e58a819dd40734d8ba3f18680f62830a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 Promotion Unit 5 - slide 11 1
Promotion Unit 5 - slide 11 1
 Marketing is about communication with consumers, and promotion is the method used to pass information to the consumer. Unit 5 - slide 11 2
Marketing is about communication with consumers, and promotion is the method used to pass information to the consumer. Unit 5 - slide 11 2
 Communication with consumers Promotion is the method used to pass info to the consumers. (educate) Keeps existing customers (remind) Gets new customers (persuade) Unit 5 - slide 11 3
Communication with consumers Promotion is the method used to pass info to the consumers. (educate) Keeps existing customers (remind) Gets new customers (persuade) Unit 5 - slide 11 3
 Advertising Unit 5 - slide 11 4
Advertising Unit 5 - slide 11 4
 Informative Advertising Passing information to the consumer about new or improved products. Give information about a technical product Other uses Government uses informative advertising in the press, TV and government publications. E. g. HEBS regularly run adverts on TV about the dangers of smoking. Unit 5 - slide 11 5
Informative Advertising Passing information to the consumer about new or improved products. Give information about a technical product Other uses Government uses informative advertising in the press, TV and government publications. E. g. HEBS regularly run adverts on TV about the dangers of smoking. Unit 5 - slide 11 5
 Persuasive Advertising Attempt by manufacturers to get us to buy their product. Used in very competitive markets where there is little different between one product and another. Use powerful images and language to imply good things about you if you buy this product Tries to build an emotional reaction in the consumer. Uses qualitative statements (opinions) not facts – “probably the world’s favourite lager”. Unit 5 - slide 11 6
Persuasive Advertising Attempt by manufacturers to get us to buy their product. Used in very competitive markets where there is little different between one product and another. Use powerful images and language to imply good things about you if you buy this product Tries to build an emotional reaction in the consumer. Uses qualitative statements (opinions) not facts – “probably the world’s favourite lager”. Unit 5 - slide 11 6
 Corporate Advertising Concerned with promoting the whole company rather than individual products. Put forward the image of being responsible and caring. E. g. BP do not try to get you to buy their petrol, don’t advertise prices, but to convey a “green” social image. Use slogans or catchlines to help this become established. “the world’s favourite airline” Unit 5 - slide 11 7
Corporate Advertising Concerned with promoting the whole company rather than individual products. Put forward the image of being responsible and caring. E. g. BP do not try to get you to buy their petrol, don’t advertise prices, but to convey a “green” social image. Use slogans or catchlines to help this become established. “the world’s favourite airline” Unit 5 - slide 11 7
 Generic Advertising Here a number of advertisers or the whole industry come together to promote the industry rather than individual products. Scottish Beef Milk Unit 5 - slide 11 8
Generic Advertising Here a number of advertisers or the whole industry come together to promote the industry rather than individual products. Scottish Beef Milk Unit 5 - slide 11 8
 Choice of advertising media Unit 5 - slide 11 9
Choice of advertising media Unit 5 - slide 11 9
 Choice Will depend upon how it can best reach its existing and potential customers. Targeted advertising is more successful and effective. Type of Consumer (Market Segment) Younger audiences would be targeted through magazines aimed at the youth market or advertising during TV programmes like Hollyoaks. Older audiences you may use advertising in the Sunday papers or during daytime TV. Whole market would be targeted during popular TV programmes like Coronation Street. Unit 5 - slide 11 10
