b330fff44bcc95671159b87eee68eb2e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 Proposal for a World Defense Initiative and an International Linear Collider Yes, we can! H. Sugawara , DESY, 2009 -working together with J. Arafune and J. Fujimoto-also with advice of Yoshitaka Kimura on accelerator technology-
Proposal for a World Defense Initiative and an International Linear Collider Yes, we can! H. Sugawara , DESY, 2009 -working together with J. Arafune and J. Fujimoto-also with advice of Yoshitaka Kimura on accelerator technology-
 Proposal for a dual mission lab In global collaboration create a dual mission laboratory for WDI and ILC: Anti-ballistic missile system using gamma rays and Linear Collider for particle physics research
Proposal for a dual mission lab In global collaboration create a dual mission laboratory for WDI and ILC: Anti-ballistic missile system using gamma rays and Linear Collider for particle physics research
 Same Technology for WDI & ILC The dual mission can be achieved because the technology is the same: • A high power laser and • A high intensity, high gradient accelerator
Same Technology for WDI & ILC The dual mission can be achieved because the technology is the same: • A high power laser and • A high intensity, high gradient accelerator
 Motivation First: physicists can contribute to world peace. Second: I do not believe governments are ready now to support a $10 B project solely for fundamental physics.
Motivation First: physicists can contribute to world peace. Second: I do not believe governments are ready now to support a $10 B project solely for fundamental physics.
 To Start • Create a committee or a working group under ICFA, ILCSC, or GDE to discuss the issue. • The proposal, if agreed upon, would then be submitted to all member nations of the United Nations.
