seminar 3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 85
 Protein folding and folds
Protein folding and folds
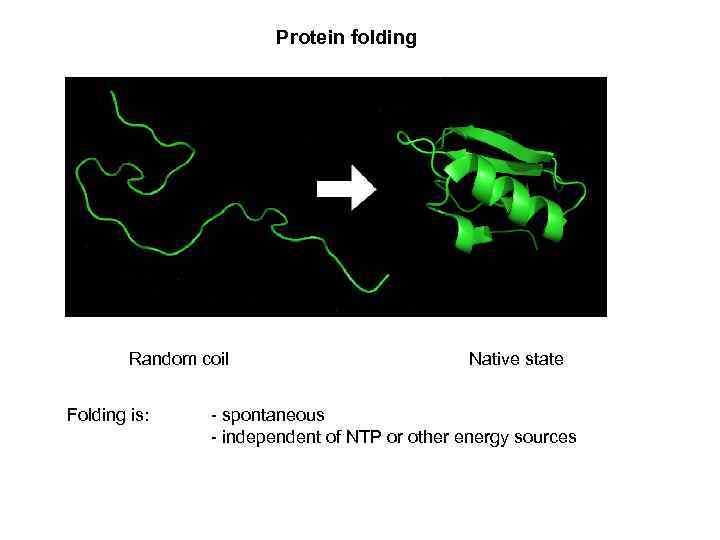 Protein folding Random coil Folding is: Native state - spontaneous - independent of NTP or other energy sources
Protein folding Random coil Folding is: Native state - spontaneous - independent of NTP or other energy sources
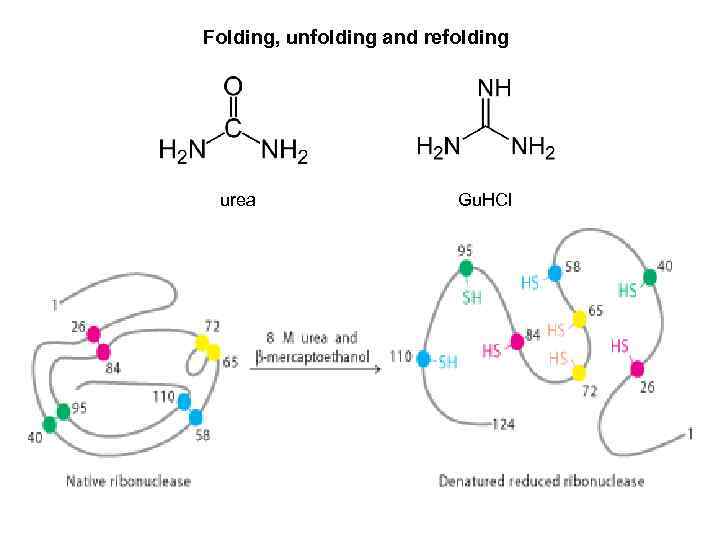 Folding, unfolding and refolding urea Gu. HCl
Folding, unfolding and refolding urea Gu. HCl
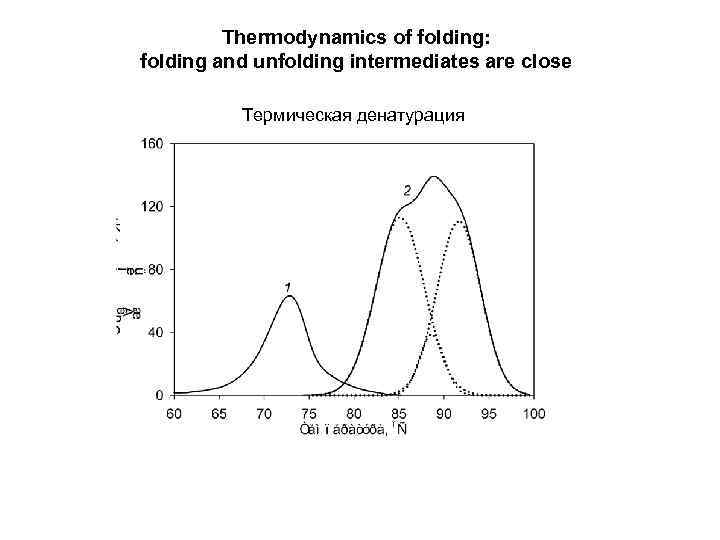 Thermodynamics of folding: folding and unfolding intermediates are close Термическая денатурация
Thermodynamics of folding: folding and unfolding intermediates are close Термическая денатурация
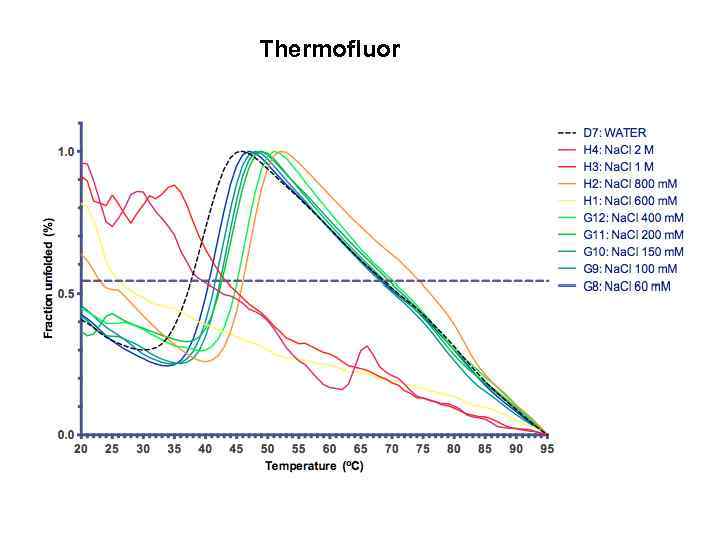 Thermofluor
Thermofluor
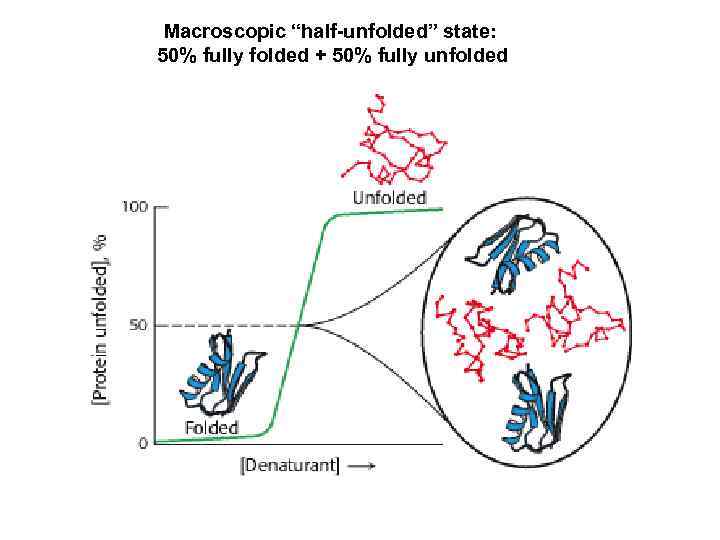 Macroscopic “half-unfolded” state: 50% fully folded + 50% fully unfolded
Macroscopic “half-unfolded” state: 50% fully folded + 50% fully unfolded
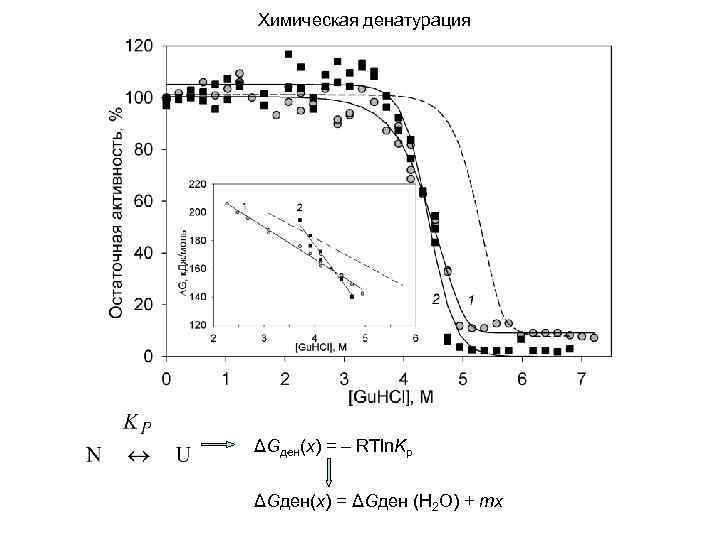 Химическая денатурация ΔGден(x) = – RTln. Kр ΔGден(x) = ΔGден (H 2 O) + mx
Химическая денатурация ΔGден(x) = – RTln. Kр ΔGден(x) = ΔGден (H 2 O) + mx
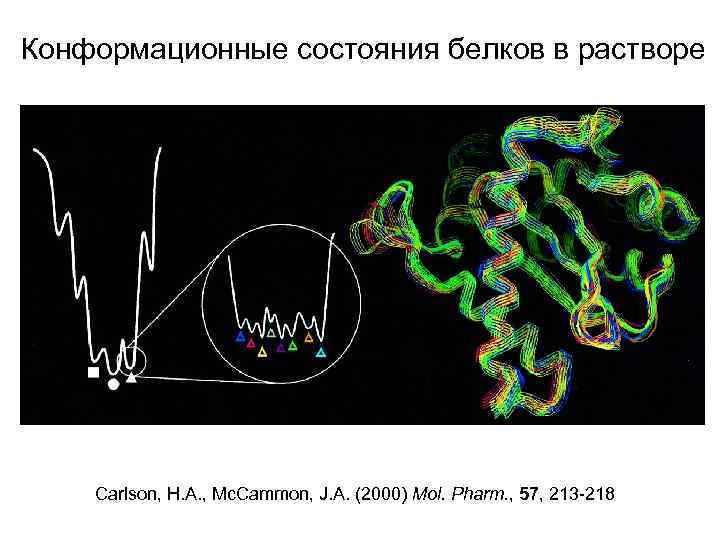 Конформационные состояния белков в растворе Carlson, H. A. , Mc. Cammon, J. A. (2000) Mol. Pharm. , 57, 213 -218
Конформационные состояния белков в растворе Carlson, H. A. , Mc. Cammon, J. A. (2000) Mol. Pharm. , 57, 213 -218
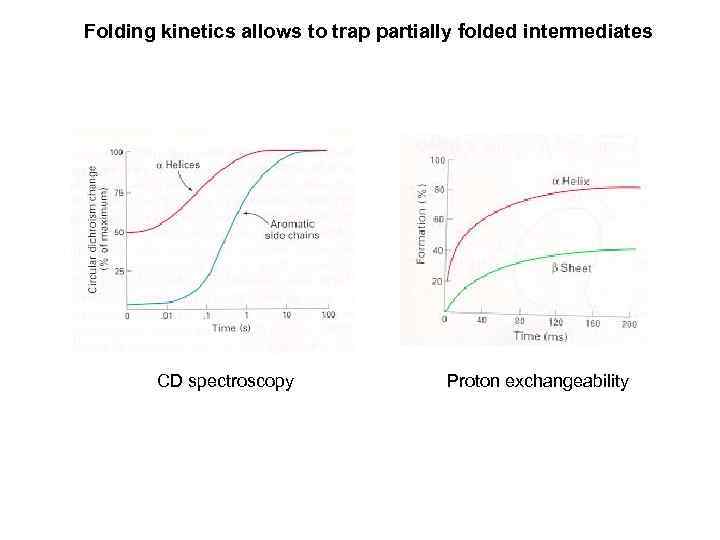 Folding kinetics allows to trap partially folded intermediates CD spectroscopy Proton exchangeability
Folding kinetics allows to trap partially folded intermediates CD spectroscopy Proton exchangeability
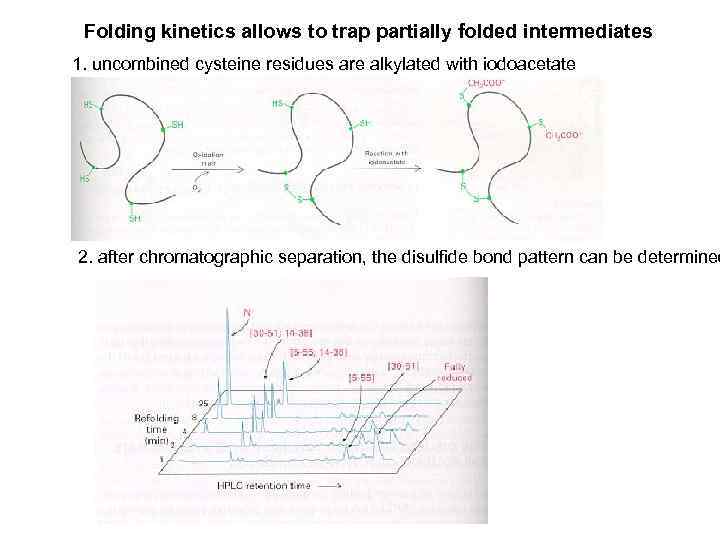 Folding kinetics allows to trap partially folded intermediates 1. uncombined cysteine residues are alkylated with iodoacetate 2. after chromatographic separation, the disulfide bond pattern can be determined
Folding kinetics allows to trap partially folded intermediates 1. uncombined cysteine residues are alkylated with iodoacetate 2. after chromatographic separation, the disulfide bond pattern can be determined
 Folding mechanism: “Random search” vs “Progressive stabilization” Levinthal's paradox: 100 AA residues 3 conformations each total number of structures 3100 = 5 × 1047 10 -13 s to convert one structure into another total search time: 5 × 1047 × 10 -13 s = 5 × 1034 s = 1. 6 × 1027 years definitely not “random search”.
Folding mechanism: “Random search” vs “Progressive stabilization” Levinthal's paradox: 100 AA residues 3 conformations each total number of structures 3100 = 5 × 1047 10 -13 s to convert one structure into another total search time: 5 × 1047 × 10 -13 s = 5 × 1034 s = 1. 6 × 1027 years definitely not “random search”.
