Protectionism FINAL_alina modified.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 12
 Protectionism
Protectionism
 Protectionism “Government actions and policies that restrict or restrain international trade, often done with the intent of protecting local businesses and jobs from foreign competition. ” - Investopedia (2014) Mercantilism (16 th – 18 th Century) That all imports of foreign goods be discouraged as much as possible. That as much as possible, imports be confined to raw materials that can be finished in the home country. That no importation be allowed if such goods are sufficiently and suitably supplied at home
Protectionism “Government actions and policies that restrict or restrain international trade, often done with the intent of protecting local businesses and jobs from foreign competition. ” - Investopedia (2014) Mercantilism (16 th – 18 th Century) That all imports of foreign goods be discouraged as much as possible. That as much as possible, imports be confined to raw materials that can be finished in the home country. That no importation be allowed if such goods are sufficiently and suitably supplied at home
 protectionism PRO CONTRA Anti-dumping Reduces comparative advantage Reduction of dependence Increased prices for consumers Infant industries Less domestic competition Reduction of trade deficit Tariffs on imports Domestic labour protection
protectionism PRO CONTRA Anti-dumping Reduces comparative advantage Reduction of dependence Increased prices for consumers Infant industries Less domestic competition Reduction of trade deficit Tariffs on imports Domestic labour protection
 Types of Protectionism Import tariffs: Tax on imported goods Import quotas: Physical limits on the quantity of imports Domestic subsidies: Government provides cheap loans or subsidizes costs to domestic companies that increases their competitiveness Administrative barriers: Excessive government regulations e. g. imposing minimum environmental standards Exchange rates: Foreign exchange market intervention to lower the valuation of a currency Embargo: Total ban of a good
Types of Protectionism Import tariffs: Tax on imported goods Import quotas: Physical limits on the quantity of imports Domestic subsidies: Government provides cheap loans or subsidizes costs to domestic companies that increases their competitiveness Administrative barriers: Excessive government regulations e. g. imposing minimum environmental standards Exchange rates: Foreign exchange market intervention to lower the valuation of a currency Embargo: Total ban of a good
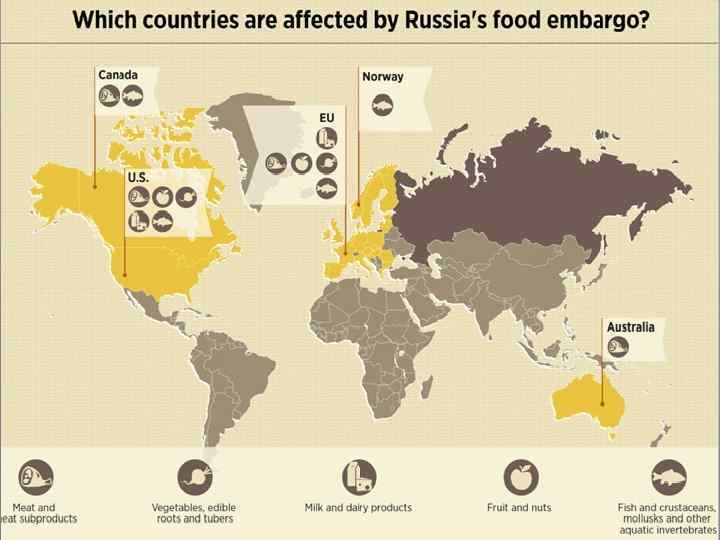
 Russian embargo Germany: Major food and agricultural produce exporter to Russia France: 100, 000 tonnes of foodstuff Fruits and vegetables have limited shelf life Spain: Fruit, vegetables and meat concerns Warm weather in spring prolonged the season Poland: "stand up to Putin by eating apples" social media campaign 40% of pepper is exported United Kingdom: Most valuable stock is mackerel 20% is transported to Russia Increased quota by 80%
Russian embargo Germany: Major food and agricultural produce exporter to Russia France: 100, 000 tonnes of foodstuff Fruits and vegetables have limited shelf life Spain: Fruit, vegetables and meat concerns Warm weather in spring prolonged the season Poland: "stand up to Putin by eating apples" social media campaign 40% of pepper is exported United Kingdom: Most valuable stock is mackerel 20% is transported to Russia Increased quota by 80%
 Russia Alternative trade partners: • Turkey, Egypt, Brazil, Chile, Ecuador What is expected from the import ban? • A strengthening domestic food market • Development of own production • Restriction on low quality European goods Corrections: Lactose-free milk, milk products, food supplements, set onions, sweet corn for sowing and peas for sowing, vitamin and mineral supplements, flavor additives, protein concentrates of animal and vegetable origins Seed potato
Russia Alternative trade partners: • Turkey, Egypt, Brazil, Chile, Ecuador What is expected from the import ban? • A strengthening domestic food market • Development of own production • Restriction on low quality European goods Corrections: Lactose-free milk, milk products, food supplements, set onions, sweet corn for sowing and peas for sowing, vitamin and mineral supplements, flavor additives, protein concentrates of animal and vegetable origins Seed potato
 CAP: Common Agricultural Policy The CAP is the agricultural policy of the European Union. It was established in 1962 and has undertaken different reforms and changes since then, despite remaining focused on some key points. MAIN GOALS • Market unity and stability • Increase agricultural productivity • Support farmers HOW IT WORKS • Subsidies to farmers • Import tariffs • Quotas on production
CAP: Common Agricultural Policy The CAP is the agricultural policy of the European Union. It was established in 1962 and has undertaken different reforms and changes since then, despite remaining focused on some key points. MAIN GOALS • Market unity and stability • Increase agricultural productivity • Support farmers HOW IT WORKS • Subsidies to farmers • Import tariffs • Quotas on production
 CAP: Common Agricultural Policy PROS + Stable market + Increased productivity and ensured food supply + Guarantee a fair living standard for farmers + Guarantee safety quality standards CONS - More expensive food - Oversupply - Difficulties for farmers in other countries - Environmental problems - Huge cost (In 2011 it accounted for 43% of the EU's annual budget € 58 billion) CAP reform post 2013
CAP: Common Agricultural Policy PROS + Stable market + Increased productivity and ensured food supply + Guarantee a fair living standard for farmers + Guarantee safety quality standards CONS - More expensive food - Oversupply - Difficulties for farmers in other countries - Environmental problems - Huge cost (In 2011 it accounted for 43% of the EU's annual budget € 58 billion) CAP reform post 2013
 BRAZIL Brazil‘s POV Defensive strategy Tariffs are in compliance with the international rules Even local businesses are questioning the measures Foreign POV Setting tariffs block the development of an industrial base It has long-term costs, so-called „Brazil costs“ Brazil Costs increased operational costs associated with doing business in Brazil - Lack of qualified labour - Legal uncertainty - Excessive bureaucracy for importing and exporting It is expected that Brazil will not be redirected toward free trade, however protectionism will decrease.
