4648bc223afe8375ad4b771132920a92.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 44
 Proposed Diffserv Evaluation for Emerge Sites Volker Sander sander@mcs. anl. gov Argonne National Laboratory 1/20/2000
Proposed Diffserv Evaluation for Emerge Sites Volker Sander sander@mcs. anl. gov Argonne National Laboratory 1/20/2000
 Outline l Basic GARA overview l New GARA-features l Basic set of experiments l Installation of GARA l Running the experiments using GARA l Timeline 2
Outline l Basic GARA overview l New GARA-features l Basic set of experiments l Installation of GARA l Running the experiments using GARA l Timeline 2
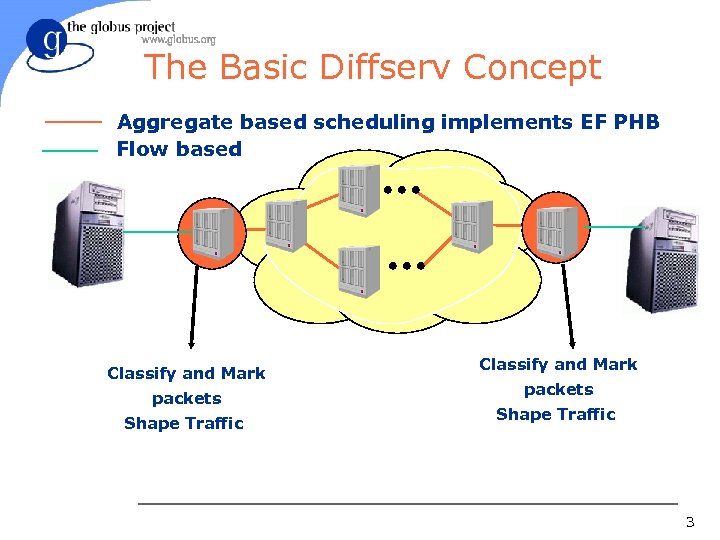 The Basic Diffserv Concept Aggregate based scheduling implements EF PHB Flow based Classify and Mark packets Shape Traffic 3
The Basic Diffserv Concept Aggregate based scheduling implements EF PHB Flow based Classify and Mark packets Shape Traffic 3
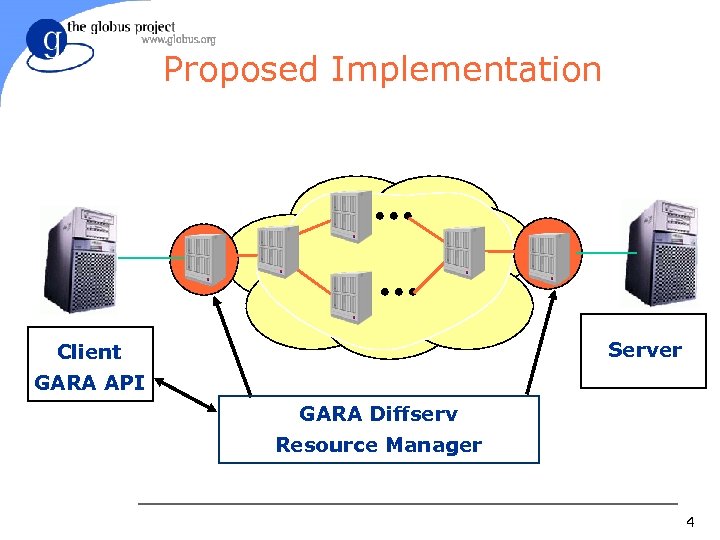 Proposed Implementation Server Client GARA API GARA Diffserv Resource Manager 4
Proposed Implementation Server Client GARA API GARA Diffserv Resource Manager 4
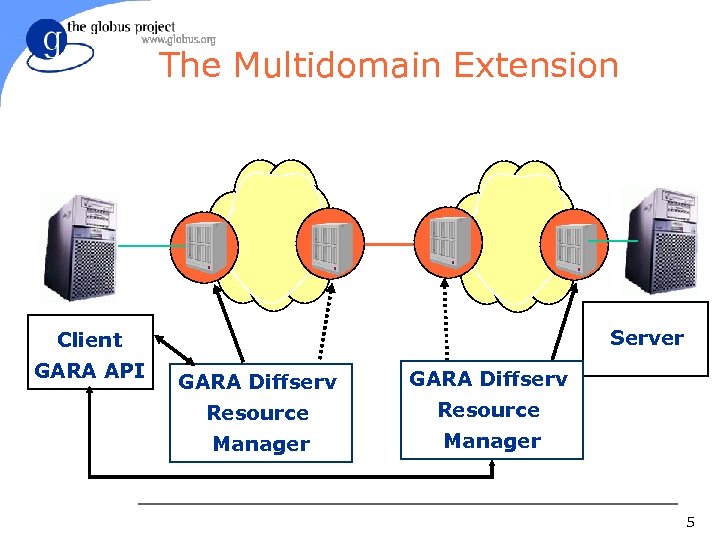 The Multidomain Extension Server Client GARA API GARA Diffserv Resource Manager 5
The Multidomain Extension Server Client GARA API GARA Diffserv Resource Manager 5
 GARA Globus Architecture for Reservation and Allocation l Three important contributions: – Support for Advance Reservations (AG) – Uniform treatment of underlying resources > Network, disk, CPU etc… > Currently supported: Differentiated Services, DPSS, and DSRT – Layered architecture enables generic coreservation agents > User is able to select API best suitable for his need 6
GARA Globus Architecture for Reservation and Allocation l Three important contributions: – Support for Advance Reservations (AG) – Uniform treatment of underlying resources > Network, disk, CPU etc… > Currently supported: Differentiated Services, DPSS, and DSRT – Layered architecture enables generic coreservation agents > User is able to select API best suitable for his need 6
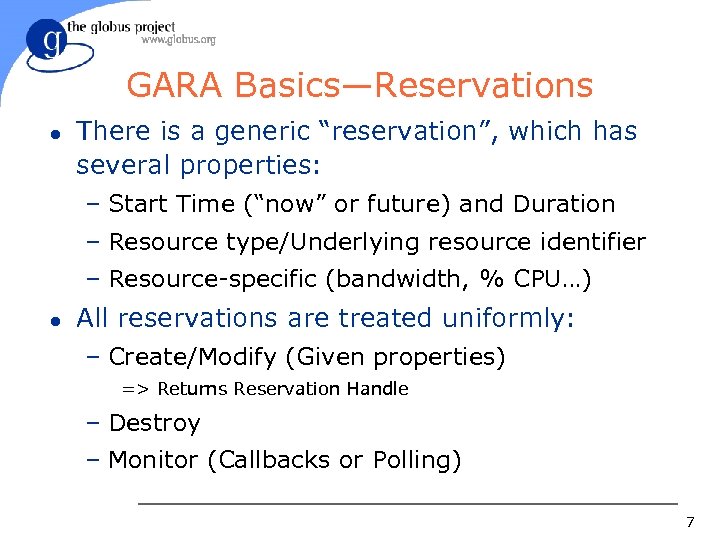 GARA Basics—Reservations l There is a generic “reservation”, which has several properties: – Start Time (“now” or future) and Duration – Resource type/Underlying resource identifier – Resource-specific (bandwidth, % CPU…) l All reservations are treated uniformly: – Create/Modify (Given properties) => Returns Reservation Handle – Destroy – Monitor (Callbacks or Polling) 7
GARA Basics—Reservations l There is a generic “reservation”, which has several properties: – Start Time (“now” or future) and Duration – Resource type/Underlying resource identifier – Resource-specific (bandwidth, % CPU…) l All reservations are treated uniformly: – Create/Modify (Given properties) => Returns Reservation Handle – Destroy – Monitor (Callbacks or Polling) 7
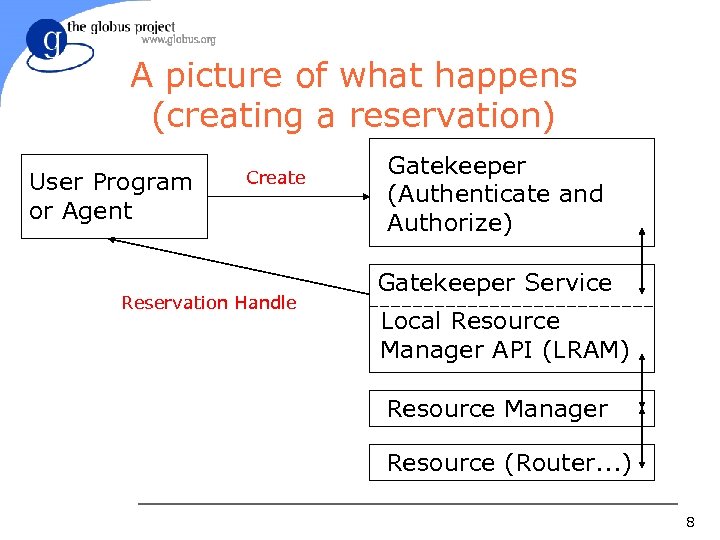 A picture of what happens (creating a reservation) User Program or Agent Create Reservation Handle Gatekeeper (Authenticate and Authorize) Gatekeeper Service Local Resource Manager API (LRAM) Resource Manager Resource (Router. . . ) 8