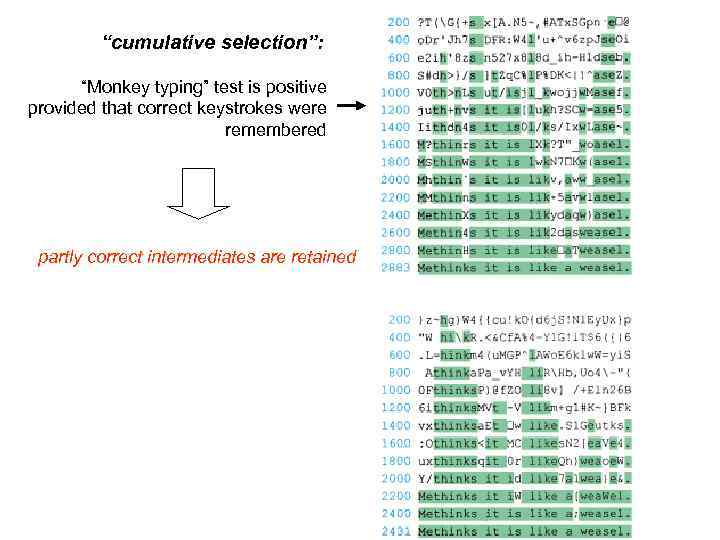 “cumulative selection”: “Monkey typing” test is positive provided that correct keystrokes were remembered partly correct intermediates are retained
“cumulative selection”: “Monkey typing” test is positive provided that correct keystrokes were remembered partly correct intermediates are retained
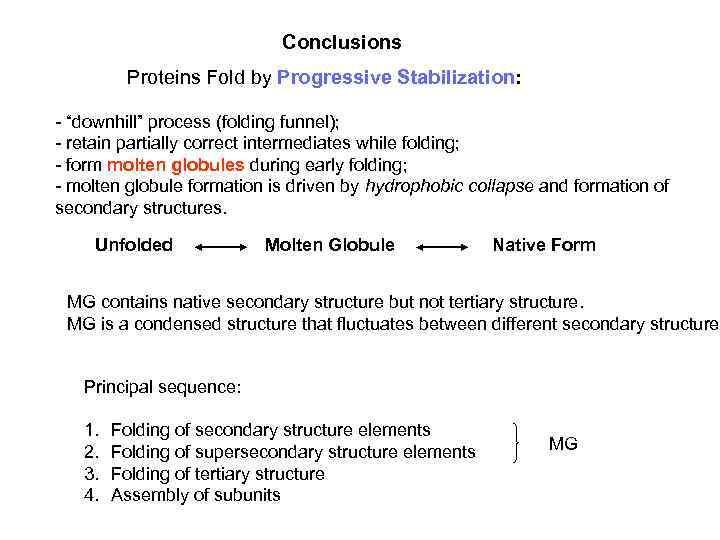 Conclusions Proteins Fold by Progressive Stabilization: - “downhill” process (folding funnel); - retain partially correct intermediates while folding; - form molten globules during early folding; - molten globule formation is driven by hydrophobic collapse and formation of secondary structures. Unfolded Molten Globule Native Form MG contains native secondary structure but not tertiary structure. MG is a condensed structure that fluctuates between different secondary structures Principal sequence: 1. 2. 3. 4. Folding of secondary structure elements Folding of supersecondary structure elements Folding of tertiary structure Assembly of subunits MG
Conclusions Proteins Fold by Progressive Stabilization: - “downhill” process (folding funnel); - retain partially correct intermediates while folding; - form molten globules during early folding; - molten globule formation is driven by hydrophobic collapse and formation of secondary structures. Unfolded Molten Globule Native Form MG contains native secondary structure but not tertiary structure. MG is a condensed structure that fluctuates between different secondary structures Principal sequence: 1. 2. 3. 4. Folding of secondary structure elements Folding of supersecondary structure elements Folding of tertiary structure Assembly of subunits MG
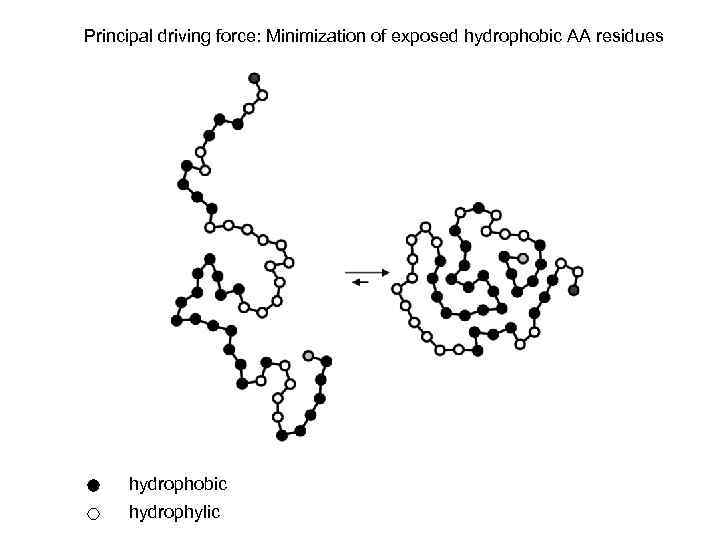 Principal driving force: Minimization of exposed hydrophobic AA residues hydrophobic hydrophylic
Principal driving force: Minimization of exposed hydrophobic AA residues hydrophobic hydrophylic
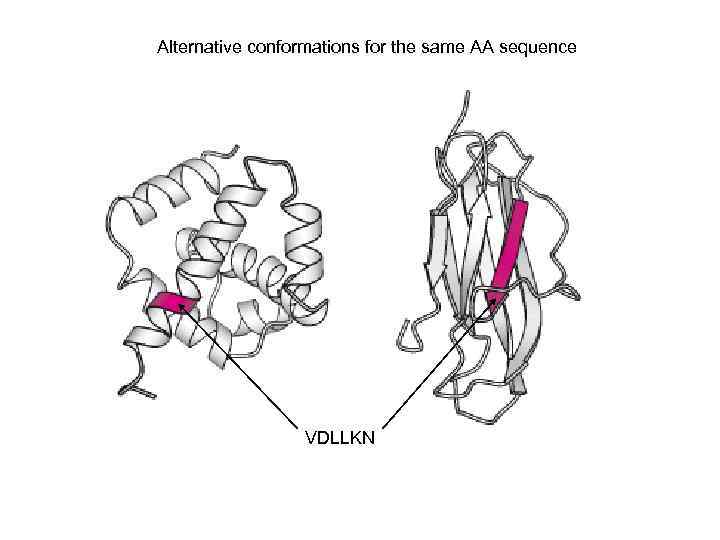 Alternative conformations for the same AA sequence VDLLKN
Alternative conformations for the same AA sequence VDLLKN
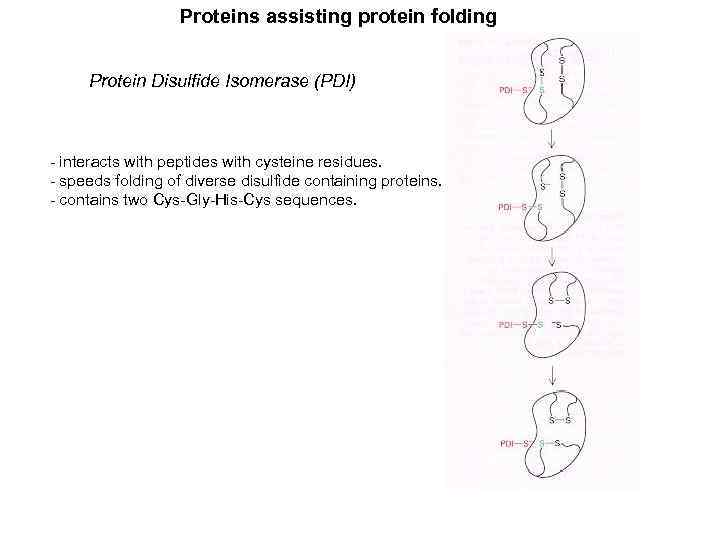 Proteins assisting protein folding Protein Disulfide Isomerase (PDI) - interacts with peptides with cysteine residues. - speeds folding of diverse disulfide containing proteins. - contains two Cys-Gly-His-Cys sequences.
Proteins assisting protein folding Protein Disulfide Isomerase (PDI) - interacts with peptides with cysteine residues. - speeds folding of diverse disulfide containing proteins. - contains two Cys-Gly-His-Cys sequences.
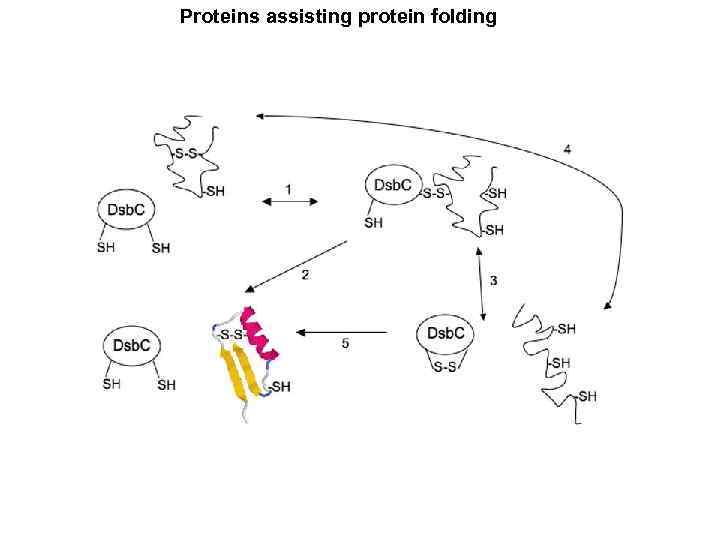 Proteins assisting protein folding
Proteins assisting protein folding
 Proteins assisting protein folding Peptidyl prolyl isomerase (PPIase) - accelerates cis-trans isomerization - twists peptide bond so that C, O, and N atoms are no longer planar
Proteins assisting protein folding Peptidyl prolyl isomerase (PPIase) - accelerates cis-trans isomerization - twists peptide bond so that C, O, and N atoms are no longer planar
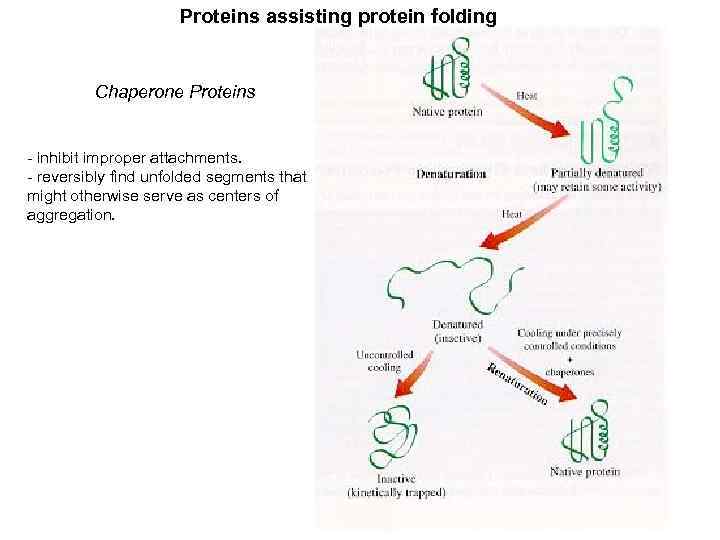 Proteins assisting protein folding Chaperone Proteins - inhibit improper attachments. - reversibly find unfolded segments that might otherwise serve as centers of aggregation.
Proteins assisting protein folding Chaperone Proteins - inhibit improper attachments. - reversibly find unfolded segments that might otherwise serve as centers of aggregation.
