fb141eaeecc9bcf523163126386853c3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
PROOF: the Parallel ROOT Facility Scheduling and Load-balancing ACAT 2007 Jan Iwaszkiewicz ¹ ² Gerardo Ganis ¹ Fons Rademakers ¹ ACAT 23 - 27 th of April 2007 ¹ CERN PH/SFT ² University of Warsaw Jan Iwaszkiewicz, CERN PH/SFT
Outline • Introduction to Parallel ROOT Facility • Packetizer – load balancing • Resource Scheduling ACAT 23 - 27 th of April 2007 Jan Iwaszkiewicz, CERN PH/SFT 2
Analysis of the Large Hadron Collier data • Necessity of distributed analysis • ROOT – popular particle physics data analysis framework • PROOF (ROOT’s extension) – automatically parallelizes processing to computing clusters or multicore machines ACAT 23 - 27 th of April 2007 Jan Iwaszkiewicz, CERN PH/SFT 3

Who is using PROOF • PHOBOS – MIT, dedicated cluster, interfaced with Condor – Real data analysis, in production Very positive experience • functionality, large speedup, efficient But not really the LHC scenario • Usage limited to a few experienced users • ALICE – CERN Analysis Facility (CAF) • CMS – Santander group, dedicated cluster – Physics TDR analysis ACAT 23 - 27 th of April 2007 Jan Iwaszkiewicz, CERN PH/SFT 4
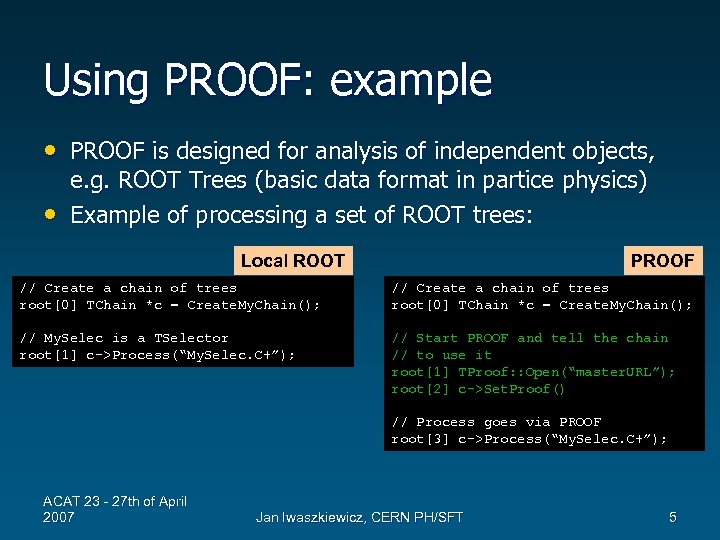
