69f41f6d15a72be572755b9ae2771c46.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 44
 Protein analysis and proteomics (Part 2 of 2)
Protein analysis and proteomics (Part 2 of 2)
 Copyright notice Many of the images in this powerpoint presentation are from Bioinformatics and Functional Genomics by Jonathan Pevsner (ISBN 0 -471 -21004 -8). Copyright © 2003 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. These images and materials may not be used without permission from the publisher. We welcome instructors to use these powerpoints for educational purposes, but please acknowledge the source. The book has a homepage at http: //www. bioinfbook. org Including hyperlinks to the book chapters.
Copyright notice Many of the images in this powerpoint presentation are from Bioinformatics and Functional Genomics by Jonathan Pevsner (ISBN 0 -471 -21004 -8). Copyright © 2003 by John Wiley & Sons, Inc. These images and materials may not be used without permission from the publisher. We welcome instructors to use these powerpoints for educational purposes, but please acknowledge the source. The book has a homepage at http: //www. bioinfbook. org Including hyperlinks to the book chapters.
 Proteomics: High throughput protein analysis Proteomics is the study of the entire collection of proteins encoded by a genome “Proteomics” refers to all the proteins in a cell and/or all the proteins in an organism Large-scale protein analysis 2 D protein gels Yeast two-hybrid Rosetta Stone approach Pathways Page 247