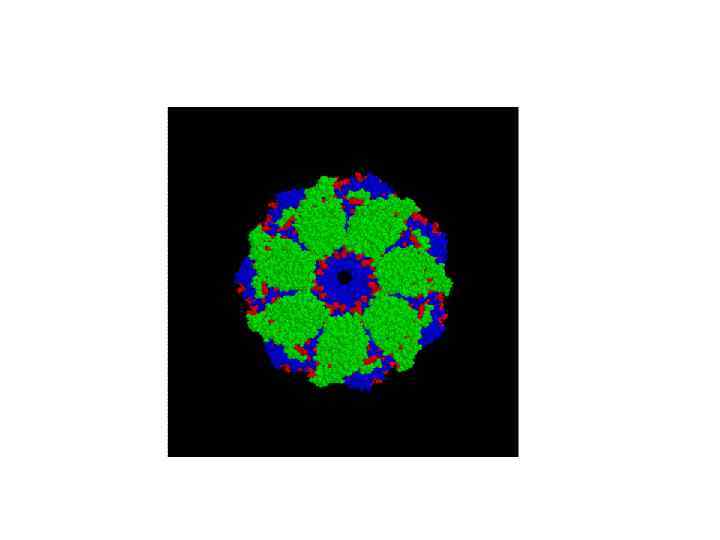
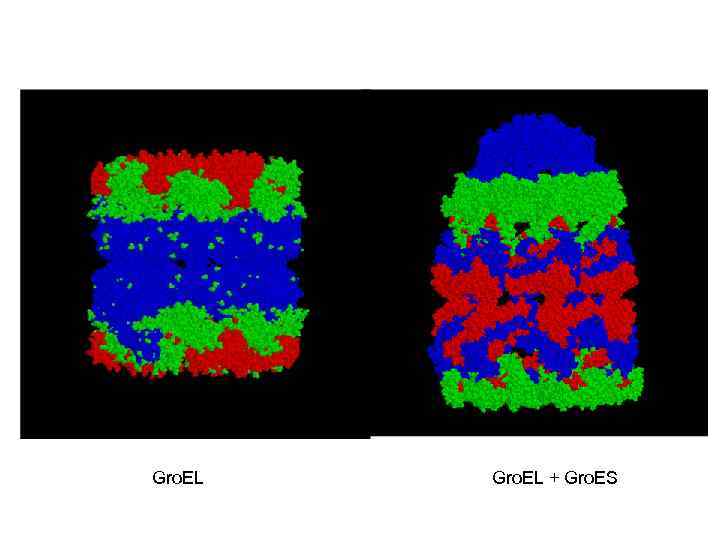 Gro. EL + Gro. ES
Gro. EL + Gro. ES
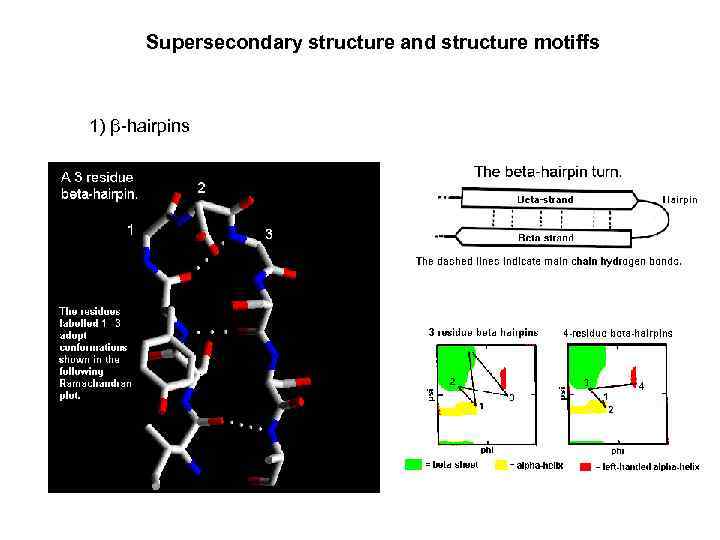 Supersecondary structure and structure motiffs 1) β-hairpins
Supersecondary structure and structure motiffs 1) β-hairpins
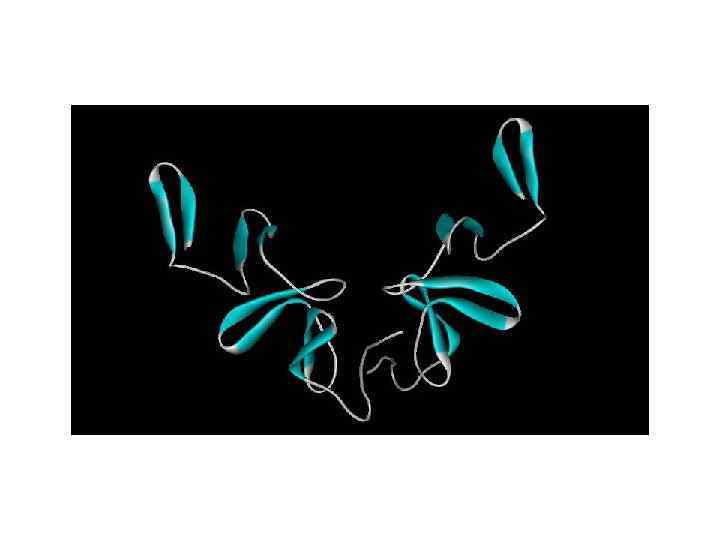
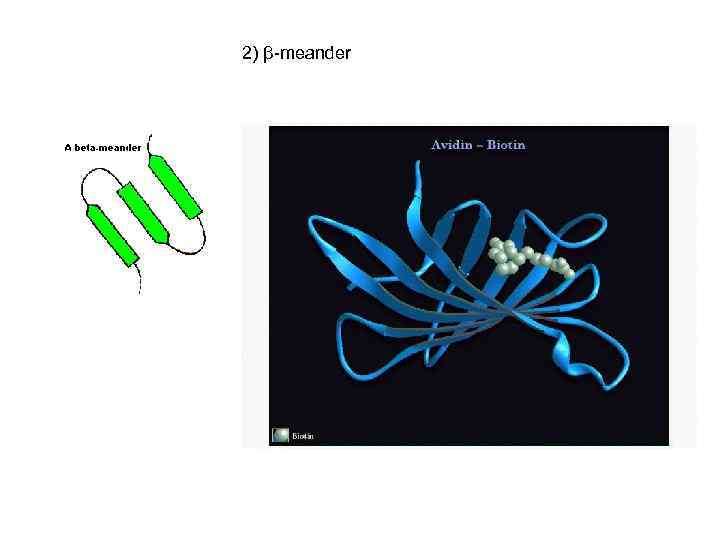 2) β-meander
2) β-meander
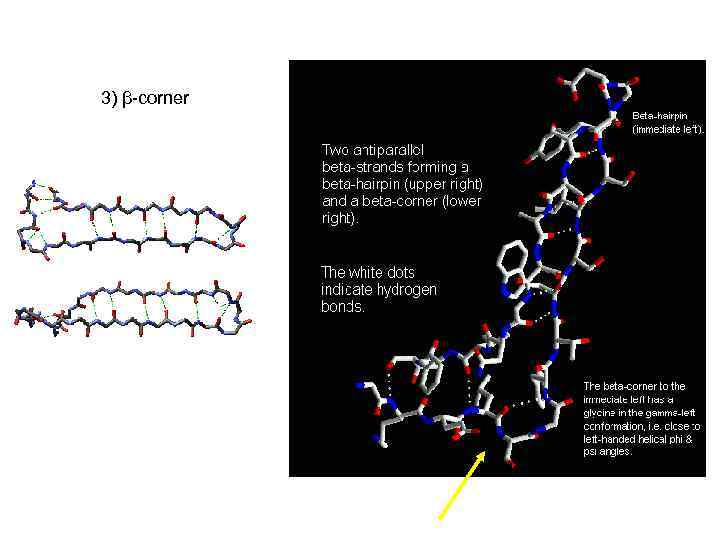 3) β-corner
3) β-corner
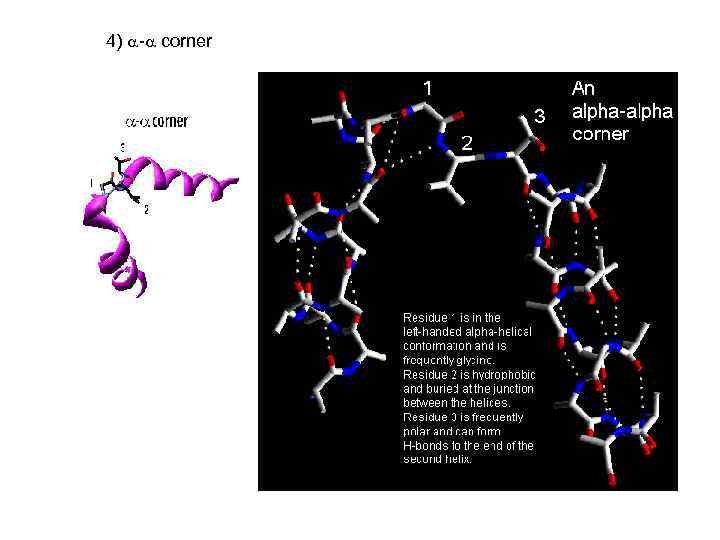 4) - corner
4) - corner
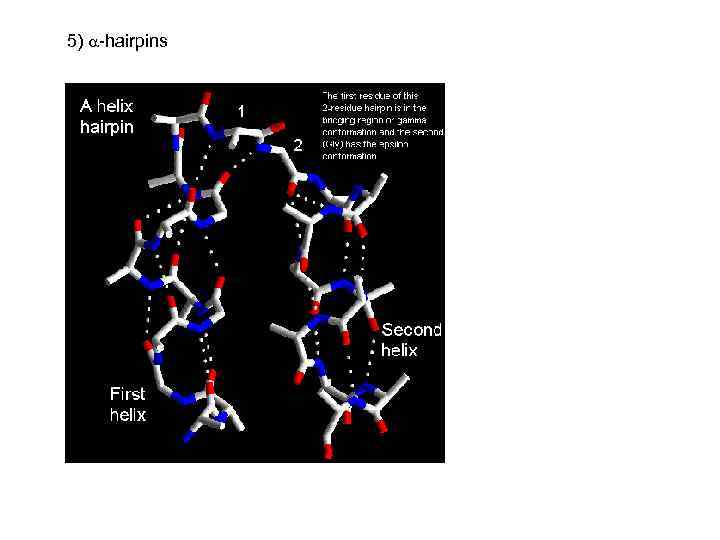 5) -hairpins
5) -hairpins
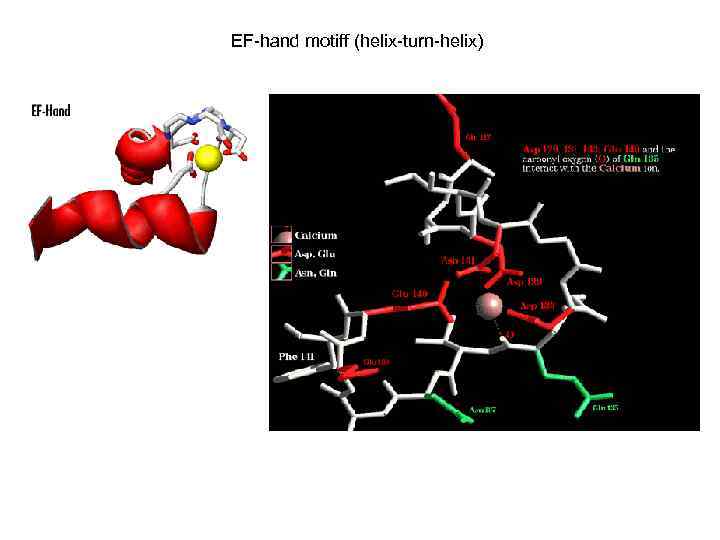 EF-hand motiff (helix-turn-helix)
EF-hand motiff (helix-turn-helix)
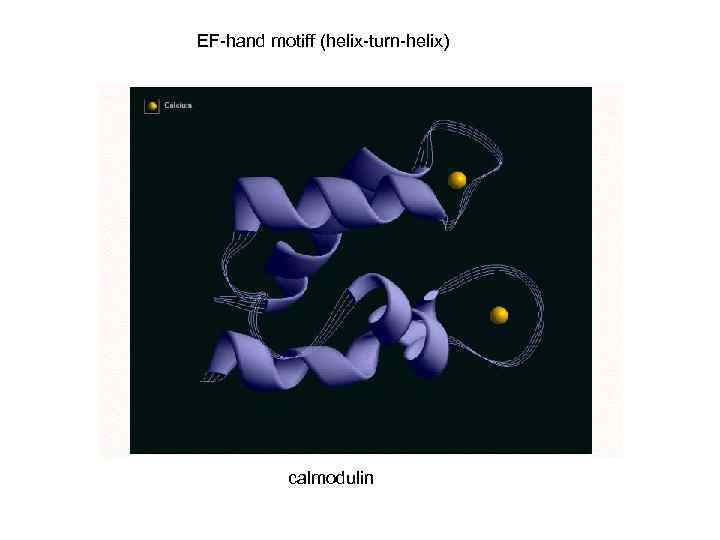 EF-hand motiff (helix-turn-helix) calmodulin
EF-hand motiff (helix-turn-helix) calmodulin
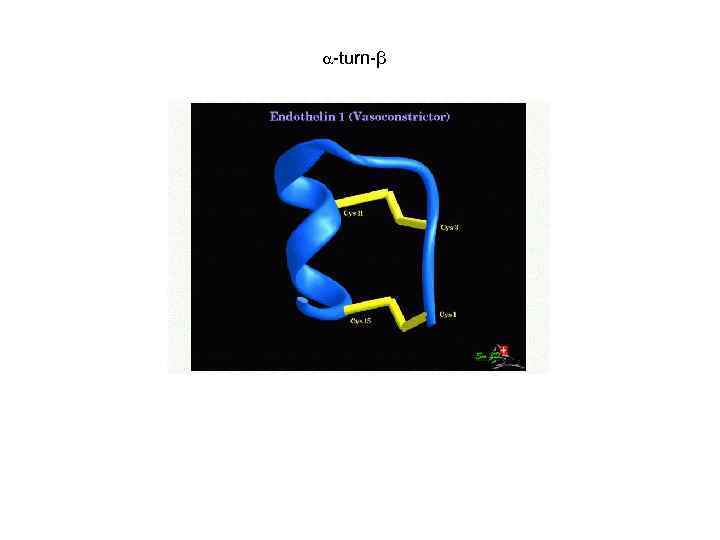 -turn-β
-turn-β
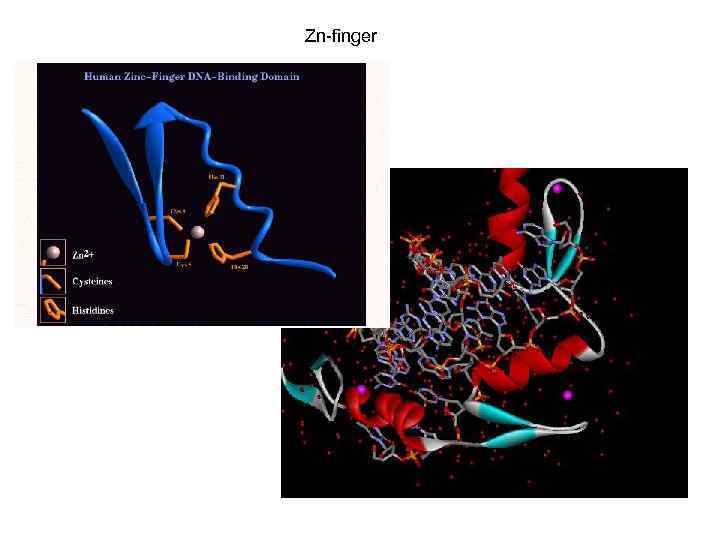 Zn-finger
Zn-finger
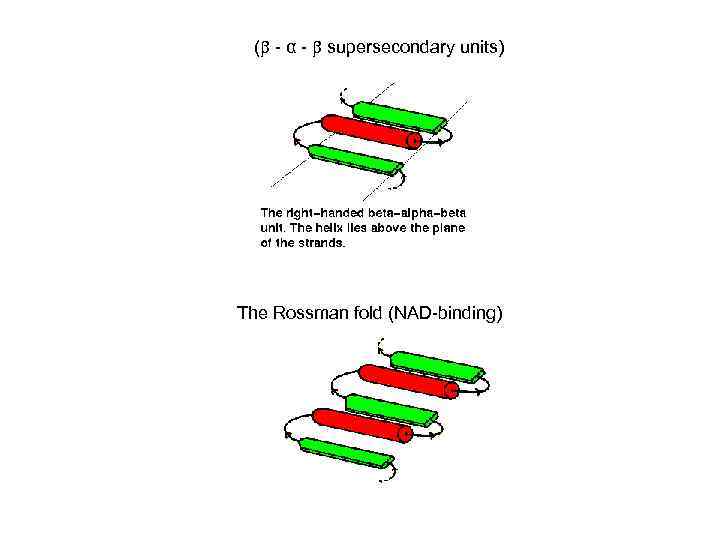 ( - α - supersecondary units) The Rossman fold (NAD-binding)
( - α - supersecondary units) The Rossman fold (NAD-binding)
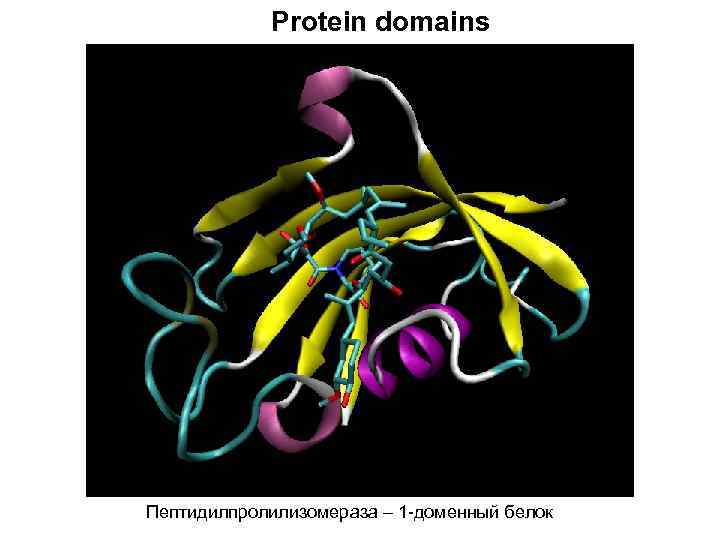 Protein domains Пептидилпролилизомераза – 1 -доменный белок
Protein domains Пептидилпролилизомераза – 1 -доменный белок
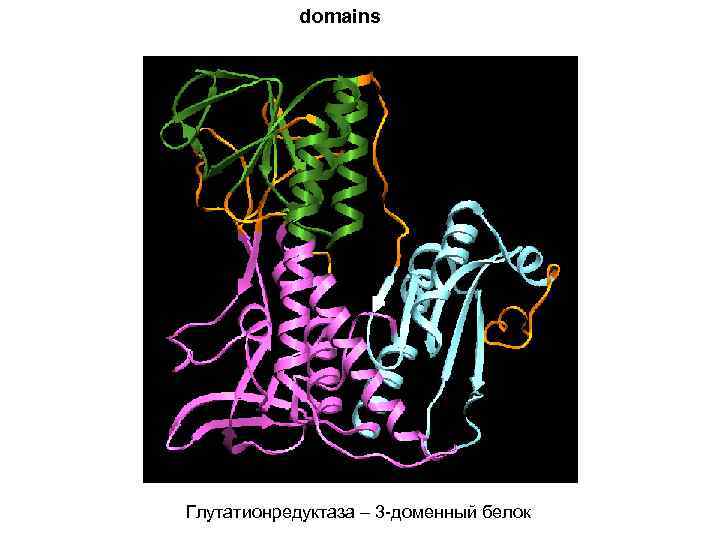 domains Глутатионредуктаза – 3 -доменный белок
domains Глутатионредуктаза – 3 -доменный белок
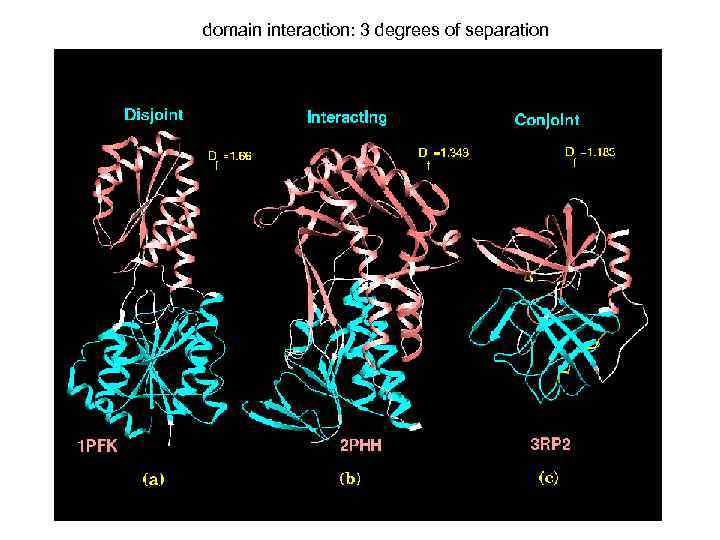 domain interaction: 3 degrees of separation
domain interaction: 3 degrees of separation
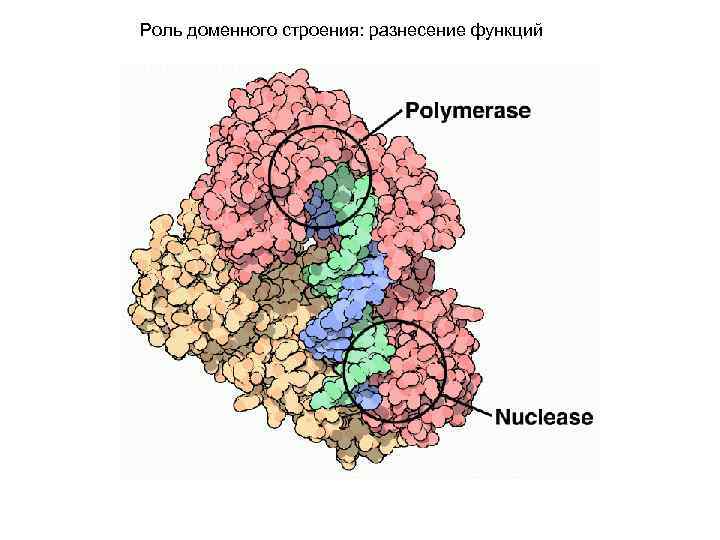 Роль доменного строения: разнесение функций