Using PROOF: example • PROOF is designed for analysis of independent objects, • e. g. ROOT Trees (basic data format in partice physics) Example of processing a set of ROOT trees: Local ROOT PROOF // Create a chain of trees root[0] TChain *c = Create. My. Chain(); // My. Selec is a TSelector root[1] c->Process(“My. Selec. C+”); // Start PROOF and tell the chain // to use it root[1] TProof: : Open(“master. URL”); root[2] c->Set. Proof() // Process goes via PROOF root[3] c->Process(“My. Selec. C+”); ACAT 23 - 27 th of April 2007 Jan Iwaszkiewicz, CERN PH/SFT 5
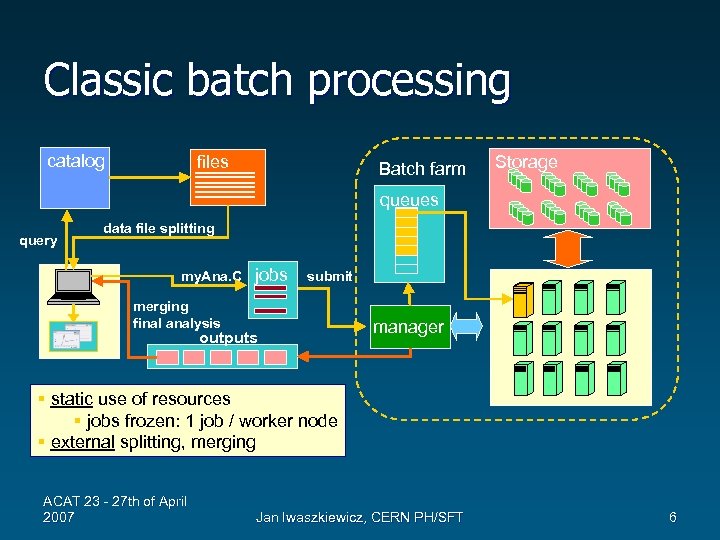
Classic batch processing catalog files Batch farm Storage queues query data file splitting my. Ana. C jobs submit merging final analysis outputs manager § static use of resources § jobs frozen: 1 job / worker node § external splitting, merging ACAT 23 - 27 th of April 2007 Jan Iwaszkiewicz, CERN PH/SFT 6
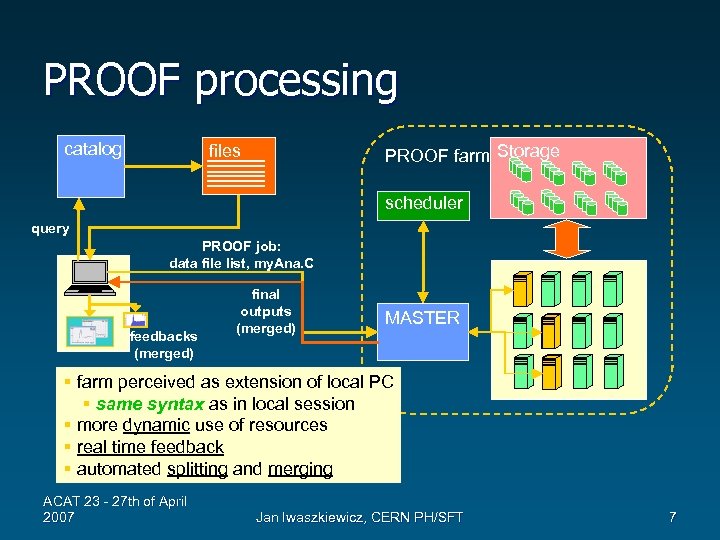
PROOF processing catalog files PROOF farm Storage scheduler query PROOF job: data file list, my. Ana. C feedbacks (merged) final outputs (merged) MASTER § farm perceived as extension of local PC § same syntax as in local session § more dynamic use of resources § real time feedback § automated splitting and merging ACAT 23 - 27 th of April 2007 Jan Iwaszkiewicz, CERN PH/SFT 7