To Start • Create a committee or a working group under ICFA, ILCSC, or GDE to discuss the issue. • The proposal, if agreed upon, would then be submitted to all member nations of the United Nations.
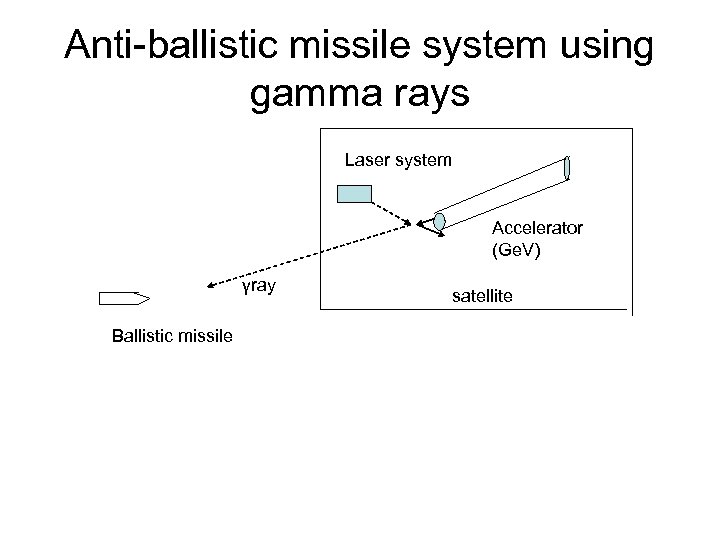 Anti-ballistic missile system using gamma rays Laser system Accelerator (Ge. V) γray Ballistic missile satellite
Anti-ballistic missile system using gamma rays Laser system Accelerator (Ge. V) γray Ballistic missile satellite
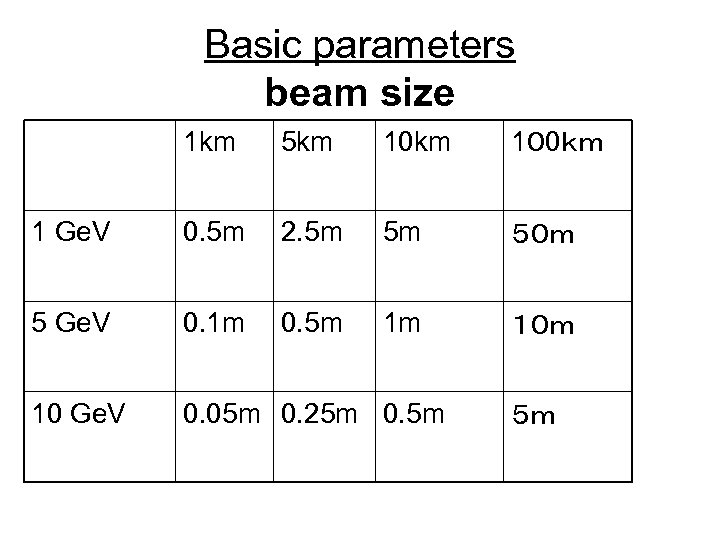 Basic parameters beam size 1 km 5 km 10 km 10 0km 1 Ge. V 0. 5 m 2. 5 m 5 m 50m 5 Ge. V 0. 1 m 0. 5 m 1 m 10m 10 Ge. V 0. 05 m 0. 25 m 0. 5 m 5m
Basic parameters beam size 1 km 5 km 10 km 10 0km 1 Ge. V 0. 5 m 2. 5 m 5 m 50m 5 Ge. V 0. 1 m 0. 5 m 1 m 10m 10 Ge. V 0. 05 m 0. 25 m 0. 5 m 5m
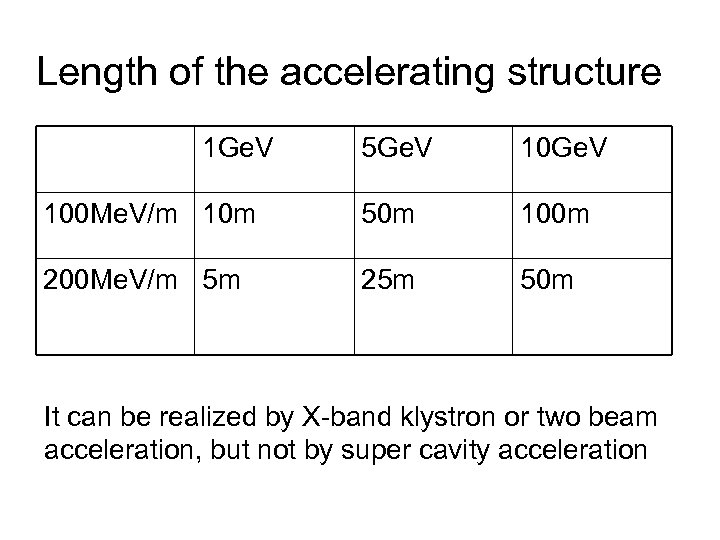 Length of the accelerating structure 1 Ge. V 5 Ge. V 100 Me. V/m 10 m 50 m 100 m 200 Me. V/m 5 m 25 m 50 m It can be realized by X-band klystron or two beam acceleration, but not by super cavity acceleration
Length of the accelerating structure 1 Ge. V 5 Ge. V 100 Me. V/m 10 m 50 m 100 m 200 Me. V/m 5 m 25 m 50 m It can be realized by X-band klystron or two beam acceleration, but not by super cavity acceleration
 Laser power • For 1 Ge. V • This will become 100 KW and 10 TW for 10 Ge. V
Laser power • For 1 Ge. V • This will become 100 KW and 10 TW for 10 Ge. V
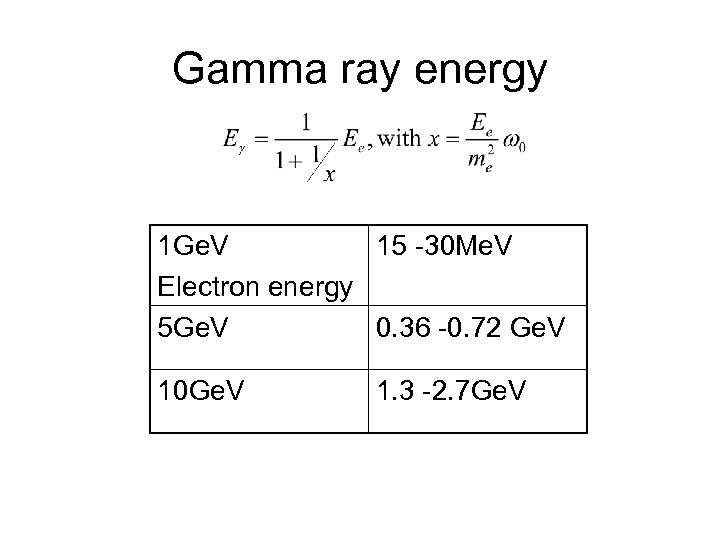 Gamma ray energy 1 Ge. V 15 -30 Me. V Electron energy 5 Ge. V 0. 36 -0. 72 Ge. V 10 Ge. V 1. 3 -2. 7 Ge. V
Gamma ray energy 1 Ge. V 15 -30 Me. V Electron energy 5 Ge. V 0. 36 -0. 72 Ge. V 10 Ge. V 1. 3 -2. 7 Ge. V
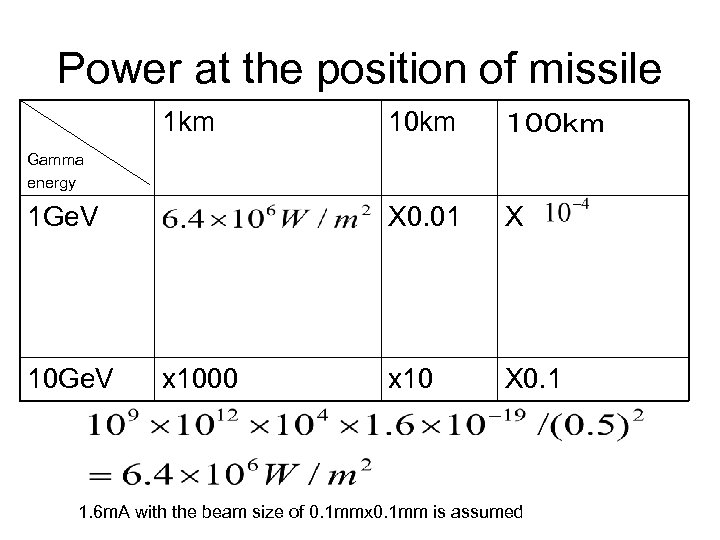 Power at the position of missile 1 km 10 km 100km X 0. 01 X x 10 X 0. 1 Gamma energy 1 Ge. V 10 Ge. V x 1000 1. 6 m. A with the beam size of 0. 1 mmx 0. 1 mm is assumed