A picture of what happens (creating a reservation) User Program or Agent Create Reservation Handle Gatekeeper (Authenticate and Authorize) Gatekeeper Service Local Resource Manager API (LRAM) Resource Manager Resource (Router. . . ) 8
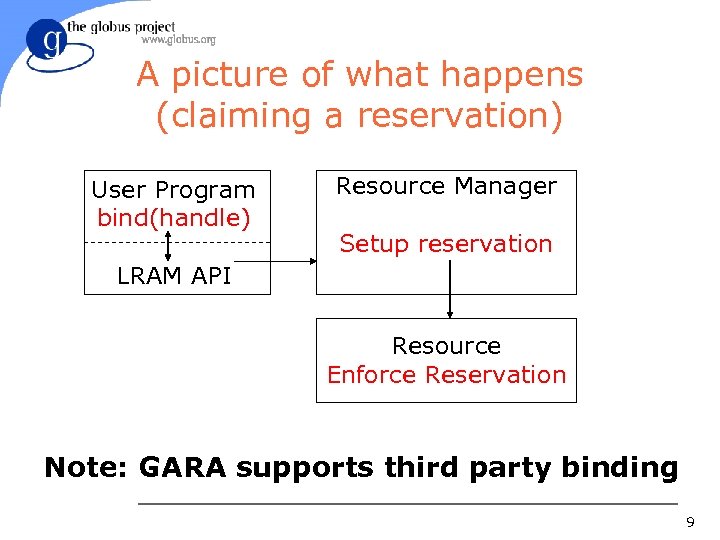 A picture of what happens (claiming a reservation) User Program bind(handle) Resource Manager Setup reservation LRAM API Resource Enforce Reservation Note: GARA supports third party binding 9
A picture of what happens (claiming a reservation) User Program bind(handle) Resource Manager Setup reservation LRAM API Resource Enforce Reservation Note: GARA supports third party binding 9
 10
10
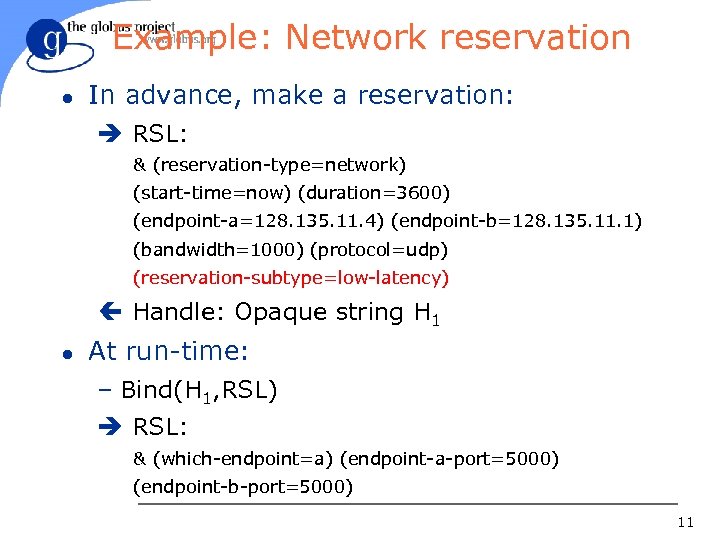 Example: Network reservation l In advance, make a reservation: è RSL: & (reservation-type=network) (start-time=now) (duration=3600) (endpoint-a=128. 135. 11. 4) (endpoint-b=128. 135. 11. 1) (bandwidth=1000) (protocol=udp) (reservation-subtype=low-latency) ç Handle: Opaque string H 1 l At run-time: – Bind(H 1, RSL) è RSL: & (which-endpoint=a) (endpoint-a-port=5000) (endpoint-b-port=5000) 11
Example: Network reservation l In advance, make a reservation: è RSL: & (reservation-type=network) (start-time=now) (duration=3600) (endpoint-a=128. 135. 11. 4) (endpoint-b=128. 135. 11. 1) (bandwidth=1000) (protocol=udp) (reservation-subtype=low-latency) ç Handle: Opaque string H 1 l At run-time: – Bind(H 1, RSL) è RSL: & (which-endpoint=a) (endpoint-a-port=5000) (endpoint-b-port=5000) 11
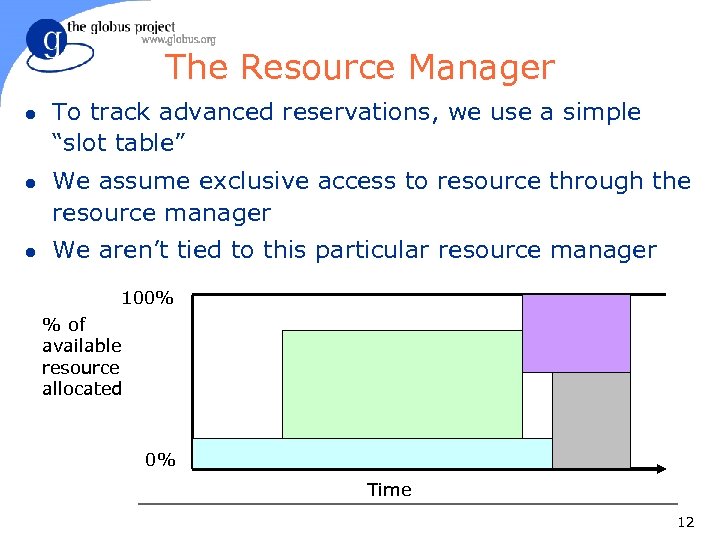 The Resource Manager l l l To track advanced reservations, we use a simple “slot table” We assume exclusive access to resource through the resource manager We aren’t tied to this particular resource manager 100% % of available resource allocated 0% Time 12
The Resource Manager l l l To track advanced reservations, we use a simple “slot table” We assume exclusive access to resource through the resource manager We aren’t tied to this particular resource manager 100% % of available resource allocated 0% Time 12
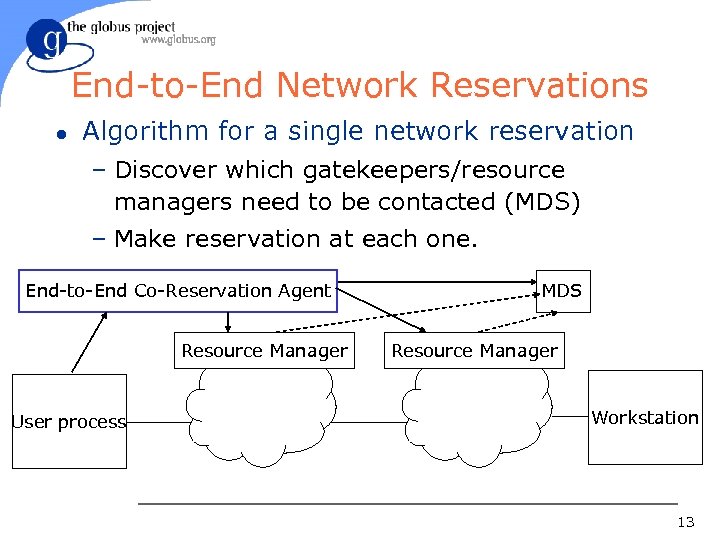 End-to-End Network Reservations l Algorithm for a single network reservation – Discover which gatekeepers/resource managers need to be contacted (MDS) – Make reservation at each one. End-to-End Co-Reservation Agent Resource Manager User process MDS Resource Manager Workstation 13
End-to-End Network Reservations l Algorithm for a single network reservation – Discover which gatekeepers/resource managers need to be contacted (MDS) – Make reservation at each one. End-to-End Co-Reservation Agent Resource Manager User process MDS Resource Manager Workstation 13
 The GARA API l globus_gara_reservation_create() è Gatekeeper contact è RSL reservation specification ç Reservation Handle or Error l globus_gara_reservation_modify() è Old Reservation Handle è RSL reservation specification ç New Reservation Handle or Error 14
The GARA API l globus_gara_reservation_create() è Gatekeeper contact è RSL reservation specification ç Reservation Handle or Error l globus_gara_reservation_modify() è Old Reservation Handle è RSL reservation specification ç New Reservation Handle or Error 14