Proteomics: High throughput protein analysis Proteomics is the study of the entire collection of proteins encoded by a genome “Proteomics” refers to all the proteins in a cell and/or all the proteins in an organism Large-scale protein analysis 2 D protein gels Yeast two-hybrid Rosetta Stone approach Pathways Page 247
 Classical biochemical approach Identify an activity Develop a bioassay Perform a biochemical purification Strategies: size, charge, hydrophobicity Purify protein to homogeneity Clone c. DNA, express recombinant protein Grow crystals, solve structure (Wednesday) Page 247
Classical biochemical approach Identify an activity Develop a bioassay Perform a biochemical purification Strategies: size, charge, hydrophobicity Purify protein to homogeneity Clone c. DNA, express recombinant protein Grow crystals, solve structure (Wednesday) Page 247
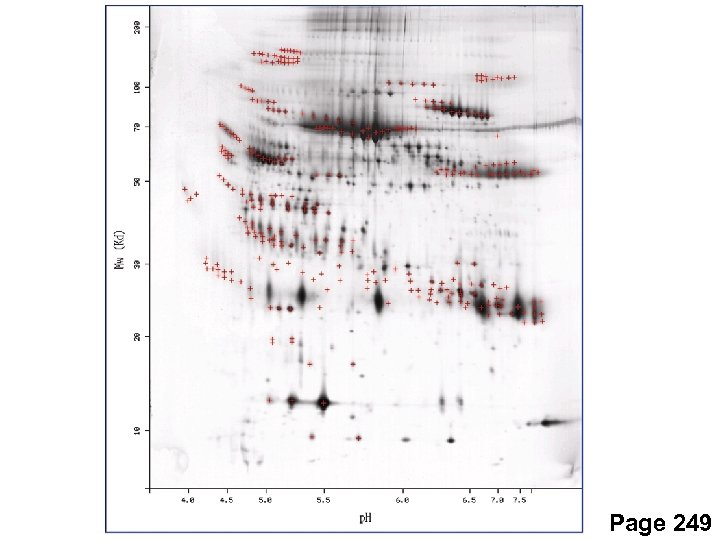
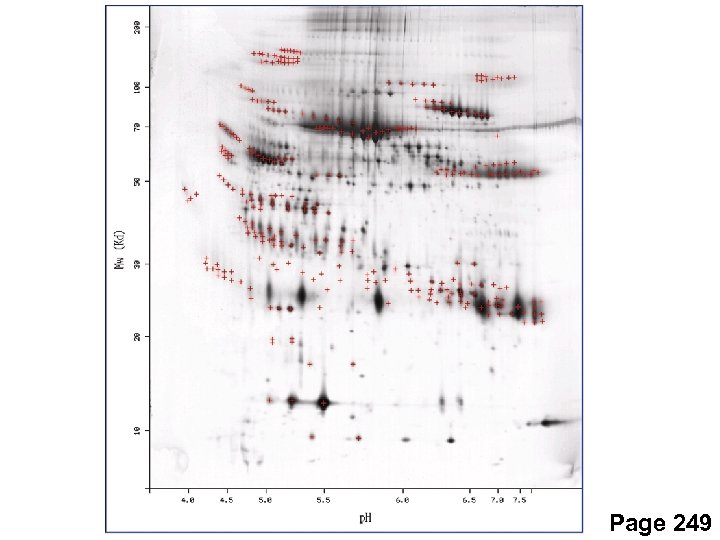
 Two-dimensional protein gels First dimension: isoelectric focusing Second dimension: SDS-PAGE Page 248
Two-dimensional protein gels First dimension: isoelectric focusing Second dimension: SDS-PAGE Page 248
 Page 249
Page 249
 Two-dimensional protein gels First dimension: isoelectric focusing Electrophorese ampholytes to establish a p. H gradient Can use a pre-made strip Proteins migrate to their isoelectric point (p. I) then stop (net charge is zero) Range of p. I typically 4 -9 (5 -8 most common) Page 248
Two-dimensional protein gels First dimension: isoelectric focusing Electrophorese ampholytes to establish a p. H gradient Can use a pre-made strip Proteins migrate to their isoelectric point (p. I) then stop (net charge is zero) Range of p. I typically 4 -9 (5 -8 most common) Page 248