Роль доменного строения: разнесение функций
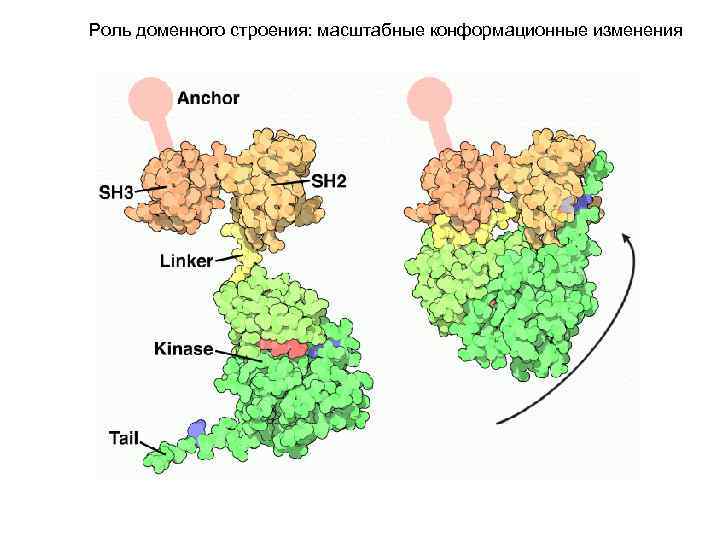 Роль доменного строения: масштабные конформационные изменения
Роль доменного строения: масштабные конформационные изменения
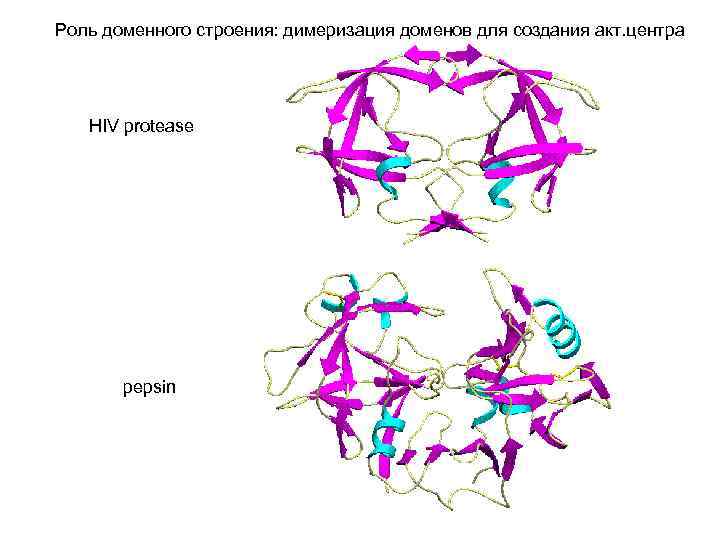 Роль доменного строения: димеризация доменов для создания акт. центра HIV protease pepsin
Роль доменного строения: димеризация доменов для создания акт. центра HIV protease pepsin
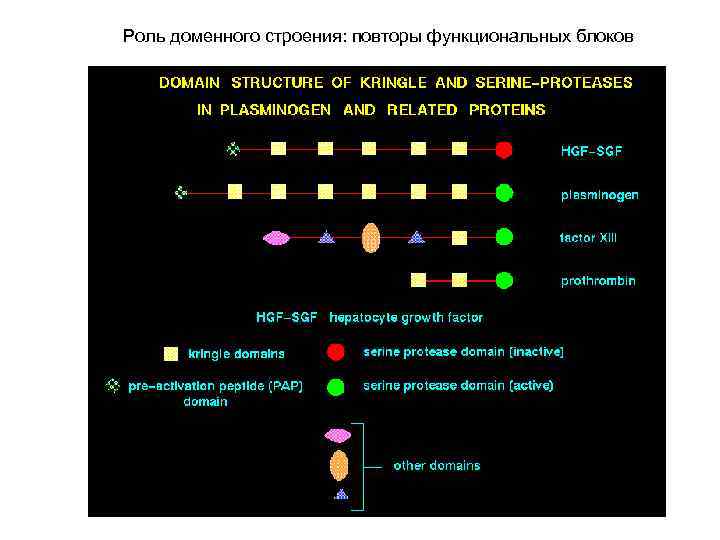 Роль доменного строения: повторы функциональных блоков
Роль доменного строения: повторы функциональных блоков
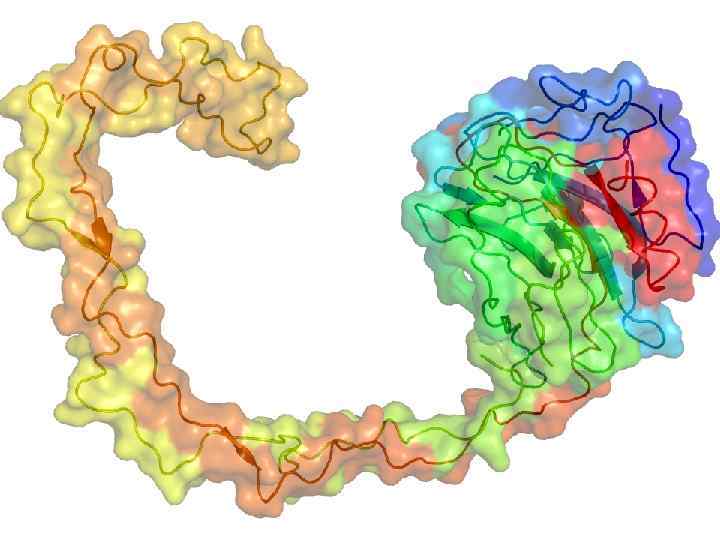
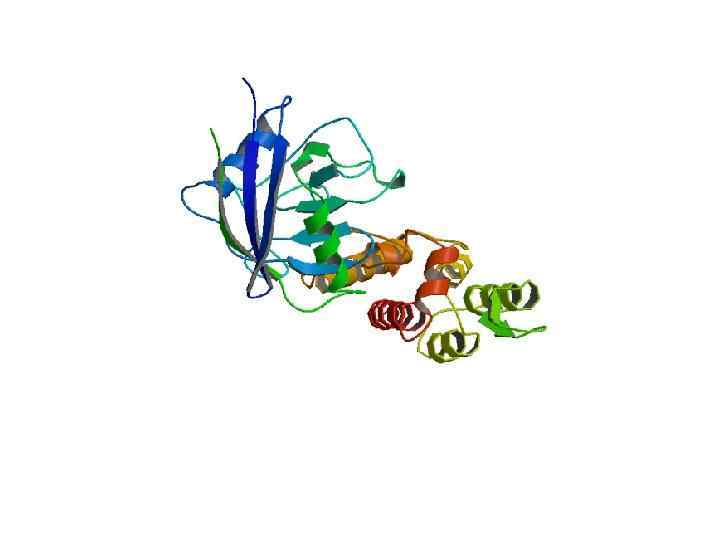
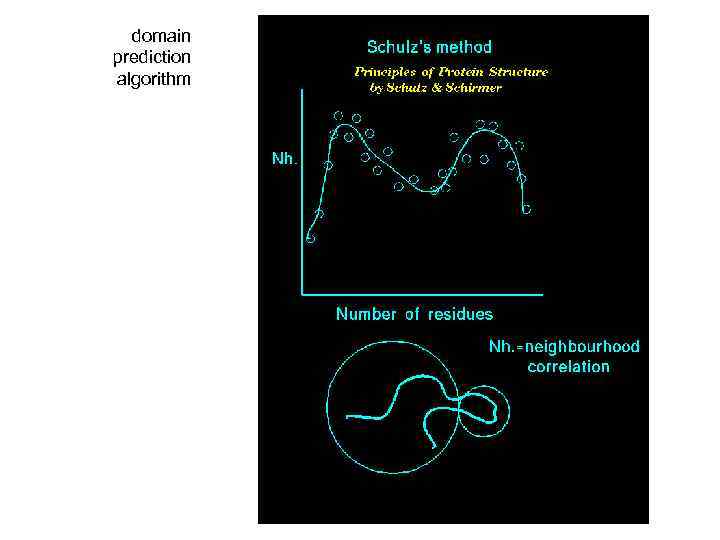 domain prediction algorithm
domain prediction algorithm
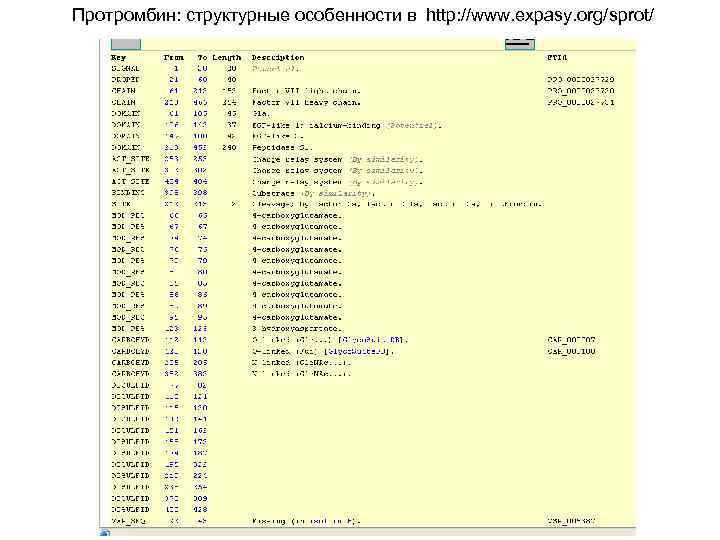 Протромбин: структурные особенности в http: //www. expasy. org/sprot/
Протромбин: структурные особенности в http: //www. expasy. org/sprot/
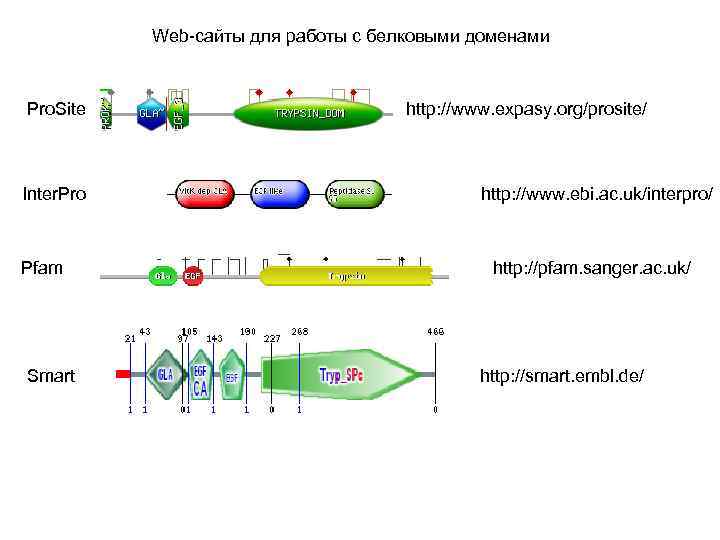 Web-сайты для работы с белковыми доменами Pro. Site Inter. Pro Pfam Smart http: //www. expasy. org/prosite/ http: //www. ebi. ac. uk/interpro/ http: //pfam. sanger. ac. uk/ http: //smart. embl. de/
Web-сайты для работы с белковыми доменами Pro. Site Inter. Pro Pfam Smart http: //www. expasy. org/prosite/ http: //www. ebi. ac. uk/interpro/ http: //pfam. sanger. ac. uk/ http: //smart. embl. de/
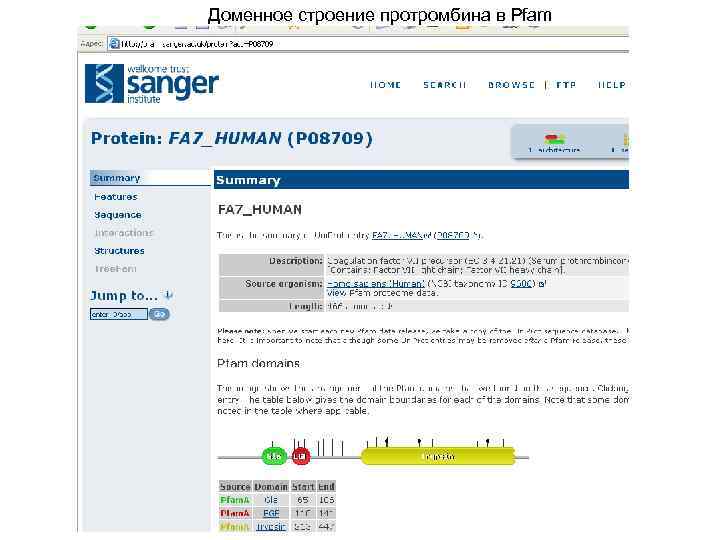 Доменное строение протромбина в Pfam
Доменное строение протромбина в Pfam
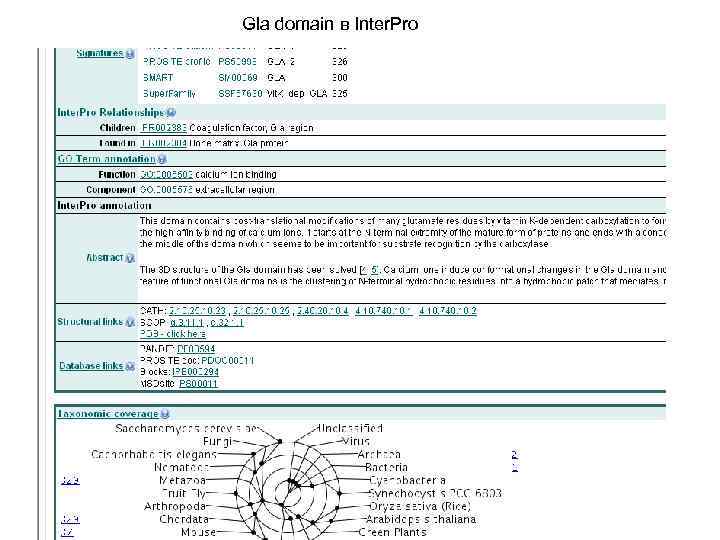 Gla domain в Inter. Pro
Gla domain в Inter. Pro
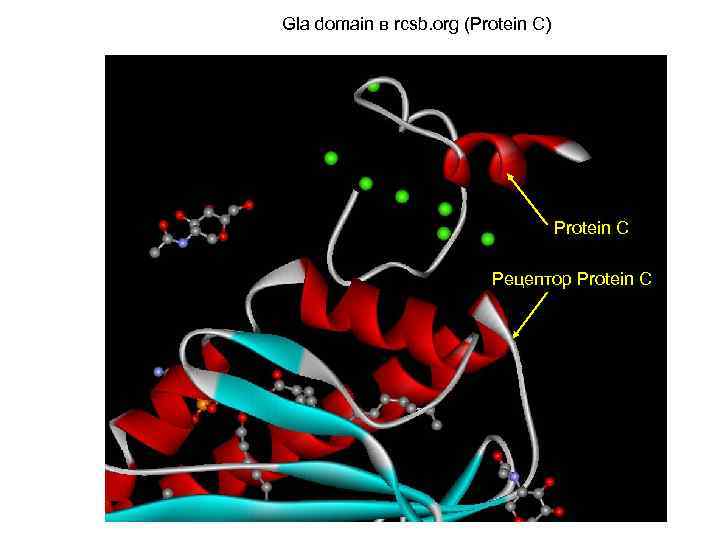 Gla domain в rcsb. org (Protein C) Protein C Рецептор Protein C