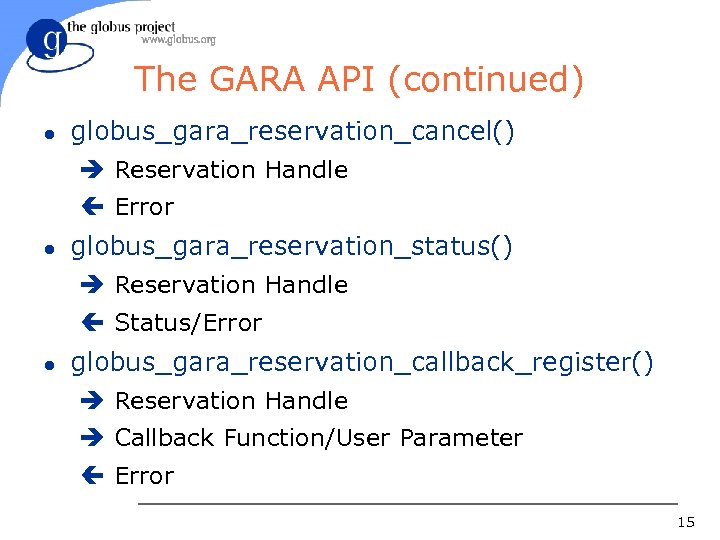 The GARA API (continued) l globus_gara_reservation_cancel() è Reservation Handle ç Error l globus_gara_reservation_status() è Reservation Handle ç Status/Error l globus_gara_reservation_callback_register() è Reservation Handle è Callback Function/User Parameter ç Error 15
The GARA API (continued) l globus_gara_reservation_cancel() è Reservation Handle ç Error l globus_gara_reservation_status() è Reservation Handle ç Status/Error l globus_gara_reservation_callback_register() è Reservation Handle è Callback Function/User Parameter ç Error 15
 New GARA features l New Reservation-Subtypes – low-latency > Used to support jitter sensitive applications using the same EF aggregate behavior as high-throughput TCP applications > Based on traffic shaping and Priority-Queuing > Currently being evaluated – background > Used to support bulk transfers, including deadline support. Takes at least the amount of premium traffic required to fulfill the deadline; more if not used actively l Monitoring of the network edges – Provides feedback to applications when they send too fast 16
New GARA features l New Reservation-Subtypes – low-latency > Used to support jitter sensitive applications using the same EF aggregate behavior as high-throughput TCP applications > Based on traffic shaping and Priority-Queuing > Currently being evaluated – background > Used to support bulk transfers, including deadline support. Takes at least the amount of premium traffic required to fulfill the deadline; more if not used actively l Monitoring of the network edges – Provides feedback to applications when they send too fast 16
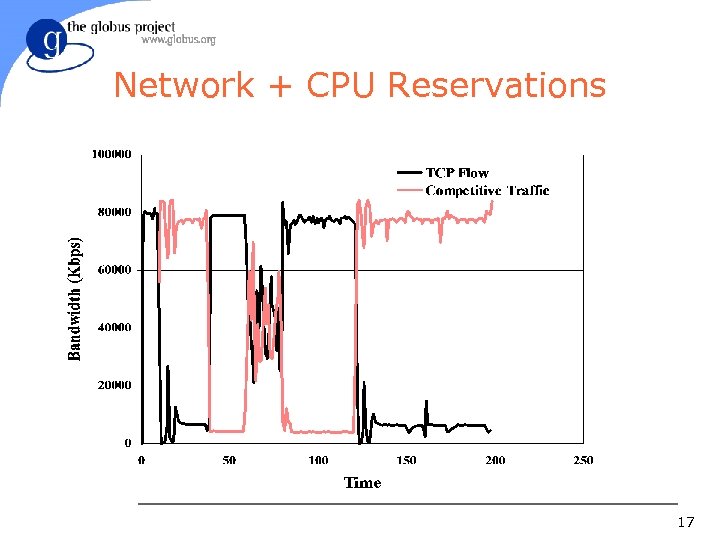 Network + CPU Reservations 17
Network + CPU Reservations 17
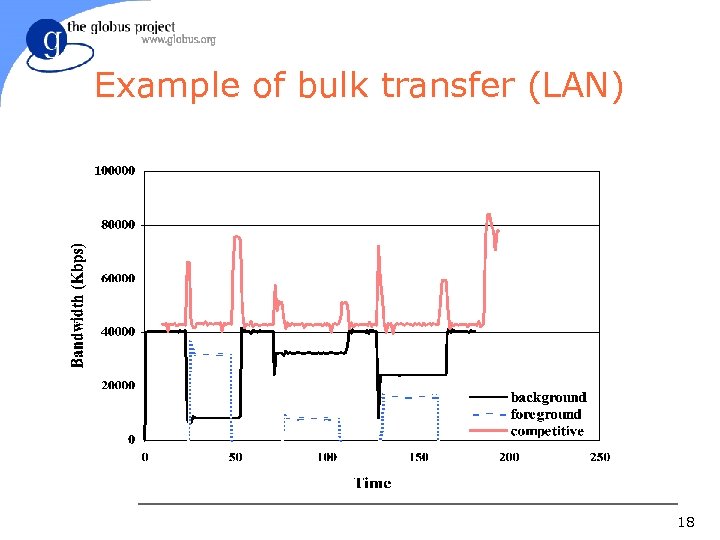 Example of bulk transfer (LAN) 18
Example of bulk transfer (LAN) 18
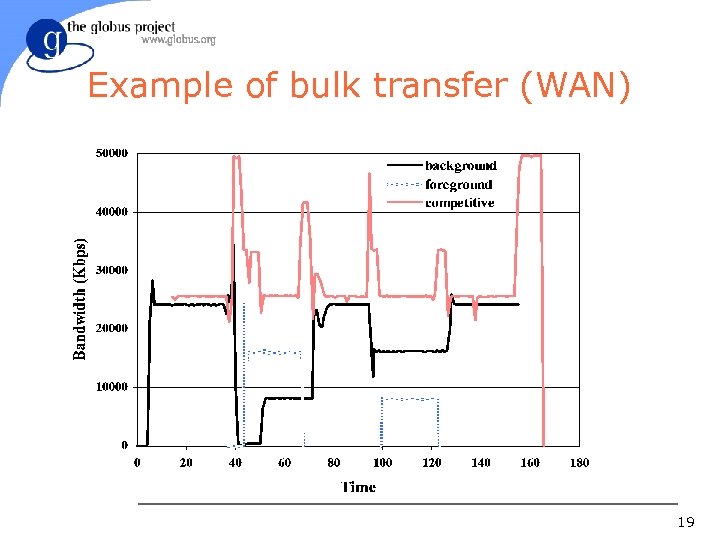 Example of bulk transfer (WAN) 19
Example of bulk transfer (WAN) 19
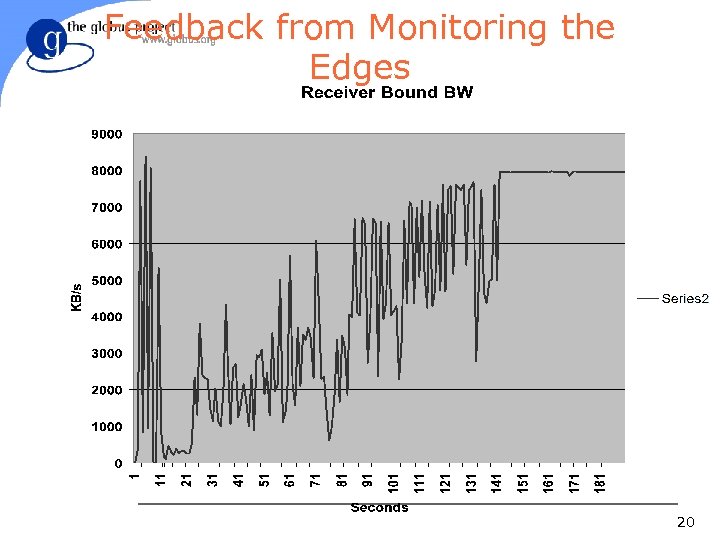 Feedback from Monitoring the Edges 20
Feedback from Monitoring the Edges 20
 Evaluation Tools l UDP Traffic Generator – Modified Version of Andy Adamson’s gen_send and gen_recv > Evaluate admission control > Creating competing traffic – MGEN/Drec > Evaluate delay and Jitter for Premium UDP Flow l Modified Version of ttcp – GARA-enabled (wait for reservation) – Support for a desired application rate > long term control > short term control – Consecutive bandwidth reporting – Bulk transfer ttcp 21
Evaluation Tools l UDP Traffic Generator – Modified Version of Andy Adamson’s gen_send and gen_recv > Evaluate admission control > Creating competing traffic – MGEN/Drec > Evaluate delay and Jitter for Premium UDP Flow l Modified Version of ttcp – GARA-enabled (wait for reservation) – Support for a desired application rate > long term control > short term control – Consecutive bandwidth reporting – Bulk transfer ttcp 21