 Two-dimensional protein gels Second dimension: SDS-PAGE Electrophorese proteins through an acrylamide matrix Proteins are charged and migrate through an electric field v = Eq / d 6 prh Conditions are denaturing Can resolve hundreds to thousands of proteins Page 248
Two-dimensional protein gels Second dimension: SDS-PAGE Electrophorese proteins through an acrylamide matrix Proteins are charged and migrate through an electric field v = Eq / d 6 prh Conditions are denaturing Can resolve hundreds to thousands of proteins Page 248
 Page 249
Page 249
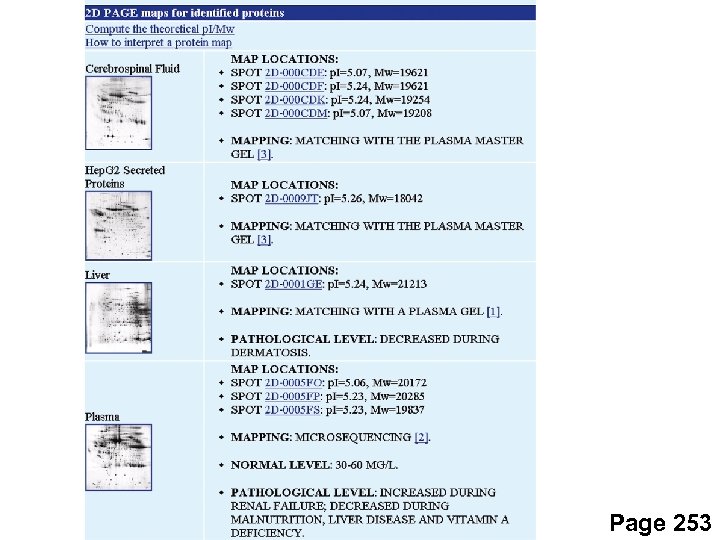
 Proteins identified on 2 D gels (IEF/SDS-PAGE) Direct protein microsequencing by Edman degradations -- done at Hopkins, other cores -- typically need 5 picomoles -- often get 10 to 20 amino acids sequenced Protein mass analysis by MALDI-TOF -- done at core facilities -- often detect posttranslational modifications -- matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight spectroscopy Page 250 -1
Proteins identified on 2 D gels (IEF/SDS-PAGE) Direct protein microsequencing by Edman degradations -- done at Hopkins, other cores -- typically need 5 picomoles -- often get 10 to 20 amino acids sequenced Protein mass analysis by MALDI-TOF -- done at core facilities -- often detect posttranslational modifications -- matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight spectroscopy Page 250 -1
 Page 252
Page 252
 Page 253
Page 253
 Page 253
Page 253
 Page 254
Page 254
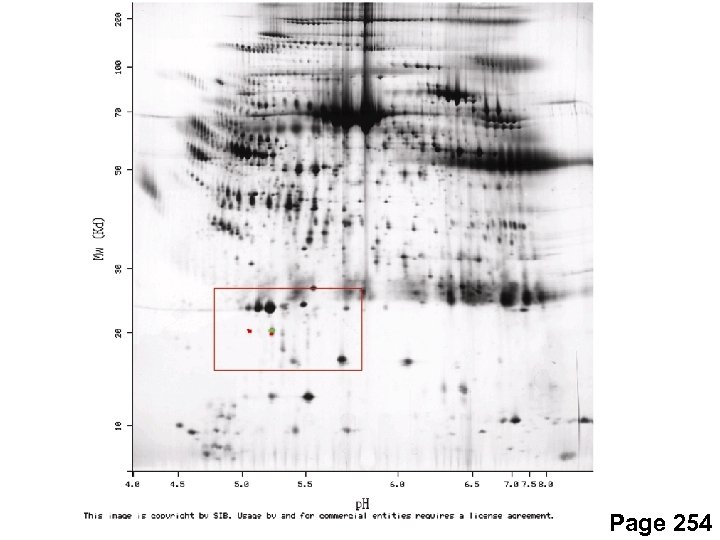