Gla domain в rcsb. org (Protein C) Protein C Рецептор Protein C
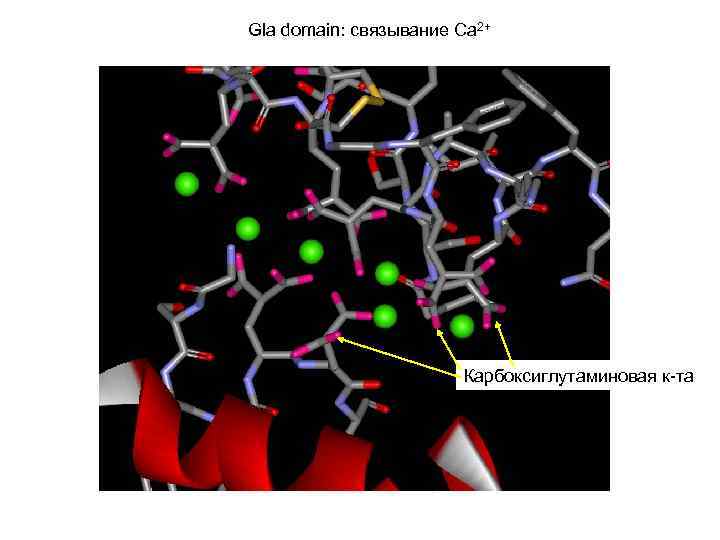 Gla domain: связывание Ca 2+ Карбоксиглутаминовая к-та
Gla domain: связывание Ca 2+ Карбоксиглутаминовая к-та
 EGF domain в Inter. Pro
EGF domain в Inter. Pro
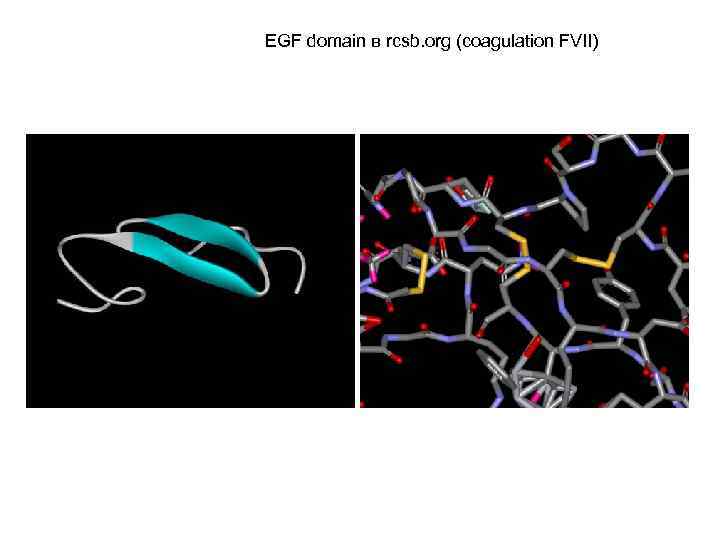 EGF domain в rcsb. org (coagulation FVII)
EGF domain в rcsb. org (coagulation FVII)
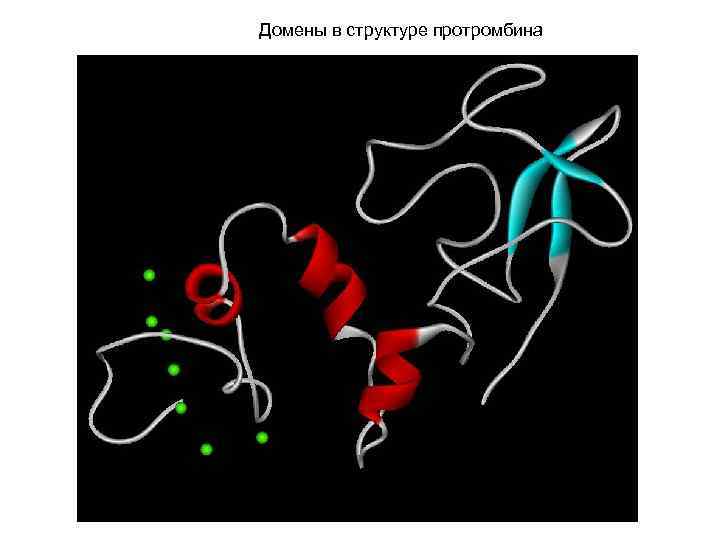 Домены в структуре протромбина
Домены в структуре протромбина
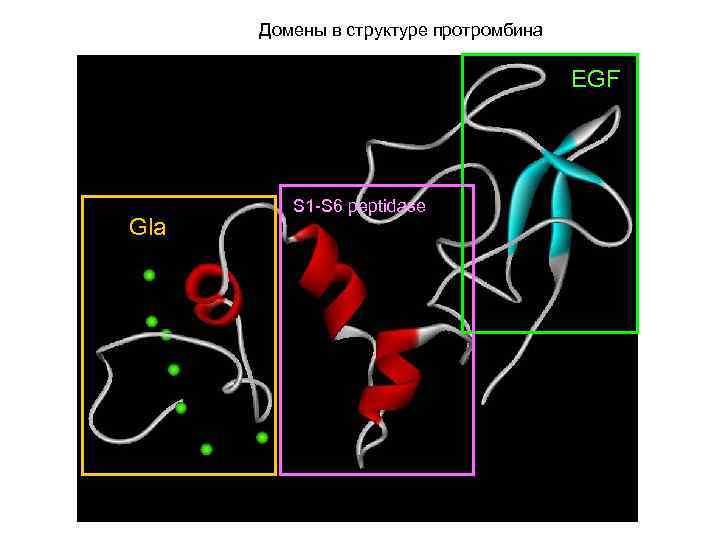 Домены в структуре протромбина EGF Gla S 1 -S 6 peptidase
Домены в структуре протромбина EGF Gla S 1 -S 6 peptidase
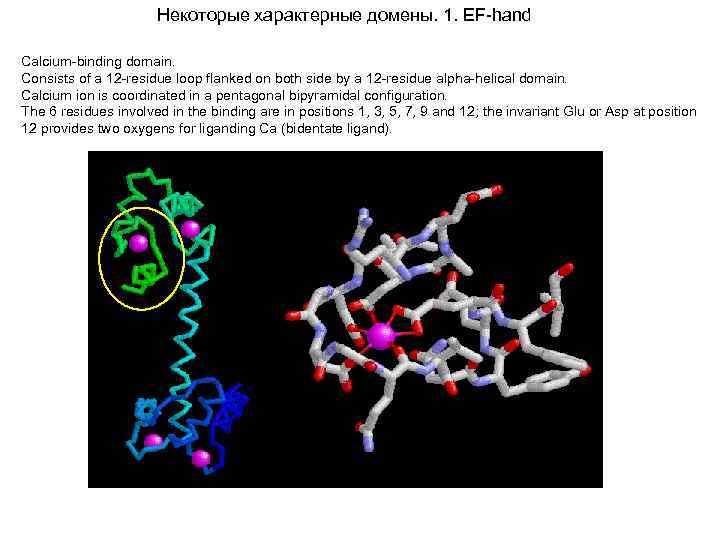 Некоторые характерные домены. 1. EF-hand Calcium-binding domain. Consists of a 12 -residue loop flanked on both side by a 12 -residue alpha-helical domain. Calcium ion is coordinated in a pentagonal bipyramidal configuration. The 6 residues involved in the binding are in positions 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 and 12; the invariant Glu or Asp at position 12 provides two oxygens for liganding Ca (bidentate ligand).
Некоторые характерные домены. 1. EF-hand Calcium-binding domain. Consists of a 12 -residue loop flanked on both side by a 12 -residue alpha-helical domain. Calcium ion is coordinated in a pentagonal bipyramidal configuration. The 6 residues involved in the binding are in positions 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 and 12; the invariant Glu or Asp at position 12 provides two oxygens for liganding Ca (bidentate ligand).