 Basic Experiments l Evaluate Admission Control l Evaluate premium TCP Flows under Congestion – Analyze network traces with tcpdump l Evaluate UDP – Delay – Jitter l Evaluate Inter-Domain Issues Fundamental idea: Get the necessary knowledge to be able to experiment with REAL applications 22
Basic Experiments l Evaluate Admission Control l Evaluate premium TCP Flows under Congestion – Analyze network traces with tcpdump l Evaluate UDP – Delay – Jitter l Evaluate Inter-Domain Issues Fundamental idea: Get the necessary knowledge to be able to experiment with REAL applications 22
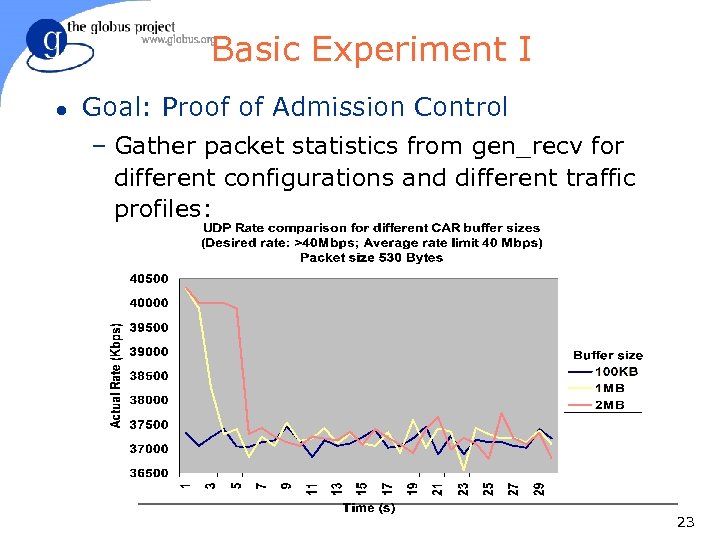 Basic Experiment I l Goal: Proof of Admission Control – Gather packet statistics from gen_recv for different configurations and different traffic profiles: 23
Basic Experiment I l Goal: Proof of Admission Control – Gather packet statistics from gen_recv for different configurations and different traffic profiles: 23
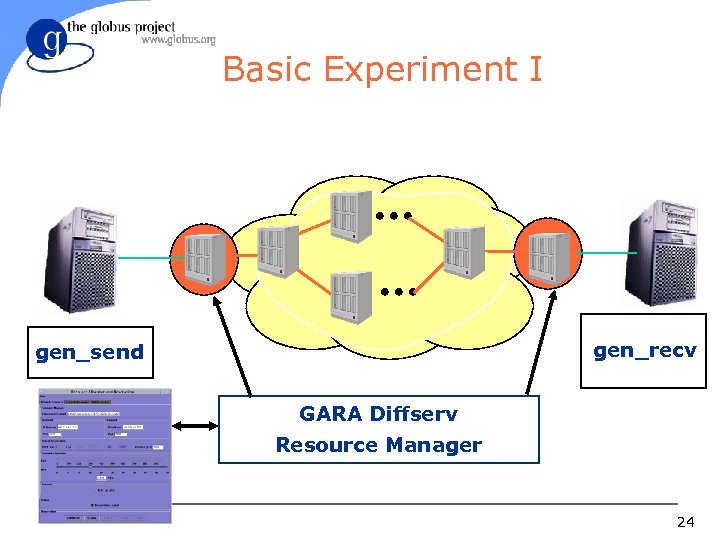 Basic Experiment I gen_recv gen_send GARA Diffserv Resource Manager 24
Basic Experiment I gen_recv gen_send GARA Diffserv Resource Manager 24
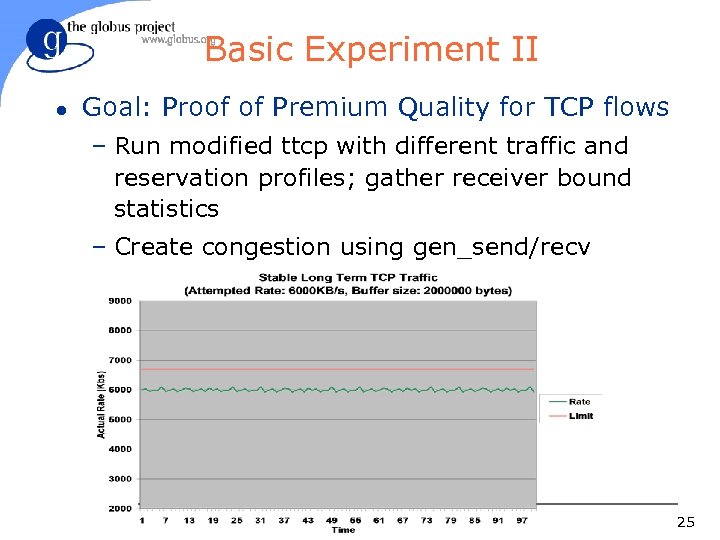 Basic Experiment II l Goal: Proof of Premium Quality for TCP flows – Run modified ttcp with different traffic and reservation profiles; gather receiver bound statistics – Create congestion using gen_send/recv 25
Basic Experiment II l Goal: Proof of Premium Quality for TCP flows – Run modified ttcp with different traffic and reservation profiles; gather receiver bound statistics – Create congestion using gen_send/recv 25
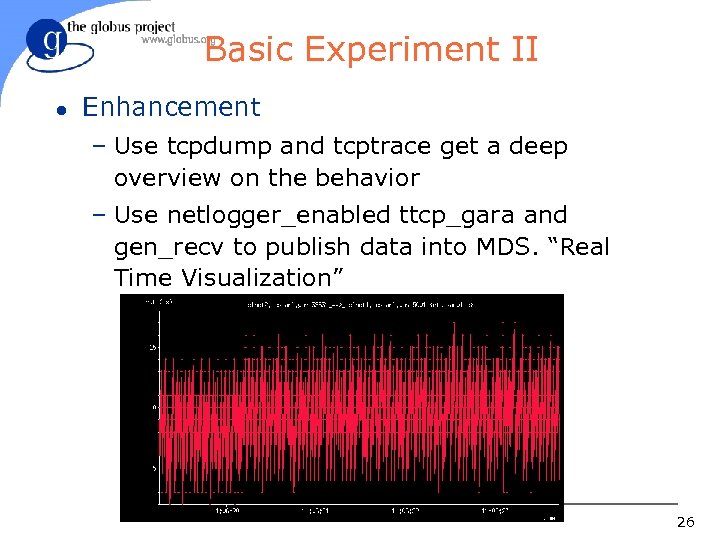 Basic Experiment II l Enhancement – Use tcpdump and tcptrace get a deep overview on the behavior – Use netlogger_enabled ttcp_gara and gen_recv to publish data into MDS. “Real Time Visualization” 26
Basic Experiment II l Enhancement – Use tcpdump and tcptrace get a deep overview on the behavior – Use netlogger_enabled ttcp_gara and gen_recv to publish data into MDS. “Real Time Visualization” 26
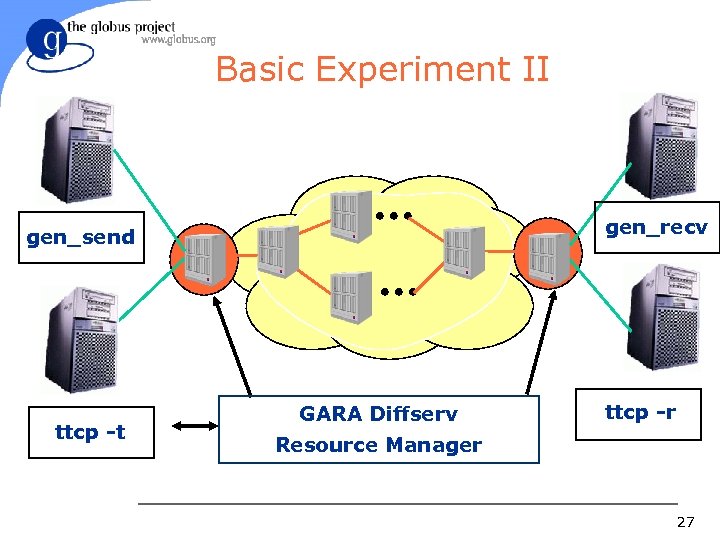 Basic Experiment II gen_recv gen_send ttcp -t GARA Diffserv ttcp -r Resource Manager 27
Basic Experiment II gen_recv gen_send ttcp -t GARA Diffserv ttcp -r Resource Manager 27
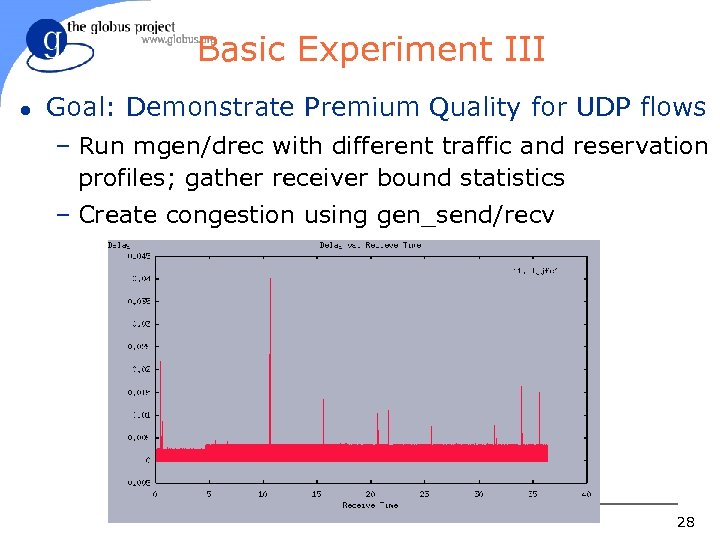 Basic Experiment III l Goal: Demonstrate Premium Quality for UDP flows – Run mgen/drec with different traffic and reservation profiles; gather receiver bound statistics – Create congestion using gen_send/recv 28
Basic Experiment III l Goal: Demonstrate Premium Quality for UDP flows – Run mgen/drec with different traffic and reservation profiles; gather receiver bound statistics – Create congestion using gen_send/recv 28
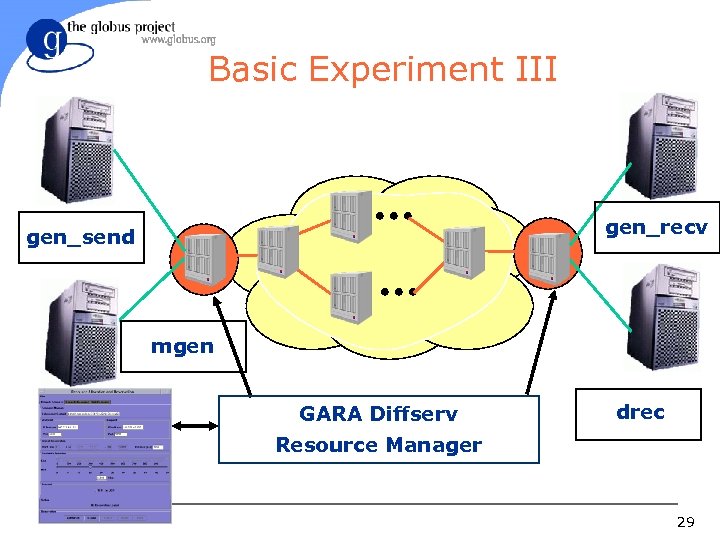 Basic Experiment III gen_recv gen_send mgen GARA Diffserv drec Resource Manager 29
Basic Experiment III gen_recv gen_send mgen GARA Diffserv drec Resource Manager 29
 Basic Experiment IV l Goal: Proof Premium Quality for UDP flows sharing one EF aggregate – Run mgen/drec with different traffic and reservation profiles; gather receiver bound statistics – Run high-throughput ttcp using a correct reservation – Create congestion using gen_send/recv 30