Choice Will depend upon how it can best reach its existing and potential customers. Targeted advertising is more successful and effective. Type of Consumer (Market Segment) Younger audiences would be targeted through magazines aimed at the youth market or advertising during TV programmes like Hollyoaks. Older audiences you may use advertising in the Sunday papers or during daytime TV. Whole market would be targeted during popular TV programmes like Coronation Street. Unit 5 - slide 11 10
 Choice contd. the size of the market the cost the type of product the advertising of competitors the impact the law Unit 5 - slide 11 11
Choice contd. the size of the market the cost the type of product the advertising of competitors the impact the law Unit 5 - slide 11 11
 Types of advertising media Print – newspapers and magazines Broadcast – television, radio and Internet Outdoor – billboards, football grounds, buses etc. Above the line Unit 5 - slide 11 12
Types of advertising media Print – newspapers and magazines Broadcast – television, radio and Internet Outdoor – billboards, football grounds, buses etc. Above the line Unit 5 - slide 11 12
 Which is used will depend on the following factors: COST – television can be the most expensive, newspapers designed to target specific socio-economic groups etc COMPETITORS ADVERTISING – in order to compete effectively it may be necessary to match your competitors choice of media IMPACT REQUIRED – if launching new products you may need to use a variety of methods THE LAW – legal restrictions and guidelines on what advertising can take place eg alcohol and tobacco Unit 5 - slide 11 13
Which is used will depend on the following factors: COST – television can be the most expensive, newspapers designed to target specific socio-economic groups etc COMPETITORS ADVERTISING – in order to compete effectively it may be necessary to match your competitors choice of media IMPACT REQUIRED – if launching new products you may need to use a variety of methods THE LAW – legal restrictions and guidelines on what advertising can take place eg alcohol and tobacco Unit 5 - slide 11 13
 Controls on Advertising Standards Authority – voluntary body set up to monitor advertising in the UK Independent Television Commission – body controls advertising on television and radio Pressure Groups – seek to influence advertising eg FOREST who aim to defend the rights of tobacco firms to advertise Trades Descriptions Act 1968 – law states that the product must match the claims made about them in the advertising Unit 5 - slide 11 14
Controls on Advertising Standards Authority – voluntary body set up to monitor advertising in the UK Independent Television Commission – body controls advertising on television and radio Pressure Groups – seek to influence advertising eg FOREST who aim to defend the rights of tobacco firms to advertise Trades Descriptions Act 1968 – law states that the product must match the claims made about them in the advertising Unit 5 - slide 11 14
 Sales Promotions Unit 5 - slide 11 15
Sales Promotions Unit 5 - slide 11 15
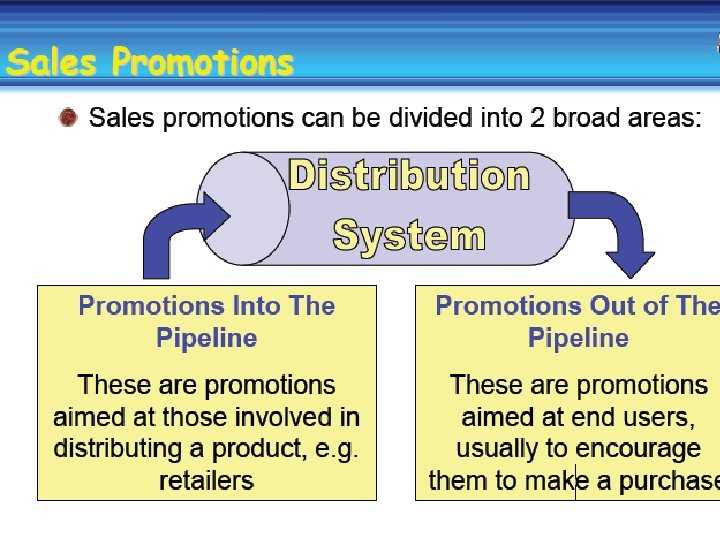
 Promotions Short term inducements used to encourage customers to react quickly and make a purchase. Can be given by the wholesaler (Cadbury’s) or the retailer (Safeway). Below the line – short duration, limit specific group Unit 5 - slide 11 16
Promotions Short term inducements used to encourage customers to react quickly and make a purchase. Can be given by the wholesaler (Cadbury’s) or the retailer (Safeway). Below the line – short duration, limit specific group Unit 5 - slide 11 16
 Unit 5 - slide 11 17
Unit 5 - slide 11 17
 Unit 5 - slide 11 18
Unit 5 - slide 11 18
 Unit 5 - slide 11 19
Unit 5 - slide 11 19
 Public Relations Unit 5 - slide 11 20
Public Relations Unit 5 - slide 11 20
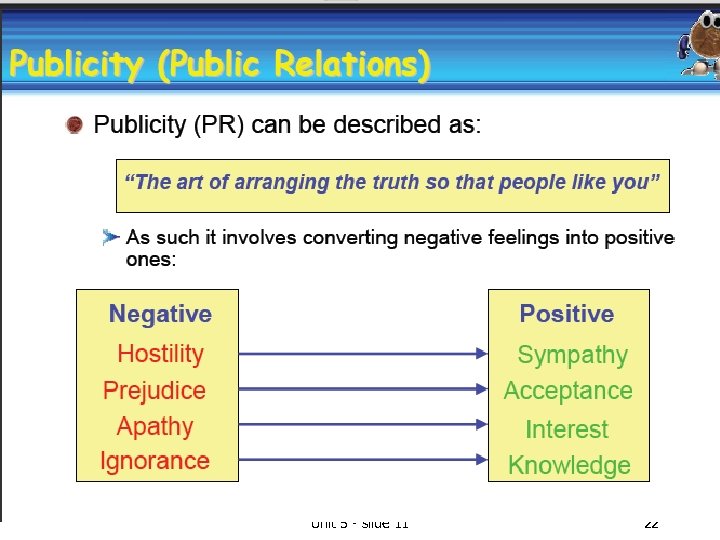
 Public Relations Organisation communicates at corporate level with the community. Includes the public, press, government and shareholders. Used to enhance the image of the organisation. Unit 5 - slide 11 21
Public Relations Organisation communicates at corporate level with the community. Includes the public, press, government and shareholders. Used to enhance the image of the organisation. Unit 5 - slide 11 21
