28709c5aae5e33577bc672aae8ff0c26.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27

Proposed Guidelines for Food Safety Training in Dubai Presented by Bashir Hassan Yousif Food Safety Specialist Dubai Municipality

Attention! Views expressed in this presentation are not yet requirements They are still under review Your inputs will be very valuable for the effective implementation of the proposed guidelines.

Acknowledgement Consultation: We extend our thanks and appreciation to Prof. Chris Griffith & Mr. Richard Sprenger for their valuable guidance and support References: Food Standards Agency of Ireland National Guideline for food safety training, Canada FSANZ US Food code

What is missing in our current training system? What is the role of the manager/owner? What is the role of the trainer? Are the training programs up to date and relevant? What is the role of the government?

More reasons to add…. .

The guidelines are divided into four main components 1. Role of Food Establishment 2. Trainer Classification & Competency Requirements 3. Course Contents & Course Delivery 4. Training Evaluation & Maintenance

1. 1 Role of Food Establishment The proprietor or registered owner of a food business has a legal obligation to ensure that: A) All food handlers are supervised and instructed and/or trained in food safety matters commensurate with their work activity B) Training programs are compliant with the requirements concerning persons working in the specific food sector.

1. 2 Role of Food Establishment The primary responsibility to choose a competent trainer who has specific skills and attributes lies with the food business operator. The establishment should consider: Size of the operation Risk associated with the product Complexity of the process

1. 3 Role of food establishment Training Options: There a number of ways that food establishments can meet their legal obligations regarding training of employees. These options include: A. Designing, developing and delivering their own in-house training program B. Recruiting the services of a training provider to either design or deliver training specifically for their businesses needs C. Attending training courses which are offered by training providers and training companies

2. 1 Trainer Classification Level 3 Authorized to provide Advanced food hygiene training to food handlers in high risk businesses Approval will be specific to the Category of food industry for eg: Dairy Industry, Baking, Fresh Juices etc Level 4 Authorized to conduct Intermediate food hygiene training for food handlers in low and medium risk businesses In high risk businesses, approval will be specific to the type of industry Level 2 Grade A: Authorized to conduct Basic food hygiene program in High Risk Food Businesses Grade B: Authorized to conduct Basic food hygiene program in Medium and Low Risk Food Businesses Level 1 Authorized to provide induction training program for food handlers Must posses process specific knowledge of high-risk food businesses May provide similar training at lower levels

2. 2 Trainer Competency Level 4 Technical competency in food safety and HACCP, including risk assessment Technical competency in the processes and technologies of particular industry sectors Knowledge of the application of food law within the particular jurisdiction Should be able to demonstrate knowledge as well as verbal and written communication skills Level 3 Technical competency in the processes and technologies of particular industry sectors, Knowledge of the application of food law within the particular jurisdiction, At least 2 years’ experience providing level 2 training with a minimum of 20 training sessions Should be able to demonstrate knowledge as well as verbal and written communication skills Level 2 At least 1 year’s experience providing level 1 training with a minimum of 10 training sessions Knowledge of the application of food law within the particular jurisdiction, Should be able to demonstrate knowledge as well as verbal and written communication skills

2. 3 Competency- Summary Generic trainer competencies Generic food safety competencies, Personal attributes, Knowledge of food safety management system and client requirements, Industry specific skills and knowledge, and Communication skills.

2. 4 Trainer Competency 1. Qualifications: Food Safety Qualification (Eg. Food Science, Food Microbiology, Public / Environmental health, Biological Science, Applied science etc) 1. Successful completion of course to be taught ( 2. 3. 4. more than 80% marks) Work Experience Training Skills: Eg. Train the Trainer Session Evidence of Continuous Professional Development

2. 5 Trainer Competency Assessment A combination of qualifications, personal skills demonstration and workplace assessment

2. 6 Alternative Assessment through demonstration of skills Prospective trainers who do not have the qualification or experience as listed in the requirements will be provided an opportunity to demonstrate their competency and training skills.

2. 6 Use of External Assessors Service of Competent External Assessors will be used by DM if required to asses the competency of trainers, especially level 3 and 4.

3. 1 Course Contents Microbiology Food Safety Operations Personal Hygiene Structural Hygiene Food Safety Management Food Poisoning etc…

3. 2 Course Contents Accurate and Current Logical progression of contents Based on anticipated capability of trainees Provide examples that are applicable to work Consider regional requirements

3. 3 Course delivery Duration of course Course materials Delivery format Languages in which course is offered Activities and assignments required to complete the course

4. 1 Training program Evaluation Random examination of trainees by DM Weighted score for understanding about food safety risks Course evaluation surveys regarding effectiveness of trainer, training materials, teaching methods etc

4. 2 Workplace Assessment Workplace assessment for level 2 and level 3 trainers

4. 3 Ongoing Professional Development Trainers should be able to demonstrate that they participate in a scheme or have a scheme in place for ongoing professional development. Evidence through documents

4. 4 Ongoing Professional Development CPD is a commitment to lifelong learning and allows you to: Keep your knowledge of the law up to date Improve and update your current skills Keep up to date on the impact of government policies Learn new skills Broaden your knowledge base Meet professional colleagues

4. 5 Ongoing Professional Development Minimum CPD hours required per year will be provided by DM. Trainers should be able to provide evidence of Continuous Professional Development
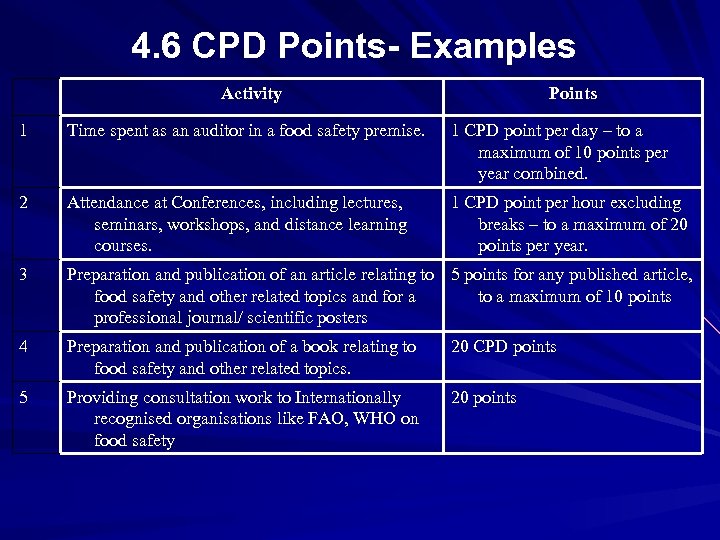
4. 6 CPD Points- Examples Activity Points 1 Time spent as an auditor in a food safety premise. 1 CPD point per day – to a maximum of 10 points per year combined. 2 Attendance at Conferences, including lectures, seminars, workshops, and distance learning courses. 1 CPD point per hour excluding breaks – to a maximum of 20 points per year. 3 Preparation and publication of an article relating to 5 points for any published article, food safety and other related topics and for a to a maximum of 10 points professional journal/ scientific posters 4 Preparation and publication of a book relating to food safety and other related topics. 20 CPD points 5 Providing consultation work to Internationally recognised organisations like FAO, WHO on food safety 20 points

Where is this? No Prize for guessing!

Is That it? Our work will be ongoing……. Let us work as a team Thank you! Food Control Department Dubai Municipality
28709c5aae5e33577bc672aae8ff0c26.ppt