Basic Experiment IV l Goal: Proof Premium Quality for UDP flows sharing one EF aggregate – Run mgen/drec with different traffic and reservation profiles; gather receiver bound statistics – Run high-throughput ttcp using a correct reservation – Create congestion using gen_send/recv 30
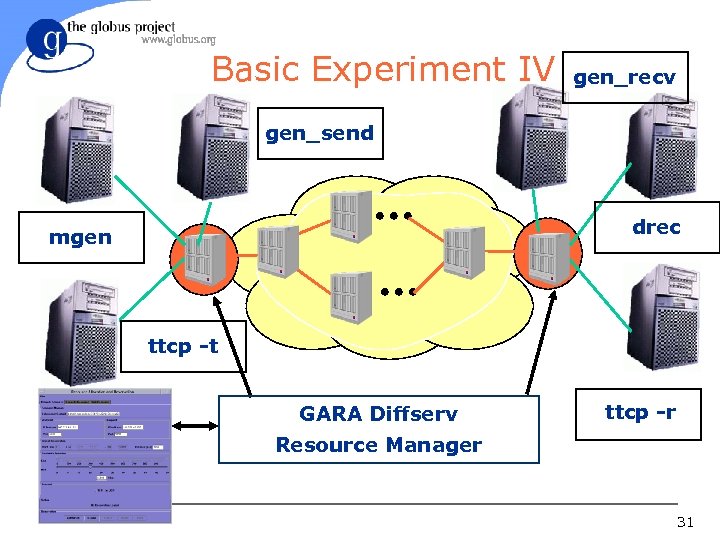 Basic Experiment IV gen_recv gen_send drec mgen ttcp -t GARA Diffserv ttcp -r Resource Manager 31
Basic Experiment IV gen_recv gen_send drec mgen ttcp -t GARA Diffserv ttcp -r Resource Manager 31
 Additional Experiments l Bulk-Transfer l Reevaluate inter-domain behavior – Add Traffic-Shaping between domains l Test Inter-Domain Admission control l Prepare the Instrumentation l Go with real applications 32
Additional Experiments l Bulk-Transfer l Reevaluate inter-domain behavior – Add Traffic-Shaping between domains l Test Inter-Domain Admission control l Prepare the Instrumentation l Go with real applications 32
 Installing GARA l Get GARA – (currently through E-Mail from sander/roy @mcs. anl. gov) l Get SSLeay 0. 9. 0 and install it l Get Globus 1. 1 configure and compile it deploy is not necessary for doing tests but recommended Run grid-cert-request to apply for a Grid X 509 Certificate add “gara-service stderr_log, local_cred $GARA_DIR/gara/programs/globus_gatekeeper_gara_service -d” to $GLOBUS_DEPLOY_DIR/etc/globus-services l Read gara/docs/* l Edit gara/build l Run gara/build l Customize GARA – gara/resource_manager/programs/diffserv_manager. conf – gara/resource_manager/programs/setup_flow. cfg – (Samples are in the documentation directory) 33
Installing GARA l Get GARA – (currently through E-Mail from sander/roy @mcs. anl. gov) l Get SSLeay 0. 9. 0 and install it l Get Globus 1. 1 configure and compile it deploy is not necessary for doing tests but recommended Run grid-cert-request to apply for a Grid X 509 Certificate add “gara-service stderr_log, local_cred $GARA_DIR/gara/programs/globus_gatekeeper_gara_service -d” to $GLOBUS_DEPLOY_DIR/etc/globus-services l Read gara/docs/* l Edit gara/build l Run gara/build l Customize GARA – gara/resource_manager/programs/diffserv_manager. conf – gara/resource_manager/programs/setup_flow. cfg – (Samples are in the documentation directory) 33
 Building GARA l $GARA_DIR/build l #!/bin/ksh l CC=cc l CXX=CC l CFLAGS="-g -v -mt" l GLOBUS_DIR=/soft/pub/packages/globus-1. 1. 0/development/sparc-sun-solaris 2. 7_pt l hreads_standard_debug l SSL_LIBRARY_DIR=/soft/pub/packages/SSLeay-0. 9. 0/lib l export CC CXX CFLAGS GLOBUS_DIR SSL_LIBRARY_DIR l configure l make clean l make depend l make all l # For portability reasons you might not want to do a make withdsrt. . l # in case: just comment out this line. l #make withdsrt l Run build 34
Building GARA l $GARA_DIR/build l #!/bin/ksh l CC=cc l CXX=CC l CFLAGS="-g -v -mt" l GLOBUS_DIR=/soft/pub/packages/globus-1. 1. 0/development/sparc-sun-solaris 2. 7_pt l hreads_standard_debug l SSL_LIBRARY_DIR=/soft/pub/packages/SSLeay-0. 9. 0/lib l export CC CXX CFLAGS GLOBUS_DIR SSL_LIBRARY_DIR l configure l make clean l make depend l make all l # For portability reasons you might not want to do a make withdsrt. . l # in case: just comment out this line. l #make withdsrt l Run build 34