 Evaluation of 2 D gels (IEF/SDS-PAGE) Advantages: Visualize hundreds to thousands of proteins Improved identification of protein spots Disadvantages: Limited number of samples can be processed Mostly abundant proteins visualized Technically difficult Page 251
Evaluation of 2 D gels (IEF/SDS-PAGE) Advantages: Visualize hundreds to thousands of proteins Improved identification of protein spots Disadvantages: Limited number of samples can be processed Mostly abundant proteins visualized Technically difficult Page 251
 Affinity chromatography/mass spec GST Bait protein Page 252
Affinity chromatography/mass spec GST Bait protein Page 252
 Affinity chromatography/mass spec GST Bait protein Add yeast extract Protein complexes bind Most proteins do not bind Page 252
Affinity chromatography/mass spec GST Bait protein Add yeast extract Protein complexes bind Most proteins do not bind Page 252
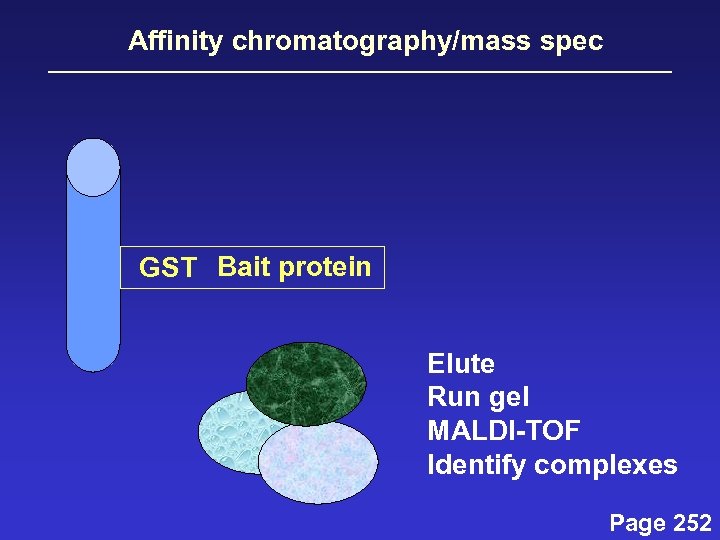 Affinity chromatography/mass spec GST Bait protein Elute Run gel MALDI-TOF Identify complexes Page 252
Affinity chromatography/mass spec GST Bait protein Elute Run gel MALDI-TOF Identify complexes Page 252
 Affinity chromatography/mass spec Data on complexes deposited in databases http: //yeast. cellzome. com http: //www. bind. ca Page 252
Affinity chromatography/mass spec Data on complexes deposited in databases http: //yeast. cellzome. com http: //www. bind. ca Page 252
 Page 252
Page 252
 Page 252
Page 252
 Evaluation of affinity chromatography/mass spec Advantages: Thousands of protein complexes identified Functions can be assigned to proteins Disadvantages: False negative results False positive results Page 253 -254