 Некоторые характерные домены. 2. SH 2 The Src homology 2 (SH 2) domain. Found in many signaltransducing proteins. Functions as a regulatory module of intracellular signalling cascades. Interacts with high affinity to phosphotyrosine-containing target peptides in a sequence-specific manner. Recognizes between 3 -6 residues C-terminal to the phosphorylated tyrosine in a fashion that differs from one SH 2 domain to another, and strictly phosphorylation-dependent manner. Are frequently found as repeats in a single protein sequence and will then often bind both mono- and di-phosphorylated substrates. The structure of the SH 2 domain belongs to the alpha+beta class, its overall shape forming a compact flattened hemisphere. The core structural elements comprise a central hydrophobic anti-parallel beta-sheet, flanked by 2 short alphahelices. The loop between strands 2 and 3 provides many of the binding interactions with the phosphate group of its phosphopeptide ligand, and is hence designated the phosphate binding loop, the phosphorylated ligand binds perpendicular to the beta-sheet and typically interacts with the phosphate binding loop and a hydrophobic binding pocket that interacts with a p. Y+3 side chain. The N- and C-termini of the domain are close together in space and on the opposite face from the phosphopeptide binding surface and it has been speculated that this has facilitated their integration into surface -exposed regions of host proteins.
Некоторые характерные домены. 2. SH 2 The Src homology 2 (SH 2) domain. Found in many signaltransducing proteins. Functions as a regulatory module of intracellular signalling cascades. Interacts with high affinity to phosphotyrosine-containing target peptides in a sequence-specific manner. Recognizes between 3 -6 residues C-terminal to the phosphorylated tyrosine in a fashion that differs from one SH 2 domain to another, and strictly phosphorylation-dependent manner. Are frequently found as repeats in a single protein sequence and will then often bind both mono- and di-phosphorylated substrates. The structure of the SH 2 domain belongs to the alpha+beta class, its overall shape forming a compact flattened hemisphere. The core structural elements comprise a central hydrophobic anti-parallel beta-sheet, flanked by 2 short alphahelices. The loop between strands 2 and 3 provides many of the binding interactions with the phosphate group of its phosphopeptide ligand, and is hence designated the phosphate binding loop, the phosphorylated ligand binds perpendicular to the beta-sheet and typically interacts with the phosphate binding loop and a hydrophobic binding pocket that interacts with a p. Y+3 side chain. The N- and C-termini of the domain are close together in space and on the opposite face from the phosphopeptide binding surface and it has been speculated that this has facilitated their integration into surface -exposed regions of host proteins.
 Некоторые характерные домены. 3. P-loop ATP-binding motif. A Gly-rich loop preceded by a β-sheet and followed by an α-helix. It interacts with the phosphate groups of the nucleotide and the Mg 2+ ion, which coordinates the βand the γ-phosphates. Consensus signature: Gxxxx. GK(S/T), which is often referred to as Walker’s A motif.
Некоторые характерные домены. 3. P-loop ATP-binding motif. A Gly-rich loop preceded by a β-sheet and followed by an α-helix. It interacts with the phosphate groups of the nucleotide and the Mg 2+ ion, which coordinates the βand the γ-phosphates. Consensus signature: Gxxxx. GK(S/T), which is often referred to as Walker’s A motif.