BRAZIL Brazil‘s POV Defensive strategy Tariffs are in compliance with the international rules Even local businesses are questioning the measures Foreign POV Setting tariffs block the development of an industrial base It has long-term costs, so-called „Brazil costs“ Brazil Costs increased operational costs associated with doing business in Brazil - Lack of qualified labour - Legal uncertainty - Excessive bureaucracy for importing and exporting It is expected that Brazil will not be redirected toward free trade, however protectionism will decrease.
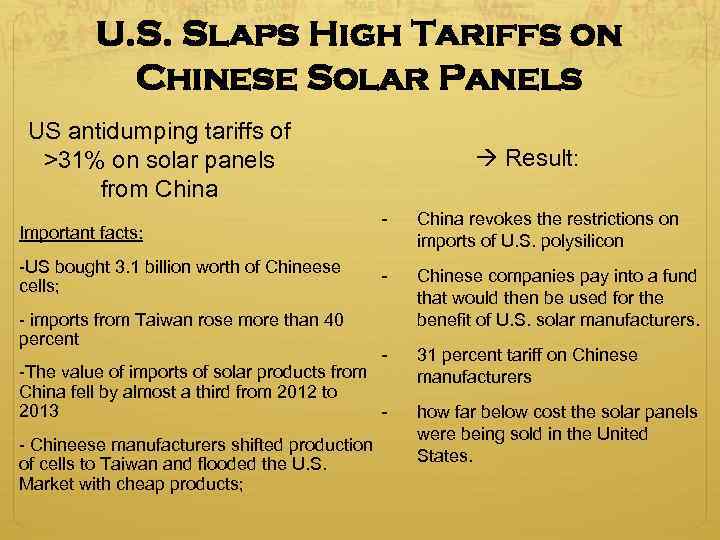 U. S. Slaps High Tariffs on Chinese Solar Panels US antidumping tariffs of >31% on solar panels from China Important facts: -US bought 3. 1 billion worth of Chineese cells; - imports from Taiwan rose more than 40 percent Result: - China revokes the restrictions on imports of U. S. polysilicon - Chinese companies pay into a fund that would then be used for the benefit of U. S. solar manufacturers. - 31 percent tariff on Chinese manufacturers -The value of imports of solar products from China fell by almost a third from 2012 to 2013 - Chineese manufacturers shifted production of cells to Taiwan and flooded the U. S. Market with cheap products; how far below cost the solar panels were being sold in the United States.
U. S. Slaps High Tariffs on Chinese Solar Panels US antidumping tariffs of >31% on solar panels from China Important facts: -US bought 3. 1 billion worth of Chineese cells; - imports from Taiwan rose more than 40 percent Result: - China revokes the restrictions on imports of U. S. polysilicon - Chinese companies pay into a fund that would then be used for the benefit of U. S. solar manufacturers. - 31 percent tariff on Chinese manufacturers -The value of imports of solar products from China fell by almost a third from 2012 to 2013 - Chineese manufacturers shifted production of cells to Taiwan and flooded the U. S. Market with cheap products; how far below cost the solar panels were being sold in the United States.
 Conclusion Protectionism serves both as an advantage and disadvantage however, costs must be weighted! Pros (+) • The creation of new trading opportunities between Russia and Turkey, Egypt, Brazil, Chile, Ecuador; • CAP provides target prices for farmers on foodstuffs income on products with low prices; • US defends its domestic solar panel market Cons (-) • CAP outlays: surplus of food, which had to be covered by EU • CAP has caused economic difficulties for farmers in other countries; • China‘s solar markets got underminded: cost leakages through trariffs imposition
Conclusion Protectionism serves both as an advantage and disadvantage however, costs must be weighted! Pros (+) • The creation of new trading opportunities between Russia and Turkey, Egypt, Brazil, Chile, Ecuador; • CAP provides target prices for farmers on foodstuffs income on products with low prices; • US defends its domestic solar panel market Cons (-) • CAP outlays: surplus of food, which had to be covered by EU • CAP has caused economic difficulties for farmers in other countries; • China‘s solar markets got underminded: cost leakages through trariffs imposition


