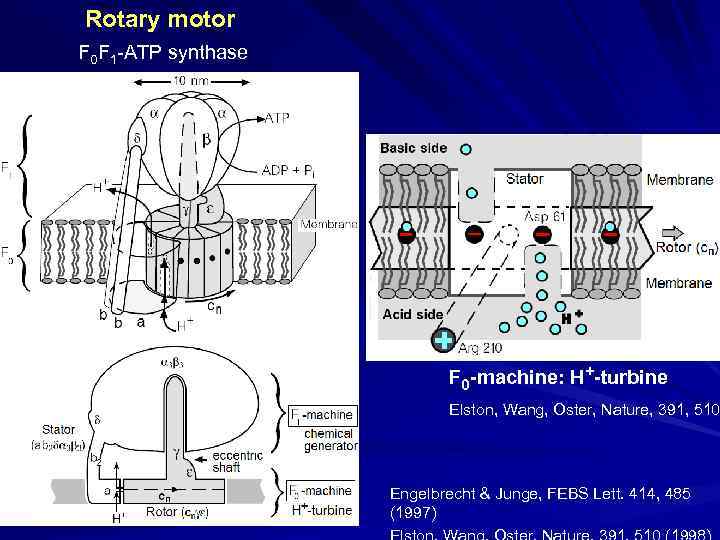 Rotary motor F 0 F 1 -ATP synthase Basic side Acid side F 0 -machine: H+-turbine Elston, Wang, Oster, Nature, 391, 510 Engelbrecht & Junge, FEBS Lett. 414, 485 (1997)
Rotary motor F 0 F 1 -ATP synthase Basic side Acid side F 0 -machine: H+-turbine Elston, Wang, Oster, Nature, 391, 510 Engelbrecht & Junge, FEBS Lett. 414, 485 (1997)
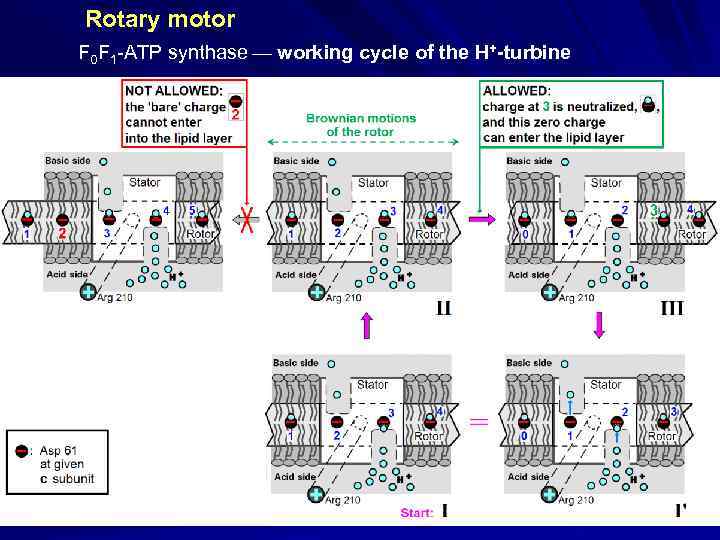 Rotary motor F 0 F 1 -ATP synthase working cycle of the H+-turbine
Rotary motor F 0 F 1 -ATP synthase working cycle of the H+-turbine
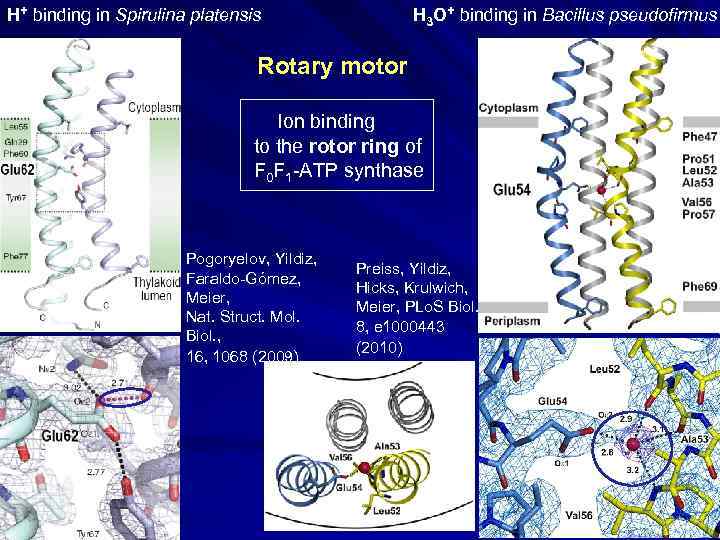 H+ binding in Spirulina platensis H 3 O+ binding in Bacillus pseudofirmus Rotary motor Ion binding to the rotor ring of F 0 F 1 -ATP synthase Pogoryelov, Yildiz, Faraldo-Gómez, Meier, Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. , 16, 1068 (2009) Preiss, Yildiz, Hicks, Krulwich, Meier, PLo. S Biol. 8, e 1000443 (2010)
H+ binding in Spirulina platensis H 3 O+ binding in Bacillus pseudofirmus Rotary motor Ion binding to the rotor ring of F 0 F 1 -ATP synthase Pogoryelov, Yildiz, Faraldo-Gómez, Meier, Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. , 16, 1068 (2009) Preiss, Yildiz, Hicks, Krulwich, Meier, PLo. S Biol. 8, e 1000443 (2010)
 SUMMARY
SUMMARY
 PROTEIN PHYSICS · Interactions · Structures · Selection · States & transitions
PROTEIN PHYSICS · Interactions · Structures · Selection · States & transitions
 · Intermediates & nuclei · Structure prediction & bioinformatics · Protein engineering & design · Functioning
· Intermediates & nuclei · Structure prediction & bioinformatics · Protein engineering & design · Functioning