 Configuring GARA l resource_manager/programs/diffserv_manager. conf Publication. Method web mds LDAPDistinguished. Name "dslnet 1. mcs. anl. gov: 34880: /C=US/O=Globus/O=Argonne Nati onal Laboratory/OU=MCS/CN=roy” MDSPublish. Password “password” WEBPublish. File /home/sander/public_html/diffserv_manager_slots. html No. Of. Routers 2 IPAddresses. Served[1] 140. 221. 48. 162, 140. 221. 48. 146, 140. 221. 48. 164, 140. 221. 48. 1 65, 140. 221. 48. 166, 140. 221. 48. 167, 140. 221. 48. 34 IPAddresses. Served[2] 140. 221. 48. 98, 140. 221. 48. 114, 140. 221. 48. 102, 140. 221. 48. 10 3, 140. 221. 48. 104, 140. 221. 48. 105 l Parameters: "LDAPDistinguished. Name", "MDSPublish. Password", "WEBPublish. File", "FILEPublish. File", "Quantity", "Clear. Slot. Table", "Slot. Table. Filename", "Verbose", "Publication. Method", "Dont. Really. Bind. Reservations" 35
Configuring GARA l resource_manager/programs/diffserv_manager. conf Publication. Method web mds LDAPDistinguished. Name "dslnet 1. mcs. anl. gov: 34880: /C=US/O=Globus/O=Argonne Nati onal Laboratory/OU=MCS/CN=roy” MDSPublish. Password “password” WEBPublish. File /home/sander/public_html/diffserv_manager_slots. html No. Of. Routers 2 IPAddresses. Served[1] 140. 221. 48. 162, 140. 221. 48. 146, 140. 221. 48. 164, 140. 221. 48. 1 65, 140. 221. 48. 166, 140. 221. 48. 167, 140. 221. 48. 34 IPAddresses. Served[2] 140. 221. 48. 98, 140. 221. 48. 114, 140. 221. 48. 102, 140. 221. 48. 10 3, 140. 221. 48. 104, 140. 221. 48. 105 l Parameters: "LDAPDistinguished. Name", "MDSPublish. Password", "WEBPublish. File", "FILEPublish. File", "Quantity", "Clear. Slot. Table", "Slot. Table. Filename", "Verbose", "Publication. Method", "Dont. Really. Bind. Reservations" 35
 Configuring GARA l resource_manager/programs/setup_flow. conf 1_ROUTER 140. 221. 48. 145 1_USERNAME my_userid 1_PASSWORD password 1_INTERFACE 1 Fast. Ethernet 1/0/1 140. 221. 48. 162 1_INTERFACE 2 Fast. Ethernet 1/0/1 140. 221. 48. 164 1_INTERFACE 3 Fast. Ethernet 1/0/1 140. 221. 48. 165 1_INTERFACE 4 Fast. Ethernet 1/0/1 140. 221. 48. 166 1_INTERFACE 5 Fast. Ethernet 1/0/1 140. 221. 48. 167 1_INTERFACE 6 Fast. Ethernet 1/0/0 140. 221. 48. 146 # # 2_ROUTER baku 2_USERNAME my_userid 2_PASSWORD password 2_INTERFACE 1 Fast. Ethernet 1/0/1 140. 221. 48. 98 2_INTERFACE 2 Fast. Ethernet 1/0/1 140. 221. 48. 102 2_INTERFACE 3 Fast. Ethernet 1/0/1 140. 221. 48. 103 2_INTERFACE 4 Fast. Ethernet 1/0/1 140. 221. 48. 104 2_INTERFACE 5 Fast. Ethernet 1/0/1 140. 221. 48. 105 2_INTERFACE 6 Fast. Ethernet 1/0/0 140. 221. 48. 114 36