Evaluation of affinity chromatography/mass spec Advantages: Thousands of protein complexes identified Functions can be assigned to proteins Disadvantages: False negative results False positive results Page 253 -254
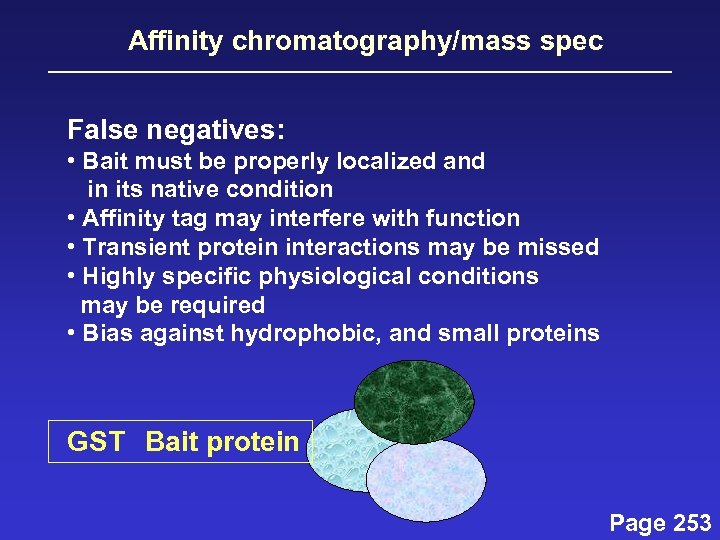 Affinity chromatography/mass spec False negatives: • Bait must be properly localized and in its native condition • Affinity tag may interfere with function • Transient protein interactions may be missed • Highly specific physiological conditions may be required • Bias against hydrophobic, and small proteins GST Bait protein Page 253
Affinity chromatography/mass spec False negatives: • Bait must be properly localized and in its native condition • Affinity tag may interfere with function • Transient protein interactions may be missed • Highly specific physiological conditions may be required • Bias against hydrophobic, and small proteins GST Bait protein Page 253
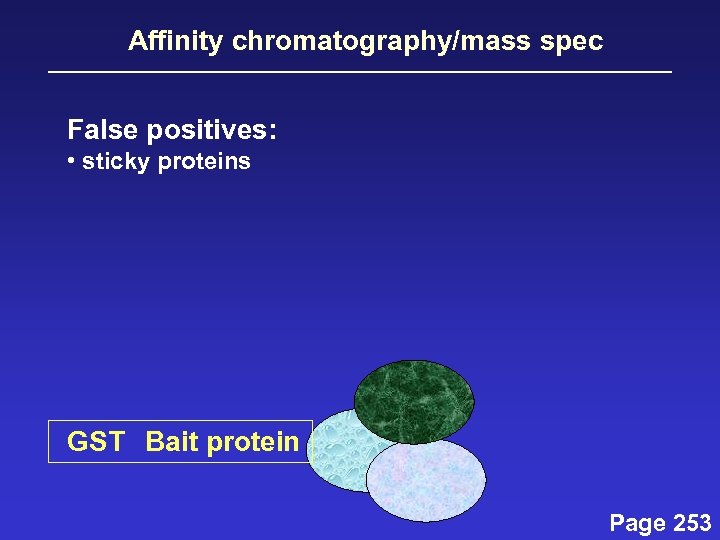 Affinity chromatography/mass spec False positives: • sticky proteins GST Bait protein Page 253
Affinity chromatography/mass spec False positives: • sticky proteins GST Bait protein Page 253
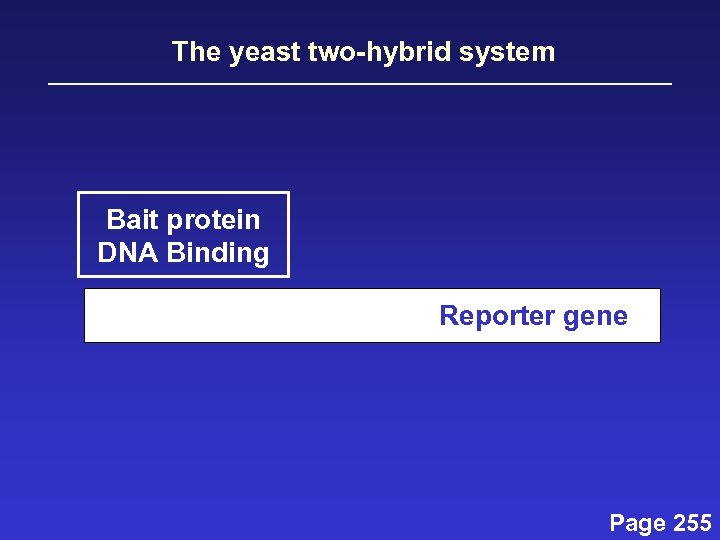 The yeast two-hybrid system Bait protein DNA Binding Reporter gene Page 255
The yeast two-hybrid system Bait protein DNA Binding Reporter gene Page 255
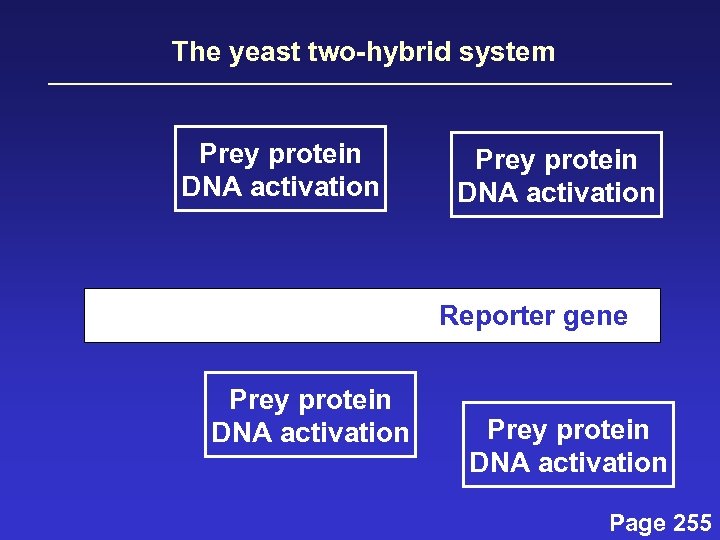 The yeast two-hybrid system Prey protein DNA activation Reporter gene Prey protein DNA activation Page 255
The yeast two-hybrid system Prey protein DNA activation Reporter gene Prey protein DNA activation Page 255