Challenges for PROOF • Remain efficient under heavy load • 100% exploitation of resources • Reliability ACAT 23 - 27 th of April 2007 Jan Iwaszkiewicz, CERN PH/SFT 8
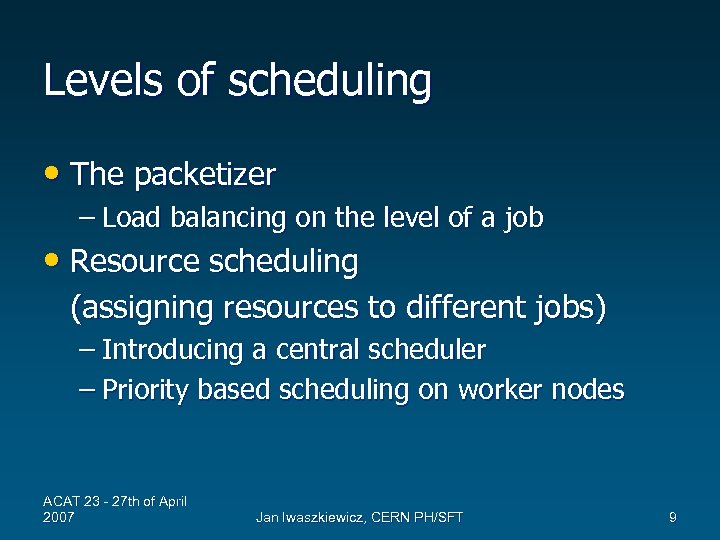
Levels of scheduling • The packetizer – Load balancing on the level of a job • Resource scheduling (assigning resources to different jobs) – Introducing a central scheduler – Priority based scheduling on worker nodes ACAT 23 - 27 th of April 2007 Jan Iwaszkiewicz, CERN PH/SFT 9
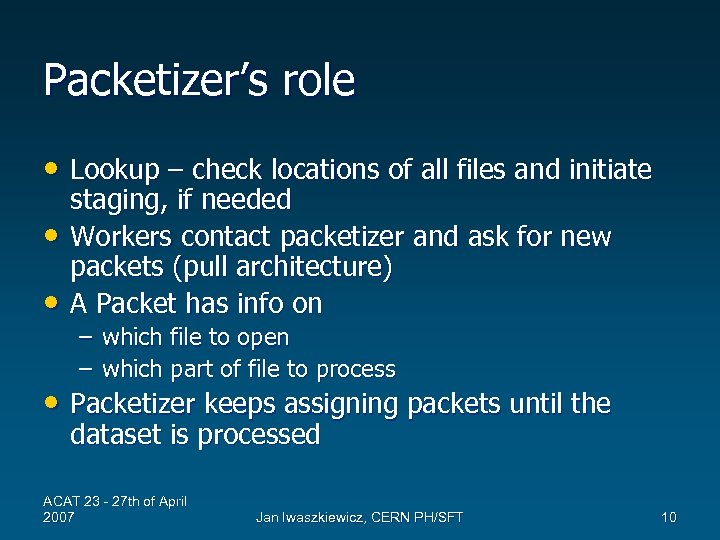
Packetizer’s role • Lookup – check locations of all files and initiate • • staging, if needed Workers contact packetizer and ask for new packets (pull architecture) A Packet has info on – which file to open – which part of file to process • Packetizer keeps assigning packets until the dataset is processed ACAT 23 - 27 th of April 2007 Jan Iwaszkiewicz, CERN PH/SFT 10
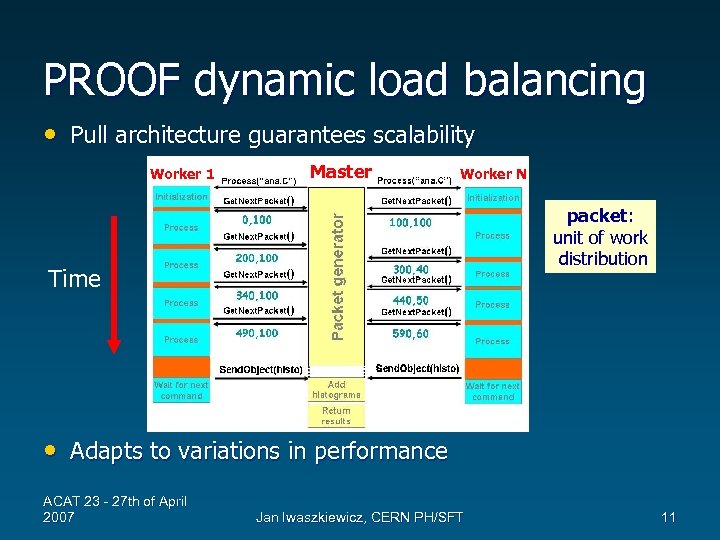
PROOF dynamic load balancing • Pull architecture guarantees scalability Worker 1 Master Worker N packet: unit of work distribution Time • Adapts to variations in performance ACAT 23 - 27 th of April 2007 Jan Iwaszkiewicz, CERN PH/SFT 11