Configuring GARA l resource_manager/programs/setup_flow. conf 1_ROUTER 140. 221. 48. 145 1_USERNAME my_userid 1_PASSWORD password 1_INTERFACE 1 Fast. Ethernet 1/0/1 140. 221. 48. 162 1_INTERFACE 2 Fast. Ethernet 1/0/1 140. 221. 48. 164 1_INTERFACE 3 Fast. Ethernet 1/0/1 140. 221. 48. 165 1_INTERFACE 4 Fast. Ethernet 1/0/1 140. 221. 48. 166 1_INTERFACE 5 Fast. Ethernet 1/0/1 140. 221. 48. 167 1_INTERFACE 6 Fast. Ethernet 1/0/0 140. 221. 48. 146 # # 2_ROUTER baku 2_USERNAME my_userid 2_PASSWORD password 2_INTERFACE 1 Fast. Ethernet 1/0/1 140. 221. 48. 98 2_INTERFACE 2 Fast. Ethernet 1/0/1 140. 221. 48. 102 2_INTERFACE 3 Fast. Ethernet 1/0/1 140. 221. 48. 103 2_INTERFACE 4 Fast. Ethernet 1/0/1 140. 221. 48. 104 2_INTERFACE 5 Fast. Ethernet 1/0/1 140. 221. 48. 105 2_INTERFACE 6 Fast. Ethernet 1/0/0 140. 221. 48. 114 36
 l Setting up the routers Get new IOS XE beta release IOS (tm) RSP Software (RSP-PV-M), Experimental Version 12. 0(19991129: 193607) [rolsen-conn_isp_llq 144] Available at ftp: //ftpeng. cisco. com/rolsen/rsp-pv-mz. 120699 l Edge-Routers (Update of setup_flow required) class-map match-all EF match ip dscp 46 class-map match-all priority-qos match qos-group 99 policy-map emerge class EF bandwidth 30000 queue-limit 500 class priority-qos priority policy-map set-precedence – Attach service-policy set-precendence to every input – Attach service-policy emerge to every output interface 37
l Setting up the routers Get new IOS XE beta release IOS (tm) RSP Software (RSP-PV-M), Experimental Version 12. 0(19991129: 193607) [rolsen-conn_isp_llq 144] Available at ftp: //ftpeng. cisco. com/rolsen/rsp-pv-mz. 120699 l Edge-Routers (Update of setup_flow required) class-map match-all EF match ip dscp 46 class-map match-all priority-qos match qos-group 99 policy-map emerge class EF bandwidth 30000 queue-limit 500 class priority-qos priority policy-map set-precedence – Attach service-policy set-precendence to every input – Attach service-policy emerge to every output interface 37
 Setting up the routers l Interior-Routers (Update of setup_flow required) class-map match-all EF match ip dscp 46 policy-map emerge class EF bandwidth 30000 queue-limit 500 – Attach service-policy emerge to every output interface 38
Setting up the routers l Interior-Routers (Update of setup_flow required) class-map match-all EF match ip dscp 46 policy-map emerge class EF bandwidth 30000 queue-limit 500 – Attach service-policy emerge to every output interface 38
 Updating setup_flow l setup_flow is the script which is configuring the router l Possible update of setup_flow (is) 197 expect_after default { close; continue } 198 199 200 l expect "name: " expect "word: " { send "$usernamer" } { send "$passwordr" } Might be (without tacacs+) 197 expect_after default { close; continue } 198 199 expect ”word: " { send "$passwordr” } 200 expect “#” { send “enabler” } 201 expect "word: " { send "$passwordr" } 39
Updating setup_flow l setup_flow is the script which is configuring the router l Possible update of setup_flow (is) 197 expect_after default { close; continue } 198 199 200 l expect "name: " expect "word: " { send "$usernamer" } { send "$passwordr" } Might be (without tacacs+) 197 expect_after default { close; continue } 198 199 expect ”word: " { send "$passwordr” } 200 expect “#” { send “enabler” } 201 expect "word: " { send "$passwordr" } 39