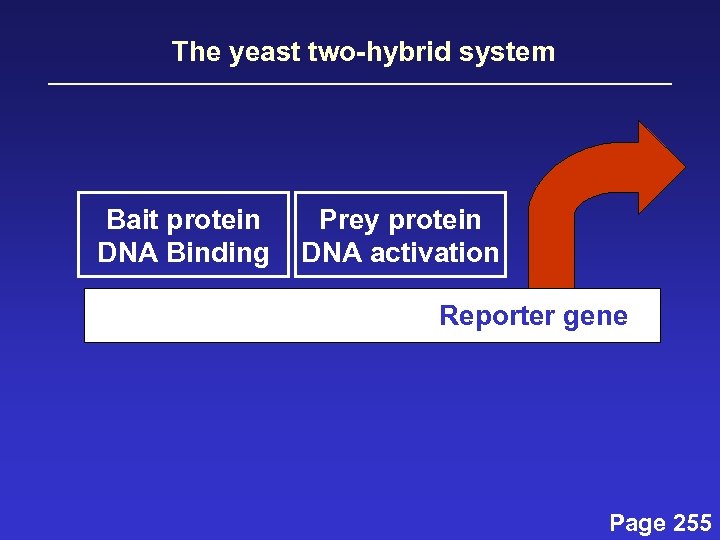 The yeast two-hybrid system Bait protein DNA Binding Prey protein DNA activation Reporter gene Page 255
The yeast two-hybrid system Bait protein DNA Binding Prey protein DNA activation Reporter gene Page 255
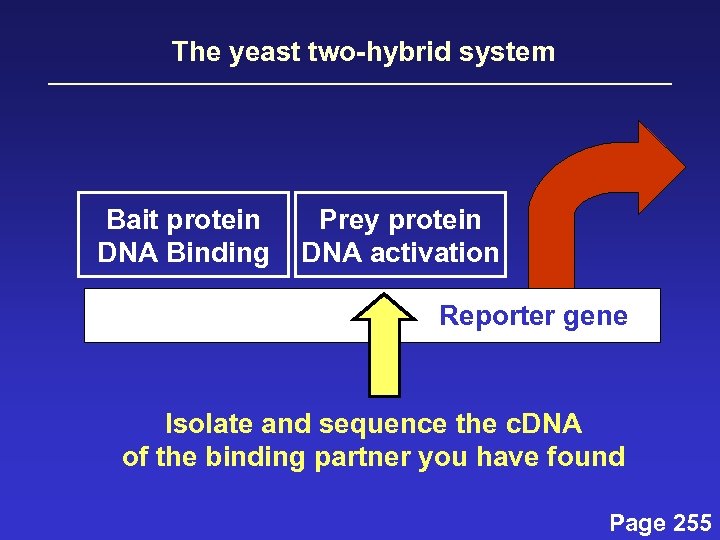 The yeast two-hybrid system Bait protein DNA Binding Prey protein DNA activation Reporter gene Isolate and sequence the c. DNA of the binding partner you have found Page 255
The yeast two-hybrid system Bait protein DNA Binding Prey protein DNA activation Reporter gene Isolate and sequence the c. DNA of the binding partner you have found Page 255
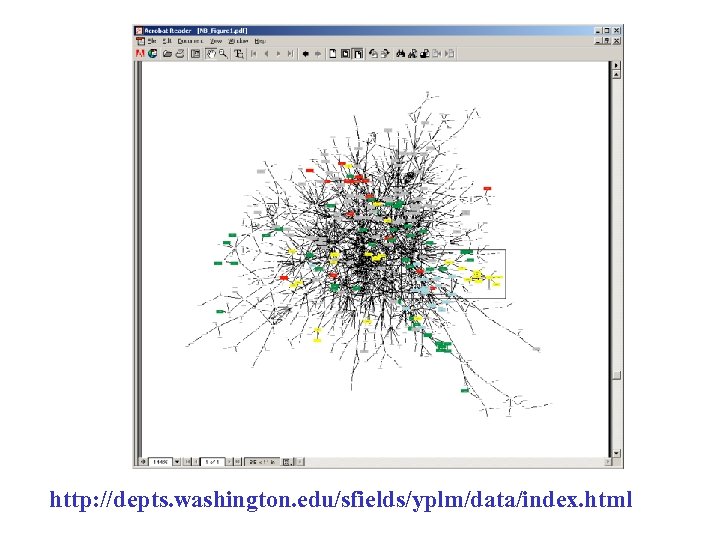 http: //depts. washington. edu/sfields/yplm/data/index. html
http: //depts. washington. edu/sfields/yplm/data/index. html
 red = cellular role & subcellular localization of interacting proteins are identical; blue = localizations are identical; green = cellular roles are identical
red = cellular role & subcellular localization of interacting proteins are identical; blue = localizations are identical; green = cellular roles are identical
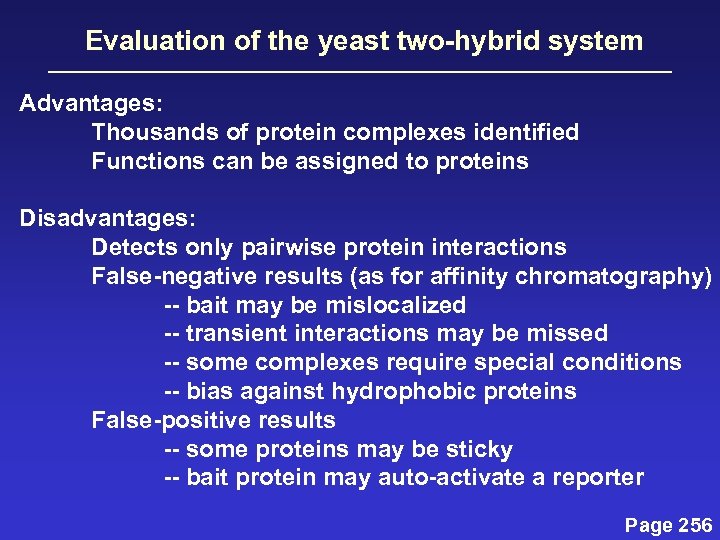 Evaluation of the yeast two-hybrid system Advantages: Thousands of protein complexes identified Functions can be assigned to proteins Disadvantages: Detects only pairwise protein interactions False-negative results (as for affinity chromatography) -- bait may be mislocalized -- transient interactions may be missed -- some complexes require special conditions -- bias against hydrophobic proteins False-positive results -- some proteins may be sticky -- bait protein may auto-activate a reporter Page 256