Power at the position of missile 1 km 10 km 100km X 0. 01 X x 10 X 0. 1 Gamma energy 1 Ge. V 10 Ge. V x 1000 1. 6 m. A with the beam size of 0. 1 mmx 0. 1 mm is assumed
 Temperature increase of the missile • Case of 1 Ge. V-1 km
Temperature increase of the missile • Case of 1 Ge. V-1 km
 We see that: to melt down a missile from a distance of 100 km in two seconds, • we might need 10 m. A current and a 20 Ge. V machine(200 MW). • We need less power to ignite the explosive material in the missile.
We see that: to melt down a missile from a distance of 100 km in two seconds, • we might need 10 m. A current and a 20 Ge. V machine(200 MW). • We need less power to ignite the explosive material in the missile.
 • If 10 m. A is too large, we might make 10 accelerators of 1 m. A. • 100µ x 0. 001(or 0. 0001) emittance is not difficult if the current is not so large.
• If 10 m. A is too large, we might make 10 accelerators of 1 m. A. • 100µ x 0. 001(or 0. 0001) emittance is not difficult if the current is not so large.
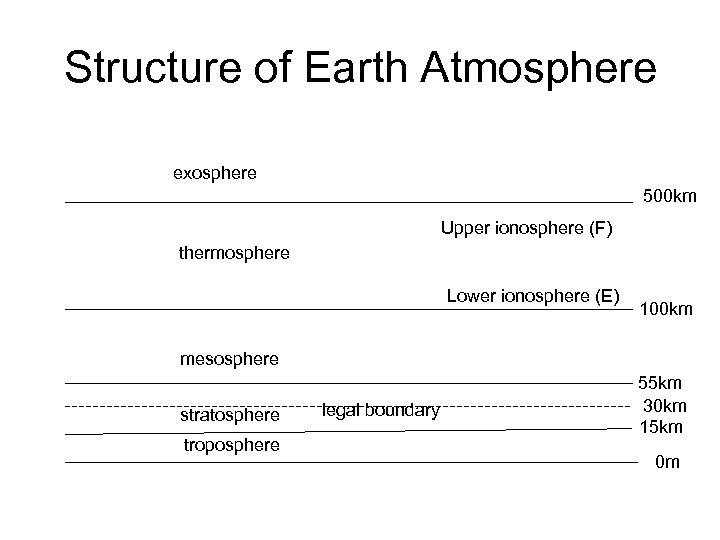 Structure of Earth Atmosphere exosphere 500 km Upper ionosphere (F) thermosphere Lower ionosphere (E) 100 km mesosphere stratosphere troposphere legal boundary 55 km 30 km 15 km 0 m
Structure of Earth Atmosphere exosphere 500 km Upper ionosphere (F) thermosphere Lower ionosphere (E) 100 km mesosphere stratosphere troposphere legal boundary 55 km 30 km 15 km 0 m
 Density of the atmosphere Estimate done using International Standard Atmosphere http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/International_Standard_Atmosphere
Density of the atmosphere Estimate done using International Standard Atmosphere http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/International_Standard_Atmosphere
 Using the absorption cross section of the gamma (10 mb ) we get the following radiation length (including pair creation) :