TPacketizer: the original packetizer • Strategy – Each worker processes its local files and then processes remaining remote files – Fixed size packets – Avoid overloading data server by allowing max 4 remote files to be served • Problems with the TPacketizer – Long tails with some I/O bound jobs ACAT 23 - 27 th of April 2007 Jan Iwaszkiewicz, CERN PH/SFT 12

Performance tests with ALICE • 35 PCs, dual Xeon 2. 8 Ghz, ~200 GB disk – Standard CERN hardware for LHC • Machine pools managed by xrootd – Data of Physics Data Challenge ’ 06 distributed (~ 1 M events) • Tests performed – Speedup (scalability) tests – System response when running a combination of job types for increasing # of concurrent users ACAT 23 - 27 th of April 2007 Jan Iwaszkiewicz, CERN PH/SFT 13
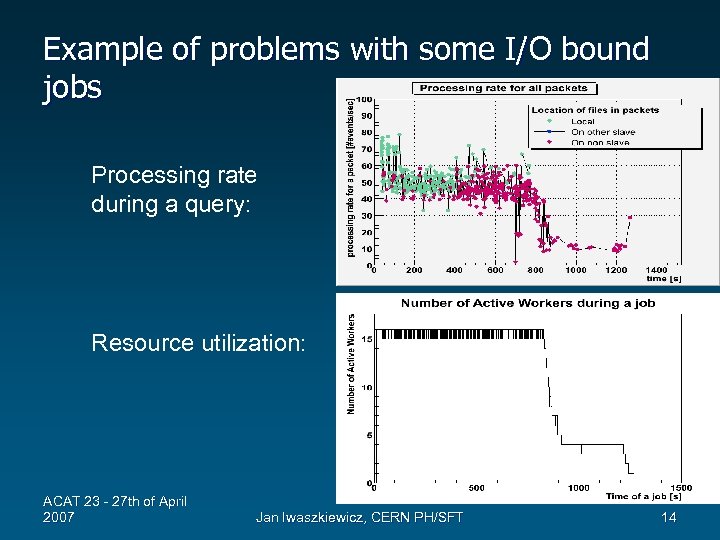
Example of problems with some I/O bound jobs Processing rate during a query: Resource utilization: ACAT 23 - 27 th of April 2007 Jan Iwaszkiewicz, CERN PH/SFT 14

How to improve • Focus on I/O based jobs – Limited by hard drive or network bandwidth • Predict which data servers can become bottlenecks • Make sure that other workers help analyzing data from those servers • Use time-based packet sizes ACAT 23 - 27 th of April 2007 Jan Iwaszkiewicz, CERN PH/SFT 15

TAdaptive. Packetizer • Strategy – Predicting the processing time of local files for each worker – For the workers that are expected to finish faster, keep assigning remote files from the beginning of the job. – Assign remote files from the most heavily loaded file servers – Variable packet size ACAT 23 - 27 th of April 2007 Jan Iwaszkiewicz, CERN PH/SFT 16
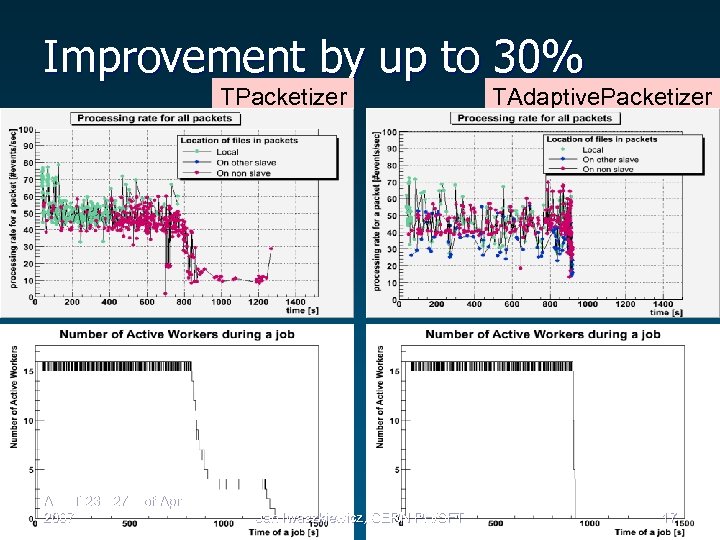
Improvement by up to 30% TPacketizer ACAT 23 - 27 th of April 2007 Jan Iwaszkiewicz, CERN PH/SFT TAdaptive. Packetizer 17
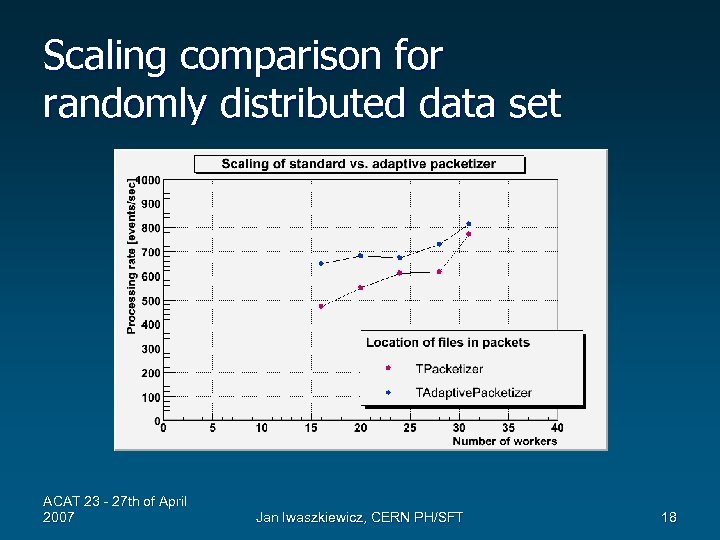
Scaling comparison for randomly distributed data set ACAT 23 - 27 th of April 2007 Jan Iwaszkiewicz, CERN PH/SFT 18