Evaluation of the yeast two-hybrid system Advantages: Thousands of protein complexes identified Functions can be assigned to proteins Disadvantages: Detects only pairwise protein interactions False-negative results (as for affinity chromatography) -- bait may be mislocalized -- transient interactions may be missed -- some complexes require special conditions -- bias against hydrophobic proteins False-positive results -- some proteins may be sticky -- bait protein may auto-activate a reporter Page 256
 The Rosetta Stone approach Marcotte et al. (1999) and other groups hypothesized that some pairs of interacting proteins are encoded by two genes in many genomes, but occasionally they are fused into a single gene. By scanning many genomes for examples of “fused genes, ” several thousand protein-protein predictions have been made. Page 258
The Rosetta Stone approach Marcotte et al. (1999) and other groups hypothesized that some pairs of interacting proteins are encoded by two genes in many genomes, but occasionally they are fused into a single gene. By scanning many genomes for examples of “fused genes, ” several thousand protein-protein predictions have been made. Page 258
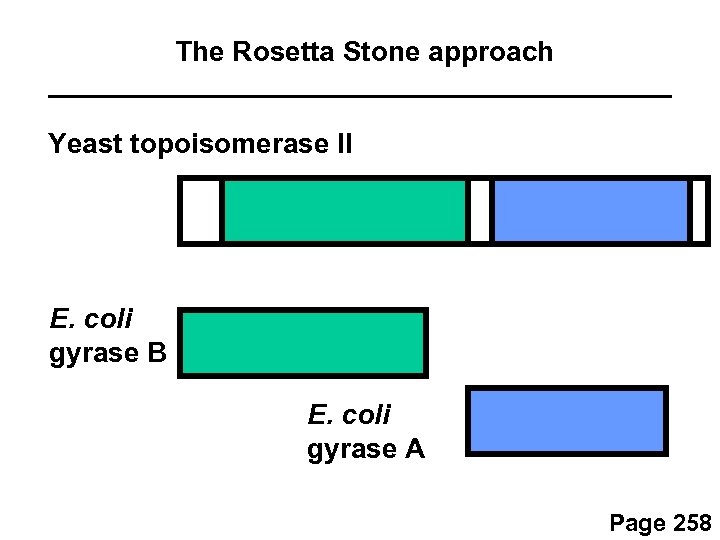 The Rosetta Stone approach Yeast topoisomerase II E. coli gyrase B E. coli gyrase A Page 258
The Rosetta Stone approach Yeast topoisomerase II E. coli gyrase B E. coli gyrase A Page 258

 http: //depts. washington. edu/sfields/yp_project/index. html
http: //depts. washington. edu/sfields/yp_project/index. html