Using the absorption cross section of the gamma (10 mb ) we get the following radiation length (including pair creation) :
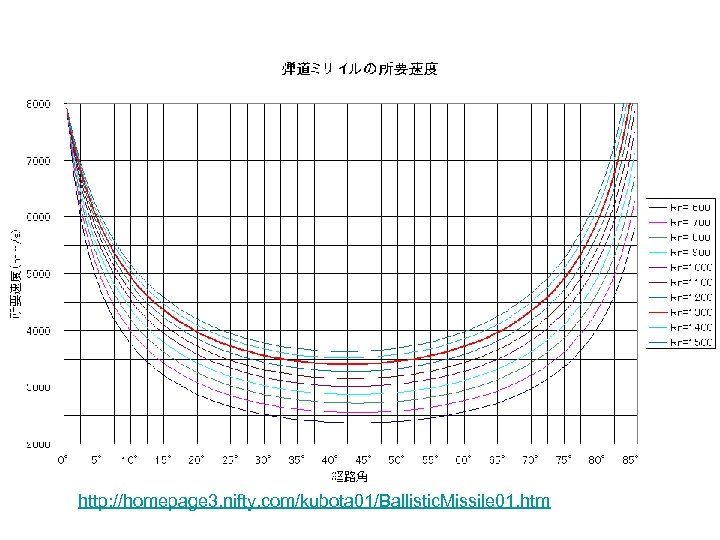 http: //homepage 3. nifty. com/kubota 01/Ballistic. Missile 01. htm
http: //homepage 3. nifty. com/kubota 01/Ballistic. Missile 01. htm
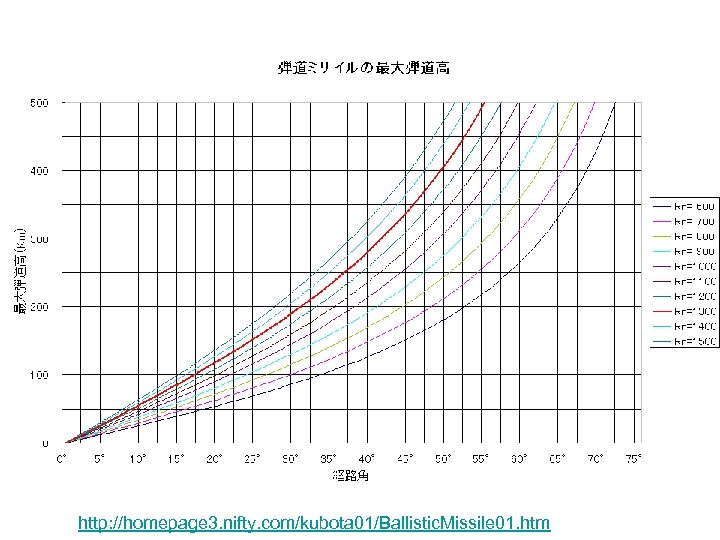 http: //homepage 3. nifty. com/kubota 01/Ballistic. Missile 01. htm
http: //homepage 3. nifty. com/kubota 01/Ballistic. Missile 01. htm
 Politics • Any warhead in space above 30 km should be banned by international law • WDI can be seen as a means to enforce this provision. • Enforcement could be done by the United Nations Security Council or under a new multilateral agreement
Politics • Any warhead in space above 30 km should be banned by international law • WDI can be seen as a means to enforce this provision. • Enforcement could be done by the United Nations Security Council or under a new multilateral agreement
 Cruise missiles also could be banned, but the enforcement mechanism (possibly airborne gamma ray system) is not as effective.
Cruise missiles also could be banned, but the enforcement mechanism (possibly airborne gamma ray system) is not as effective.
 Military Perspective • WDI is a purely defensive weapon (because the gamma intensity on the ground is given by ) • WMD becomes useless; thus, they are abolished totally. • It is not adequate for a single nation to engage in WDI R&D; thus, global collaboration is necessary.
Military Perspective • WDI is a purely defensive weapon (because the gamma intensity on the ground is given by ) • WMD becomes useless; thus, they are abolished totally. • It is not adequate for a single nation to engage in WDI R&D; thus, global collaboration is necessary.
 Yes, we can!
Yes, we can!