Resource scheduling • Motivation • Central scheduler – Model – Interface • Priority based scheduling on worker nodes ACAT 23 - 27 th of April 2007 Jan Iwaszkiewicz, CERN PH/SFT 19

Why scheduling? • Controlling resources and how they are used • Improving efficiency – assigning to a job those nodes that have data which needs to be analyzed. • Implementing different scheduling policies – e. g. fair share, group priorities & quotas • Efficient use even in case of congestion ACAT 23 - 27 th of April 2007 Jan Iwaszkiewicz, CERN PH/SFT 20

PROOF specific requirements • Interactive system – Jobs should be processed as soon as submitted. – However when max. system throughput is reached some jobs has to postponed • I/O bound jobs use more resources at the start • • • and less at the end (file distribution) Try to process data locally User defines a dataset not the #workers Possibility to remove/add workers during a job ACAT 23 - 27 th of April 2007 Jan Iwaszkiewicz, CERN PH/SFT 21
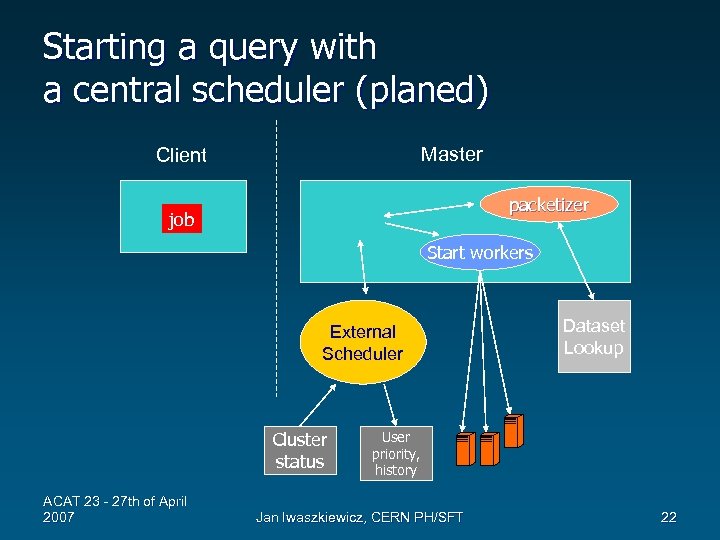
Starting a query with a central scheduler (planed) Master Client packetizer job Start workers External Scheduler Cluster status ACAT 23 - 27 th of April 2007 Dataset Lookup User priority, history Jan Iwaszkiewicz, CERN PH/SFT 22
Plans • Interface for scheduling "per job” – Special functionality will allow to change the set of nodes during a session without loosing user libraries and other settings • Removing workers during a job • Integration with a scheduler – Maui, LSF? ACAT 23 - 27 th of April 2007 Jan Iwaszkiewicz, CERN PH/SFT 23
Priority based scheduling on nodes • Priority-based worker level load balancing – Simple and solid implementation, no central unit – Group priorities defined in the configuration file • Performed on each worker node independently • Lower priority processes slowdown – sleep before next packet request ACAT 23 - 27 th of April 2007 Jan Iwaszkiewicz, CERN PH/SFT 24
Summary • The adaptive packetizer is working very well in current environment. Will be further tuned after introducing the scheduler • Advanced work on PROOF interface to scheduler. • Priority-based scheduling on nodes is being tested ACAT 23 - 27 th of April 2007 Jan Iwaszkiewicz, CERN PH/SFT 25

The PROOF Team • Maarten Ballintijn • Bertrand Bellenot • Rene Brun • Gerardo Ganis • Jan Iwaszkiewicz • Andreas Peters • Fons Rademakers http: //root. cern. ch ACAT 23 - 27 th of April 2007 Jan Iwaszkiewicz, CERN PH/SFT 26
fb141eaeecc9bcf523163126386853c3.ppt