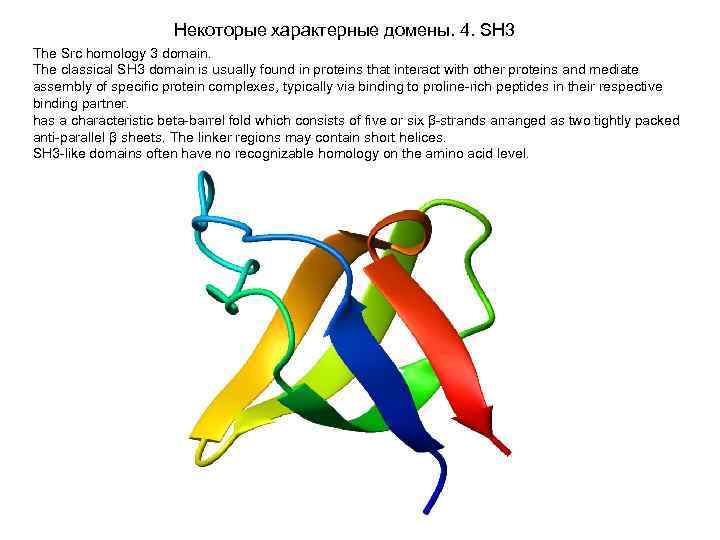 Некоторые характерные домены. 4. SH 3 The Src homology 3 domain. The classical SH 3 domain is usually found in proteins that interact with other proteins and mediate assembly of specific protein complexes, typically via binding to proline-rich peptides in their respective binding partner. has a characteristic beta-barrel fold which consists of five or six β-strands arranged as two tightly packed anti-parallel β sheets. The linker regions may contain short helices. SH 3 -like domains often have no recognizable homology on the amino acid level.
Некоторые характерные домены. 4. SH 3 The Src homology 3 domain. The classical SH 3 domain is usually found in proteins that interact with other proteins and mediate assembly of specific protein complexes, typically via binding to proline-rich peptides in their respective binding partner. has a characteristic beta-barrel fold which consists of five or six β-strands arranged as two tightly packed anti-parallel β sheets. The linker regions may contain short helices. SH 3 -like domains often have no recognizable homology on the amino acid level.
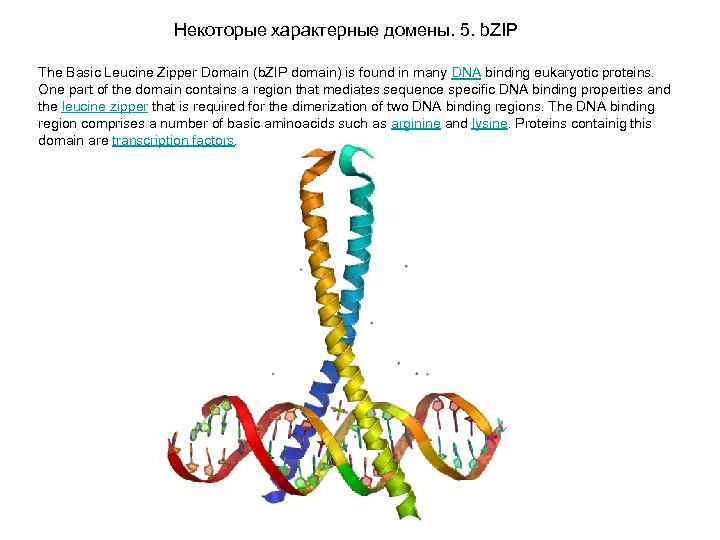 Некоторые характерные домены. 5. b. ZIP The Basic Leucine Zipper Domain (b. ZIP domain) is found in many DNA binding eukaryotic proteins. One part of the domain contains a region that mediates sequence specific DNA binding properties and the leucine zipper that is required for the dimerization of two DNA binding regions. The DNA binding region comprises a number of basic aminoacids such as arginine and lysine. Proteins containig this domain are transcription factors.
Некоторые характерные домены. 5. b. ZIP The Basic Leucine Zipper Domain (b. ZIP domain) is found in many DNA binding eukaryotic proteins. One part of the domain contains a region that mediates sequence specific DNA binding properties and the leucine zipper that is required for the dimerization of two DNA binding regions. The DNA binding region comprises a number of basic aminoacids such as arginine and lysine. Proteins containig this domain are transcription factors.
 Protein folds
Protein folds
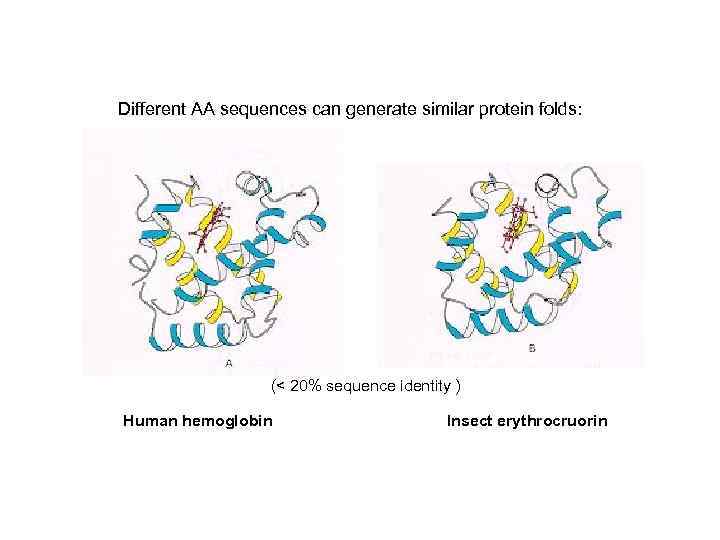 Different AA sequences can generate similar protein folds: (< 20% sequence identity ) Human hemoglobin Insect erythrocruorin
Different AA sequences can generate similar protein folds: (< 20% sequence identity ) Human hemoglobin Insect erythrocruorin
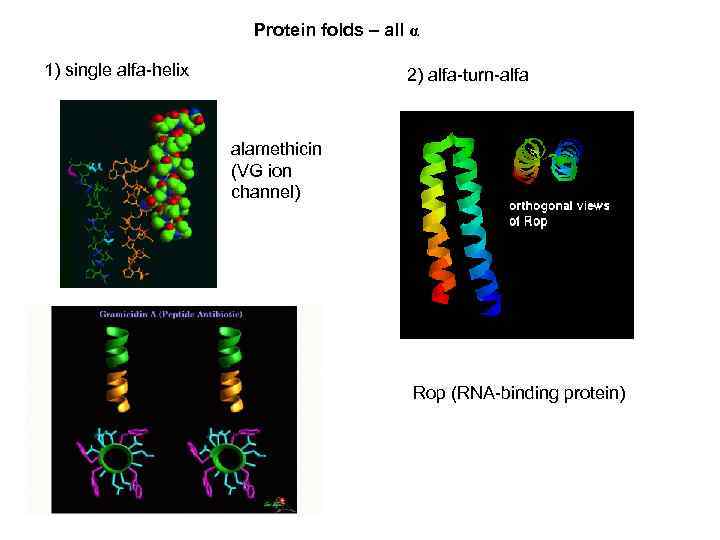 Protein folds – all α 1) single alfa-helix 2) alfa-turn-alfa alamethicin (VG ion channel) Rop (RNA-binding protein)
Protein folds – all α 1) single alfa-helix 2) alfa-turn-alfa alamethicin (VG ion channel) Rop (RNA-binding protein)
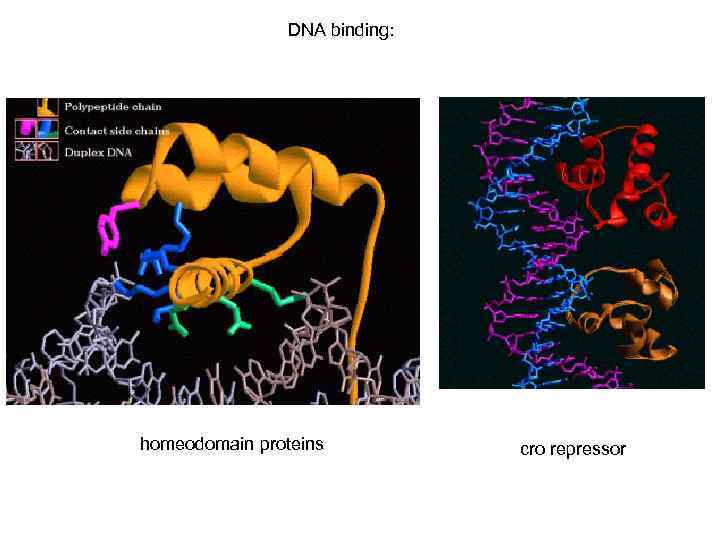 DNA binding: homeodomain proteins cro repressor
DNA binding: homeodomain proteins cro repressor
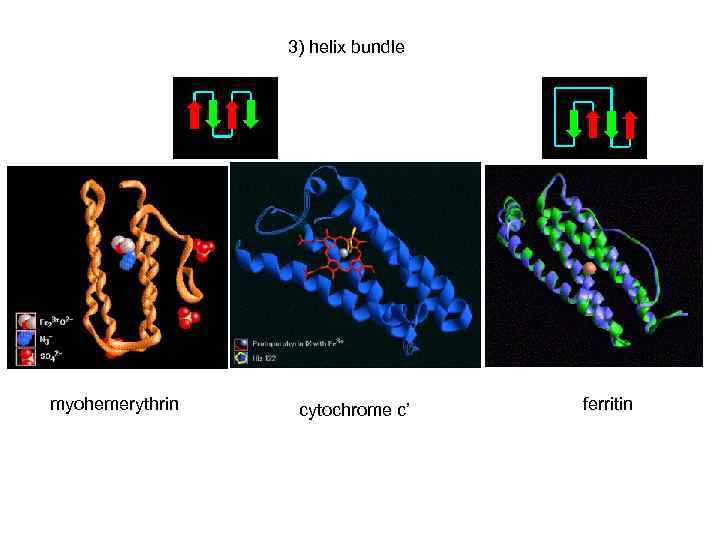 3) helix bundle myohemerythrin cytochrome c’ ferritin
3) helix bundle myohemerythrin cytochrome c’ ferritin
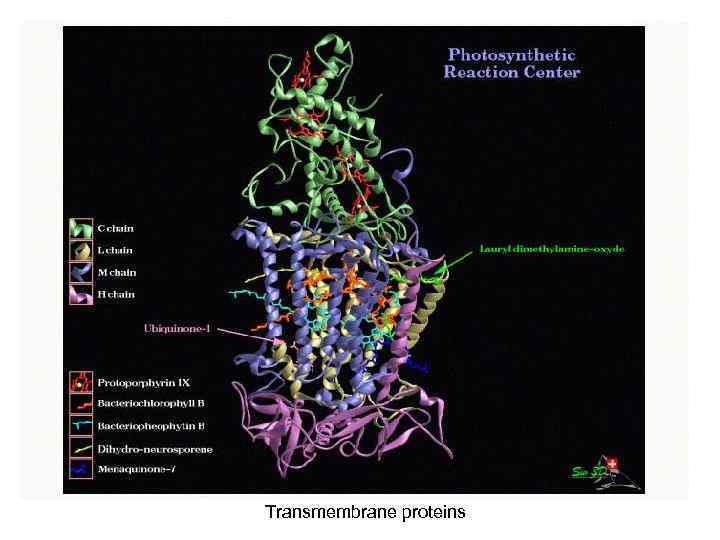 Transmembrane proteins
Transmembrane proteins
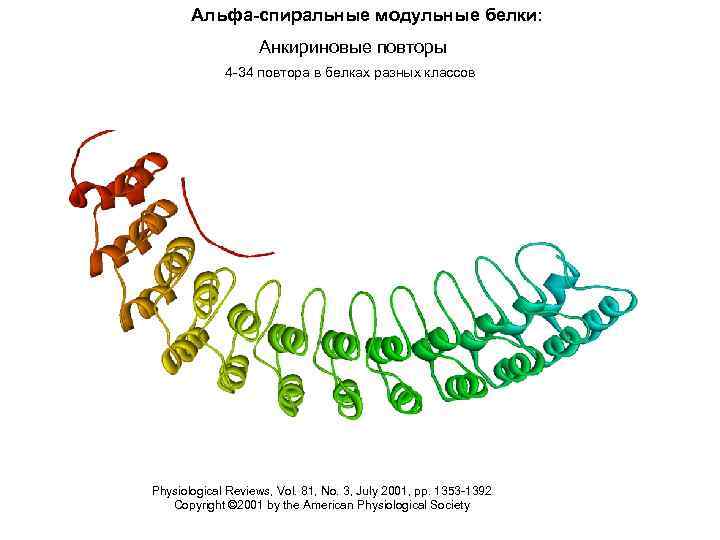 Альфа-спиральные модульные белки: Анкириновые повторы 4 -34 повтора в белках разных классов Physiological Reviews, Vol. 81, No. 3, July 2001, pp. 1353 -1392 Copyright © 2001 by the American Physiological Society
Альфа-спиральные модульные белки: Анкириновые повторы 4 -34 повтора в белках разных классов Physiological Reviews, Vol. 81, No. 3, July 2001, pp. 1353 -1392 Copyright © 2001 by the American Physiological Society
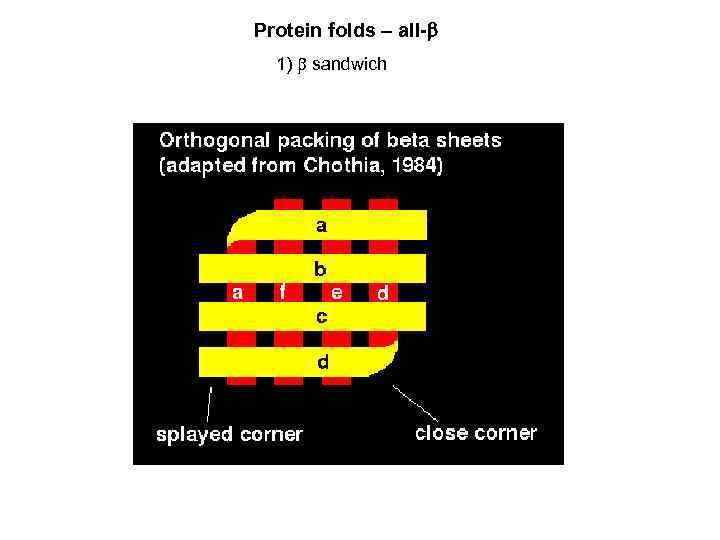 Protein folds – all- 1) sandwich
Protein folds – all- 1) sandwich
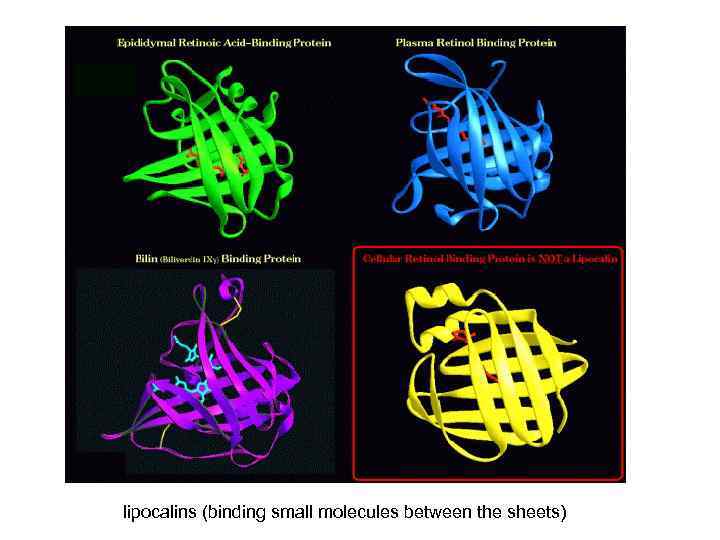 lipocalins (binding small molecules between the sheets)
lipocalins (binding small molecules between the sheets)
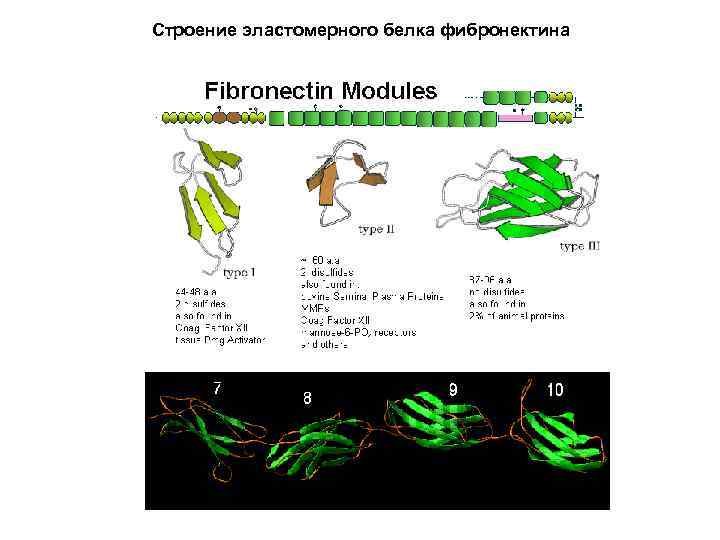 Строение эластомерного белка фибронектина
Строение эластомерного белка фибронектина