 Updating the MDS l End-to-end API searches for end-systems in MDS l Publish information for all end-systems into MDS dslnet 1. cldif: ----------dn: hn=dslnet 1. mcs. anl. gov, ou=Mathematics and Computer Science Division, o=Argonne National Laboratory, o=Globus, c=US …. If the machine is already in MDS this is enough networkreservationcontact: dslnet 1. mcs. anl. gov: 30000: /C=US/O=Globus/O=Argonne National Laboratory/OU=MCS/CN=roy 197 continue } expect_after default { close; – run grid-info-update l Tools will be available soon 40
Updating the MDS l End-to-end API searches for end-systems in MDS l Publish information for all end-systems into MDS dslnet 1. cldif: ----------dn: hn=dslnet 1. mcs. anl. gov, ou=Mathematics and Computer Science Division, o=Argonne National Laboratory, o=Globus, c=US …. If the machine is already in MDS this is enough networkreservationcontact: dslnet 1. mcs. anl. gov: 30000: /C=US/O=Globus/O=Argonne National Laboratory/OU=MCS/CN=roy 197 continue } expect_after default { close; – run grid-info-update l Tools will be available soon 40
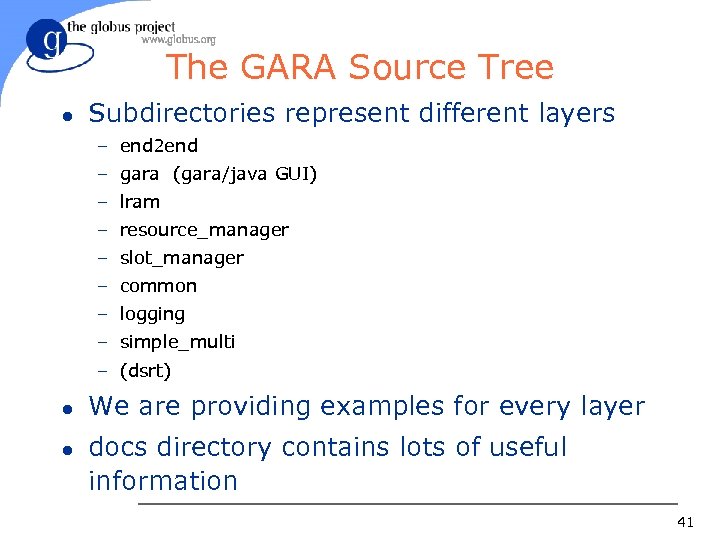 The GARA Source Tree l Subdirectories represent different layers – end 2 end – gara (gara/java GUI) – lram – resource_manager – slot_manager – common – logging – simple_multi – (dsrt) l l We are providing examples for every layer docs directory contains lots of useful information 41
The GARA Source Tree l Subdirectories represent different layers – end 2 end – gara (gara/java GUI) – lram – resource_manager – slot_manager – common – logging – simple_multi – (dsrt) l l We are providing examples for every layer docs directory contains lots of useful information 41
 Doing Further Tests l Select your favorite application l Determine port numbers l l l edit (set endpoint systems) and run script: gara/utilities/demo_make_reservation Create congestion Try demo_modify_reservation for getting different premium bandwidth l Try demo_cancel_reservation l Or use the GUI 42
Doing Further Tests l Select your favorite application l Determine port numbers l l l edit (set endpoint systems) and run script: gara/utilities/demo_make_reservation Create congestion Try demo_modify_reservation for getting different premium bandwidth l Try demo_cancel_reservation l Or use the GUI 42
 Timeline l Establish connectivity (January) – mostly done! – Setup accounts for Emerge-User (January!) – Check connectivity l Install and customize GARA (Jan - Feb) – partly done – Configure and check with GUI without any application (Just look at differv_manager and router) l Do basic experiments (February-March) l Start with multi-domain issues (March-April) l Port real applications to the Testbed (Feb-? ) 43
Timeline l Establish connectivity (January) – mostly done! – Setup accounts for Emerge-User (January!) – Check connectivity l Install and customize GARA (Jan - Feb) – partly done – Configure and check with GUI without any application (Just look at differv_manager and router) l Do basic experiments (February-March) l Start with multi-domain issues (March-April) l Port real applications to the Testbed (Feb-? ) 43
 Questions. . . l Now or later… (sander/roy @ mcs. anl. gov) 44
Questions. . . l Now or later… (sander/roy @ mcs. anl. gov) 44