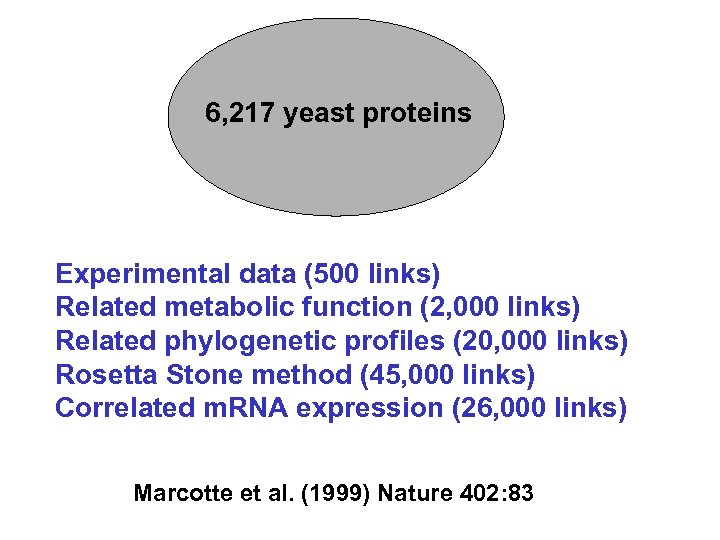 6, 217 yeast proteins Experimental data (500 links) Related metabolic function (2, 000 links) Related phylogenetic profiles (20, 000 links) Rosetta Stone method (45, 000 links) Correlated m. RNA expression (26, 000 links) Marcotte et al. (1999) Nature 402: 83
6, 217 yeast proteins Experimental data (500 links) Related metabolic function (2, 000 links) Related phylogenetic profiles (20, 000 links) Rosetta Stone method (45, 000 links) Correlated m. RNA expression (26, 000 links) Marcotte et al. (1999) Nature 402: 83
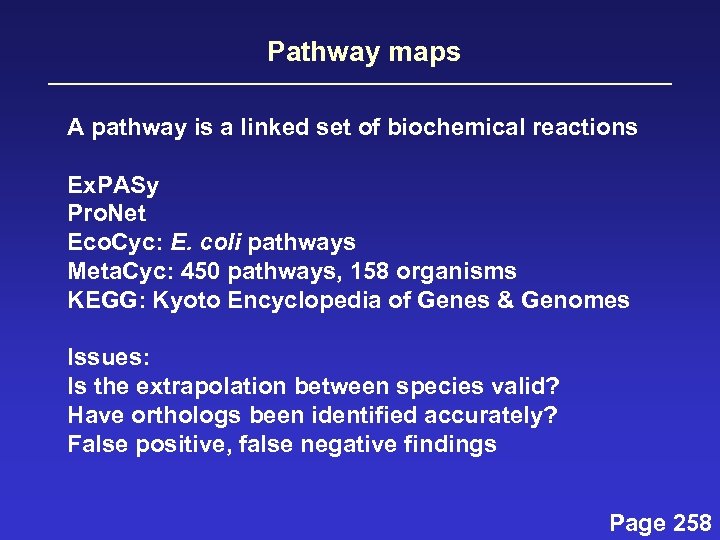 Pathway maps A pathway is a linked set of biochemical reactions Ex. PASy Pro. Net Eco. Cyc: E. coli pathways Meta. Cyc: 450 pathways, 158 organisms KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes & Genomes Issues: Is the extrapolation between species valid? Have orthologs been identified accurately? False positive, false negative findings Page 258
Pathway maps A pathway is a linked set of biochemical reactions Ex. PASy Pro. Net Eco. Cyc: E. coli pathways Meta. Cyc: 450 pathways, 158 organisms KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes & Genomes Issues: Is the extrapolation between species valid? Have orthologs been identified accurately? False positive, false negative findings Page 258
 Page 257
Page 257
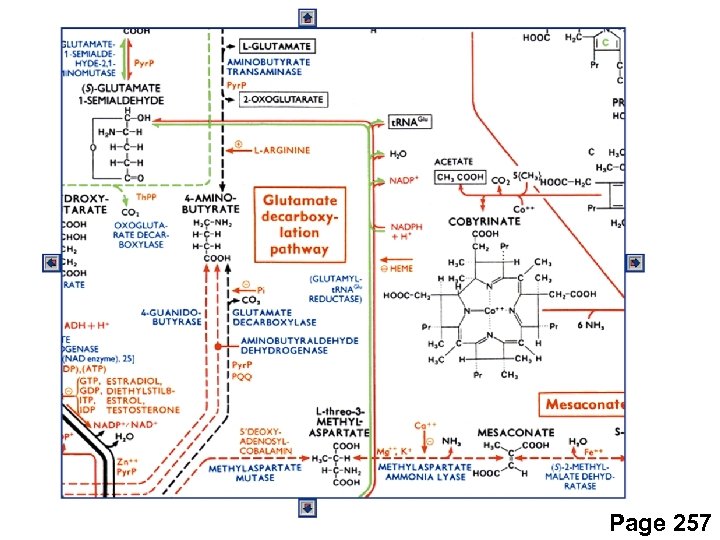 Page 257
Page 257
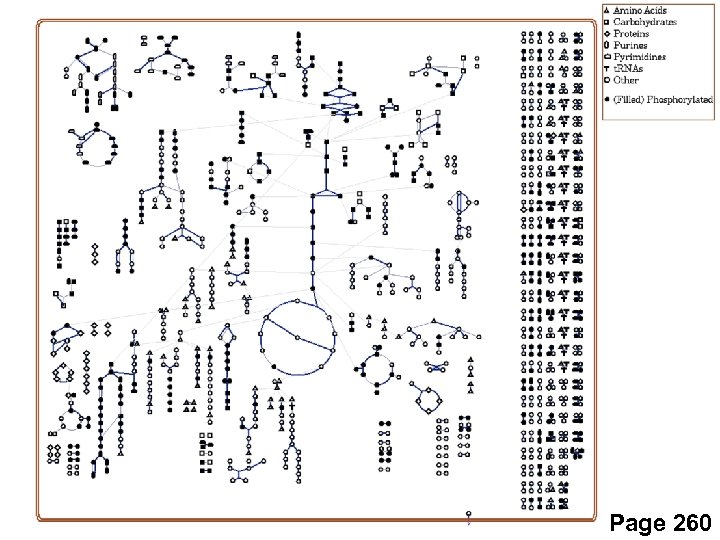 Page 260
Page 260
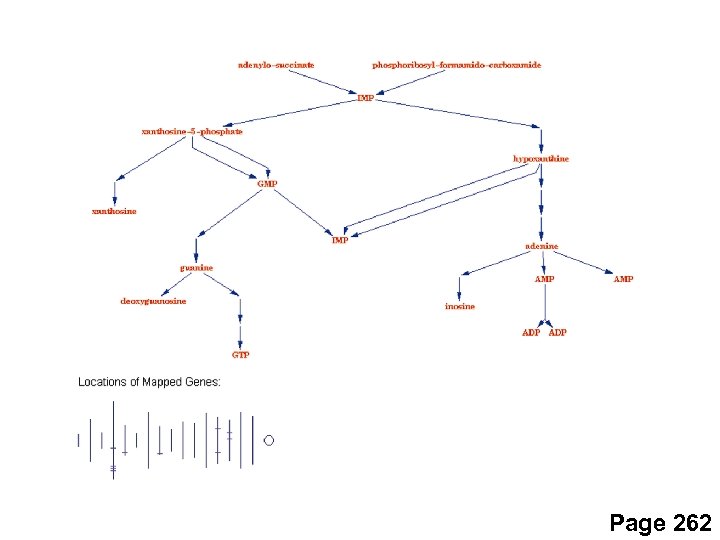 Page 262
Page 262
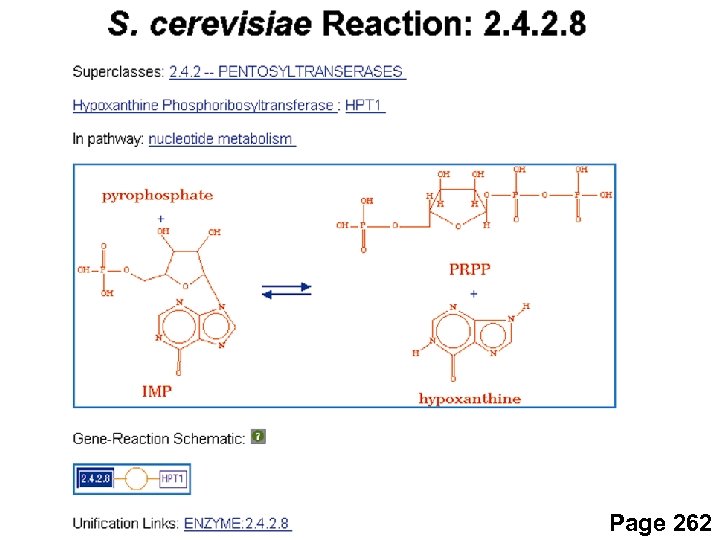 Page 262
Page 262