 Unit 5 - slide 11 22
Unit 5 - slide 11 22
 PUBLICITY within the organisation by the company itself through press releases or public announcements. Outwith the organisation through news reports or through consumer programmes (watchdog) or publications (which). can have a negative effect on the company if the publicity is poor. If the publicity is good it can become a form of advertising. Unit 5 - slide 11 23
PUBLICITY within the organisation by the company itself through press releases or public announcements. Outwith the organisation through news reports or through consumer programmes (watchdog) or publications (which). can have a negative effect on the company if the publicity is poor. If the publicity is good it can become a form of advertising. Unit 5 - slide 11 23
 Unit 5 - slide 11 24
Unit 5 - slide 11 24
 Packaging Sometimes referred to as the 5 th P. Important element of marketing as good packaging increases sales. Unit 5 - slide 11 25
Packaging Sometimes referred to as the 5 th P. Important element of marketing as good packaging increases sales. Unit 5 - slide 11 25
 Factors Shape and Weight – affects how easy the product is to distribute and handle which can lead to high costs. Protection – must be robust to ensure that product and packaging is not damaged during transit. Convenience – easy for customer to handle; awkward shapes and sizes put customers off. Unit 5 - slide 11 26
Factors Shape and Weight – affects how easy the product is to distribute and handle which can lead to high costs. Protection – must be robust to ensure that product and packaging is not damaged during transit. Convenience – easy for customer to handle; awkward shapes and sizes put customers off. Unit 5 - slide 11 26
 Design – eye-catching to allow it to be distinguished easily from competitors brands. Information – e. g. food products are subject to legal requirements about their ingredients appearing on the packaging; some technical products must show the amp and wattage. Environmental factors – growing concern about recyclable materials being used. Unit 5 - slide 11 27
Design – eye-catching to allow it to be distinguished easily from competitors brands. Information – e. g. food products are subject to legal requirements about their ingredients appearing on the packaging; some technical products must show the amp and wattage. Environmental factors – growing concern about recyclable materials being used. Unit 5 - slide 11 27
 Merchandising Unit 5 - slide 11 28
Merchandising Unit 5 - slide 11 28
 Merchandising Used in an attempt to encourage the customer to buy at the point of sale. Displays materials such as Window displays In-store posters Unit 5 - slide 11 29
Merchandising Used in an attempt to encourage the customer to buy at the point of sale. Displays materials such as Window displays In-store posters Unit 5 - slide 11 29
 The layout of products can encourage customers to follow particular routes around the store. E. g. popular items at the back in order that customers have to pass other products. Related items will be kept together Position of the item on the shelves is important – eye-level is the best position to achieve sales. Unit 5 - slide 11 30
The layout of products can encourage customers to follow particular routes around the store. E. g. popular items at the back in order that customers have to pass other products. Related items will be kept together Position of the item on the shelves is important – eye-level is the best position to achieve sales. Unit 5 - slide 11 30
 Shelves should be well stocked Creation of the right atmosphere within the store will affect customers buying. Bright light next to fresh food items to give an image of cleanliness. Bread and coffee smells to make the customer hungrier. Unit 5 - slide 11 31
Shelves should be well stocked Creation of the right atmosphere within the store will affect customers buying. Bright light next to fresh food items to give an image of cleanliness. Bread and coffee smells to make the customer hungrier. Unit 5 - slide 11 31