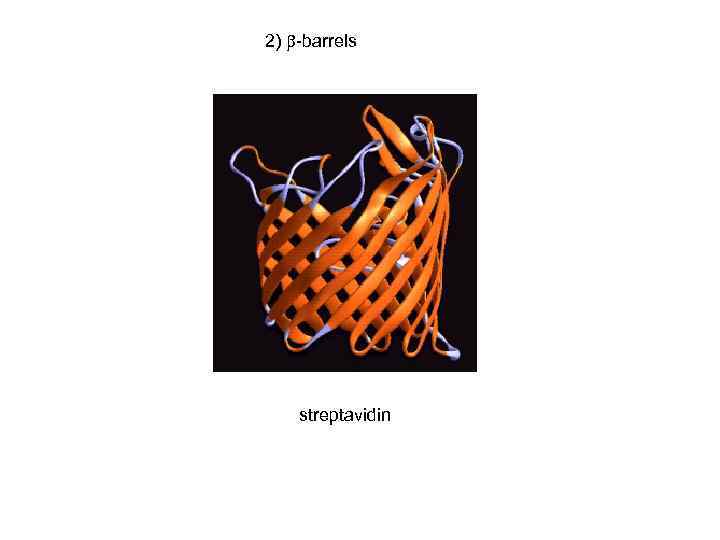 2) -barrels streptavidin
2) -barrels streptavidin
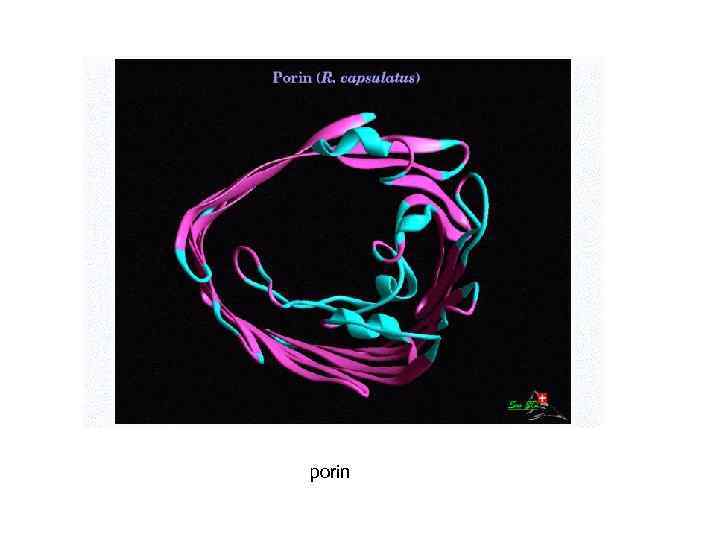 porin
porin
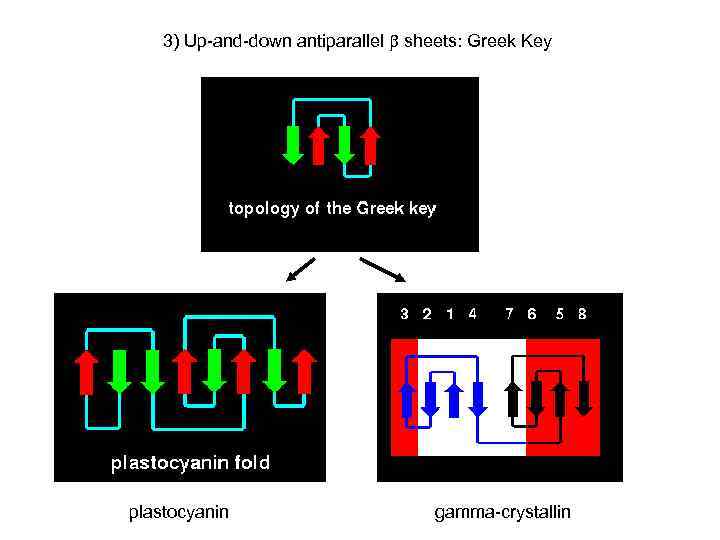 3) Up-and-down antiparallel sheets: Greek Key plastocyanin gamma-crystallin
3) Up-and-down antiparallel sheets: Greek Key plastocyanin gamma-crystallin
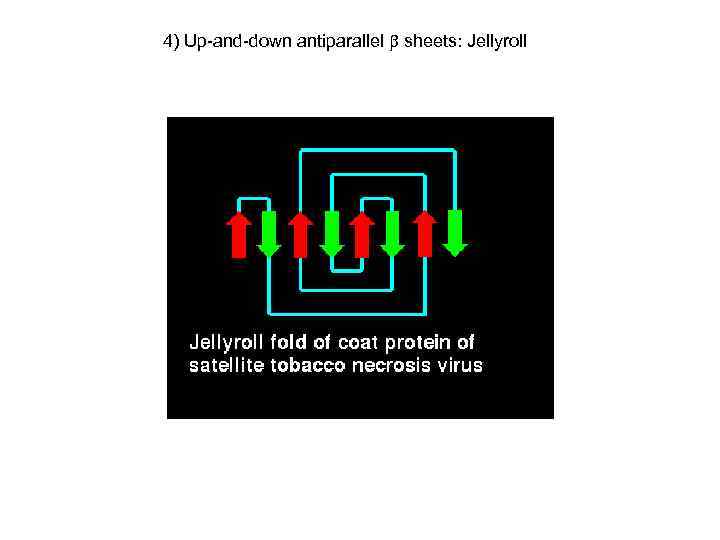 4) Up-and-down antiparallel sheets: Jellyroll
4) Up-and-down antiparallel sheets: Jellyroll
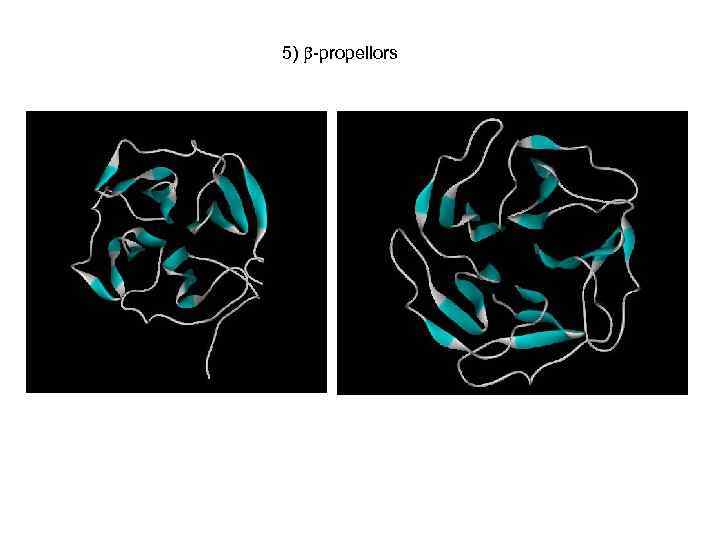 5) -propellors
5) -propellors
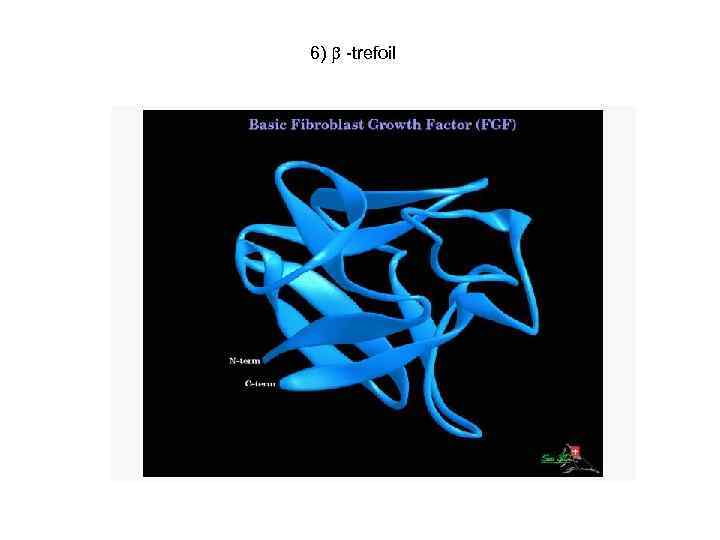 6) -trefoil
6) -trefoil
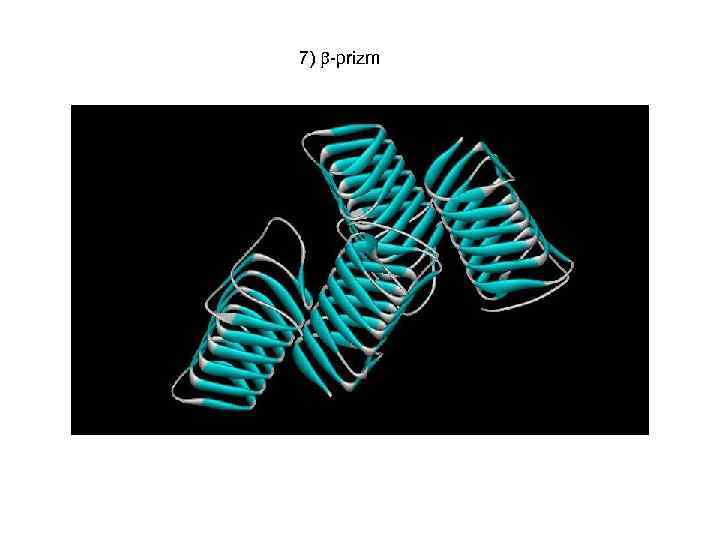 7) -prizm
7) -prizm
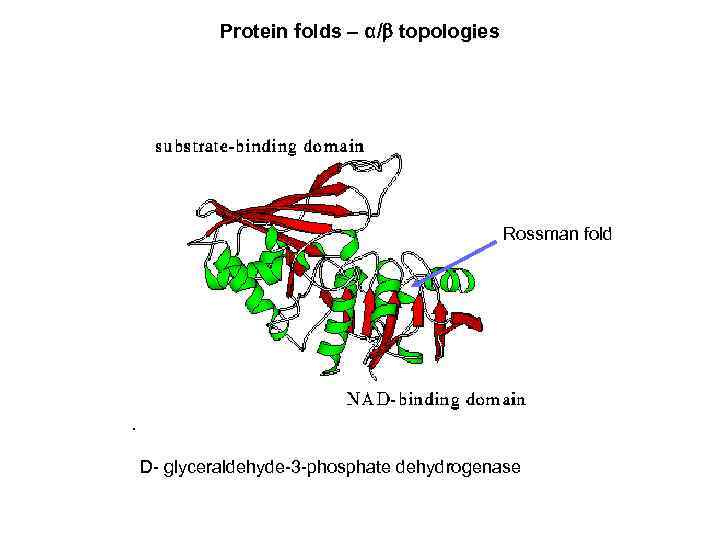 Protein folds – α/ topologies Rossman fold D- glyceraldehyde-3 -phosphate dehydrogenase
Protein folds – α/ topologies Rossman fold D- glyceraldehyde-3 -phosphate dehydrogenase
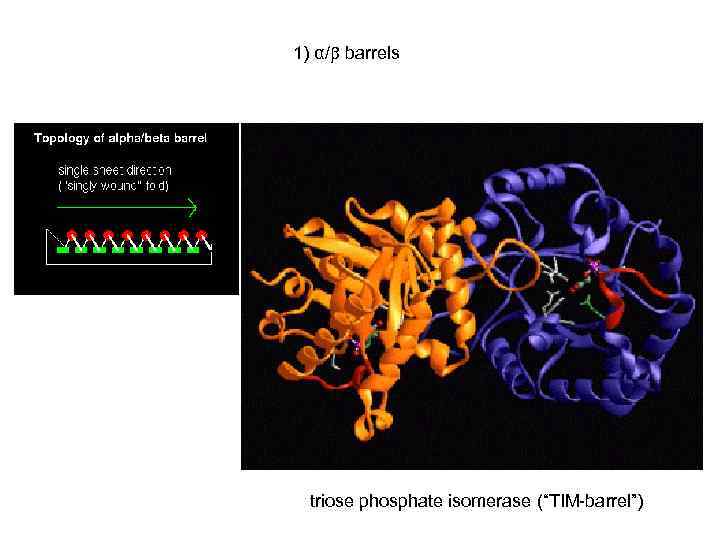 1) α/ barrels triose phosphate isomerase (“TIM-barrel”)
1) α/ barrels triose phosphate isomerase (“TIM-barrel”)
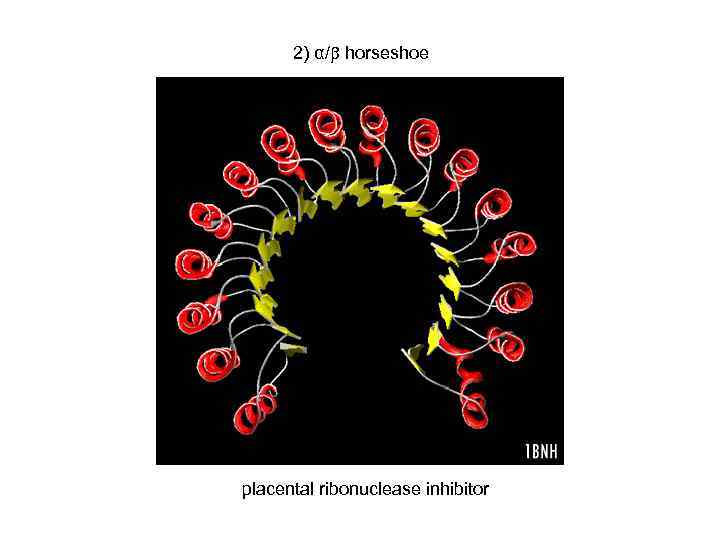 2) α/ horseshoe placental ribonuclease inhibitor
2) α/ horseshoe placental ribonuclease inhibitor
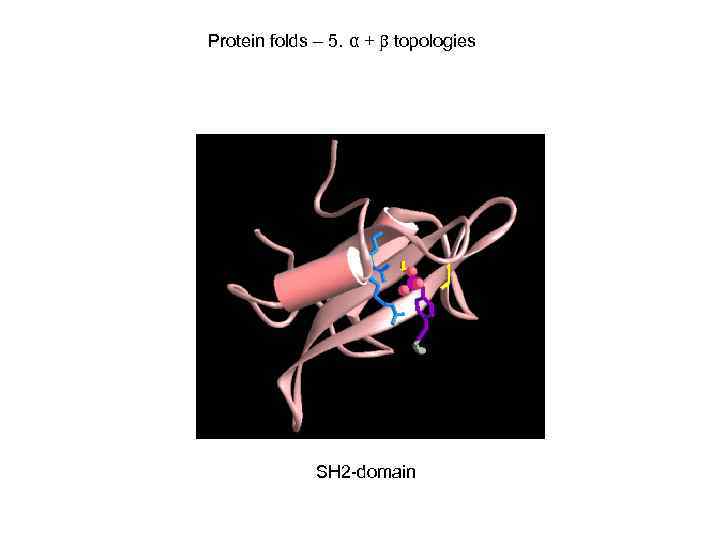 Protein folds – 5. α + topologies SH 2 -domain
Protein folds – 5. α + topologies SH 2 -domain
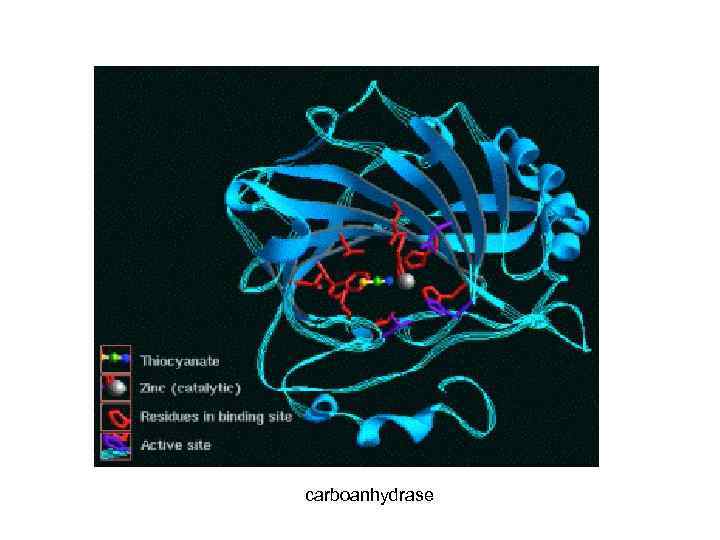 carboanhydrase
carboanhydrase
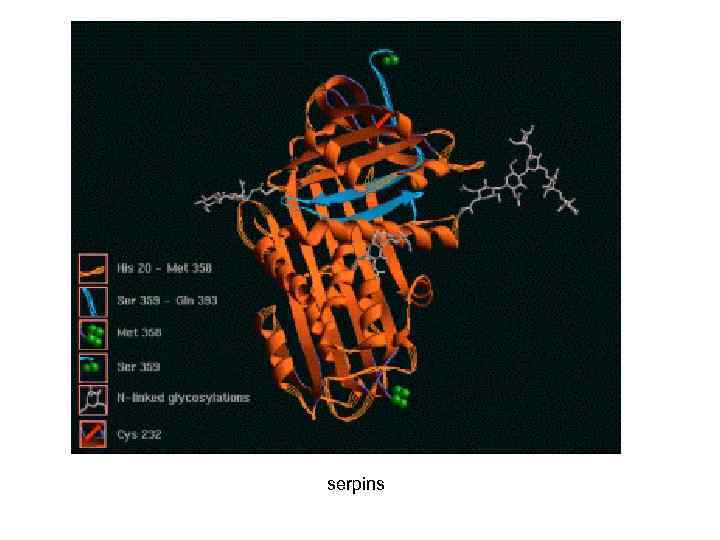 serpins
serpins
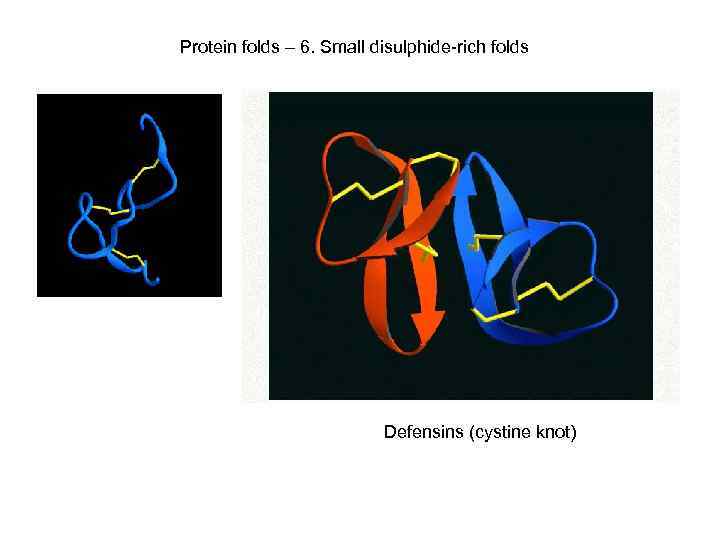 Protein folds – 6. Small disulphide-rich folds Kringle domain Defensins (cystine knot)
Protein folds – 6. Small disulphide-rich folds Kringle domain Defensins (cystine knot)
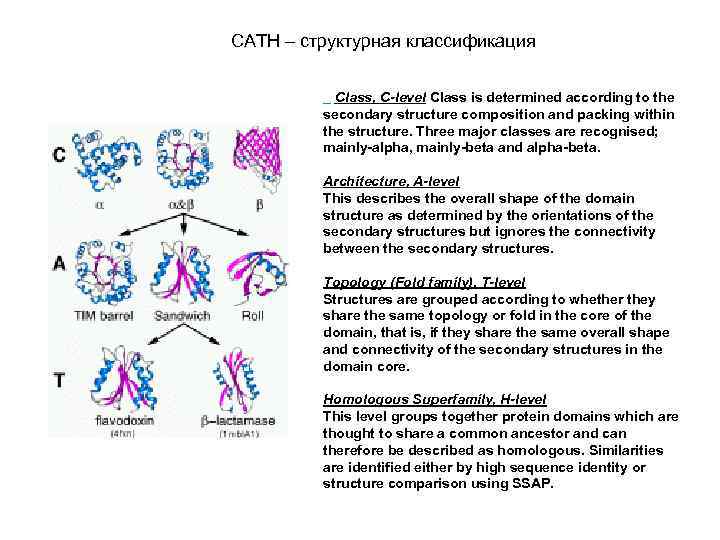 CATH – структурная классификация Class, C-level Class is determined according to the secondary structure composition and packing within the structure. Three major classes are recognised; mainly-alpha, mainly-beta and alpha-beta. Architecture, A-level This describes the overall shape of the domain structure as determined by the orientations of the secondary structures but ignores the connectivity between the secondary structures. Topology (Fold family), T-level Structures are grouped according to whether they share the same topology or fold in the core of the domain, that is, if they share the same overall shape and connectivity of the secondary structures in the domain core. Homologous Superfamily, H-level This level groups together protein domains which are thought to share a common ancestor and can therefore be described as homologous. Similarities are identified either by high sequence identity or structure comparison using SSAP.
CATH – структурная классификация Class, C-level Class is determined according to the secondary structure composition and packing within the structure. Three major classes are recognised; mainly-alpha, mainly-beta and alpha-beta. Architecture, A-level This describes the overall shape of the domain structure as determined by the orientations of the secondary structures but ignores the connectivity between the secondary structures. Topology (Fold family), T-level Structures are grouped according to whether they share the same topology or fold in the core of the domain, that is, if they share the same overall shape and connectivity of the secondary structures in the domain core. Homologous Superfamily, H-level This level groups together protein domains which are thought to share a common ancestor and can therefore be described as homologous. Similarities are identified either by high sequence identity or structure comparison using SSAP.
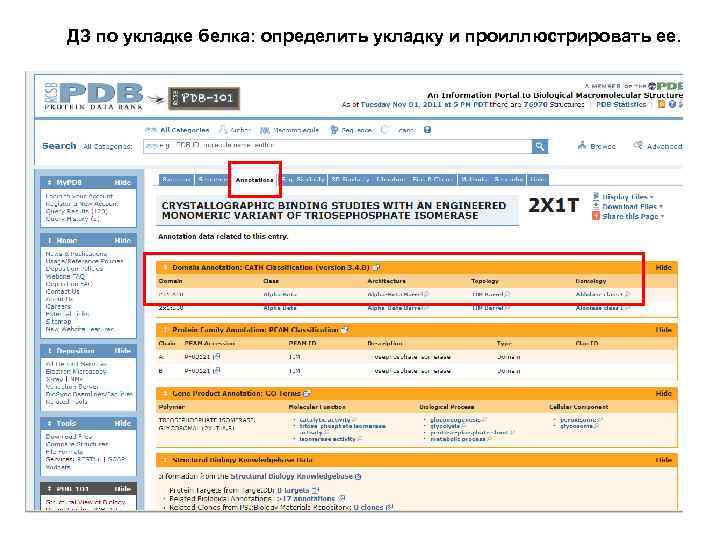 ДЗ по укладке белка: определить укладку и проиллюстрировать ее.
ДЗ по укладке белка: определить укладку и проиллюстрировать ее.