 Appendix A short history of defense systems for ballistic missiles (mostly US, but also Russia and Israel) From Wikipedia: • 1980’s SDI (Reagan): laser technical failure • Global Protection Against Limited Strikes (G. H. W. Bush) THAAD, PAC-3 • TMD, NMD (Clinton) Against Tepodon (NK), Shahab 3 (Iran) • BMD (G. W. Bush) Unified TMD and NMD • Russia S-300, Israel Arrow
Appendix A short history of defense systems for ballistic missiles (mostly US, but also Russia and Israel) From Wikipedia: • 1980’s SDI (Reagan): laser technical failure • Global Protection Against Limited Strikes (G. H. W. Bush) THAAD, PAC-3 • TMD, NMD (Clinton) Against Tepodon (NK), Shahab 3 (Iran) • BMD (G. W. Bush) Unified TMD and NMD • Russia S-300, Israel Arrow
 Ballistic Missile Defense (BMD) United States • Most important early detection and information control Defense Support Program (DSP) Space Based Infrared System (SBIRS)
Ballistic Missile Defense (BMD) United States • Most important early detection and information control Defense Support Program (DSP) Space Based Infrared System (SBIRS)
 1. Boost phase: ABL, Kinetic Energy Intercepter (KEI) 2. Midcourse phase: Aegis BMD a. SM-3 Light weight Exo-atmospheric projectile (LEAP) b. AN/SPY-1 radar system covering 1000 km** Ground based BMD a. Ground Based Interceptor (GBI) b. Exo-atmospheric Kill Vehicle (EKV) c. b. Sea-based X-band radar (SBX)
1. Boost phase: ABL, Kinetic Energy Intercepter (KEI) 2. Midcourse phase: Aegis BMD a. SM-3 Light weight Exo-atmospheric projectile (LEAP) b. AN/SPY-1 radar system covering 1000 km** Ground based BMD a. Ground Based Interceptor (GBI) b. Exo-atmospheric Kill Vehicle (EKV) c. b. Sea-based X-band radar (SBX)
 3. Terminal phase • Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD) a. Kinetic Kill Vehicle (KKV) b. Movable X-band radar (FBX-T) • Patriot missile (Pac-3)
3. Terminal phase • Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD) a. Kinetic Kill Vehicle (KKV) b. Movable X-band radar (FBX-T) • Patriot missile (Pac-3)
 Cruise Missiles ALCM, GLCM, SLCM • US RGM-6, Snark, Hound Dog, AGM-86 B/C, Tomahawk, AGM-129 etc. • Russia Kh-55, Kh 90 -AS-19, Kh-65, Kh-101/102, Kh-555 • France ASMP, ASN, SCALP-EG • China HN-3, TJ-1, DH-10
Cruise Missiles ALCM, GLCM, SLCM • US RGM-6, Snark, Hound Dog, AGM-86 B/C, Tomahawk, AGM-129 etc. • Russia Kh-55, Kh 90 -AS-19, Kh-65, Kh-101/102, Kh-555 • France ASMP, ASN, SCALP-EG • China HN-3, TJ-1, DH-10
 • Taiwan Yuhu 2 E • South Korea Chonrin, Porame, Hyom 3, Genbu 3 B, Genbu 3 C • Pakistan Hatf 7, Hatf 8 • India-Russia PJ-10 Brahmos • Germany-Sweden TAURUS KEPD 350 • UK-France-Italy Storm Shadow -------------Anti-cruise missile system Patriot TMD (US), Chu-Sam (Japan)
• Taiwan Yuhu 2 E • South Korea Chonrin, Porame, Hyom 3, Genbu 3 B, Genbu 3 C • Pakistan Hatf 7, Hatf 8 • India-Russia PJ-10 Brahmos • Germany-Sweden TAURUS KEPD 350 • UK-France-Italy Storm Shadow -------------Anti-cruise missile system Patriot TMD (US), Chu-Sam (Japan)
 Laser Systems • Tactical High Energy Laser (THEL) collaboration of US and Israel, ground based system DF(3. 8µ) laser Problem: weight, volume, power • Airborne Laser (ABL) US Air Force (AL-1) “This does not have such large power as in science fiction to destroy a missile, but it ignites the fuel explosion right after the launching of the missile. Therefore, it is necessary for an aircraft carrying the laser to be on enemy territory. ”
Laser Systems • Tactical High Energy Laser (THEL) collaboration of US and Israel, ground based system DF(3. 8µ) laser Problem: weight, volume, power • Airborne Laser (ABL) US Air Force (AL-1) “This does not have such large power as in science fiction to destroy a missile, but it ignites the fuel explosion right after the launching of the missile. Therefore, it is necessary for an aircraft carrying the laser to be on enemy territory. ”


